Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
4, 5, 6 and 7-indole and indoiine derivatives, their preparation and use
The present invention relates to novel 4, 5, 6 and 7-indole and indoline
derivatives
which are potent serotonin reuptake inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions
containing these compounds and the use thereof for the treatment of disorders
or
diseases responsive to the inhibition of serotonin re-uptake. The compounds of
the
invention also possess antagonistic activity at 5-HT,A receptors and are
considered to
be particularly useful for the treatment of depression.
Background
Selective serotonin (or 5-HT) reuptake inhibitors (SSRI's) such as fluoxetine,
paroxetine, sertraline, fluvoxamine and citalopram represent a major step
forward in
the treatment of depression because they have fewer and less severe side
effects
compared to first generation antidepressant (tricyclics and non-selective MAO
inhibitors). The side effects associated with first generation antidepressants
are such
that they cause some patients to withdraw from treatment.
SSRI's and all other antidepressants currently available suffer from a serious
drawback in that several weeks of treatment is necessary to produce the
therapeutic
effect. The late onset of action is a significant problem, particularly in the
treatment
of patients with severe depression and suicide potential. Further, one in
three patients
are not responsive to SSRI's.
Electrophysiological experiments in rats have shown that acute administration
of
SSRI's reduces firing of 5-HT neurons of dorsal raphe nucleus in the rodent
brain,
whereas sustained treatment with SSRI's leads to normalization of the firing
activity
of the 5-HT neurons (Arborelius, L. et al, Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch.
Pharmacol.
1995, 352, 157; Gartside, S.E. et al, Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995,115, 1064;
Chaput, Y. et
al, Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1986, 33, 342).
CONFIRMATION COPY
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO '99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
2
Further, it has been shown that the recovery of the firing activity of 5-HT
neurons is
linked to desensitization of somatodendritic 5-HT,A autoreceptors (Le Poul, E.
et al,
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1995, 352, 141; Invernizzi, R. et al,
Eur. J.
Pharmacol. 1994, 260, 243).
It has thus been suggested that simultaneous administration of SSRI's and an
agent
causing rapid desensitization or inhibition of the 5-HT,A receptor mediated
feed back
mechanism would lead to rapid onset of antidepressive effect (Artigas, F. et
al, Trends
Neurosci. 1996, 19, 378; De Vry, J., et al, Drug News Perspec. 1996, 9, 270).
The effect of combined administration of a compound that inhibits serotonin
reuptake
and a 5-HT,A receptor antagonist has been evaluated in several studies (Innis,
R.B. et
al., Eur. J. Pharmacol., 1987, 143, p 195-204 and Gartside, S.E., Br. J.
Pharmacol.
1995,115, p 1064-1070, Blier, P. et al, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1994, I S,
220). In
these studies it was found that 5-HT,A receptor antagonists inhibit the
decrease in
firing caused by acute administration of serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Further, treatment with a combination of pindolol (a well known 5-HT,A
receptor and
(3-adrenoceptor antagonist) and SSRI's has been evaluated in clinical trials.
A remarkable improvement of the mood of patients was reported within one week.
In
addition, combined administration of pindolol and a SSRI was shown to have a
good
effect on patients who were non-responsive to treatment with currently
available
antidepressants (Ai~tigas F. et al., Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 1994, 51, p 248-
251 and
Blier, P. et al., J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1995, 1 S, p 217-222).
Several patent applications have been filed which cover the use of a
combination of a
5-HT,A antagonist and a serotonin reuptake inhibitor for the treatment of
depression
(see EP-A2-687 472 and EP-A2-714 663).
3o DE patent application No. 4414113 discloses certain 4-(indol-3-yl)-1-(indol-
3-yl-
alkylene)-piperidines having the general formula
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO' 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
3
\N
R< Rp ~~~R~
wherein n is 2-6 and the other substituents are as defined in the application.
The
compounds herein are claimed to have serotonin antagonistic and agonistic
activities
and to have effect on DOPA-accumulation in striatum and 5-HTP accumulation in
N.
Raphe. No biological data are given.
WO patent publication No. 94/21626 discloses compounds having the general
formula
R3
Rz N _ ~~ R
\ /\Rs
N~
N
R
io wherein R'- is heteroaryl and the other substituents are as defined in the
application.
A compound wherein RZ is 5-indolyl which is structurally closely related to
the
compounds of the invention is specifically mentioned herein. No data are
given. The
compounds are only said to give K; values of less than 1.5 pM in a test for
displacement of 3H spiperone from human dopamine D4 receptor subtypes in
clonal
cell lines. WO patent publication No. 94/21627 and No. 94/21630 relate to
similar
compounds having affinity for human dopamine D4 receptors.
WO patent publication No. 95/33721 relates to 1-(indanemethyl, dihydrobenzo-
furanylmethyl, dihydrobenzothiophenylmethyl)piperidine,tetrahydro-pyridine, or
piperazine derivatives having the general formula
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
4
R~
R' Re R3
Re
I ~ ~N~Rz
R°
wherein one of X and Y is CHZ and the other is selected from the group
consisting of
CH2, O, or S, Ar is aryl or heteroaryl, e.g. 1-, 2-, or 3-indolyl and the
other
substituents is as defined in the application. The compounds interact with
central
5-HT receptors, in particular with S-HT,A and 5-HTZA receptors. Some of the
compounds are said to have 5-HT reuptake inhibiting effect.
Object of the Invention
It is the object of the present invention to provide compounds with potent
serotonin
reuptake inhibiting activity as well as antagonistic properties at 5-HT,A
receptors.
Such compounds may be useful as fast onset of action medicaments for the
treatment
of affective disorders, such as depression.
A further object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical
composition
comprising these compounds as active ingredients.
Summary of the Invention
2o The invention then, inter alia, comprises the following alone or in
combination:
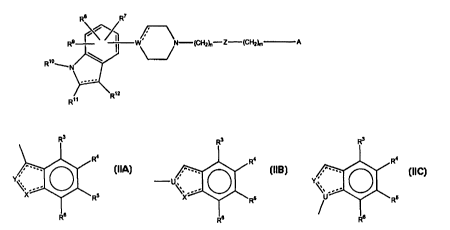
A substituted 4-, 5-, 6-, or 7-indole or indoline derivative of formula (I)
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
R8 R~
n
R9 W N-(CHy)n-Z-'(CH2~m A
R~°~..
N
R~z L1)
R~~
wherein W is N, C, CH or COH and the dotted lines indicate optional bonds and
wherein A is a group having the formula
Ra
R5
Ro (IfA)
wherein X is CR'", CHR'", N, NR'B, O, or S, where R' ' is as defined for R' to
R9 below, and where R'B is as defined for R"' below;
Y is CRZ", CHRz", N, NR2B, O, or S, where Rl'' is as defined for R' to R9
below
and where R2B is as defined for R'° below, and
the dotted lines indicate optional bonds;
provided that X and Y are not both O or S;
A is a group having the formula
ZO
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO' 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
6
R4
U\~
Rs
(IIB)
Rs
wherein X is CR'", CHR'", N, NR'B, O, or S, where R'" is as defined for R' to
R9 below, and where R'B is as defined for R'° below;
U is C, CH, or N; and
the dotted lines indicate optional bonds;
l0 A is a group having the formula
R3
Ra
/ U .. Rs
(lIC)
Rs
wherein U is C, CH, or N;
Y is CRZ~, CHRZ~, N, NRZB, O, or S, where RzA is as defined for R' to R9 below
and where R28 is as defined for R'° below;
and the dotted lines indicate optional bonds;
nis0, 1,2,3,4,or5,andmis0, 1,2,3,4,or5;
Z is CH2, O, S, CO, SO, or SO2, provided that if n is 0 then Z is CH2;
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
7
R3-R9 and R" to R'2 are independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, cyano,
nitro,
C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, C,-6 alkoxy, C,_6 alkyithio, hydroxy, hydroxy-C,_6 alkyl,
C,_6 alkoxycarbonyl, C3_g-cycloalk(en)yl, C,_g cycloalk(en)yl-C,_6
alk(en/yn)yl,
C,_6 alkylcarbonyl, phenylcarbonyl, halogen substituted phenylcarbonyl,
trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy, C,_6 alkylsulfonyl, aryl and
heteroaryl,
and/or two adjacent groups taken from R' - R9 may together form a
methylenedioxy
group,
and/or two adjacent groups R7 - R9 may together form a cyclopentyl or
cyclohexyl
ring which may be substituted with one or more methyl groups,
and/or one of R3-R9 may alternatively be a group -NR"R'° wherein R" is
as defined
for R'° below and R'4 is hydrogen, C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, C,_s-
cycloalk(en)yl, C,_g-
cycloalk(en)yl-C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C,_~ alkyl, or
heteroaryl-C,_6
alkyl;
R'° is
~ hydrogen, C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, C3_g cycloalk(en)yl, C,_8-cycloalk(en)yl-C,_6
alk(en/yn)yl, aryl, heteroaryl, aryl-C,_6 alkyl, heteroaryl-C,_~-alkyl, acyl,
thioacyl,
C,_6 alkylsulfonyl, trifluoromethylsulfonyl, arylsulfonyl, or
heteroarylsulfonyl;
~ R'SVCO- wherein V is O or S and R'S is C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, C,_x-
cycloalk(en)yl,
2o C3_g-cycloalk(en)yl-C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, aryl, or heteroaryl; or
~ a group R'6R"NCO- or R'6R"NCS- wherein R'G and R" are independently
selected from hydrogen, C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, C3_8-cycloalk(en)yl, C3_8-
cycloalk(en)yl-
C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, heteroaryl, or aryl, or R'6 and R" together with the N-atom
to
which they are linked, form a pyrrolidinyl, piperidinyl, morpholinyl, or
perhydroazepin group;
or an acid addition salt thereof.
In a particular embodiment, the compounds of the invention are compounds
wherein
3o A is a group of formula (IIA) including such compounds wherein A is a group
having
the formulas illustrated below:
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
8
R3 Rs
Ra Ra Ra
Rs Rs Rs
R°
Ra Ra Ra
Rs Rs Rs
R" n_ Ro
Ra
O~
Rs
R°
wherein R' to R6 and the dotted lines are as defined above.
In a particular embodiment A is a group having the formula
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
9
R4 Ra Ra
Rs Rs R5
R Rb
Ra
or
Rs
wherein R3 to R6 and the dotted lines are as defined above.
In another particular embodiment the present invention relates to compounds
having
the formula
N-ICHZ)r,-Z-(CH2)m-A
(II)
R"
to wherein R7 to R'2, W, A, Z , n, m and the dotted lines are as defined
above.
