Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 P~'T/US00/01540
COMPOUNDS WHICH INHIBIT LEUKOCYTE ADHESION
MEDIATED BY VLA-4
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
This application claims the benefit of U.S. Serial No. 60/116,923,
filed January 22, 1999, and U.S. Serial No. 60/160,999, filed October 21,
1999; the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by reference in their
entirety.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to compounds which inhibit leukocyte adhesion
and, in particular, leukocyte adhesion mediated by VLA-4.
References
The following publications, patents and patent applications are cited
in this application as superscript numbers:
15
' Hemler and Takada, European Patent Application Publication
No. 330,506, published August 30, 1989
Elices, et al., Cell, 60:577-584 (1990)
Springer, Nature, x:425-434 (1990)
Osborn, Cell, 62:3-6 (1990)
5 Vedder, et al., Surgery, 106:509 (1989)
Pretolani, et al. , J. Exp. Med. , 1~0: 795 ( 1994)
' Abraham, et al. , J. Clin. Invest. , 93 :776 ( 1994)
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 2 __
Mulligan, et al., J. Immunology, 150:2407
(1993)
Cybulsky, et al., Science, 251:788 (1991)
' Li, et al., Arterioscler. Thromb., 13:197
(1993)
" Sasseville, et al., Am. J. Path., 144:27
(1994)
'z Yang, et al., Proc. Nat. Acad. Science (USA),
90:10494
(1993)
'3 Burkly, et al., Diabetes, 43:529 (1994)
'4 Baron, et al., J. Clin. Invest., 93:1700
(1994)
's Hamann, et al., J. Immunology, 152:3238
(1994)
'6 yednock, et al., Nature, 356:63 (1992)
" Baron, et al. , J. Exp. Med. , 177:57 (
1993)
'g van Dinther-Janssen, et al., J. Immunology,
147:4207 (1991)
'9 van Dinther-Janssen, et al. , Annals. Rheumatic
Dis. , 52:672
(1993)
zo Elices, et al., J. Clin. Invest., 93:405
(1994)
z' Postigo, et al., J. Clin. Invest., 89:1445
(1991)
zz pain, et al. , Transpl. Proceed. , 25: 813
( 1993)
zs Okarhara, et al., Can. Res., 54:3233 (1994)
z' Paavonen, et al. , Int. J. Can. , ~ :298
( 1994)
zs Schadendorf, et al., J. Path., 170:429 (1993)
z6 Bao, et al., Diff., 52:239 (1993)
z' Lauri, et al., British J. Cancer, Cz8:862
(1993)
zg Kawaguchi, et al . , Japanese J. Cancer
Res. , 83 :1304 ( 1992)
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/I1S00/01540
-- 3 __
29 Kogan, et al. , U. S. Patent No. 5, 510, 332, issued April 23,
1996
3o International Patent Appl. Publication No. WO 96/01644.
All of the above publications, patents and patent applications are
herein incorporated by reference in their entirety to the same extent as if
each individual publication, patent or patent application was specifically and
individually indicated to be incorporated by reference in its entirety.
State of the Art
VLA-4 (also referred to as a4~3, integrin and CD49d/CD29), first
identified by Hemler and Takada' is a member of the (31 integrin family of
cell surface receptors, each of which comprises two subunits, an a chain and
a ~3 chain. VLA-4 contains an a4 chain and a X31 chain. There are at least
nine X31 integrins, all sharing the same (31 chain and each having a distinct
a
chain. These nine receptors all bind a different complement of the various
cell matrix molecules, such as fibronectin, laminin, and collagen. VLA-4,
for example, binds to fibronectin. VLA-4 also binds non-matrix molecules
that are expressed by endothelial and other cells. These non-matrix
molecules include VCAM-1, which is expressed on cytokine-activated
human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture. Distinct epitopes of VLA-
4 are responsible for the fibronectin and VCAM-1 binding activities and each
activity has been shown to be inhibited independently.2
Intercellular adhesion mediated by VLA-4 and other cell surface
receptors is associated with a number of inflammatory responses. At the site
of an injury or other inflammatory stimulus, activated vascular endothelial
cells express molecules that are adhesive for leukocytes. The mechanics of
leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells involves, in part, the recognition and
binding of cell surface receptors on leukocytes to the corresponding cell
surface molecules on endothelial cells. Once bound, the leukocytes migrate
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 4 __
across the blood vessel wall to enter the injured site and release chemical
mediators to combat infection. For reviews of adhesion receptors of the
immune system, see, for example, Springer3 and Osborn4.
Inflammatory brain disorders, such as experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis (EAE), multiple sclerosis (MS) and meningitis, are
examples of central nervous system disorders in which the
endothelium/leukocyte adhesion mechanism results in destruction to
otherwise healthy brain tissue. Large numbers of leukocytes migrate across
the blood brain barrier (BBB) in subjects with these inflammatory diseases.
The leukocytes release toxic mediators that cause extensive tissue damage
resulting in impaired nerve conduction and paralysis.
In other organ systems, tissue damage also occurs via an adhesion
mechanism resulting in migration or activation of leukocytes. For example,
it has been shown that the initial insult following myocardial ischemia to
heart tissue can be further complicated by leukocyte entry to the injured
tissue causing still further insult (Vedder et a1.5). Other inflammatory
conditions mediated by an adhesion mechanism include, by way of example,
asthma~8, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis9-'°, AIDS dementia",
diabetes'z-'a (including acute juvenile onset diabetes), inflammatory bowel
disease's (including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease), multiple
sclerosis's", rheumatoid arthritis's-2', tissue transplantation22, tumor
metastasis'3-Zg, meningitis, encephalitis, stroke, and other cerebral traumas,
nephritis, retinitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, myocardial ischemia and
acute leukocyte-mediated lung injury such as that which occurs in adult
respiratory distress syndrome.
In view of the above, assays for determining the VLA-4 level in a
biological sample containing VLA-4 would be useful, for example, to
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 5 __
diagnosis VLA-4 mediated conditions. Additionally, despite these advances
in the understanding of leukocyte adhesion, the art has only recently
addressed the use of inhibitors of adhesion in the treatment of inflammatory
brain diseases and other inflammatory conditionsz9.3o. The present invention
addresses these and other needs.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
This invention provides compounds which bind to VLA-4. Such
compounds can be used, for example, for treating diseases mediated by
VLA-4, to assay for the presence of VLA-4 in a sample, and in
pharmaceutical compositions to inhibit cellular adhesion mediated by VLA-
4, for example, binding of VCAM-1 to VLA-4. The compounds of this
invention have a binding affinity to VLA-4 as expressed by an ICSO of about
,uM or less (as measured using the procedures described in Example A
15 below).
Accordingly, in one aspect, this invention is directed to a method for
treating a disease mediated by VLA-4 in a patient, which method comprises
administering to said patient a pharmaceutical composition comprising a
pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a therapeutically effective amount of
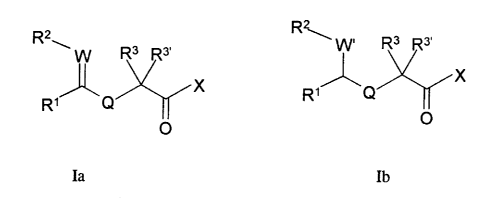
a compound of formula Ia and/or Ib:
R
Rz~ w R3 R3, ~ W, R3 R3.
X and ~ X
R~ Q
R O ~ O
O
Ia Ib
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 6 __
wherein, in formula Ia, R' and RZ, together with the carbon atom and
W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form an aryl,
cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in
the aryl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group and optionally
containing or additionally containing in the case of heteroaryl and
heterocyclic groups 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of
oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur, and wherein the heteroaryl or heterocyclic
group is monocyclic;
in formula Ib, R' and R2, together with the carbon atom and W' to
which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in the
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group and optionally containing or
additionally containing in the case of the heterocyclic group 1 to 3
heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and
sulfur, and wherein the heterocyclic group is monocyclic;
and further wherein said aryl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or
heterocyclic group of formula Ia or Ib is optionally substituted, on any ring
atom capable of substitution, with 1-3 substituents selected from the group
consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, acyl,
acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, substituted amino, amidino,
alkyl amidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino,
aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy,
substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, cyano, halogen,
hydroxyl, nitro, oxo, carboxyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)2-alkyl, -OS(O)Z
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)Z-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted aryl, -OS(O)2-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)Z-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where each R is independently hydrogen or alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-alkyl, -NRS(O)z-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)2-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)z-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRS(O)2-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-
alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O),-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -N[S(Oh-R']2 and -N[S(O)z-
NR']2 where each R' is independently selected from the group consisting of
alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic;
R3 and R3' are independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, isopropyl, -CH~Z where Z is selected from the group consisting
of hydrogen, hydroxyl, acylamino, alkyl, alkoxy, aryloxy, aryl, aryloxyaryl,
carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl, carboxyl-cycloalkyl,
carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-substituted aryl,
carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl, carboxylheterocyclic,
carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl, substituted alkyl, substituted
alkoxy, substituted aryl, substituted aryloxy, substituted aryloxyaryl,
substituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and
substituted heterocyclic, and
where R3 and R3' are joined to form a substituent selected from the
group consisting of =CHZ where Z is defined above provided that Z is not
hydroxyl or thiol, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic;
Q is selected from the group consisting of -O-, -S-, -S(O)-, -S(Oh,
and -NR4-;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/i1S00/01540
__ g __
R4 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic
or, optionally, R4 and RI or R4 and R2, together with the atoms to which they
are bound, are joined to form a heteroaryl, a substituted heteroaryl, a
heterocyclic or a substituted heterocyclic group;
W is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen and carbon; and
W' is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, carbon, oxygen,
sulfur, S(O), and S(O)z;
X is selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl, alkoxy,
substituted alkoxy, alkenoxy, substituted alkenoxy, cycloalkoxy, substituted
cycloalkoxy, cycloalkenoxy, substituted cycloalkenoxy, aryloxy, substituted
aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy,
substituted heterocyclyloxy and -NR"R" where each R" is independently
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl,
substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and
substituted heterocyclic;
and enantiomers, diastereomers, and pharmaceutically acceptable
salts thereof; provided that:
(i) the compound of formula Ia or Ib has a binding affinity to VLA-4 as
expressed by an ICso of about 15~,M or less; and
(ii) in formula Ia and Ib, R' and R2, together with the carbon atom and W
to which they are bound respectively, do not form a substituted or
unsubstituted pyridazine ring.
Preferably, in the above method, R3 is -(CHZ)x-Ar-R9, where Ar is
aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; R9 is selected
from the group consisting acyl, acylamino, acyloxy, aminoacyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__9__
aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy,
oxycarbonylamino, thioamidino, thiocarbonylamino, aminosulfonylamino,
aminosulfonyloxy, aminosulfonyl, oxysulfonylamino, and oxysulfonyl; x is
an integer from 0 to 4; and R3' is hydrogen.
More preferably, R3 is a group of the formula:
R9
X
wherein R9 is as defined herein. Preferably, R9 is in the para
position of the phenyl ring and x is an integer from 1 to 4, more preferably x
is 1.
Preferably, R9 is selected from -O-Z-NR"R"' and -O-Z-R'z wherein
R" and R"' are independently selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic,
and where R'i and R'1' are joined to form a heterocycle or a substituted
heterocycle, R'z is selected from the group consisting of heterocycle and
substituted heterocycle, and Z is selected from the group consisting of -
C(O)- and -SOz-, Z is preferably -C(O)-. In a more preferred embodiment,
R9 is -OC(O)NR"R"', wherein R" and R"' are as defined herein, more
preferably preferably R9 is -OC(O)N(CH3)z.
In the above method, Q is preferably -NR4- wherein R4 is as defined
above, more preferably R4 is hydrogen or alkyl, even more preferably R°
is
hydrogen.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 10 --
In another preferred embodiment, R' and R2, together with the carbon
atom and W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a
substituted or unsubstituted monocyclic heteroaryl or heterocyclic group
wherein the heteroaryl group has 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from the group
consisting of N, O, or S and the heterocyclic group contains 1 to 3
heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of N, O, or S(O)n wherein n
isOto2.
More preferably, the above method employs a compound of formula
IIa, IIb, or IIc:
R3 Rs,
A
O X
O
IIa
R3 Rs,
~X
O
RS.N,R6 O
IIb
R3 R3,
C
Q X
O
IIc
wherein:
ring A is selected from the group consisting of pyrrole, pyrazole,
imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, and
thiophene wherein each of said pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, and thiophene
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 11 --
ring is substituted with 1 to 3 substituent(s), and each of said pyrimidine,
1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, and tetrazole ring is substituted with 1 to 2
substituent(s), independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl,
alkoxy, halogen, nitro, amino, substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyle, substitued heterocycle, and -
SOZRa (wherein Ra is alkyl, aryl, or substituted aryl);
ring B forms a 1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole or a 1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-
thiadiazole ring;
ring C is pyridine or 1,3,5-triazine ring wherein each of said ring is
substituted with 1 to 2 substituent(s) independently selected from the group
consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy, amino,
substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyle, and substitued heterocycle;
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl;
or optionally, one of, R4 and ring B, R4 and R5, R4 and R6, or RS and
R6, together with the atoms to which they are bound, can be joined to form a
heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring; and
R3, R3', Q and X are as defined herein; and
enantiomers, diastereomers, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/~JS00/01540
-- 12 --
Within the above preferred and more preferred groups, an even more
preferred group of compounds is represented by formula IIa', IIb' , or IIc'
R3
A
N~X
R4 ~(O
IIa'
R3
N X
R5.N,R6 R4 O
IIb'
R~
N~N R3
RB~N~N~X
R4 O
IIc'
wherein:
R4 is hydrogen or alkyl; preferably hydrogen or methyl; more
preferably hydrogen;
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 13 --
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, substituted amino, heterocycle, and substituted heterocyle;
Rg is selected from the group consisting of substituted amino,
heterocycle, and substituted heterocycle;
b is 1 or 2; and
A, B, R3, R5, and R6 are as defined above; and
enantiomers, diastereomers, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Within these preferred groups, an even preferred group of
compounds is represented by formula IIa", IIb", IIc", or IId":
R9
OH
N
H O
IIa"
s
/ ~'R
b
N.S,N
OH
N
R5~N~R6 H O
IIb"
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 14 --
Rs
R7 ~ ' \
N~N
Ra~N~N OH
H O
IIc"
Rs
NR3sRao / ~1
OH
N
O
IId"
wherein:
A is 3-nitrothiophen-2-yl, 1-phenyltetrazol-5-yl, 1,5-dimethyl-4-
nitropyazol-3-yl, 1-ethylpyrazol-5-yl, 4-phenylsulfonylthiophen-3-yl, 1,4-
diphenylpyrazol-5-yl, 1-phenylimidazol-2-yl, or 5-benzoylmethylsulfinyl-4-
(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy,
chloro, and -NR3°R3' wherein R3° is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted
alkyl, or
alkenyl; and R3' is alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or -SOZR3z (wherein R3z is aryl or
substituted aryl); or R3° and R3' together with the nitrogen atom to
which
they are attached form a heterocycle or substituted heterocycle, preferably R'
is hydrogen, hydroxy, chloro, N (2-methylpropyl)amino, N (phenyl)amino,
N (benzyl)amino, N (2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (2-(4-methoxy-
phenyl)ethyl)amino, N (1-phenylethyl)amino, N (4-chlorobenzyl)amino,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 15 --
N ( cyclopentyl)amino, N (cyclohexyl)amino, N (2-methylpropyl)amino, N
(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino, N (furan-2-ylmethyl)amino, N ( cyclohexyl-
methyl)amino, N (4-aminosulfonyl-benzyl)amino, N (3,4-methylenedioxy-
benzyl)amino, N (2-methyoxyethyl)-amino, N,N bis-(2-methoxyethyl)amino,
N (2-propyl)-N benzylamino, N methyl-N (2-phenylethyl)amino, N methyl-
N [2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethyl]amino, N ethyl-N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-
amino, N-methyl-N (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino, N ethyl-N [2-(4-methoxy-
phenyl)-1-methylethyl]amino, N (4-aminosulfonylbenzyl)amino, N methyl-N
(3-dimethylaminopropyl)amino, N,N bis-benzylamino, N methyl-N [2-
(pyridin-2-yl)ethyl]amino, N methyl-N benzylamino, N [2-(1-methyl-
pyrrolidin-2-yl)ethyl]amino, N furan-2-ylmethylamino, N,N bis-
propylamino, N benzyl-N (2-dimethylaminoethyl)-amino, N (6-nitro-
benzothiazol-2-yl)amino, piperidin-1-yl, N (4-aminosulfonylbenzyl)amino,
N methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-amino, or N (2-(4-aminosulfonyl-
phenyl)ethyl)amino;
R8 is -NR33Rsa wherein R33 is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, or
aryl; and R34 is alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocycle substituted heterocycle, or -
SOZR35 (wherein R35 is substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocycle, or substituted heterocycle); or R33 and
R'4 together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached form a
heterocycle or substituted heterocycle; preferably Rg is N (5-methylisoxazol-
3-yl)amino, N (2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethylamino, N methyl-N (2-
pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N,N-bis-(2-methoxyethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-
pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-phenylethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-
(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N
(2-methoxyethyl)amino, N (furan-2-ylmethyl)amino, N (4-aminosulfonyl-
benzyl)amino, N (2-piperidin-1-ylethyl)amino, N (2-(4-methylphenyl)-
ethyl)amino, N (1-phenylethyl)amino, N (4-chlorobenzyl)amino, N (2-
propyl)-N (benzyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-phenylethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 16 --
(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N ethyl-N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino, N
(benzyl)-N (1-phenylethyl)amino, N allyl-N (cyclohexyl)amino, N ethyl-N
(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino, N propyl-N (4-nitronenzyl)-
amino, N methyl-N (2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N,N bis-(benzyl)amino, N
benzyl-N (2-cyanoethyl)amino, N benzyl-N (2-dimethylaminoethyl)amino, N
ethyl-N (3,4-dichlorobenzyl)amino, N ethyl-N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino, N
methyl-N (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino, N,N bis-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino,
N,N bis-benzylamino, N benzyl-N (2-cyanoethyl)amino, N phenyl-N
(pyridin-2-yl)amino, N methyl-N (4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino, N,N bis-
(cyclohexyl)amino, N (2-phenyl-1-aminocarbonylethyl)amino, N (2-phenyl-
1,1-dimethylethyl)amino, N (2-phenylethyl)amino, N (2-(2-methoxyphenyl)-
ethyl)amino, N (2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (2-(4-fluoro-
phenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino, N (1-phenyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)-
amino, N methyl-N (2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-
phenylethyl)amino, N ethyl-N (1-methyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-ethyl)amino,
N benzyl-N (1-phenyl)ethyl)amino, N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-amino, N
(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino, N (pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino, N 2-(4-benzyl-
piperizin-1-yl)ethylamino, N 2-ethylhexyl-N (pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-amino, N
(3,3-diphenylpropyl)amino, N (2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N (4-ethoxy-3-
methoxyphenyl)ethylamino, N (2-phenylpropyl)amino, N (4-(piperazin-3,5-
dione-1-sulfonylphenyl)amino, N,N bis-methyl, N (2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethyl)-
amino, N (phenyl-1-aminocarbonylethyl)amino, N (2-phenyl-1,1-dimethyl-
ethyl)amino, N (2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl)-amino, N (1-phenyl-
2-(2-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (3-imidazol-1-ylpropyl)amino, N (2-
morpholin-4-ylethyl)amino, N (2-piperidin-1-ylethyl)amino, N (2-pyrrolidin-
1-ylethyl)amino, N (1-ethoxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-yl)amino, N (2-phenoxy-
ethyl)amino, N (3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropyl)amino, N (5-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-
pyrazol-4-ylsulfonyl)amino, N (benzylsulfonyl)amino, N (2-carboxy-1-
phenylethyl)amino, N (1-phenyl-1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl)amino, N benzyl-
N (1-carboxy-2-phenylethyl)amino, N 2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethylamino,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 1~ __
N (1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-amino, 4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl, 4-acetyl-
piperazin-1-yl, piperidin-1-yl, 4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl, 2,5-dimethylpiperidin-
1-yl, 4-cyclohexylpiperazin-1-yl, 4-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenylmethyl)-
piperazin-1-yl, 4-(diphenylmethyl)-piperazin-1-yl, 3-methylpiperidin-1-yl,
2,6-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl, 2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethylamino, 4-(2-
propylaminocarbonylmethyl)-piperazin-1-yl, 4-(1-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl,
4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl, 4-(furan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl, 4-(1-
phenylpropen-1-yl)piperazin-1-yl, 4-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)piperazin-1-yl,
1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl, 4-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl,
piperazin-1-yl, 4-(2-methoxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl, 2-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-
1-yl, 2-ethoxycarbonylmethyl-3-oxopiperazin-1-yl, 3-(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-
1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl, or 3-carboxy-1,2,3,4-
tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl; R39 is selected from the group consisting of
hydrogen and alkyl; preferably hydrogen, methyl, or hexyl;
R4° is selected from the group consisting of alkyl and substituted
alkyl; or R39 and R4° together with the nitrogen atom to which they are
attached form a heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring; preferably
methyl, hexyl, or 2-(3-methylphenylureido)ethyl; and
R9 selected from the group consisting of -O-Z-NR"R"' and -O-Z-R''-
wherein Z is -C(O)- or -SOZ-; R" and R"' are independently selected from
the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl,
substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic,
substituted heterocyclic and where Rll and R"' are joined together to form a
heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring; and R'Z is selected from the
group consisting of heterocycle and substituted heterocycle; preferably R9 is
-OCON(CH3)Z and is located at the 4-position of the phenyl, and
RS and R6 are as defined above; enantiomers, diastereomers, and
pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 1 g __
Within above more preferred groups, particularly preferred
compounds are those selected from compounds of formulae IIb" or IIc".
In another of its method aspects, this invention is directed to a
method for treating a disease mediated by VLA-4 in a patient, which method
comprises administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a
pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a therapeutically effective amount of
a compound of formula IVa and/or IVb:
R2 R2
~ W R14 R15 ~ W~ R14 R15
' 1 X
R1 i X and R
R13 R13
IVa IVb
wherein, in formula IVa, R1 and RZ, together with the carbon atom
and W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form an aryl,
cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in
the aryl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group and optionally
containing or additionally containing in the case of heteroaryl and
heterocyclic groups 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of
oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur, and wherein the heteroaryl or heterocyclic
group is mono-cyclic;
in formula IVb, R' and RZ, together with the carbon atom and W' to
which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in the
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group and optionally containing or
additionally containing in the case the heterocyclic group 1 to 3 heteroatoms
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 1 g __
selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur, and
wherein the heterocyclic group is mono-cyclic;
and further wherein said aryl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or
heterocyclic group of formula IVa or IVb is optionally substituted, on any
ring atom capable of substitution, with 1-3 substituents selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, substituted alkoxy,
acyl,
acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, substituted amino, amidino,
alkyl amidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino,
aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy,
substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, cyano, halogen,
hydroxyl, nitro, oxo, carboxyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)2-
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)Z-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted aryl, -OS(O)2-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)Z-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where each R is independently hydrogen or alkyl,
-NRS(O)Z-alkyl, -NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)z-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRS(O)Z-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-
alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -N[S(O~-R']2 and -N[S(O)2-
NR']2 where each R' is independently selected from the group consisting of
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/~JS00/01540
-- 20 --
alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic;
R'3 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C,_~o alkyl,
Cy, and Cy-C,_,o alkyl, wherein alkyl is optionally substituted with one to
four substituents independently selected from Ra; and Cy is optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from Rb;
R'4 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, Cl_,o alkyl,
C,_,o alkenyl, CZ_lo alkynyl, Cy, Cy-C,_lo alkyl, Cy-CZ_,o alkenyl and Cy-
CZ_,o
alkynyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl, and alkynyl are optionally substituted with
one to four substituents selected from phenyl and RX, and Cy is optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from Ry;
or R'3, R'a and the atoms to which they are attached together form a
mono- or bicyclic ring containing 0-2 additional heteratoms selected from N,
O and S;
R'S is selected from the group consisting of C,_,o alkyl, CZ_lo alkenyl,
C,_,o alkynyl, aryl, aryl-C,_lo alkyl, heteroaryl, heteroaryl-C,_,o alkyl,
wherein alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl are optionally substituted with one to four
substituents selected from Rx, and aryl and heteroaryl are optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from RY;
or R'°, R's and the carbon to which they are attached form a 3-7
membered mono- or bicyclic ring containing 0-2 heteroatoms selected from
N, O and S;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of Cy and a group selected
from RX, wherein Cy is optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R
Rb is selected from the group consisting of Ra, C,_,o alkyl, CZ_,o
alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, aryl C,_,oalkyl, heteroaryl C,_,o alkyl, wherein
alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, heteroaryl are optionally substituted with a group
independently selected from R';
R~ is selected from the group consisting of halogen, NOz, C(O)ORf,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 21 --
C,_4 alkyl, C1_4 alkoxy, aryl, aryl C,_4 alkyl, aryloxy, heteroaryl, NRfRg,
RfC(O)Rg, NRfC(O)NRfRg, and CN;
Rd and Re are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl, CZ_,o
alkenyl, CZ_lo alkynyl, Cy and Cy C,_,oalkyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl and Cy are optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R';
or Rd and Re together with the atoms to which they are attached form
a heterocyclic ring of 5 to 7 members containing 0-2 additional
heteroatoms independently selected from oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen;
Rf and Rg are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl, Cy
and Cy-C,_,o alkyl wherein Cy is optionally substituted with C,_lo alkyl; or
Rf and Rg together with the carbon to which they are attached form a
ring of 5 to 7 members containing 0-2 heteroatoms independently
selected from oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen;
R" is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl, CZ_,o
alkenyl, CZ_~o alkynyl, cyano, aryl, aryl C,_,o alkyl, heteroaryl, heteroaryl
C,_
,o alkyl, and -SOzR'; wherein alkyl, alkenyl, and alkynl are optionally
substituted with one to four substitutents independently selected from R~; and
aryl and heteroaryl are each optionally substituted with one to four
substituents independently selected from R";
R' is selected from the group consisting of C,_,o alkyl, CZ_,o alkenyl,
CZ_lo alkynyl, and aryl; wherein alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl and aryl are each
optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently selected
from R';
Rx is selected from the group consisting of -ORd, -NO2, halogen,
-S(O)mRd, -SRd, -S(O)20Rd, -S(O)mNRdRe, -NRdRe, -O(CRfRg)"NRdRe,
-C(O)Rd, -COZRd, -COZ(CRfRg)~CONRdRe, -OC(O)Rd, -CN, -C(O)NRdRe,
-NRdC(O)Re, -OC(O)NRdRe, -NRdC(O)ORe, -NRdC(O)NRdRe, -CRd(N-ORe),
CF3, oxo, NR°C(O)NRdSOZR', NRdS(O)mRe, -OS(O)ZORd, and
-OP(O)(ORd)2;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 22 --
Ry is selected from the group consisting of RX, C,_~o alkyl, CZ_,o
alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, aryl C,_,oalkyl, heteroaryl C,_,o alkyl, cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl; wherein alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl and aryl are each optionally
substituted with one to four substitutents independently selected from RX;
Cy is cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, or heteroaryl;
m is an integer from 1 to 2;
n is an integer from 1 to 10;
W is selected from the group consisting of carbon and nitrogen;
W' is selected from the group consisting of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen,
sulfur, S(O) and S(O)Z;
X' is selected from the group consisting of -C(O)ORd,
-P(O)(ORd)(OR~), -P(O)(Rd)(ORe), -S(O)mORd, -C(O)NRdR", and -5-
tetrazolyl;
and enantiomers, diastereomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts
thereof; provided that:
(i) the compound of formula IVa or IVb has a binding affinity to VLA-4
as expressed by an ICSO of about IS~cM or less; and
(ii) in formula IVa and IVb, R' and RZ, together with the carbon atom
and W to which they are bound respectively, do not form a substituted or
unsubstituted pyridazine ring.
Preferably, in the above method, R' and R2, together with the carbon
atom and W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a
substituted or unsubstituted monocyclic heteroaryl or heterocyclic ring
wherein the heteroaryl ring contains 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N, O
or S and the heterocyclic ring contains 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N,
O, or S(O)n wherein n is 0 to 2, preferably Ri and Rz, together with the
carbon atom and W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form
substituted or unsubstituted pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, 1,2,3-triazole,
1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, thiophene, pyridine, pyrimidine, 1,3,5-triazine, 1-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 23 --
oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole or 1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole ring; more preferably,
substituted 1,3,5-triazine, or l,l-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole ring.
Preferably, X' is -C(O)ORd.
In a preferred embodiment, the above method employs a compound
of formula Va, Vb, or Vc:
~ R~4 R~s
A
N~X'
R13
Va
,~, ~ b
N; S%N R~4R~s
5~N~N~X
R R R~3
Vb
R~
N~N R~4Ris
I ~
RB~N~N~X'
R13
VC
wherein:
ring A is selected from the group consisting of pyrrole, pyrazole,
imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, and
thiophene wherein each of said pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, and thiophene
ring is substituted with 1 to 3 substituent(s), and each of said pyrimidine,
1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, and tetrazole ring is substituted with 1 to 2
substituent(s), independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 24 --
alkoxy, halogen, nitro, amino, substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyle, substitued heterocycle, and -
SOZRS (wherein RS is alkyl, aryl, or substituted aryl);
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, and substituted heteroaryl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, substituted amino, heterocycle, and substituted heterocyle;
Rg is selected from the group consisting of substituted amino,
heterocycle, and substituted heterocycle;
b is 1 or 2; and
R'3, R'4, R'S, and X' are as defined above.
