Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
WIRELESS PROVISION OF AUDIO CONTENT
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to the field of provision of audio content,
particularly wireless
provision of audio content via a cellular telephone.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The maj ority of cars and other vehicles contain in-vehicle audio systems
containing relatively
high quality audio components such as amplifiers and speakers. Such in-vehicle
audio systems
typically include radios, and cassette, CD and minidisk players, and the like.
However, the range
of audio content available to a listener of in-vehicle audio devices is
limited.
A listener to a radio is limited temporally to the programming available at
that time. If a
listener misses a desired radio program at its normal broadcast time, he is
unable to listen to that
program later, at a time convenient for him, unless he recorded it during
broadcast, A radio listener
is also limited geographically to the programming broadcast from a within-
range radio transmitter.
It is currently not possible for a radio listener to travel abroad and still
receive broadcasts from his
home country's local radio stations on an in-vehicle radio. There is thus a
need for a method for
listening to a radio program via an in-vehicle radio system, while the radio
program is not being
currently transmitted on an in-range transmitter, without the listener having
to pre-record the
program.
A listener to in-vehicle audio devices, such as a cassette or CD player, is
limited to the
selection of prerecorded audio content, typically music, that he has available
in the appropriate
format.
A large amount of audio content, including both music and spoken content, is
available over
the Internet. The majority of in-vehicle audio systems are not Internet-
enabled, however.
A large number of listeners to in-vehicle audio devices also possess cellular
phones. New
generations of cellular phones are Internet-enabled, allowing audio content to
be downloaded from
the Internet. The sound quality from cellular phones is typically poor as they
are designed to
IL9-2000-0037
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
minimize size and weight and are intended to be used by a single user, while
being held close to the
ear. Cellular phones are not designed for broadcasting music to a number of
listeners. There is thus
also a need for apparatus and a method for improving the sound quality of
audio content downloaded
from a network such as the Internet, through a cellular phone.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention seeks to provide apparatus and methods for receiving
audio content,
typically in the form of files, from a network such as the Internet via a
cellular phone, and for
playing the downloaded audio content over regular radio or stereo equipment.
In one embodiment,
the radio or stereo equipment is located within a vehicle. The vehicle stereo
provides high quality
sound, not available from the cellular telephone, and may also provide a
buffering memory, e.g., a
hard disk, for storing downloaded audio files for playback. The cellular phone
provides a user
interface and data channel to an application server as an extension to the car
radio/stereo.
In a preferred embodiment, the cellular phone is Internet enabled, using a
protocol such as
WAP (Wireless Access Protocol), to retrieve audio files from the Internet. In
an alternative
embodiment, the cellular phone uses packet-oriented cellular protocols and
networks. A typical, but
non-limiting, example of a packet-oriented cellular protocol is GPRS (General
Packet Radio
Service), which is a data service currently offered in some GSM networks.
In a preferred embodiment, the cellular phone and the radio or stereo
equipment are able to
communicate with each other over a short-range wireless channel, using a
communication protocol
such as BluetoothTM.
In a preferred embodiment, a user specifies the desired radio stations, or
individual radio
programs, typically by presetting a radio to the desired program or station.
This information is
transmitted from the radio to the telephone, which then contacts an
application server which has an
accessible archive of the radio station's programs, and downloads the
requested programming,
typically as audio files. The audio content is transferred from the telephone
to the radio for playback
to the user. Thus, the user is able to listen to programming at substantially
any desired time and
place, without being bound by the geographical limits and programming schedule
of a given radio
station.
IL9-2000-0037
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
There is thus provided in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
present invention,
apparatus for in-vehicle provision of audio content to a listener. The
apparatus includes a cellular
telephone adapted to receive broadcast radio content over a wireless network,
and an in-vehicle
audio system, adapted to be fixedly installed in a vehicle, and coupled to
receive the broadcast radio
content from the cellular telephone, and to play the content in the vehicle.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the cellular
telephone is adapted to receive the broadcast radio content over the wireless
network at a time when
the radio content is not being broadcast over radio channels.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the cellular
telephone is adapted to receive the broadcast radio content over the wireless
network at a location
where the radio content cannot be received over radio channels.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the
broadcast radio content received over the wireless network is user-selected.
