Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
Method and Device for Guiding and Supporting a Thin Sheet or Metal Strip
The invention relates to a method as well as a device for guiding and
supporting a
comparatively thin sheet metal or metal strip during transport across a
conveying device,
such as a rolling table, and/or during, before or after a cutting process when
passing
through shears, wherein the sheet metal or strip at least at its underside is
loaded with an
energy-rich bundle of jets of a liquid or gaseous medium and is thereby
supported and
guided by means of impulse energy and the medium is guided under pressure
through
supply channels in the interior of the transport and/or blade carrier drums to
jet nozzles at
their periphery and exits as a closed jet from them before and/or behind the
support areas
of the drum, or as closely as possible adjacent to the blades of the blade
drum, against the
sheet metal or strip at a slant or a substantially perpendicular angle
relative to the sheet
metal or s t r i p .
In the rolling technology, it has been proven particularly difficult in
practice to safely
guide thin sheet metal or strips across a conveying device, such as a rolling
table,
or to shears because thin strips have the tendency to drop or lift after
leaving a
guiding element and, as a result of this, to impact a subsequently arranged
device or a
guide element or to fly up and to thereby become deformed. In particular, this
problem
is observed in connection with shears, without cutting action but also during
cutting,
when the leading edge of the strip passes through.
In accordance with the developmental tendency toward sheet metal or metal
strips that are
thinner and thinner, in particular, of non-ferrous metals such as copper or
aluminum, but also
in connection with very thin steel sheet, this phenomenon results in
increasingly greater
difficulties. Up to now, no practice-oriented and safe solution h a s b a a n
found for
overcoming them.
DE 14 27 231 discloses a device for dividing rolling stock, in particular,
sheet metal strips to
commercial lengths by means of shears with carriages with a clamping member,
wherein the
the carriages are arranged at the inlet side upstream of the shears and
movable along the
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
transport path. The clamping carriage arranged at the inlet side continuously
measures the
advancement of the sheet metal by means of a pulse generator within the pulse
graduation.
When a preselected partial length of the sheet metal p o rt i o n has passed
through the cutting
plane of the shears, the sheet metal advancement is stopped by means of a
digital control
member. The one or more clamping carriages grip the transported g o o d s from
above and
c o m p r i s a , for temporary coupling the transported goods, solenoids or
tongues that are
hydraulically operated or operated by known means.
The closest prior art is disclosed in the document DE-C 944 919. This document
discloses a
method for guiding and supporting a material strip during transport across a
conveying device
such as a roll table and/or during, before or after a cutting process when
passing through
shears, wherein the material strip is supported at least at its underside with
energy-rich
bundles of jets of a gaseous medium and is thereby supported and guided by
impulse energy.
The g a s a o a s m a d i a m is guided out of the interior of the drums by
means of j et nozzles on
the drum periphery.
Based on the aforementioned prior art, it is an object of the invention to
safely guide thin
sheet metal or s t r i p s d a r i n g transport across a conveying device,
such as a roll t a b 1 a ,
and/or during, before or after a cutting process when passing through shears
and
to have the medium act only in that area which is beneficial for stabilizing
the strip, and,
on the other hand, t o prevent an ineffective media use and, at the same time,
to avoid
flooding of the surroundings of the strip or the shears and the transport
device with excess
medium.
As a solution to this object it is proposed with the invention in connection
with a method
for guiding and supporting a comparatively thin sheet metal or metal strip
during transport
across a conveying device, such as a rolling table and/or during, before or
after a cutting
process when passing through shears wherein the sheet metal or strip is loaded
at least form
its underside with energy-rich jet bundles of liquid or gaseous medium and is
thus supported
and guided by means of impulse energy, that the medium, by means of a rotary
valve
arranged at an end face of the rotatable transport or blade drum, exits in a
limited angular
position of a drum from jet nozzles directed against the sheet metal or metal
strip.
2
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
Further advantageous embodiments of the method according to the invention are
provided
a c c o r d i n g t o t h a features of the dependent claims.
Because the stabilization of the strip and particularly of the 1 a a d i n g a
d g a o f the strip or
of the s t r i p head is not provided by mechanical means, but by means of
impulse energy of
a j et bundle of a liquid or gaseous medium, a collision or impact of the
strip or the
leading edge of the strip or the strip head on a construction component of any
possible type of the roll table or the shears is safely prevented. The jet
nozzles can
be arranged according to the invention about the entire strip width or across
the entire
drum length.
With the inventively important embodiment of the method, according to which
the
medium flows out of jet nozzles oriented against the sheet metal or the strip
in
a limitable angular position of one drum by employing a rotary valve,
preferably
arranged in an end face of a rotatable transport drum or blade carrier drum,
it is
achieved in an advantageous way that the medium is effective only in the area
which is
beneficial for stabilizing the strip and that, on the other hand, no
inefficient media use
takes place. At the same time, overflowing of the direct vicinity of the strip
or the shears
of the conveying device with excess medium is prevented.