In a particular embodiment Z is CHZ and n + m is 0, l, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6.
In another embodiment the present invention relates to compounds having the
formula II above and A is a group having the formula IIA above.
RB R~
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
In another particular embodiment the present invention relates to compounds
having
the formula II above and A is a group having the formula
R4 Ra R4
Rs Rs Rs
Rb Ro Ro
Ra
R4 R4
N\
Rs Rs \N s
R
Rb Rs
R3
R°
or
Rs
Ro
wherein R3 to R6 and the dotted lines are as defined above.
l0 In a further particular embodiment the present invention relates to
compounds having
the formula II above and A is a group having the formula
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
11
R4 R°
R5 R5
R~ R
R4
or
R5
R°
wherein R3 to R6 and the dotted lines are as defined above.
In a particular embodiment the compounds of the invention are the compounds
wherein R'-R9 and R"-R'' is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, nitro, C,_6 alkyl, C,_6
alkoxy
hydroxy, hydroxy-C,_6 alkyl, C,_6 alkoxycarbonyl and trifluoromethyl; and
R'° is
hydrogen.
to
In another particular embodiment of the invention, W is N.
Examples of compounds according to the invention are the compounds
1-(2-(3-Benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(3-Benzofuranylmethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(4-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)-1-butyl)-4.-( 1 H-indo I-4-yl)pip erazine,
1-(2-( 1 H-Indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(3-( 1 H-Indol-3-yl)-1-propyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-{4-( 1 H-Indol-3-yl)-1-butyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(3-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl )-1-propyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
12
1-(2-(2-Methyl-4, 5,6,7-tetrafluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(3-Indazo lyl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-3-indazolyl)ethyl)-4-(1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(7-Cyano-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(4-Chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Fluoro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl) ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)-1,2, 3, 6-
tetrahydropyridine,
1-(2-(5-Fluoro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)-1,2,3,6-
tetrahydropyridine,
l0 1-(2-(7-Bromo-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-( 1-Allyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(6-chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-( 1-Allyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(5-fluoro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-( 1-Benzyl-1 H-indo l-4-yl)-4-(2-(6-chloro-1 H-indo l-3-yl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-( 1-B enzyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(5-fluoro-1 H-indo 1-3-yl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-( 1-Benzyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(5-bromo-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1-propargyl-1 H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine,
1-(2-( 1 H-Indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1-propargyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(S-Fluoro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1-propargyl-1 H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Bromo-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1-propargyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
2o 1-(1-Benzyl-1H-indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Bromo-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(1H-indol-5-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-5-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(S-Fluoro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-hydroxymethyl-1 H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-hydroxymethyl-1 H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Bromo-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-hydroxymethyl-1 H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine,
1-(3-(6-Fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-propyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-{2-( 1 H-Indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-methoxycarbonyl-1 H-indo 1-4-yl)piperazine,
1-{2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-methoxycarbonyl-1 H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(6-methoxycarbonyl-1H-indol-4-
3o yl)piperazine,
1-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranylmethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(3-Cyano-1 H-indol-4-yl)-4-(2-( 1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)piperazine,
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
13
1-(3-Cyano-1H-indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(5-fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(3-cyano-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(3-Benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(3-cyano-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(1H-Indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(5-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(4-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine,
1-(3-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)-1-propyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)-1,2,3,6-
tetrahydropyridine,
1-(2-(S-Chloro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)p iperazine,
1-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl)-4-(2-{6-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine,
l0 1-(2-(7-Chloro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(4-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(3-cyano-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)-4-(1 H-indol-4-yl)piperidine,
1-(2-(5-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl )piperazine,
1-(2-(7-Bromo-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(4-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-{ 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-{2-(6-Trifluoromethyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(5-methyl-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl )piperazine,
1-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(6-methyl-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl )piperazine,
1-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl)-4-(2-(7-methyl-1 H-indol-3-yl )ethyl )piperazine,
2o 1-(2-(4,5-Dichloro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(5-Bromo-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-{4-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl )piperidine,
4-(1 H-Indol-4-yl)-1-(2-(5-methyl-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)piperidine,
4-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl)-1-(2-( 1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)piperidine,
1-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl )-4-(3-(4-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)-1-propyl)piperazine,
4-( 1 H-Indol-4-yl)-1-(3-(4-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)-1-propyl)piperidine,
1-(3-(4-Chloro-3-benzofuranyl)-1-propyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-chloro-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-fluoro-1 H-indo l-4-yl)piperazine,
3o 1-(2-(6-Chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(6-cyano-1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(7-chloro-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(7-cyano-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine,
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
14
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1$-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(2-cyano-1 H-indol-4-yl~iperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indolin-4-yl)piperazine,
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-(1H-indol-6-yl)piperazine and
1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-( 1 H-indol-7-yl)piperazine,
or an acid addition salt thereof.
The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a
compound of
the invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt thereof and
at least
one pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent.
to
In another aspect the invention relates to the use of a compound of the
invention or a
pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt thereof for the preparation of
a
medicament for the treatment of a disorder or disease responsive to the
inhibition of
serotonin reuptake and antagonism of 5-HT,A receptors.
i5
In a final object, the present invention relates to a method for the treatment
of a
disorder or disease of living animal body, including a human, which is
responsive to
the inhibition of serotonin reuptake and antagonism of 5-HT,A receptors
comprising
administering to such a living animal body, including a human, a
therapeutically
2o effective amount of a compound as above or a pharmaceutically acceptable
acid
addition salt thereof.
Diseases or disorders responsive to the inhibition of serotonin re-uptake and
antagonistic activity at 5-HT,A receptors include affective disorders, such as
25 depression, psychosis, anxiety disorders including general anxiety disorder
and panic
disorder and obsessive compulsive disorder.
Due to their combined antagonism of 5-HT,A receptors and serotonin reuptake
inhibiting effect, the compounds of the invention are particularly useful as
fast onset
30 of action medicaments for the treatment of depression. The compounds may
also be
useful for the treatment of depression in patients who are resistant to
treatment with
currently available antidepressants.
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
In the groups of formula (IIA.), (IIB) and (IIC), the presence and position of
double
bonds in the ring containing X, U and Y depend on the meaning of X, U and Y.
Thus, as regards the group of formula (IIA), it is very clear to a person
skilled in the
5 art, that when a dotted line emanating from X is a bond, then X is N or
CR'~, and
when the dotted line is not a bond then X is CHR'~, NR'B, O, or S; and when a
dotted
line emanating from Y is a bond, then Y is N, or CR'B and when the dotted line
is not
a bond Y is CHR2~, NRzB, O, or S.
to Further, as regards the group of formula (IIB), it is very clear to a
person skilled in the
art, that when a dotted line emanating from X is a bond then X is N, or CR'~
and when
the dotted line is not a bond then X is CHR'~, NR'B, O, or S; and when a
dotted line
emanating from U is a bond then U is C and when the dotted line is not a bond
U is
CH, or N.
And finally as regards the group of formula (IIC), it is very clear to a
person skilled in
the art that when a dotted line emanating from U is a bond then U is C and
when the
dotted line is not a bond U is CH, or N; and when a dotted line emanating from
Y is a
bond then Y is N, or CR2~ and when the dotted line is not a bond then Y is
CHRZ~,
2o NR2H, O, or S.
The same applies to W, which is N, CH, or COH when the dotted line emanating
from
W does not indicate a bond and C when it indicates a bond.
The expression C,_6-alk(en/yn)yl means a C,_6 alkyl, C,_6 alkenyl, or a CZ_6
alkynyl
group. The expression C3_g cycloalk(en)yl means a C3_$ cycloalkyl- or
cycloalkenyl
group.
The term C,_6 alkyl refers to a branched or unbranched alkyl group having from
one to
six carbon atoms inclusive, including but not limited to methyl, ethyl, 1-
propyl, 2-
propyl, 1-butyl, 2-butyl, 2-methyl-2-propyl and 2-methyl-1-propyl.
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
16
Similarly, CZ_6 alkenyl and CZ_6 alkynyl, respectively, designate such groups
having
from two to six carbon atoms, including one double bond and one triple bond
respectively, including but not limited to ethenyl, propenyl, butenyl,
ethynyl,
propynyl, and butynyl.
The terms C,_6 alkoxy, C,_6 alkylthio, C,_6 alkylsulfonyl, C,_6 alkylamino,
C,_6 alkylcarbonyl, hydroxy-C,~ alkyl etc. designate such groups in which the
C,_6 alkyl is as defined above.
The term C3_$ cycloalkyl designates a monocyclic or bicyclic carbocycle having
three
to eight C-atoms, including but not limited to cyclopropyl, cyclopentyl,
cyclohexyl,
etc.
The term C3_$ cycloalkenyl designates a monocyclic or bicyclic carbocycle
having
three to eight C-atoms and including one double bond.
In the term C3_g-cycloalk(en)yl-C,_6 alk(en/yn)yl, C,_g-cycloalk(en)yl and
C,_6
alk(en/yn)yl are as defined above.
The term aryl refers to a carbocyclic aromatic group, such as phenyl,
naphthyl, in
particular phenyl. As used herein aryl may be substituted one or more times
with
halogen, nitro, cyano, trifluoromethyl, C,_6 alkyl, hydroxy and C,_6 alkoxy.
The term heteroaryl refers to a mono- or bicyclic heterocyclic group such as
indolyl,
thienyl, pyrimidyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, imidazolyl,
benzofuranyl, benzothienyl, pyridyl and furanyl, in particular pyrimidyl,
indolyl, and
thienyl.
As used herein heteroaryl may be substituted one or more times with halogen,
nitro,
cyano, trifluoromethyl, C,_6 alkyl, hydroxy and C,_6 alkoxy.
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
17
In aryl-C,_6-alkyl and heteroaryl-C,_6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl and C,~ alkyl
is as defined
above.
Halogen means fluoro, chloro, bromo or iodo.
As used herein the term acyl refers to fonmyl, C,_6 alk(en/yn)ylcarbonyl,
arylcarbonyl,
aryl-C,_6-alk(en/yn)ylcarbonyl, C,$ cycloalk(en)ylcarbonyl, or a C3_g-
cycloalk(en)yl-
C,_6alk(en/yn)yl-carbonyl group and the term thioacyl is as the corresponding
acyl
group in which the carbonyl group is replaced with a thiocarbonyl group.
