Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
SYSTEM FOR DETECTING AND CONTROLLING ZONAL
TRANSITIONS OF OBJECTS
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention pertains to the field of electronic monitoring of object
movement between
specified regions.
BACKGROUND
There are a number of electronic devices that can be used to identify and
track the movement of
people and objects. Such devices may be useful in electronic animal
identification, baggage
tracking, parcel tracking, inventory management applications, asset
identification and tracking,
and other applications involving identification and tracking of people and
things. For example,
these applications may involve transmitting stored information from a RFID
tag, memory card or
microprocessor card to an exciter/reader system in close proximity with these
units. Also, these
applications may involve writing information to a unit.
Radio frequency identification tags are frequently used for personal
identification in automated
gate sentry applications protecting secured buildings or areas. These tags
often take the form of
access control cards. Information stored on the radio frequency identification
tag identifies the
person seeking access to the secured building or area. Older automated gate
sentry applications
require the person accessing the building to insert or swipe their
identification tag into or through
a reader for the system to read the information from the identification tag.
Newer radio
frequency identification tag systems allow the radio frequency identification
tag to be read at a
short distance using radio frequency data transmission technology, thereby
eliminating the need
to insert or swipe an identification tag into or through a reader. Most
typically, the user simply
holds or places the radio frequency identification tag near a base station,
which is coupled to a
security system securing the building or area. The base station transmits an
excitation signal to
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
the radio frequency identification tag that powers circuitry contained on the
radio frequency
identification tag. The circuitry, in response to the excitation signal,
communicates stored
information from the radio frequency tag to the base station, which receives
and decodes the
information. The information read is used by the security system to determine
if access is
appropriate. Also, radio frequency identification tags may be written remotely
by an excitation
signal appropriately modulated in a predetermined manner.
These types of tracking systems may be also used to track the movement of
people and things.
For example, PCT Patent Application Number PCT/US99/20685 provides an object
tracking and
IO control system that is particularly suited to implementation at an
automobile dealership. The
system includes a Key Track system adapted to control access to and log the
check out and check
in of keys to vehicles on the lot. RFID tags are provided on the vehicles and
tag readers are
embedded at selected locations within the dealership parking lot to detect
movement of vehicles.
In one embodiment, the lot is subdivided into zones and the readers are
located at transitions
regions between the zones. Information about the check out and check in of
keys from the Key
Track system is combined and integrated with information about the movement of
vehicles about
the lot to reach conclusions regarding authorised movement to provide useful
information to
dealership management.
In addition, U.S. Patent No. 4,275,385 discloses a personnel locator system
using a periodic
unique infrared identification code emitted from a battery-powered transmitter
unit to identify the
person carrying the transmitter unit to an overhead infrared receiver as the
person enters the
receiver's monitoring zone. The transmitter unit identification code together
with the receiver
identification code is communicated to a common control unit which displays
the location of all
of the transmitter units. Additionally, the system controls electronic locks
for restricting access
of users to certain locations or equipment.
Furthermore, there are credit card-sized devices having memory, processing
logic or other digital
and analog electronics which are commonly known as microprocessor cards or
"smart cards".
Typically, microprocessor cards may be programmed to perform a wide variety of
functions. For
2
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
example, a single microprocessor card may be programmed to open doors as a
key, store medical
information and serve as an electronic credit card and may contain data about
the cardholder.
There a particular types of smart cards that require contact with a reader
device in order to
transfer information, however certain types of smart cards, commonly known as
contactless
smart cards, can communicate data with a reader device via a wireless radio
frequency (RF),
inductive or similar communication link that does not require electrical
(galvanic) contact
between the smart card and reader device.
For example, smart farecards have been used for, among other purposes, payment
of mass-transit
fares. A patron can purchase a farecard having a certain denomination or value
that corresponds
to an account balance. To board a mass-transit vehicle, the patron places the
farecard in the
vicinity of the reader device. Via wireless or otherwise contactless
communication between the
reader and farecard, the reader device detects the presence of the farecard,
identifies the account
associated with that farecard, and debits the account balance. If the account
balance is greater
than the fare, the reader indicates such and allows the patron to board the
vehicle. The
transaction may include other steps as welt, such as confirming the
authenticity of the farecard.
In some mass-transit systems, patrons must also present their farecards to the
reader device upon
exiting the vehicle. Such systems are sometimes referred to as check-in check-
out (CICO)
systems because a patron must use the reader both upon entering or checking
into the vehicle and
exiting or checking out of the vehicle. A CICO system can base the fare upon
distance travelled,
travel zones crossed or time elapsed.
