Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR REELING A TRAVELING PAPER WEB
BACKGROUND OF THE INV NTir'y
The invention relates to the reeling of a traveling web of paper, such as
that which is being continuously produced by a papermaking machine,
continuously onto successive reel spools to produce a corresponding
succession of relatively large diameter wound paper web rolls. More
particularly, the invention relates to a method and apparatus for continuously
producing a wound paper web roll without transferring the wound web roll from
one nip actuating apparatus to another.
Two known reeling apparatus of this type are Beloit Corporation's TNTT""
and ATRT"" reels. The former is disclosed in U.S Patent No. 5,370,327, and
the latter is disclosed in U.S Patent Application No. 08/574,824 filed
December
19, 1995.
The ATR (Advanced Tissue Reel) reel was developed with a view to
apply all the advantages of the TNT (Tension, Nip and Torque) reel to high
bulk
grades of paper, especially tissue. These grades of paper require winding at
little or no nip pressure so that as much of their inherent bulk can be
retained
as possible. In order to attain control of very low nips, the ATR reel
utilizes a
large diameter reel drum on a fixed stand. Also, hydraulically controlled
carriages which act as nip load controllers hold the building roll of paper
against the reel drum. The nip load is measured either via load cells under
the
reel drum or via pressure transducers in the hydraulic.carriage loading
system.
The ATR reel differs from the TNT reel in that with the TNT reel, the reel
drum can be raised or lowered in elevation. This allows the paper to be
transferred to the new reel spool on the wet-end side of the reel drum
(upstream in the paper machine process). After winding of the paper begins,
the reel spool/winding roll of paper is moved downstream by its guiding
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
- 2 - F ,
carriages. This movement requires the reel drum to move downwards to allow
the winding roll of paper over the top of the reel drum. As the reel drum is
of
considerable weight, there is a limit to how accurately the nip can be
controlled
at low nip loading values while also having a large moving mass controlling
the
nip.
It was decided that if the reel drum was fixed on stands (i.e., its weight is
supported) and the weight of the winding roll of paper is also supported on
rails, then it would be easier to attain control of nip pressure at very low
levels.
The problem with fixing the reel drum in position is that the whole roll
winding
process must now happen on the dry-end side (downstream) of the reel drum
in order for any component of the nip load from being provided by the weight
of
the new reel spool and any web wrapped on it. This means that to allow
reeling to be a continuous process, the new reel spool must at some stage be
inserted between the winding roll of paper and the reel drum without breaking
the sheet of paper as it winds onto the roll.
It was found that if a reel drum of 2,130 mm diameter were used with a
reel spool of up to 500 mm diameter then the new reel spool could be inserted
into the gap between the winding roll of paper and the reel drum at any time
after the winding roll of paper exceeds 2000 mm in diameter. This was made
possible by placing the reel spool support rails at such a height that the
empty
reel spool first contacts the reel drum at a nip point 14 degrees past top-
dead-
center of the reel drum. This system is applicable to any reel where the reel
spool is 500 mm or less in diameter, and where the particular reeling process
allows for full sheet transfer of paper from the old roll of paper to the new
reel
spool only when the old roll of paper is above 2000 mm diameter. Below 2000
rim diameter, the sheet must be broken back from the reel to the last stage in
the papermaking process and fed through again onto the new reel spool when
it is in position.
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
- 3 -
One method of overcoming the above limitation is to replace the large
reel drum with a fabric belt system. The belt is supported, tensioned and
guided with one part of the belt run suspended at an angle chosen to suit the
reeling process. It is this angled section of belt against which the winding
roll
of paper is "nipped". The nip pressure is measured and controlled by sensing
changes in belt tension, for example by mounting one or more of the support
rolls on tension load cells.
The reel spool guiding carriages will be driven/positioned by a control
system (e.g. hydraulic cylinders operating in load control). Thus, as the
paper
diameter wound onto the reel spool increases, nip pressure increases and the
reel spool carriages move downstream in order to bring the nip pressure back
to the pre-determined set-point value. Because the belt is suspended at an
angle, the winding roll of paper is moved further downstream from its initial
position than when nipped against a reel drum whose surface is curved.
Due to the flexible nature of the belt, the nip width is wider and thus the
nip intensity lower than with a hard roll. This minimizes loss of bulk in the
paper.
Using a belt as described above also makes it possible to increase the
size of the reel spool that can be used with low bulk grades of paper. Instead
of placing load cells under a large diameter reel drum, low nips can be sensed
by measuring changes in belt tension.
