Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02367883 2002-O1-15
SLIDING FENCE FOR A COMPOUND MITER SAW
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to fences for miter saws and in particular, to
compound miter saws.
2. Background Art
Compound miter saws both of the fixed pivot arm type and the sliding type are
generally provided
with a rotary table, right and left f~~i table sections which collectively
define a horizontal planer table surface
and a stationary fence which extends perpendicularly upward from the rear edge
of the table surface. A
workpiece to be cut is supported and/or clamped against the horizontal table
and the fence to stabilize the
workpiece during the cutting process. Miter saw fences are typically provided
with an open center section
1 S aligned at the saw blade and right and left vertical support surface on
opposite sides of the saw blade. In order
to maintain the right and left fence portions in a common plane, fences are
frequently made of unitary casting
with the right and left fence portions interconnected by a low profile C-
shaped section located sufficiently
behind the back of the saw Made so as to avoid interference.
If the user wants to vary the miter angle, the rotary table and the rotary
cutting blade are pivoted about
a generally vertical axis. In order to make a compound miter cut, the saw
blade and motor assembly is tilted
about a horizontal axis which lies proximate the plane of the rotary table.
Typically, the saw blade will be
able to be adjusted from a vertical position to a 45° counter-clockwise
when viewed from the front of the miter
saw. In order to accommodate blade movement, the left fence portion needs to
be cut away sufficiently so
as to not interfere with the saw blade or the associated protective guard
housing when the saw is being used
at the maximum tilt angle. Unfortunately, when the saw is used with the blade
perpendicular to the table, i.e.
"0" tilt, the cutaway left fence provides less support than desirable,
particularly when cutting short OR tall
workpieces. To address this problem in the past, some users have installed
temporary fence extensions, such
as'/Z" thick hardwood boards overlying the right and left fence members. These
fence extensions can be taller
and extend inwardly toward the saw blade as far as possible without
interfering with the blade or guard
moving at the "0" tilt orientafion. When the saw blade needs to be tilt, the
fence extension must be removed
in order for the rotary blade and motor arm assembly to tilt.
CA 02367883 2002-O1-15
In an effort to maximize the fence area and workpiece support, efforts have
been made to create fences
which are shiftable by the user. Shiftable fences must be set using a trial
and error technique, typically by
moving the fence inboard while holding the blade in the plunged position in
order to maximize support while
protecting interference. Simply setting the fence by eye can result in
interference between the blade guard
and the fence during a cut which invariably will result in a less than perfect
cut in the workpiece since the
workpiece will have to be unclamped and the fence readjusted, the workpiece
reclamped and the cutting
process continued.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is intended to provide a slidable fence to enable the
position of the fence to be
varied inwardly in order to maximize the support at various tilt angles of the
blade assembly. Accordingly,
a compound miter saw is provided with a fence assembly having a right and left
fence portion extending on
opposite sides of the tiltable blade assembly. At least one of the fence
assemblies is provided with an
adjustable portion which may be moved transversely toward and away from the
blade and fixable to the table
at various positions which provides clearance between the blade and fence, yet
maximizes the support of the
workpiece in the region immediate the saw blade. A scale is provided on the
fixed and adjustable fence
portion providing an indication of maximum inboard position for various tilt
angles.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
FIGURE 1 is a front perspective view of a miter saw incorporating a fence of
the present invention
at a "0" blade tilt orientation;
FIGURE 2 is a view of the miter saw of Figure 1 with the blade tilted at
45°;
FIGURE 3 is a front perspective view of an alternative miter saw embodiment;
FIGURE 4 is a left quarter perspective view of the miter saw of Figure 3;
FIGURE 5 is a front view of a sliding fence assembly utilized on the miter saw
of Figure 3 with the
fence position at the "0" tilt orientation;
2
CA 02367883 2002-O1-15
FIGURE 6 is an enlarged partial view of the sliding fence of Figure 5 with the
fence position at the
15° tilt orientation;
FIGURE 7 is an enlarged partial front view of the sliding fence of Figure 5
with the fence position
at the 30° tilt orientation;
FIGURE 8 is a rear view of the sliding fence of Figure 5;
FIGURE 9 is an exploded perspective view of the rear side with a sliding
fence; and
FIGURE 10 is a front view illustrating an alternative scale embodiment, hut
otherwise corresponding
to the adjustable fence section shown in Figure 7.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS)
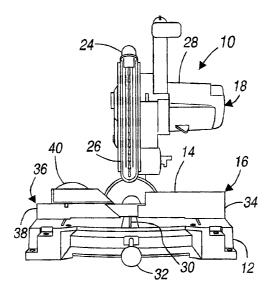
Figures 1 and 2 illustrate a first compound miter saw 10 incorporating the
present invention.