One embodiment of the method provides that for chisel-type shears comprising a
lower
or upper drum, provided with a cutting chisel, and a counter drum configured
as an anvil, the sheet metal or strip to be cut is loaded with at least one
medium jet, respectively, out of each of the drums preferably before and/or
behind
the cutting plane from above and/or from below. This provides a particularly
efficient
s t a b i 1 i z a t i o n o f the strip or sheet metal passing through, and
this in connection with
an economically acceptable expenditure of stabilizing medium.
According to another embodiment of the method it is provided that in
connection with
shearing-off shears, comprising a blade drum each with a blade having
oppositely
oriented cutting edges, respectively, the sheet metal or strip to be cut is
loaded before
and/or behind the separating plane with a supporting medium jet or a plurality
of such
3
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
medium j ets from above and/or from below.
This achieves the goal that the strip or sheet metal is lifted off the blade
drum in order to
better guide it to the devices downstream. For example, the jet nozzles in the
smooth anvil
drum are to prevent riveting and thus adhesion of the cut leading edge of the
strip, and,
moreover, an adhesion on the chisel or blade.
Finally, the method according to the invention provides further that during
advancing o f
the sheet metal or strip, in particular, during introduction of its head into
the shears, the
entry of the head into the area of a guide wedge, arranged stationarily
upstream of the
shears, as well as its advancing speed are determined by a signaling device
and the head is
loaded from below by at least one row of medium jets exiting from the guide
wedge
approximately perpendicularly against the sheet metal or strip and is guided
thereby.
A device for guiding and supporting a thin sheet metal or metal strip, in
particular, for
performing the method according to the invention, comprising transport drums
and/or
blade carrier drums, wherein the drums at their periphery have jet nozzles
arranged in
axis-parallel alignment in at least one row which, upon loading with a medium,
are
oriented against the top surface and /or bottom surface of the sheet metal or
the metal
strip, wherein the jet nozzles are connectable, starting at supply channels
extending in the
interior of the drums is characterized in that between the supply channels of
a drum and a
source for the medium to be supplied under pressure at least one pump and at
least one
rotary valve are arranged and in that the rotary valve is preferably arranged
at an end face
of a drum.
Further advantageous embodiments of the device are provided according to the
characterizing features of the dependant claims of the device.
In this connection, the measure can be used advantageously that in the case of
a drum
provided with a blade or a cutting chisel the jet nozzles of a row are
arranged as closely as
possible adjacent to the blade and/or the chisel.
4
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
In a further development of the invention it is provided that the guide wedges
comprise jet
nozzles on supply channels provided for media and that the latter are
connected to media
supply lines with a pressure pump and a media source arranged therein and that
above the
sheet metal or strip a signal device monitoring the entry of the strip is
arranged which
communicates by means of a control signal line with the motor of the pump.
Accordingly, in one aspect, the present invention resides in method of guiding
and supporting
a comparatively thin metal sheet or metal strip (1) during transport by way of
a conveying
device (10) such as a roller path, and/or during, before or after a separating
process on running
through a cutter (3), wherein the metal sheet or strip (1) is acted on at
least from its underside
( 1') by energy-rich j ets (2, 2') of a liquid or gaseous medium and in that
case supported and
guided by means of pulsed energy and the medium is conducted under pressure
through feed
channels (4) in the interior of transport and/or knife carrier drums (7, 8) to
nozzles (5) at the
peripheries thereof and flows out of these in front of and/or behind the
carrier regions of the
drums or as close as possible to the knives (6) of the knife drums (8)
obliquely or at an
approximately perpendicular angle relative to the metal sheet or strip (1) in
a closed jet against
this, wherein the medium flows out of nozzles (5), which are directed against
the metal plate
or metal sheet (1), at a confinable angular setting of a drum (7, 8) with use
of a rotary slide
valve (9) preferably arranged at an end face of a rotatable transport or knife
carrier drum (7,
8).
In yet a further aspect, the present invention resides in a device for guiding
and supporting a
thin metal sheet or metal strip (1), comprising transport drums and/or knife
carrier drums (7,
8) which have, at their periphery in axially parallel orientation, jets (5)
which are arranged in
at least row and which on loading with a medium point towards the upper and/or
lower surface
of the metal sheet or metal strip, wherein the jets (5) are connectible by
feed channels (4),
which extend in the interiors of the drums (7, 8) to sources (25), which are
provided outside
the drums, with connecting elements (21, 21') for medium feedable under
pressure, wherein at
least one pump (22) and at least one rotary slide valve (9) are arranged
between the feed
channels (4) of a drum (7, 8) and a source (25) for a medium feedable under
pressure and the
valve is preferably arranged at an end face of a drum (7, 8).
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Further details, features, and advantages of the invention result from the
following
explanation of several embodiments illustrated schematically in the drawings
it is shown in:
Fig. 1 in a representation similar to a flow sheet a transport drum with
supply
channels and jet nozzles arranged therein, with a rotary valve at the end
face,
pressure pump, and media source;
Fig. 2 in a side view and partially in section, shearing-off shears with an
arrangement of the jet nozzles according to the invention
Fig. 3 in a side view a similar arrangement with chisel-type shears
furnished according to the invention with jet nozzles;
Fig. 4 in a side view shears with stationary guide wedges arranged upstream
and
downstream and with jet nozzles arranged therein.
