Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
MODULE AND METHOD FOR INTERCONNECTING OPTOELECTRONIC CARDS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to modules for holding and
interconnecting data communications cards, and in
particular, to an interconnection module for holding and
interconnecting optoelectronic cards, and to a method of
interconnecting thereof.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
When several plug-in optoelectronic cards have to be
interconnected according to a required connection scheme,
there is a common practice to use a backplane to provide
the connection point between the cards. A typical prior art
interconnection module 1 is illustrated in Figures 1 and 2.
A backplane 10, having front and rear sides 12 and 14
respectively, has front side blind mate optical connectors
15 providing connection to the front side of the backplane,
and rear side hand inserted optical connectors 18 providing
connection to the rear side 14 of the backplane and
extending outwardly from the rear surface as shown in
Figure 1. Optical connectors 15 have adaptors 17, which ar~~
formed on the front side 12 of the backplane 10 and face
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
outwardly from the front side, and corresponding connector'
portions 16 carried by optoelectronic cards 22 and inserted
in the adaptors 17. Connector portions 16 or the adaptors
17 may optionally have floating features, which allow for
required connection tolerances. Each one of the adaptors 17
and connector portions 16 may have one of the connector
receptacle and connector plug to mate with each other and
to receive the cards 22 as illustrated in Figures 1 and 2.
The rear side 14 of the backplane 10 provides an
interconnect from one card to another card through optical
patch cords 26 which have corresponding fiber optic
connector portions mating with rear side connectors 18.
Alternatively, instead of using patch cords, fiber optic
strands may be laminated into the backplane in order to
provide connection between the cards (not shown). Products
matching these configurations are sold on the open market
and represent the current prior art, see, e.g.
"Interconnecting for Networking", Catalog 1307515, issued
9-99, p.675.
Thus, in order to connect two optoelectronic cards, a
fiber optic connector is required on each card as well as
on each end of the patch cord. When more than two cards
have to be interconnected, it will require multiple optical
2
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
connectors of different types on both sides of the
backplane and a corresponding number of optical patch
cords. Use of multiple patch cords results in ineffective
utilization of space and makes the design of the
interconnection module complicated and expensive.
Additionally, the use of patch cords or laminated fiber
strands causes substantial optical signal degradation due
to the insertion losses through multiple connection points.
Accordingly, there is a need in the industry to
develop an alternative interconnection module and method of
interconnecting multiple optoelectronic cards which would
be less complicated while more flexible and efficient.
SU1~1ARY OF THE INVENTION
Therefore it is an object of the invention to provide
an interconnection module and method of interconnecting
multiple optoelectronic cards, which would avoid or
minimize the above-mentioned problems.
According to one aspect of the invention there is
provided an interconnection module, comprising:
a midplane, having a front side and a rear side;
a coupling sleeve formed on the midplane, the sleeve
having a front portion and a rear portion extending
3
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
outwardly from the front side and the rear side of the
midplane respectively and providing optical coupling
between the front and rear sides of the midplane;
the front and rear portions of the sleeve receiving a
front connector and a rear connector respectively so that
the connector on each side of the midplane is arranged
within the sleeve in one of the first and second positions,
wherein in the second position the connector is being
rotated approximately by 90 degrees with regard to the
first position.
Preferably, the connectors are blind mate optical
connectors having floating members to provide required
connection tolerances. Depending on system requirements,
the connectors may be single fiber connectors or multi-
fiber connectors, and each of the front and rear connectors
and front and rear portions of the sleeve may have one of
the optical receptacle and optical plug selected so as to
provide mating between the corresponding connector and
portion of the coupling sleeve. Advantageously, the front
and rear portions of the sleeve have same shape so that
each portion of the sleeve is capable of receiving one of
the rear and front connectors, thereby providing that the
same connector can be connected on both sides of the
4
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
midplane. Conveniently, the connectors and the sleeve may
have a square or circular cross-section.
Beneficially, the front and rear connectors are
carried by front and rear optoelectronic cards arranged on
the front and rear sides of the midplane respectively,
thereby providing that the cards are arranged on opposite
sides of the midplane in one of the two positions, in the
first position the front and rear cards being substantially
parallel to each other, and in the second position the
cards being substantially perpendicular to each other.