Compound miter saw 10 is provided with a fixed base 12, rotary table 14 which
is pivotable relative to the
fixed base 12 about a vertical axis. Fixed base 12 and rotary table 14
collectively define a horizontal planer
support surface as illustrated. Attached to fixed base 12 and spanning across
rotary table 14 is fence assembly
16 which provides a vertical planer support surface which is perpendicular to
the horizontal table surface of
fixed base 12 and rotary table 14. The horizontal table surface and the
perpendicular support surface of the
fence collectively support workpieces while they are being cut on the compound
miter saw. The compound
miter saw further includes a pivoting arm rotary saw assembly 18 which
operates in a conventional fashion.
The arm assembly is provided with a fixed end 20 pivotally connected to rotary
table 14 and a distal end
terminating in a handle 22. Intermediate the fixed distal ends of the arm
rotary is saw assembly 18 which has
a rotary saw blade 24 protected by a suitable guard 26 and driven by a
conventional motor assembly 28.
In use, to make a conventional square cut in a workpiece, the saw as oriented
in the position shown
in Figure l, is capable of being downwardly pivoting about fixed end 20 on the
rotary saw blade 24 to pass
through the workpiece supported on the horizontal table surface and continue
on through slide 30 until the
workpiece is completely severed in two. In order to form a miter cut, table
lock 32 is released enabling the
entire table saw blade and arm assembly to rotate relative to fence assembly
16. Alternatively, one can make
a simple miter cut by tilting the saw blade as illustrated by the miter saw
position shown in Figure 2 where
CA 02367883 2002-O1-15
the arm assembly and saw blades are rotated and locked at a selected angle
about a generally horizontal axis
aligned parallel to rotary table 14 and slot 30 formed therein. When making a
compound miter cut, rotary
table 14 is oriented so that slide 30 extends at an angle relative to fence 16
in addition to having the blade
tilted relative to the table surface as shown in Figure 2.
When the saw blade is tilted counter-clockwise to the left, when viewed from
the front as shown in
Figure 2, the fence portion to the left of saw blade 24 must be appropriately
cut away to provide clearance for
the saw blade and surrounding guard 26. Conventional fence assemblies are cut
away in order to provide
clearance for the saw blade and surrounding guard at the maximum tilt angle
throughout the entire range of
table rotation. Accordingly, the left fence is frequently undersized and
provides less support than desirable
when cutting tall short length workpieces. To solve this problem, the present
fence assembly 16 is made up
of a first fined fence portion 34 on the right hand side of the table surface
and a second fence portion 36 on
the left side ofthe table. The second fence portion includes a fixed section
38 mounted on the horizontal table
surface of base 12 and an adjustable section 40 which slidably mounts on fixed
section 38 for transverse
movement toward and away from saw blade 24. In the illustration of Figure 1,
adjustable fence 40 is moved
toward the saw blade 24 and locked in a position which provides maximum
support for a tall short length
workpiece. When it is desired to tilt the saw blade to a 45° angle as
shown in Figure 2, adjustable fence
section 40 is shifted away from the saw blade and locked in position to
provide adequate clearance for the saw
blade and the surrounding guard assembly.
An alternative embodiment of the miter saw of the present invention is
illustrated in Figures 3 and
4 with details of the adjustable fence assembly further illustrated in Figures
5-9. Compound miter saw SO
illustrated in Figures 3 and 4, function in a similar manner to miter saw 10
described with reference to Figures
1 and 2, the differences being primarily routine design choices. Compound
miter saw 50 is similarly provided
with an adjustable fence assembly 52 and a first fence portion 54 and a second
fence portion 56 made up of
a fixed section 58 and an adjustable section 60: The fixed and adjustable
sections 58 and 60 of the second
fence portion 54 collectively define a planer vertical fence surface to the
left of rotary saw blade 62 which is
generally co-planer with a corresponding planer support surface associated
with first fence portion 54 to the
right of saw blade 62.