In yet another of its method aspects, this invention is directed to a
method for treating a disease mediated by VLA-4 in a patient, which method
comprises administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a
pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a therapeutically effective amount of
a compound of formula VIa and/or VIb:
2
R2~ W R24 R25 R ~ ~/' R24 R25
N X
N X
I and
R23 ~23
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/~JS00/01540
-- 25 --
VIa VIb
wherein, in formula VIa, R' and R2, together with the carbon atom
and W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form an aryl,
cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in
the aryl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group and optionally
containing or additionally containing in the case of heteroaryl and
heterocyclic groups 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of
oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur, and wherein the heteroaryl or heterocyclic
group is mono-cyclic;
in formula VIb, R' and R2, together with the carbon atom and W' to
which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in the
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group and optionally containing or
additionally containing in the case of the heterocyclic group 1 to 3
heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and
sulfur, and wherein the heterocyclic group is mono-cyclic;
and further wherein said aryl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or
heterocyclic group of formula VIa or VIb is optionally substituted, on any
ring atom capable of substitution, with 1-3 substituents selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, substituted alkoxy,
acyl,
acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, substituted amino, amidino,
alkyl amidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino,
aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy,
substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, cyano, halogen,
hydroxyl, nitro, oxo, carboxyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 26 --
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)2-
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)2-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted aryl, -OS(O)Z-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)Z-heterocyclic, -OS(O)~-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where each R is independently hydrogen or alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-aryl, -NRS(O)z-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRS(O)Z-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-
alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -N[S(O~-R']2 and -N[S(O)Z-
NR']2 where each R' is independently selected from the group consisting of
alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic;
R23 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl
optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently selected
from Ra~ and Cy optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from Rb~;
R24 is selected from the group consisting of Ar'-Ar2-C1_,o alkyl,
Arl-Arz-CZ_~o alkenyl, Ar'-Arz-CZ_,o alkynyl, wherein Ar' and Arz are
independently aryl or heteroaryl each of which is optionally substituted with
one to four substituents independently selected from Rb~; alkyl, alkenyl and
alkynyl are optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently
selected from Ra~;
R25 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, Cl_,o alkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 2~ __
Cz_,o alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, aryl, aryl Cl_loalkyl, heteroaryl, and
heteroaryl
C,_,o alkyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl are optionally substituted
with
one to four substituents selected from Ra~, and aryl and heteroaryl are
optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently selected
from R"';
Ra' is selected from the group consisting of Cy, -ORd', -NOZ, halogen
-S(O)",Rd~, -SRd', -S(O)zOR°~, -S(O)mNRd'R'~, -NRd'Re', -
O(CR'"Rg~)~NRd'Re',
-C(O)Rd~, -COZR~', -COZ(CR'~~Rg')~CONRd~R'~, -OC(O)R~', -CN,
-C(O)NRd~Re~, -NRd'C(O)Re~, -OC(O)NRd~R'', -NRd~C(O)ORe~,
-NRd~C(O)NRd'R'', -CRd~(N-ORe~), CF3, and -OCF3;
wherein Cy is optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R'';
R"' is selected from the group consisting of Ra~, C,_,o alkyl, CZ_lo
alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, aryl C,_,o alkyl, heteroaryl C,_loalkyl,
wherein alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, heteroaryl are optionally substituted
with a group independently selected from R'~;
R'' is selected from the group consisting of halogen, amino, carboxy,
C,_4 alkyl, C,_~ alkoxy, aryl, aryl C,_4_alkyl, hydroxy, CF3, and aryloxy;
Rd~ and R'~ are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl, C,_
,o alkenyl, CZ_lo alkynyl, Cy and Cy C,_~oalkyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl and Cy are optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R''; or Rd' and R'' together with the atoms to
which they are attached form a heterocyclic ring of 5 to 7 members
containing 0-2 additional heteroatoms independently selected from oxygen,
sulfur and nitrogen;
Rf~ and Rg' are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_~o alkyl, Cy
and Cy-C1_IO alkyl; or Rf' and Rg' together with the carbon to which they are
attached form a ring of 5 to 7 members containing 0-2 heteroatoms
independently selected from oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen;
R"' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/LJS00/01540
__ 2g __
C,_lo alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, cyano, aryl, aryl Cl_,o alkyl, heteroaryl,
heteroaryl C,_,o alkyl, or -SOZR'';
wherein alkyl, alkenyl, and alkynyl are optionally substituted with
one to four substitutents independently selected from Ra'; and aryl and
heteroaryl are each optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from Rb';
R'' is selected from the group consisting of C,_,o alkyl, CZ_,o alkenyl,
Cz_,o alkynyl, and aryl;
wherein alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl and aryl are each optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from I~';
Cy is cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, or heteroaryl;
X" is selected from the group consisting of -C(O)ORd',
-P(O)(OR°')(ORe'), -P(O)(Rd')(OR~~), -S(O)mORd', -C(O)NRd~R"~, and -5-
tetrazolyl;
m is an integer from 1 to 2;
n is an integer from 1 to 10;
and enantiomers, diastereomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts
thereof; provided that:
(i) the compound of formula VIa or VIb has a binding affinity to VLA-4
as expressed by an ICso of about IS~cM or less; and
(ii) in formula VIa and VIb, R' and Rz, together with the carbon atom
and W to which they are bound respectively, do not form a substituted or
unsubstituted pyridazine ring.
Preferably, in the above method, X" is -C(O)ORd'.
Preferably, R' and Rz, together with the carbon atom and W to which
they are bound respectively, are joined to form a substituted or unsubstituted
monocyclic heteroaryl or heterocyclic group wherein the heteroaryl aryl
group has 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of N, O, or
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 29 --
S and the heterocyclic group contains 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from the
group consisting of N, O, or S(O)n wherein n is 0 to 2.
Preferably, R24 is -CHZ-Ar2-Arl and RZS is hydrogen.
In a preferred embodiment, the above method employs a compound
of formula VIIa, VIIb, or VIII:
R24 R25
A
l0 Nix'
R23
Vlla
~~~b
N~S~N R24R25
~N~X'
RS.N.R6 ~ 23
R
Vllb
R~
N~N R24R25
I ~
RB~N~N~X'
R23
Vlic
wherein:
ring A is selected from the group consisting of pyrrole, pyrazole,
imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, and
thiophene wherein each of said pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, and thiophene
ring is substituted with 1 to 3 substituent(s), and each of said pyrimidine,
1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, and tetrazole ring is substituted with 1 to 2
substituent(s), independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl,
alkoxy, halogen, nitro, amino, substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
--30--
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyle, substitued heterocycle, and -
SO~Ra (wherein R~ is alkyl, aryl, or substituted aryl);
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, and substituted heteroaryl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, substituted amino, heterocycle, and substituted heterocyle;
Rg is selected from the group consisting of substituted amino,
heterocycle, and substituted heterocycle;
b is 1 or 2; and
Rz3, Rza, Rzs, and X' are as defined above.
The compounds and pharmaceutical compositions of this invention
are useful for treating VLA-4 mediated disease conditions. Such disease
conditions include, by way of example, asthma, Alzheimer's disease,
atherosclerosis, AIDS dementia, diabetes (including acute juvenile onset
diabetes), inflammatory bowel disease (including ulcerative colitis and
Crohn's disease), multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, tissue
transplantation, tumor metastasis, meningitis, encephalitis, stroke, and other
cerebral traumas, nephritis, retinitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis,
myocardial
ischemia and acute leukocyte-mediated lung injury such as that which occurs
in adult respiratory distress syndrome.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 31 --
Other disease conditions include, but are not limited to, inflammatory
conditions such as erythema nodosum, allergic conjunctivitis, optic neuritis,
uveitis, allergic rhinitis, Ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis,
vasculitis, Reiter's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, progressive
systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, Wegner's
granulomatosis, aortitis, sarcoidosis, lymphocytopenia, temporal arteritis,
pericarditis, myocarditis, congestive heart failure, polyarteritis nodosa,
hypersensitivity syndromes, allergy, hypereosinophilic syndromes, Churg-
Strauss syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypersensitivity
pneumonitis, chronic active hepatitis, interstitial cystitis, autoimmune
endocrine failure, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune aplastic anemia,
chronic persistent hepatitis and thyroiditis.
In a preferred embodiment, the disease mediated by VLA-4 is an
inflammatory disease.
The present invention is also directed to novel compounds useful for
treating a disease mediated by VLA-4. Accordingly, in one of its
composition aspects, this invention is directed to a compound of formula Ia
and Ib:
R2~ W R3 R3, R~ w~ R3 R3,
X and ~ X
R O O R' Q
O
Ia Ib
wherein, in formula Ia, R' and Rz, together with the carbon atom and
W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form an aryl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 32 --
cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in
the aryl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group and optionally
containing or additionally containing in the case of heteroaryl and
heterocyclic groups 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of
oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur, and wherein the heteroaryl or heterocyclic
group is mono-cyclic;
in formula Ib, R' and RZ, together with the carbon atom and W' to
which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in the
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group and optionally containing or
additionally containing in the case of the heterocyclic group 1 to 3
heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and
sulfur, and wherein the heterocyclic group is mono-cyclic;
and further wherein said aryl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or
heterocyclic group of formula Ia or Ib is optionally substituted, on any ring
atom capable of substitution, with 1-3 substituents selected from the group
consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, acyl,
acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, substituted amino, amidino,
alkyl amidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino,
aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy,
substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, cyano, halogen,
hydroxyl, nitre, oxo, carboxyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidine, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)2-alkyl, -OS(O)z-
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)Z-aryl, -OS(O)2-substituted aryl, -OS(O)2-heteroaryl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 33 --
-OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where each R is independently hydrogen or alkyl,
-NRS(O)Z-alkyl, -NRS(O)Z substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)2-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRS(O)2-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z NR-
alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -N[S(O~-R']Z and -N[S(O)Z-
NR']2 where each R' is independently selected from the group consisting of
alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic;
R3 is -(CHZ)x-Ar-R9, where Ar is aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl
and substituted heteroaryl; R9 is selected from the group consisting of acyl,
acylamino, acyloxy, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonyl-
amino, aminocarbonyloxy, oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino,
thioamidino, thiocarbonylamino, aminosulfonylamino, aminosulfonyloxy,
aminosulfonyl, oxysulfonylamino and oxysulfonyl, x is an integer from 0 to
4;
R3' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, isopropyl, -
CHZZ wherein Z is hydrogen, hydroxy, acylamino, alkyl, alkoxy, aryloxy,
aryl, arloxyaryl, carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl,
carboxyl-cycloalkyl, carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-
substituted aryl, carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl,
carboxylheterocyclic, carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl,
substituted alkyl, substituted alkoxy, substituted aryl, substituted aryloxy,
substituted aryloxyaryl, substituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic, or substituted heterocyclic;
Q is selected from the group consisting of -O-, -S-, -S(O)-, -S(Oh,
and -NR4-;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 34 --
R4 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic
or, optionally, R' and R' or R4 and R2, together with the atoms to which they
are bound, are joined to form a heteroaryl, a substituted heteroaryl, a
heterocyclic or a substituted heterocyclic group;
W is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen and carbon; and
W' is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, carbon, oxygen,
sulfur, S(O), and S(O)Z;
X is selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl, alkoxy,
substituted alkoxy, alkenoxy, substituted alkenoxy, cycloalkoxy, substituted
cycloalkoxy, cycloalkenoxy, substituted cycloalkenoxy, aryloxy, substituted
aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy,
substituted heterocyclyloxy and -NR"R" where each R" is independently
selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl,
substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and
substituted heterocyclic;
and enantiomers, diasteromers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts
thereof; provided that:
(i) the compound of formula Ia or Ib has a binding affinity to VLA-4 as
expressed by an ICso of about lS~cM or less; and
(ii) in formula Ia and Ib, R' and R2, together with the carbon atom and W
to which they are bound respectively, do not form a substituted or
unsubstituted pyridazine ring.
Preferably, in the above compounds, R3 is a group of the formula:
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 35 --
R9
x
wherein R9 and x are as defined herein. Preferably, R9 is in the para
position of the phenyl ring; and x is an integer from 1 to 4, more preferably
x is 1.
Preferably, R9 is selected from the group consisting of -O-Z-NR' 'R' ''
and -O-Z-R'Z wherein R' ' and R"' are independently selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, and where R" and R"' are joined to form a heterocycle or a
substituted heterocycle, R'2 is selected from the group consisting of
heterocycle and substituted heterocycle, and Z is selected from the group
consisting of -C(O)- and -SOZ-, preferably Z is -C(O)-. More preferably, R9
is -OC(O)NR"R"', wherein R" and R"' are as defined herein, even more
preferably R9 is -OC(O)N(CH3)2.
Preferably, in the above compounds, Q is -NR4- wherein R4 is
hydrogen or alkyl, preferably hydrogen.
In another preferred embodiment, this invention is directed to
compounds of formula IIa, IIb, or IIc:
R3 Rs,
~X
j~Q
O
IIa
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 36 --
R3 R3,
~X
Q
RS.N.Rs O
IIb
R3 Rs,
C ~X
l0 QQ
O
IIc
wherein:
ring A is a substituted or unsubstituted monocyclic heteroaryl ring
containing 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of N, O, or
S, preferably ring A is selected from the group consisting of pyrrole,
pyrazole, imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole,
and
thiophene wherein each of said pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, and thiophene
ring is substituted with 1 to 3 substituent(s), and each of said pyrimidine,
1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, and tetrazole ring is substituted with 1 to 2
substituent(s), independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl,
alkoxy, halogen, nitro, amino, substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyle, substitued heterocycle, and -
SOZRS (wherein RS is alkyl, aryl, or substituted aryl);
ring B forms a 1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole or a 1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-
thiadiazole ring;
ring C is a substituted or unsubstituted monocyclic heteroaryl ring
containing 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of N, O, or
S, preferably ring C is pyridine or 1,3,5-triazine ring wherein each of said
ring is substituted with 1 or 2 substituent(s) independently selected from the
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 3~ __
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, halogen, hydroxy,
amino, substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyle, and substitued heterocycle;
R3 is -(CHZ)X Ar-R9, where Ar is aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and
substituted heteroaryl; R9 is selected from the group consisting of acyl,
acylamino, acyloxy, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino,
aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, oxycarbonylamino,
oxythiocarbonylamino, thioamidino, thiocarbonylamino,
aminosulfonylamino, aminosulfonyloxy, aminosulfonyl, oxysulfonylamino
and oxysulfonyl; x is an integer from 0 to 4;
R3' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, isopropyl, -
CH~Z wherein Z is hydrogen, hydroxy, acylamino, alkyl, alkoxy, aryloxy,
aryl, arloxyaryl, carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl,
carboxyl-cycloalkyl, carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-
substituted aryl, carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl,
carboxylheterocyclic, carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl,
substituted alkyl, substituted alkoxy, substituted aryl, substituted aryloxy,
substituted aryloxyaryl, substituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic, or substituted heterocyclic;
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 3g __
or optionally, one of, R4 and ring B, R4 and R5, R4 and R6, or RS and
R6, together with the atoms to which they are bound, can be joined to form a
heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring; and
Q and X are as defined above.
Within the above preferred group, a more preferred group of
compounds is represented by formula IIa', IIb' , or IIc'
R3
~X
N
R4 O
IIa'
R3
N X
Rs.N.Rs R4 O
IIb'
R
N' \ N Rs
RB~N~N~X
R4 O
IIc'
wherein:
R4 is hydrogen or alkyl;
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 39 --
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, substituted amino, heterocycle, and substituted heterocyle;
R8 is selected from the group consisting of substituted amino,
heterocycle, and substituted heterocycle;
b is 1 or 2; and
A, B, R3, and X are as defined above.
Within this more preferred group, an even more preferred group of
compounds is represented by formula IIa", IIb", IIc", or IId":
Rs
i
N OH
H O
IIa"
s
b
N.S,N
OH
RS.N.Rs H
O
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 40 --
IIb"
R9
R~ ~ ' \
N~N
RB~N~N OH
H O
IIc"
R9
NR39Rao ~
OH
N H
O
IId"
wherein:
A is 3-nitrothiophen-2-yl, 1-phenyltetrazol-5-yl, 1,5-dimethyl-4-
nitropyazol-3-yl, 1-ethylpyrazol-5-yl, 4-phenylsulfonylthiophen-3-yl, 1,4-
diphenylpyrazol-5-yl, 1-phenylimidazol-2-yl, or 5-benzoylmethylsulfinyl-4-
(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy,
chloro, and -NR3°R3' wherein R3° is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted
alkyl, or
alkenyl; and R3' is alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, cycloalkyl, or -SOZR3z (wherein R32 is aryl or
substituted aryl); or R3° and R3' together with the nitrogen atom to
which
they are attached form a heterocycle or substituted heterocycle; preferably R'
is hydrogen, hydroxy, chloro, N (2-methylpropyl)amino, N (phenyl)amino,
N (benzyl)amino, N (2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (2-(4-methoxy-
phenyl)ethyl)amino, N (1-phenylethyl)amino, N (4-chlorobenzyl)-amino, N
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 41 --
cyclopentyl)amino, N (cyclohexyl)amino, N (2-methylpropyl)-amino, N (5-
methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino, N (furan-2-ylmethyl)amino, N ( cyclohexyl-
methyl)amino, N (4-aminosulfonyl-benzyl)amino, N (3,4-
methylenedioxybenzyl)amino, N (2-methyoxyethyl)-amino, N,N bis-(2-
methoxyethyl)amino, N (2-propyl)-N benzylamino, N methyl-N (2-
phenylethyl)amino, N methyl-N [2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethyl]amino, N
ethyl-N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino, N-methyl-N (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino,
N ethyl-N [2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl]amino, N (4-aminosulfonyl-
benzyl)amino, N methyl-N (3-dimethylaminopropyl)amino, N,N bis-
benzylamino, N methyl-N [2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethyl]amino, N methyl-N
benzylamino, N [2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethyl]amino, N furan-2-
ylmethylamino, N,N bis-propylamino, N benzyl-N (2-dimethylaminoethyl)-
amino, N (6-nitrobenzothiazol-2-yl)amino, piperidin-1-yl, N (4-
aminosulfonylbenzyl)amino, N methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-amino, or
N (2-(4-aminosulfonylphenyl)ethyl)amino;
Rg is -NR33R'a wherein R33 is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, or
aryl; and R34 is alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocycle substituted heterocycle, or -
SOZR35 (wherein R35 is substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocycle, or substituted heterocycle); or R33 and
R34 together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached form a
heterocycle or substituted heterocycle; preferably Rg is N (5-methylisoxazol-
3-yl)amino, N (2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethylamino, N methyl-N (2-
pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N,N-bis-(2-methoxyethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-
pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-phenylethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-
(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N
(2-methoxyethyl)amino, N (furan-2-ylmethyl)amino, N (4-aminosulfonyl-
benzyl)amino, N (2-piperidin-1-ylethyl)amino, N (2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)-
amino, N (1-phenylethyl)amino, N (4-chlorobenzyl)amino, N (2-propyl)-N
(benzyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-phenylethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-(3,4-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 42 --
dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N ethyl-N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino, N
(benzyl)-N (1-phenylethyl)amino, N allyl-N (cyclohexyl)amino, N ethyl-N
(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino, N propyl-N (4-nitronenzyl)-
amino, N methyl-N (2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N,N bis-(benzyl)amino, N
benzyl-N (2-cyanoethyl)amino, N benzyl-N (2-dimethylaminoethyl)amino, N
ethyl-N (3,4-dichlorobenzyl)amino, N ethyl-N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino, N
methyl-N (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino, N,N bis-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino,
N,N bis-benzylamino, N benzyl-N (2-cyanoethyl)amino, N phenyl-N
(pyridin-2-yl)amino, N methyl-N (4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino, N,N bis-
(cyclohexyl)amino, N (2-phenyl-1-aminocarbonylethyl)amino, N (2-phenyl-
1,1-dimethylethyl)amino, N (2-phenylethyl)amino, N (2-(2-methoxyphenyl)-
ethyl)amino, N (2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (2-(4-fluoro-
phenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino, N (1-phenyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)-
ethyl)amino, N methyl-N (2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino, N methyl-N
(2-phenylethyl)amino, N ethyl-N (1-methyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-
ethyl)amino, N benzyl-N (1-phenyl)ethyl)amino, N (pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-
amino, N (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino, N (pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino, N 2-(4-
benzylpiperizin-1-yl)ethylamino, N 2-ethylhexyl-N (pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-
amino, N (3,3-diphenylpropyl)amino, N (2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino, N (4-
ethoxy-3-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino, N (2-phenylpropyl)amino, N (4-
(piperazin-3,5-dione-1-sulfonylphenyl)amino, N,N bis-methyl, N (2-
pyrrolidin-1-ylethyl)amino, N (phenyl-1-aminocarbonylethyl)amino, N (2-
phenyl-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino, N(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-l,l-dimethylethyl)-
amino, N (1-phenyl-2-(2-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino, N (3-imidazol-1-
ylpropyl)amino, N (2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)amino, N (2-piperidin-1-ylethyl)-
amino, N (2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethyl)amino, N (1-ethoxycarbonyl-piperidin-4-
yl)amino, N (2-phenoxyethyl)amino, N (3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropyl)-amino, N
(S-chloro-1,3-dimethylpyrazol-4-ylsulfonyl)amino, N (benzylsulfonyl)amino,
N (2-carboxy-1-phenylethyl)amino, N (1-phenyl-1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-
amino, N benzyl-N (1-carboxy-2-phenylethyl)amino, N 2-(4-benzylpiperazin-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 43 --
1-yl)ethylamino, N (1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-amino, 4-phenylpiperazin-1-
yl, 4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl, piperidin-1-yl, 4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl, 2,5-
dimethylpiperidin-1-yl, 4-cyclohexylpiperazin-1-yl, 4-(3,4-methylenedioxy-
phenylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl, 4-(diphenylmethyl)-piperazin-1-yl, 3-methyl-
piperidin-1-yl, 2,6-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl, 2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)-
ethylamino, 4-(2-propylaminocarbonylmethyl)-piperazin-1-yl, 4-(1-phenyl-
ethyl)piperazin-1-yl, 4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl, 4-(furan-2-ylcarbonyl)-
piperazin-1-yl, 4-(1-phenylpropen-1-yl)piperazin-1-yl, 4-(2-morpholin-4-
ylethyl)piperazin-1-yl, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl, 4-(ethoxy-
carbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl, piperazin-1-yl, 4-(2-methoxyethyl)piperazin-
1-yl, 2-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-1-yl, 2-ethoxycarbonylmethyl-3-oxo-
piperazin-1-yl, 3-(S)-ethoxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl, or
3-carboxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl; R39 is selected from the group
consisting of hydrogen and alkyl;
R4° is selected from the group consisting of alkyl and substituted
alkyl; or R39 and R4° together with the nitrogen atom to which they are
attached form a heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring; and
R9 selected from the group consisting of -O-Z-NR"R"' and -O-Z-R'2
wherein Z is -C(O)- or -SOZ-; R'1 and R"~ are independently selected from
the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl,
substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic,
substituted heterocyclic and where R" and R"' are joined together to form a
heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring; and R'Z is selected from the
group consisting of heterocycle and substituted heterocycle; preferably R9 is
-OCON(CH3)2 and is located at the 4-position of the phenyl, and
RS and R6 are as defined above; enantiomers, diastereomers,
pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ q.4 __
In another of its composition aspects, this invention is directed to a
compound of formula IVa:
R2
R14 R15
R1 N X'
~13
IVa
wherein R' and R', together with the carbon atom and W to which
they are bound respectively, are joined to form a monocyclic heteroaryl ring
having 1 to 4 heteroatoms in the ring selected from the group nitrogen or
sulfur; or a monocyclic heterocyclic ring having 1 to 3 hetereoatoms in the
ring selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, oxygen, or S(O)n
(wherein n is o to 2);
and further wherein said heteroaryl or heterocyclic ring is optionally
substituted, on any ring atom capable of substitution, with 1-3 substituents
selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy,
substituted alkoxy, acyl, acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino,
substituted amino, amidino, alkyl amidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl,
aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl,
substituted aryl, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted
aryloxyaryl, cyano, halogen, hydroxyl, nitre, oxo, carboxyl, cycloalkyl,
substituted cycloalkyl, guanidine, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl,
substituted thioalkyl, thioaryl, substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl,
substituted thiocycloalkyl, thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl,
thioheterocyclic, substituted thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/IJS00/01540
-- 45 --
cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy,
substituted heterocyclyloxy, oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino,
-OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)Z-substituted alkyl, -OS(O)Z-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted
aryl, -OS(O)Z-heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-
heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where each R is
independently hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O),-alkyl, -NRS(O)z-substituted
alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted aryl, -NRS(O)Z-heteroaryl,
-NRS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)z-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-
substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-substituted aryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heterocyclic,
-NRS(O)2-NR-substituted heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl,
-N[S(O)2-R']Z and -N[S(O)2-NR']Z where each R' is independently selected
from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic;
R'3 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl,
Cy, and Cy-C1_lo alkyl, wherein alkyl is optionally substituted with one to
four substituents independently selected from Ra; and Cy is optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from Rb;
R'4 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, Cl_,o alkyl, CZ_
,o alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, Cy, Cy-Cl_IO alkyl, Cy-CZ_,o alkenyl and Cy-CZ_,o
alkynyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl, and alkynyl are optionally substituted with
one to four substituents selected from phenyl and R", and Cy is optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from Ry;
or R'3, R'a and the atoms to which they are attached together form a
mono- or bicyclic ring containing 0-2 additional heteratoms selected from N,
O and S;
R'S is selected from the group consisting of Cl_lo alkyl,
C~_,o alkenyl, CZ_lo alkynyl, aryl, aryl-C1_~o alkyl, heteroaryl, heteroaryl-
C,_,o
alkyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl are optionally substituted with one
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/CTS00/01540
-- 46 --
to four substituents selected from RX, and aryl and heteroaryl are optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from Ry;
or R'4, R's and the carbon to which they are attached form a 3-7
membered mono- or bicyclic ring containing 0-2 heteroatoms selected from
N, O and S;
Ra is selected from the group consisting of Cy and a group selected
from RX, wherein Cy is optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R
R" is selected from the group consisting of Ra, C,_lo alkyl, CZ_Io
alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, aryl C,_,oalkyl, heteroaryl C1_,o alkyl, wherein
alkyl,
alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, heteroaryl are optionally substituted with a group
independently selected from R';
R~ is selected from the group consisting of halogen, NOz, C(O)ORS,
C,_4 alkyl, C,_4 alkoxy, aryl, aryl C,_4 alkyl, aryloxy, heteroaryl, NRfRg,
RfC(O)Rg, NRfC(O)NRfRg, and CN;
R° and Re are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl,
Cz_,o
alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, Cy and Cy C,_,oalkyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl and Cy are optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R';
or Rd and Re together with the atoms to which they are attached form
a heterocyclic ring of 5 to 7 members containing 0-2 additional
heteroatoms independently selected from oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen;
Rf and Rg are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_~o alkyl, Cy
and Cy-C,_,o alkyl wherein Cy is optionally substituted with C,_~o alkyl; or
Rf and Rg together with the carbon to which they are attached form a
ring of 5 to 7 members containing 0-2 heteroatoms independently
selected from oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen;
R" is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, Cl_~o alkyl, CZ_,o
alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, cyano, aryl, aryl C,_lo alkyl, heteroaryl, heteroaryl
Cl_
,o alkyl, and -SOZR'; wherein alkyl, alkenyl, and alkynl are optionally
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
substituted with one to four substitutents independently selected from Ra; and
aryl and heteroaryl are each optionally substituted with one to four
substituents independently selected from R";
R' is selected from the group consisting of C,_,o alkyl, CZ_,o alkenyl,
CZ_,o alkynyl, and aryl; wherein alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl and aryl are each
optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently selected
from R~;
RX is selected from the group consisting of -ORd, -NOZ, halogen,
-S(O)",R~, -SRd, -S(O),ORd, -S(O)",NRdRe, -NRdRe, -O(CRfRg)~NRdRe,
-C(O)Rd, -COZRd, -COZ(CRfRg)~CONRdRe, -OC(O)Rd, -CN, -C(O)NRdRe,
-NRdC(O)Re, -OC(O)NRdRe, -NRdC(O)ORe, -NRdC(O)NRdRe, -CRd(N-ORe),
CF3, oxo, NR~C(O)NRdSO2R', NRdS(O)mR~, -OS(O)zORd, and
-OP(O)(OR°)2;
Ry is selected from the group consisting of Rx, C,_IO alkyl, CZ_,o
alkenyl, Cz_,o alkynyl, aryl C,_,oalkyl, heteroaryl C,_,o alkyl, cycloalkyl,
heterocyclyl; wherein alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl and aryl are each optionally
substituted with one to four substitutents independently selected from Rx;
Cy is cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, or heteroaryl;
m is an integer from 1 to 2;
n is an integer from 1 to 10;
W is selected from the group consisting of carbon and nitrogen;
W' is selected from the group consisting of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen,
sulfur, S(O) and S(O)2;
X' is selected from the group consisting of -C(O)ORd,
-P(O)(ORd)(ORe), -P(O)(Rd)(ORe), -S(O)mORd, -C(O)NRdR", and -5-
tetrazolyl;
and enatiomers, diastereomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts
thereof; provided that:
(i) the compound of formula Va has a binding affinity to VLA-4. as
expressed by an ICso of about 15~,M or less; and
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 4g __
(ii) when R' and RZ, together with the carbon atom and W to which they
are bound respectively, are joined to form a 2-arylpyrimidin-4-yl group and
R'4 is hydrogen, then R'S is not alkyl of from 1 to 6 carbon atoms optionally
substituted with hydroxyl; and
S (iii) when R' and Rz, together with the carbon atom and W to which they
are attached respectively, are joined to form a 5-arylpyrazin-2-yl group and
R'4 is hydrogen, then R'S is not 4-hydroxybenzyl.
Preferably, in the above compounds, R' and R2, together with the
carbon atom and W to which they are attached respectively, are joined to
form substituted or unsubstituted pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, pyrimidine,
1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, thiophene, pyrimidine, 1,2,3-
triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole rings, 1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole, 1,1-dioxo-
1,2,5-thiadiazole, pyridine or 1,3,5-triazine ring and X is -C(O)ORd.
In a more preferred embodiment, this invention is directed to
compounds of formula Va, Vb, or Vc:
25
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 49 --
R14 R15
A
N~X'
R13
Va
~,~, ~b
N~S~N R\~4Ri5
S~N~N~X'
R R R~3
Vb
R~
N~N R~4R~5
I
R$~N~N~X'
Ris
Vc
wherein:
ring A is selected from the group consisting of pyrrole, pyrazole,
imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, and
thiophene wherein each of said pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, and thiophene
ring is substituted with 1 to 3 substituent(s), and each of said pyrimidine,
1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, and tetrazole ring is substituted with 1 to 2
substituent(s), independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl,
alkoxy, halogen, nitro, amino, substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyle, substitued heterocycle, and -
SOZRa (wherein Ra is alkyl, aryl, or substituted aryl);
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/~IS00/01540
--50--
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
S group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, and substituted heteroaryl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, substituted amino, heterocycle, and substituted heterocyle;
R8 is selected from the group consisting of substituted amino,
heterocycle, and substituted heterocycle;
b is 1 or 2; and
R'3, R'4, R'S, and X' are as defined above.