While each of the above mentioned types of electronic card systems provide the
desired results,
these electronic cards can be used by any person if for example they are
misplaced or stolen. In
order to prevent this situation, these cards may have information imprinted
thereon including
pictures for example thereby identifying the authorised user. However, this
only allows a
particular card to be used by one person and it thus cannot be reused easily.
Therefore there is a
need for an improved electronic card for use with object tracking and
identification incorporating
an adjustable image display.
3
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
This background information is provided for the purpose of making known
information believed
by the applicant to be of possible relevance to the present invention. No
admission is necessarily
intended, nor should be construed, that any of the preceding information
constitutes prior art
against the present invention.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
An object of the present invention is to provide a system for detecting and
controlling zonal
transitions of objects. In accordance with an aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a
system for detecting and controlling zonal transitions of one or more objects
within a predefined
area comprising two or more zones, said system comprising: one or more memory
means for
storing information relating to said object including a unique identification
number; an adjustable
electronic display for displaying information relating to the object to which
the portable unit is
connected; transmitting and receiving means for communication with one or more
reader units;
and a control means for controlling the functionality of the portable unit,
wherein said control
means is in electronic communication with said one or more memory means, said
adjustable
electronic display and said transmitting and receiving means enabling transfer
of information
therebetween; one or more reader units positioned at predetermined locations
within the
predefined area comprising a means for communication with the one or more
portable units; and
a database system for storing, managing and analysing information relating to
said objects,
wherein said database system comprises a means for communication with the one
or more reader
units for detecting zonal transitions of objects within the predefined area.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
Figure 1 illustrates a schematic of the components of the system according to
one embodiment of
the present invention.
Figure 2 illustrates a schematic of the components of a portable unit
according to one
embodiment of the present invention.
4
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention provides a system for detecting and controlling zonal
transitions of one or
more objects within a predefined area, wherein said area comprises two or more
zones. In one
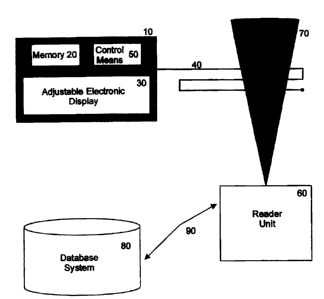
embodiment of the present invention and with reference to Figure 1, the system
comprises: a
portable unit 10 wherein a portable unit can be connected to each object and
the portable unit 10
comprises one or more memory means 20; an adjustable electronic display 30;
transmitting and
receiving means 40; and a control means 50. The system of the present
invention further
comprises one or more reader units 60 positioned at predetermined locations
within the
predefined area and a database system 80 for storing, managing and analysing
information
relating to said objects.
In one embodiment of the present invention, each reader unit can establish a
communication field
70 enabling the communication between a portable unit 10 and a reader unit 60.
In addition,
each reader unit 60 is interconnected with the database system 80 via a
communication link 90,
enabling the transfer of information between the one or more reader units GO
and the database
system 80. The database system, by correlating the position of each of the
reader units with the
detection of the one or more portable units, can establish the zonal position
of a portable unit and
hence the object to which it is attached.
Portable Unit
In one embodiment of the present invention, a portable unit comprises one or
more memory
means for storing information relating to said object including a unique
identification number; an
adjustable electronic display for displaying information relating to the
object to which the
portable unit is connected; transmitting and receiving means for communication
with one or
more reader units and a control means for controlling the functionality of the
portable unit. Each
5
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
of these components is in electronic communication with one another in order
to provide a means
for the transfer of information between the multiple components of a portable
unit.
In one embodiment the memory means can be incorporated into a microprocessor
card otherwise
known as a "smart card" which can comprise a region of permanent memory and a
region of
transitory memory. For example, information which is contained in the
permanent memory can
comprise a plurality of instructions that relate to the control of the
adjustable electronic display
and the control of the modulation and demodulation of signals transmitted
between a portable
unit and a reader unit. The permanent memory of a portable unit can also
comprise a unique
identification number enabling the identification of a particular portable
unit by a reader unit
independent of the object to which it is attached. The transitory memory can
comprise
information that relates to the object to which the portable unit is
connected, for example, the
name of the object possibly including graphical images of the same, the
security level attributed
to the object, biometric identification. In addition, it may contain
information relating to
payment of fees for access to particular zones by the object, for example
electronic ticket
information. In one embodiment, this transitory information can be encoded
into the memory
means of a portable unit using for an encoding device, for example. In one
embodiment, this
information can be modified during a communication session between said
portable unit and a
reader unit or both.