Generally, a plurality of coupling sleeves may be arranged
on the midplane so as to accommodate a plurality of optical
connectors carried by optoelectronic cards and to provide
connection between N cards on one side of the midplane and
M cards on the other side of the midplane. In most
practical situations N=1,... 20 and M=1,...20.
Conveniently, a plurality of coupling sleeves is arranged
on the midplane so as to accommodate a plurality of optical
connectors carried by N optoelectronic cards on one side oi=
the midplane and M cards on the other side of the midplane
and to provide connection between the cards so that each of
the N cards on one side of the midplane is connected to a
subset of cards on the other side of the midplane, for each
5
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
of the N cards the number of cards in the subset being
variable and less or equal to M in total. If required, the
midplane and the cards may carry corresponding electrical
connectors.
According to another aspect of the invention there is
provided an optical midplane, comprising:
a midplane having a front side and a rear side; and
a coupling sleeve formed on the midplane, the sleeve
having a front portion and a rear portion extending
outwardly from the front side and the rear side of the
midplane respectively and providing optical coupling
between the front and rear sides of the midplane;
the front and rear portions of the sleeve being
capable of receiving front and rear connectors respectively
so that each connector is arranged within the sleeve in one
of the first and second positions, wherein in the second
position the connector is being rotated by approximately 90
degrees with regard to the first position.
According to yet another aspect of the invention there
is provided a combination of a data shelf and a plurality
of interconnection modules as described above;
the data shelf having stations provided for receiving
and fixing the interconnection modules in the shelf.
6
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
According to still yet another aspect of the invention
there is provided a method of interconnecting
optoelectronic cards, comprising the steps of:
providing a midplane, having a front side and a rear
side, and a coupling sleeve formed on the midplane for
providing optical coupling between the front and rear sides
of the midplane, the sleeve having a front portion and a
rear portion extending outwardly from the front side and
the rear side of the midplane respectively;
providing front and rear optoelectronic cards carrying
front and rear optical connectors respectively;
inserting front and rear connectors into the front and
rear portions of the sleeve respectively so that the
connector on each side of the midplane is arranged within
the sleeve in one of the first and second positions,
wherein in the second position the connector is being
rotated approximately by 90 degrees with regard to the
first position;
thereby providing that the cards are interconnected
and arranged in one of the two positions, in the first
position the front and rear cards being substantially
parallel to each other, and in the second position the
cards being substantially perpendicular to each other.
7
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
According to one more aspect of the invention there is
provided an interconnection module, comprising:
a combined midplane having a midplane section and a
backplane section;
the midplane section having a front side and a rear
side, and a coupling sleeve formed on the midplane section,
the sleeve providing optical coupling between the front
side and rear side of the midplane section and having a
front portion and a rear portion extending outwardly from
the front side and the rear side of the midplane section
respectively;
the front and rear portions of the sleeve being
capable of receiving front and rear connectors respectively
so that the connector on each side of the midplane is
arranged within the sleeve in one of the first and second
positions, wherein in the second position the connector is
being rotated by approximately 90 degrees with regard to
the first position, thereby providing connection between
different sides of the midplane section;
the backplane section being formed as an extension of
the midplane section to form the combined midplane; and
8
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
the backplane section having corresponding backplane
adaptors for receiving backplane connectors to provide
connection between the same side of the backplane section.
Conveniently, the backplane section is formed so as to
be substantially in a plane of the midplane section.
Alternatively, it may be formed so as to be substantially
perpendicular to the midplane section. Preferably, the
midplane and backplane sections are formed as integral
parts of the combined midplane.
According to one more aspect of the invention there is
provided an interconnection module, comprising:
a combined midplane having a midplane section and a
backplane section;
the midplane section having a front side and a rear
side, and a coupling sleeve formed on the midplane section,
the sleeve having a front portion and a rear portion
extending outwardly from the front side and the rear side
of the midplane section respectively and providing optical
coupling between the front side and rear side of the
midplane section;
the backplane section being formed as an extension of
the midplane section to form the combined midplane; and
9
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
the backplane section having corresponding backplane
adaptors for receiving backplane connectors providing
connection between same side of the backplane section.