An enlarged front view of the fence assembly removed from the miter saw is
shown in Figure 5.
Adjustable section 60 is preferably provided with a high handle region 64 at
the upper edge of the adjustable
section to be grasped by the user. Adjustable section 60 is slidably movable
relative to fixed section 58. In
4
CA 02367883 2002-O1-15
the embodiment illustrated, this sliding connection is achieved by a tongue
and groove connection. Tongue
66 is provided on adjustable section 60 and a groove 68 (best seen in Figure
9) is provided in fixed section
58. Ideally, the rear side of tongue 66 will be provided with a groove 70 into
which the end of the bolt portion
of locking knob 72 will extend. Locking knob 72 is provided with a threaded
bolt section which threadily
cooperates with bore 74 in second fence fixed section 58 as illustrated in
Figure 9.
The operator can conveniently grasp the knob portion of block member 72 to
loosen and re-tighten
the lock knob to facilitate adjustment and re-locking of adjustable section 60
relative to fixed section 58 of
the second fence portion 56. Of course, other sliding joints and other forms
of locking mechanisms can be
alternatively used such as through slots extending through one of the fixed or
adjustable fence portions and
a corresponding bolt or other forms of linear guide ways. Additionally, while
only one locking knob 72 is
illustrated, multiple locking knobs or additional screws or structure can be
added to interconnect the fixed and
adjustable sections of the second fence portion.
In order to maintain the second fence portion face square to the table, the
adjustable and fixed sections
of the second fence forming the planar fence face are machine surfaces.
Ideally, at least a portion of the
sliding contact between the fixed and adjustable fence will similarly be
machined in order to maintain the
fixed and adjustable fences in coplanar alignment. Preferably, as is
conventionally known, the first fence
portion and the second fence portion are maintained in proper alignment by
integrally forming the fence
portions from a common casting as illustrated in Figure 8. First fence portion
56 and the fixed section of
second fence portion 56 are interconnected by a generally C-shaped bight
section 76. Bight section 76
extends sufficiently rearward of the blade at maximum ends of cut when
providing blade clearance, yet, has
sufficient cross-section to provide rigidity to the fence assembly. The fence
assembly is affixed to the base
of the miter saw in a conventional manner using bolts which extend through
apertures 78 and the fence
assembly.
In order to make it easier for the operator to position the adjustable section
60 of the second fence,
indicia is provided on the second fence fixed and adjustable portions as
illustrated in Figures 5, 6 and 7. In
the embodiment of the invention illustrated in Figures 3-9, second fence fixed
section 58 is provided with a
pointer 80 cast into the face surface as illustrated. Corresponding pointer
markers 80, 84, 86 and 88 are
formed in the adjustable section 60. Marker 82 is provided with "0" i:ndicia
indicating that marker 82 should
be aligned with pointer 80 when the blade is oriented at the "0" tilt angle.
As blade tilt increases, adjustable
section of the second fence 60 must be moved to the left and accordingly,
additional markers 85, 86 and 88
CA 02367883 2002-O1-15
having 15°, 30°, and 45° indicia are provided to assist
the operator at locating the adjustable section of the
second fence at various blade tilt angles.
Alternatively, as illustrated in Figure 10, a pointer 90 may be located on the
adjustable section of the
second fence and the corresponding indicia markers located on the fixed
section. The preferred embodiment
of the invention illustrated is only a representative example of how the
present invention can be implemented
in a compound miter saw. Alternatively, the present fence invention could be
used on a sliding compound
miter saw or it could be adapted to be used on both the right and left fence
portions of miter saws which are
capable of tilting in both directions.
While embodiments of the invention have been illustrated and described, it is
not intended that these
embodiments illustrate and describe all possible forms of the invention.
Rather, the words used in the
specification are words of description rather than limitation, and it is
understood that various changes rnay be
made without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention.
6