In one embodiment, the unique identification number of a particular portable
unit can be in the
form of an RFID (radio frequency identification) tag that is incorporated into
the portable unit.
As is known to a worker skilled in the art, many RFID tags are passive devices
that store a
unique code and are powered by capturing a fraction of the energy radiated by
a reader unit when
the tag is in the vicinity said reader unit. More specifically, RFID tags
typically comprise a small
antenna coupled to an integrated circuit chip, which includes a memory for
storing an
identification code and perhaps other information in addition to controlling
mechanisms for
transmitting the code to be received by a reader unit. Active RFID tags are
also available as
alternatives to passive tags. Generally, active tags have an on board power
source and many are
6
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
able to receive and store data as well as communicate data to a reader, as do
passive tags. Each
of these types of RFID tags can be incorporated into the present invention.
In one embodiment, the adjustable electronic display presents information
relating to the object
to which the portable unit is connected, wherein this information can be
stored in the memory
means of the portable unit. The adjustable electronic display device can be
selected from a
number of display systems for example LCD (liquid crystal display), LED (light
emitting diode)
and electrophoretic displays such as E-inkTM or Smart PaperTM. Other
electronic display systems
that provide the ability to adjust the information being presented and can be
constructed in a
compact form, would be known to a worker skilled in the art.
In one embodiment the adjustable electronic display is selected such that the
power consumption
of the adjustable electronic display is minimal. For example the display can
be selected such that
minimal or no power consumption is required by the adjustable electronic
display when the
image is static and power consumption occurs primarily during the adjustment
of the display
image. In a preferred embodiment, an adjustable electronic display for use
with the present
invention formed using E-inkTM or Smart PaperTM.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the adjustable electronic display
can be used to
present a plurality of information. This information can be determined based
on the application
of the system according to the present invention. For example, this
information can be
alphanumeric and/or image identification of the object with which a particular
portable unit is
associated, the security clearance of the associated object, the current
location status of the object
or any other type of information which would be appropriate for the intended
use of the system.
In one embodiment of the present invention receiving and transmitting means
are provided in the
form of an antenna as would be known to a worker skilled in the art. Using
this type of device
the communication between a portable device and a reader unit is performed
using
electromagnetic radiation projected and received by an antenna. In one
embodiment, there are a
number of antennas associated with one particular portable unit, wherein one
antenna can be
7
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
associated with an RFID tag and a further antenna can be associated with an
integrated circuit
being a component of a microprocessor card, for example.
In one embodiment, a portable unit further comprises a control means that can
be a component of
an integrated circuit, wherein said control means controls the functionality
of the portable unit.
For example the control means can access information contained within the
memory means for
instructions to enable the communication between a portable unit and a reader
unit. The control
means further controls the information which is transmitted to the adjustable
electronic display
and thus monitors and amends the display based on information contained within
the memory
means of the portable unit or based on information transmitted by a reader
device. The control
means can also regulate a plurality of additional functions of the portable
unit as would be known
to a worker skilled in the art.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the elements of a portable unit
can be provided in a
plurality of forms by means of a number of different components. In addition,
a number of
elements of a portable unit may be provided by one component, for example, an
integrated
circuit chip can incorporate a memory means, a transmitting and receiving
means and a control
means, thus enabling these functions to be provided by a single component.
In one embodiment of the present invention and with reference to Figure 2, a
portable unit 10 can
be separated into two main components, these being the main housing 100 and an
integrated
circuit card 200. The main housing 100 comprises an adjustable electronic
display 110 and a
radio frequency identification chip 120. The integrated circuit card 200
comprises one or more
integrated circuit chips 210, 220 and a power source 230. In addition, this
embodiment
incorporates two antennas 140, 240 into the portable unit, wherein one antenna
140 provides a
means for communication with the RFID chip 120 and the other antenna 240
provides a means
for communication with the components of the integrated circuit card 200.
These two main
components can be separate entities and prior to deployment of the portable
unit, the integrated
circuit card 200 can be inserted into the main housing 100. Optionally, a
portable unit 10 can be
8
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
fabricated such that the integrated circuit card 200 and the main housing 100
are constructed as a
single entity.