More particularly, the invention provides an apparatus comprising a
frame and first and second generally parallel, generally horizontal rails
mounted on the frame. Each rail has an upper surface for supporting a
respective end of a reel spool. The apparatus also comprises a support belt
mounted on the frame for movement along an endless path, the belt having an
upper run extending horizontally in the cross machine direction and extending
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
- 4 -
at a non-horizontal angle in the machine direction such that the upper run is
angled downwardly in the downstream direction. First and second carriages
are operatively associated with the first and second rails, respectively, for
longitudinal movement parallel to the rails. Each of the carriages is
selectively
operative to engage a respective end of the reel spool such that the reel
spool
moves with the carriages along the rails. A drive selectively engages and
rotates the reel spool when the reel spool is engaged by the carriages. The
apparatus also comprises a positioning device for (1) selectively positioning
the
carriages in an initial reeling position in which the web is reeled onto the
reel
spool engaged by the carriages and in which the upper run of the belt is in
nipping engagement with the web being wound onto the reel spool, and (2)
positioning the carriages downstream of the initial reeling position to
control the
nip pressure between the belt and the web being wound onto the reel spool
during reeling of the wound web roll, whereby the wound web roll is moved
downstream while being horizontally supported by the rails, rotatably driven
by
the drive, and nipped by the belt until the desired web roll diameter is
reached.
The invention also provides a method for reeling a traveling paper web
into a wound web roll on a reel spool, the method comprising the steps of: {a)
supporting the reel spool for rotation and for translational movement
generally
horizontally; (b) rotating the reel spool so as to wind the traveling web onto
the
reel spool to form thereon a wound web roll; (c) providing a support belt
mounted for movement along an endless path, the belt having an upper run
extending horizontally in the cross machine direction and extending at a non-
horizontal angle in the machine direction such that the upper run extends
downwardly in the downstream direction; (d) placing the upper run of the belt
in
nipping engagement with the web being wound onto the reel spool; (e)
maintaining horizontal support and rotation of the wound web roll and nipping
engagement of the roll by the belt as the diameter of the roll increases and
the
roll moves downstream along the belt; and (f) controlling the nip pressure
between the belt and the web being wound onto the reel spool during reeling of
the wound web roll and movement of the roll along the belt.
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
- 5 -
Other features and advantages of the invention will become apparent to
those skilled in the art upon review of the following detailed description,
claims
and drawings.
Fig. 1 is a side elevational view of an apparatus embodying the
invention:
Fig. 2 is a view showing movement of the wound web roll along the belt.
Fig. 3 is a top plan view of the apparatus.
Fig. 4 is a view taken along line 4--4 in Fig. 1.
Before one embodiment of the invention is explained in detail, it is to be
understood that the invention is not limited in its application to the details
of the
construction and the arrangements of components set forth in the following
description or illustrated in the drawings. The invention is capable of other
embodiments and of being practiced or being carried out in various ways.
Also, it is understood that the phraseology and terminology used herein is for
the purpose of description and should not be regarded as limiting.
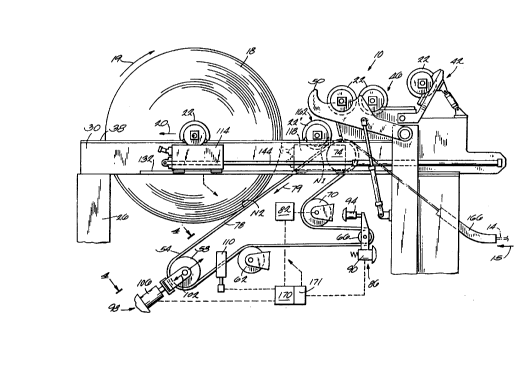
An apparatus 10 embodying the invention is shown in the drawings.
The apparatus 10, which reels a traveling paper web 14 into a wound web roll
18 on a reel spool 22, has a machine direction (from right to left in Fig. 1)
and a
cross machine direction (into and out of the paper in Fig. 1 and from right to
left
in Fig. 3). Many of the components of the apparatus 10 are substantially
identical to components of, and are described in greater detail in, pending
U.S.
Patent Application Serial No. 081574,824, which is assigned to the assignee
hereof and which is incorporated herein by reference.
The apparatus 10 comprises a frame 26 supporting a pair of spaced,
parallel, horizontal rails 30 and 34. Each of the rails 30 and 34 has a
horizontal
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
- 6 -
upper surface 38 for supporting a respective end of a reel spool 22. The
apparatus 10 has front and back sides {the right and left sides in Fig. 3),
with
the front side being shown in Fig. 1. The front and back sides are
substantially
identical, and only the components of the front side are shown in detail in
Fig.
1, it being understood that the corresponding components of the back side of
the apparatus 10 are substantially identical.