The purely schematic illustration of Fig. 1 shows supply channels 4 arranged
in a transport
drum 7 for supplying the jet nozzles 5 and 5' formed therein. Opposite the end
face of the
transport drum 7 a rotary valve 9 is arranged which is connected with a
central bore 20 to
a conveying line 23, extending from a pressure pump 22, for a liquid medium.
The rotary
valve 9 is arranged so as to be non-rotatable while the transport drum 7
rotates relative
thereto, when functioning as a transport drum 7 or blade drum 8, as is known,
in the art.
Connecting channels 21, 21' beginning at the central bore 20 and having exit
openings at
the side facing the end face of the transport drum 7 are provided in the
rotary valve 9.
Medium that is under pressure is released always when the openings of the
supply
channels 4 coincide with the oppositely oriented openings of the connecting
channels 21 in
the rotational direction to thus allow flow in a limited angular range. In
other angular
positions of the transport drum 7, the supply channels 4 of the transport drum
7 cannot be
flushed with pressure medium. It is also possible to adjust different ejection
widths with the
jet nozzles.
Moreover, the pressure pump 22 with its motor 22' can be controlled via a
signal and
6
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
switching device, similar to the device illustrated i n Fig. 4, for example,
according to the
requirements of an incoming metal strip 1. The pressure pump 22 takes in a
liquid
medium from the medium source 25 through the intake line 24.
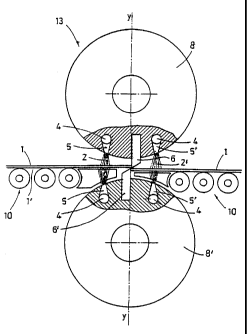
Fig. 2 shows as an example a blade carrier drum 8, 8' with a device for
guiding and
supporting a comparatively thin sheet metal or metal strip 1. The blade
carrier drums are
provided with blades 6 in a manner known in the art which interact with one
another and
cut the metal strip 1 in the cutting plane y-y when contacting one another.
The latter is
transported on the rolling table 10 and during the cutting process is guided
and stabilized
from below or from below and from above by bundles of jets 2, 2' exiting from
the jet
nozzles 5. The jet nozzles 5, 5' are arranged such that they secure at both
sides of the
cutting plane y-y the strip 1 in the given position and, in particular,
prevent a slanting out
of the transport direction. Moreover, in regard to the shearing-off shears 13,
same
elements are identified with same reference numerals.
In Fig. 3 a similar arrangement is shown with the difference that the shears
are chisel-type
shears 3 with a cutting chisel 11 wherein a counter drum 8' is correlated with
the blade
drum 8 provided with the chisel. In this connection, it must be prevented that
the strip 1
during cutting by the cutting chisel 11 is riveted to the smooth surface or
adheres thereto
because then the cut leading edge of the strip would be deformed. Accordingly,
the blade
drum 8 and, in particular, the anvil drum 8' are provided with supply channels
4 in the
aforementioned axis-parallel arrangement which have jet nozzles from which jet
bundles 2,
2' of a liquid medium exit and reliably prevent the leading edge of the strip
that has
been cut from being riveted to or adhering on the counter drum 8'.
Fig. 4 shows a further similar arrangement with chisel-type shears 3 in which
between the
shears and the rolling table 10 guide wedges 15 are arranged. They have jet
nozzles 5 for
medium-loaded supply, channels 4 which are connected to medium supply lines 29
having
a pressure pump 27 arranged therein. Above the sheet metal or metal strip 1 a
signaling
device 19 monitoring the introduction of the strip at the strip head 16 is
provided,
wherein the signaling device is in communication via a signal line 26 with the
motor 28 of
7
CA 02338217 2006-10-04
the pressure pump. The pressure pump is supplied with the 1 i q a i d medium
in a manner
known in the art from the medium source 25 by means of a suction line. The
passage of the
strip head 16 of the metal strip 1 is detected by the signaling device 19
which then
activates via the signal line 26 the switch for the motor 28 and thus starts
the pressure
pump 27. The latter conveys the pressure medium through the supply line 29 via
the supply
channels 4 to the jet nozzles 5. The principle holds true for all jet nozzles,
also those in
the drums. A signaling device must detected the strip head and the cut. The
jet nozzles are
then loaded only briefly at the strip head and the cut. The signal can also be
used by a device
which is already present anyway.
Moreover, the chisel drum of the chisel-type shears 3 is in communication via
the rotary
valve 9 (not shown in Fig. 4) with this supply channel 4' and the jet nozzles
5' such
that a bundled medium jet 2' exits with high energy from below against the
metal strip 1 in
the area of the strip head 16 and prevents that the comparatively thin and
bendable strip 1
bends downwardly and impacts against the guide wedge 15' to the right and is
thereby
deformed.
Only during the further course of the strip transport, after a certain amount
of time or a
measured advancing of the metal strip 1, the chisel-type shears 3 are
activated and a
predetermined length of strip is cut off, wherein the supply channels 4 " of
the, chisel drum
and the counter drum previously unused cooperate with the rotary valve 9 take
over the
guiding of the strip 1 by means of energy-rich media jets.
8