The acid addition salts of the invention are preferably pharmaceutically
acceptable
salts of the compounds of the invention formed with non-toxic acids. Exemplary
of
such organic salts are those with malefic, fumaric, benzoic, ascorbic,
succinic, oxalic,
bis-methylenesalicylic, methanesulfonic, ethanedisulfonic, acetic, propionic,
tartaric,
salicylic, citric, gluconic, lactic, malic, mandelic, cinnamic, citraconic,
aspartic,
stearic, palmitic, itaconic, glycolic, p-aminobenzoic, glutamic,
benzenesulfonic, and
theophylline acetic acids, as well as the 8-halotheophyllines, for example 8-
bromotheophylline. Exemplary of such inorganic salts are those with
hydrochloric,
hydrobromic, sulfuric, sulfamic, phosphoric, and nitric acids.
Further, the compounds of this invention may exist in unsolvated as well as in
solvated forms with pharmaceutically acceptable solvents such as water,
ethanol and
the like. In general, the solvated foams are considered equivalent to the
unsolvated
forms for the purposes of this invention.
Some of the compounds of the present invention contain chiral centres and such
compounds exist in the form of isomers (i.e. enantiomers). The invention
includes all
such isomers and any mixtures thereof including racemic mixtures.
3o Racemic forms can be resolved into the optical antipodes by known methods,
for
example, by separation of diastereomeric salts thereof with an optically
active acid,
and liberating the optically active amine compound by treatment with a base.
Another
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
18
method for resolving racemates into the optical antipodes is based upon
chromatography on an optically active matrix. Racemic compounds of the present
invention can also be resolved into their optical antipodes, e.g., by
fractional
crystallization of d- or 1- (tartrates, mandelates, or camphorsulphonate)
salts for
example. The compounds of the present invention may also be resolved by the
formation of diastereomeric derivatives.
Additional methods for the resolution of optical isomers, known to those
skilled in the
art, may be used. Such methods include those discussed by J. Jaques, A.
Collet, and S.
Wilen in "Enantiomers, Racemates, and Resolutions", John Wiley and Sons, New
York (1981).
Optically active compounds can also be prepared from optically active starting
materials.
Finally, formula (I) includes any tautomeric forms of the compounds of the
invention.
The compounds of the invention can be prepared by one of the following methods
comprising:
a) reducing the carbonyl groups of a compound of formula (III)
Re R~ ~a
s ~~~~ yy ~~N
R
RS
R,o,.~
N
R12 n
R~ ~
(III)
wherein R'-R'2, W and the dotted lines are as defined above;
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
19
b) alkylating an amine of formula (IV)
Re R~
R9 ~~~~ W~~NH
R' o
N
Rtz
R" (IV)
wherein R'-R'Z, W and the dotted lines are as defined above with a reagent of
formula
N)
G-(CH2M--Z-(CHz)m-A
(V)
wherein A, Z, n, and m are as defined above and G is a suitable leaving group
such as
halogen, mesylate, or tosylate;
c) reductive alkylation of an amine of formula
RB R~
R9 W NH
R'o
N
R~2
R" (IV)
wherein R'-R'Z, W and the dotted lines are as defined above with a reagent of
formula
(VI)
E-(CHz)"--Z-(CHy~"-A
IS (VI)
wherein A, Z, n and m are as defined above and E is either an aldehyde or a
carboxylic acid group;
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
d) reducing the double bond of the indole ring, which is attached to the
cyclic
amine moiety, of formula (I) in order to obtain the corresponding 2,3-
dihydroindole
derivatives;
5 e) reducing the double bond of a tetrahydropyridine of formula (VII)
N-(CHZIn-Z-(CHz)<n-A
Rio--.. \~//-
R, , (VII)
wherein R7-R'2, A, Z, n, m, and the dotted lines are as previously defined, on
order to
10 obtain the corresponding piperidine derivatives;
f) reducing the amide group of a compound of formula (VIII)
RB R~
r\~/
R9 I w N (CHzlo-~-Z-(CH2~n-A
R~o_
N
R~z
R~ ~ (VIII)
is wherein R7-R'z, A, W, Z, n, m, and the dotted lines are as previously
defined;
g) reductive removal of one or more of the halogen substitutents R3-R9 and R"-
R'2 in a compound of formula (I) in which one or more of these substituents
are
selected from chloro, bromo, or iodo;
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO' 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
21
h) dialkylating an amine of formula (IX)
R~o~
(IX)
R"
wherein R7-R'2 and the dotted line are as defined above with a reagent of
formula (X)
(CHz~,-Z-(CHz~" A
(X)
wherein A, Z, n, and m are as defined above and G is a suitable leaving group
such as
halogen, mesylate, or tosylate;
to i) dialkylating an amine of formula (XI)
HzN----(CHz~,-Z-(CHzlm A
(XI)
wherein A, Z, n, and m are as defined above with a reagent of formula (XII)
Ra R~ G
Rs ~ W
Rto'
N G
R~z (XII)
R"
wherein R7-R'2, W, and the dotted line are as defined above and G is a
suitable leaving
group such as halogen, mesylate, or tosylate;
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
22
j) alkylating, arylating, or acylating one or both indole nitrogen atoms of a
compound of formula (I) in which R'° is hydrogen, and /or X and/or Y is
NH; or
k) reducing a compound of formula (I) in which R', R8, or R9 is an
alkoxycarbonyl group in order to obtain the corresponding hydroxymethyl group;
whereupon the compounds of formula (I) are isolated as the free base or in the
form of
an acid addition salt thereof.
to The reduction according to method a) is preferably carried out in an inert
organic
solvent such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran in the presence of lithium
aluminium
hydride at reflux temperature. Starting compounds of formula (III) are
generally
prepared by condensation of 3-chlorooxalyl indoles (prepared as described in
Houben-
Weyl, Methoden der Organischen Chemie, Vol E6B2, p. 1058) with amines of
formula (IV) in the presence of a base such as triethylamine or potassium
carbonate.
The alkylation according to method b) is conveniently performed in a inert
organic
solvent such as a suitably boiling alcohol or ketone, preferably in the
presence of an
organic or inorganic base (potassium carbonate or triethylamine) at reflux
2o temperature.
Indolylpiperazine derivatives of formula (IV) are conveniently prepared from
the
corresponding arylamine according to the method described by Martin et al, J.
Med.
Chem. 32 (1989) 1052, or the method described by Kruse et al, Rec. Trav. Chim.
Pays-Bas 107 (1988) 303. The starting arylamines are either commercially
available
or are well-described in the literature.
Indolyl tetrahydropyridine derivatives of formula (IV) are known from
literature (see
eg. French Pat. 2458549). Conveniently, 1-protected 4, 5, 6, or 7-bromoindole
is
lithiated with BuLi followed by addition of 1-protected 4-piperidone and
subsequent
dehydration as outlined in an example below. The starting bromoindoles are
either
commercially available or well-described in the literature. Reagents of
formula (V) are
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W(3 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
23
either commercially available or can be prepared by literature methods, eg.
from the
corresponding carboxylic acid derivative by reduction to the corresponding
hydroxy
derivatives and subsequent conversion of the hydroxy group to the group G by
conventional methods.
The reductive alkylation according to method c) is performed by standard
literature
methods. The reaction can be performed in two steps, ie. coupling of
derivatives of
formula (IV) and the reagent of formula (VI) by standard methods via the
carboxylic
acid chloride or by use of coupling reagents such as eg. dicyclohexyl
carbodiimide
to followed by reduction of the resulting amide with lithium aluminium hydride
or alane.
The reaction can also be performed by a standard one-pot procedure. Carboxylic
acids
or aldehydes of formula (VI) are either commercially available or described in
the
literature.
15 Reduction of the indole double bond according to method d) is conveniently
performed by treatment with diborane or a diborane precursor such as the
trimethylamine or dimethylsulfide complex in an inert solvent such as eg.
tetrahydrofuran or dioxane from 0 °C to reflux temperature followed by
acid
catalyzed hydrolysis of the intermediate borane derivative. The reduction can
2o alternatively be performed by treatment with sodium cyanoborohydride in
trifluoroacetic acid.
Reduction of the double bonds according to method e) is most conveniently
performed by hydrogenation in an alcohol in the presence of a noble metal
catalyst,
25 such as eg. platinum or palladium.
Reduction of amide groups according to method fj is most conveniently
performed
with lithium aluminium hydride or alane in an inert organic solvent such as
eg.
tetrahydrofuran or diethylether from 0 °C to reflux temperature.
The removal of halogen substituents according to method g) is conveniently
performed by catalytic hydrogenation in an alcohol in the presence of a
palladium
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
24
catalyst or by treatment with ammomium formate in an alcohol at elevated
temperatures in the presence of a palladium catalyst.
The dialkylation of amines according to methods h) and i) is most conveniently
performed at elevated temperatures in an inert solvent such as eg.
chlorobenzene,
toluene, N-methylpyrrolidinone, dimethylformamide, or acetonitrile. The
reaction
might be performed in the presence of base such as eg. potassium carbonate or
triethylamine. Starting material for processes h) and i) are commercially
available or
can be prepared using conventional methods.
The indole N-alkylation or N-acylation are performed in an inert solvent such
as eg.
an alcohol or ketone at elevated temperatures in the presence of base, eg.
potassium
carbonate or triethylamine. Alternatively, a phase-transfer reagent can be
used. The
corresponding N-arylation is best performed under Ullmann-conditions as
described
in the literature.
The reduction of alkoxycarbonyl groups according to method k) is most
conveniently
performed with lithium aluminium hydride or alane in an inert organic solvent
such as
e.g. tetrahydrofuran.
The following examples will illustrate the invention further. They are,
however, not to
be construed as limiting.
Examples
Melting points were determined on a Biichi B-540 apparatus and are
uncorrected.
Mass spectra were obtained on a Quattro MS-MS system from VG Biotech, Fisons
Instruments or on a Sciex API 150EX from Perkin Elmer. Spectra were obtained
at
two sets of operating conditions using electrospray ionisation: one set to
obtain
molecular weight information (MH+, 20 eV) and the other set to induce
fragmentation
3o patterns (70-100 eV). The background was substracted. The relative
intensities of the
ions are obtained from the fragmentation pattern. When no intensity is
indicated for
the molecular ion (MH+) this ion was only present under the first set of
operating
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
conditions. 'H NMR spectra were recorded at 250 MHz on a Broker AC 250 or at
500
MHz on a Broker DItX 500. Deuterated chloroform (99.8% D) or dimethylsulfoxide
(99.9% D) were used as solvents. TMS was used as internal reference standard.