The backplane section of the interconnection module is
formed so as to be substantially in a plane of the midplane
section. Alternatively, the backplane section may be
formed so as to be substantially perpendicular to the
midplane section. Beneficially, the midplane and backplane
sections are formed as integral parts of the combined
midplane.
The interconnection modules as described in the
embodiments of the invention provide the following
advantages. They reduce the accumulation of optical signal
degradation due to insertion loss through multiple
connection points, and provide a cost advantage by reducing
the total number of the optical connectors. Additionally,
the modules provide flexible system architecture which
allows required interconnection between the cards on
opposite and same sides of the midplane. Such flexibility
becomes extremely important for optical cards carrying
optical switches, splitters and other components, which
require multiple interconnects.
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-O:i2
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Embodiments of the invention will now be described, by
way of example, with reference to the accompanying drawings
in which:
Figure 1 is a top view of an interconnection module
for holding and interconnecting optoelectronic cards
according to the prior art;
Figure 2 is an isometric view of the interconnection
module of Figure 1, illustrating connection of the
optoelectronic cards to a backplane;
Figure 3 is a top view of an interconnection module
for holding and interconnecting optoelectronic cards
according to a first embodiment of the invention;
Figure 4 is a side view of the module shown in Figure
3;
Figure 5 is a three dimensional view of the
interconnection module of the first embodiment with the
cards on opposite sides of a midplane being perpendicular to
each other;
Figure 6 is a three dimensional view of the
interconnection module of the first embodiment with the
cards on opposite sides of a midplane being parallel to each
other; and
11
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
Figure 7 is a rear view of an interconnection module
for holding and interconnecting optoelectronic cards
according to a second embodiment of the invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE E1~ODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION
An interconnection module for holding and
interconnecting multiple optical data cards according to
the first embodiment of the invention is schematically
shown in Figures 3 to 6. It includes an optical midplane
110, having front and rear sides 112 and 114 respectively,
and a plurality of coupling sleeves 120 formed on the
midplane through openings in the midplane so as to provide
connection between the opposite sides of the midplane. Each
sleeve has a front portion 119 and a rear portion 121
(shown in Figures 5 and 6) which extend outwardly from the
front side 112 and the rear side 114 of the midplane 110
respectively. The front portion 119 of the sleeve 120
receives a front connector 116 carried by the
optoelectronic card 122 arranged on the front side 112 of
the midplane 110, and the rear portion 121 of the sleeve
120 receives a rear connector 118 carried by the
optoelectronic card 125 arranged on the rear side 114 of
the midplane 110. Connectors 116 and 118 are blind mate
12
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
single fiber optical connectors, which have corresponding
floating alignment connector members 126 and 128 in order
to accommodate tolerance build-up and to allow for a
precise alignment. The floating alignment members 126 and
S 128 of the connectors receive corresponding fiber
termination connector members 130 and 132 which have keying
features 134 and 136 respectively as illustrated in Figures
and 6. The connectors 116, 118 and the sleeve 120 have
corresponding alignment features shown as alignment tongues
140 on the sleeve 120, facets at the ends of floating
members 126, 128, and fiber alignment features (not shown)
which ensure proper alignment between the fibers. The
coupling sleeve 120 has a shape which has a 90° symmetry
and matches the shape of the connectors 116 and 118, thus
allowing an arrangement of each of the connectors within
the sleeve 120 in one of the first and second positions,
where in the second position the connector is rotated
approximately by 90 degrees with regard to the first
position. In the first embodiment, the sleeve and the
connectors have a square cross-section. Additionally, the
front and rear portions 119 and 121 of the sleeve 120 are
also designed so as to have same shape so that each portion
of the sleeve is capable of receiving either one of the
13
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
rear and front connectors 118 and 116 respectively, thereby
providing that same connector can be connected on both
sides of the midplane 110. In the first embodiment of the
invention the connectors 116 and 118 are optical plugs,
while the coupling sleeve performs the function of an
optical receptacle, the plugs and receptacles being an SC-
type connector developed by AT&T as described, e.g. in the
background section of US patent No.5,436,995 to Yoshizawa.