Also in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
cellular
telephone is adapted to receive, from a user, an input including at least one
detail regarding the
broadcast radio content to be received, and to transmit the at least one
detail to a content provider
over the wireless network.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the input
comprises a verbal input.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the cellular
telephone comprises buttons, and the input comprises contacting the buttons.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the audio
system is adapted to receive, from a user, an input including at least one
detail regarding the
broadcast radio content to be received, and to transmit the at least one
detail to the cellular telephone.
Also in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
in-vehicle
audio system can function as a radio independent of the cellular phone, and is
adapted to receive, as
the input, at least one identification detail of the radio station to which
the radio is tuned.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the at least one
identification detail is selected from the group consisting of radio station
name, radio station ID
IL9-2000-0037 3
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
code, radio station broadcast frequency, and radio station URL.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the cellular
telephone is adapted to transfer the audio content to the in-vehicle audio
system via a wireless link
therebetween.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the cellular
telephone is adapted to transfer the audio content to the in-vehicle audio
system via a wired link
therebetween.
There is also provided in accordance with another preferred embodiment of the
present
invention, apparatus for storing user radio station preferences. The apparatus
includes a cellular
telephone having a memory, and an in-vehicle audio system, adapted to be
fixedly installed in a
vehicle and to play broadcast radio content therein, and adapted to receive,
from a user, at least one
identification detail regarding a radio station preferred by the user, and to
transmit the at least one
detail to the cellular telephone for storage in the memory.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the cellular
telephone is adapted to transmit the at least one detail of the preferred
radio station to another in-
vehicle audio system.
Still fizrther in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the other
in-vehicle audio system is adapted to receive the at least one detail from the
cellular telephone and,
responsive thereto, to receive and play broadcast radio content from the
preferred radio station.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the cellular
telephone is adapted to receive broadcast radio content from the preferred
radio station over a
wireless network, and the other in-vehicle audio system is coupled to receive
the broadcast radio
content from the cellular telephone, and to play the content in the vehicle.
There is further provided in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
present
invention, a method for the in-vehicle provision of audio content to a
listener. The method
comprises downloading broadcast radio content over a wireless network to a
cellular telephone,
transferring the content from the cellular telephone to an in-vehicle audio
system, and playing the
content on the in-vehicle audio system to the listener.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the step of
IL9-2000-0037
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
downloading content over the wireless network is performed at a time when the
content is not being
broadcast over radio channels.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the step of
downloading content over the wireless network is performed at a location where
the content can not
be received over radio channels.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the method
also includes the step of selecting the content to be downloaded.
Also in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
selecting step
includes a user inputting at least one detail regarding the broadcast radio
content to be downloaded,
and transmitting the at least one detail to a content provider over the
wireless network.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the at least one
detail is input to the cellular telephone.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the at least
one detail is input to the cellular telephone verbally.
Additionally in accordance with apreferred embodiment ofthe present invention,
the cellular
telephone comprises input buttons, and the at least one detail is input to the
cellular telephone
through contact with the buttons.
Also in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
at least one
detail is input via the audio system.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the audio system
functions as a radio independent of the cellular phone, and the at least one
detail includes at least one
identification detail of the radio station to which the radio is tuned.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the at least
one detail is stored in a memory in the cellular telephone.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the
wireless network is the Internet and the cellular telephone is WAP enabled.
Also in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
cellular
telephone communicates with the wireless network using a packet-oriented
cellular protocol.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the wireless
IL9-2000-0037
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
network is a GSM network and the packet-oriented cellular protocol is GPRS.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the content
is transferred from the cellular telephone to the audio system via a wireless
link therebetween.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the
wireless link uses a Bluetooth communication protocol.
Also in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
content is
transferred from the cellular telephone to the audio system via a wired link
therebetween.
There is further provided in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
present
invention, a method for storing a user's radio station preferences. The method
includes inputting
at least one identification detail regarding a radio station preferred by a
user to an in-vehicle audio
system, transmitting the at least one identification detail to a cellular
telephone, and storing the at
least one detail in a memory in the cellular telephone.
Further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention,
the method also
includes transmitting the stored at least one identification detail to another
in-vehicle audio system.
Still further in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the method
also includes identifying the preferred radio station from the at least one
detail, and responsive
thereto, receiving and playing broadcast radio content from the preferred
radio station.