As would be known to a worker skilled in the art, an integrated circuit chip
can be a contact chip
which requires electrical (galvanic) contact in order for information to be
transferred or a
contactless chip which can transmit and receive information in a wireless
manner using for
example electro-magnetic radiation. The choice of the type of integrated
circuit chip can be
based on, for example, the application for which the device is being used or
the frequency of use
of the device.
In one embodiment of the present invention, a portable unit can comprise both
a contact
integrated circuit chip and a contactless integrated circuit chip. For
example, the contact chip can
contain information relating to the fuctionality of the adjustable electronic
display, wherein this
information may be adjusted only when the portable unit is associated with
another object.
Furthermore, the contactless integrated circuit chip may contain information
which is required by
reader units on a frequent basis, for example information relating to
electronic ticketing, security
clearance or identification information. There are plurality of manufacturers
of integrated circuit
chips which may be incorporated into the present invention. These
manufacturers can be for
example, MikronTM, MotorolaTM or SiemensTM.
In one embodiment, the main housing of a portable unit is foamed using
polycarbonate (PC),
polyvinylchloride (PVC), acrylonitrile butadiene styrol (ABS), fibreglass,
carbon fibre or any
other material which is resilient, lightweight and non-conductive as would be
known to a worker
skilled in the art.
In one embodiment of the present invention, a portable unit is constructed
such that it is
approximately the size of a typical employee identification card. In addition,
a portable unit is
constructed such that the weight of the device is minimal, thereby allowing
for a clipping device
to secure a portable unit to a person's jacket, for example.
9
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
Reader Unit
In one embodiment of the present invention, a reader unit is capable of
communication with each
portable unit within the system in addition to the database system. This
enables the information
collected by a reader unit from each of the portable units to be transmitted
to the database
system. A reader unit can also transmit instructions or information to a
portable unit, wherein
these transmissions can be instructions for the performance of a particular
action. For example,
these instructions can be to change the adjustable display or to amend the
information which is
stored by the memory means associated with the portable unit.
In one embodiment of the present invention, a reader unit can communicate with
a portable unit
in a contact or contactless manner, wherein the mode of communication is
determined by the
type of integrated circuit which is associated with the portable unit as
previously described. For
example, a contact reader can have a slot or any other type of configuration
as would be known
to a worker skilled in the art, providing a means for establishing electrical
contact between the
portable unit and the reader unit. In this manner a reader unit can inter
ogate the portable unit for
required information and can transmit information to the portable unit in
response to the
previously acquired information. In a preferred embodiment, the communication
between a
reader unit and a portable unit is performed in a contactless manner. For
example, the reader unit
can produce a communication field of electro-magnetic radiation wherein this
field provides a
means for the transfer of information between a portable unit and a reader
unit as would be
known to a worker skilled in the art. In one embodiment, the contactless
communication
between a reader unit and a portable unit can be designed to be compatible
with many different
wireless communication standards, for example, BluetoothTM, WiFi 802.11a-g, or
Home RF.
In addition, the communication field produced by a reader unit can further
enable a passive
integrated circuit or RFID tag within a portable unit, to generate power to
enable it to function, as
would be known to a worker skilled in the art.
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
In one embodiment, the process of information transfer between the reader
units and the database
system can be performed in a number of different formats. For example, each
reader unit can be
hardwired to the database system by means of ether cabling, for example,
enabling information
transfer. In addition, a wireless communication network can be established for
communication
using for example, BluetoothT'", WiFi 802.11a-g, or Home RF. The selection of
the method of
communication between the reader units and the database system can be
determined by the
application of use of the present invention. For example, if the system is
being used in a
permanent manner and the reader units will be located at specific locations
for extended periods
of time, a hardwired system may be the most cost effective. However, if the
system is being
operated at a particular site for a short period of time, wireless
communication between the
reader units and the database system may be more effective.
In one embodiment, the information gathered by the reader units may be
transferred to an
intermediate location prior to transmission to the database system. In this
type of configuration a
main node can receive information from the reader units and subsequently
transmit this
information to the database system, thereby reducing the transmissions
received by the database
system. This type of configuration may be convenient if the database system is
remotely located
in relation to the reader units. The main node can communicate with the reader
units using the
method as previously described for communication with the database system. In
addition, the
main node can communicate with the remotely located database system using for
example the
Internet, wherein said main node gains access to the Internet through an
Internet gateway which
may be configured as a wireless or hardwired gateway as would be understood by
a worker
skilled in the art. Security of the information transmitted over the Internet
can be provided using
Internet information transfer protocols, for example Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL).