In yet another of its composition aspects, this invention is directed to
a compound of formula VIa and VIb:
R2~ R2a R25 R2
W ~ ~ R2a R2s
R ~ N X and
R~ N X
~23
~23
VIa VIb
wherein, in formula VIa, R' and R2, together with the carbon atom
and W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form an aryl,
cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in
the aryl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group and optionally
containing or additionally containing in the case of heteroaryl and
heterocyclic groups 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 51 --
oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur, and wherein the heteroaryl or heterocyclic
group is mono-cyclic;
in formula VIb, R' and RZ, together with the carbon atom and W' to
which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a cycloalkyl,
cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group having at least five atoms in the
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl or heterocyclic group and optionally containing or
additionally containing in the case of the heterocyclic group 1 to 3
heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of oxygen, nitrogen and
sulfur, and wherein the heterocyclic group is mono-cyclic;
and further wherein said aryl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, heteroaryl or
heterocyclic group of formula VIa or VIb is optionally substituted, on any
ring atom capable of substitution, with 1-3 substituents selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, substituted alkoxy,
acyl,
acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, substituted amino, amidino,
alkyl amidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino,
aminothiocarbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy,
substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, cyano, halogen,
hydroxyl, nitro, oxo, carboxyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)2-alkyl, -OS(O)2-
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)Z-aryl, -OS(O)2-substituted aryl, -OS(O)z-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where each R is independently hydrogen or alkyl,
-NRS(O)Z-alkyl, -NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)Z-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)Z-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 52 --
-NRS(O)Z-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)z-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-
alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -N[S(Oh-R']z and -N[S(O)Z_
NR']2 where each R' is independently selected from the group consisting of
alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic;
R23 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, Cl_,o alkyl
optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently selected
from Ra~ and Cy optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from Rb~;
Rz4 is selected from the group consisting of Ar'-Ar2-C,_,o alkyl,
Ar'-Ar2-CZ_lo alkenyl, Ar'-Ar2-CZ_~o alkynyl, wherein Ar' and Arz are
independently aryl or heteroaryl each of which is optionally substituted with
one to four substituents independently selected from Rb'; alkyl, alkenyl and
alkynyl are optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently
selected from Ra';
R25 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C,_'o alkyl,
CZ_lo alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, aryl, aryl Cl_,oalkyl, heteroaryl, and
heteroaryl
C,_,o alkyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl are optionally substituted
with
one to four substituents selected from R~', and aryl and heteroaryl are
optionally substituted with one to four substituents independently selected
from Rb~;
Ra' is selected from the group consisting of Cy, -ORd~, -NOZ, halogen
-S(O)mRd~, -SRd', -S(O)zORd~, -S(O)mNRd~Re~, -NRd~Re~, -O(CRf~Rg~)~NRd~Re~,
-C(O)Rd~, -COZR°~, -COZ(CRf~Rg~)~CONRd~Re', -OC(O)Rd~, -CN,
-C(O)NRd~Re~, -NRd'C(O)Re~, -OC(O)NRd~Re~, -NRd~C(O)ORe~,
-Nrd~C(O)NRd~Re~, -CRd'(N-ORe~), CF3, and -OCF3;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 53 --
wherein Cy is optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R'';
R"' is selected from the group consisting of Ra', C,_,o alkyl, CZ_,o
alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, aryl C,_lo alkyl, heteroaryl C,_,oalkyl,
wherein alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, heteroaryl are optionally substituted
with a group independently selected from R~~;
R'~ is selected from the group consisting of halogen, amino, carboxy,
CI_4 alkyl, CI~ alkoxy, aryl, aryl C,_4 alkyl, hydroxy, CF3, and aryloxy;
Rd' and Re' are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_lo alkyl, CZ_
,o alkenyl, CZ_,o alkynyl, Cy and Cy C,_,oalkyl, wherein alkyl, alkenyl,
alkynyl and Cy are optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R~'; or Rd' and Re' together with the atoms to
which they are attached form a heterocyclic ring of 5 to 7 members
containing 0-2 additional heteroatoms independently selected from oxygen,
sulfur and nitrogen;
Rf~ and Rg' are independently selected from hydrogen, C,_,o alkyl, Cy
and Cy-C,_lo alkyl; or Rf' and Rg~ together with the carbon to which they are
attached form a ring of 5 to 7 members containing 0-2 heteroatoms
independently selected from oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen;
R"' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C,_lo alkyl,
CZ_lo alkenyl, C,_IO alkynyl, cyano, aryl, aryl C,_,o alkyl, heteroaryl,
heteroaryl C,_,o alkyl, or -SOZR'';
wherein alkyl, alkenyl, and alkynyl are optionally substituted with
one to four substitutents independently selected from Ra'; and aryl and
heteroaryl are each optionally substituted with one to four substituents
independently selected from R"';
R'~ is selected from the group consisting of Cl_,o alkyl, CZ_~o alkenyl,
CZ_,o alkynyl, and aryl;
wherein alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl and aryl are each optionally
substituted with one to four substituents independently selected from I~';
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
--54--
Cy is cycloalkyl, heterocyclyl, aryl, or heteroaryl;
X" is selected from the group consisting of -C(O)ORd',
-P(O)(ORd')(ORe~), -P(O)(Rd~)(ORe'), -S(O)mORd', -C(O)NRd'R"~, and -S-
tetrazolyl;
m is an integer from 1 to 2;
n is an integer from 1 to 10;
and enantiomers, diastereomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts
thereof; provided that:
(i) the compound of formula VIa or VIb has a binding affinity to VLA-4
as expressed by an ICSO of about 15~,M or less; and
(ii) in formula VIa and VIb, R' and R2, together with the carbon atom
and W to which they are bound respectively, do not form a substituted or
unsubstituted pyridazine ring.
In the above embodiment, R' and Rz, together with the carbon atom
and W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form a substituted
or unsubstituted monocyclic heteroaryl or heterocyclic ring wherein the
heteroaryl ring contains 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from N, O or S and the
heterocyclic ring contains 1 to 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O, or S(O)n
wherein n is 0 to 2, preferably R' and RZ, together with the carbon atom and
W to which they are bound respectively, are joined to form substituted or
unsubstituted pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole,
tetrazole, thiophene, pyridine, pyrimidine, 1,3,5-triazine, 1-oxo-1,2,5-
thiadiazole or 1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole ring; more preferably, substituted
1,3,5-triazine, or 1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole ring.
Preferably, X" is -C(O)ORd'.
In the above compounds, R24 is preferably -CHI-Ar'-Arl and R25 is
preferably hydrogen.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 55 --
In a more preferred embodiment, this invention is directed to
compounds of formula VIIa, VIIb, or VIII:
R24 R25
N X
R23
Vlla
~~~b
N~S~N R24R25
~N~X'
RS.N.R6 ~ 23
R
Vllb
R7
N~N R24R25
R$~N~N~X'
R23
Vlic
wherein:
ring A is selected from the group consisting of pyrrole, pyrazole,
imidazole, pyrimidine, 1,2,3-triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, tetrazole, and
thiophene wherein each of said pyrrole, pyrazole, imidazole, and thiophene
ring is substituted with 1 to 3 substituent(s), and the pyrimidine, 1,2,3-
triazole, 1,2,4-triazole, and tetrazole rings are substituted with 1 to 2
substituent(s), independently selected from the group consisting of alkyl,
alkoxy, halogen, vitro, amino, substituted amino, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyle, substitued heterocycle, and -
SOZRa (wherein Ra is alkyl, aryl, or substituted aryl);
RS is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl,
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/~JS00/01540
-- 56 --
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocylic, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;
R6 is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl,
substituted
cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and -SOZR'° where R'° is
selected from the
group consisting of alkyl, substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, heterocyclic, substituted
heterocyclic, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, and substituted heteroaryl;
R' is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen,
hydroxy, substituted amino, heterocycle, and substituted heterocyle;
Rg is selected from the group consisting of substituted amino,
heterocycle, and substituted heterocycle;
b is 1 ro 2; and
Rz3~ Rza~ Rzs~ and X" are as defined above.
This invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising
a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a therapeutically effective amount
of the compounds defined above.
In the above compounds, when X is other than -OH or
pharmaceutical salts thereof, X is a substituent which will convert (e.g.,
hydrolyze, metabolize, etc.) in vivo to a compound where X is -OH or a salt
thereof. Accordingly, suitable X groups are any art recognized
pharmaceutically acceptable groups which will hydrolyze or otherwise
convert in vivo to a hydroxyl group or a salt thereof including, by way of
example, esters (X is alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, cycloalkoxy, substituted
cycloalkoxy, alkenoxy, substituted alkenoxy, cycloalkenoxy, substituted
cycloalkenoxy, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted
heteroaryloxy, heterocyclooxy, substituted heterocyclooxy, and the like).
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
In the compounds of formula Ia-b, IVa-b, VIa-b above, R' and RZ are
preferably joined to form a substituted 1,3,5-triazine group.
Unless otherwise defined, R3 and R'S in the above compounds are
preferably selected from all possible isomers arising by substitution with the
following groups:
4-methylbenzyl,
4-hydroxybenzyl,
4-methoxybenzyl,
4-t-butoxybenzyl,
4-benzyloxybenzyl,
4-[~-CH(CH3)O-]benzyl,
4-[~-CH(COOH)O-]benzyl,
4-[BocNHCHZC(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-chlorobenzyl,
4-[NHZCH~C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-carboxybenzyl,
4-[CbzNHCH2CHZNH-]benzyl,
3-hydroxy-4-(~-OC(O)NH-)benzyl,
4-[HOOCCHZCHZC(O)NH-]benzyl,
benzyl,
4-[2'-carboxylphenoxy-]benzyl,
4-[~-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
3-carboxybenzyl,
4-iodobenzyl,
4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodobenzyl,
4-hydroxy-3-iodobenzyl,
4-[2'-carboxyphenyl-]benzyl,
~-CHZCHZ-,
4-nitrobenzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/CTS00/01540
-_ 5g _-
2-carboxybenzyl,
4-[dibenzylamino]-benzyl,
4-[(1'-cyclopropylpiperidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)CHZNHBoc]benzyl,
4-carboxybenzyl,
4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)CH(CH3)NHBoc]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)CH(CH2~)NHBoc]benzyl,
isobutyl,
methyl,
4-[CH3C(O)NH-]benzyl,
-CH,-(3-indolyl),
n-butyl,
t-butyl-OC(O)CHZ-,
t-butyl-OC(O)CHZCHZ ,
HZNC(O)CHZ-,
HZNC(O)CHZCHZ-,
BocNH-(CHZ),~-,
t-butyl-OC(O)-(CH~)Z-,
HOOCCHZ-,
HOOC(CHZ)z-,
HZN(CHZ)4-,
isopropyl,
( 1-naphthyl)-CHZ-,
(2-naphthyl)-CHZ-,
(2-thiophenyl)-CHz-,
(~-CHZ-OC(O)NH-(CHZ)4-,
cyclohexyl-CH,-,
benzyloxy-CHI-,
HOCHZ-,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
--59--
5-(3-N-benzyl)imidazolyl-CHZ-,
2-pyridyl-CHz-,
3-pyridyl-CHZ-,
4-pyridyl-CHZ-,
5-(3-N-methyl)imidazolyl-CHZ-,
N-benzylpiperid-4-yl-CHZ-,
N-Boc-piperidin-4-yl-CHZ-,
N-(phenyl-carbonyl)piperidin-4-yl-CHZ-,
H3CSCHZCH2-,
1-N-benzylimidazol-4-yl-CHZ-,
iso-propyl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
iso-butyl-C(O)NH-(CHz)a-,
phenyl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
benzyl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
allyl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
4-(3-N-methylimidazolyl)-CHZ-,
4-imidazolyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNCH~CH,CHZ-O-]benzyl,
4-[(benzyl)zN-]-benzyl,
4-aminobenzyl,
allyloxy-C(O)NH(CHz)4-,
allyloxy-C(O)NH(CHZ)3-,
allyloxy-C(O)NH(CHZ)2-,
NHZC(O)CHZ-,
~-CH = ,
2-pyridyl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
4-methylpyrid-3-yl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
3-methylthien-2-yl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
2-pyrrolyl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
2-furanyl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)a-,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 60 --
4-methylphenyl-SOZ-N(CH3)CHZC(O)NH(CHZ)a-,
4-[cyclopentylacetylenylJ-benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-(N-Boc)-pyrrolidin-2-yl)]-benzyl-,
1-N-methylimidazol-4-yl-CHZ-,
1-N-methy limidazol-5-yl-CHz-,
imidazol-5-yl-CHZ-,
6-methylpyrid-3-yl-C(O)NH-(CHZ)4 ,
4-[2'-carboxymethylphenyl]-benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)NHCH~CHZCHZ-~]-benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)NHCHZCHz-~]-benzyl,
-CH.,C(O)NH(CHz)a~,
4-[~(CHZ)a0-]-benzyl,
4-(-C = C-~-4' ~]-benzy l,
4-[-C---C-CHZ-O-S(O)2-4'-CH3-~]-benzyl,
4-[-C---C-CHZNHC(O)NHz]-benzyl,
4-[-C---C-CHZ-O-4'-COOCH,CH3-~]-benzyl,
4-[-C---C-CH(NHZ)-cyclohexyl]-benzyl,
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)CH,-3-indolyl,
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)CH,CHZ-3-indolyl,
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)-3-(5-methoxyindolyl),
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)-3-( 1-methylindolyl),
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)-4-(-SOZ(CH3)-~),
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)-4-(C(O)CH3)-phenyl,
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)-4-fluorophenyl,
-(CHZ)aNHC(O)CHzO-4-fluorophenyl,
4-(-C=C-(2-pyridyl)]benzyl,
4-[-C---C-CHZ-O-phenyl]benzyl,
4-[-C---C-CHzOCH3]benzyl,
4-[-C=C-(3-hydroxyphenyl)]benzyl,
4-[-C=C-CHZ-O-4'-(-C(O)OCzHs)phenyl]benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 61 --
4-[-C---C-CHZCH(C(O)OCH3)2]benzyl;
4-[-C---C-CHZNH-(4,5-dihydro-4-oxo-5-phenyl-oxazol-2-yl),
3-aminobenzyl,
4-[-C---C-CHzCH( NHC(O)CH3)C(O)OH]-benzyl,
-CHZC(O)NHCH(CH3)~,
-CHIC(O)NHCH~-(4-dimethylamino)-~,
-CHZC(O)NHCHz-4-nitrophenyl,
-CHzCH2C(O)N(CH3)CHZ-~,
-CHZCHZC(O)NHCH,CHZ-(N-methyl)-2-pyrrolyl,
-CHZCH~C(O)NHCH,CH~CHZCH3,
-CHZCHZC(O)NHCHZCHz-3-indolyl,
-CHzC(O)N(CH3)CHZphenyl,
-CHIC(O)NH(CHZ)Z-(N-methyl)-2-pyrrolyl,
-CHZC(O)NHCHZCHZCHZCH3,
-CHzC(O)NHCHZCHZ-3-indolyl,
-(CHZ)zC(O)NHCH(CH3)~,
-(CHZ)zC(O)NHCHZ-4-dimethylaminophenyl,
-(CHZ)ZC(O)NHCH~-4-nitrophenyl,
-CHIC(O)NH-4-[-NHC(O)CH3-phenyl],
-CHZC(O)NH-4-pyridyl,
-CHIC(O)NH-4-[dimethylaminophenyl],
-CHzC(O)NH-3-methoxyphenyl,
-CHZCHZC(O)NH-4-chlorophenyl,
-CHZCHZC(O)NH-2-pyridyl,
-CHZCHZC(O)NH-4-methoxyphenyl,
-CHZCHZC(O)NH-3-pyridyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNCH,CH20-]benzyl,
-(CHZ)3NHC(NH)NH-SOZ-4-methylphenyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNCHzCHzO-]benzyl,
-(CHZ)4NHC(O)NHCHZCH3,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 62 --
-(CHZ)4NHC(O)NH-phenyl,
-(CHZ)4NHC(O)NH-4-methoxyphenyl,
4-[4'-pyridyl-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[3'-pyridyl-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)NH-3'-methylphenyl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)CHZNHC(O)NH-3'-methylphenyl)benzyl;
4-[-NHC(O)-(2',3'-dihydroindol-2-yl)]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-(2',3'-dihydro-N-Boc-indol-2-yl)]benzyl,
p-[-OCHZCHZ-1'-(4'-pyrimidinyl)-piperazinyl]benzyl,
4-[-OCH~CHZ-(1'-piperidinyl)benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCH~-( 1'-pyrrolidinyl)]benzyl,
4-(-OCHZCHZCHZ-(1'-piperidinyl)Jbenzyl-,
-CHZ-3-( 1,2,4-triazolyl),
4-[-OCHZCHZCHZ-4-(3'-chlorophenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZN(~)CHzCH3Jbenzyl,
4-[-OCHZ-3'-(N-Boc)-piperidinylJbenzyl,
4-[di-n-pentylamino]benzyl,
4-[n-pentylaminoJbenzyl,
4-[di-iso-propylamino-CH~CHzO-Jbenzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZ-(N-morpholinyl)]benzyl,
4-[-O-(3'-(N-Boc)-piperidinyl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCH(NHBoc)CHZCyclohexyl]benzyl,
p-[OCHZCHZ-(N-piperidinyl)benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZCHZ-(4-m-chlorophenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]benzyl,
4-[-OCH~CHZ-(N-homopiperidinyl)benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-3'-(N-Boc)-piperidinyl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZN(benzyl)2]benzyl,
-CHZ-2-thiazolyl,
3-hydroxybenzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZCHZN(CH3)2]benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 63 --
4-[-NHC(S)NHCHZCHZ-(N-morpholino)]benzyl,
4-[-OCH,CHZN(C~HS)2]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCH~CHZN(CZHS)z]benzyl,
4-[CH3(CHz)4NH-]benzyl,
4-[N-n-butyl,N-n-pentylamino-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-4'-piperidinyl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)CH(NHBoc)(CHZ)4NHCbz]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-( 1' ,2' ,3' ,4'-tetrahydro-N-Boc-isoquinolin-1'-yl]benzyl,
p-[-OCHZCHZCHZ-1'-(4'-methyl)-piperazinyl]benzyl,
-(CHZ)4NH-Boc,
3-[-OCHZCHzCH2N(CH3)Z]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZCHZN(CH3)2]benzyl,
3-[-OCHzCH2-( 1'-pyrrolidinyl)]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZCH~N(CH3)benzyl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(S)NHCHZCHZCHZ-(N-morpholino)]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZ-(N-morpholino)]benzyl,
4-[-NHCHZ-(4'-chlorophenyl)]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)NH-(4'-cyanophenyl)]benzyl,
4-[-OCH~COOH]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCOO-t-butyl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-5'-fluoroindol-2-yl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(S)NH(CHZ)Z-1-piperidinyl]benzyl,
4-[-N(SOZCH3)(CHZ)3-N(CH3)Zlbenzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)CHZCH(C(O)OCH2~)-NHCbz]benzyl,
4-[-NHS(O)ZCF3]benzyl,
3-[-O-(N-methylpiperidin-4'-yl]benzyl,
4-[-C(=NH)NHZ]benzyl,
4-[-NHSOZ-CH~CI]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-( 1' ,2' , 3' ,4'-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2'-yl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(S)NH(CHZ)3-N-morpholino]benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 64 --
4-[-NHC(O)CH(CHzCHZCHZCHZNH2)NHBoc]benzyl,
4-[-C(O)NHZ)benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)NH-3'-methoxyphenyl)benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZ-indol-3'-yl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZC(O)NH-benzyl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZC(O)O-benzyl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZC(O)OH]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZ-2'-(4',5'-dihydro)imidazolyl]benzyl,
-CHIC(O)NHCHZ-(4-dimethylamino)phenyl,
-CHIC(O)NHCHz-(4-dimethylamino)phenyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-L-2'-pyrrolidinyl-N-SOZ-4'-methylphenyl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)NHCHZCHZCH3]benzyl,
4-aminobenzyl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZ-1-(4-hydroxy-4-(3-methoxypyrrol-2-yl)-
piperazinyl]benzyl,
4-[-O-(N-methylpiperidin-4'-yl)]benzyl,
3-methoxybenzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-piperidin-3'-yl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-pyridin-2'-yl]benzyl,
4-[-NHCHZ-(4'-chlorophenyl)]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-(N-(4'-CH3-~-SOZ)-L-pyrrolidin-2'-yl)]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)NHCHZCHZ-~]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZC(O)NHZ]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZC(O)NH-t-butyl]benzyl,
4-[-OCHZCHZ-1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenyl)-piperidinyl]benzyl,
4-[-NHSOZ-CH =CHZ]benzyl,
4-[-NHSOZ-CHZCHZCI]benzyl,
-CHZC(O)NHCHZCHZN(CH3)2,
4-[(1'-Cbz-piperidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(1'-Boc-piperidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 65 --
4-[(2'-bromophenyl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-pyridin-4'-yl]benzyl,
4-[(4'-(CH3)zNC(O)O-)phenyl)-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-1'-methylpiperidin-4'-yl-]benzyl,
4-(dimethylamino)benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-(1'-N-Boc)-piperidin-2'-yl]benzyl,
3-[-NHC(O)-pyridin-4'-yl]benzyl,
4-[(tert-butyl-O(O)CCHZ-O-benzyl)-NH-]benzyl,
[BocNHCH,C(O)NH-)butyl,
4-benzylbenzyl,
2-hydroxyethyl,
4-[(Et)ZNCH~CH~CHZNHC(S)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(1'-Boc-4'-hydroxypyrrolidin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[~CH~CHZCHZNHC(S)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(perhydroindolin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
2-[4-hydroxy-4-(3-methoxythien-2-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl,
4-[(1'-Boc-perhydroindolin-2'-yl)-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[N 3-methylbutyl-N trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amino]benzyl,
4-[N vinylsulfonyl)amino]benzyl,
4-[2-(2-azabicyclo[3 .2.2]octan-2-yl)ethyl-O-]benzyl,
4-[4'-hydroxypyrrolidin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-(~NHC(S)NH)benzyl,
4-(EtNHC(S)NH)benzyl,
4-(~CHZNHC(S)NH)benzyl,
3-[(1'-Boc-piperidin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
3-[piperidin-2'-yl-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(3'-Boc-thiazolidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-(pyridin-3'-yl-NHC(S)NH)benzyl,
4-(CH3-NHC(S)NH)benzyl,
4-(HZNCHZCHZCHZC(O)NH)benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 66 --
4-(BocHNCH2CH~CH2C(O)NH)benzyl,
4-(pyridin-4'-yl-CHZNH)benzyl,
4-[(N,N di(4-N,N dimethylamino)benzyl)amino]benzyl,
4-[(1-Cbz-piperidin-4-yl)C(O)NH-]butyl,
4-[~CHZOCHZ(BocHN)CHC(O)NH]benzyl,
4-[(piperidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(pyrrolidin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-(pyridin-3'-yl-C(O)NH)butyl,
4-(pyridin-4'-yl-C(O)NH)butyl,
4-(pyridin-3'-yl-C(O)NH)benzyl,
4-[CH3NHCHZCHZCHZC(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[CH3N(Boc)CH,CHZCH,C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-(aminomethyl)benzyl,
4-[~CHZOCHZ(HZN)CHC(O)NH]benzyl,
4-[(1',4'-di(Boc)piperazin-2'-yl)-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(piperazin-2'-yl)-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(N toluenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]butyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-4'-piperidinyl]butyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-1'-N-Boc-piperidin-2'-yl]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-piperidin-2'-yl)benzyl,
4-[(1'-N-Boc-2',3'-dihydroindolin-2'-yl)-C(O)NH]benzyl,
4-(pyridin-3'-yl-CH~NH)benzyl,
4-[(piperidin-1'-yl)C(O)CHZ-O-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZCH)ZNC(O)CHZ-O-)benzyl,
4-[HO(O)C(Cbz-NH)CHCHZCHZ-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[~CHZO(O)C(Cbz-NH)CHCHZCHZ-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-2'-methoxyphenyl]benzyl,
4-[(pyrazin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[HO(O)C(NHZ)CHCHZCHZ-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
4-(2'-formyl-1',2',3',4'-tetrahydroisoquinolin-3'-yl-CHZNH-)benzyl,
N Cbz-NHCHZ-,
4-[(4'-methylpiperazin-1'-yl)C(O)O-)benzyl,
4-[CH3(N Boc)NCHZC(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-(1',2',3',4'-tetrahydro-N-Boc-isoquinolin-3'-yl)-benzyl,
4-[CH3NHCHZC(O)NH-]benzyl,
(CH3)zNC(O)CHZ-,
4-(N methylacetamido)benzyl,
4-(1',2',3',4'-tetrahydroisoquinolin-3'-yl-CH~NH-)benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNHCH~C(O)NH-]benzyl,
(1-toluenesulfonylimidizol-4-yl)methyl,
4-[(1'-Boc-piperidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-trifluoromethylbenzyl,
4-[(2'-bromophenyl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNC(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[CH30C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNC(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNC(O)N(CH3)-]benzyl,
4-[CH30C(O)N(CH3)-]benzyl,
4-(N methyltrifluoroacetamido)benzyl,
4-[(1'-methoxycarbonylpiperidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(4'-phenylpiperidin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(4'-phenyl-1'-Boc-piperidin-4'-yl)-C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(piperidin-4'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl, 4-[(1'-methylpiperidin-4'-yl)-
O-)benzyl,
4-[(1'-methylpiperidin-4'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(4'-methylpiperazin-1'-yl)C(O)NH-)benzyl,
3-((CH3)ZNC(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(4'-phenyl-1'-Boc-piperidin-4'-yl)-C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-(N toluenesulfonylamino)benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 6g __
4-[(CH3)3CC(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(morpholin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3CH2)ZNC(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-C(O)NH-(4'-piperidinyl)]benzyl,
4-[(2'-trifluoromethylphenyl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(2'-methylphenyl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNS(O)ZO-]benzyl,
4-((pyrrolidin-2'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[-NHC(O)-piperidin-1'-yl]benzyl,
4-[(thiomorpholin-4'-yl)C(O)NH-]benzyl,
4-[(thiomorpholin-4'-yl sulfone)-C(O)NH-Jbenzyl,
4-[(morpholin-4'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
3-nitro-4-(CH30C(O)CH~O-)benzyl,
(2-benzoxazolinon-6-yl)methyl-,
(2H 1,4-benzoxazin-3(4Fn-one-7-yl)methyl-,
4-[(CH3)ZNS(O)ZNH-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNS(O)zN(CH3)-]benzyl,
4-[(thiomorpholin-4'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(thiomorpholin-4'-yl sulfone)-C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(piperidin-1'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(pyrrolidin-1'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(4'-methylpiperazin-1'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(2'-methylpyrrolidin-1'-yl)-,
(pyridin-4-yl)methyl-,
4-((piperazin-4'-yl)-C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(1'-Boc-piperazin-4'-yl)-C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(4'-acetylpiperazin-1'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
p-[(4'-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1'-yl)-benzyl,
3-nitro-4-[(morpholin-4'-yl)-C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-{ [(CH3)ZNC(S)]ZN-}benzyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 69 --
N Boc-2-aminoethyl-,
4-[(1,1-dioxothiomorpholin-4-yl)-C(O)O-]benzyl,
4-[(CH3)ZNS(O)Z-]benzyl,
4-(imidazolid-2'-one-1'-yl)benzyl,
4-[(piperidin-1'-yl)C(O)O-]benzyl,
1-N-benzyl-imidazol-4-yl-CHZ-,
3,4-dioxyethylenebenzyl (i.e., 3,4-ethylenedioxybenzyl),
3,4-dioxymethylenebenzyl (i.e., 3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl),
4-[-N(SOZ)(CH3)CH~CHZCHZN(CH3)Z]benzyl,
4-(3'-formylimidazolid-2'-one-1'-yl)benzyl,
4-[NHC(O)CH(CHZCHZCHZCHZNHZ)NHBoc]benzyl,
[2'-[4"-hydroxy-4"-(3"'-methoxythien-2"'-yl)piperidin-2"-
yl]ethoxy]benzyl, and
p-[(CH3)ZNCH,CHZN(CH3)C(O)O-]benzyl.
Preferably, in the compounds of formula 1-VII above, R3' is
preferably hydrogen.
Preferably, in the compounds of formula I-VII above, R4 is
preferably hydrogen and X is preferably hydroxyl or alkoxy.
In the compounds of formula IVa-b and V, preferred R'3, R'4 and R'S
groups correspond to the R3, R° and RS groups, respectively, disclosed
in
International Patent Application Publication No. WO 98/53814 which
application is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
In the compounds of formula VIa-b, preferred Rz3, Rza and R25 groups
correspond to the R5, R6 and R' groups, respectively, found in International
Patent Application Publication No. WO 98/53817 which application is
incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. In a preferred embodiment,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__
in compounds of formula IVa-b and VII, R24 is -CHI-Arz-Ar' and RZS is
hydrogen.
This invention also provides methods for binding VLA-4 in a
biological sample which method comprises contacting the biological sample
with a compound of formula I-VII above under conditions wherein said
compound binds to VLA-4.
Certain of the compounds of formula I-VII above are also useful in
reducing VLA-4 mediated inflammation in vivo.
This invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising
a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a therapeutically effective amount
of one or more of the compounds of formula I-VII above. Preferably, R3
and R3~ are derived from L-amino acids or other similarly configured starting
materials. Alternatively, racemic mixtures can be used.
The pharmaceutical compositions may be used to treat VLA-4
mediated disease conditions. Such disease conditions include, by way of
example, asthma, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, AIDS dementia,
diabetes (including acute juvenile onset diabetes), inflammatory bowel
disease (including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease), multiple
sclerosis,
rheumatoid arthritis, tissue transplantation, tumor metastasis, meningitis,
encephalitis, stroke, and other cerebral traumas, nephritis, retinitis, atopic
dermatitis, psoriasis, myocardial ischemia and acute leukocyte-mediated lung
injury such as that which occurs in adult respiratory distress syndrome.
Other disease conditions include, but are not limited to, inflammatory
conditions such as erythema nodosum, allergic conjunctivitis, optic neuritis,
uveitis, allergic rhinitis, Ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ ~ 1 __
vasculitis, Reiter's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, progressive
systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, Wegner's
granulomatosis, aortitis, sarcoidosis, lymphocytopenia, temporal arteritis,
pericarditis, myocarditis, congestive heart failure, polyarteritis nodosa,
hypersensitivity syndromes, allergy, hypereosinophilic syndromes, Churg-
Strauss syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypersensitivity
pneumonitis, chronic active hepatitis, interstitial cystitis, autoimmune
endocrine failure, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune aplastic anemia,
chronic persistent hepatitis and thyroiditis.
Accordingly, this invention also provides methods for the treatment
of an inflammatory disease in a patient mediated by VLA-4 which methods
comprise administering to the patient the pharmaceutical compositions
described above.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
72
N
ri
>,
N L'i
N ~'
.
r
3 v
o z .c
O o
0
O
.r
z= '' o
. v~1
O M N
~
i. ~
r
~ >>
>, c~
~ ' >' (V
~ >, O 4 ..~ ~
>, M
C
~,
'~
> tl. s"'>> N ~
Q ~ C M
. . _i
~"' ~ :O ~ N 'Cf G) ~' O
,
,,
.
.
.
O ~ ~. M N ~. ch .~
O
m Q M ~--i.-r .-a~ .-~ ~ V1 ,.
.--~
'd
O
O
O
Cl.
.O
U U .-~ N M d' ~ ~D ~ 00
O
cC
G
N
~.
Q.
O
~i
'n O V1
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
73
a
...
b
...
~.
>, >, a,
c
_b
a
G
c
w w w
c a
O. ~. N _ A
>, i
~ >,
G d' a' b ...
>, v ~
V ~ a 'ct
z O '~ ~'i
,~ z ; ~ ~ z
~', a
a a ~ b a
V~
\O M M V1 d' M M
~ N M
O~ .--~. .
-v -i
O
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
74
>, >,
~
N V
'
b b
._.,
'
~, i.
CL Q,
O O
C
C
G
w
Z= ~
G
N N
~1.O.
>, >,
y
N
~r
z z
z z
a
d cn cn
U ~ ~-~ ~ c~
~n o
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
.c
a~ a~ a~ a~
.-. .. .~. ,-,
>, >, >,
>, >, >, ~_ c
M M M._~._~.b.b
i i
O O O O
N N N i~-~ N s.~.
O O O ~
_~ _~ _~ ~
N N N
N N y
~r ~ 'r
V ~ ~ ~ N N N N N
Z
0
0
Z=
~x x x x x x x x
Z
Z=
Z
M
er
M
O
O
_~C~ n
O
~"~ c,"
~~ ~ .O
i<
a ~ ~ o
.fir ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ o
o ~ ~ G. v
i ~ i
Qi N Qr .~ ~ a a v
'O
G.
U ...., c~.~ M ~ ~n ~ t~
o w,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
76
>,
C
>, ~.
>, ~, >,
O _ _ .c ~ _ _
_~ .~ .--~ , ~ ~, .G
'~ M ~
b .C ..~0 ,~ yes.,
~ O b ~ y .~C 0 O ~' p
b j 0 j
N ~, U ~ .~ 0 0 N >, ~G' ~'
~ ~ ~ ~ N ~ ~ c~ c.~.
~. ~ ~. Q. ~ ~ ~~.,
~1 i ~ i i , ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~t
N N N N N N N N N N v~ N ~
O
~_
U ~ x ~
x G N ~ ~ ~ r~ix x xi ~, x'.x x x x x
O
.
.
. O
_~ ~ _~ ,~
.c~ O _~ ~ .c~~V.~'~C
?, c~ O M CL C~. G. Q.
Q. C1. Q. ~ O ~ .C ~ U
L1 St j O O O O
f~,t7.O. p" ~, ~ ~~"'~ p ~ ~.
O ~' _ ~ ~, A. C. C. Q.
~ N ~ N y ~, N ~ ~ ~ ~, ~ ~, >,
U _O ~ ~ ,~ O p x ..r
~
U N N N N U vi c.~ra d' U N N N N
U
O -~ N M ~' V1 ~O I~ 00 Cv O ~ N M it
00 Ov "-'''.~~' '".'~' ~".'~~ .-~.-~~ N N N N N
O v~
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
77
x
>, ~, ~ ~.. ~ ..
