Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02356893 2001-06-28
WO 00!44540 PCT/SE00/00186
METHOD AND ARRANGEMENT FOR THE CONTINUOUS MANUFACTURE OF
PROFILED LIGNOCELLULOSE-CONTAINING BOARD OR STRIP-LIKE
PRODUCTS
The present invention relates to a method of continuously producing pro-
filed lignocellulose-containing board or strip-like products according to the
pream-
ble of claim 1, and to an arrangement for carrying out the method in
accordance
with the preamble of claim 7.
A common way of producing, e.g., profiled structural elements such as
to skirting boards, cornices, window linings, architraving or furniture
components is to
plane or mill the desired profile either from solid wood or from fibreboard,
prefera-
bly MDF (Medium Density Fibreboard). The unsuitability of using this technique
to
mill such products from medium density fibreboard is obvious. Firstly, it
would in-
volve a production chain and transport chain consisting of many expensive
inter-
mediate steps and operations and would mean that the profiled product would
have different densities in cross-section and therewith absorb different
amounts of
paint or varnish at discrete locations. The milling operation would also
result in
high material losses. For instance, more than 50% of the starting material can
be
lost when milling products to pronounced profile depths.
2 o A standard example of this production chain may be as follows: Dried and
glue-coated fibres are produced in the MDF plant and shaped into mats which
are
pressed into boards which are then edge-trimmed and ground. Losses are experi-
enced in the form of edge trim and dust from the grinding operations. The next
link
in the production chain consists in the transportation of board to the
production
unit for the profiled products. In the third link, the medium density
fibreboards are
sawn into strips which form the starting blanks for the profiled products,
these
starting blanks being milled and ground as well as lacquered with layers of
paint or
varnish or are coated with some type of film for priming or decoration
purposes.
The object of the present invention is to avoid the drawbacks associated
3 o with the aforesaid production process in an economical fashion and,
instead, to
provide a continuous process up to the finished profiled product with as
little mate-
CA 02356893 2001-06-28
WO 00/44540 PCT/SE00/00186
2
rial loss as possible. This object is achieved in accordance with the
invention
having the characteristic features set forth in the following Claims.
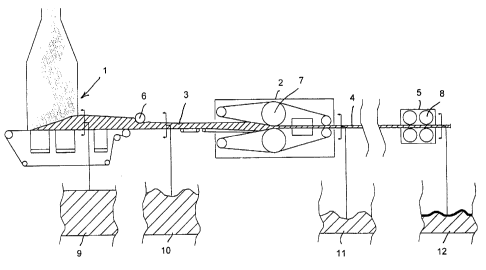
The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the
accompanying drawing, which illustrates schematically in longitudinal section
an
inventive plant with four separate cross-sections shown in larger scale.
The illustrated plant is based on the plant illustrated in SE 502 272, which
describes a continuous steam injection process. Disintegrated, dried and glue-
coated lignocellulosic fibre material is delivered to a forming station 1 and
there
formed into a fibre mat 3 which is fed into a steam injection press 2. The
fibre mat
1 o is pressed in the press into a board product 4 which is hardened, or
cured, to an
extent at which the board is solid and has a given mechanical strength. The
sur-
faces are further densified in a surface densifying unit 5. This process
results in
board that has a dense outer surface.
According to the invention, the plant is designed for the production of pro-
filed board or strip products in one and the same two-step process. To this
end, a
milling or cutting roll 6 is arranged between the forming station 1 and the
steam
injection press 2. The cutting roll 6 functions to impart a profiled surface
structure
to the lignocellulosic, glue-coated starting material in the form of the fibre
mat 3
that has a density of between 20 and 200 kg/m3. To this end, the diameter of
the
2 o cutting roll 6 varies across its width. The profile imparted to the cross-
section of
the mat will coincide essentially with the cross-section of the finished
product. The
profiled mat 3, which may be precompressed, is transported continuously into
the
steam injection press 2. This press includes a profiled steam roll 7 that has
the
same profile as the cutting roll 6. The mat 3 is compressed here and hardened
to
form a board or strip 4 that has the intended cross-section, by injecting
saturated
or superheated steam into the mat. The surface layers are further compressed
in
a second step, by allowing the board or the strip 4 to pass through the
surface
densifying unit 5 that includes one or more hot, compression roll-pairs 8 that
have .
the same geometry as the steam roll 7 but a smaller cross-sectional area so as
to
obtain the desired surface compression. The surface temperature of the roll
pairs
8 may lie between 100 and 350°C, preferably between 150 and
250°C.
CA 02356893 2001-06-28
WO 00/44540 PCT/SE00/00186
3
The drawing shows the cross-section 9 of the formed fibre mat 3 prior to
profiling the mat. The cross-section 10 downstream of the cutting roll 6
illustrates
the profile of the upper surface. Downstream of the steam injection press 2,
the
board 4 pressed therein will have the cross-section 11, and the surface sheet
in
the cross-section 12 downstream of the surface densifying unit 5 will have a
higher density but the same profile.
The underside of the board can be profiled with the same technique. In
this respect, a cutting roll 6 is also arranged on the other side of the fibre
mat 3
and the lower rolls 7 and 8 in the steam injection press 2 and the surface
densify-
1 o ing unit 5 are provided with the same surface profile as the lower cutting
roll
across the respective widths thereof.
It may be of interest in certain applications to provide certain parts of the
profile with a greater density, e.g. on exposed tops. This is made possible by
al-
lowing the profile on the rolls 7 and 8 to deviate from the profile on the
cutting roll
6 at these points.
In one alternative embodiment, the board or the strip produced in the first
step, i.e. in the steam injection press, can be divided into several narrower
strips
in a continuous process, these narrower strips then being passed through one
or
more hot roll pairs 8 in the surface densifying unit 5. Separation of the
board or
2 o strip into a plurality of strips may be effected by sawing, for instance.
The invention enables the production of profiled lignocellulose-containing
products in the form of boards and strips of uniform density throughout the
whole
of their cross-section and with dense surfaces that absorb equal amounts of
paint
over the entire product in a rapid and continuous process. Furthermore, this
is
achieved in the absence of losses in starting material, apart from the small
losses
that occur when sawing the board or strip.