Chemical shi8s are expressed as ppm values. The following abbreviations are
used for
5 multiplicity of NMR signals: s=singlet, d=doublet, t=triplet, q=quartet,
qv=quintet,
h=heptet, dd---double doublet, dt=double triplet, dq=double quartet,
tt=triplet of
triplets, m= multiplet, b=broad. NMR signals corresponding to acidic protons
are to
some extent omitted. Content of water in crystalline compounds were determined
by
Karl Fischer titration. Proper elemental analysis for all target compounds
were
10 obtained. Standard work-up procedures refer to extraction with the
indicated organic
solvent from proper aqueous solutions, drying of combined organic extracts
(anhydrous MgS04 or NaS04), filtering, and evaporation of the solvent in
vacuo. For
column chromatography silica gel of type Kieselgel 60, 40-60 mesh ASTM was
used.
15 Preyaration of Intermediates
A. Preparation of 1-(1H-indol-4-yl)piperazines:
1-(1H-Indol-4-yl)y erazine
Dinitrotoluene (25 g) was dissolved in DMSO (60 mL). Triton-B (40% in
methanol,
6.4 mL) was added resulting in a dark purple solution. The mixture was heated
to 30
2o °C followed by slow addition of a solution of paraformaldehyde (4.5
g) in DMSO (40
mL). After addition the mixture was heated to 65 °C for 1.5 hours.
Standard work-up
with ethyl acetate gave 2-(2,6-dinitrophenyl)ethanol (29 g) as a dark red oil.
The oil (27 g) was dissolved in ethanol (250 mL) and 5% palladium on charcoal
(3 g)
was added. The mixture was treated with hydrogen gas at 3 atmospheres of
pressure in
25 a Purr apparatus for 16 h. Filtration and removal of solvent in vacuo gave
2-(2,6-
diaminophenyl)ethanol (19.4 g) as brown oil that crystallized upon standing.
Part of this product (15.8 g) was dissolved in toluen (250 mL) and
tris(triphenylphosphine)ruthenium(II)chloride {2.9 g) was added. The mixture
was
refluxed with a water separator for 8 hours followed by removal of solvent in
vacuo.
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/b7237 PCT/DK99/00326
26
The remaining reaction mixture was purified by flash chromatography (eluent:
heptane/ethyl acetate 3:1) giving 4-amino-1H-indole as a crystalline solid
(7.6 g).
The solid was dissolved in chlorobenzene (150 mL) and bis(2-chloroethyl)amine
hydrochloride (9 g) was added followed by reflux for 90 hours. Filtration gave
a
crystalline product (9.2 g) which was heated in a mixture of cone. aq. ammonia
(50
mL) and ethyl acetate (200 mL) for 15 min. Separation of the organic phase,
drying
and evaporation gave the titel compound as a crystalline material (5.6 g).
The following piperazines were prepared analogously:
l0 1-(6-Methoxycarbonyl-1 H-Tndo l-4-yl)piperazine.
1-(6-t-Butyl-5-methoxy-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine.
1-(6-t-Butyl-7-methoxy-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine.
1-(6,7-Dihydro-6,6, 8, 8-tetramethylcyclopent(g)-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine
i5 This piperazine was prepared by treatment of 5-aminoindole with and bis(2-
chloroethyl)amine by a procedure analogous to the procedure described above
for the
preparation of 1-(1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine.
1-l3-Cvano-1 H-indol-4-vl)piperazine.
2o A mixture of 1-{1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine hydrochloride (1 g) and potassium
carbonate (2.9 g) in tetrahydrofuran (25 mL) and water (25 mL) was stirred for
15 min
followed by addition of a solution of di-t-butyl dicarbonate (2.3 g) in a 1:1
mixture of
tetrahydrofi~ran and water (20 mL). The mixture was stirred at 50 °C
for 16 hours.
Standard work-up with ethyl acetate gave 1-t-butoxycarbonyl-4-(1H-indol-4-
25 yl)piperazine as a heavy oil (1.1 g).
The oil was dissolved in acetonitrile (50 mL) followed by dropwise addition of
chlorosulfonyl isocyanate (1 mL) at -20 °C. The mixture was kept at low
temperature
during dropwise addition of dimethylformamide (5 mL) over 20 min. Finally, the
mixture was stirred for 30 min at 0 °C. An aqueous solution of sodium
carbonate (30
3o mL) was added and the mixture stirred for 30 min. The organic phase was
separated,
dried and concentrated. The resulting oil was purified by column
chromatography
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
27
(eluent: ethyl acetate/heptane/methanol 16:3:1) giving 1-t-butoxycarbonyl-4-(3-
cyano-
1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine as a yellow oil (0.5 g).
The oil was dissolved in methanol (2 mL) and etheral hydrogenchloride (20 mL)
was
added. Stirring for 2 hours and filtration gave the title compound as a
crystalline
material (0.34 g).
A solution of 1-t-butoxycarbonyl-4-(1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine (prepared as
described
above) in tetrahydrofuran (50 mL) was added dropwise to a suspension of sodium
hydride (0.7 g of a 60% mineral oil suspension) in tetrahydrofuran (150 mL) at
room
temperature. After stirring for further 30 min a solution of allyl bromide
(3.5 mL) in
tetrahydrofuran (50 mL) was added dropwise. After stirring for 48 h the
mixture was
poured onto ice-water followed by standard work-up with ethyl acetate giving
an oil,
which was purified by flash chromatography (eluent: heptane/ethyl acetate
85:15)
giving 1-t-butoxycarbonyl-4-(1-allyl-1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine as an oil (3.2
g).
The oil was dissolved in methanol (15 mL) and a saturated solution of HCl in
diethyl
ether (100 mL) was added. After stirring for 16 h at room temperature, the
resulting
colorless crystals consisting of the hydrochloride of the title compound (2.5
g) was
collected by filtration and dried in vacuo.
The following piperazines were prepared analogously:
1-( 1-Benzyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine
1-( 1-Propargyl-1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine
B. Preparation of 4-(1H-indol-4-yl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.
A solution of 4-bromo-1H-indole (36 g) in dimethylformamide (80 mL) was
treated
with a suspension of NaH (60% in mineraloil, 6.9 g) in dimethylformamide (200
mL)
at 20 °C. After stirnng for 30 min the mixture was cooled to -10
°C an treated
portionwise with t-butyldimethylsilyl chloride (38 g) followed by stirring for
1 h at
room temperature. Standard work-up with ethyl acetate gave and oil which was
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
28
purified by flash chromatography giving 4-bromo-1-(t-butyldimethylsilyl)-1H-
indole
(38 g) as a crystalline material.
The product was dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (S00 mL), cooled to -78
°C, and
treated dropwise with 1.6 M BuLi in hexane (154 mL). After stirring for 30 min
at -78
°C, a solution of 1-carbethoxy-4-piperidone (18.2 mL) in
tetrahydrofuran (200 mL)
was added dropwise followed by stirring for 16 h under slow raise in
temperature to
room temperature. Standard work-up with diethyl ether gave and oil which was
purified by flash chromatography (eluent: heptane/ethyl acetate/triethylamine
6:3:1 )
giving 1-{t-butyldimethylsilyl)-4-(1-carbethoxy-4-hydroxy-4-piperidinyl)-IH-
indole
l0 as a crystalline compound (20.5 g).
Treatment of this product with trifluoroacetic acid (15 mL) in methylene
chloride (250
mL) at 0 °C for 20-30 min (reaction is followed by thin layer
chromatography on
silica gel, eluent ethyl acetate/heptane/triethylamine 10:9:1 ). Addition of 2
M sodium
hydroxide, separation of the organic phase, drying, and removal of solvent in
vacuo
gave an oil, which was purified by flash chromatographt (eluent as mentioned
above
for TLC) giving 1-carbethoxy-4-(1H-indol-4-yl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (9.1
g) as
a crystalline material.
Treatment with potassium hydroxide (5 g) in ethanol (150 mL) with a small
amount of
water (2 mL) at reflux for 3 days gave after standard work-up the titel
compound as a
2o yellow oil (4.5 g).
C. Preparation of 5-fluorobenzofuran-3-acetic acid.
A solution of 5-fluorobenzofuran-3-carboxylic acid (56 g) and saturated
etheral
solution of hydrochloric gas (300 mL) in methanol (600 mL) was stirred for 16
h at
room temperature. Further etheral HCI was added {300 mL) followed by stirnng
for
24 h. Concentration in vacuo gave a dark crystalline material, methyl 5-
fluorobenzofuran-3-carboxylate (58 g).
Lithium aluminium hydride (15 g) was suspended in tetrahydrofuran (400 mL)
under
a nitrogen atmosphere followed by dropwise addition of a solution of methyl 5-
3o fluorobenzofuran-3-carboxylate (58 g) in tetrahydrofuran (300 mL). The
temperature
increased to 55 °C during the addition. After stirnng for 2 h the
reaction was
quenched succesively with water (30 mL), 15% aq. sodium hydroxide (IS mL), and
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
29
water (75 mL). Further tetrahydrofuran (500 mL) was added and the mixture
stirred
for 1 h. The mixture was filtered and the precipitate extracted with a mixture
of
methylene chloride ( 1 L) and ethanol (0.5 L). The combined organic phases
were
concentrated in vacuo giving an oil which was applied to silica gel flash
chromatography (eluent: methylene chloride/25% aq. NH3 99:1). The resulting
yellow
oil, 5-fluorobenzofuran-3-ylmethanol (14.4 g) crystallised on standing.
A solution of 5-fluorobenzofuran-3-ylmethanol (14 g) in methylene chloride
(250 mL)
was treated succesively with 5 drops of dimethylformamide and thionyl chloride
(28
mL). After stirring for 16 h at room temperature the reaction was concentrated
in
l0 vacuo giving 3-chloromethyl-5-fluorobenzofuran as an oil (19.4 g).
A suspension of sodium cyanide (10 g) in dimethylsulfoxide (150 mL) was heated
to
80 °C followed by quick addition of a solution of 3-chloromethyl-5-
fluorobenzofuran
(10 g) in dimethylsulfoxide (50 mL). The mixture was kept at 80 °C
for'/z h and then
poured onto ice. Standard work-up with diethyl ether gave a dark crystalline
material,
5-fluorobenzofuran-3-ylacetonitrile (8.8 g).
A solution of 5-fluorobenzofuran-3-ylacetonitrile (8.8 g) in methanol (350 mL)
was
treated with a saturated etheral solution of hydrochloric gas (350 mL) and
stirred for
16 h at room temperature. The mixture was concentrated in vacuo and standard
work-
up with. diethyl ether/water gave methyl 5-fluorobenzofuran-3-ylacetate (9.4
g) as an
oil.