>, ~ ~, c
.a ~ a ~. .c
~ ~ ' ~ a~ ~ a~ a,
>, a~ .~ .~_ n~ .a ._~ >,
a~ a~ ~ ~. -~ ~ o
a. .~ x ~ a. ' ' >,
O A. n. ~ ~ ~ ~ X N ~ y U
U ._i: O
.C ._~._.C7, ~, ~ .L ~' O O ~'
N N U N O j a~ d
~ _Q.~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ N ~. ~ N ~
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O' O ~
d' C. ~ ~ v'.r~ C3,Cl.~ a t~..U ~ 1.~. N N
N N N N N ~ .~ ~ ~ cG~,~ ~ c~
N
>,
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x N
C ~ C G
>, >, ~ >,
O .~~O .a .t~.O p ..
D O O k ~
7, N ~ O O O O
of ~ >, G ~ ~
~ i~G N ~ N U ~ O O
O N O p ~ c~ y
N ~ U U U N C~ p
~h O O ~ ~ ~ ~ O O O
U U c~ .O ~ ' i ~ i ~-~
'r U U ~ ~ ~. ~ U U U U
d' N ct ~ U U M M M M U
W O t~ 00 Ov O --~N M et VW O l~ oo O~ O
N N N N N M M M M M M M M M M ~" ~i'
O V1
~-i
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
78
>,
>'
c
.~ ~ ~. ...>, "" o
>, >, ~ >,
~' U a ?' '~ .n d' M ~ a
' ~ ~ a~ o M ~ r"''
~ ~ .L7~ ~ O C C ~ A"'
a o N 'd O ~' U ~ O >'
O ~ .~, ~, z b b v ~ .;,
U ~ y ~. ~ z ~ .;,~;, ~ ~'
y V' N ~ N N M GL O. CL N t1,
>,
.r
U
>,
i
M
_ ~ i
_ p ~ >, ~, >, ~ :b >' >'
.~ ~ ~. .C .~ ~ N
~ ~' O.'~ .D ~ .fl N ~ ~ ~
U c~ U ~ ~ N U ~ A. Cw
O
C
."
_
O G",
O
Q' ~ ,~~,~ ~
O ~
O O O O O O O O O >, ~ i! k it
~ O O O z
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 '~ ~, ~ ~ ~O~,
~ ~, ~, ~ ~ U Z
U U U U U U U U U N .a .~ N N N
N M ~ vW O I~ oo a\ O -~ N M d' v'1v0 I~ 00
~h '~'Wit'~h ~ ~!' d' ~h ~n ~n ~ ~n ~n vo v~ v'~v'~
~7 O v~
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
79
>, ~, >, ~, >, >, >, >, ~, ~, >, >, >, >, ~, a
c o ~ ~ a a a o ~ ~ o o a
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
w w w w w w ~ w w w ~ ~ w w w w
C ~ C G C ~ ~ G ~ ~ C G ~ C
a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~ a~
c. a. a. a. a a. a. a, o. a. a, s~,a. o, n. c.
x
I I .~ .r ..~~ .~ ~ .r .r ~ .r ~ .~ .~ ...
, , I ~ I , I , I I , I I ,
~ ~t ~r ~r ~r ~t ~r ~t ~t ~r ~r ~r ~r ~ ~r ~r
~, >, >, >, >, >, >, >, >, ~, >, >, >, >,
x ar ad
ar ar yr a..~a..~ar a.uy.~au y au a au ar
_~
CAS
C~
~ O O
O N ~_ ~ ~ ~~.. 7,
Cat ~ O I
>, ~ ~'' I .'~C~ ~ >, G
b O :d ~
G~. ~ ~ ~ O .O N ~ O
N M 'b .... O w
w.r , >, N
.D wr .b f., G,' M ,~ ~,
I N N >' ~ d. _~ a ~ I
i '~ ~ ,In., ~ ~ .~
I z z_ z ~~ v--,
z ~ z z z _z ~ y Gi
L'1 z .C~r~ "': .~ ,~ ~1 ~ ~1 ~1 ~1
a., ~ ~ ~1 ~ ._~C.fl._C.C ~ O
,O' y C~ ~ N ,~'~ ~r N N N N
N O ~ ~ N ~ N p. ~ Z ~ ~ CV z
~ ~ ~ z z z
z z z z z z z z z z
z z ~
01 O ~ N M ~t vW O I~ 00 O~ O ~ N M d'
~O ~O ~O ~O ~D ~D ~ ~O ~O ~O t~ I~ r l~ I~
'n O
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
a~
_
>, a~
a~
a~ y ~ _ a~
>, ~, >, >, "-~~>, >, >, ~
,~ :~
a ~ a a >, >, ~ '~ ~ i .~ >, O
w ~ w w ~ ~ N N
N ~ N ~ ~ ~ N ~ V '-, ~p
.C .~ .C .C y 7, O .C .~ .C ~',~ ~ ~ ~',
G. G. G. O. ~ "O O. C. G. ~ ' "C 'b
J, ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ >, ~ ~, ~ O
.C .~ .C >, G ~ .O .C ~, C C ' G.
N ~ ~ .C O b ~ N .C ~ .C ~ ~!
~ ~' G C. A~ Q. ~ a
V' ~' '~ U CY ~' V' N " N N N a
~ 'Ct a
Aw
O
Lr
by b0 tiQb0 b-0GO b4
x O ~ ~ ~ ~ 'C b b b b 'b b
N ~ N ~ .C ~ ~ .C
c~ ~
>,
O
O
N .~ G
C O
;~ ~ ~'
~ O_ i G) >,
~ ~ ~ M
~i b O
O
i i~ k
a O O O ~ do tinan o4 do an on cn
:o z ...,
r '
.;. ' ~ o o ~ a o 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
" ~ ~
z z U U U ~ ~ ~ .~C~".~C~,.~C~
z z z ~
~O h o0 Ov O ~..-~N M ~h ~ ~O h o0 01 O
h h h h h o0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 Ov Ov
'n O v~
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
81
a~
>, a
_, o.
.~ = ~ _ _ _ o
C.~. ~'' ._~._C._~'N ~_ ~ .C
j, ~f:, p~,~
O ~ ~ U U N ~ U U U ~ N G, ,4
,~ ~ ~
"C ~, ~ ~ ~ 'a ~ C. ~ M ~, ~ O
p ~, ~' >, N ~ ~ >, ~ >, ~ N N
'~ N ~, M ~ ~ N ,~ >, N O C.
U ~ ~ C ~ b ~ ~ ~ G. C M ~ Q.
.C ~ U b b ~" i ,~ b b 'C G b ~ ~
N ' ~.'a. ~ '~ ~ '~.' '~ c~,-~.b w d: a.
N ~ --~ p.,t1,N N N O, M p.,~.,aa.N N
p.,N
N
>,
C ~ ~ G N C ~ ~ C ~ G C ~
_ N U U U ~ N U N U U N N U
~, d4 dD d0 b0 O bD by Gp GO ap b0 b4 b4
N ~ O O O O ;.d O O O O O O O O
N y 'b b b 'b ~E. b b 'O b b b 'b b
N ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 7, ~ >, 7,
.fl ..~.~ .~ ~ Q. .C .~ .~ .~ .~ .C
bO GUpbO bUDbU4bU4bU4bUA bU4bU0
.d .~ .~ _O _O O O O _O p ~ O O O O O O
~ .C .~ .C:~ .C .~ .~ ~ ~ >, ~, ~,
.L" ,~ .~ U U U U U U U .C .~ ~ .C .~ ..~.L"
N M ~ ~ ~p t~ 00 O~ O O O O O O O O O
Ov Ov Qv Ov O~ Ov Qv O~ .-~ .-i..-~,--r,-,.~ ~ ...,~
O tI1
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
82
0
4. ~ ~ ~ $ >, ~, ~
>, -" a~
o .~ a ~~~',.v >, ,~ a
~ p ;~ '_;',
~n >, .~ .,o ~ ~ o a.
,n ~ ''~~'~ '..~.~~vi
G _ sr ~. :o i'O..~ a~ a~ 7,
~' U .~ '~ .O ~ M
cC ~, "' G' .-r.-~~ O O
;_~ ._',. ~_~~ ~ ~ N
G. O G ~ ~, O ~ ~' O ~' b
>, ~ s.' C ~ ~h O O ' ~
Q. ~ ~ r1 cn ' .~
N Q. .n..C .~~1,..r~ ~ G1 'gin'
tt ~ N N N Q. N N N N -~ ~.,
G. N ~ GL
>,
a,
N
N ~ ~ G C C O C C C ~ Q G
O ~ _ O ~ N N N N ~ N ~ N _ O
b0 a0 ti0ap C4 dp b0 bD b0 CO b0
:O O ~ O O O O O O O O O O .C
~, .C w ~. Z. ~. sr s~ ~. ~ c. ~. .b
C~.~b '"'.O .O .O p 'C b 'n b 'L~'p ~.
~ ~ .~ ~ x ~ .~ ~ .C .~ ~ ~ ~ .C
G
p O O O ~ >t iG iG DG iG i< iC it iG iG
c. s,.,,."O O O O O O O O O O O
.b ~. ~. s..~. i, w. ~. s. w t~ ~,
O O O .O, -d 'C 'C 'O TJ 'C7TJ 'O 'T~TJ
..C,U U U .C .L.'.C',t',i.~".C . .C ,.C.' .C .C
'L,"
O~ O
O -i r.,..N-i,-M,~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O~ O N N N
.-.,,-..~.-~,--m.-i.-.-~,-..~..-a~ ,--~ ,--i
'n O
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
83
?~ ~: a~
_v >,
>, ~' ~ c''.a~'. >, ~ .a _:
~ a_.>, o o ._~ .~ ~ G
a? ' Q. o, c, ~ ~ G ~ j~ ~ a
>' ~ ?~ a ~' ~' ~ ,~ o x Q.
'O 'O M O 'O",~ ~ G.
~ N i N N
O G. O ~ O ;b ;' ~ ~ ~ ~ ~,
~ ~ ~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ .~ .G
G s-',~ s..s.. N O >, y" C~ N s..s..
i f3.N G..f3~O. O. U ~ ~ U ~ L1. U U
i i i i i i i i O N i ~ ~ i i
N N N ~ N M M ~ W n t7 N .~
O O ~ G O G G Q C C C
G~ a) N N ~ ~ N N ~ ~ ~ N
b0 bD C4 bD by b.pd0 r. bD by b0 b0 b0
O O O O O O O >, O O O O O
s..t~ ~..~, i. i. w, a.. s..4, c. 4, .n .a
~ ..C .C .~ .C .~
x x x x x x x x x x x x x
0 0 0 0 0 ~ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ~ o
b w c v b W e o ~o v b w b
.L,"..C,.C .i,".fiU .f"...C,'.C ..CiSr"~C .ti U ..Ci
~t v1 v0 I~ oo Ov O ~ N M d' vW 0 I~ o0
N N N N N N M M M M M M M M M
O
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
84
,
0
...
..~, ?> >, o ~.
>, p >,
c >, .~_ ~ ~ o ~, ~,
0 0 ,~ ~ ~ ~ a. ~ ~
~ ~ >, ~ a
~ ~ N o N N
'N '~ N ~ ,~ ~ ~ Cl,
~ ~ M ~ ,
O .-~.-~, ~ ~ C
s"' ~' b b N O
, ~ ~ ~ O C. .C ,~ O N s.. ~~.
~ ~ O. G. ~ O. G. C. O. U
ct' , , , , , U , , , , ,
CL f3.N N N ~ .-,, m-rN N -~ N
~--
C ~ C O G O C C G
O O O ~ O O O O O O ~ ~ >, O
t-. s..~. .C L, w. w. c ~. t. .C .~ a..
b .b b ~' .O '~ .O .d .b .o
.C ~ .~ ~ ~ .~ .~ .~ ~ .C ~ E
O
G
,
..
e~
N
G O O O G O G O O O i~GG C
N N ~ N N N ~ CJ N N O ~ N
b0 b0 GI7b4 b0 GD by b4 b4 d4 O ,~ d0 GO
O O O O O O O O O O ~ O O
~. ~. z. i. ~. ~, r~ w. ~, ~" ~ ~. ~.
~ T ~ ~ ~ ~ >, ~ O ~ ~ 'O
,.O.C .~ .C .C .~ .~ ,~ .O U N
Gv O ~ N M d' v1 ~C t~ 00 01 O ~ N
M ch d' d' ~ d- ~' d' ~t ~ et ~ ~ V7
O ~n
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
N
~
'~ ~ ,~
I
_
~
i. C!S ftS C~
r
G. ~ ~ w -i Q, ~ ~ Q"
~ ~ ~ ~
.rni b _ b _ Y b ~
b 'b
~. C~ Q. Ar L1.G1 C~ O, CC .a
z ~ ~ w w w w ~ w
0
Z
O
O
y
G ~ N O
O
O
O ~ ~ ~-'~ .-r O
> . ~ >' O ~ p
>
, , N j' ~ ~ ~
~
N ~ O O
. ~ ~ .~ N ~ ~ ~
... _
~ i 0 O
. .r U ~_l.CC
~r N N ~r ~, ~ ~ G. d' .D U
~C
.d
Q.
U ,-~N c~ ~r Tw o t~ 00 ov
o w,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
86
>,
....
>,
~N ~' ...,_,
cat ,.,.,
,', _ i '~ .-r.~ C i
.-r~ ~ ~ '~
_C ~' ~ ....G:
i ~ ~ p. G O ~
~N N O ~ ~.r ~ M
b O ,~ ~ ~ c~ cCt ~t3~
O C ._.... 'N ~ .-H~ 4.,it N
p,~ ~ ~O. ~ O O G ~ O. L1. >'
p~. ~ ~' ~N ~3'~, ~ b ~ .~ O A. A' p"
.O N ~ 'O O O C3. ~ .~ ~, ~, s..
s.~.~~ ~ ~ t3.~ p' ~ ~ .~C .
O ~, a~ ~ ~, ~ p" --~~ ~ ~ a: 7, ~.
y d' C~ A, .~ .O ~, ~ i
~ p" ~ ' ~ ~ iG ~ :Zj~ ~ .C ,.O ~ .C
O M ~p V ,~ b b O O N '~tN ~ N
U wr 'r cG C~ ~ ~D ~ ~ p.,'r wr y r wr wr
~ U ~
N '~t~ d' ~ M N N ~ M p.,N '~'~t d'
O O
~_ ~
_
c~ c~
Q
w w cV
G O
>,
C. O. C
N
w
z i
z
;,
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ~ ~ ~ 0 0 0 0 0 0
O O O O O O O V ~ ~ ~ O O O O O O
U U U U U U U U z z N U U U U U V
N M ~t ~n ~O l~ 00 01 O -~ N M ~ w 0 l~
~' ~' ~' ~' ~' ~' ~' ~-~~ N N N N N N N N
O
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
87
>,
-'. >, >, ~ 0 ~o ~o
>, _ ~, ~.. ~
=i ~ r; ~ ~' G~ >, O
p" 'N >, N ~ ~' y,~,~ O
~ ~ N ~N ~N C1. ~ O
G G_.._~_~ ~ ~ ii ~ ' i ~O
Oa N ~ O tt ~O
~GLO O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ M 'O b
y N C1..~~O O t3.C7. ~ ~ M ~ J, J,
~ '~ ~ ~ .O ._C C_3, ,_~.,~ _
O Q. v~0Ova ~ O p.,O. G~ C_3.~,
O '~'0 O~ O ~ Gr , ~ M M
~, >, cU~C~ >, j~ O O ~ 0 0 'L,'~"~ ~
N ~ ~ ~ ~ c~v O ~ ~ ~ ice! ~' r-i
p, G , ~,,y, U U .~ ",OU U U ~
G. G. u~..~~ ~ ~ O O ~ O O O O .O ,D
i M M ,~ ~ t~ i ~ .~
d' Wit''W N.rN N ~ N U N ~ ''''~ c U
~!'~ ~-r,~ ' i A" wr N N N ~ O"' U
~' G. ~ N N M wr M M
O
M.~
~'r ~.,"t.,"G.,"
O O O O ~ O ~ Q ~ O O O O ~ O .d
.d .~ .b .b _O .b O ..d_O O _O _O O .b O
U .C U .C U U U U U .,C U
00 C~ O ~ N M Wit'v O t~ 00 01 O .-r N M
N N M M M M M M M M M M 'Chct
O t/~
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
88
>, >,
N
G
~
N
, C
~, ~ p, .
C
N~ Q.
ih
~ , O ~ Z
C M V
.a
. b Z
.a >, ~ O
.y
.r a~ ~ .r
a~ c~.a~ ,
~
~o ~ cs.~ ;' ~ O
b ~ ~ ~ ~
M
O O O Z
~
T ~ ~y O
~ i ~ ~ G
c ~ c .
U C ~ U a
U ' U
ar ~ G~ ~1 ~1 ~,A"~C O
,
O CpsO O .-.,p ~ Z=
M ~ N C ~ V
.
a. GZ.~ N cctU
r N
~ ~ ~C.1,N N V~'M Z ~ \Z
Z=~
O
O
,
....
c~
O ~ ~ O O ~ O
O O O O O A''O
O
i. ~..c~ ~. s..
.O .C .~ ,~ ~ U
d' d' d' d' ~ d'
O
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
89
~
N
c~
L'L.-~
_ C
CL
~.'i-~.
N U
O.
C ~,
O
ces
U .C
.~
p_, ~ .C
'' C. O O
U N
N
" "
z ~,
w
a? a~ O
G. Q. N ~ ~ ~ ~ C p
.C C b ~ ~' ~ C .C".,
'~"~..Ar C3n '~ M .C'..,S'
.a A CL O.
d' N N G~.N N N N
>,
Q.
O
Q.
_ N _ _ _ _ _ N G
U
' ,~.,~ O ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ O O
N
fx M N ~ ~ ~ N ~ ~ b b
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ .C
.b
CL
U ~ N cn ~ v p t~ oo av
~n o ~n
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 90 --
Accordingly, this invention is directed to each of the following
compounds
N (3-nitrothiophen-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
S
N [1-phenyltetrazol-5-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N [1,3-dimethyl-4-nitropyrazol-S-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyl-
oxy)phenylalanine;
N [1-ethylpyrazol-5-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (4-phenylsulfonylthiophen-3-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (1,4-diphenyl-1,2,3-triazol-5-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (1-phenylimidazol-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (6-bromopyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N [6-(naphth-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {3-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]pyridin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {3-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]pyridin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N (5-trifluoropyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {5-[[5-phenylcarbonylmethylthio-4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)]
1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]pyridin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)
phenylalanine;
N (4-methyl-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 91 --
N (3,5-dinitropyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {3-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino)pyridin-4-yl}-L-
phenylalanine;
N [4-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-6-(2-methylpropylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(phenylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(benzylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethylamino]-6-[2-(4-
methylphenyl)ethylamino)]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[2-(4-methoxlphenyl)ethylamino)]-6-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-
yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[(4-chlorobenzyl)amino))-6-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-
yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethylamino]-4-[1-(phenyl)ethyl-
amino))-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N [4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-S-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-[N-methyl-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)-
amino]-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-[N,N-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-
amino]-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-[N-methyl-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-
1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 92 --
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-methyl-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-
ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-[2-(4-methoxylphenyl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N (4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N (6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(methoxyethylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [6-(chlorobenzylamino)-4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(cyclohexylmethylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-4-(2-methylpropylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(2-methylpropylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(benzylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(4-chlorobenzylamino)-6-[2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 93 --
N {4-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino)]-6-[2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl-
amino]-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(4-chlorobenzylamino)-6-[2-(4-methylphenyl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-[2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[2-(4-methoxybenzyl)amino)-1,3,5
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(1-cyclhexylethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino)-6-(3,4-methylenedioxy-
benzylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzylamino)
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-chlorobenzylamino)-4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzylamino)-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl-
amino)-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(cyclohexylmethylamino)-6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-benzyl-N-(2-propyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 94 --
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(allyl)-N-(cyclopentyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)-
amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(n-propyl)-N-(4-nitrobenzyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N,N-bis-(benzyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(2-cyanoethyl)-N-(benzyl)amino]-1,3,5
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)amino]-4-(2-methylpropyl-
amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 95 --
N {4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-[N,N-bis-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-
aminoJ-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-[N,N-bis-(benzyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-[N-(phenyl)-N-(pyridin-2-yl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N,N-bis-(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-4-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(benzyl)-N-(2-propyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1, 3 , 5-triazin-2-yl }-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)aminoJ-1, 3, 5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-6-[N-
(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1, 3 , 5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(ethyl)-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)aminoJ-1, 3 , 5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)aminoJ-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino]-6-(N-
(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)aminoJ-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methyl-
phenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-
N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)aminoJ-1, 3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 96 --
N {4-[N,N-bis-(benzyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(benzyl)amino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methyl-
phenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-lyl)ethylamino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N,N bis-(n-propyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(benzyl)-N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-
(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(5-methylisoxazol-3-ylamino)-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-
methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino]-l , 3, 5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N,N-bis-cyclohexylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-methylpropyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-phenyl-1-carboxamidoethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-[2-phenyl-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-(2-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (1-phenyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3.,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 9g __
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N-pyridin-4-ylmethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N-pyridin-3-ylmethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(2-ethylhexyl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N-pyridin-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(3,3-diphenylpropyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-pyridin-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-pyridin-3-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-2-(4-ethoxy-3-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4.-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-2-phenylpropylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-1(5~-phenylethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-ethylhexyl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 99 --
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(4-(3,5-dioxopiperazin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N,N-dimethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N (2-phenylpropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-phenyl-1-carboxamidoethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-phenyl-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-(2-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-phenyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(4-(3,5-dioxopiperazin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl)-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin- 2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-3-(imidazol-2-yl)propylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 100 --
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2- yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(N-2-(phenoxy)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-(S~-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(5-chloro-1,3-dimethylpyrazol-4-yl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(benzylsulfonyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(N-(1-(R)-phenyl-2-carboxyethyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-phenyl-1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-carboxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(4-(3,5-dioxopiperazin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 101 --
N {4-[N-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-lyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-(2-phenoxyethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-carboxy-1-(R)-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(1-ethoxycarbonyl-1-phenylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-(2-carboxy-1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L- 4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-2-methylpropylamino)-6-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-2-methylpropylamino)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-6-nitrobenzthiazol-2-ylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,IV dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-furan-2-ylmethylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-1-phenylethylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-4-chlorobenzylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 102 --
N {4-(piperidin-1-yl)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-benzylamino)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-cyclopentylamino)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(5-ethyl-2-methylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-diphenylmethylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3-methylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3,S-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N-{4-(N-cyclohexylamino-6-(3,5-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-6-(4-cyclohexyl-
piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 103 --
N {4-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-6-(3-methyl
piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-(4-aminosulfonylphenyl)ethyl)amino]-6-(piperidin-1-yl)
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(isopropylaminocarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(1-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(furan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(1-phenylpropen-1-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(isopropylaminocarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(furan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/fJS00/01540
-- 104 --
N {4-hydroxy-6-[4-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-(2-methoxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(2-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[2-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-3-oxopiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[2-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-3-oxopiperazin-1-yl)-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(3-(R)methoxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroiso-
quinolin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroiso-
quinolin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroiso-
quinolin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyl-
oxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 105 --
N {4-[2-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-3-oxopiperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(3-carboxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-methylpropyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino)-
pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-
pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-phenylethyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(benzyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]pyrimidin-
4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-methyl-2-phenylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[4-(2-propylaminocarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl)pyrimidin-4-
yl}-L-4.-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[4-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 106 --
and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
As above, this invention relates to compounds which inhibit
leukocyte adhesion and, in particular, leukocyte adhesion mediated by VLA-
4. However, prior to describing this invention in further detail, the
following terms will first be defined.
Definitions
As used herein, "alkyl" refers to alkyl groups preferably having from
1 to 10 carbon atoms and more preferably 1 to 6 carbon atoms. This term is
exemplified by groups such as methyl, t-butyl, n-heptyl, octyl and the like.
"Substituted alkyl" refers to an alkyl group, preferably of from 1 to
10 carbon atoms, having from 1 to 5 substituents selected from the group
consisting of alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, acyl, acylamino,
thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, amidino, alkyl amidino,thioamidino,
aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonylamino,
aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy,
aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, cyano, halogen, hydroxyl, nitro,
carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl, carboxyl-cycloalkyl,
carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-substituted aryl,
carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl, carboxylheterocyclic,
carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 107 --
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)2-
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)2-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted aryl, -OS(O)Z-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ NRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O~-alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)~-substituted aryl,
-NRS(O)Z-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z
heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)z-NR-alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)z-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and di-
substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and di-
substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and substituted alkyl groups having amino groups blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
alkyl/substituted alkyl groups substituted with -SOZ-alkyl, -SOZ-substituted
alkyl, -SOZ-alkenyl, -SO,-substituted alkenyl, -SOZ-cycloalkyl, -SOZ-
substituted cycloalkyl, -SOZ-aryl, -SOZ-substituted aryl, -SOZ-heteroaryl,
-SOZ-substituted heteroaryl, -SOZ-heterocyclic, -SO,-substituted heterocyclic
and -SOZNRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
"Alkoxy" refers to the group "alkyl-O-" which includes, by way of
example, methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, iso-propoxy, n-butoxy, tert-butoxy,
sec-butoxy, n-pentoxy, n-hexoxy, 1,2-dimethylbutoxy, and the like.
"Substituted alkoxy" refers to the group "substituted alkyl-O-".
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 108 --
"Alkenoxy" refers to the group "alkenyl-O-" .
"Substituted alkenoxy" refers to the group "substituted alkenyl-O-"
"Acyl" refers to the groups H-C(O)-, alkyl-C(O)-, substituted alkyl-
C(O)-, alkenyl-C(O)-, substituted alkenyl-C(O)-, alkynyl-C(O)-, substituted
alkynyl-C(O)- cycloalkyl-C(O)-, substituted cycloalkyl-C(O)-, aryl-C(O)-,
substituted aryl-C(O)-, heteroaryl-C(O)-, substituted heteroaryl-C(O),
heterocyclic-C(O)-, and substituted heterocyclic-C(O)- wherein alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl,
cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as
defined herein.
"Acylamino" refers to the group -C(O)NRR where each R is
independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl,
aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic and where each
R is joined to form together with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or
substituted heterocyclic ring wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl,
substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Thiocarbonylamino" refers to the group -C(S)NRR where each R is
independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl,
aryl, substituted aryl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic and where each
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 109 --
R is joined to form, together with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or
substituted heterocyclic ring wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl,
substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl; aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Acyloxy" refers to the groups alkyl-C(O)O-, substituted alkyl-
C(O)O-, alkenyl-C(O)O-, substituted alkenyl-C(O)O-, alkynyl-C(O)O-,
substituted alkynyl-C(O)O-, aryl-C(O)O-, substituted aryl-C(O)O-,
cycloalkyl-C(O)O-, substituted cycloalkyl-C(O)O-, heteroaryl-C(O)O-,
substituted heteroaryl-C(O)O-, heterocyclic-C(O)O-, and substituted
heterocyclic-C(O)O- wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted
alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
aryl,
substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and
substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Alkenyl" refers to alkenyl group preferably having from 2 to 10
carbon atoms and more preferably 2 to 6 carbon atoms and having at least 1
and preferably from 1-2 sites of alkenyl unsaturation.
"Substituted alkenyl" refers to alkenyl groups having from 1 to 5
substituents selected from the group consisting of alkoxy, substituted alkoxy,
acyl, acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, amidino,
alkylamidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino, aminothio-
carbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy,
substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, halogen, hydroxyl,
cyano, nitro, carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl, carboxyl-
cycloalkyl, carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-
substituted aryl, carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl,
carboxylheterocyclic, carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 110 --
substituted cycloalkyl, guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl,
substituted thioalkyl, thioaryl, substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl,
substituted thiocycloalkyl, thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl,
thioheterocyclic, substituted thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted
cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy,
substituted heterocyclyloxy, oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino,
-OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)Z-substituted alkyl, -OS(O)Z-aryl, -OS(O)2-substituted
aryl, -OS(O)2-heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)Z-
heterocyclic, -OS(O),-substituted heterocyclic, -OSO~-NRR where R is
hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-alkyl, -NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)~-
aryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted aryl, ,-NRS(O)Z-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heterocyclic,
-NRS(O)2-NR-alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-aryl,
-NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted aryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-
substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and di-
substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and di-
substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and substituted alkenyl groups having amino groups blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
alkenyl/substituted alkenyl groups substituted with -SOZ-alkyl, -SOZ-
substituted alkyl, -SOZ-alkenyl, -SOZ-substituted alkenyl, -SOZ-cycloalkyl,
-SOZ-substituted cycloalkyl, -SOZ-aryl, -SO,-substituted aryl, -SOZ-
heteroaryl, -SOz-substituted heteroaryl, -SOZ-heterocyclic, -SOZ-substituted
heterocyclic and -SOZNRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/fJS00/01540
--111--
"Alkynyl" refers to alkynyl group preferably having from 2 to 10
carbon atoms and more preferably 3 to 6 carbon atoms and having at least 1
and preferably from 1-2 sites of alkynyl unsaturation.
"Substituted alkynyl" refers to alkynyl groups having from 1 to 5
substituents selected from the group consisting of alkoxy, substituted alkoxy,
acyl, acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, amidino,
alkylamidino, thioamidino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino, aminothio-
carbonylamino, aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy,
substituted aryloxy, aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, halogen, hydroxyl,
cyano, vitro, carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl, carboxyl-
cycloalkyl, carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-
substituted aryl, carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl,
carboxylheterocyclic, carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl,
substituted cycloalkyl, guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl,
substituted thioalkyl, thioaryl, substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl,
substituted thiocycloalkyl, thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl,
thioheterocyclic, substituted thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted
cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy,
substituted heterocyclyloxy, oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino,
-OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -OS(O)Z-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted
aryl, -OS(O)2-heteroaryl, -OS(O)Z substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)Z-
heterocyclic, -OS(O)z-substituted heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where R is
hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O)2-alkyl, -NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-
aryl, -NRS(O)Z substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heterocyclic,
-NRS(O)2-NR-alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-aryl,
-NRS(O)2-NR-substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)~-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 112 --
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and di-
substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and di-
substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and substituted alkynyl groups having amino groups blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
alkynyl/substituted alkynyl groups substituted with -SO,-alkyl, -SOZ-
substituted alkyl, -SO~-alkenyl, -SOZ-substituted alkenyl, -SOZ-cycloalkyl,
-SOZ-substituted cycloalkyl, -SOZ-aryl, -SOZ-substituted aryl, -SOZ-
heteroaryl, -SOZ-substituted heteroaryl, -SOZ-heterocyclic, -SOZ-substituted
heterocyclic and -SO,NRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
"Amidino" refers to the group HZNC(=NH)- and the term
"alkylamidino" refers to compounds having 1 to 3 alkyl groups (e.g.,
alkylHNC(=NH)-).
"Thioamidino" refers to the group RSC(=NH)- where R is hydrogen
or alkyl.
"Amino" refers to the group -NHz.
"Substituted amino" refers to the group -NRR, where each R group is
independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl,
cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, -SOZ-alkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 113 --
-SOZ-substituted alkyl, -SO~-alkenyl, -SOZ-substituted alkenyl, -SOz-
cycloalkyl, -SO~-substituted cycloalkyl, -SOZ-aryl, -SOZ-substituted aryl,
-SOZ-heteroaryl, -SOZ-substituted heteroaryl, -SOZ-heterocyclic, -SOz-
substituted heterocyclic, provided that both R groups are not hydrogen; or
the R groups can be joined together with the nitrogen atom to form a
heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring.
"Aminoacyl" refers to the groups -NRC(O)alkyl,
-NRC(O)substituted alkyl, -NRC(O)cycloalkyl, -NRC(O)substituted
cycloalkyl, -NRC(O)alkenyl, -NRC(O)substituted alkenyl, -NRC(O)alkynyl,
-NRC(O)substituted alkynyl, -NRC(O)aryl, -NRC(O)substituted aryl,
-NRC(O)heteroaryl, -NRC(O)substituted heteroaryl, -NRC(O)heterocyclic,
and -NRC(O)substituted heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl and
wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl,
substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted
aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic
are as defined herein.