Additionally in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present
invention, the method
also includes transmitting the stored at least one identification detail, over
a wireless network, to an
audio content provider, identifying the preferred radio station from the at
least one detail,
downloading broadcast radio content over the wireless network to the cellular
telephone, transferring
the content from the cellular telephone to the in-vehicle audio system, and
playing the content on
the in-vehicle audio system to a listener.
Also in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the
at least one
identification detail is selected from the group consisting of radio station
name, radio station ID
code, radio station broadcast frequency, and radio station URL.
IL9-2000-0037
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The present invention will be understood and appreciated more fully from the
following
detailed description, taken in conjunction with the drawings in which:
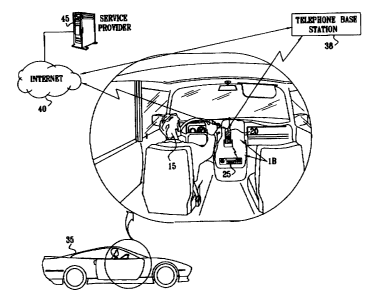
Fig. lA is a schematic illustration of apparatus for the provision of radio
services via a
cellular telephone to an in-vehicle audio system, constructed and operative in
accordance with a
preferred embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 1 B is a schematic illustration of the cellular telephone and in-vehicle
audio system of
Fig. 1 A, constructed and operative in accordance with a preferred embodiment
of the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is a flowchart detailing a method of downloading and playing desired
radio programs
to a user via a cellular telephone, in accordance with a preferred embodiment
of the present
invention;
Fig. 3 is a flow chart detailing a method of receiving desired radio channels
when the desired
channels are not within broadcast range, in accordance with another preferred
embodiment of the
presentinvention;
Fig. 4 is a flow chart detailing a method of downloading and playing desired
audio content
from the Internet, via a cellular phone, in accordance with another preferred
embodiment of the
present invention; and
Fig. 5 is a schematic illustration of a system for the download and playing of
audio content
from the Internet via a cellular telephone to an in-vehicle stereo,
constructed and operative in
accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Reference is now made to Fig. lA, which is a schematic illustration of
apparatus for the
provision of radio services via a cellular telephone to an in-vehicle stereo,
constructed and operative
in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention. As shown,
a user 15 possesses
a cellular telephone 20, and is the driver of a car 35 which is equipped with
a car audio system 25.
Cellular telephone 20 may be any conventional cellular telephone with data
communication
capabilities, such as a WAP-enabled telephone connected to a GSM or UTMS
network. Audio
IL9-2000-0037
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
system 25 may be any conventional car stereo as is known in the art, and
typically comprises a radio
receiver, an amplifier and two or more speakers connected thereto.
Reference is now made to Fig. 1 B which is a schematic illustration of the
cellular telephone
and in-vehicle audio system of Fig. 1 A, constructed and operative in
accordance with a preferred
embodiment of the present invention. Cellular telephone 20 and car audio
system 25 communicate
with each other, typically via transceivers 30, 32, using an internationally
accepted wireless
communication protocol such as Bluetootha, http: //www. motorola.
comlbluetoothlactiohlaction. html.
Alternatively, telephone 20 and audio system 25 may communicate via a wired
connection.
In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, if the user wishes to
listen to audio
content that is not immediately available, such as a radio program not being
currently broadcast from
an in-range transmitter, or music that the user does not possess in the
appropriate prerecorded format,
the user may select to download the desired content using cellular telephone
20. Audio content is
downloaded via a cellular network to which cellular telephone 20 is connected,
which in turn
transmits the downloaded audio content to car stereo 25 for playing.
Typically, the cellular network
is linked to a land network, such as the Internet 40, so that the audio
content can be retrieved and
served to the user from different, widely-dispersed geographic locations.
Exemplary uses of preferred embodiments of the present invention are described
below with
reference to Figures 2-5.
Reference is now made to Fig. 2 which is a flowchart detailing a method of
downloading and
playing desired radio programs to a user cellular telephone 20, in accordance
with a first preferred
embodiment of the present invention. The method is typically used when a
desired radio program
cannot be received via the radio receiver, either because the receiver is not
in broadcast range, or the
program is not currently being broadcast.