Referring to Fig. 1, a storage station 42 is mounted on the frame 26
above the right end of the rails 30 and 34. The storage station 42 includes a
storage rack 46 for storing a supply of new reel spools 22, and a pair of
spool
arms 50 (only one is shown) mounted on the frame 26 below the rack 46 for
pivotal movement between a spool receiving position (shown in Fig. 1 ) and a
spool depositing position (not shown). In the spool receiving position, the
arms
50 receive a new spool 22 from the storage rack 46. In the spool depositing
position, the arms 50 deposit the new spool 22 on the upper surfaces 38 of the
rails 30 and 34.
The apparatus 10 also comprises a support belt 54 mounted on the
frame 26 for movement along an endless path. The belt 54 is preferably made
of a porous, low stretch fabric such as, for example, dryer felt. The belt 54
is
supported on rolls 58, fit, 66, ?0 and 74, each of which is mounted on the
frame 26 for rotation about a respective horizontal axis extending in the
cross
machine direction. The belt 54 has a generally linear upper run 78 that
extends horizontally in the cross machine direction and is angled downwardly
in the downstream direction. In other words, the upper run 78 extends at a
non-horizontal angle in the machine direction, as generally designated by
arrow
20. A drive 82 is operably connected to the roll 70 for moving the belt 54
along
its endless path such that the belt upper run moves from right to left in Fig.
1,
i.e., in the direction of arrow 79 corresponding to the rotational direction
of the
wound roll 18, shown by arrow 19, at the point of engagement between the belt
54 and the roll 18. Any suitable drive can be employed.
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
The roll 74 is preferably a vacuum roll. The vacuum ro(I 74 resists web
floating, i.e., helps keep the web 14 in place. A belt tension assembly 86
controls the tension of the belt 54. The belt tension assembly 86 includes
tfie
roll 66, which is preferably a tension roll mounted on tension load cells 90
(shown schematically). The roll 66 is loaded against the belt 54 at a
controlled
tension using, for example, hydraulic cylinder/piston assemblies 94.
A belt guide assembly 98 maintains the proper position of the belt 54 on
the rolls 58, 62, 66, 70 and 74. The belt guide assembly 98 includes the roll
58, which is, at one end (the left end in Fig. 4), fixed against translational
movement but pivotable about an axis 100 perpendicular to the roll axis and to
the belt upper run 78. The other end of .the roll 58 (the right end in Fig. 4
and
the end shown in.Fig. 1) is translationally or arcuately movable in the
direction
of the arrow 102 so that the roll 58 can be "skewed" to control the position
of
the belt 54 on the roll 58. A suitable device, such as a hydraulic
cylinderlpiston
assembly 106, is connected to the free end of the roll 58 for providing the
necessary skewing of the roll 58. The belt guide assembly 98 also includes a
guide palm 110 for sensing the position of the belt 54 in the cross machine
direction. The guide palm 110 is operably connected to the hydraulic assembly
106 for controlling skewing of the roll 58. This provides a closed loop
control of
the belt position on the roll 58. Such a belt guide assembly is known in the
art
and need not be described in greater detail. See, for example, U.S. Patent No.
4,790,908, which is incorporated herein by reference.
The apparatus 10 also comprises (see Figs. 1 and 3) an outer carriage
114 mounted on the outside of the rail 30, an inner carriage 118 mounted on
the inside of the rail 30, an inner carriage 124 mounted on the inside of the
rail
34, and an outer carriage 128 mounted on the outside of the rail 34. Each of
the carriages 114, 118, 124 and 128 is supported for longitudinal movement
parallel to the rails 30 and 34. More particularly, each of the carriages 114,
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
_ 8 _
118, 124 and 128 is supported on a respective guide 132 (see Fig. 1 ) for
reciprocal movement along the associated rail. Each of the carriages 114, 118,
124 and 128 is selectively operative to engage the end of a reel spool 22, as
is
known in the art. The carriages operate in pairs, as explained below, with the
carriages 114 and 124 cooperating to engage the opposite ends of a spool 22,
and with the carriages 118 and 128 cooperating to engage the opposite ends
of a different spool 22.
The apparatus 10 further comprises (see Fig. 3) drives 136 and 140,
each of which is operable to selectively engage and rotate a reel spool 22
when the reel spool 22 is engaged by a pair of the carriages. ~~Aore
particularly,
the drive 136 engages and rotates a spool 22 engaged by the carriages 114
and 124, and the drive 140 engages and rotates a spool 22 engaged by the
carriages 118 and 128. Each of the drives 136 and 140 is supported for
movement parallel to the rails 30 and 34 and with the engaged reel spool 22.