"Aminosulfonyl" refers to the groups -NRSO,alkyl,
-NRSO~substituted alkyl, -NRSOZCycloalkyl, -NRSO,substituted cycloalkyl,
-NRSO~alkenyl, -NRSOZSUbstituted alkenyl, -NRSOZalkynyl,
-NRSO,substituted alkynyl, -NRSOzaryl, -NRSOZSUbstituted aryl,
-NRSOZheteroaryl, -NRSOZSUbstituted heteroaryl, -NRSO~heterocyclic, and
-NRSOZSUbstituted heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl and wherein
alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted
alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as
defined herein.
"Aminocarbonyloxy" refers to the groups -NRC(O)O-alkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 114 --
-NRC(O)O-substituted alkyl, -NRC(O)O-alkenyl, -NRC(O)O-substituted
alkenyl, -NRC(O)O-alkynyl, -NRC(O)O-substituted alkynyl, -NRC(O)O-
cycloalkyl, -NRC(O)O-substituted cycloalkyl, -NRC(O)O-aryl, -NRC(O)O-
substituted aryl, -NRC(O)O-heteroaryl, -NRC(O)O-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRC(O)O-heterocyclic, and -NRC(O)O-substituted heterocyclic where R is
hydrogen or alkyl and wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted
alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl; substituted cycloalkyl,
aryl,
substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and
substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Aminosulfonyloxy" refers to the groups -NRSO20-alkyl,
-NRSO20-substituted alkyl, -NRSO,O-alkenyl, -NRSOZO-substituted
alkenyl, -NRSO20-alkynyl, -NRSO20-substituted alkynyl, -NRSO20-
cycloalkyl, -NRSO20-substituted cycloalkyl, -NRSOZO-aryl, -NRSO20-
substituted aryl, -NRSOzO-heteroaryl, -NRSO20-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRSOzO-heterocyclic, and -NRSOZO-substituted heterocyclic where R is
hydrogen or alkyl and wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted
alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
aryl,
substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and
substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Oxycarbonylamino" refers to the groups -OC(O)NH2, -OC(O)NRR,
-OC(O)NR-alkyl, -OC(O)NR-substituted alkyl, -OC(O)NR-alkenyl,
-OC(O)NR-substituted alkenyl, -OC(O)NR-alkynyl, -OC(O)NR-substituted
alkynyl, -OC(O)NR-cycloalkyl, -OC(O)NR-substituted cycloalkyl,
-OC(O)NR-aryl, -OC(O)NR-substituted aryl, -OC(O)NR-heteroaryl,
-OC(O)NR-substituted heteroaryl,- OC(O)NR-heterocyclic, and
-OC(O)NR-substituted heterocyclic where R is hydrogen, alkyl or where
each R is joined to form, together with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or
substituted heterocyclic ring and wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 115 --
substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Oxysulfonylamino" refers to the groups -OSOZNHZ, -OSOZNRR,
-OSOzNR-alkyl, -OSOZNR-substituted alkyl, -OS02NR-alkenyl,
-OSOZNR-substituted alkenyl, -OSOZNR-alkynyl, -OSO~NR-substituted
alkynyl, -OSOZNR-cycloalkyl, -OSOZNR-substituted cycloalkyl,
-OSOZNR-aryl, -OSOZNR-substituted aryl, -OSO~NR-heteroaryl,
-OSO~NR-substituted heteroaryl, -OSOzNR-heterocyclic, and
-OSO~NR-substituted heterocyclic where R is hydrogen, alkyl or where each
R is joined to form, together with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or
substituted heterocyclic ring and wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl,
substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Oxysulfonyl" refers to the groups alkyl-SOZO-, substituted alkyl-
SOZO-, alkenyl-SOZO-, substituted alkenyl-SO~O-, alkynyl-SOZO-,
substituted alkynyl-SOZO-, aryl-SO20-, substituted aryl-SO,O-, cycloalkyl
SOZO-, substituted cycloalkyl-SO~O-, heteroaryl-SOZO-, substituted
heteroaryl-SOZO-, heterocyclic-SO~O-, and substituted heterocyclic-SOZO-
wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl,
substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted
aryl,
heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic
are as defined herein.
"Oxythiocarbonylamino" refers to the groups -OC(S)NH2,
-OC(S)NRR, -OC(S)NR-alkyl, -OC(S)NR-substituted alkyl, -OC(S)NR
alkenyl, -OC(S)NR-substituted alkenyl, -OC(S)NR-alkynyl, -OC(S)NR-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 116 --
substituted alkynyl, -OC(S)NR-cycloalkyl, -OC(S)NR-substituted cycloalkyl,
-OC(S)NR-aryl, -OC(S)NR-substituted aryl, -OC(S)NR-heteroaryl,
-OC(S)NR-substituted heteroaryl, -OC(S)NR-heterocyclic, and
-OC(S)NR-substituted heterocyclic where R is hydrogen, alkyl or where
each R is joined to form together with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or
substituted heterocyclic ring and wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl,
substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Aminocarbonylamino" refers to the groups -NRC(O)NRR,
-NRC(O)NR-alkyl, -NRC(O)NR-substituted alkyl, -NRC(O)NR-alkenyl,
-NRC(O)NR-substituted alkenyl, -NRC(O)NR-alkynyl,
-NRC(O)NR-substituted alkynyl, -NRC(O)NR-aryl, -NRC(O)NR-substituted
aryl, -NRC(O)NR-cycloalkyl, -NRC(O)NR-substituted cycloalkyl,
-NRC(O)NR-heteroaryl, and -NRC(O)NR-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRC(O)NR-heterocyclic, and -NRC(O)NR-substituted heterocyclic where
each R is independently hydrogen, alkyl or where each R is joined to form
together with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic
ring as well as where one of the amino groups is blocked by conventional
blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like and wherein alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl,
cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as
defined herein.
"Aminothiocarbonylamino" refers to the groups -NRC(S)NRR,
-NRC(S)NR-alkyl, -NRC(S)NR-substituted alkyl, -NRC(S)NR-alkenyl,
-NRC(S)NR-substituted alkenyl, -NRC(S)NR-alkynyl, -NRC(S)NR-
substituted alkynyl, -NRC(S)NR-aryl, -NRC(S)NR-substituted aryl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 117 --
-NRC(S)NR-cycloalkyl, -NRC(S)NR-substituted cycloalkyl, -NRC(S)NR-
heteroaryl, and -NRC(S)NR-substituted heteroaryl, -NRC(S)NR-
heterocyclic, and -NRC(S)NR-substituted heterocyclic where each R is
independently hydrogen, alkyl or where each R is joined to form together
with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic ring as well
as where one of the amino groups is blocked by conventional blocking
groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like and wherein alkyl, substituted
alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Aminosulfonylamino" refers to the groups -NRSOZNRR,
-NRSOZNR-alkyl, -NRSOZNR-substituted alkyl, -NRSOZNR-alkenyl,
-NRSOZNR-substituted alkenyl, -NRSOZNR-alkynyl,
-NRSO~NR-substituted alkynyl, -NRSOzNR-aryl, -NRSOZNR-substituted
aryl, -NRSOZNR-cycloalkyl, -NRSOZNR-substituted cycloalkyl,
-NRSOZNR-heteroaryl, and -NRSOZNR-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRSOzNR-heterocyclic, and -NRSO~NR-substituted heterocyclic, where
each R is independently hydrogen, alkyl or where each R is joined to form
together with the nitrogen atom a heterocyclic or substituted heterocyclic
ring as well as where one of the amino groups is blocked by conventional
blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like and wherein alkyl,
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl,
cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as
defined herein.
"Aryl" or "Ar" refers to an unsaturated aromatic carbocyclic group
of from 6 to 14 carbon atoms having a single ring (e.g., phenyl) or multiple
condensed rings (e.g., naphthyl or anthryl) which condensed rings may or.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 118 --
may not be aromatic (e.g., 2-benzoxazolinone, 2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-
one-7y1, and the like). Preferred aryls include phenyl and naphthyl.
Substituted aryl refers to aryl groups which are substituted with from
S 1 to 3 substituents selected from the group consisting of hydroxy, acyl,
acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy,
substituted alkoxy, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted
alkynyl,
amidino, alkylamidino, thioamidino, amino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonyloxy,
aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonylamino, aryl, substituted aryl,
aryloxy, substituted aryloxy, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy,
heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted
heterocyclyloxy, carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl,
carboxyl-cycloalkyl, carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-
substituted aryl, carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl,
carboxylheterocyclic, carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, carboxylamido,
cyano, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl, thioaryl, substituted
thioaryl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted
thiocycloalkyl, thioheterocyclic, substituted thioheterocyclic, cycloalkyl,
substituted cycloalkyl, guanidino, guanidinosulfone, halo, nitro, heteroaryl,
substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy,
substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy,
heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy, oxycarbonylamino,
oxythiocarbonylamino, -S(O)2-alkyl, -S(O)2-substituted alkyl, -S(O)2-
cycloalkyl, -S(O)Z-substituted cycloalkyl, -S(O)Z-alkenyl, -S(O)Z-substituted
alkenyl, -S(O)2-aryl, -S(O)2-substituted aryl, -S(O)2-heteroaryl, -S(O)2-
substituted heteroaryl, -S(O)Z-heterocyclic, -S(O)z-substituted heterocyclic,
-OS(O)2-alkyl, -OS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -OS(O)2-aryl, -OS(O)z-substituted
aryl, -OS(O)Z-heteroaryl, -OS(O)z-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)Z-
heterocyclic, -OS(O)z-substituted heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where R is
hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-alkyl, -NRS(O)z-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 119 --
aryl, -NRS(O)z-substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heterocyclic,
-NRS(O)2-NR-alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-aryl,
-NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and di-
substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and di-
substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and amino groups on the substituted aryl blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
substituted with -SOZNRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
"Aryloxy" refers to the group aryl-O- which includes, by way of
example, phenoxy, naphthoxy, and the like.
"Substituted aryloxy" refers to substituted aryl-O- groups.
"Aryloxyaryl" refers to the group -aryl-O-aryl.
"Substituted aryloxyaryl" refers to aryloxyaryl groups substituted
with from 1 to 3 substituents on either or both aryl rings selected from the
group consisting of hydroxy, acyl, acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy,
alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, alkenyl, substituted
alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, amidino, alkylamidino, thioamidino,
amino, aminoacyl, aminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonylamino, aminothio-
carbonylamino, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 120 --
cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted
heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy, carboxyl,
carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl, carboxyl-cycloalkyl, carboxyl-
substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-substituted aryl,
carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl, carboxylheterocyclic,
carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, carboxylamido, cyano, thiol, thioalkyl,
substituted thioalkyl, thioaryl, substituted thioaryl, thioheteroaryl,
substituted thioheteroaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheterocyclic, substituted thioheterocyclic, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, guanidino, guanidinosulfone, halo, vitro, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted
cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy,
substituted heterocyclyloxy, oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino,
-S(O)Z-alkyl, -S(O)2-substituted alkyl, -S(O)Z-cycloalkyl, -S(O)z-substituted
cycloalkyl, -S(O)Z-alkenyl, -S(O)Z-substituted alkenyl, -S(O)z-aryl, -S(O)2-
substituted aryl, -S(O)Z-heteroaryl, -S(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -S(O)Z-
heterocyclic, -S(O)2-substituted heterocyclic, -OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)z-
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)2-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted aryl, -OS(O)2-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O~-alkyl,
-NRS(O)z-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted aryl,
-NRS(O)2-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-
heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)z-NR-alkyl,
-NRS(O)z-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)~ NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and di-
substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and di-
substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 121 --
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and amino groups on the substituted aryl blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
substituted with -SOZNRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
"Cycloalkyl" refers to cyclic alkyl groups of from 3 to 8 carbon
atoms having a single cyclic ring including, by way of example, cyclopropyl,
cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclooctyl and the like. Excluded from this
definition are mufti-ring alkyl groups such as adamantanyl, etc.
"Cycloalkenyl" refers to cyclic alkenyl groups of from 3 to 8 carbon
atoms having single or multiple unsaturation but which are not aromatic.
"Substituted cycloalkyl" and "substituted cycloalkenyl" refer to a
cycloalkyl and cycloalkenyl groups, preferably of from 3 to 8 carbon atoms,
having from 1 to 5 substituents selected from the group consisting of oxo
(=O), thioxo (=S), alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, acyl, acylamino,
thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, amidino, alkylamidino, thioamidino,
aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonylamino,
aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy,
aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, halogen, hydroxyl, cyano, nitro,
carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl, carboxyl-cycloalkyl,
carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-substituted aryl,
carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl, carboxylheterocyclic,
carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 122 --
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)2_
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)2-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted aryl, -OS(O)Z-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O~-alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-aryl, -NRS(O)z-substituted aryl,
-NRS(O)2-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-
heterocyclic, -NRS(O),-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)z-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and di-
substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and di-
substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and substituted alkynyl groups having amino groups blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
alkynyl/substituted alkynyl groups substituted with -SOZ-alkyl, -SOZ-
substituted alkyl, -SOZ-alkenyl, -SOZ-substituted alkenyl, -SOZ-cycloalkyl,
-SOZ-substituted cycloalkyl, -SOZ-aryl, -SOZ-substituted aryl, -SOZ-
heteroaryl, -SOZ-substituted heteroaryl, -SOZ-heterocyclic, -SO~-substituted
heterocyclic and -SOZNRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
"Cycloalkoxy" refers to -O-cycloalkyl groups.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 123 --
"Substituted cycloalkoxy" refers to -O-substituted cycloalkyl groups.
"Cycloalkenoxy" refers to -O-cycloalkenyl groups.
"Substituted cycloalkenoxy" refers to -O-substituted cycloalkenyl
groups.
"Guanidino" refers to the groups -NRC(=NR)NRR,
-NRC(=NR)NR-alkyl, -NRC(=NR)NR-substituted alkyl, -NRC(=NR)NR-
alkenyl, -NRC(=NR)NR-substituted alkenyl, -NRC(=NR)NR-alkynyl,
-NRC(=NR)NR-substituted alkynyl, -NRC(=NR)NR-aryl,
-NRC(=NR)NR-substituted aryl, -NRC(=NR)NR-cycloalkyl,
-NRC(=NR)NR-heteroaryl, -NRC(=NR)NR-substituted heteroaryl,
-NRC(=NR)NR-heterocyclic, and -NRC(=NR)NR-substituted heterocyclic
where each R is independently hydrogen and alkyl as well as where one of
the amino groups is blocked by conventional blocking groups such as Boc,
Cbz, formyl, and the like and wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl,
substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Guanidinosulfone" refers to the groups -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-alkyl,
-NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-substituted alkyl, -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-alkenyl,
-NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-substituted alkenyl, -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-alkynyl,
-NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-substituted alkynyl, -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-aryl,
-NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-substituted aryl, -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-cycloalkyl,
-NRC(=NR)NRSOz-substituted cycloalkyl, -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-heteroaryl,
and -NRC(=NR)NRSO~-substituted heteroaryl, -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-
heterocyclic, and -NRC(=NR)NRSOZ-substituted heterocyclic where each R
is independently hydrogen and alkyl and wherein alkyl, substituted alkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 124 --
alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, cycloalkyl,
substituted cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted
heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic are as defined herein.
"Halo" or "halogen" refers to fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo and
preferably is either chloro or bromo.
"Heteroaryl" refers to an aromatic carbocyclic group of from 2 to 10
carbon atoms and 1 to 4 heteroatoms selected from oxygen, nitrogen and
sulfur within the ring or oxides thereof. Such heteroaryl groups can have a
single ring (e.g., pyridyl or furyl) or multiple condensed rings (e.g.,
indolizinyl or benzothienyl). Preferred heteroaryls include pyridyl, pyrrolyl,
indolyl and furyl.
"Substituted heteroaryl" refers to heteroaryl groups which are
substituted with from 1 to 3 substituents selected from the group consisting
of hydroxy, acyl, acylamino, thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, alkyl, substituted
alkyl, alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl,
substituted alkynyl, amidino, alkylamidino, thioamidino, amino, aminoacyl,
aminocarbonyloxy, aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonylamino, aryl,
substituted aryl, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy, cycloalkoxy, substituted
cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy,
substituted heterocyclyloxy, carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted
alkyl, carboxyl-cycloalkyl, carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl,
carboxyl-substituted aryl, carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted
heteroaryl, carboxylheterocyclic, carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic,
carboxylamido, cyano, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl, thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl,
thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl, guanidino,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 125 --
guanidinosulfone, halo, vitro, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl,
heterocyclic, substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy,
heteroaryloxy, substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted
heterocyclyloxy, oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -S(O)S-alkyl,
-S(O)Z-substituted alkyl, -S(O)Z-cycloalkyl, -S(O)2-substituted cycloalkyl,
-S(O)Z-alkenyl, -S(O)2-substituted alkenyl, -S(O)2-aryl, -S(O)2-substituted
aryl, -S(O)Z-heteroaryl, -S(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl, -S(O)2-heterocyclic,
-S(O)Z-substituted heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-alkyl, -OS(O)Z-substituted alkyl,
-OS(O)2-aryl, -OS(O)2-substituted aryl, -OS(O)Z-heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-
substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(O~-alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-aryl, -NRS(O)Z-substituted aryl,
-NRS(O)z-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z
heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-alkyl,
-NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and di-
substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and di-
substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and amino groups on the substituted aryl blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
substituted with -SOZNRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
"Heteroaryloxy" refers to the group -O-heteroaryl and "substituted
heteroaryloxy" refers to the group -O-substituted heteroaryl.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 126 --
"Heterocycle" or "heterocyclic" refers to a saturated or unsaturated
group having a single ring or multiple condensed rings, from 1 to 10 carbon
atoms and from 1 to 4 hetero atoms selected from nitrogen, sulfur or oxygen
within the ring wherein, in fused ring systems, one or more of the rings can
S be aryl or heteroaryl.
"Substituted heterocyclic" refers to heterocycle groups which are
substituted with from 1 to 3 substituents selected from the group consisting
of oxo (=O), thioxo (=S), alkoxy, substituted alkoxy, acyl, acylamino,
thiocarbonylamino, acyloxy, amino, amidino, alkylamidino, thioamidino,
aminoacyl, aminocarbonylamino, aminothiocarbonylamino,
aminocarbonyloxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aryloxy, substituted aryloxy,
aryloxyaryl, substituted aryloxyaryl, halogen, hydroxyl, cyano, nitro,
carboxyl, carboxylalkyl, carboxyl-substituted alkyl, carboxyl-cycloalkyl,
carboxyl-substituted cycloalkyl, carboxylaryl, carboxyl-substituted aryl,
carboxylheteroaryl, carboxyl-substituted heteroaryl, carboxylheterocyclic,
carboxyl-substituted heterocyclic, cycloalkyl, substituted cycloalkyl,
guanidino, guanidinosulfone, thiol, thioalkyl, substituted thioalkyl,
thioaryl,
substituted thioaryl, thiocycloalkyl, substituted thiocycloalkyl,
thioheteroaryl, substituted thioheteroaryl, thioheterocyclic, substituted
thioheterocyclic, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic,
substituted
heterocyclic, cycloalkoxy, substituted cycloalkoxy, heteroaryloxy,
substituted heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy, substituted heterocyclyloxy,
oxycarbonylamino, oxythiocarbonylamino, -OS(O)Z-alkyl, -OS(O)2-
substituted alkyl, -OS(O)2-aryl, -OS(O)Z-substituted aryl, -OS(O)z-heteroaryl,
-OS(O)Z-substituted heteroaryl, -OS(O)2-heterocyclic, -OS(O)2-substituted
heterocyclic, -OSOZ-NRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl, -NRS(Oh-alkyl,
-NRS(O)2-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)2-aryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted aryl,
-NRS(O)z-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-substituted heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-
heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-substituted heterocyclic, -NRS(O)2-NR-alkyl,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 127 --
-NRS(O)2-NR-substituted alkyl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-
substituted aryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-heteroaryl, -NRS(O)2-NR-substituted
heteroaryl, -NRS(O)Z-NR-heterocyclic, -NRS(O)Z-NR-substituted
heterocyclic where R is hydrogen or alkyl, mono- and di-alkylamino, mono-
and di-(substituted alkyl)amino, mono- and di-arylamino, mono- and
di-substituted arylamino, mono- and di-heteroarylamino, mono- and
di-substituted heteroarylamino, mono- and di-heterocyclic amino, mono- and
di-substituted heterocyclic amino, unsymmetric di-substituted amines having
different substituents selected from alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl,
substituted
aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, heterocyclic and substituted
heterocyclic and substituted alkynyl groups having amino groups blocked by
conventional blocking groups such as Boc, Cbz, formyl, and the like or
alkynyl/substituted alkynyl groups substituted with -SOZ-alkyl, -SOZ-
substituted alkyl, -SOZ-alkenyl, -SOZ-substituted alkenyl, -SOZ-cycloalkyl,
-SOZ-substituted cycloalkyl, -SOZ-aryl, -SOZ-substituted aryl, -SOZ_
heteroaryl, -SOZ-substituted heteroaryl, -SOZ-heterocyclic, -SO,-substituted
heterocyclic and -SOZNRR where R is hydrogen or alkyl.
Examples of heterocycles and heteroaryls include, but are not limited
to, azetidine, pyrrole, imidazole, pyrazole, pyridine, pyrazine, pyrimidine,
pyridazine, indolizine, isoindole, indole, dihydroindole, indazole, purine,
quinolizine, isoquinoline, quinoline, phthalazine, naphthylpyridine,
quinoxaline, quinazoline, cinnoline, pteridine, carbazole, carboline,
phenanthridine, acridine, phenanthroline, isothiazole, phenazine, isoxazole,
phenoxazine, phenothiazine, imidazolidine, imidazoline, piperidine,
piperazine, indoline, phthalimide, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, 4,5,6,7-
tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene, thiazole, thiazolidine, thiophene,
benzo[b]thiophene, morpholino, thiomorpholino, piperidinyl, pyrrolidine,
tetrahydrofuranyl, and the like.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 128 --
"Heterocyclyloxy" refers to the group -O-heterocyclic and
"substituted heterocyclyloxy" refers to the group -O-substituted heterocyclic.
"Thiol" refers to the group -SH.
"Thioalkyl" refers to the groups -S-alkyl
"Substituted thioalkyl" refers to the group -S-substituted alkyl.
"Thiocycloalkyl" refers to the groups -S-cycloalkyl.
"Substituted thiocycloalkyl" refers to the group -S-substituted
cycloalkyl.
"Thioaryl" refers to the group -S-aryl and "substituted thioaryl"
refers to the group -S-substituted aryl.
"Thioheteroaryl" refers to the group -S-heteroaryl and "substituted
thioheteroaryl" refers to the group -S-substituted heteroaryl.
"Thioheterocyclic" refers to the group -S-heterocyclic and
"substituted thioheterocyclic" refers to the group -S-substituted
heterocyclic.
"Pharmaceutically acceptable salt" refers to pharmaceutically
acceptable salts of a compound of Formula I which salts are derived from a
variety of organic and inorganic counter ions well known in the art and
include, by way of example only, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium,
ammonium, tetraalkylammonium, and the like; and when the molecule
contains a basic functionality, salts of organic or inorganic acids, such as
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 129 --
hydrochloride, hydrobromide, tartrate, mesylate, acetate, maleate, oxalate
and the like.
Compound Preparation
The compounds of this invention can be prepared from readily
available starting materials using the following general methods and
procedures. It will be appreciated that where typical or preferred process
conditions (i.e., reaction temperatures, times, mole ratios of reactants,
solvents, pressures, etc.) are given, other process conditions can also be
used
unless otherwise stated. Optimum reaction conditions may vary with the
particular reactants or solvent used, but such conditions can be determined
by one skilled in the art by routine optimization procedures.
Additionally, as will be apparent to those skilled in the art,
conventional protecting groups may be necessary to prevent certain
functional groups from undergoing undesired reactions. Suitable protecting
groups for various functional groups as well as suitable conditions for
protecting and deprotecting particular functional groups are well known in
the art. For example, numerous protecting groups are described in T. W.
Greene and G. M. Wuts, Protecting Groups in Organic Synthesis, Second
Edition, Wiley, New York, 1991, and references cited therein.
Furthermore, the compounds of this invention will typically contain
one or more chiral centers. Accordingly, if desired, such compounds can be
prepared or isolated as pure stereoisomers, i.e., as individual enantiomers or
diastereomers, or as stereoisomer-enriched mixtures. All such stereoisomers
(and enriched mixtures) are included within the scope of this invention,
unless otherwise indicated. Pure stereoisomers (or enriched mixtures) may
be prepared using, for example, optically active starting materials or
stereoselective reagents well-known in the art. Alternatively, racemic
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 130 --
mixtures of such compounds can be separated using, for example, chiral
column chromatography, chiral resolving agents and the like.
In a preferred method of synthesis, the compounds of this invention
are prepared by coupling an amino acid derivative of the formula:
3 3'
OY
H2N
O
where R3 and R3' are as defined herein and Y is an alkyl group such
as methyl, ethyl and the like, with a suitably functionalized aryl,
heteroaryl,
cycloalkyl or cycloalkenyl intermediate. For example, such coupling
reactions may be performed by displacing a leaving group, such as chloro,
bromo, iodo, tosyl and the like, from the aryl, heteroaryl, cycloalkyl or
cycloalkenyl intermediate with the amino group of the amino acid derivative;
or by reductive alkylation of the amino group of amino acid derivative with a
carbonyl-functionalized intermediate. Such coupling reactions are well-
known to those skilled in the art.
By way of illustration, the synthesis of some representative
compounds of formula IIb wherein B is a substituted 1,3,5-triazine, Q is -
NH-, R3' is hydrogen, and X is alkoxy or hydroxy is shown in Scheme 1
below.
Scheme 1
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 131 --
R3
CI~N~CI
CI N\ HN~C(O)X
N ~ N + HzN C(O)X
N ~N
C (X = alkoxy)
1 2 CI
R3 R3
NR3°R3' CI N\ HN~C(O)X NR33R34 NRssRsa N\ HN~C(O)X
N Y N ~ N Y N
NR3°Ra~ NI Rs°Rs~
H20, H+
IIb (c) IIb'
1H1 (b) (c)
R3 R3
N~ HN ~C(O)X R~ N~ HN ~C(O)OH
N ~N -> N ~N
RsoRs~ (c) RsoRs~
IIb" Ilb"'
(R~is hydrogen, chloro or
-NR33R34 )
A compound of formula IIb where B is a triazine ring carrying a
chloro, hydrogen, or substituted amino group at the 4- position and
substituted amino group at the 6-position can prepared as shown in Scheme 1
above.
Reaction of 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine 1 (commercially available
from Aldrich Chemical Company, Milwaukee, Wisconsin USA) with about
one molar equivalent of an amino acid derivative of the formula:
HZN-CH(R3)C(O)X
2
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 132 --
where R3 is as defined in the Summary of the Invention and X is
alkoxy such as methoxy, ethoxy, or tent-butyoxy and the like, in the presence
of a trialkylamine, such as diisopropylethylamine (DIEA), provides a
compound of formula 3. This reaction is typically conducted in an inert
solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, at a temperature ranging from about
0°C to
about ambient temperature for about 5 min. to about 6 hours, preferably 2
hours.
Compound 3 is then reacted with an amine of formula 4 wherein R3o
and R31 are as defined above to provide a compound of formula IIb wherein
the triazine ring is substituted with a chloro at the 4-position and a
substituted amino at the 6-position. The reaction is carried out in the
presence of a non-nucleophilic base such as N,N-diisopropylethylamine,
pyridine, and the like and in an inert solvent such as N,N-dimethyl-
formamide, tetrahydrofuran, and the like.
A compound of formula IIb can be converted to other compounds of
formula IIb by methods well known in the art. For example, as shown in
method (a), reaction of a compound of formula IIb with an amine of formula
NR33Rsa (wherein R33 and R34 are as defined above) provides a compound of
formula II' wherein the triazine ring is substituted with a substituted amino
group at the 4 and the 6-positions. As shown in method (b), a compound of
formula IIb with a chloro group in the triazine ring can hydrogenated to
provide a corresponding de-chlorinated compound of formula IIb". Lastly,
as shown in method (c), compounds of formulae IIb, IIb', and IIb"
where X is alkoxy can be converted to a corresponding compound of formula
IIb"' where X is hydroxy under acidic hydrolysis reaction condition.
Suitable acids are hydrochloric acid, trifluoroacetic acid, and the like.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 133 --
Other heteroaryls may also be employed in the above described
reactions including, but not limited to, 2-chloro-4-methyl-3-nitropyridine, 2-
chloro-3-nitropyridine (Aldrich Chemical Co.); 4-chloro-3-nitropyridine (J.
Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 2474-2485); 4-chloro-5-nitroimidazole (J. Chem.
Soc. 1930, 268); and the like, to provide compounds of this invention.
The amino acid derivatives employed in the above reactions are either
known compounds or compounds that can be prepared from known
compounds by conventional synthetic procedures. For example, amino acid
derivatives can be prepared by Galkylating commercially available diethyl
2-acetamidomalonate (Aldrich, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA) with an alkyl
or substituted alkyl halide. This reaction is typically conducted by treating
the diethyl 2-acetamidomalonate with at least one equivalent of sodium
ethoxide and at least one equivalent of an alkyl or substituted alkyl halide
in
refluxing ethanol for about 6 to about 12 hours. The resulting C-alkylated
malonate is then deacetylated, hydrolyzed and decarboxylated by heating in
aqueous hydrochloric acid at reflux for about 6 to about 12 hours to provide
the amino acid, typically as the hydrochloride salt.
Examples of amino acid derivatives suitable for use in the above
reactions include, but are not limited to, L-alanine methyl ester, L-
isoleucine
methyl ester, L-leucine methyl ester, L-valine methyl ester, ~i-tert-butyl-L-
aspartic acid methyl ester, L-asparagine tert-butyl ester, E-Boc-L-lysine
methyl ester, E-Cbz-L-lysine methyl ester, y-tert-butyl-L-glutamic acid
methyl ester, L-glutamine tent-butyl ester, L-(N methyl)histidine methyl
ester, L-(N benzyl)histidine methyl ester, L-methionine methyl ester, L-(O-
benzyl)serine methyl ester, L-tryptophan methyl ester, L-phenylalanine
methyl ester, L-phenylalanine isopropyl ester, L-phenylalanine benzyl ester,
L-phenylalaninamide, N methyl-L-phenylalanine benzyl ester, 3-carboxy-
D,L-phenylalanine methyl ester, 4-carboxy-D,L-phenylalanine methyl ester,
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 134 --
L-4-chlorophenylalanine methyl ester, L-4-(3-dimethylaminopropyloxy)-
phenylalanine methyl ester, L-4-iodophenylalanine methyl ester, L-3,4-
methylenedioxyphenylalanine methyl ester, L-3,4-ethylenedioxy-
phenylalanine methyl ester, L-4-nitrophenylalanine methyl ester, L-tyrosine
methyl ester, D,L-homophenylalanine methyl ester, L-(O-methyl)tyrosine
methyl ester, L-(O-tent-butyl)tyrosine methyl ester, L-(O-benzyl)tyrosine
methyl ester, L-3,5-diiodotyrosine methyl ester, L-3-iodotyrosine methyl
ester, ~3-(1-naphthyl)-L-alanine methyl ester, ~i-(2-naphthyl)-L-alanine
methyl
ester, ~3-(2-thienyl)-L-alanine methyl ester, ~i-cyclohexyl-L-alanine methyl
ester, (3-(2-pyridyl)-L-alanine methyl ester, ~i-(3-pyridyl)-L-alanine methyl
ester, (3-(4-pyridyl)-L-alanine methyl ester, (3-(2-thiazolyl)-D,L-alanine
methyl ester, ~3-(1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-D,L-alanine methyl ester, and the like.
If desired, of course, other esters or amides of the above-described
compounds may also be employed.