The obtained methyl ester was dissolved in methanol (200 mL) and 6 M aq.
sodium
hydroxide (400 mL) was added followed by stirring for 16 at room temperature.
Organic solvent was removed in vacuo followed by acidification with 6 M
hydrochloric acid. Standard work-up with ethyl acetate gave 5-fluorobenzofuran-
3-
ylacetic acid (9.2 g) as a crystalline material.
The following benzofuran-3-acetic acids were prepared analogously:
2-Methyl-4,5,6,7-tetrafluorobenzofuran-3-acetic acid
Benzofuran-3-acetic acid
6-Methylbenzofuran-3-acetic acid
5-Methylbenzofuran-3-acetic acid
4-Methylbenzofuran-3-acetic acid
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
7-Chlorobenzofuran-3-acetic acid
5-Chlorobenzofuran-3-acetic acid
5-Fluorobenzofuran-3-propionic acid and -butanoic acid, respectively, were
prepared
5 by chain prolongation procedures analogously to the procedure described
above.
6-Chloroindazol-3-acetic acid was prepared according to J. Med. Chem. 35
(1992)
2155.
3-(6-Fluorobenz[1,2]isoxazol-3-yl)propionic acid was prepared according to
Drug
Design Discov. 8 ( 1992) 225.
Preuaration of the compounds of the Invention
Example 1
lap 1_(2-(3-Benzo ranvl, et y~)-4-~(IH indol-4 y~~~erazine. oxalate.
A mixture of 2-(3-benzofuranyl)acetic acid (0.95 g), 1-(1H-indol-4-
yl)piperazine (1.3
g), and N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide ( 1.3 g) in a mixture of dry
tetrahydrofuran (50
mL) and dry dimethylformamide (10 mL) was stirred for 16 h at room
temperature.
Filtration and removal of solvent in vacuo gave an oil which was purified by
flash
chromatography (eluent: ethyl acetate/heptane/triethylamine 10:9:1 ) giving 1-
(3-
benzofuranyl)methylcarbonyl-4-( 1 H-indol-4-yl)piperazine (0.5 g) as an oil.
The oil was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) and treated with a suspension
of
lithium aluminium hydride (0.26 g) in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) at room
temperature
under a nitrogen atmosphere followed by reflux for 4 hours. The reaction
mixture was
cooled to 0 °C and treated subsequently with water (1 mL), 15% aq.
sodium
hydroxide (0.5 mL), and water (2.5 mL). After stirring for 30 min the mixture
was
filtered and concentrated. The remaining oil was dissolved in acetone followed
by
addition of oxalic acid and filtration, giving the title compound as a
crystalline
material (0.4 g). Mp 130-32 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 3.05-3.15 (m, 2H);
3.15-3.30
(m, 6H); 3.35 (s, 4H); 6.45 (s, 1H); 6.55 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.10 (d, 1H);
7.20-7.40
(m, 3H); 7.60 (d, 1 H); 7.75 (d, 1 H); 7.90 (s, 1 H); 11.10 (s, 1 H). MS m/z
(%): 346
(MH+, 3%), 214 (31%), 199 (19%), 171 (14%).
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
31
The following compounds were prepared analogously:
lb, 1-(3-Benzofuranylmethyl)-4-(1 H indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 226-28°C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 3.10-3.20 (m, 4H); 3.20-3.40 (m, 4H);
4.25 (s,
2H); 6.40 (t, 1 H); 6.45 (d, 1 H); 7.00 (t, 1 H); 7.10 (d, 1 H); 7.25 (dt, 1
H);
7.30-7.45 (m, ZH); 7.65 (dd, 1H); 7.95 (dd, 1H); 8.15 (s, 1H); 11.10 (s, 1H).
MS m/z (%): 332 (MH+, 10%), 158 (10%), 131 (100%).
lc, 1-(2-(S-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
1o Mp 196-97 °C,'H NMR (DMSO-db): 3.05 (t, 2H); 3.20-3.45 (m, lOH);
6.44 (s, 1H);
6.50 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.10 (d, 1H); 7.20 (dt, 1H); 7.30 (t, IH); 7.55-
7.65 (m, 2H);
8.00 (s, 1H); 11.12 (s, 1H), MS mlz (%) : 364 (MH+, 7%), 214 (42%), 199 (20%),
171 {14%).
ld, 1-(4-(S-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)-1-butyl)-4-(ltl-iudol-4-vl)piperazine,
dihydrochloride.
Mp 241-44 °C,'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 1.65-1.95 (m, 4H); 2.70 (t, 2H); 3.15-
3.40 (m,
6H); 3.60 (d, 2H); 3.70 (d, 2H); 6.50 (s, 1 H); 6.55 ( d, 1 H ); 7.UU (t, 1
H); 7.10 (d, 1 H);
7.15 (dt, 1 H); 7.30 (t, 1 H); 7.45-7.60 (m, 2H); 7.90 ( s, 1 H ); 10.95 (b, 1
H); 11.20 (s,
1H). MS mlz (%): 392 (MH?, 90%), 234 (19%), 199 (23%), 163 (49%), 131 (11%).
le, I-(2-(1H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)piperazine, hemioxalate.
Mp 167-69 °C, 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 3.05 (s, 4H); 3.1 S (s, 41-I); 3.30 (s,
4H); 6.40 (s,
1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 6.90-7.15 (m, 4H); 7.25 (dd, 2H); 7.35 (d, 1H); 7.60 (d,
1H); 10.90
(s, 1H); 11.10 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 345 (MH+, 5%), 199 (13%), 144 (54%), 107
(9%).
lf, l-(3-(IH indol-3 yl)-1 propyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 198-204 °C.'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.05 (qv, 2H); 2.75 (t, 2H); 3.15 (t,
2H); 3.35
(s, 8H); 6.45 (s, 1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 2H); 7.10 (t, 2H); 7.20 (d.lH);
7.25 (t, 1H);
7.35 (d, 1H); 7.55 {d, 1H); 10.85 (b, 1H); 11.15 (b, 1H).
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
32
lg; l-(4-(IH indol-3 yl)-1-butyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 189-93 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 1.60-1.85 (m, 4H); 2.75 (t, 2H); 3.05
(t, 2H);
3.15-3.50 (m, 8H); 6.45 (s, 1H); 6.50 (s, 1H); 6.90-7.20 (m, 5H); 7.30
(s, 1 H); 7.35 (d, 1 H); 7.55 (d, 1 H); 8.20 (b, 2H); 10.90 (s, 1 H); 11.20
(s, 1 H).
lh, 1-(3-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)-1 propyl)-4-(1H indol-4 yl)piperazine,
dihydrochloride.
Mp 230-34 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.20 (qv, 2H); 2.75 (t, 2H); 3.20-3.30
(m, 2H);
3.30-3.45 (m, 4H); 3.55-3.80 (m, 4H); 6.55 (s, 1 H); 6.65 (d, 1 H); 7.00
l0 (t, 1H); 7.10-7.20 (m, 2H); 7.30 (t, 1H); 7.50-7.65 (m, 2H); 7.95 (s, 1H);
11.25 (s,
1H); 11.40 (b, 1H). MS m/z (%): 378 (MH+, 70%), 220 (26%), 199 (25%), 177
(18%), 159 (100%).
li, I-(2-(2-Methyl-4,S,b,7-tetrafluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(lll indol-4-
yl)piperazine, dihydrochloride.
Mp 181-87 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.50 (s, 3H); 3.15-3.50 (m, 8H);
3.65-3.85 (m, 4H); 6.50 (s, 1H); 6.60 (t, 1H); 7.05 (t, 1H); 7.15 (d, 1H);
7.35 (d, 1H);
11.20 (s, 1H); 11.75 (b, 1H). MS m/z (%): 414 (MH+- F, 13%), 396 (11%), 214
(72%), 199 (23%), 195 (34%), 159 (26%).
lj,1-(2-(3-Indazolyl)ethyl)-4-(IH-indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 149-51 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 3.05-3.15 (m, 4H); 3.15-3.20 (m, 2H);
3.20-3.35
(m, 6 H); 6.40 (s, 1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.05 (d, 1H); 7.10 (t,
1H); 7.25 (s,
1H); 7.35 (t, 1H); 7.50 (d, 1H); 7.80 (d, 1H); 11.10 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 346
(MH+,
40%); 199 (80%); 144 ( 100%).
lk, 1-(2-(b-Chloro-3-indazolyl)ethyl)-4-(1H indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 255-58 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 3.10-3.15 (m, 4H); 3.15-3.20 (m, 2H);
3.20-3.30
{m, 6H); 6.40 (s, 1H); 6.50 {d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.10 (d, 1H); 7.15 (d, 1H);
7.25 (s,
1H); 7.55 (s, 1H); 7.85 (d, 1H); ). MS m/z {%): 380 (MH+, 100%), 214 (30%),
139
(50%).
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
33
11,1-(2-(7-Cyano-1H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1H indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 241-43 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 3.15 (t, 2H); 3.30 (t, 2H); 3.30-3.50
(m, 8H);
6.45 (s, 1 H); 6.50 (d, 1 H); 7.00 (t, 1 H); 7.10 (d, 1 H); 7.20 (t, 1 H);
7.30 {s, 1 H); 7.50
(s, 1H); 7.60 (d, 1H); 8.00 (d, 1H); 11.15 (s, 1H); 11.90 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%):
370
(MH+, 100%), 214 (28%), 156 (42%).
Example 2
2a 1 (,,~ l6-Chloro-1H indol-3-y~~(IH indol-4-vl)Dinerazine. oxalate.
l0 A solution of 6-chloro-1H-indole (15 g) in diethyl ether (300 mL) was
cooled to 0 °C
and treated with a solution of oxalyl chloride (9.4 mL) in diethyl ether (30
mL). The
mixture was stirred for 16 hours at room temperature. Filtration gave 2-(6-
chloro-1H-
indol-3-yl)-2-oxoacetyl chloride as a crystalline material (15.5 g).
A part of this product (2.5 g) was dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (25 mL)
and added
dropwise to a solution of 1-{1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine (1.4 g) and
triethylamine (15
mL) in tetrahydrofuran ( 100 mL). After stirnng for I 6 hours the reaction
mixture was
concentrated in vacuo. The remaining oil was purified by flash chromatography
(eluent: ethyl acetate/methanol/triethylamine 85:10:5) giving 1-(2-(6-chloro-
1H-indol-
3-yl)-1,2-dioxoethyl)-4-{1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine (1.6 g) as a crystalline
material.
2o This product was suspended in tetrahydrofuran (25 mL) and added dropwise to
a
suspension of lithium aluminium hydride (1.5 g) in tetrahydrofuran (50 mL).
