Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02341398 2001-02-21
marina/siebectantamendedpages
Device for Carrying Out ReWair and Service Work on Rotvr Blades of Wind
Turbine Generators .
The invention relates to a deviice for carrying out repair and service work on
rotor
blades, exposed to the effects of the weather, of wind turbine generators of
the type
described in the generic clause of claim 1, as described, for example, in DE-U
296 03
278.
For repairs on surfaces of non-metallic materials special conditions must
usually be
adhered to. The "Germanic Lloyd", for example, issues guidelines relating to
such
repair work of structural components.
In .order to be able to meet all these special characteristics, it is known,
for example,
when repairing rotor blades of wind turbine generators, to dismantle the rotor
blades
and to transport them to a workshop hall in order to bring about there the
external
conditions in such a manner as. to comply with the standards and
recommendations
of the "Germanic Lloyd". The eiffort involved is considerable, the stand down
periods
of the wind turbine generators are correspondingly high so that one seeks, if
at all
possible, to perform these repair and maintenance services on site directly on
the
roto r.
Repair platforms are therefore known, which may be lifted and lowered on the
mast
of a wind turbine generator, for example, by winches, openly surrounding a
rotor
blade in the process. Such an arrangement is described in DE-43 39 638-A1 or
DE-
197 26 408-C1. A similar installation is shown in the genus constituting DE-
296 03
278-U 1, which is characterised in that the suspension device is fitted to the
root of
the two rotor blades pointing upwardly while the third rotor blade is being
serviced,
which presupposes that a wind turbine generator is designed to comprise three
blades.
The drawback shared by these working platforms resides in particular in the
fact that
they can only be used in good weather conditions, as otherwise the parameters
prescribed by the "Germanic Lloyd" cannot be adhered to.
This is where the object of the invention comes into play, which consists in
providing
a device, which permits maintenance and repair work on such objects during
virtually
all types of weather conditions.
AMENDED PAGE
CA 02341398 2001-02-21
marina/siebertantamendedpages
This object is attained according to the invention by a device of the type
described in
the opening paragraph in that the working platform forms part of a working
cabin,
substantially U-shaped when viewed in plan view, for accommodating the rotor
blade
on the side comprising a walking and working deck, U-shaped when viewed in
plan
view, as well as sealing means for sealing the working cabin from the effects
of the
environment prevailing in the work location as well as for sealing, in
particular, the
ceiling and floor in relation to the portion of the rotor blade inside the
working cabin.
In such a working cabin encompassing a portion of the rotor blade, all
required
parameters, necessary for peifiorming the tasks, can be set. In this manner
the
temperature, the air humidity and the like, to name but one example, may be
set. It
may be mentioned here that extraction hoods, e.g. for facade cleaning, are
available,
see EP-A-0 396 815.
Embodiments of the invention are apparent from the subsidiary claims.
The device may, of course, also be equipped with a lifting device, for example
with
winches as disclosed in prior art, or with gantry arms of a lifting platform
or the like.
Since the rotor blade passes through the cabin, the latter comprises sealing
components in the floor and ceiling as well, the said sealing components
ideally
being formed by a plurality of plungers, which can travel from a starting
position to a
sealing position. It may be advantageous in the process to fit the joint
plunger ends
with an inflatable tube body in order to permit particularly good sealing off
from the
environment. Actuating these sealing plungers may be performed pneumatically,
hydraulically, magnetically or electrically.
AMENDED PAGE ,
CA 02341398 2001-02-21
marina~specs~siebertantpct
which, when a rotor blade is dismantled and removed from the mast of the wind
turbine generator, displaces the rotor blade in the working cabin in such a
manner
that an approximately central point of gravity of the system as a whole is
attained. .
The lifting element of the working cabin subsequently lowers these in the
direction
towards the ground and deposits the working cabin in such a manner as to be
employed as a slip carriage.
An alternative embodiment may be that the lifting device is. formed by a rail
comprising a cable pull arrangement for transporting the working cabin, fitted
to
and/or adapted to be fitted to the mast of the wind turbine generators, in
which case
the rail may, for example, be designed as a telescopic component of a mounted
vehicle structure.