Additionally, a-hydroxy and a-thio carboxylic acids may also be
employed in the above-described reactions. Such compounds are well-
known in the art and are either commercially available or may be prepared
from commercially available starting materials using conventional reagents
and reaction conditions.
In another preferred embodiment, compounds of this invention may
be prepared by displacement of a leaving group as shown in Scheme 2:
Scheme 2
R3 R3
A' QH -1- ~~ X -,-~. A'
O O
7 8 9
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 135 --
where R3, Q and X are as defined herein; A' is cycloalkyl, substituted
cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, substituted cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl,
heterocyclic and substituted heterocyclic; and L' is a leaving group, such as
chloro, bromo, iodo, sulfonate ester and the like.
Typically, this reaction is conducted by combining approximately
stoichiometric equivalents of 7 and 8 in a suitable inert diluent such as
water,
dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and the like, with an excess of a suitable base
such as sodium bicarbonate, sodium hydroxide, etc. to scavenge the acid
generated by the reaction. The reaction is preferably conducted at from
about 25°C to about 100°C until reaction completion which
typically occurs
within 1 to about 24 hours. This reaction is further described in U.S. Patent
No. 3,598,859, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
Upon reaction completion, the product 9 is recovered by conventional
methods including precipitation, chromatography, filtration and the like.
In still another alternative embodiment, compounds of this invention
in which Q is NR4 can be prepared by reductive amination of a suitable 2-
oxocarboxylic acid ester, 10, such as a pyruvate ester, as shown in Scheme
3:
Scheme 3
R3 R3
A' N H2 -~- O X ---~ ,4'
O O
11 10 12
where A', R3 and X are as defined herein.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 136 --
Generally, this reaction is conducted by combining equamolar
amounts of 10 and 11 in an inert diluent such as methanol, ethanol and the
like under conditions which provide for imine formation (not shown). The
imine formed is then reduced under conventional conditions by a suitable
reducing agent such as sodium cyanoborohydride, Hz/palladium on carbon
and the like to form the product 12. In a particularly preferred embodiment,
the reducing agent is HZ/palladium on carbon which is incorporated into the
initial reaction medium thereby permitting imine reduction in situ in a one
pot procedure to provide 12. The reaction is preferably conducted at from
about 20°C to about 80°C at a pressure of from 1 to 10
atmospheres until
reaction completion which typically occurs within 1 to about 24 hours.
Upon reaction completion, the product 12 is recovered by conventional
methods including chromatography, filtration and the like.
Alternatively, certain compounds of this invention can be prepared
via a rhodium-catalyzed insertion reaction as shown in Scheme 4:
Scheme 4
R3 R3
X ~ A~~ H X
O O
13 14 15
where A" is aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl, and
R3 and X (preferably alkoxy) are as defined herein. Typically, this reaction
is conducted using rhodium acetate dimer, Rh2(OAc)4, in an inert diluent
such as toluene at a temperature ranging from about 25°C to about
80°C for
about 1 to 12 hours to afford 15. This reaction is described further in B. R.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 137 --
Henke et. al., J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 5020-5036 and references cited
therein.
Similarly, certain compounds of this invention can be prepared by the
S copper-catalyzed coupling reaction shown in Scheme 5:
Scheme 5
Rs R3
X
A~~ X3 + H N X -
O O
16 17 15
where A" is aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl, X'
is halogen, such as chloro, bromo or iodo (preferably iodo), and R3 and X
(preferably alkoxy) are as defined herein. Typically, this reaction is
conducted using copper iodide (CuI) and potassium carbonate in an inert
diluent such as N,N dimethyl acetamide (DMA) at a temperature ranging
from about 60°C to about 120°C for about 12 to 36 hours to
afford 15. This
reaction is described further in D. Ma et. al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120,
12459-12467 and references cited therein.
For ease of synthesis, the compounds of this invention are typically
prepared as an ester, i.e., where X is an alkoxy or substituted alkoxy group
and the like. If desired, the ester group can be hydrolysed using
conventional conditions and reagents to provide the corresponding carboxylic
acid. Typically, this reaction is conducted by treating the ester with at
least
one equivalent of an alkali metal hydroxide, such as lithium, sodium or
potassium hydroxide, in an inert diluent, such as methanol or mixtures of
methanol and water, at a temperature ranging about 0°C to about
24°C for
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 138 --
about 1 to about 12 hours. Alternatively, benzyl esters may be removed by
hydrogenolysis using a palladium catalyst, such as palladium on carbon, and
tent-butyl esters can be removed using formic acid to afford the
corresponding carboxylic acid.
As will be apparent to those skilled in the art, other functional groups
present on any of the substituents of the compounds of formulas I-VII can be
readily modified or derivatized either before or after the above-described
synthetic reactions using well-known synthetic procedures. For example, a
nitro group present on a substituent of a compound of formula I-VII or an
intermediate thereof may be readily reduced by hydrogenation in the
presence of a palladium catalyst, such as palladium on carbon, to provide the
corresponding amino group. This reaction is typically conducted at a
temperature of from about 20°C to about 50°C for about 6 to
about 24 hours
in an inert diluent, such as methanol. Compounds having a nitro group on
the R3 and/or R3' substituent can be prepared, for example, by using a 4-
nitrophenylalanine derivative and the like in the above-described coupling
reactions.
Similarly, a pyridyl group can be hydrogenated in the presence of a
platinum catalyst, such as platinum oxide, in an acidic diluent to provide the
corresponding piperidinyl analogue. Generally, this reaction is conducted by
treating the pyridine compound with hydrogen at a pressure ranging from
about 20 psi to about 60 psi, preferably about 40 psi, in the presence of the
catalyst at a temperature of about 20°C to about 50°C for about
2 to about
24 hours in an acidic diluent, such as a mixture of methanol and aqueous
hydrochloric acid.
Additionally, when the R3 and/or R3' substituent of a compound of
formula I-VII or an intermediate thereof contains a primary or secondary
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/LTS00/01540
-- 139 --
amino group, such amino groups can be further derivatized either before or
after the above coupling reactions to provide, by way of example, amides,
sulfonamides, ureas, thioureas, carbamates, secondary or tertiary amines and
the like. Compounds having a primary amino group on the R3 and/or R3'
substituent may be prepared, for example, by reduction of the corresponding
nitro compound as described above.
By way of illustration, a compound of formula I-VII or an
intermediate thereof having a substituent containing a primary or secondary
amino group, such as where R3 is a (4-aminophenyl)methyl group, can be
readily N acylated using conventional acylating reagents and conditions to
provide the corresponding amide. This acylation reaction is typically
conducted by treating the amino compound with at least one equivalent,
preferably about 1.1 to about 1.2 equivalents, of a carboxylic acid in the
presence of a coupling reagent such as a carbodiimide, BOP reagent
(benzotriazol-1-yloxy-tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium
hexafluorophosphonate) and the like, in an inert diluent, such as
dichloromethane, chloroform, acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran, N,N
dimethylformamide and the like, at a temperature ranging from about 0°C
to
about 37°C for about 4 to about 24 hours. Preferably, a promoter, such
as
N hydroxysuccinimide, 1-hydroxy-benzotriazole and the like, is used to
facilitate the acylation reaction. Examples of carboxylic acids suitable for
use in this reaction include, but are not limited to, N tert-
butyloxycarbonylglycine, N tert-butyloxycarbonyl-L-phenylalanine, N tert-
butyloxycarbonyl-L-aspartic acid benzyl ester, benzoic acid, N tert-
butyloxycarbonylisonipecotic acid, N methylisonipecotic acid, N tert-
butyloxycarbonylnipecotic acid, N tert-butyloxycarbonyl-L-
tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid, N (toluene-4-sulfonyl)-L-proline
and the like.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 140 --
Alternatively, a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate
thereof containing a primary or secondary amino group can be N acylated
using an acyl halide or a carboxylic acid anhydride to form the
corresponding amide. This reaction is typically conducted by contacting the
amino compound with at least one equivalent, preferably about 1.1 to about
1.2 equivalents, of the acyl halide or carboxylic acid anhydride in an inert
diluent, such as dichloromethane, at a temperature ranging from about -
70°C
to about 40°C for about 1 to about 24 hours. If desired, an acylation
catalyst
such as 4-(N,N dimethylamino)pyridine may be used to promote the
acylation reaction. The acylation reaction is preferably conducted in the
presence of a suitable base to scavenge the acid generated during the
reaction. Suitable bases include, by way of example, tertiary amines, such
as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, N methylmorpholine and the like.
Alternatively, the reaction can be conducted under Schotten-Baumann-type
conditions using aqueous alkali, such as sodium hydroxide and the like.
Examples of acyl halides and carboxylic acid anhydrides suitable for
use in this reaction include, but are not limited to, 2-methylpropionyl
chloride, trimethylacetyl chloride, phenylacetyl chloride, benzoyl chloride,
2-bromobenzoyl chloride, 2-methylbenzoyl chloride, 2-trifluoro-
methylbenzoyl chloride, isonicotinoyl chloride, nicotinoyl chloride,
picolinoyl chloride, acetic anhydride, succinic anhydride, and the like.
Carbamyl chlorides, such as N,N dimethylcarbamyl chloride, N,N
diethylcarbamyl chloride and the like, can also be used in this reaction to
provide ureas. Similarly, dicarbonates, such as di-tert-butyl dicarbonate,
may be employed to provide carbamates.
In a similar manner, a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate
thereof containing a primary or secondary amino group may be N sulfonated
to form a sulfonamide using a sulfonyl halide or a sulfonic acid anhydride.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/I1S00/01540
-- 141 --
Sulfonyl halides and sulfonic acid anhydrides suitable for use in this
reaction
include, but are not limited to, methanesulfonyl chloride, chloromethane-
sulfonyl chloride, p-toluenesulfonyl chloride, trifluoromethanesulfonic
anhydride, and the like. Similarly, sulfamoyl chlorides, such as
dimethylsulfamoyl chloride, can be used to provide sulfamides (e.g., > N-
SOZ-N < ).
Additionally, a primary and secondary amino group present on a
substituent of a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate thereof can be
reacted with an isocyanate or a thioisocyanate to give a urea or thiourea,
respectively. This reaction is typically conducted by contacting the amino
compound with at least one equivalent, preferably about 1.1 to about 1.2
equivalents, of the isocyanate or thioisocyanate in an inert diluent, such as
toluene and the like, at a temperature ranging from about 24°C to about
37°C for about 12 to about 24 hours. The isocyanates and
thioisocyanates
used in this reaction are commercially available or can be prepared from
commercially available compounds using well-known synthetic procedures.
For example, isocyanates and thioisocyanates are readily prepared by
reacting the appropriate amine with phosgene or thiophosgene. Examples of
isocyanates and thioisocyanates suitable for use in this reaction include, but
are not limited to, ethyl isocyanate, n-propyl isocyanate, 4-cyanophenyl
isocyanate, 3-methoxyphenyl isocyanate, 2-phenylethyl isocyanate, methyl
thioisocyanate, ethyl thioisocyanate, 2-phenylethyl thioisocyanate, 3-
phenylpropyl thioisocyanate, 3-(N,N diethylamino)propyl thioisocyanate,
phenyl thioisocyanate, benzyl thioisocyanate, 3-pyridyl thioisocyanate,
fluorescein isothiocyanate (isomer I) and the like.
Furthermore, when a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate
thereof contains a primary or secondary amino group, the amino group can
be reductively alkylated using aldehydes or ketones to form a secondary or
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 142 --
tertiary amino group. This reaction is typically conducted by contacting the
amino compound with at least one equivalent, preferably about 1. l to about
1.5 equivalents, of an aldehyde or ketone and at least one equivalent based
on the amino compound of a metal hydride reducing agent, such as sodium
cyanoborohydride, in an inert diluent, such as methanol, tetrahydrofuran,
mixtures thereof and the like, at a temperature ranging from about 0°C
to
about 50°C for about 1 to about 72 hours. Aldehydes and ketones
suitable
for use in this reaction include, by way of example, benzaldehyde, 4-
chlorobenzaldehyde, valeraldehyde and the like.
In a similar manner, when a compound of formula I-VII or an
intermediate thereof has a substituent containing a hydroxyl group, the
hydroxyl group can be further modified or derivatized either before or after
the above coupling reactions to provide, by way of example, ethers,
carbamates and the like. Compounds having a hydroxyl group on the R3
substituent, for example, can be prepared using an amino acid derivative
derived from tyrosine and the like in the above-described reactions.
By way of example, a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate
thereof having a substituent containing a hydroxyl group, such as where R3
is a (4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl group, can be readily O-alkylated to form
ethers. This O-alkylation reaction is typically conducted by contacting the
hydroxy compound with a suitable alkali or alkaline earth metal base, such
as potassium carbonate, in an inert diluent, such as acetone, 2-butanone and
the like, to form the alkali or alkaline earth metal salt of the hydroxyl
group.
This salt is generally not isolated, but is reacted in situ with at least one
equivalent of an alkyl or substituted alkyl halide or sulfonate, such as an
alkyl chloride, bromide, iodide, mesylate or tosylate, to afford the ether.
Generally, this reaction is conducted at a temperature ranging from about
60°C to about 150°C for about 24 to about 72 hours. Preferably,
a catalytic
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 143 --
amount of sodium or potassium iodide is added to the reaction mixture when
an alkyl chloride or bromide is employed in the reaction.
Examples of alkyl or substituted alkyl halides and sulfonates suitable
for use in this reaction include, but are not limited to, tent-butyl
bromoacetate, N tent-butyl chloroacetamide, 1-bromoethylbenzene, ethyl a-
bromophenylacetate, 2-(N ethyl-N phenylamino)ethyl chloride, 2-(N,N
ethylamino)ethyl chloride, 2-(N,N diisopropylamino)ethyl chloride, 2-(N,N
dibenzylamino)ethyl chloride, 3-(N,N ethylamino)propyl chloride, 3-(N
benzyl-N methylamino)propyl chloride, N (2-chloroethyl)morpholine, 2-
(hexamethyleneimino)ethyl chloride, 3-(N methylpiperazine)propyl chloride,
1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(3-chloropropyl)piperazine, 2-(4-hydroxy-4-
phenylpiperidine)ethyl chloride, N tent-butyloxycarbonyl-3-piperidinemethyl
tosylate, and the like.
Alternatively, a hydroxyl group present on a substituent of a
compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate thereof can be D-alkylating
using the Mitsunobu reaction. In this reaction, an alcohol, such as 3-(N,N
dimethylamino)-1-propanol and the like, is reacted with about 1.0 to about
1.3 equivalents of triphenylphosphine and about 1.0 to about 1.3 equivalents
of diethyl azodicarboxylate in an inert diluent, such as tetrahydrofuran, at a
temperature ranging from about -10°C to about 5°C for about 0.25
to about
1 hour. About 1.0 to about 1.3 equivalents of a hydroxy compound, such as
N tent-butyltyrosine methyl ester, is then added and the reaction mixture is
stirred at a temperature of about 0°C to about 30°C for about 2
to about 48
hours to provide the O-alkylated product.
In a similar manner, a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate
thereof containing an aryl hydroxy group can be reacted with an aryl iodide
to provide a diaryl ether. Generally, this reaction is conducted by forming
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 1q.4 __
the alkali metal salt of the hydroxyl group using a suitable base, such as
sodium hydride, in an inert diluent such as xylenes at a temperature of about
-25°C to about 10°C. The salt is then treated with about 1.1 to
about 1.5
equivalents of cuprous bromide dimethyl sulfide complex at a temperature
ranging from about 10°C to about 30°C for about 0.5 to about 2.0
hours,
followed by about 1.1 to about 1.5 equivalents of an aryl iodide, such as
sodium 2-iodobenzoate and the like. The reaction is then heated to about
70°C to about 150°C for about 2 to about 24 hours to provide the
diaryl
ether.
Additionally, a hydroxy-containing compound can also be readily
derivatized to form a carbamate. In one method for preparing such
carbamates, a hydroxy compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate thereof
is contacted with about 1.0 to about 1.2 equivalents of 4-nitrophenyl
chloroformate in an inert diluent, such as dichloromethane, at a temperature
ranging from about -25°C to about 0°C for about 0.5 to about 2.0
hours.
Treatment of the resulting carbonate with an excess, preferably about 2 to
about 5 equivalents, of a trialkylamine, such as triethylamine, for about 0.5
to 2 hours, followed by about 1.0 to about 1.5 equivalents of a primary or
secondary amine provides the carbamate. Examples of amines suitable for
using in this reaction include, but are not limited to, piperazine, 1-
methylpiperazine, 1-acetylpiperazine, morpholine, thiomorpholine,
pyrrolidine, piperidine and the like.
Alternatively, in another method for preparing carbamates, a
hydroxy-containing compound is contacted with about 1.0 to about 1.5
equivalents of a carbamyl chloride in an inert diluent, such as
dichloromethane, at a temperature ranging from about 25°C to about
70°C
for about 2 to about 72 hours. Typically, this reaction is conducted in the
presence of a suitable base to scavenge the acid generated during the
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/LTS00/01540
-- 145 --
reaction. Suitable bases include, by way of example, tertiary amines, such
as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, N methylmorpholine and the like.
Additionally, at least one equivalent (based on the hydroxy compound) of
4-(N,N dimethylamino)pyridine is preferably added to the reaction mixture to
facilitate the reaction. Examples of carbamyl chlorides suitable for use in
this reaction include, by way of example, dimethylcarbamyl chloride,
diethylcarbamyl chloride and the like.
Likewise, when a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate
thereof contains a primary or secondary hydroxyl group, such hydroxyl
groups can be readily converted into a leaving group and displaced to form,
for example, amines, sulfides and fluorides. Generally, when a chiral
compound is employed in these reactions, the stereochemistry at the carbon
atom attached to the derivatized hydroxyl group is typically inverted.
These reactions are typically conducted by first converting the
hydroxyl group into a leaving group, such as a tosylate, by treatment of the
hydroxy compound with at least one equivalent of a sulfonyl halide, such as
p-toluenesulfonyl chloride and the like, in pyridine. This reaction is
generally conducted at a temperature of from about 0°C to about
70°C for
about 1 to about 48 hours. The resulting tosylate can then be readily
displaced with sodium azide, for example, by contacting the tosylate with at
least one equivalent of sodium azide in an inert diluent, such as a mixture of
N,N dimethylformamide and water, at a temperature ranging from about
0°C
to about 37°C for about 1 to about 12 hours to provide the
corresponding
azido compound. The azido group can then be reduced by, for example,
hydrogenation using a palladium on carbon catalyst to provide the amino
(-NHz) compound.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 146 --
Similarly, a tosylate group can be readily displaced by a thiol to form
a sulfide. This reaction is typically conducted by contacting the tosylate
with
at least one equivalent of a thiol, such as thiophenol, in the presence of a
suitable base, such as 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU), in an inert
diluent, such as N,N dimethylformamide, at a temperature of from about
0°C to about 37°C for about 1 to about 12 hours to provide the
sulfide.
Additionally, treatment of a tosylate with morpholinosulfur trifluoride in an
inert diluent, such as dichloromethane, at a temperature ranging from about
0°C to about 37°C for about 12 to about 24 hours affords the
corresponding
fluoro compound.
Furthermore, a compound of formula I-VII or an intermediate thereof
having a substituent containing an iodoaryl group, for example, when R3 is a
(4-iodophenyl)methyl group, can be readily converted either before or after
the above coupling reactions into a biaryl compound. Typically, this
reaction is conducted by treating the iodoaryl compound with about 1.1 to
about 2 equivalents of an arylzinc iodide, such as 2-(methoxycarbonyl)-
phenylzinc iodide, in the presence of a palladium catalyst, such as palladium
tetra(triphenylphosphine), in an inert diluent, such as tetrahydrofuran, at a
temperature ranging from about 24°C to about 30°C until reaction
completion. This reaction is further described, for example, in Rieke, J.
Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 1445. Additional methods for preparing biaryl
derivatives are disclosed in International Publication Number WO 98/53817,
published December 3, 1998, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein
by reference in its entirety.
In some cases, the compounds of formula I-VII or intermediates
thereof may contain substituents having one or more sulfur atoms. When
present, such sulfur atoms can be oxidized either before or after the above
coupling reactions to provide a sulfoxide or sulfone compound using
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 147 --
conventional reagents and reaction conditions. Suitable reagents for
oxidizing a sulfide compound to a sulfoxide include, by way of example,
hydrogen peroxide, 3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA), sodium periodate
and the like. The oxidation reaction is typically conducted by contacting the
sulfide compound with about 0.95 to about 1.1 equivalents of the oxidizing
reagent in an inert diluent, such as dichloromethane, at a temperature
ranging from about -50°C to about 75°C for about 1 to about 24
hours. The
resulting sulfoxide can then be further oxidized to the corresponding sulfone
by contacting the sulfoxide with at least one additional equivalent of an
oxidizing reagent, such as hydrogen peroxide, MCPBA, potassium
permanganate and the like. Alternatively, the sulfone can be prepared
directly by contacting the sulfide with at least two equivalents, and
preferably an excess, of the oxidizing reagent. Such reactions are described
further in March, "Advanced Organic Chemistry", 4th Ed., pp. 1201-1202,
Wiley Publisher, 1992.
Other procedures and reaction conditions for preparing the
compounds of this invention are described in the examples set forth below.
Pharmaceutical Formulations
When employed as pharmaceuticals, the compounds of this invention
are usually administered in the form of pharmaceutical compositions. These
compounds can be administered by a variety of routes including oral, rectal,
transdermal, subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, and intranasal.
These compounds are effective as both injectable and oral compositions.
Such compositions are prepared in a manner well known in the
pharmaceutical art and comprise at least one active compound.
This invention also includes pharmaceutical compositions which
contain, as the active ingredient, one or more of the compounds of formula
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 148 --
I-VII above associated with pharmaceutically acceptable carriers. In making
the compositions of this invention, the active ingredient is usually mixed
with an excipient, diluted by an excipient or enclosed within such a carrier
which can be in the form of a capsule, sachet, paper or other container.
When the excipient serves as a diluent, it can be a solid, semi-solid, or
liquid
material, which acts as a vehicle, carrier or medium for the active
ingredient. Thus, the compositions can be in the form of tablets, pills,
powders, lozenges, sachets, cachets, elixirs, suspensions, emulsions,
solutions, syrups, aerosols (as a solid or in a liquid medium), ointments
containing, for example, up to 10% by weight of the active compound, soft
and hard gelatin capsules, suppositories, sterile injectable solutions, and
sterile packaged powders.
In preparing a formulation, it may be necessary to mill the active
compound to provide the appropriate particle size prior to combining with
the other ingredients. If the active compound is substantially insoluble, it
ordinarily is milled to a particle size of less than 200 mesh. If the active
compound is substantially water soluble, the particle size is normally
adjusted by milling to provide a substantially uniform distribution in the
formulation, e.g. about 40 mesh.
Some examples of suitable excipients include lactose, dextrose,
sucrose, sorbitol, mannitol, starches, gum acacia, calcium phosphate,
alginates, tragacanth, gelatin, calcium silicate, microcrystalline cellulose,
polyvinylpyrrolidone, cellulose, water, syrup, and methyl cellulose. The
formulations can additionally include: lubricating agents such as talc,
magnesium stearate, and mineral oil; wetting agents; emulsifying and
suspending agents; preserving agents such as methyl- and propylhydroxy-
benzoates; sweetening agents; and flavoring agents. The compositions of the
invention can be formulated so as to provide quick, sustained or delayed
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 149 --
release of the active ingredient after administration to the patient by
employing procedures known in the art.
The compositions are preferably formulated in a unit dosage form,
each dosage containing from about 5 to about 100 mg, more usually about 10
to about 30 mg, of the active ingredient. The term "unit dosage forms"
refers to physically discrete units suitable as unitary dosages for human
subjects and other mammals, each unit containing a predetermined quantity
of active material calculated to produce the desired therapeutic effect, in
association with a suitable pharmaceutical excipient.
The active compound is effective over a wide dosage range and is
generally administered in a pharmaceutically effective amount. It, will be
understood, however, that the amount of the compound actually administered
will be determined by a physician, in the light of the relevant circumstances,
including the condition to be treated, the chosen route of administration, the
actual compound administered, the age, weight, and response of the
individual patient, the severity of the patient's symptoms, and the like.
For preparing solid compositions such as tablets, the principal active
ingredient is mixed with a pharmaceutical excipient to form a solid
preformulation composition containing a homogeneous mixture of a
compound of the present invention. When referring to these preformulation
compositions as homogeneous, it is meant that the active ingredient is
dispersed evenly throughout the composition so that the composition may be
readily subdivided into equally effective unit dosage forms such as tablets,
pills and capsules. This solid preformulation is then subdivided into unit
dosage forms of the type described above containing from, for example, 0.1
to about 500 mg of the active ingredient of the present invention.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 150 --
The tablets or pills of the present invention may be coated or
otherwise compounded to provide a dosage form affording the advantage of
prolonged action. For example, the tablet or pill can comprise an inner
dosage and an outer dosage component, the latter being in the form of an
S envelope over the former. The two components can be separated by an
enteric layer which serves to resist disintegration in the stomach and permit
the inner component to pass intact into the duodenum or to be delayed in
release. A variety of materials can be used for such enteric layers or
coatings, such materials including a number of polymeric acids and mixtures
of polymeric acids with such materials as shellac, cetyl alcohol, and
cellulose
acetate.
The liquid forms in which the novel compositions of the present
invention may be incorporated for administration orally or by injection
include aqueous solutions suitably flavored syrups, aqueous or oil
suspensions, and flavored emulsions with edible oils such as cottonseed oil,
sesame oil, coconut oil, or peanut oil, as well as elixirs and similar
pharmaceutical vehicles.
Compositions for inhalation or insufflation include solutions and
suspensions in pharmaceutically acceptable, aqueous or organic solvents, or
mixtures thereof, and powders. The liquid or solid compositions may
contain suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients as described supra.
Preferably the compositions are administered by the oral or nasal respiratory
route for local or systemic effect. Compositions in preferably
pharmaceutically acceptable solvents may be nebulized by use of inert gases.
Nebulized solutions may be breathed directly from the nebulizing device or
the nebulizing device may be attached to a face masks tent, or intermittent
positive pressure breathing machine. Solution, suspension, or powder
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 151 --
compositions may be administered, preferably orally or nasally, from
devices which deliver the formulation in an appropriate manner.
The following formulation examples illustrate the pharmaceutical
compositions of the present invention.
Formulation Example 1
Hard gelatin capsules containing the following ingredients are
prepared:
Quantity
In reg dient ~m~/capsulel-
Active Ingredient 30.0
Starch 305.0
Magnesium stearate 5.0
The above ingredients are mixed and filled into hard gelatin capsules
in 340 mg quantities.
Formulation Example 2
A tablet formula is prepared using the ingredients below:
Quantity
In rent m /tablet
Active Ingredient 25.0
Cellulose, microcrystalline 200.0
Colloidal silicon dioxide 10.0
Stearic acid 5.0
The components are blended and compressed to form tablets, each
weighing 240 mg.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 152 --
Formulation Example 3
A dry powder inhaler formulation is prepared containing the
following components:
In reg diem Wei ht o
Active Ingredient 5
Lactose 95
The active mixture is mixed with the lactose and the mixture is added
to a dry powder inhaling appliance.
Formulation Example 4
Tablets, each containing 30 mg of active ingredient, are prepared as
follows:
Quantity
Ingredient ,~m~/tablet~
Active Ingredient 30.0 mg
Starch 45.0 mg
Microcrystalline cellulose 35.0 mg
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
(as 10 % solution in water) 4.0 mg
Sodium carboxymethyl starch 4.5 mg
Magnesium stearate 0.5 mg
Talc 1. m
Total 120 mg
The active ingredient, starch and cellulose are passed through a No.
20 mesh U.S. sieve and mixed thoroughly. The solution of polyvinyl-
pyrrolidone is mixed with the resultant powders, which are then passed
through a 16 mesh U.S. sieve. The granules so produced are dried at 50°
to
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 153 --
60°C and passed through a 16 mesh U.S. sieve. The sodium carboxymethyl
starch, magnesium stearate, and talc, previously passed through a No. 30
mesh U.S. sieve, are then added to the granules which, after mixing, are
compressed on a tablet machine to yield tablets each weighing 150 mg.
Formulation Example 5
Capsules, each containing 40 mg of medicament are made as follows:
Quantity
In red; diem ~mg/ca~sulel_
Active Ingredient 40.0 mg
Starch 109.0 mg
Magnesium stearate 10 mg
Total 150.0 mg
The active ingredient, cellulose, starch, an magnesium stearate are
blended, passed through a No. 20 mesh U.S. sieve, and filled into hard
gelatin capsules in 150 mg quantities.
Formulation Example 6
Suppositories, each containing 25 mg of active ingredient are made as
follows:
Ingredient Amount
Active Ingredient 25 mg
Saturated fatty acid glycerides to 2,000 mg
The active ingredient is passed through a No. 60 mesh U.S. sieve and
suspended in the saturated fatty acid glycerides previously melted using the
minimum heat necessary. The mixture is then poured into a suppository
mold of nominal 2.0 g capacity and allowed to cool.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 154 --
Formulation Example 7
Suspensions, each containing 50 mg of medicament per 5.0 ml dose are
made as follows:
Ingredient Am un
Active Ingredient 50.0 mg
Xanthan gum 4.0 mg
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (11 %
)
Microcrystalline cellulose (89 % ) 50.0 mg
Sucrose 1.75 g
Sodium benzoate 10.0 mg
Flavor and Color q.v.
Purified water to 5.0 ml
The medicament, sucrose and xanthan gum are blended, passed through
a No. 10 mesh U.S. sieve, and then mixed with a previously made solution
of the microcrystalline cellulose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose in
water. The sodium benzoate, flavor, and color are diluted with some of the
water and added with stirring. Sufficient water is then added to produce the
required volume.
Formulation Example 8
Quantity
Ingredient !mg/capsule)
Active Ingredient 15.0 mg
Starch 407.0 mg
Magnesium stearate 3._ 0 m~
Total 425.0 mg
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 155 --
The active ingredient, cellulose, starch, and magnesium stearate are
blended, passed through a No. 20 mesh U.S. sieve, and filled into hard
gelatin capsules in 560 mg quantities.
Formulation Example 9
An intravenous formulation may be prepared as follows:
In reg diem uantit
Active Ingredient 250.0 mg
Isotonic saline 1000 ml
Formulation Example 10
A topical formulation may be prepared as follows:
Ingredient uan it
Active Ingredient 1-10 g
Emulsifying Wax 30 g
Liquid Paraffin 20 g
White Soft Paraffin to 100 g
The white soft parafftn is heated until molten. The liquid paraffin and
emulsifying wax are incorporated and stirred until dissolved. The active
ingredient is added and stirring is continued until dispersed. The mixture is
then cooled until solid.
Another preferred formulation employed in the methods of the present
invention employs transdermal delivery devices ("patches"). Such
transdermal patches may be used to provide continuous or discontinuous
infusion of the compounds of the present invention in controlled amounts.
The construction and use of transdermal patches for the delivery of
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 156 --
pharmaceutical agents is well known in the art. See. e.~., U.S. Patent
5,023,252, issued June 11, 1991, herein incorporated by reference. Such
patches may be constructed for continuous, pulsatile, or on demand delivery
of pharmaceutical agents.
Direct or indirect placement techniques may be used when it is desirable
or necessary to introduce the pharmaceutical composition to the brain.
Direct techniques usually involve placement of a drug delivery catheter into
the host's ventricular system to bypass the blood-brain barrier. One such
implantable delivery system used for the transport of biological factors to
specific anatomical regions of the body is described in U.S. Patent 5,011,472
which is herein incorporated by reference.
Indirect techniques, which are generally preferred, usually involve
formulating the compositions to provide for drug latentiation by the
conversion of hydrophilic drugs into lipid-soluble drugs. Latentiation is
generally achieved through blocking of the hydroxy, carbonyl, sulfate, and
primary amine groups present on the drug to render the drug more lipid
soluble and amenable to transportation across the blood-brain barrier.
Alternatively, the delivery of hydrophilic drugs may be enhanced by
intra-arterial infusion of hypertonic solutions which can transiently open the
blood-brain barrier.