Database System
In one embodiment of the present invention, the database system contains a
plurality of
information relating to the objects, portable units and reader units of the
present invention. This
information can be original information in addition to supplemental
information obtained during
communication sessions between reader units and portable units. For example,
the information
11
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
contained within the database system comprises the location and identification
of each reader
unit, the identification of each portable unit and information relating to the
objects with which a
portable unit is associated. Through the con elation of information relating
to the location of the
reader units and the portable units identified by particular reader units, the
database system can
calculate the zonal location of each portable unit within the predefined area.
In one embodiment, the database system comprises means for controlling a
plurality of access
points in relation to zonal transition areas, for example door locks, alarm
systems and the like.
By the determination of the location of a particular portable unit in relation
to a zonal transition
area identified by a reader unit, the database system can evaluate the access
rights of the portable
unit and hence the object with which it is associated, for entrance into the
adjacent zone
associated with the zonal transition area. If for example, the object does not
have access rights
for the adjacent zone, the database system can keep the "door" locked, or
activate an alarm
system to indicate unauthorised entrance attempt.
In one embodiment, the original information relating to an object can be the
security clearance or
access rights of this object to particular zones within the predetermined
area. Therefore, the
database system, upon identification of a particular portable unit and hence
the associated object,
can determine if this object has access rights to a particular zone or a
connected zone. In this
manner the system according to the present invention can provide security
within the
predetermined area.
In one embodiment, the database system can be located at the site of the
deployment of the
present invention or can equally well be remotely located in relation to the
deployment site. For
example, the use of a remotely or locally situated database system can be
determined based on
the permanence of the use or the scale of use of the system of the present
invention. It would be
obvious to a worker skilled in the art that the functionality of a single
database system can be
optimised in relation to the quantity of reader units and portable units with
which it is associated.
This form of optimisation provides a means for effectively utilising the
computational
capabilities of a database system, while not over loading the system resulting
in diminished
12
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
performance. This optimisation of a system according to the present invention
can determine if it
is more effective to have a remote or locally situated database system. If,
for example a remotely
located database system is selected, a single database system can be
associated with multiple
deployment sites.
In one embodiment, the database system can operate using an application like
BeehiveT"' in order
to manage the information relating to the original object information and the
supplemental
information collected by the reader units during communication sessions with
the plurality of
portable units. The BeehiveTM application comprises a SQL (structured query
language)
database and a plurality of active server pages. This type of database system
application can also
be based on and integrated into a MicrosoftTM platform. In addition, alternate
configurations of
the database system can incorporate JavaTM programming incorporated into an
OracleTM
database. Further configurations of the database system would be known to a
worker skilled in
the art.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the database system can be mufti-
tiered, wherein
computational actions are performed by one tier of the database system and the
storage of the
plurality of information is performed by a further tier of the database
system. This type of multi-
tiering of the database system would be known to a worker skilled in the art.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the database system further
correlates the plurality
of information relating to the zonal tracking of each portable unit including
zonal transitions,
thereby enabling the complete history of the movement of each portable unit to
be monitored.
Encoding Device
In one embodiment of the present invention, an encoding device is used to
encode information
onto the one or more integrated circuits incorporated into a particular
portable unit. This
encoded information typically comprises data relating to the object with which
the particular
portable unit is to be associated. For example, encoding devices providing the
required
functionality for the present invention are produced by Gemplus International
SA and Verifone
13
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
Ltd. Other encoding devices which may be incorporated into the present
invention would be
known to a worker skilled in the art.
In one embodiment, the data encoded on the portable unit can comprise alpha-
numerical
information, graphical or image information, executable programs wherein
parameters for
execution can be provided by a reader unit during communication with the
portable unit, or any
other information which may be relevant to the object in question or
information required for a
particular application. During communication with reader units and the
database system this
encoded information may be amended. As would be known to a worker skilled in
the art
information relating to the function of the various components of a portable
unit are permanently
contained within the integrated circuits and this information cannot be
modified after it is
installed.
In one embodiment, the method of encoding which is used by an encoding device
is directly
related to the type integrated circuit which it is encoding, for example,
contact or contactless
integrated circuits. Applicable forms of the encoding device for each of these
types of encoding
procedures would be known to a worker skilled in the art.