The
mixture was refluxed for 4 hours and cooled to 0 °C followed by
subsequent addition
of water (3 mL), 15% aq. sodium hydroxide {1.5 mL), and water (7.5 mL).
Filtration
and standard work-up gave a yellow oil which was converted to the title
oxalate salt
(1.5 g) from an acetone solution by addition of oxalic acid. Mp 229-31
°C.'H NMR
(DMSO-db): 3.10 (t, 2H); 3.25-3.55 (m, lOH); 6.45 (s, 1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 6.90-
7.10
(m, 3H); 7.25-7.35 (m, 2H); 7.45 (s.lH); 7.65 (d, 1H); 11.12 (s, 2H), MS m/z
(%):
379 (MH+, 18%), 214 (16%), 199 (17%), 178 (16%), 143 (13%).
3o The following compounds were prepared analogously:
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
34
2b, 1-(2-(4-Chloro-1 H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1 H indol-4 yl)piperazine,
oxalate.
Mp 245-47 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 3.30-3.50 {m, 12H); 6.45 (s, IH);
6.50 (d, 1H); 6.95-7.10 (m, 4H); 7.30 (s, IH); 7.35-7.40 {m, 2H); 11.15 (s,
IH); 11.40
(s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 379 (MH+, 28%), 178 (41%), 143 (100%).
2c, 1-(2-(S-Fluoro-1 H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1 H indol-4 yl)piperazine,
fumarate.
Mp 212=15 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.75-3.10 (m, 8H); 3.10 -3.35 (m, 4H);
6.40 (s,
1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 6.60 (s, 2H); 6.85-7.10 (m, 3H); 7.20-7.40 (m, 4H); 10.95
(s, 1H);
11.05 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 363 {MH+, 18%), 214 (100%), 202 (34%), 199 (I9%),
171 ( 12%), 162 {87%).
2g, 1-(2-(6-Chloro-1H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)-1,2,3,6-
tetrahydropyridine,1.5 fumarate.
Mp 225-26 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.60-2.?0 (m, 2H); 2.85-3.10 (m,6H);
3.40-3.50
(m, 2H); 6.10 (s, 1H); 6.60 (s, 3H); 6.90-7.10 (m, 3H), 7.20-7.40
(m, 3H); 7.40 (d, 1 H); 7.60 (d, 1 H); 11.05 (s, 1 H); 11.15 (s, 1 H). MS m/z
(%):
376 (MH+, 12%), 179 (80%), 143 (100%).
2b, 1-(2-(5-Fluoro-IH indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)-1,2,3,6-
tetrahydropyridine,
trifumarate.
Mp 204-6 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.70-2.85 (m, 2H); 3.00-3.20 (m, 4H);
3.25 (t,
2H); 3.70-3.80 (m, 2H); 6.05-6.15 (m, 1H); 6.60 (s, 6H); 6.85-7.00 (m, 2H);
7.10 (t,
1H); 7.30-7.45 (m, 6H); 11.00 (s, IH); 11.20 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 360 (MH+),
162
( 100%).
2i, 1-(2-(7-Bromo-IH indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)piperazine,
hemioxalate.
Mp 149-51 °C. 'H NMR {DMSO-db): 2.95-3.20 (m, 8H); 3.20-3.40 (m, 4H);
6.40 (s,
1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 7.00 (dt, 2H); 7.10 (d, 1H); 7.25 (t, IH); 7.30-7.40 (m,
2H); 7.60 (d,
1H); 11.05 (s, 1H); 11.10 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 423 (MH+, 9%), 222 (20%), 214
(29%), 143 ( 100%).
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
2j, l-(1-Allyl-IH indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(6-chloro-1H indol-3 yl)ethyl)piperazine,
fumarate.
Mp 230-32 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.70-3.00 (m, 8H); 3.10-3.30 (m, 4H);
4.75 (d,
2H); 5.00 (d, 1 H); 5.15 (d, 1 H); 5.85-6.05 (m, 1 H); 6.40 (d, 1 H); 6.55
(dd, 1 H); 6.60
(s, 2H}; 6.95-7.10 (m, 3H); 7.20-7.30 (m, 2H); 7.40 (d, 1H); 7.55 (d, 1H). MS
m/z
5 (%): 419 (MH+, 13%), 254 (21%), 143 (100%).
2k, l-(1-Allyl-1H indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(S fluoro-1H indol-3 yl)ethyl)piperazine,
1.25
fumarate.
Mp 210-12 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.75-3.00 (m, 8H); 3.10-3.30 (m, 4H);
4.80 (d,
l0 2H); 5.00 (d, 1H); 5.15 (d, 1H); 5.90-6.10 (m, 1H); 6.40 (d, 1H); 6.50 (dd,
1H), 6.60
(s, 2H); 6.90 (dt, 1H); 7.00-7.10 (m, 1H); 7.20-7.40 (m, 4H); 10.95 (s, 1H).
MS m/z
(%): 403 (MH+, 25%), 239 (30%), 162 ( 100%).
21,1-(1-Benzyl-IH indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(6-chloro-IH-indol-3-nl)ethvl)piperazine,
15 hemifumarate.
Mp 237-39 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d~): 2.65-2.85 (m, 6H); 2.90 {t, 2H); 3.10-
3.25 (m,
4H); 5.40 (s, ZH); 6.45 (d, 1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 6.60 (s, 1 H); 6.95-7.10 (m,
3H); 7.15 (d,
1H); 7.20-7.35 (m, SH); 7.35-7.45 (m, 2H); 7.60 (d, 1H), 11.00 (s, 1H). MS m/z
(%):
469 (MH+, 20%), 304 (32%), 289 (22%), 143 ( 100%).
2m, l-(1-Benzyl-IH indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(5 Jluoro-IH-indol-3 yl)ethyl)piperazine,
fumarate.
Mp 178-80 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.70-3.00 (m, 8H); 3.10-3.30 (m, 4H);
5.40 (s,
2H); 6.45 (d, 1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 6.60 (s, 2H); 6.90 (dt, 1H); 7.00 (d, 1H);
7.10 (d, 1H);
7.15 (d, 1H); 7.20-7.40 (m, SH); 7.45 (d, 1H); 10.95 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 453
(MH+,
28%), 304 (39%), 162 (100%).
2n, l-(1-Benzyl-IH-indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(S-bromo-lhl indol-3 yl)ethyl)piperazine,
fumarate.
3o Mp 230-32 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.75-3.05 (m, 8H); 3.10-3.35 (m,
4H); 5.45 (s,
2H); 6.45 (d, 1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 6.60 (s, 2H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.10 (d, 1H);
7.10-7.20 (m,
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99J00326
36
2H); 7.20-7.40 (m, SH); 7.40 (d, 1 H); 7.80 (s, 1 H); 11.05 (s, 1 H). MS m/z
(%): 513
(MH+, 14%), 304 (30%), 142 (100%).
20,1-(2-(6-Chloro-1 H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1 propargyl-1 H indol-4
yl)piperazine.
Mp 197-99 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.70-2.95 (m, 6H); 3.00 (t, 2H); 3.20-
3.40 (m,
5H); 4.85 (d, 2H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 6.65 (d, 1H); 7.00-7.30 (m, SH); 7.35 (s,
1H); 7.55 (d,
1H); 8.00 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 417 (MH+, 15%), 252 (24%), 237 (17%), 143
(100%).
l0 2p, 1-(2-(1 H Indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(l propargyl-I H indol-4 yl)piperazine,
hemifumarate.
Mp 193-95 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.60-2.85 (m, 6H); 2.90 (t, 2H); 3.10-
3.25 (m,
4H); 3.35 (t, 1H); 5.00 (d, 2H); 6.45 (d, 1H); 6.55 (d, 1H); 6.60 (s, 1H);
6.90-7.25 (m,
5H); 7.25-7.40 (m, 2H); 7.55 (d, 1H), 10.75 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 383 (MH+,
44%),
252 (55%), 143 (100%).
2q, l-(2-(5-Fluoro-IH indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1 propargyl-IH-indol-4
yl)piperazine.
Mp 153-55 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.70-2.90 (m, 6H), 2.90-3.10 (m, 3H);
3.25-3.45
(m, 4H); 4.85 (d, 2H); 6.55 (d. 1H); 6.65 (d, 1H); 6.95 (dt, 1H); 7.00-7.35
(m, 6H);
8.00 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 401 {MH+, 48%), 237 (27%), 162 (81%), 115 (100%).
2r, 1-(2-(S-Bromo-1 H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1 propargyl-1 H-indol-4
yl)piperazine.
Mp 154-56 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.70-2.90 (m, 6H); 2.90-3.00 (m, 3H);
3.25-3.40
(m, 4H); 4.85 (d, 2H); 6.55 (d, 1H); 6.65 (d, 1H); 7.00-7.10 (m, 2H); 7.10-
7.35 (m,
4H); 7.75 (s, 1H); 8.05 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 461 (MH+, 5%), 252 (16%), 237
(12%),
143 (100%).
2s, I-(1-Benzyl-1H indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(IH indol-3 yl)ethyl)piperazine,
hemifumarate.
Mp 188-90 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.65-2.85 (m, 6H); 2.95 (t, 2H); 3.10-
3.30 (m,
4H); 5.45 {s, 2H); 6.45 (d, 1 H); 6.50 (d, 1 H); 6.60 (s, 1 H); 6.90-7.10 (m,
4H); 7.10-
7.35 (m, 7H); 7.40 (d, 1H); 7.55 (d, 1H); 10.80 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 435 (MH+,
22%), 304 (52%), 143 (100%).
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
37
2t, 1-(2-(5-Bromo-IH indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1H indol-S yl)piperazine, fumarate.
Mp 231-33 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.80 (t, 2H); 2.80-2.90 {m, 4H); 2.95
(t, 2H);
3.10-3.20 (m, 4H); 6.30 (s, 1 H); 6.60 (s, 2H); 6.85 (dd, 1 H); 7.05 (s, 1 H);
7.20 (dd,
1H); 7.25 (t, 1H); 7.25-7.30 (m, 2H); 7.35 (d, 1H); 7.75 (s, 1H); 10.80 (s,
1H); 11.05
(s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 425 (MH+, 11%), 223 (14%), 143 (100%).
2u, l-(2-(S-Chloro-1H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(1H indol-5 yl)piperazine,
hemifumarate.