'lit
The compounds of this invention can be employed to bind VLA-4 (aa~3,
integrin) in biological samples and, accordingly have utility in, for example,
assaying such samples for VLA-4. In such assays, the compounds can be
bound to a solid support and the VLA-4 sample added thereto. The amount
of VLA-4 in the sample can be determined by conventional methods such as
use of a sandwich ELISA assay. Alternatively, labeled VLA-4 can be used
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 157 --
in a competitive assay to measure for the presence of VLA-4 in the sample.
Other suitable assays are well known in the art.
In addition, certain of the compounds of this invention inhibit, in vivo,
S adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells mediated by VLA-4 and,
accordingly, can be used in the treatment of diseases mediated by VLA-4.
Such diseases include inflammatory diseases in mammalian patients
such as asthma, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, AIDS dementia,
diabetes (including acute juvenile onset diabetes), inflammatory bowel
disease (including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease), multiple
sclerosis,
rheumatoid arthritis, tissue transplantation, tumor metastasis, meningitis,
encephalitis, stroke, and other cerebral traumas, nephritis, retinitis, atopic
dermatitis, psoriasis, myocardial ischemia and acute leukocyte-mediated lung
injury such as that which occurs in adult respiratory distress syndrome.
The biological activity of the compounds identified above may be
assayed in a variety of systems. For example, a compound can be
immobilized on a solid surface and adhesion of cells expressing VLA-4 can
be measured. Using such formats, large numbers of compounds can be
screened. Cells suitable for this assay include any leukocytes known to
express VLA-4 such as T cells, B cells, monocytes, eosinophils, and
basophils. A number of leukocyte cell lines can also be used, examples
include Jurkat and U937.
The test compounds can also be tested for the ability to competitively
inhibit binding between VLA-4 and VCAM-1, or between VLA-4 and a
labeled compound known to bind VLA-4 such as a compound of this
invention or antibodies to VLA-4. In these assays, the VCAM-1 can be
immobilized on a solid surface. VCAM-1 may also be expressed as a
recombinant fusion protein having an Ig tail (e.g., IgG) so that binding to
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 158 --
VLA-4 may be detected in an immunoassay. Alternatively, VCAM-1
expressing cells, such as activated endothelial cells or VCAM-1 transfected
fibroblasts can be used. For assays to measure the ability to block adhesion
to brain endothelial cells, the assays described in International Patent
Application Publication No. WO 91/05038 are particularly preferred. This
application is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
Many assay formats employ labelled assay components. The labelling
systems can be in a variety of forms. The label may be coupled directly or
indirectly to the desired component of the assay according to methods well
known in the art. A wide variety of labels may be used. The component
may be labelled by any one of several methods. The most common method
of detection is the use of autoradiography with 3H, lzsl~ sss~ laC~ or 32p
labelled compounds or the like. Non-radioactive labels include ligands
which bind to labelled antibodies, fluorophores, chemiluminescent agents,
enzymes and antibodies which can serve as specific binding pair members for
a labelled ligand. The choice of label depends on sensitivity required, ease
of
conjugation with the compound, stability requirements, and available
instrumentation.
Appropriate in vivo models for demonstrating efficacy in treating
inflammatory responses include EAE (experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis) in mice, rats, guinea pigs or primates, as well as other
inflammatory models dependent upon a4 integrins.
Compounds having the desired biological activity may be modified as
necessary to provide desired properties such as improved pharmacological
properties (e.g., in vivo stability, bio-availability), or the ability to be
detected in diagnostic applications. For instance, inclusion of one or more
D-amino acids in the sulfonamides of this invention typically increases in
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/L1S00/01540
-- 159 --
vivo stability. Stability can be assayed in a variety of ways such as by
measuring the half life of the proteins during incubation with peptidases or
human plasma or serum. A number of such protein stability assays have
been described (see, e.g., Verhoef et al., Eur. J. Drug Metab.
Pharmacokinet., 1990, 15121:83-93).
For diagnostic purposes, a wide variety of labels may be linked to the
compounds, which may provide, directly or indirectly, a detectable signal.
Thus, the compounds of the subject invention may be modified in a variety
of ways for a variety of end purposes while still retaining biological
activity.
In addition, various reactive sites may be introduced at the terminus for
linking to particles, solid substrates, macromolecules, or the like.
Labeled compounds can be used in a variety of in vivo or in vitro
applications. A wide variety of labels may be employed, such as
radionuclides (e.g., gamma-emitting radioisotopes such as technetium-99 or
indium-111), fluorescers (e.g., fluorescein), enzymes, enzyme substrates,
enzyme cofactors, enzyme inhibitors, chemiluminescent compounds,
bioluminescent compounds, and the like. Those of ordinary skill in the art
will know of other suitable labels for binding to the complexes, or will be
able to ascertain such using routine experimentation. The binding of these
labels is achieved using standard techniques common to those of ordinary
skill in the art.
In vitro uses include diagnostic applications such as monitoring
inflammatory responses by detecting the presence of leukocytes expressing
VLA-4. The compounds of this invention can also be used for isolating or
labeling such cells. In addition, as mentioned above, the compounds of the
invention can be used to assay for potential inhibitors of VLA-4/VCAM-1
interactions.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 160 --
For in vivo diagnostic imaging to identify, e.g., sites of inflammation,
radioisotopes are typically used in accordance with well known techniques.
The radioisotopes may be bound to the peptide either directly or indirectly
using intermediate functional groups. For instance, chelating agents such as
diethylenetriaminepentacetic acid (DTPA) and ethylenediaminetetraacetic
acid (EDTA) and similar molecules have been used to bind proteins to
metallic ion radioisotopes.
The complexes can also be labeled with a paramagnetic isotope for
purposes of in vivo diagnosis, as in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or
electron spin resonance (ESR), both of which are well known. In general,
any conventional method for visualizing diagnostic imaging can be used.
Usually gamma- and positron-emitting radioisotopes are used for camera
imaging and paramagnetic isotopes are used for MRI. Thus, the compounds
can be used to monitor the course of amelioration of an inflammatory
response in an individual. By measuring the increase or decrease in
lymphocytes expressing VLA-4 it is possible to determine whether a
particular therapeutic regimen aimed at ameliorating the disease is effective.
The pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention can be used to
block or inhibit cellular adhesion associated with a number of diseases and
disorders. For instance, a number of inflammatory disorders are associated
with integrins or leukocytes. Treatable disorders include, e.g.,
transplantation rejection (e.g., allograft rejection), Alzheimer's disease,
atherosclerosis, AIDS dementia, diabetes (including acute juvenile onset
diabetes), retinitis, cancer metastases, rheumatoid arthritis, acute
leukocyte-mediated lung injury (e.g., adult respiratory distress syndrome),
asthma, nephritis, and acute and chronic inflammation, including atopic
dermatitis, psoriasis, myocardial ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease
(including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis). In preferred embodiments
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 161 --
the pharmaceutical compositions are used to treat inflammatory brain
disorders, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), viral meningitis and encephalitis.
Inflammatory bowel disease is a collective term for two similar diseases
referred to as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Crohn's disease is an
idiopathic, chronic ulceroconstrictive inflammatory disease characterized by
sharply delimited and typically transmural involvement of all layers of the
bowel wall by a granulomatous inflammatory reaction. Any segment of the
gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus, may be involved, although
the disease most commonly affects the terminal ileum and/or colon.
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory response limited largely to the colonic
mucosa and submucosa. Lymphocytes and macrophages are numerous in
lesions of inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to inflammatory
injury.
Asthma is a disease characterized by increased responsiveness of the
tracheobronchial tree to various stimuli potentiating paroxysmal constriction
of the bronchial airways. The stimuli cause release of various mediators of
inflammation from IgE-coated mast cells including histamine, eosinophilic
and neutrophilic chemotactic factors, leukotrines, prostaglandin and platelet
activating factor. Release of these factors recruits basophils, eosinophils
and
neutrophils, which cause inflammatory injury.
Atherosclerosis is a disease of arteries (e.g., coronary, carotid, aorta
and iliac). The basic lesion, the atheroma, consists of a raised focal plaque
within the intima, having a core of lipid and a covering fibrous cap.
Atheromas compromise arterial blood flow and weaken affected arteries.
Myocardial and cerebral infarcts are a major consequence of this disease.
Macrophages and leukocytes are recruited to atheromas and contribute to
inflammatory injury.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 162 --
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory disease that
primarily causes impairment and destruction of joints. Rheumatoid arthritis
usually first affects the small joints of the hands and feet but then may
involve the wrists, elbows, ankles and knees. The arthritis results from
interaction of synovial cells with leukocytes that infiltrate from the
circulation into the synovial lining of the joints. See e.g., Paul, Immunology
(3d ed., Raven Press, 1993).
Another indication for the compounds of this invention is in treatment of
organ or graft rejection mediated by VLA-4. Over recent years there has
been a considerable improvement in the efficiency of surgical techniques for
transplanting tissues and organs such as skin, kidney, liver, heart, lung,
pancreas and bone marrow. Perhaps the principal outstanding problem is the
lack of satisfactory agents for inducing immunotolerance in the recipient to
the transplanted allograft or organ. When allogeneic cells or organs are
transplanted into a host (i.e., the donor and donee are different individuals
from the same species), the host immune system is likely to mount an
immune response to foreign antigens in the transplant (host-versus-graft
disease) leading to destruction of the transplanted tissue. CD8+ cells, CD4
cells and monocytes are all involved in the rejection of transplant tissues.
Compounds of this invention which bind to alpha-4 integrin are useful, inter
alia, to block alloantigen-induced immune responses in the donee thereby
preventing such cells from participating in the destruction of the
transplanted
tissue or organ. See, e. g. , Paul et al. , Transplant International 9, 420-
425
(1996); Georczynski et al., Immunology 87, 573-580 (1996); Georcyznski et
al., Transplant. Immunol. 3, 55-61 (1995); Yang et al., Transplantation 60,
71-76 (1995); Anderson et al., APMIS 102, 23-27 (1994).
A related use for compounds of this invention which bind to VLA-4 is in
modulating the immune response involved in "graft versus host" disease
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 163 --
(GVHD). See e.g., Schlegel et al., J. Immunol. 155, 3856-3865 (1995).
GVHD is a potentially fatal disease that occurs when immunologically
competent cells are transferred to an allogeneic recipient. In this situation,
the donor's immunocompetent cells may attack tissues in the recipient.
Tissues of the skin, gut epithelia and liver are frequent targets and may be
destroyed during the course of GVHD. The disease presents an especially
severe problem when immune tissue is being transplanted, such as in bone
marrow transplantation; but less severe GVHD has also been reported in
other cases as well, including heart and liver transplants. The therapeutic
agents of the present invention are used, inter alia, to block activation of
the
donor T-cells thereby interfering with their ability to lyse target cells in
the
host.
A further use of the compounds of this invention is inhibiting tumor
metastasis. Several tumor cells have been reported to express VLA-4 and
compounds which bind VLA-4 block adhesion of such cells to endothelial
cells. Steinback et al., Urol. Res. 23, 175-83 (1995); Orosz et al., Int. J.
Cancer 60, 867-71 (1995); Freedman et al., Leuk. Lymphoma 13, 47-52
(1994); Okahara et al., Cancer Res. 54, 3233-6 (1994).
A further use of the compounds of this invention is in treating multiple
sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis is a progressive neurological autoimmune
disease that affects an estimated 250,000 to 350,000 people in the United
States. Multiple sclerosis is thought to be the result of a specific
autoimmune reaction in which certain leukocytes attack and initiate the
destruction of myelin, the insulating sheath covering nerve fibers. In an
animal model for multiple sclerosis, murine monoclonal antibodies directed
against VLA-4 have been shown to block the adhesion of leukocytes to the
endothelium, and thus prevent inflammation of the central nervous system
and subsequent paralysis in the animals'6.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 164 --
Pharmaceutical compositions of the invention are suitable for use in a
variety of drug delivery systems. Suitable formulations for use in the present
invention are found in Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences, Mace
Publishing Company, Philadelphia, PA, 17th ed. (1985).
In order to enhance serum half life, the compounds may be
encapsulated, introduced into the lumen of liposomes, prepared as a colloid,
or other conventional techniques may be employed which provide an
extended serum half life of the compounds. A variety of methods are
available for preparing liposomes, as described in, e.g., Szoka, et al., U.S.
Patent Nos. 4,235,871, 4,501,728 and 4,837,028 each of which is
incorporated herein by reference.
The amount administered to the patient will vary depending upon what is
being administered, the purpose of the administration, such as prophylaxis or
therapy, the state of the patient, the manner of administration, and the like.
In therapeutic applications, compositions are administered to a patient
already suffering from a disease in an amount sufficient to cure or at least
partially arrest the symptoms of the disease and its complications. An
amount adequate to accomplish this is defined as "therapeutically effective
dose." Amounts effective for this use will depend on the disease condition
being treated as well as by the judgment of the attending clinician depending
upon factors such as the severity of the inflammation, the age, weight and
general condition of the patient, and the like.
The compositions administered to a patient are in the form of
pharmaceutical compositions described above. These compositions may be
sterilized by conventional sterilization techniques, or may be sterile
filtered.
The resulting aqueous solutions may be packaged for use as is, or
lyophilized, the lyophilized preparation being combined with a sterile
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 165 --
aqueous carrier prior to administration. The pH of the compound
preparations typically will be between 3 and 11, more preferably from 5 to 9
and most preferably from 7 to 8. It will be understood that use of certain of
the foregoing excipients, carriers, or stabilizers will result in the
formation
of pharmaceutical salts.
The therapeutic dosage of the compounds of the present invention will
vary according to, for example, the particular use for which the treatment is
made, the manner of administration of the compound, the health and
condition of the patient, and the judgment of the prescribing physician. For
example, for intravenous administration, the dose will typically be in the
range of about 20 ,ug to about 500 ,ug per kilogram body weight, preferably
about 100 ,ug to about 300 ~cg per kilogram body weight. Suitable dosage
ranges for intranasal administration are generally about 0.1 pg to 1 mg per
kilogram body weight. Effective doses can be extrapolated from
dose-response curves derived from in vitro or animal model test systems.
Compounds of this invention are also capable of binding or antagonizing
the actions of a6~3,, a9~31, a4(3,, aa(3z, a~~3, integrins (although aa~i, and
a9~3,
are preferred in this invention). Accordingly, compounds of this invention
are also useful for preventing or reversing the symptoms, disorders or
diseases induced by the binding of these integrins to their respective
ligands.
For example, International Publication Number WO 98/53817,
published December 3, 1998 (the disclosure of which is incorporated herein
by reference in its entirety) and references cited therein describe disorders
mediated by a4~3,. This reference also describes an assay for determining
antagonism of a4~i, dependent binding to VCAM-Ig fusion protein.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 166 --
Additionally, compounds that bind ad~i2 and ae~3, integrins are
particularly useful for the treatment of asthma and related lung diseases.
See, for example, M. H. Grayson et al., J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188(11) 2187-
2191. Compounds that bind ae~3, integrin are also useful for the treatment of
systemic lupus erythematosus (see, for example, M. Pang et al., Arthritis
Rheum. 1998, 41(8), 1456-1463); Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and
infammatory bowel disease (IBD) (see, for example, D. Elewaut et al.,
Scand J. Gastroenterol 1998, 33(7) 743-748); Sjogren's syndrome (see, for
example, U. Kroneld et al., Scand J. Gastroenterol 1998, 27(3), 215-218);
and rheumatoid arthritis (see, for example, Scand J. Gastroenterol 1996,
44(3), 293-298). And compounds that bind ae(3, may be useful in preventing
fertilization (see, for example, H. Chen et al., Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 1-10).
The following synthetic and biological examples are offered to illustrate
this invention and are not to be construed in any way as limiting the scope of
this invention. Unless otherwise stated, all temperatures are in degrees
Celsius.
EXAMPLES
In the examples below, the following abbreviations have the following
meanings. If an abbreviation is not defined, it has its generally accepted
meaning.
aq or aq. - aqueous
AcOH - acetic acid
bd - broad doublet
bm - broad multiplet
bs - broad singlet
Bn - benzyl
Boc - N tent-butoxylcarbonyl
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 167 --
BoczO - di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
BOP - benzotriazol-1-yloxy-
tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium
hexafluorophosphate
Cbz - carbobenzyloxy
CHC13 - chloroform
CHZC12 - dichloromethane
(COCI)Z - oxalyl chloride
d - doublet
dd - doublet of doublets
dt - doublet of triplets
DBU - 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene
DCC - 1,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
DMAP - 4-N,N dimethylaminopyridine
DME - ethylene glycol dimethyl
ether
DMF - N,N dimethylformamide
DMSO - dimethylsulfoxide
EDC - 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-
ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
Et3N - triethylamine
Et20 - diethyl ether
EtOAc - ethyl acetate
EtOH - ethanol
eq or eq. - equivalent
Fmoc - N (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl)
FmocONSu - N (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl)-
succinimide
g - grams
h - hour
H20 - water
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 168 --
HBr - hydrobromic acid
HCl - hydrochloric acid
HOBT - 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate
hr - hour
KZC03 - potassium carbonate
L - liter
m - multiplet
MeOH - methanol
mg - milligram
MgS04 - magnesium sulfate
mL - milliliter
mm - millimeter
mM - millimolar
mmol - millimol
mp - melting point
N - normal
NaCI - sodium chloride
Na2C03 - sodium carbonate
NaHC03 - sodium bicarbonate
NaOEt - sodium ethoxide
NaOH - sodium hydroxide
NH4Cl - ammonium chloride
NMM - N methylmorpholine
Phe - L-phenylalanine
Pro - L-proline
psi - pounds per square inch
Pt02 - platinum oxide
q - quartet
quint. - quintet
rt - room temperature
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 169 --
s - singlet
sat - saturated
t - triplet
t-BuOH - tert-butanol
TFA - trifluoroacetic acid
THF - tetrahydrofuran
TLC or tlc - thin layer chromatography
Ts - tosyl
TsCI - tosyl chloride
TsOH - tosylate
~L - microliter
The following Methods may be used to prepare the compounds of this
invention.
Method A
Methyl Ester Preparation Procedure
Amino acid methyl esters can be prepared using the method of Brenner
and Huber Helv. Chim. Acta 1953, 36, 1109.
Method B
BOP Coupling Procedure
The desired dipeptide ester was prepared by the reaction of a carboxylic
acid (1 equivalent) with the appropriate amino acid ester or amino acid ester
hydrochloride (1 equivalent), benzotriazol-1-yloxy-tris(dimethylamino)
phosphonium hexafluorophosphate [BOP] (2.0 equivalent), triethylamine (1.1
equivalent), and DMF. The reaction mixture was stirred at room
temperature overnight. The crude product is purified flash chromatography
to afford the dipeptide ester.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 170 --
Method C
Hydrogenation Procedure I
Hydrogenation was performed using 10% palladium on carbon (10% by
weight) in methanol at 30 psi overnight. The mixture was filtered through a
pad of Celite and the filtrate concentrated to yield the desired compound.
Method D
Hydrolysis Procedure I
To a chilled (0°C) THF/Hz0 solution (2:1, 5 - 10 mL) of the
appropriate ester was added LiOH (or NaOH) (0.95 equivalents). The
temperature was maintained at 0°C and the reaction was complete in 1-3
hours. The reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and the
aqueous phase was lyophilized resulting in the desired carboxylate salt.
Method E
Ester Hydrolysis Procedure II
To a chilled (0°C) THF/H20 solution (2:1, 5 - 10 mL) of the
appropriate ester was added LiOH (1.1 equivalents). The temperature was
maintained at 0°C and the reaction was complete in 1-3 hours. The
reaction
mixture was concentrated and the residue was taken up into HZO and the pH
adjusted to 2-3 with aqueous HCI. The product was extracted with ethyl
acetate and the combined organic phase was washed with brine, dried over
MgS04, filtered and concentrated to yield the desired acid.
Method F
Ester Hydrolysis Procedure III
The appropriate ester was dissolved in dioxane/HZO (1:1) and 0.9
equivalents of 0.5 N NaOH was added. The reaction was stirred for 3-16
hours and then concentrated. The resulting residue was dissolved in Hz0
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 171 --
and extracted with ethyl acetate. The aqueous phase was lyophilized to yield
the desired carboxylate sodium salt.
Method G
BOC Removal Procedure
Anhydrous hydrochloride (HCI) gas was bubbled through a methanolic
solution of the appropriate Boc-amino acid ester at 0°C for 15 minutes
and
the reaction mixture was stirred for three hours. The solution was
concentrated to a syrup and dissolved in Et20 and reconcentrated. This
procedure was repeated and the resulting solid was placed under high
vacuum overnight.
Method H
tent-Butyl Ester Hydrolysis Procedure I
The tert-butyl ester was dissolved in CHZC12 and treated with TFA. The
reaction was complete in 1-3 hr at which time the reaction mixture was
concentrated and the residue dissolved in HZO and lyophilized to yield the
desired acid.
Method I
EDC Coupling Procedure I
To a CHZCI, solution (5-20 mL) of a carboxylic acid (1 equivalent), the
appropriate amino acid ester hydrochloride (1 equivalent), N-
methylmorpholine (1.1-2.2 equivalents) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (2
equivalents) were mixed, placed in an ice bath and 1-(3-
dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide (1.1 equivalents) added. The
reaction was allowed to rise to room temperature and stirred overnight. The
reaction mixture was poured into H20 and the organic phase was washed
with sat. NaHC03, brine, dried (MgS04 or NaZS04), filtered and
concentrated. The crude product was purified by column chromatography.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 172 --
Method J
EDC Coupling Procedure II
To a DMF solution (S-20 mL) of a carboxylic acid (1 equivalent), the
appropriated amino acid ester hydrochloride (1 equivalent), Et3N (1.1
equivalents) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (2 equivalents) were mixed, placed
in an ice bath and 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide (1.1
equivalents) added. The reaction was allowed to rise to room temperature
and stirred overnight. The reaction mixture was partitioned between EtOAc
and Hz0 and the organic phase washed with 0.2 N citric acid, I-i~0, sat.
NaHC03, brine, dried (MgS04 or Na2S04), filtered and concentrated. The
crude product was purified by column chromatography or preparative TLC.
Method K
tent-Butyl Ester Hydrolysis Procedure II
The tent-butyl ester was dissolved in CHZC12 (5 mL) and treated with
TFA (5 mL). The reaction was complete in 1-3 hours at which time the
reaction mixture was concentrated and the residue dissolved in H,O and
concentrated. The residue was redissolved in HZO and lyophilized to yield
the desired product.
Method L
Carbamate Formation Procedure I
Into a reaction vial were combined 15.2 mmol, 1.0 eq. of the starting
hydroxy compound (typically a tyrosine derivative) and 1.86 g (15.2 mmol,
1.0 eq) DMAP. Methylene chloride (50 mL), triethylamine (2.12 mL, 1.54
g, 15.2 mmol, 1.0 eq), and dimethylcarbamyl chloride (1.68 mL, 1.96 g,
18.2 mmol, 1.2 eq) were then added. The vial was capped tightly, and the
reaction solution swirled to obtain a homogeneous solution. The reaction
solution was then heated to 40°C. After 48 h, TLC of the resulting
colorless
solution indicated complete conversion. The work-up of the reaction
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 173 --
solution was as follows: 50 mL EtOAc and 50 mL hexanes was added to the
reaction mixture, and the resulting mixture was washed with 0.5 M citric
acid (3 x 50 mL), water (2 x 50 mL),10 % KZC03 (2 x 50 mL), and sat. NaCI
(1 x 50 mL); dried with MgS04, filtered and evaporated to afford the desired
compound.
Method M
Carbamate Formation Procedure II
Into a reaction vial were combined 84.34 mmol (1.0 eq) of the starting
hydroxy compound (typically a tyrosine derivative) and 17.0 g (84.34 mmol,
1.0 eq) 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate. Methylene chloride (700 mL) was
added and the vial was capped with a septum. A nitrogen line was attached
and the vial was immersed in a 4:1 water/ethanol dry ice slurry with stirring
to cool to -15°C. Triethylamine (29.38 mL, 21.33 g, 210.81 mmol, 2.5
eq)
was added over five minutes with stirring and the stirring was continued at -
10 to -15°C for 1 h. N Methyl piperazine (9.35 mL, 8.45 g, 84.34 mmol,
1.0 eq) was added over three minutes with stirring and stirring was continued
overnight while warming to room temperature. The reaction mixture was
diluted with 700 mL hexanes and the resulting mixture was washed
repeatedly with 10% KZC03, until no yellow color (from 4-nitrophenol) is
observed in the aqueous layer. The mixture was then washed with sat.
NaCI, dried over anhydrous MgS04, filtered and evaporated. The residue
was dissolved in 500 mL of ethanol and evaporated to remove triethylamine.
The residue was again dissolved in 500 mL of ethanol and evaporated to
remove triethylamine. The residue was then dissolved in 400 mL of ethanol
and 600 mL of water was added with stirring to precipitate a solid or oil. If
an oil if formed, the oil is stirred vigorously to induce it to solidify. The
solid is then isolated by filtration. Dissolution, precipitation, and
filtration
are repeated once and the resulting solid is rinsed with water to remove
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 174 --
traces of yellow color. The solid is then subjected to high vacuum until the
mass remains constant thereby affording the desired carbamyloxy compound.
Method N
Purification Method
Unless otherwise stated, the compounds of this method were purified by
LC/MS using 10% to 90% acetonitrile/water gradient with 0.1
trifluoroacetic acid (12 min. run time).
Method O
Analytical Method
Unless otherwise stated, the compounds of this method were analyzed
by LC/MS using 10% to 90% acetonitrile/water gradient with 0.1%
trifluoroacetic acid (5.5 min run time).
Example 1
Synthesis of
N {6-(N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-4-chloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine
OC(O)N(CH3)2
w ~ / 1
N ~N
N~N~N OH
O
I i
Step A
Cyanuric chloride (0.045 mmol), t-butyl tyrosine O-(N,N-
dimethyl)carbamate (0.0545 mmol), and diisopropylethylamine (0.18 mmol)
were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (4.0 mL) and shaken at room temperature.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 175 --
After two hours, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure providing
N (4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine tert-butyl ester without purification. (m/e 456).
Step B
N (4,6-Dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine tert-butyl ester (0.045 mmol), N benzyl-N phenethylamine
(0.045 mmol) and diisopropylethylamine (0.18 mmol) were dissolved in
THF and heated to 60°C overnight. The solvent was removed under
reduced
pressure providing N {6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-4-chloro-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine tert-butyl
ester, which was used without purification. (m/e 631)
Step,_3
The N {6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-4-chloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine tent-butyl ester (0.022
mmol) was dissolved in a 1/1 solution of TFA/CHZC12 (1.0 mL) and shaken
for 1 hour. The solvent was removed and the crude product was dissolved in
a 1/1 solution of DMSO/CH3CN and purified by preparative LC/MS
described above providing N {6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-4-
chloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine.
( m/e 575)
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 176 --
Example 2
Synthesis of
N {4-[N-(Benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine
OC(O)N(CH3)2
/ 1
N~N
N~N~N OH
O
I
i
N {6-[N (Benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-4-chloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine tert-butyl ester (0.022 mmol)
was dissolved in methanol. Sodium Bicarbonate (0.18 mmol), 10 % Pd/C
(0.0022 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was degassed twice and
purged with HZ twice. The suspension was stirred under HZ for 4 hours,
filtered through celite and the solvent removed. The resulting oil was
dissolved in EtOAc and extracted with water (2 X 0.5 mL). The organic
layer was dried over MgS04, filtered and the solvent removed. The resulting
oil was dissolved in a 1/1 solution of TFA/CHZC12 and shaken for 2 hours,
then the solvent was removed. The crude material was dissolved in a 1/1
solution of DMSO/CH3CN and purified by preparative LC/MS providing N
{4-[N-(benzyl)-N-( 1-phenylethyl)amino]-1, 3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)-phenylalanine. (m/e 541).
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 177 -_
Example 3
Synthesis of
N {4-Chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(p-toluenesulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine
OC(O)N(CH3)2
N ~N
\N~N~N OH
S02 O
a 1
N-Methyl p-toluenesulfonamide (0.98 mmol) was added to a solution of
N (4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine tert-butyl ester (0.89 mmol) in THF (50 mL) and stirred for 5
min. Cesium carbonate (2.7 mmol) was added and the mixture was heated at
60°C overnight. The solid was filtered and the solvent removed under
reduced pressure. The crude product N {4-chloro-6-[N (methyl)-N (p-
toluenesulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine tert-butyl ester was used without purification. (m/e 605)
Step 2
N {4-Chloro-6-[N (methyl)-N (p-toluenesulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-phenylalanine ten-butyl ester (0.017
mmol) was dissolved in a 1/1 solution of TFA/CHZCIz and shaken for 2
hours, then the solvent was removed. The crude material was dissolved in a
1/1 solution of DMSO/CH3CN and purified by preparative LC/MS providing
N {4-chloro-6-[N (methyl)-N (p-toluenesulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine. (m/e 549)
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 178 -_
Example 4
Synthesis of
N {4-Chloro-6-(N,N-dihexylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}phenylalanine ethyl
ester
N ~N
CsH~N~N~N OCH2CH3
CsH~ ~ O
St- e~l_
Dihexylamine (6.3 mL, 27 mmol) was added to a mixture of cyanuric
chloride (5.0 g, 27 mmol) and sodium carbonate (2.9 g, 27 mmol) in
acetonitrile (50 mL). The reaction mixture was heated to reflux for 16 h and
then allowed to col to ambient temperature. The mixture was diluted with
ethyl acetate and water. The phases were separated and the organic phase
was washed with brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated
under reduced pressure. The crude material was purified by flash column
chromatography through silica gel (elution with 3:1 hexanes:chloroform) to
afford 2,4-dichloro-6-dihexylamino-1,3,5-triazine.
S_ tep 2
L-phenylalanine ethyl ester hydrochloride (1.0 g, 4.4 mmol) was added
to a mixture of 2,4-dichloro-6-dihexylamino-1,3,5-triazine (1.5 g, 4.5 mmol)
and sodium carbonate (0.92 g, 8.7 mmol) in acetonitrile (40 mL). The
reaction mixture was heated to reflux for 16 h and then allowed to col to
ambient temperature. The mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and water.
The phases were separated and the organic phase was washed with brine,
dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
The crude material was purified by flash column chromatography through
silica gel (elution with chloroform) to afford N {4-chloro-6-(N,N-
dihexylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}phenylalanine ethyl ester. Anal. Calcd. for
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 179 --
Cz6HaoClNsOz: C, 63.72; H, 8.23; N 14.29. Found: C, 63.67; H, 8.06; N
14.24.
Example 5
Synthesis of
N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-tyrosine
OH
OSO
a
~sHi~ ~ I OH
N
CgH~~ H O
Step 1
3,4-Diethyloxy-1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole and 3,4-Diethyloxy-1,1-dioxo-
1,2,5-thiadiazole were prepared according to the procedures described in R.
Y. Wen et al, J Org Chem., (1975) 40, 2743; and R. Y. Wen et al, Org
Prep Proceed. , ( 1969) 1, 255.
Step 2
Dihexylamine (90 mg, 0.48 mmol) was added to a solution of 3,4-
diethyloxy-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole (100 mg, 0.48 mmol) in ethanol (5
mL) and the reaction stirred overnight at room temperature. The solvent was
removed under reduced pressure and the residue absorbed onto silica gel,
and purified by flash column chromatography (silica, hexane:EtOAc 3:1) to
yield 4-(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)-3-ethoxy-l,l-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole (120
mg, 72%). MS ( EI, m/e 345).
Step 3
A solution of 4-(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)-3-ethoxy-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-
thiadiazole (400 mg, 1.02 mmol) and L-tyrosine t-butyl ester (261 mg, 1.1
mmol) in EtOH (10 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 36 hrs. The
solvent was removed under reduced pressure residue purified by flash
column chromatography (silica, hexane:EtOAc 3:1 then 1:1) to give N-(4-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 180 --
(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-tyrosine tent-butyl
ester as a white waxy solid (400 mg, 73%). Anal. Calc'd for C27H44N405
5Ø55EtOAc: C, 59.93; H, 8.34; N, 9.57. Found: C,59.84; H, 8.44;
N,9.62.