Uses of the System
Security Application
In one embodiment, the system of the present invention can be used to provide
security within a
building or other area where there are a plurality of different zones, wherein
each of these
different zones may require a particular level of security clearance in order
for access to be
granted. For example a facility of this type may be an airport, a research and
development
facility, a nuclear power plant, government agency facilities or other similar
locations where
security is essential. In this type of application at a facility, portable
units can be associated with
both visitor and employees, thereby providing a means for monitoring the zonal
transitions of
individuals within the facility, in addition to providing access, if
appropriate, to zones within the
facility.
14
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
For example, in this type of application of the system, a portable unit can be
associated with a
particular person and this unit can be encoded with the personal information
of the wearer, for
example name, occupation, employee number, security clearance level, picture,
biometric
identification and/or any other personal information which may be relevant to
the desired
application. Using the system of the present invention, the tracking of zonal
transitions of a
person and providing access to particular zones within the area or building
based on the security
clearance of the person is possible. The system can monitor the tonal location
of a plurality of
people within a predefined area through the communication between reader units
and portable
units. Since the location of each reader unit is predetermined, the location
of a portable unit can
be determined based on the identification of the reader unit with which it
communicates. Upon
identification of the portable unit and hence the person using it, the system
can provide access to
an adjacent zone if an acceptable clearance level is provided. This access to
the adjacent zone
can be provided by unlocking a door, for example. If for example, a person
accidentally gains
access to a zone for which they do not have security clearance, the system can
deny any further
tonal transition of this person thereby isolating said person within said
zone.
The adjustable electronic display associated with the portable unit can
display selected pieces of
the individual's personal information for visual examination by security
personnel thereby
enabling the verification of the appropriate owner of a particular portable
unit. For example, this
displayed information can comprise a picture, name, security clearance level,
employee number
or any other type of information enabling easy visual identification. In
addition, if during
communication between a portable unit and a reader unit, it is established
that the individual
associated with the portable unit does not have security clearance to access
the adjacent zone, the
reader unit can send instructions to the portable unit to modify the
adjustable electronic display
to indicate that access is denied. In this manner, it is again easy for visual
evaluation of the
security clearance of an individual by security personnel, for example.
In one embodiment, a biometric identification device can be associated with
each transition zone,
thereby enabling the verification of the person associated with a particular
portable unit. In this
manner the personal information encoded on the portable device can be
correlated with the
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
biometric identification information acquired at the zonal transition area,
prior to authorisation of
a zonal transition of the individual and the associated portable unit.
Conference Application
In one embodiment, the system of the present invention can be used in a
conference setting, thus
enabling the tracking and access control of delegates to particular
presentations and meetings, for
example. For this application, each delegate can receive a personally encoded
portable unit at the
commencement of the conference, wherein the adjustable electronic display is
capable of visually
presenting the delegate's personal identification information, for example
name and picture,
enabling visual identification by other delegates. In addition, reader units
can be strategically
located at the entrances of conference and meeting rooms for monitoring and
controlling zonal
transitions of the delegates.
For example, just prior to a delegate entering a particular conference room,
their portable unit is
interrogated for identification by the reader unit associated with this
particular room. The reader
unit upon identification of the portable unit can send this zonal transition
information to the
database system for correlation. In this manner, the conference organisers, by
accessing the
correlated information within the database system, can track the attendance
figures for the
presentations at the conference in addition to evaluating the performance of
the presenters. The
performance of a presenter can be partially established by determining the
number of delegates at
the beginning of a particular presentation, relative to the number of
delegates leaving the
presentation at its conclusion.
In one embodiment, during a communication session between a portable unit and
a reader unit,
the reader unit can transmit instructions to the portable unit for adjustment
of the adjustable
electronic display. For example, typically at conferences there are particular
identification tags
for speakers, organisers or support staff providing easy visual identification
of these individuals
during the conference. By using the system of the present invention, as a
speaker is entering the
room in which they are to be presenting, the reader unit can transmit
instructions to the portable
unit of the speaker for the adjustable electronic display to indicate the
speaker of the session.
16
CA 02366140 2001-12-21
This enables the organisers to limit the amount of additional articles
distributed to the delegates
upon registering for the conference, since the portable unit can display
relevant information at
particular times, with this plurality of information being contained within
the database system.
The invention being thus described, it will be obvious that the same may be
varied in many ways.
Such variations are not to be regarded as a departure from the spirit and
scope of the invention,
and aI1 such modifications as would be obvious to one skilled in the art are
intended to be
included within the scope of the following claims.
17