Such a construction allows to use the carrying capacity of the mast as well in
order to
move the working cabin according to the invention. Depending on the location
and
the construction, the rail may also be an integral component of the mast.
The rail arrangement may be equipped with fixation means for fixation on the
mast of
the wind turbine generators, as is also contemplated by the invention in a
further
embodiment.
Further features, details and advantages of the invention are set out on the
basis of
the following description as welll as with reference to the drawing. There is
shown in a
very simplified illustration in
Fig. 1 a device according to the invention in working position in a side
elevation,
Fig. 2 a working cabin viewed in plan view in its open state,
Fig. 3 a working cabin viewed in plan view in its closed state,
Fig. 4 a working cabin in section IV-IV according to Fig. 2,
Fig. 5 a working cabin section V-V according to Fig. 3 as well as in
Fig. 6 the side elevation of a wind turbine generator with a rail arrangement
against
the mast.
CA 02341398 2001-02-21
marinalspecs~siebertantpct 4
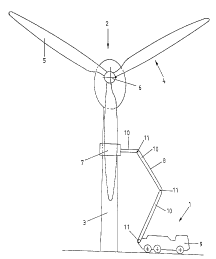
Fig. 1 shows a device 1 for thE: maintenance of wind turbine generators in
working
position of a wind turbine generator 2. The wind turbine , generator 2
comprises a
support mast 3 in the upper region of which a rotor 4 is provided. The latter
comprises three rotor blades 5, fitted to a hub 6. The hub 6 serves
simultaneously as
the rotational axis of the rotor 4 and is connected in known manner, for
example, by
way of a transmission gear, not shown in the present case, to a generator,
likewise
not shown. The power take-off of the hub 6 is so designed in known manner that
the
latter may be locked in a plurality of positions, so that, for example,
dismantling of the
rotor blades 5 may be performed.
The device for servicing wind turbine generators 1 comprises a working cabin
7,
connected to a vehicle 9 by a lifting arm 8. The vehicle 9 may be an
independent
truck or may, for example, takE: the form of a trailer with auxiliary
aggregates. The
lifting arm 8 comprises a plurality of arm segments 10, interlinked by joints
11. In the
embodiment here illustrated three arm segments 10 are used, however, the
number
of arm segments 10 is, in principle, variable at will. The arm segments
themselves
may be designed as telescopic arms so that the maximum attainable working
height
of the working cabin 7 may be increased. The joints 11 may, for example, be
moved
by hydraulic cylinders.
Fig. 2 shows the working cabin 7 in a first configuration when viewed from the
top. It
comprises a transverse wall 12:, rigidly fitted to an arm segment 10. On the
side of
the transverse wall 12 facing away from the arm segment 10 a longitudinal wall
13
each is provided on both sides. On its top surface and its bottom surface, see
Fig. 4,
the working cabin is closed in each case by a ground plate 14 cut out in U-
shape as
well as by a ceiling plate 15. As a result the working cabin 7 possesses a
channel-
like rebate 16 into which a rotor blade 5 may be inserted. In the case of a
fixed rotor
4 the rotor blade 5 may be brought into the operating position according to
Fig. 2 by
moving the working cabin 7 by means of the lifting arm 8.
Both in the region of the bottom panel 14 and in the region of the ceiling
panel 15 the
working cabin 7 comprises a i:ube body 17, fitted on both sides of the U-
shaped
rebate. This tube body may be inflated and pressed against the surface of the
rotor
blade 5 by plungers 18, see Fig. 3. The plungers 18 may, for example, be moved
hydraulically or by compressed air. For this purpose the plungers 18 are
movably
arranged in the bottom panel) 14, the ceiling panel 15 respectively. Instead
of
CA 02341398 2001-02-21
marinahpecs\siebertantpct
individual plungers. 18 larger panel segments may also be used in the present
example.