User 15, wishing to listen to a particular radio program which is not
currently being
broadcast, presets the radio to the station of the desired program (step 100),
in substantially the same
manner as tuning the radio for normal radio reception. The user initiates the
download of the
program, e.g., by pressing a specific button SO on radio 25 or button 55 on
telephone 20 (step 105),
to signal that the user wishes to listen to a recorded program, rather than
the program that is currently
being broadcast by the station. In response to pressing this button, car
stereo 25 typically transmits
IL9-2000-0037 g
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
the radio station ID to telephone 20 (step 110), which in turn contacts the
radio station, typically via
a telephone system base station 38, to check whether the radio station has an
accessible program
archive (step 120).
If the radio station does not have an accessible archive, or if the radio
station cannot be
contacted, telephone 20 typically informs user 15 that no radio programs are
available for that station
(step 125). The telephone may ask the user whether he wishes to download a
program from a
different radio station (step 130).
If the radio station does have an accessible archive, telephone 20 typically
takes the user
through a series of steps to identify the desired program (steps 135-170).
Steps 135, 145, 155, 165
are telephone prompts for information from user 1 S, and are typically verbal
prompts. Alternatively,
the prompts could be displayed on a screen on telephone 20, or radio 25.
Steps, 140, 1 S0, 160 and
170 are user responses, which may be input either by pressing buttons,
typically either on cellular
telephone 20 or car stereo 25. It is appreciated however, that user response
steps, 140, 150, 160 and
170 could be voice inputs, with voice recognition software to interpret the
user's speech. In a
preferred embodiment, pressing a voice activation button, such as a button 60
on car stereo 25, at
any stage during the interaction switches to voice input mode rather than
button pressing mode.
Once user 15 has specified a desired program to the telephone 20, telephone 20
connects via
Internet 40 (via base station 38 or through a separate wireless data network)
to an application server
45. The server typically converts the user's selection of a desired program
into a URL, and
downloads the program (step 175), typically in a MP3 file or other compressed
digital audio format.
The desired program may be downloaded in its entirety via telephone 20, and
stored in a
memory (step 180) before being played. The memory may be in telephone 20 or
car stereo 25. The
program is then transferred to the car stereo 25 (step 185) for playing.
Alternatively, the download
may be asynchronous, and once a batch of n minutes has been downloaded, it is
transferred to car
stereo 25 for playing, during which time, telephone 20 downloads the following
batch.
Reference is now made to Fig. 3 which is a flow chart detailing a method of
receiving desired
radio stations when the desired stations are not within broadcast range, in
accordance with another
preferred embodiment of the present invention. The method is typically used
when a user travels
IL9-2000-0037 9
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
abroad, and wants to listen to his home country radio stations. It is
appreciated that this method
applies to any situation where a desired radio station is not within broadcast
range.
User 15 presets the radio to the desired radio stations, typically while in
range of their
broadcasts (step 200) and initiates the download of the stations' details,
e.g., by pressing button 50
on radio 25 or button 55 on telephone 20 (step 205). Such details typically
include identification
details, such as name, frequency, alternative frequency and URL, etc. Car
stereo 25 typically
transmits the radio stations' identification details to telephone 20 (step
210), which in turn contacts
the radio stations, typically via telephone system base station 38 (step 215),
to check whether the
radio stations have an accessible program archive or Web site (step 220).
If one of the radio stations does not have an accessible archive, or cannot be
contacted,
telephone 20 typically informs user 15 that the specific radio station is not
available (step 225). The
telephone may ask user 15 whether he wishes to select a different radio
station (step 230).
Telephone 20 downloads and stores the URL or IP addresses of as many of the
desired radio stations
as it can find (step 235). The information is preferably stored in a memory of
the telephone, such
as in a subscriber identity module (SIM).
When travelling abroad, user 15 downloads the stored desired radio stations
from telephone
to car stereo 25 of a rental car (step 240). When user 15 selects a preset
station on radio 25, radio
requests telephone 20 to download the current program of that station in real-
time. If the user is
in a different time-zone in relation to the desired radio station, the user
may choose to compensate
20 for the time difference. For example, if there is a two hour time
difference between the user's home
time and his current local time, the user may either download the home 8:00 AM
news broadcast at
8:00 AM local time or 6:00 AM local time. Alternatively, the user may select a
program that was
broadcast at another, earlier time, using a method such as that described
above with reference to Fig.