A suitable drive arrangement is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 5,370,327, which
is incorporated herein by reference.
The apparatus 10 further comprises a positioning device for selectively
positioning the carriages 114, 118, 124 and 128 relative to the rails 30 and
34.
The positioning device preferably includes (see Fig. 3) extendable linkages
144, 148, 154 and 158 (partially shown) connected between the frame 26 and
the carriages 114, 118, 124 and 128, respectively. In the illustrated
construction, the linkages 144, 148, 154 and 158 are hydraulic cylinder/piston
apparatus. Other suitable linkages, such as ball screw and chain and sprocket
apparatus, can be employed. The hydraulic apparatus 144, 148, 154 and 158
are controlled such that, as described above, the carriage 114 is operatively
linked with and moves with the carriage 124, and the carriage 118 is
operatively linked with and moves with the carriage 128. In this manner, two
sets of cooperating pairs of carriages are operative to move two reel spools
22,
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
_ 9 - . ,
22' along the rails 30 and 34. The operation of the hydraulic apparatus 144
and 154 and the associated carriage pair will be described first.
The hydraulic apparatus 144 and 154 are operable to position the
carriages 114 and 124 in an initial reeling position (indicated by reference
numeral 162 in Figs. 1 and 2) in which the carriages 114 and 124 receive a
reel
spool 22 deposited on the rails 30 and 34 by the storage station 42, in which
the web 14 is thereafter brought into nipping engagement N1 with a fresh reel
spool 22 and reeled onto the reel spool 22 engaged by the carriages 114 and
124, and in which the upper run of the belt 54 is in nipping engagement with
the web 14 at nip N2 being wound onto the reel spool 22. The paper web 14
travels over the right or upper end of the belt 54 and down the upper run of
the
belt before being reeled onto the reel spool 22. A paper web tail guiding
apparatus 166 (Fig. 1 ) is mounted on the frame 26 and guides the oncoming
paper web tail in the direction of arrow 15 onto the belt 54.
The hydraulic apparatus 144 and 154 thereafter position the carriages _
114 and 124 downstream of the initial reeling position to control the nip
pressure between the belt 54 and the web 14 being wound onto the reel spool
22 during reeling of the wound web roll 18. A controller 170 (shown
schematically in Fig. 1 ) senses the nip pressure between the belt 54 and the
wound web roll 18 and controls the hydraulic apparatus 144 and 154 so as to
adjust the nip pressure. More particularly, in the illustrated construction,
the
load cells 90 sense the tension in the belt 54 and thereby sense the nip
pressure. Any tension increase due to nip between the roll 18 and the belt 54
is sensed by the load cells 90 and used to control the hydraulic apparatus 144
and 154.
The controller 170 preferably also includes a device 171 for sensing the
position of the carriages 114, 118,124 and 128, the carriage position being
indicative of the diameter of the wound web roll 18. In the illustrated
CA 02328189 2000-09-25
WO 98/55384 PCT/EP97/02962
- 10 -
construction, each of the hydraulic apparatus 144, 148, 154 and 158 (i.e.,
positioning devices) has a built-in linear variable displacement transducer
(LVDT) that indicates roll diameter. The roll diameter can be used to control
the drive speed profilelnip profile throughout the buildup of the roll.
The hydraulic apparatus 144 and 154 are also operable to position the
carriages 114 and 124 to move the wound web roll 18 out of nipping
engagement with the belt 54 (to the left of the belt 54 in Fig. 1 ) when the
desired web roll diameter is reached. The wound web roll 18 is then removed
from the carriages 114 and 124 and from the apparatus 10, as is known in the
art.
Thus, the wound web roll 18 is moved downstream in the direction of
arrow 20 while being horizontally supported by the rails 30 and 34, rotatably
driven by the drive 136, and nipped by the belt 54 until the desired web roll
diameter is reached.
The hydraulic apparatus 148 and 158 are operable in the same manner
as the hydraulic apparatus 144 and 154. After the carriages 114 and 124
move downstream from the initial position, the hydraulic apparatus 148 and
158 position the carriages 118 and 128 in the initial position to receive the
next
reel spool 22' deposited by the storage station 42. After the preceding reel
spool 22 (engaged by the carriages 114 and 124) moves downstream of the
belt 54, the arms 50 deposit the next spool 22' on the rails 30 and 34 in
engagement with the carriages 118 and 128, and the hydraulic apparatus 148
and 158 move the carriages 118 and 128 in the same manner as described
above. The wound web roll 18 is then removed from the carriages 114 and
124, and the hydraulic apparatus 144 and 154 return the carriages 114 and
124 to the initial position to receive the next reel spool 22'.
Various features of the invention are set forth in the following claims.