Fig. 3, shows the seals in the closed position with the tube body 17 placed
against
the rotor blade 5. A sliding door 19 disposed on the side of the working cabin
7 facing
away from the arm segment 10 seals off the working cabin 7 from the outside.
In this
configuration the working cabin 7 is sealed off to a large extent from the
outside so
that work on the enclosed portion of the rotor blade 5 may be performed
without
being exposed to the effects of the weather conditions outside.
Fig. 4 shows the first configuration of the working cabin 7 according to Fig.
2 in the
section according to IV-IV. Fig. 5 shows correspondingly the working cabin 7
in the
second configuration according to Fig. 3 in the section V-V. Both figures
exemplify
that the rotor blade 5 may be fixed in the rebate 16 of the working cabin 7
even in a
position, which deviates distinctly from the vertical.
In the following a process for servicing wind turbine generators by means of
the afore
described device is illustrated. In the first configuration according to Fig.
2 or Fig. 4
the working cabin 7 is brought by means of the lifting arm 8 into such a
position that
the rotor blade locked in a position pointing approximately vertically
downwardly
comes to rest in the rebate 16. The tube body 17 is then pressed against the
surface
of the rotor blade 5 by means of the plungers 18 so that the interior of the
working
cabin 7 is sealed off to a large Extent from the environment. Maintenance work
on the
rotor blade 5 may now be performed inside the working cabin 7 regardless of
the
weather conditions.
The working cabin 7 may furi:hermore be fitted with extractor means so that,
for
example, sand blasting or grinding work is possible without negatively
influencing the
environment. As soon as a segment of a rotor blade 5 is treated, the tube body
17 is
released from the surface of the rotor blade 5 so that the working cabin 7 is
once
again returning to a configuratuon according to Fig. 2 or Fig. 4. In this
configuration
the working cabin 7 is adapted to move along the rotor blade 5 and may be
brought
into a new position.
By pressing the tube body 17 against the surface of the rotor blade 5 a closed
working space may again be brought about at the desired, new position. In this
manner the entire rotor blade 5 may gradually be covered with the working
cabin 7.
CA 02341398 2001-02-21
marinalspecs~siebertantpct
By rotating the rotor 4 and by renewed blocking, the other rotor blades 5 may
also be
treated correspondingly.
Not illustrated in detail is the possibility to equip the working cabin 7 with
a gripping
means, permitting to fasten a dismantled rotor blade 5 in order to deposit it
on the
ground by way of the lifting device 8. The working cabin 7 may in this context
also
take the form of a so-called slip carriage, for example with running wheels
fitted to
the rear wall, so that the dismantled rotor blade may be transported by the
working
cabin to a workshop hall or the like.
Fig. 6 shows an alternative embodiment of the device according to the
invention, all
elements which are identical wii:h regard to their function having the same
reference
numerals as in the preceding description.
In.the present case likewise dlenoted in general as 1, the device serves for
the
maintenance and cleaning of rotor blades 5 of the rotor 4 of a wind turbine
generator,
generally denoted as 2, at the upper end of a support mast 3. According to
this
variation a rail system 20, on which a carriage 21, including the working
cabin 7, is
movably provided, may be placed against or fitted to the support mast 3 from a
vehicle 9,.
A cable pull arrangement 22 is illustrated in dotted lines merely
symbolically, on
which the cabin 7 may be raised and lowered, the associated winch may, for ,
example, be positioned on the vehicle 9.
By way of an additional knee arm 23 Fig. 6 indicates that the rail system 20
may also
be designed as an integral structural part of the vehicle 9, for example, in
the manner
of a telescopic ladder or the likes, a segmental assembly in the manner of a
plugging-
together system may, of coursE~, also be provided. The figure further shows
clamp-
like components 24 by means of which the rail system may be fixed to the mast.
It goes without saying that the described embodiments of the invention may
vary in
many further respects without departing from the basic concept. The working
platform 7 may thus, for example, be adjustably arranged on the carriage 21 in
the
horizontal plane, in order to be able to compensate, where necessary, for
varying
rotor blade spacings, to mention just one example.