Step 4
N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-tyrosine
tert-butyl ester (100 mg, 0.19 mmol) was dissolved in formic acid and the
mixture stirred at room temperature for 36 hrs. Excess formic acid was
removed under reduced pressure to yield N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-l,l-
dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-tyrosine as a white solid (90 mg, 98 %).
Anal. Calc'd for C23H36N405 s~ C, 57.48; H, 7.55; N, 11.66.
Found: C,57.04; H, 7.23; N,11.38.
Example 6
Synthesis of
N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine
OC(O)N(CH3)2
a
CsH» ~ I OH
'N N
H
CsH » O
t 1
N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-l,l-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-tyrosine
tert-butyl ester (180 mg, 0.34 mmoL) was dissolved in pyridine (5 ml).
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride (108 mg, 1 mmol) was added dropwise and the
mixture stirred at room temperature overnight. Pyridine was removed under
high vacuum (low water bath temperature), the residue absorbed onto silica
gel and purified by flash column chromatography (silica, hexane:EtOAc 2:1)
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
--181--
to yield N-(4-(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)-l,l-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine tert-butyl ester (140 mg, 68 %).
Step 2
N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-l,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)-phenylalanine tert-butyl ester (140 mg, 0.23 mmol)
was dissolved in formic acid and the mixture stirred at room temperature
overnight. Excess formic acid was removed under reduced pressure to yield
N-(4-(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine as a white solid (110 mg, 87 % ).
Anal. Calc'd for C26H41N5~6 S~ C, 56.6; H, 7.49; N, 12.69. Found:
C,56.67; H, 7.4; N,12.46.
Example 7
Synthesis of
N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(4-
methylpiperazin-1-ylcarbonyloxy)phenylalanine
N
OSO
N~
CsHl1
'N N
H
C6H11
St_ ep 1
A solution of N-(4-(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-
yl)-L-tyrosine tert-butyl ester (500 mg, 0.93 mmol), and p-nitrophenyl
chloroformate (179 mg, 0.89 mmol) in dichloromethane (20 mL) was cooled
to 0°C under an argon atmosphere. Triethylamine (235 mg, 2.32 mmol) was
added dropwise and the mixture stirred at 0°C for 30 mins, then allowed
to
warm to room temperature for a further 40 mins. The mixture was re-cooled
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/~JS00/01540
-- 182 --
to 0°C and N-methylpiperazine (90 mg, 0.89 mmol) added. The mixture
was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for three hours. The
mixture was diluted with diethyl ether (150 mL) and the organic solution
washed with 10% potassium carbonate solution until no further yellow color
was produced in the aqueous phase. The organic layer was separated, dried
(MgS04) and the solvent removed under reduced pressure. The residue was
purified by flash column chromatography (silica, EtOAc:MeOH:Et3N
94:5:1) to give N-(4-(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-
L-4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-ylcarbonyloxy)phenylalanine tert-butyl ester as a
pale yellow foam (310 mg, 50 %). Anal. Calc'd for C33H54N606 S~ C,
59.79; H, 8.21; N, 12.68. Found: C,59.47; H, 8.25; N,12.49
Step 2
N-(4-(N,N-Di-n-hexylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(4-
methylpiperazin-1-ylcarbonyloxy)phenylalanine tert-butyl ester (200 mg, 0.3
mmol) was dissolved in formic acid (S mL) and the mixture stirred at room
temperature for 48 hrs. Excess formic acid was removed under reduced
pressure and the residue recrystallized from EtOAc/MeOH to yield N-(4-
(N,N-di-n-hexylamino)- l , l -dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(4-methyl-
piperazin-1-ylcarbonyloxy)phenylalanine as an off-white solid (120 mg, 67
% ). Anal. Calc'd for C29H46N606 5Ø75H,0: C, 56.15; H, 7.72; N,
13.55. Found: C, 56.1; H, 7.44; N, 13.46.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 183 --
Example 8
Synthesis of
N-[4-(2-(3-Methylphenylaminocarbonylamino)eth-1-ylamino)-1,1-dioxo-
S 1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine
/ OC(O)N(CH3)2
N O
\/
~N~ OH
O
Ste~l
A solution of 3,4-diethyloxy-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole (400 mg, 1.94
mmol)and L-tyrosine t-butyl ester (1.25 g, 5.2 mmol) in ethanol (25 mL)
was stirred at room temperature overnight. Solvent was removed under
reduced pressure and the product N-(4-ethoxy-l,l-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-
yl)-L-tyrosine tert-butyl ester was used in further transformations without
further purification (790 mg).
Step 2
N-Boc-Ethylene diamine (800 mg, 5 mmol) and m-tolyl isocyanate (665
mg, 5 mmol) were dissolved in acetonitrile and the mixture stirred at room
temperature for 4 hrs. Solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the
residue absorbed onto silica gel; prior to purification by flash column
chromatography (silica, hexane:EtOAc 1:1) to yield the desired compound as
a white solid (300 mg, 21 %) (MS ( +ESI, m/e) 294 (M+H)+). The N-Boc
protected compound (300 mg, 1.02 mmol) was dissolved in formic acid (10
ml) and the mixture stirred at room temperature overnight. Excess acid was
removed to yield the formate salt of 2-(3-methylphenylaminocarbonylamino)-
eth-1-ylamine as a white foam (210 mg).
Step 3
To a solution of N-(4-ethoxy-l,l-dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-tyrosine
tert-butyl ester from Step A (150 mg, 0.38 mmol) and the formate salt of 2-
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 184 --
(3-methylphenylaminocarbonylamino)eth-1-ylamine from Step B (210 mg,
0.89 mmol) in ethanol (10 mL) was added triethylamine (133 mg, 1.44
mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight. Solvent was
removed under reduced pressure and the residue purified by flash column
chromatography (silica, 5 % MeOH in EtOAc)to give N-[4-(2-(3-
methylphenylamino-carbonylamino)eth-1-ylamino)-1,1-dioxo-1,2,5-
thiadiazol-3-yl]-L-tyrosine tert-butyl ester (130 mg, 91 % ). MS ( +ESI, m/e)
545 (M+H)+.
Step 4
N-[4-(2-(3-Methylphenylamino-carbonylamino)eth-1-ylamino)-l,l-dioxo-
1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]-L-tyrosine tert-butyl ester(130 mg, 0.24 mmol) was
dissolved in pyridine (5 mL). Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride (77 mg, 0.72
mmol) was added dropwise and the mixture heated at 50°C under an argon
atmosphere overnight. Pyridine was removed under reduced pressure, the
residue absorbed onto silica gel and purified by flash column
chromatography (silica, hexane:EtOAc 1:2, then 5% MeOH in EtOAc) to
yield N-[4-(2-(3-methylphenylamino-carbonylamino)eth-1-ylamino)-1,1-
dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine
tert-butyl ester (140 mg, 93 %). MS ( +ESI, m/e) 616 (M+H)+.
St- ep 5
N-[4-(2-(3-Methylphenylamino-carbonylamino)eth-1-ylamino)-1,1-dioxo-
1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine tert-butyl
ester (120 mg, 0.19 mmol) was dissolved in formic acid (10 mL) and the
mixture stirred at room temperature for 36 hrs. Excess acid was removed to
yield N-[4-(2-(3-methylphenylamino-carbonylamino)eth-1-ylamino)-1,1-
dioxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine as
a pale yellow foam (100 mg, 93 %). MS ( +ESI, m/e) 560 (M+H)+.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 185 --
Example 9
Synthesis of
N-(4-(N,N-Dimethylamino)-1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine tert-Butyl Ester
OC(O)N(CH 3)2
O'w,0
S
a
O
-N
Step 1
A solution of 3,4-diethoxy-1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazole (1 g, 0.52 mmol) and
L-tyrosine t-butyl ester (1.25 g, 0.52 mmol) in ethanol (25 mL) was stirred
at room temperature for 60 hr. Solvent was removed under reduced pressure
and the residue purified by flash column chromatography (silica,
hexane:EtOAc 1:1 to give N-(4-ethoxy-1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-
tyrosine tert-butyl ester (1.75 g, 88 % ). MS ( +ESI, m/e) 382 (M+H)+.
Step 2
N-(4-Ethoxy-I-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-tyrosine tert-butyl ester
(400 mg, 1.05 mmol) was dissolved in pyridine (10 mL) and
dimethylcarbamoyl chloride (338 mg, 3.15 mmol) was added. The reaction
was stirred at room temperature under an inert atmosphere overnight. TLC
indicated large amounts of unreacted starting material so the mixture was
heated at 50°C for a further 48 hrs. Excess pyridine was removed under
reduced pressure and the residue purified by flash column chromatography
(silica, hexane:EtOAc 1:1 to give N-(4-ethoxy-1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-phenylalanine tent-butyl ester (280 mg, 59
%). MS ( +ESI, m/e) 453 (M+H).
Ste
A 2M solution of dimethylamine in THF (5 mL, 10 mmol) was added to
a solution of the compound from Step B (180 mg, 0.35 mmol) in ethanol (10
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 186 --
mL). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight and solvent
removed under reduced pressure. Residue was purified by flash column
chromatography (silica, EtOAc:MeOH:Et3N 90:10:1) to give N-(4-(N,N-
dimethylamino)-1-oxo-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)-L-4-(N,IV
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine tert-butyl ester as a white foam (140
mg, 88 %). Anal. Calc'd for C22H29N505 S~ C, 53.2; H, 6.47; N, 15.51.
Found: C,52.94; H, 6.18; N,15.34.
Example 10
N-[1-Toluene-4-sulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-L-phenylalanine
O
O N HO
~~OH
Step 1
To a solution of 1-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-4-piperidone (1.0 g,
3.95 mmol) and L-phenylalanine methyl ester (0.64 g, 3.58 mmol) in
methylene chloride (20 mL) was added acetic acid (0.62 mL, 10.78 mmol)
followed by sodium triacetoxyborohydride (1.9 g, 8.96 mmol). After 24 h,
the solvent was removed and the residue was taken up in ethyl acetate (50
mL), washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, saturated brine,
dried over potassium carbonate and evaporated to an amber oil which was
purified by flash chromatography (eluting with 98:1 methylene
chloride/methanol) to give N-[1-toluene-4-sulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-L-
phenylalanine methyl ester.
to 2
To a solution of N-[1-toluene-4-sulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-L-phenyl-
alanine methyl ester (0.2 g, 0.48 mmol) in THF (1 mL) was added 1N LiOH
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 187 -_
solution (0.46 mL, 0.46 mmol). After 24 h, the reaction mixture was diluted
with water (50 mL), extracted with diethyl ether and lyophilized to afford N-
[1-Toluene-4-sulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl)-L-phenylalanine as the lithium salt.
Anal. Calc'd for CZ,NZ6 NZO4SLi. SHzO: C, 57.79; H, 6.70; N, 6.42.
Found: C,57.7; H, 6.30; N,6.23.
Example 11
General Library synthesis
A solution of N (4,6-dichloro-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)-phenylalanine tert-butyl ester (0.018 mmol) in THF
(1.0 mL) was added to a solution of methylphenethylamine (0.018 mmol),
DIEA (0.036 mmol) in THF (1.0 mL) and shaken at 60°C overnight.
The
solvent was removed and the resulting oil was dissolved in DMF (0.5 mL).
To this solution was added a solution of isobutylamine (0.0213 mmol) and
DIEA (0.071 mmol) in DMF (0.5 mL). The resulting mixture was shaken at
110°C for 16 hrs. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The
oil was dissolved in a 1/1 solution of TFA/CHZCI, and shaken for 2 hours,
then the solvent was removed. The crude material was dissolved in a 1/1
solution of DMSO/CH3CN and purified by preparative LC/MS (preparative
method 2) and analyzed by LC/MS (analytical method 2) unless otherwise
noted.
Using the appropriate starting materials and reagents, the following
additional compounds were prepared:
N (3-nitrothiophen-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N [1-phenyltetrazol-5-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N [1,3-dimethyl-4-nitropyrazol-5-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyl-
oxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 188 --
N [1-ethylpyrazol-5-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (4-phenylsulfonylthiophen-3-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (1,4-diphenyl-1,2,3-triazol-5-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (1-phenylimidazol-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (6-bromopyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N [6-(naphth-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {3-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino)pyridin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {3-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino)pyridin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N (5-trifluoropyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {5-[[5-phenylcarbonylmethylthio-4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl))
1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)pyridin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)
phenylalanine;
N (4-methyl-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N (3,5-dinitropyridin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {3-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]pyridin-4-yl}-L-
phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 189 --
N [4-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-6-(2-methylpropylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(phenylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(benzylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethylamino)-6-[2-(4-
methylphenyl)ethylamino)]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[2-(4-methoxlphenyl)ethylamino))-6-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-
yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[(4-chlorobenzyl)amino)]-6-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-
yl)ethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethylamino]-4-[1-(phenyl)ethyl-
amino))-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N [4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-[N-methyl-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)-
amino)-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-(N,N-bis(2-methoxyethyl)-
amino]-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-[N-methyl-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-
1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/IJS00/01540
-- 190 --
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-methyl-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-
ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-[2-(4-methoxylphenyl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(methoxyethylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [6-(chlorobenzylamino)-4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl)-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [4-(cyclohexylmethylamino)-6-(3-methylisoxazol-5-ylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2- methylpropylamino)-6-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N [6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-4-(2-methylpropylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl]-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(2-methylpropylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalariine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(benzylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 191 --
N {4-(4-chlorobenzylamino)-6-[2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino)]-6-[2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl-
amino]-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(4-chlorobenzylamino)-6-[2-(4-methylphenyl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-[2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[2-(4-methoxybenzyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-(1-phenylethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(1-cyclhexylethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-6-(3,4-methylenedioxy-
benzylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzylamino)
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-chlorobenzylamino)-4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzylamino)-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl-
amino)-1,3,5- triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/IJS00/01540
-- 192 --
N {4-(cyclohexylmethylamino)-6-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-benzyl-N-(2-propyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(allyl)-N-(cyclopentyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(n-propyl)-N-(4-nitrobenzyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N,N-bis-(benzyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(2-cyanoethyl)-N-(benzyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 193 --
N {6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)amino]-4-(2-methylpropyl-
amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-
aminoJ-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-[N,N-bis-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-
amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methoxyethylamino)-6-[N,N-bis-(benzyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(cyclohexylamino)-6-[N-(phenyl)-N-(pyridin-2-yl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N,N-bis-(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-4-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(benzyl)-N-(2-propyl)amino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1, 3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1, 3, S-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-6-[N-
(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 194 --
N {4-[N-(ethyl)-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino]-6-[N-
(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methyl-
phenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-
N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N,N-bis-(benzyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(benzyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methyl-
phenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-methylpropylamino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-(benzylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 195 --
N {4-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-lyl)ethylamino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1, 3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N,N bis-(n-propyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenyl-
sulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4
methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(benzyl)-N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)amino]-6-[N-(methyl)-N-
(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(5-methylisoxazol-3-ylamino)-6-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-
methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino)-1, 3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N,N-bis-cyclohexylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-methylpropyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-phenyl-1-carboxamidoethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 196 --
N {4-(N-[2-phenyl-l,l-dimethylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-(2-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4.-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N (2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N (1-phenyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(ethyl)-N-(2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N-pyridin-4-ylmethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N-pyridin-3-ylmethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 197 --
N {4-chloro-6-[N-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(2-ethylhexyl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(N-pyridin-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(3,3-diphenylpropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-pyridin-2-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-pyridin-3-ylmethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-2-(4-ethoxy-3-methoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-2-phenylpropylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-1(S~-phenylethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-ethylhexyl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(4-(3,5-dioxopiperazin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N,N-dimethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 198 --
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N (2-phenylpropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-phenyl-1-carboxamidoethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-phenyl-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-(2-methoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-phenyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(4-(3,5-dioxopiperazin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl)-
amino]-1,3,5-triazin- 2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-3-(imidazol-2-yl)propylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2- yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 199 --
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-2-(phenoxy)ethylamino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-(S~-phenylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(N-(5-chloro-1,3-dimethylpyrazol-4-yl)amino]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(benzylsulfonyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-(R)-phenyl-2-carboxyethyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-phenylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[N-(1-phenyl-1-ethoxycarbonylmethyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[N-(benzyl)-N-(1-carboxy-2-phenylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(4-(3,S-dioxopiperazin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl)amino)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 200 --
N {4-[N-(2-(4-benzylpiperazin-lyl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N,N-dimethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-(2-phenoxyethyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-carboxy-1-(R)-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(1-ethoxycarbonyl-1-phenylmethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-(1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-carboxy-1-phenylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-2-methylpropylamino)-6-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-2-methylpropylamino)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-6-nitrobenzthiazol-2-ylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-furan-2-ylmethylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-1-phenylethylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 201 --
N {4-(N-4-chlorobenzylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(piperidin-1-yl)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-4-aminosulfonylbenzylamino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-benzylamino)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-
L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-cyclopentylamino)-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(5-ethyl-2-methylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(3,4-methylenedioxybenzyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-diphenylmethylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3-methylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3,5-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(N-cyclohexylamino-6-(3,5-dimethylmorpholin-4-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 202 --
N {4-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-6-(4-cyclohexyl-
piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-methyl-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-6-(3-methyl
piperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-[N-(2-(4-aminosulfonylphenyl)ethyl)amino)-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[2-(4-benzylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(isopropylaminocarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(1-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(furan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(1-phenylpropen-1-yl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(isopropylaminocarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin
2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(furan-2-ylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 203 --
N {4-chloro-6-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(4-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[4-(2-methoxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(2-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-1-yl)-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-[2-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-3-oxopiperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-[2-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-3-oxopiperazin-1-yl]-
1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(3-(R)methoxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroiso-
quinolin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-chloro-6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroiso-
quinolin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
N {4-hydroxy-6-(3-methoxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroiso-
quinolin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)-
phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 204 --
N {4-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[4-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-
4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(piperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyl-
oxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(2-ethoxycarbonylpiperidin-1-yl]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-[2-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-3-oxopiperazin-1-yl]-1,3,5-
triazin-2-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {4-(3-carboxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-methylpropyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-
pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(4-methylphenylsulfonyl)amino]-
pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(N-(methyl)-N-(2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(benzyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N
dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 205 --
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl)amino]pyrimidin-
4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(methyl)-N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-methyl-2-phenylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[4-(2-propylaminocarbonylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl)pyrimidin-4
yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[4-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)piperazin-1-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-
(N,N dimethylcarbamyloxy)phenylalanine;
N {6-[N-(2-phenylethyl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl}-L-4-(N,N dimethyl-
carbamyloxy)phenylalanine.
Example A
In vitro Assay For Determining Binding of
Candidate Compounds to VLA-4
An in vitro assay was used to assess binding of candidate compounds
to a4~3, integrin. Compounds which bind in this assay can be used to assess
VCAM-1 levels in biological samples by conventional assays (e.g.,
competitive assays). This assay is sensitive to ICSO values as low as about
lnM.
The activity of a4~31 integrin was measured by the interaction of
soluble VCAM-1 with Jurkat cells (e.g., American Type Culture Collection
Nos. TIB 152, TIB 153, and CRL 8163), a human T-cell line which
expresses high levels of a4(31 integrin. VCAM-1 interacts with the cell
surface in an a4~i, integrin-dependent fashion (Yednock, et al. J. Biol.
Chem., 1995, 270:28740).
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 206 --
Recombinant soluble VCAM-1 was expressed as a chimeric fusion
protein containing the seven extracellular domains of VCAM-1 on the N-
terminus and the human IgG, heavy chain constant region on the C-terminus.
The VCAM-1 fusion protein was made and purified by the manner described
by Yednock, supra.
Jurkat cells were grown in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10 % fetal
bovine serum, penicillin, streptomycin and glutamine as described by
Yednock, supra.
Jurkat cells were incubated with 1.5 mM MnCl2 and 5 ~cg/mL 15/7
antibody for 30 minutes on ice. Mn+2 activates the receptor to enhance
ligand binding, and 15/7 is a monoclonal antibody that recognizes an
activated/ligand occupied conformation of a~~3, integrin and locks the
molecule into this conformation thereby stabilizing the VCAM-1/a4(31
integrin interaction. Yednock, et al., supra. Antibodies similar to the 15/7
antibody have been prepared by other investigators (Luque, et al, 1996, J.
Biol. Chem. 271:11067) and may be used in this assay.
Cells were then incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature with
candidate compounds, in various concentrations ranging from 66 ~,M to 0.01
~,M using a standard 5-point serial dilution. 15 ~,L soluble recombinant
VCAM-1 fusion protein was then added to Jurkat cells and incubated for 30
minutes on ice. (Yednock et al., supra.).
Cells were then washed two times and resuspended in PE-conjugated
goat F(ab')2 anti-mouse IgG Fc (Immunotech, Westbrook, ME) at 1:200 and
incubated on ice, in the dark, for 30 minutes. Cells were washed twice and
analyzed with a standard fluorescence activated cell sorter ("FACS") analysis
as described in Yednock, et al., supra.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
__ 207 -_
Compounds having an ICSO of less than about 15~.M possess binding
affinity to a4~i, .
When tested in this assay, each of the compound prepared in the
above examples has or is expected to have an ICSO of 15 ,uM or less (or is
expected to be active in vivo).
Example B
In vitro Saturation Assay For Determining Binding of
Candidate Compounds to a4(3,
The following describes an in vitro assay to determine the plasma
levels needed for a compound to be active in the Experimental Autoimmune
Encephalomyelitis ("EAE") model, described in the next example, or in
other in vivo models.
Log-growth Jurkat cells are washed and resuspended in normal
animal plasma containing 20 ~.g/ml of the 15/7 antibody (described in the
above example).
The Jurkat cells are diluted two-fold into either normal plasma
samples containing known candidate compound amounts in various
concentrations ranging from 66 ~.M to 0.01 ~,M, using a standard 12 point
serial dilution for a standard curve, or into plasma samples obtained from the
peripheral blood of candidate compound-treated animals.
Cells are then incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature, washed
twice with phosphate-buffered saline ("PBS") containing 2 % fetal bovine
serum and 1mM each of calcium chloride and magnesium chloride (assay
medium) to remove unbound 15/7 antibody.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 208 --
The cells are then exposed to phycoerythrin-conjugated goat F(ab')Z
anti-mouse IgG Fc (Immunotech, Westbrook, ME), which has been adsorbed
for any non-specific cross-reactivity by co-incubation with 5 % serum from
the animal species being studied, at 1:200 and incubated in the dark at
4°C
S for 30 minutes.
Cells are washed twice with assay medium and resuspended in the
same. They are then analyzed with a standard fluorescence activated cell
sorter ("FACS") analysis as described in Yednock et al. J. Biol. Chem.,
1995, 270:28740.
The data is then graphed as fluorescence versus dose, e.g., in a
normal dose-response fashion. The dose levels that result in the upper
plateau of the curve represent the levels needed to obtain efficacy in an in
vivo model.
This assay may also be used to determine the plasma levels needed to
saturate the binding sites of other integrins, such as the ocy(3~ integrin,
which
is the integrin most closely related a4(3, (Palmer et al, 1993, J. Cell Bio.,
123:1289). Such binding is predictive of in vivo utility for inflammatory
conditions mediated by a9~3, integrin, including by way of example, airway
hyper-responsiveness and occlusion that occurs with chronic asthma, smooth
muscle cell proliferation in atherosclerosis, vascular occlusion following
angioplasty, fibrosis and glomerular scarring as a result of renal disease,
aortic stenosis, hypertrophy of synovial membranes in rheumatoid arthritis,
and inflammation and scarring that occur with the progression of ulcerative
colitis and Crohn's disease.
Accordingly, the above-described assay may be performed with a
human colon carcinoma cell line, SW 480 (ATTC #CCL228) transfected
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 209 --
with cDNA encoding a9 integrin (Yokosaki et al., 1994, J. Biol. Chem.,
269:26691), in place of the Jurkat cells, to measure the binding of the a9~3,
integrin. As a control, SW 480 cells which express other a and Vii, subunits
may be used.
Accordingly, another aspect of this invention is directed to a method
for treating a disease in a mammalian patient, which disease is mediated by
a9(3,, and which method comprises administering to said patient a
therapeutically effective amount of a compound of this invention. Such
compounds are preferably administered in a pharmaceutical composition
described herein above. Effective daily dosing will depend upon the age,
weight, condition of the patient which factors can be readily ascertained by
the attending clinician. However, in a preferred embodiment, the
compounds are administered from about 20 to 500 tcg/kg per day.
Example C
In vivo Evaluation
The standard multiple sclerosis model, Experimental Autoimmune (or
Allergic) Encephalomyelitis ("EAE"), was used to determine the effect of
candidate compounds to reduce motor impairment in rats or guinea pigs.
Reduction in motor impairment is based on blocking adhesion between
leukocytes and the endothelium and correlates with anti-inflammatory
activity in the candidate compound. This model has been previously
described by Keszthelyi et al., Neurology, 1996, 47:1053-1059, and
measures the delay of onset of disease.
Brains and spinal cords of adult Hartley guinea pigs were
homogenized in an equal volume of phosphate-buffered saline. An equal
volume of Freund's complete adjuvant (100 mg mycobacterium tuberculosis
plus 10 ml Freund's incomplete adjuvant) was added to the homogenate.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/~JS00/01540
-- 210 --
The mixture was emulsified by circulating it repeatedly through a 20 ml
syringe with a peristaltic pump for about 20 minutes.
Female Lewis rats (2-3 months old, 170-220 g) or Hartley guinea
pigs (20 day old, 180-200 g) were anesthetized with isoflurane and three
injections of the emulsion, 0.1 ml each, were made in each flank. Motor
impairment onset is seen in approximately 9 days.
Candidate compound treatment began on Day 8, just before onset of
symptoms. Compounds were administered subcutaneously ("SC"), orally
("PO") or intraperitoneally ("IP"). Doses were given in a range of lOmg/kg
to 200 mg/kg, bid, for five days, with typical dosing of 10 to 100 mg/kg SC,
10 to 50 mg/kg PO, and 10 to 100 mg/kg IP.
Antibody GGS/3 against a4~31 integrin (Keszthelyi et al., Neurology,
1996, 47:1053-1059), which delays the onset of symptoms, was used as a
positive control and was injected subcutaneously at 3 mg/kg on Day 8 and
11.
Body weight and motor impairment were measured daily. Motor
impairment was rated with the following clinical score:
0 no change
1 tail weakness or paralysis
2 hindlimb weakness
3 hindlimb paralysis
4 moribund or dead
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 211 --
A candidate compound was considered active if it delayed the onset of
symptoms, e.g., produced clinical scores no greater than 2 or slowed body
weight loss as compared to the control.
Example D
Asthma Model
Inflammatory conditions mediated by a4~31 integrin include, for
example, airway hyper-responsiveness and occlusion that occurs with chronic
asthma. The following describes an asthma model which can be used to
study the in vivo effects of the compounds of this invention for use in
treating
asthma.
Following the procedures described by Abraham et al, J. Clin. Invest,
93:776-787 (1994) and Abraham et al, Am J. Respir Crit Care Med,
156:696-703 (1997), both of which are incorporated by reference in their
entirety. Compounds of this invention are formulated into an aerosol and
administered to sheep which are hypersensitive to Ascaris suum antigen.
Compounds which decrease the early antigen-induced bronchial response
and/or block the late-phase airway response, e.g., have a protective effect
against antigen-induced late responses and airway hyper-responsiveness
("AHR"), are considered to be active in this model.
Allergic sheep which are shown to develop both early and late
bronchial responses to inhaled Ascaris suum antigen are used to study the
airway effects of the candidate compounds. Following topical anesthesia of
the nasal passages with 2 % lidocaine, a balloon catheter is advanced through
one nostril into the lower esophagus. The animals are then intubated with a
cuffed endotracheal tube through the other nostril with a flexible fiberoptic
bronchoscope as a guide.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 212 --
Pleural pressure is estimated according to Abraham (1994). Aerosols
(see formulation below) are generated using a disposable medical nebulizer
that provides an aerosol with a mass median aerodynamic diameter of 3.2 ~,m
as determined with an Andersen cascade impactor. The nebulizer is
connected to a dosimeter system consisting of a solenoid valve and a source
of compressed air (20 psi). The output of the nebulizer is directed into a
plastic T-piece, one end of which is connected to the inspiratory port of a
piston respirator. The solenoid valve is activated for 1 second at the
beginning of the inspiratory cycle of the respirator. Aerosols are delivered
at
VT of 500 ml and a rate of 20 breaths/minute. A 0.5 % sodium bicarbonate
solution only is used as a control.
To assess bronchial responsiveness, cumulative concentration-
response curves to carbachol can be generated according to Abraham (1994).
Bronchial biopsies can be taken prior to and following the initiation of
treatment and 24 hours after antigen challenge. Bronchial biopsies can be
preformed according to Abraham (1994).
An in vitro adhesion study of alveolar macrophages can also be
performed according to Abraham (1994), and a percentage of adherent cells
is calculated.
Aerosol Formulation
A solution of the candidate compound in 0.5 % sodium
bicarbonate/saline (w/v) at a concentration of 30.0 mg/mL is prepared using
the following procedure:
A. Preparation of 0.5 % Sodium Bicarbonate / Saline Stock Solution:
100.0 mL
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 213 --
Ingredient Gram / 100.0 Final Concentration
mL
Sodium Bicarbonate0.5 g 0.5
Saline q.s. ad 100.0 q.s. ad 100%
mL
Procedure:
1. Add O.Sg sodium bicarbonate into a 100 mL volumetric flask.
2. Add approximately 90.0 mL saline and sonicate until
dissolved.
3. Q.S. to 100.0 mL with saline and mix thoroughly.
B. Preparation of 30.0 m~/mL Candidate Compound 10 0 mL
Ingredient Gram / 10.0 mL Final Concentration
Candidate Compound0.300 g 30.0 mg/mL
0.5% Sodium q.s. ad 10.0 mL q.s ad 100%
Bicarbonate / Saline
Stock Solution
Procedure:
1. Add 0.300 g of the candidate compound into a 10.0 mL
volumetric flask.
2. Add approximately 9.7 mL of 0.5 % sodium bicarbonate /
saline stock solution.
3. Sonicate until the candidate compound is completely
dissolved.
4. Q.S. to 10.0 mL with 0.5% sodium bicarbonate / saline stock
solution and mix thoroughly.
Using a conventional oral formulation, compounds of this invention
would be active in this model.
CA 02359113 2001-07-05
WO 00/43369 PCT/US00/01540
-- 214 --
Example E
Allograft Model
Allograft rejection, associated with infiltration of inflammatory cells,
is the leading obstacle to long-term allograft survival. Cell surface adhesion
molecules facilitate alloantigen recognition in vitro and may be critical for
lymphocyte traffic in vivo. The following describes a model which can be
used to study the in vivo effects of the compounds of this invention in the
control of allograft rejection.
The following procedures are described in Coito et al. ,
Transplantation ( 1998) 65(6):699-706 and in Korom et al. , Transplantation
(1998) 65(6):854-859, both of which are incorporated by reference in their
entirety.
Following the procedures described in Coito and Korom, male adult
rats weighing approximately 200 - 250 g are used in this model. Lewis rats
are used as the recipients of cardiac allografts from Lewis X Brown Norway
rats. Hearts are transplanted into the abdominal great vessels using standard
microvascular techniques.
A candidate compound is administered to the transplant recipient in a
suitable pharmaceutical carrier for a 7-day course of treatment starting the
day of the engraftment. Doses range from 0.3 to 30 mg/kg/day. Control
recipients receive the pharmaceutical carrier only.
The rats are euthanized and their cardiac allografts are analyzed as
described in Coito and Korom.
Using conventional formulations, compounds of this invention would
be active in this model.