Figure 5 illustrates the connectors 116 and 118
plugged into the sleeve 120 in the first position, which
provides the arrangement of front and rear optoelectronic
cards 122 and 125 on opposite sides of the midplane
substantially perpendicular to each other. It is also
conveniently arranged that keying features 134 and 136 on
corresponding fiber termination connector members 134 and
136 are substantially aligned with each other. Figure 6
illustrates the connector 118 in the second position when
the connector is rotated by 90 degrees with respect to its
first position, providing thereby that the cards 122 and
125 are now substantially parallel to each other. Each one
of the floating alignment members 126 and 128 has two
keying insertion slots (not shown) arranged at 90 degrees
to each other. It provides that the fiber termination
14
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
connection members 130 and 132 can be un-plugged, rotated
by 90 degrees and plugged into the floating members in
their second positions. Accordingly, Figure 6 illustrates
the arrangement when the floating member 128 has been
rotated by 90 degrees within the rear portion 121 of the
sleeve 120, and when the fiber termination member 132 has
also been rotated by 90 degrees within the floating member
128 and in the same direction, thus providing the alignment
of the keying features 134 and 136 substantially along the
same line.
The total number of optical connectors and their
arrangement on the midplane 110 is defined by system
requirements, and more specifically, by the number of
optoelectronic cards to be mounted to the midplane and
their interconnection scheme.
In the first embodiment as illustrated in Figures 3
and 4, the interconnection module 100 has eight coupling
sleeves formed on the midplane, which provide connection
between two cards 122 on the front side 112 of the midplane
110 and four cards 125 on the rear side 114 of the midplane
110. Orientation of the front cards 122 is substantially
perpendicular to the optical midplane 110, and orientation
of the rear cards 125 is substantially perpendicular to the
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
midplane 110 and substantially perpendicular to the cards
122. Each of the front cards 122 has four connectors 116
adapted to interface with the front portions 119 of the
eight coupling sleeves, and each of four rear cards 125 has
two connectors 118 adapted to interface with the rear
portions 121 of the eight sleeves on the midplane.
Thus, a direct optical connection between two cards
122 on one side of the optical midplane 110 and four cards
125 on the other side of the optical midplane is provided.
Numerous modifications may be made to the embodiment
described above. While in the first embodiment the optical
connectors are single fiber connector, it is contemplated
that the connectors may be multi-fiber connectors having
multiple fiber terminations. Each one of the front and rear
connectors and front and rear portions of the sleeve may
have one of the optical receptacle and optical plug selected
so as to provide mating between the corresponding connector
and portion of the coupling sleeve. While in the first
embodiment the connectors and the sleeves have square cross-
section, it is contemplated that they may have any other
shape, which would provide a 90-degree symmetry, e.g. a
circular shape. In a modification to the embodiment, the
connectors may be ST, FC, MT or any other known types of
16
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-0:32
optical connectors, described, e.g. in the above cited
patent to Yoshizawa and US patents No. 5,321,784 to
Cubukciyan and No. 5,325,455 to Henson. In addition to
blind mate optical connectors, which provide optical link
between the cards, the optional electrical connectors may b~e
provided on some or all of the cards for electrical link
between the cards, the electrical connectors being
preferably blind mate connectors or other known types of
electrical connectors. It is contemplated that optical
connectors may be arranged so as to accommodate various
numbers of optoelectronic cards on each side of the midplane
and to provide parallel or perpendicular orientation between
the cards on opposite sides of the midplane. In general,
the interconnection module of the invention may provide a
direct connection between N optoelectronic cards mounted to
one side of the midplane and M optoelectronic cards on the
other side of the midplane.