Mp 232-34 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.70 (t, 2H); 2.70-2.80 (m, 4H); 2.90
(t, 2H);
3.05-3.15 (m, 4H); 6.30 (s, 1 H); 6.60 (s, 1 H); 6.85 (dd, 1 H); 7.00 (s, 1
H); 7.05 (d,
l0 1H); 7.25 (t, 1H); 7.25-7.30 (m, 2H); 7.35 (d, 1H); 7.60 (s, 1H); 10.80 (s,
1H); 11.00
(s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 379 (MH+, 18%), 143 (100%).
Example 3
~a,1-,(2-(S-Fluoro-IH indol-3 y~)e~vl)-4-f6-h roxvmetl~vl-IH-indol-4-
yl,)~~iperazine.
A solution of 1-(2-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,2-dioxoethyl)-4-(6-
methoxycarbonyl-
1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine (1.8 g, prepared from 2-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-
oxoacetyl chloride and 1-(6-methoxycarbonyl-1H-indol-4-yl)piperazine by the
procedure described in Example 2) in tetrahydrofuran (50 mL) was added
dropwise to
a suspension of lithium aluminium hydride (1.7 g) in tetrahydrofuran (125 mL)
at
room temperature followed by reflux for 4 hours. The reaction mixture was
cooled to
5 °C followed by subsequent addition of water (3.4 mL), 15% aq. sodium
hydroxide
(1.7 mL), and water (8.5 mL). Filtration and removal of solvent in vacuo gave
an oil
which was purified by flash chromatography (eluent: ethyl
acetate/methanol/triethylamine 85:10:5) giving the title product (0.9 g),
which was
crystallized from diisopropyl ether. Mp 198-200 °C.'H-NMR (DMSO-d6):
2.60-2.80
(m, 6H); 2.85 (t, 2H); 3.15 (s, 4H); 4.45-4.55 (m, 2H); 4.90-5.00 (m, 1H);
6.30 (s,
1H); 6.40 (s, 1H); 6.90 (dd, 1H); 7.00 (s, 1H); 7.20 (s, 1H); 7.25-7.35 (m,
3H); 10.85
(s, 1H); 10.95 (s, 1H).
The following compounds were prepared analogously:
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
38
3b, l-(2-(6-Chloro-1H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(6-hydroxymethyl-IH indol-4-
yl)piperazine.
Mp 194-96 °C.'H-NMR (DMSO-db): 2.60-2.80 (m, 6H); 2.90 (t, 2H); 3.1-
3.20 (m,
4H); 4.50 (d, 2H), 4.95 (t, 1 H), 6.35 (s, 1 H); 6.45 (s, 1 H); 6.95-7.05 (m,
1 H); 7.20 (t,
1H), 7.25 (d, 1H), 7.35 (d, 1H), 7.55 (d, 1H); 10.95 (s, 2H).
3c,1-(2-(5-Bromo-IH indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(6-hydroxymethyl-1H indol-4
yl)piperazine.
Mp 163-65 °C. 'H-NMR (DMSO-db): 2.65 (t, 2H); 2.70 (s, 4H); 2.90 (t,
2H); 3.15 (s,
4H); 4.50 (d, 2H); 4.95 (t, 1H); 6.35 {s, 1H); 6.45 (s, 1H); 7.00 (s, 1H);
7.10-7.20 (m,
l0 2 H); 7.25 (s, 1H); 7.30 {d, 1H); 7.70 (s, 1H); 10.90 (s, 1H); 11.00 (s,
1H).
Example 4
4a. 1-~3-(6-Fluoro-l.2-benzisoxazol-3-vl1 I-~r~rop~l)-4-(IH indol-4-
~)~nerazine
" cmarat~,
A solution of 3-(3-bromo-1-propyl)-6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazole (1.1 g), 1-(1H-
indol-
4-yl)piperazine (1.0 g), potassium carbonate (1.9 g), and potassium iodide (50
mg) in
4-methyl-2-pentanone (100 mL) was refluxed for 16 hours. Filtration and
removal of
solvent in vacuo gave an oil which was purified by flash chromatography
{eluent:
heptane/ethyl acetate/triethylamine 75:20:5) giving an oil (1.0 g) which was
crystallized as the title fumarate from acetone by addition of fumaric acid.
Mp 187-89
°C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.00 (qv, 2H); 2.55 (t, 2H); 2.60-2.80 (m, 4H);
3.05 (t, 2H);
3.05-3.20 (m, 4H); 6.40 (s, 1H); 6.45 (d, 1H); 6.60 (s, 2H); 6.90-7.05 (m,
2H); 7.20-
7.35 (m, 2H); 7.70 (dd, 1H); 8.00 (dd, 1H}; 11.00 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 379
(MH+,
10%), 178 (100%), 159 (24%).
The following compounds were prepared analogously:
4f, l -(2-(1 H Indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(6-methoxycarbonyl-1 H indol-4
yl)piperazine,
oxalate.
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
39
Mp 213-16 °C. 'H-NMR (DMSO-db): 3.10 (t, 2H); 3.20-3.60 (m, l OH); 3.80
(s, 3H);
6.55 (s, 1H); 6.90-7.10 (m, 3H); 7.25 (s, 1H); 7.35 (d, 1H); 7.50 (s, 1H);
7.60 (d, 1H);
7.75 (s, 1H); 10.90 (s, 1H); 11.55 (s, 1H).
4g, l -(2-(6-Chloro-1 H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(6-methoxycarbonyl-1 H indol-4-
yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 228-30 °C. 'H-NMR (DMSO-d6): 3.10 (t, 2H); 3.30 (t, 2H); 3.45 (s,
8H); 3.85 (s,
3H); 6.55 (s, 1H); 7.05 (dd, lHj; 7.10 (s, 1H); 7.33 (s, 1H); 7.45 (s, 1H);
7.55 (t, 1H);
7.65 (d, 1 H); 7.85 (s, 1 H); 11.1 S (s, 1 H); 11.65 (s, 1 H).
to
4h, 1-(2-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(6-methoxycarbonyl-1H indol-4-
yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 227-28 °C. 'H-NMR (DMSO-db): 3.05 (t, 2H); 3.25 (t, 2H); 3.25-3.35
(m, 4H);
3.35-3.45 (m, 4H); 3.85 (s, 3H); 6.55 (s, 1H); 7.10 (s, 1H}; 7.15 (t, 1H);
7.55 (t, 1H);
7.55-7.65 (m, 2H); 7.80 (s, 1H); 8.00 (s, 1H); 11.55 (s, IH).
41, 1-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranylmethyl)-4-(IH-indol-9-vl)pipcrazine,
dilrydrochloride.
Mp 238-40 °C.'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 3.20-3.50 (m, 4H}; 3.60 (d, 2H); 3.75
(d, 2H);
4.60 (s, 2H); 6.50 (s, 1H); 6.55 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.15 (d, IH); 7.25
(dt, 1H); 7.25-
7.30 (m, 1H); 7.70 (dd, 1H); 8.00 (dd, 1H); 8.40 (s, 1 H); 11.22 (s, 1H);
11.65 (b, 1H).
MS m/z (%): 350 (MH+, 7%), 201 (34%), 159 ( 100%), 149 (20%).
4m, 1-(3-Cyano-1 H indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(1 H indol-3 yl)ethyl)piperazine,
fumarate.
Mp >250 °C.'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.70-3.00 (m, 8H); 3.10 (s, 4H); 6.60 (s,
1H); 6.75
(dd, 1H); 6.95-7.10 (m, 2H); 7.15-7.20 (m, 3H); 7.35 (d, 1H); 8.20 (s, 1H);
10.80 (s,
1H); 12.20 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 370 (MH+, 9%), 239 (100%), 227 (25%), 224
(27%), 144 (65%).
4n, I-(3-Cyano-IH indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(S fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine,
hemifumarate.
Mp 235-37 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.60-2.95 (m, 8H); 3.10 (s, 4H); 6.60
(s, 2H);
6.75 (d, 1H); 7.05-7.25 (m, 3H); 7.45-7.60 (m, 2H); 7.95 (s, 1H); 8.20 (s,
1H); 12.15
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO- 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
(s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 389 (MH+, 8%), 239 (100%), 224 (38%), 208 (14%), 163
(15%).
40, I -(2-(6-Chloro-1 H indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(3-cyano-1 H indol-4
yl)piperazine,
5 hemifumarate.
Mp 234-36 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.70 (t, 2H); 2.80 (b, 4H); 2.90 (t,
2H); 3.10 (b,
4H); 6.60 (d, 2H); 6.75 (d, 1H); 7.00 (d, 1H); 7.15-7.20 (m, 2H); 7.25 (s,
1H); 7.35 (s,
1H); 7.55 (d, 1H); 8.20 (s, 1H); 10.90 (s, 1H); 12.10 (s, 1H}. MS m/z (%): 404
(MH+,
8%), 239 {100%), 227 (18%), 224 (30%), 178 (25%).
4p, 1-(2-(3-Benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(3-cyano-IH indol-4 yl)piperazine,
sesquioxalate.
Mp 221-23 °C.'H NMR (DMSO-db): 3.10 (t, 2H); 3.20-3.45 (m, 10 H); 6.80
(d, 1H);
7.15-7.40 (m, 4H); 7.60 (dd, 1H); 7.75 {dd, 1H); 7.90 (s, 1H); 8.25 (d, 1H);
12.30 (s,
1H). MS m/z (%): 371 (MH+, 20), 239 (63%), 145 (100%).
4q, l-(IHlndol-4 yl)-4-(2-(S-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine,
hydrochloride.
Mp 258-60 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.40 (s, 3H); 3.15-3.55 (m, 8H); 3.65-
3.80 (m,
4H}; 6.50 (d, 1 H); 6.60 (d, 1 H}; 7.00 (t, 1 H); 7.15 (d, 1 H); 7.20 (d, 1
H); 7.30 (t, 1 H);
7.45 (d; 1H); 7.60 (s, 1H); 7.90 (s, 1H); 11.20 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 360 (MH+,
10%),
214 (97%), 143 ( 100%).
4r, 1-(IH Indol-4 yl)-4-(2-(4-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 204-fi °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.05 (s, 3H); 3.30-3.50 (m, 12H); 6.45
(d, 1H);
6.50 (d, 1H); 6.95-7.05 (m, 2H); 7.10 (d, 1H); 7.20 (t, 1H); 7.30 (t, 1H);
7.40 (d, 1H);
7.85 (s, 1H); 11.10 (s,lH). ). MS m/z (%): 360 (MH+, 23%), 214 (81%), 199
(100%),
143 (53%).
4s,1-(3-(5-Fluoro-3-benzofuranyl)-1 propyl)-4-(1 H indol-4 yl)-1, 2, 3, 6-
tetrahydropyridine, fumarate.