2.
25 Telephone 20 typically connects via a network such as Internet 40 to an
application server,
as described above, which typically converts the selected radio station into a
URL, and downloads
the program (step 250). As described above with reference to Fig. 2, the
programming of the desired
station may be downloaded synchronously or asynchronously, and may be stored
on a memory in
IL9-2000-0037 10
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
either the telephone or the radio (steps 250-255). The downloaded programming
is transferred from
telephone 20 to car stereo 25 (step 260) for playing on the car stereo (step
265).
It is appreciated that the method described above with reference to steps 200-
240 of Fig. 3
can be used as a method to store, in a user's cellular phone, the user's
preferences for preset channels
for a car radio. When the user drives a different car, e.g. a new car or a
rental car, the cellular
telephone can download details of the user's preferred radio stations to the
car radio 20, thus
personalizing a user's car stereo. In place of steps 245-260, the car stereo
20 would first check to
determine whether the desired radio stations are available via regular radio
broadcasts, without first
having to download them via the cellular telephone.
Reference is now made to Fig. 4 which is a flow chart detailing a method of
downloading
and playing desired audio content from the Internet, via a cellular phone, in
accordance with another
preferred embodiment of the present invention. The method is typically used
when a user wishes
to listen to music, or other audio content, but does not have a prerecorded
copy of the music in the
appropriate storage format for car-stereo.
User 15 initiates the process of downloading music, e.g., by pressing button
50 on radio 25
or button 55 on telephone 20 (step 300). Telephone 20 typically takes the user
through a series of
steps to identify the desired music (steps 305-330). Steps 305, 315 and 325
are telephone prompts
for information from user 15, and are typically verbal prompts. Alternatively,
the prompts could be
displayed on a screen on telephone 20, or radio 25. Steps, 310, 320 and 330
are user responses,
which may be input either by pressing buttons, typically either on cellular
telephone 20 or car stereo
25. It is appreciated however, that user response steps, 310, 320 and 330
could be voice inputs, with
voice recognition software to interpret the user's speech.
Once user 15 has specified a desired piece of music to the telephone 20,
telephone 20
searches for and connects via a network such as the Internet 40 to an
application server that has the
requested piece of music available for download. (step 335), and downloads the
music (step 340).
If there is a fee involved in downloading the music, the fee may be charged to
the user's
telephone account (step 345).
The downloaded music is transferred from telephone 20 to stereo 25 (step 355),
where it is
played to user 15 (step 360).
IL9-2000-0037 11
CA 02347648 2001-05-15
The desired program may be downloaded in its entirety via telephone 20, and
stored in a
memory (step 350) before being played. The memory may be in telephone 20 or
stereo 25. The
program is transferred to stereo 25 (step 355) for playing. Alternatively, the
download may be
asynchronous, and once a batch of n minutes has been downloaded, it is
transferred to stereo 25 for
playing, during which time telephone 20 downloads the following batch.
Reference is now made to Fig. 5 which is a schematic illustration of a system
for the
download and playing of audio content from the Internet via a cellular
telephone 410 to an in-vehicle
stereo 420, constructed and operative in accordance with another preferred
embodiment of the
present invention. The system of Fig. 5 is suitable for the use with the
method of Fig. 4. As shown
in Fig. 5, a user 400 verbally requests a specific piece of music. Such a
verbal request would
typically replace steps 305-330 of Fig. 4.
Although preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described
herein with
relation to automobiles, the term vehicle as used herein also includes, but is
not limited to, land
transportation vehicles such as cars, vans, trucks, lorries, buses, jeeps,
motorcycles, bulldozers,
juggernauts and ambulances, as well as other surface vehicles.
It will be appreciated that certain features of the invention, which are, for
clarity, described
in the context of separate embodiments, may also be provided in the context of
a single embodiment.
Conversely, various features of the invention which are, for brevity,
described in the context of a
single embodiment, may also be provided separately or in any suitable
subcombination.
It will further be appreciated by persons skilled in the art that the present
invention is not
limited by what has been particularly shown and described hereinabove. Rather
the scope of the
present invention includes both combinations and subcombinations of various
features described
hereinabove as well as variations and modifications thereto which would occur
to a person of skill
in the art upon reading the above description and which are not in the prior
art.
IL9-2000-0037 12