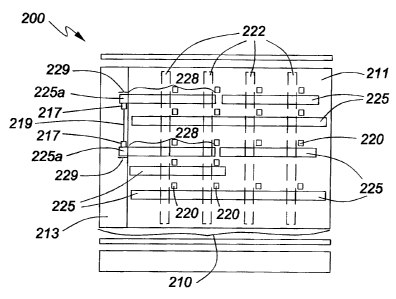
An interconnection module 200 for holding and
interconnecting optoelectronic cards according to a second
embodiment of the invention is shown in Figure 7. It is
similar to that of the first embodiment described above
except for the midplane 210 itself now being a combined
midplane having two sections, a midplane section 211 which
17
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
is similar to the midplane 110 described above, and a
backplane section 213, which is formed as an extension of
the midplane section 211 to provide connection between the
cards on same side of the midplane section 211. Similar
elements of the interconnection modules 100 and 200 are
designated by the same reference numerals incremented by 100
respectively. Figure 7 shows a rear view of the module 200
from the direction designated by arrow A on Figures 3 and 4,
thus illustrating an arrangement of cards 225 on the rear
side of the combined midplane 210. The midplane 210 holds
seven cards 225 on the rear side and four cards on the front
side 222 (noted by dotted lines), the cards are arranged so
that the following connection is provided: two out of four
cards 222 on the front side of the midplane 210 are
connected to five cards 225 on the rear side of the midplane
210, while the other two cards 222 are connected to four
cards 225 on the opposite side of the midplane, optionally
the sets of the interconnected cards being different. The
sleeves 220 and blind mate optical connectors (not shown)
are arranged on the midplane section 211 so as to
accommodate cards 225 of different sizes, the cards ranging
in length from the full width of the module to a fraction o:E
the module width. The cards 225 fill in a surface area of
18
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
the combined midplane 210 as appropriate, with some of the
cards 225, designated as 225a cards, extending over both the
midplane section 211 and the backplane section 213.
Respective parts of the cards 225a are designated by
reference numerals 228 and 229 in Figure 7. The backplane
section 213 is formed as an integral part of the combined
midplane 210 and is similar to the backplane of the prior
art described above. It has a plurality of backplane
connectors 217 formed on the backplane and joined via
laminated fiber strands 219 or optical patch cords (not
shown). Each of the cards 225a has corresponding connectors
(not shown) to mate with the connectors 219 on the backplan~~
and to ensure that cards 225a on the same side of the
combined midplane 210 are interconnected. Additional
electrical connectors may be provided on the midplane
section 211 and/or the backplane section 213 of the combined
midplane to provide electrical data flow between the cards.
In general, the interconnection module 200 may include
optical and electrical connectors arranged so as to
accommodate N cards on one side of the combined midplane
and M cards on the other side of the midplane and to
provide connection between the cards so that each of the N
cards on one side is connected to a subset of cards on the
19
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-032
other side, the number of cards in the subset being
variable for each of the N cards and less or equal to M in
total. Additionally, any required subset of cards on each
side of the combined midplane 210 may be interconnected via
backplane section of the module 200.
Thus, the interconnection module 200, which
efficiently interconnects optoelectronic cards on opposite
sides of the midplane and cards on the same side of the
midplane 210, is provided.
A plurality of interconnection modules described in
the first and second embodiments, each carrying a plurality
of data cards, is installed in a data shelf having
receiving stations for receiving and mounting the
interconnection modules in the shelf.
In a modification to the second embodiment, the
interconnection module 200 may have the backplane section
213 arranged substantially perpendicular to the midplane
section 211 and conveniently along a sidewall of the data
shelf.
The interconnection modules as described in the
embodiments of the invention provide the following
advantages. They solve the problem of accumulating opticaJ_
signal degradation due to insertion loss through multiple
CA 02349494 2004-06-02
TR-X32
connection points, and provide a cost advantage by reducing
the total number of the optical connectors compared to
common use of backplanes. This is achieved due to the
elimination or minimizing the number of the optical patch
cords or laminated fiber backplanes and by providing direct
connection between the cards. One more benefit provided by
the modules include flexible system architecture which
allows connection between the cards on opposite and same
sides of the midplane, e.g. allowing incorporation and
flexible interconnection of dense wavelength division
multiplexing (DWDM) filters, splatters, amplifiers,
switches and other optical components carried by optical
cards.
Although specific embodiments of the invention have
been described in detail, it will be apparent to one
skilled in the art that variations and modifications to the
embodiments may be made within the scope of the following
claims.
21