Mp 183-85 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 1.70-2.00 (m, 2H); 2.40-2.90 (m, 8H);
3.20-3.35
(m, 2H); 6.00-6.10 (m, 1H); 6.55 (s, 1H); 6.60 (s, 2H); 6.90 (d, 1H); 7.05 (t,
1H); 7.15
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
41
(dt, 1H); 7.25-7.40 (m, 2H); 7.50 (dd, 1H); 7.55 (dd, 1H); 7.90 (s, 1H); 11.10
(s, 1H).
MS m/z (%): 375 (MH+, 90%), 206 (100%), 149 (90%).
4t,1-(2-(S-Chloro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(IH indol-4 yl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 200-2 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 3.10 (t, 2H); 3.30-3.50 (m, lOH); 6.45
(d, 1H);
6.50 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.10 (d, 1H); 7.30 (t, 1H); 7.40 (dd, 1H); 7.65
(d, 1H); 7.90
(s, 1H); 8.00 (s, 1H); 11.10 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 380 (MH+, 50%), 214 (100%),
143
(80%).
4u, l-(IHIndol-4 yl)-4-(2-(6-methyl-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)piperazine, oxalate.
Mp 190-92 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.10 (s, 3H); 3.10 (t, 2H); 3.25-3.50
(m, l OH);
6.45 (d, 1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.10 (t, 2H); 7.30 (t, 1H); 7.40 (s,
1H); 7.65
(d, 1H); 7.80 (s, 1H); 11.15 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 360 (MH+, 14%), 214
(44%),143
(100%).
4v,1-(2-(7-Chloro-3-benzofuranyl)ethyl)-4-(1H indol-4 yl)piperazine,
hemioxalate.
Mp 216-18 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-d6): 2.85-3.15 (m, 8H); 3.15-3.40 (m, 4H);
6.40 (d,
1H); 6.50 (d, 1H); 7.00 (t, 1H); 7.05 (d, 1H); 7.25 (t, 1H); 7.30 (d, 1H);
7.45 (d, 1H);
7.75 (d, 1H); 8.00 (s, 1H); 11.05 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 380 (MH+, 13%), 199
(30%),
143 ( 100%).
4x,1-(2-(4-Chloro-IH indol-3 yl)ethyl)-4-(3-cyano-IH indol-4 yl)piperazine,
hemifumarate.
Mp >250 °C. 'H NMR (DMSO-db): 2.65-3.00 (m, 6H); 3.00-3.30 (m, 6H);
6.60 (s,
1H); 6.75 (dd, 1H); 6.90-7.10 (m, 2H); 7.10-7.25 (m, 2H); 7.25-7.40 (m, 2H);
8.20 {d,
1H); 11.20 (s, 1H); 12.10 (s, 1H). MS m/z (%): 404 (MH+, 14%), 224 (15%), 184
( 18%), 143 { 100%).
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
Example 5
42
5a.1-~2-~6-Chloro-1H indol-3-y~,~(IH indol-4-yjj~p~peridino
A solution of compound 2g (0.5 g) was dissolved in glacial acetic acid.
Platinum
catalyst (10% on charcoal, 10 mg) was added and the mixture hydrogenated in a
Parr
apparatus under 3 atmospheres of hydrogen gas for 16 hours. Filtration and
removal
of solvent gave the title compound as a crystalline material (0.4 g). Mp 205-6
°C. 'H
NMR (DMSO-db):1.75-1.90 (m, 4H); 2.10-2.20 (m, 2H); 2.60-2.70 (m, 2H); 2.85-
2.95
(m, 3H); 3.15 (d, 2H); 6.50 (s, 1H); 6.80-6.90 (m, 2H); 6.95-7.10 (m, 2H);
7.20 (s,
1H); 7.30 (s, 1H); 7.40 (s, 1H); 7.55 (d, 1H); 10.90 (s, 1H); 11.00 (s, 1H).
MS m/z
(%): 378 (MH+, 18%), 178 (100%), 143 (47%).
Pharmacological Testing
is The affinity of the compounds of the invention to 5-HT,A receptors was
determined by
measuring the inhibition of binding of a radioactive ligand at 5-HT,A
receptors as
described in the following test:
Inhibition of'H-5-CT Binding to Human 5-HT,A Receptors.
By this method the inhibition by drugs of the binding of the 5-HT,A agonist
'H-5-carboxamido tryptamine (3H-5-CT) to cloned human 5-HT", receptors stably
expressed in transfected HeLa cells (HA7) (Fargin, A. et al, J. Biol. Chen:.,
1989, 264,
14848) is determined in vitro. The assay was performed as a modification of
the
method described by Harrington, M.A. et al, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 1994,
268,
1098. Human 5-HT,A receptors (40 pg of cell homogenate) were incubated for 15
minutes at 37 °C in 50 mM Tris buffer at pH 7.7 in the presence of 3H-5-
CT. Non-
specific binding was determined by including 10 wM of metergoline. The
reaction was
terminated by rapid filtration through Unifilter GFB filters on a Tomtec Cell
Harvester. Filters were counted in a Packard Top Counter. The results obtained
are
presented in table 1:
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
43
Compound Inhibition of Compound Inhibition of
No. 3H-5-CT Binding No. 'H-5-CT Binding
ICso (nM) ICso (nM)
la 10 3b 120
lb 210 3c 1000
lc 12 4a 9,g
l d 2.5 4f 1200
le 6.9 4g 350
1 f 9.8 4h 3100
lg 13 41 330
lh 11 4m 3.2
li 3.4 4n 5.7
1 j 22 40 2,9
lk 22 4p 4.3
11 2.5 4q 21
2a 3.4 4r 10
2b 11 4s 16
2c 27 4t 9.4
2g 2.8 4u 7.0
2h 11 4v 4.3
2i 5.4 4x 5.4
2t 230 Sa 14
2u 310
3a 910 Pindolol* 100
Table 1 reference compound
The compounds of the invention have also been tested for their effect on re-
uptake of
s serotonin in the following test:
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
W0 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
44
Inhibition of'H-5-HT Uptake Into Rat Brain Synaptosomes.
Using this method the ability of drugs to inhibit the accumulation of'H-5-HT
into
whole rat brain synaptosomes is determined in vitro. The assay was performed
as
described by Hyttel, J., Psychopharmacology 1978, 60, I3.
Compound Inhibition of Compound Inhibition of
No. Serotonin reuptake No. Serotonin reuptake
ICso OM) ICso ~nM)
la 31 3b 33
lb 290 3c 46
lc 57 4a 360
ld 31 4f 14
1 a 4.4 4g 23
1 f 8.2 4h 71
lg 12 41 950
lh 6.8 4m 3.0
li nt 4n 65
1 j 360 40 19
lk 150 4p 22
11 nt 4q 34
2a 21 4r 12
2b 6.9 4s 24
2c 2.3 4t 99
2g 22 4u 93
2h 2.5 4v 4.4
2i 5.9 4x nt
2t 39 Sa 19
2u 20
3a 17 Paroxetine*0.29
Table 1 ' reference compound, nt = not tested
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
The 5-HT,A antagonistic activity of some of the compounds of the invention has
been
estimated in vitro at cloned 5-HT,A receptors stably expressed in transfected
HeLa
hells (HA7). In this test 5-HT,A antagonistic activity are estimated by
measuring the
ability of the compounds to antagonize the 5-HT induced inhibition of
forskolin
5 induced cAMP accumulation. The assay was performed as a modification of the
method described by Pauwels, P.J. et al, Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 45, 375.
Some of the compounds of the invention have also been tested for their in vivo
effect
on 5-HT,A receptors in the assay described by Sanchez. C. Et al., Eur. J.
Pharmacol.,
io 1996, 315, pp 245. In this test antagonistic effects of test compounds are
determined
by measuring the ability of the test compounds to inhibit 5-Me0-DMT induced 5-
HT
syndrome.
The compounds of the present invention possess valuable activity as serotonin
re-
15 uptake inhibitors and have antagonistic effect at 5-HT", receptors. The
compounds of
the invention are therefore considered useful for the treatment of diseases
and
disorders responsive to the inhibition of serotonin re-uptake and antagonistic
activity
at 5-HT,A receptors. Diseases responsive to the inhibition of serotonin re-
uptake are
well known in the art and include affective disorders, such as depression,
psychosis,
2o anxiety disorders including general anxiety disorder and panic disorder,
obsessive
compulsive disorder, etc.
As explained above, the antagonistic activity at 5-HT,A receptors of the
compounds of
the invention is predicted to counteract the negative feed back mechanism
induced by
25 the inhibition of serotonin reuptake. The antagonistic effect at 5-HT,A
receptors is
thus expected to improve the effect of the serotonin reuptake inhibiting
activity of the
compounds of the invention.
The compounds as claimed herein are therefore considered to be particularly
useful as
3o fast onset of action medicaments for the treatment of depression. The
compounds
may also be useful for the treatment of depressions which are non-responsive
to
currently available SSRI's.
CA 02335711 2000-12-15
WO 99/67237 PCT/DK99/00326
46
Pharmaceutical formulation
The pharmaceutical formulations of the invention may be prepared by
conventional
methods in the art. For example: Tablets may be prepared by mixing the active
ingredient with ordinary adjuvants and/or diluents and subsequently
compressing the
mixture in a conventional tabletting machine. Examples of adjuvants or
diluents
comprise: corn starch, potato starch, talcum, magnesium stearate, gelatine,
lactose,
gems, and the like. Any other adjuvants or additives usually used for such
purposes
such as colourings, flavourings, preservatives etc. may be used provided that
they are
1o compatible with the active ingredients.
Solutions for injections may be prepared by dissolving the active ingredient
and
possible additives in a part of the solvent for injection, preferably sterile
water,
adjusting the solution to desired volume, sterilization of the solution and
filling in
suitable ampules or vials. Any suitable additive conventionally used in the
art may be
added, such as tonicity agents, preservatives, antioxidants, etc.
The pharmaceutical compositions of this invention or those which are
manufactured in
accordance with this invention may be administered by any suitable route, for
example orally in the form of tablets, capsules, powders, syrups, etc., or
parenterally
in the form of solutions for injection. For preparing such compositions,
methods well
known in the art may be used, and any pharmaceutically acceptable carriers,
diluents,
excipients, or other additives normally used in the art may be used.
Conveniently, the compounds of the invention are administered in unit dosage
form
containing said compounds in an amount of about 0.01 to 100 mg. The total
daily
dose is usually in the range of about 0.05 - 500 mg, and most preferably about
0.1 to
50 mg of the active compound of the invention.