Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
34
We claim
1. A polymorphic Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Endotherms at 181.21 °C (onset at 177.70 °C)
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 8.18, 12.40, 16.66, 18.80, 19.44, 22.32, 22.84,
23.10, 23.50, 24.72, 29.84,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3249, 3062, 1709, 1587, 1489, 1374, 1272,
1243, 1112, 1043, 919, 737, 673, 543.
2. A polymorphic Form-II of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Endotherms at 131 °C, 166.24 °C and 178.96 °C
Exotherm at 169.73 °C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 6.78, 11.5, 12.08, 16.44, 19.34, 22.30, 22.72,
24.40, 26.66
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3055, 1711, 1589, 1510, 1491, 1376, 1274,
1111, 1039, 810, 730, 543.
3. A polymorphic Form-III of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
35
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Exotherm at 168.00 °C
Endotherm at 182.20 °C (onset at 171 °C),
Small endotherms at 99.66 °C, 164.38 °C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 6.80, 12.10, 15.84, 17.02, 19.40, 22.32, 22.68,
24.38, 26.36,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3061, 1710, 1588, 1510, 1491, 1379, 1273,
1110, 1040, 805, 739, and 543.
4. A polymorphic Form-IV of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid,having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Small Exotherm at 171.80 °C
Endotherms at 149.85 °C, 185.60 °C (onset at 147.78 °C)
Small Endotherm at 164.51 °C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 6.78, 12.66, 15.96, 16.54, 19.34, 22.78, 24.42,
26.70, 31.70,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3056, 1711, 1589, 1493, 1381, 1274, 1242,
1101, 1060, 805, 743, and 543.7.
5. A polymorphic Form-V of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
36
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Small exotherm at 173.82 °C
Endotherm at 185.95 °C, (onset at 178.09 °C)
Small endotherms at 119.81 °C, 164.69 °C, 172.44 °C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 6.76, 12.10, 15.96, 17.00, 18.50, 19.40, 22.38,
22.44, 24.44, 26.30,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3266, 3055, 1711, 1589, 1510, 1492, 1379,
1274, 1175, 1111, 1040, 918, 819, 730, 676, 544.
6. A polymorphic Form-VI of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Exotherm at 157.98 °C,
Endotherms at 179.11 °C and 183.69 °C (onset at 157.98
°C),
Small endotherm at 77.80 °C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): No diffraction peaks due to its amorphous
nature,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3065, 1629, 1490, 1377, 1273, 1244, 1109,
1042, 805, 740, 539.
7. A polymorphic Form-VII of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
37
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Exotherm at 132.93 °C,
Endotherms at 176.63 °C (onset at 169.06 °C) and 184.09
°C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): No diffraction peaks due to its amorphous
nature,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3065, 1629, 1490, 1377, 1273, 1109, 1042,
740,541.
8. A polymorphic Form-VIII of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Exotherm at 158.27 °C
Endotherm at 178.12 °C (onset at 167.15 °C),
Small Endotherm at 152.72 °C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 4.16, 11.02, 15.94, 19.50, 20.22, 22.22, 27.38,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3151, 1629, 1490, 1378, 1272, 1244, 1104,
1041, 742, 549.
9. A polymorphic Form-IX of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
38
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
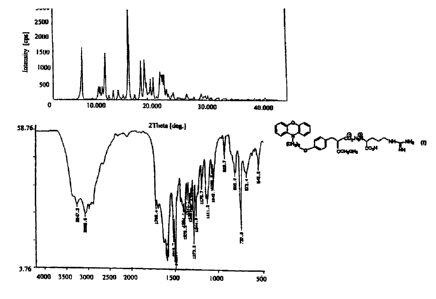
DSC: Endotherm at 176.67 °C (onset at 173.36 °C), (Fig -21)
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 8.20, 12.42, 16.66, 18.80, 19.44, 22.30, 23.08,
27.38, 28.48, 29.84, (Fig -9)
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3066, 1588, 1489, 1376, 1273, 1243, 1110,
1043, 919, 805, 737, 543, (Fig -33)
10. A polymorphic Form-X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Endotherm at 184.53 °C,)
Exotherm at, 162.67 °C
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): No diffraction peaks due to its amorphous
nature,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3413, 1630, 1511, 1491, 1377, 1273, 1244,
1176, 1108, 741.
11. A polymorphic Form-XI of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the data described hereunder:
DSC: Endotherm at 184.40 °C (onset at 177.67 °C),
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 7.38, 7.56, 11.90, 12.32, 14.80, 16.40, 19.58,
20.48, 22.34, 22.90, 23.54,
39
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3383, 2925, 1629, 1510, 1490, 1377, 1273,
1243, 1090, 1041, 739, 539.
12. A mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I,
Image
which is characterized by the following data:
DSC: Endotherms at 181.28 °C, 185.31 °C, (onset at 173.54
°C)
X-ray powder diffraction (2~): 8.16, 12.40, 16.64, 18.78, 19.42, 22.34, 22.80,
23.08, 29.84,
Infrared absorption bands (cm-1): 3247, 3066, 1708, 1587, 1510, 1489, 1375,
1273, 1244, 1178, 1111, 1043, 805, 737, 673, 543.
13. A pharmaceutical composition comprising any one of polymorphic Form
selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of L-
arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I
Image
and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, diluent, excipient or solvate.
14. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-I of L-arginine salt
of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 1, which comprises:
40
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in an organic solvent,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring to the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at a temperature of 40-80 °C for a
period in the
range of 18-30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45 °C for a period in
the range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
15. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-I of L-arginine salt
of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 1, which comprises:
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in an organic solvent,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring to the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at room temperature for a period in the
range of 90-
100 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45 °C for a period in
the range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
16. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-II of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 2, which comprises:
41
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in acetone,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring to the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at room temperature for a period in the
range of 18-
30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45 °C for a period in
the range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-II of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
17. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-III of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 3, which comprises:
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in 1,4-dioxane,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring to the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at room temperature for a period in the
range of 18-
30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45 C for a period in the range
of 4-
16 h to yield Form-III of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
18. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-IV of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 4, which comprises:
42
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in dimethyl sulfoxide,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring to the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at room temperature for a period in the
range of 18-
30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in the
range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-IV of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
19. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-V of L-arginine salt
of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 5, which comprises:
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in dimethyl formamide,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring in the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at room temperature for a period in the
range of 18-
30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(vi) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in
the range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-V of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
20. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-VI of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 6, which comprises:
43
(i) dissolving any of the polymorphic Forms I-V of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-
[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, in water and
(ii) freeze drying the resulting solution to yield an amorphous white powder
of
Form-VI of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid.
21. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-VII of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 7, which comprises
(i) dissolving any of the polymorphic Forms I-V of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-
[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, in methanol and
(ii) evaporating the resulting solution under vacuum to obtain an amorphous
white
powder of Form-VII of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
22. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-VIII of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 8, which comprises
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in an organic solvent,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring in the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at a temperature of 40-80°C for a
period in the
range of 18-30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in the
range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid,
44
(vi) refluxing the Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, obtained above in step (v) in 1,4-
dioxane for a period in the range of 8-16 h and
(vii) filtering and drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for
a period in
the range of 4-16 h to yield Form-VIII of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
23. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-IX of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 9, which comprises
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in an organic solvent,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring in the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at a temperature of 40-80°C for a
period in the
range of 18-30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in the
range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid,
(vi) refluxing the Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, obtained above in step (v) in 1,4-
dioxane for a period in the range of 8-16 h,
(vii) filtering and drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for
a period in
the range of 4-16 h to yield Form-VIII of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid,
(viii) refluxing the Form-VIII of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-
10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, obtained in step (vii) above in
isopropyl alcohol for a period in the range of 8-16 h and
45
(viii) filtering and drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C
for a period in
the range of 4-16 h to yield Form-IX of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
24. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-X of L-arginine salt
of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 10, which comprises
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in an organic solvent,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring to the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at a temperature of 40-80°C for a
period in the
range of 18-30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in the
range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid and
(vi) heating the polymorphic Form-I obtained in step (v) at 185°C and
cooling it to
room temperature to yeild Form-X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
25. A process for the preparation of the polymorphic Form-XI of L-arginine
salt of
(2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having
the characteristics defined in claim 11, which comprises
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in an organic solvent,
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring to the
solution
obtained in step (i),
46
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at a temperature of 40-80°C for a
period in the
range of 18-30 h to obtain a white crystalline precipitate,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline precipitate obtained in step (iii) above
and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in the
range of 4-
16 h to yield Form-I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid,
(vi) heating the polymorphic Form-I obtained in step (v) to 185°C and
cooling it to
room temperature to yeild Form-X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid and
(vii) heating the polymorphic Form-X obtained in step (vi) to 175°C and
cooling it to
room temperature to yield Form-XI of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
26. A process for the preparation of the mixture of polymorphic Form I and X
of L-
arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the characteristics defined in claim 11, which
comprises
(i) synthesizing (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic
acid, employing known methods and dissolving in an organic solvent
(ii) adding L-arginine dissolved in water slowly with constant stirring in the
solution
obtained in step (i),
(iii) stirring the reaction mixture at room temperature for a period in the
range of 18-
30 h to separate white crystalline powder,
(iv) filtering the white crystalline powder obtained in step (iii) and
(v) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in the
range of 4-
16 h to yield mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-
[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
47
27. A process for the preparation of polymorphic Form I of L-arginine salt of
(2S) 3-
[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the
characteristics defined in claim 1, which comprises:
(i) suspending any of the polymorphic Form II to XI or the mixture of
polymorphic
Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid in isopropyl alcohol and stirring in
dark conditions at room temperature for a period of 35-50 h,
(ii) filtering and washing with isopropyl alcohol and
(iii) drying under vacuum at a temperature of 40-45°C for a period in
the range of 4-
16 h to yield polymorphic Form of I of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-
(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid.
28. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a mixture of any of polymorphic
Forms I to XI of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, of the formula (I) and a
pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, diluent, excipient or solvate.
29. A process as claimed in claims 14 and 22 to 26, wherein the organic
solvents are
selected from acetonitrile, ethanol, methanol, 1,4-dioxane, and isopropanol.
30. A pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 13, in the form of a
tablet,
capsule, powder, syrup, solution or suspension.
31. A method of preventing or treating hyperlipemia, hypercholesteremia,
hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, obesity, glucose intolerance, leptin resistance,
insulin resistance, or diseases in which insulin resistance is the underlying
pathophysiological mechanism comprising administering a polymorphic Form
selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of L-
arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in claims 1-12 or a
pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30 to a patient in
need thereof.
48
32. A method according to claim 31, wherein the disease is type II diabetes,
impaired
glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to Syndrome X such as
hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery
disease
and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal diseases including
glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome, hypertensive
nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to endothelial
cell
activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), useful as aldose
reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in dementia and
treating
diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, myotonic
dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma and cancer.
33. A method according to claim 31 for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of
disorders related to Syndrome X, which comprises administering an agonist of
PPARa, and/or PPARy of formula (I).
34. A method of reducing plasma glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol,
LDL,
VLDL and free fatty acids in the plasma comprising administering a
polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form
I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in claims 1-12 or a
pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13 and 30.
35. A method of preventing or treating hyperlipemia, hypercholesteremia,
hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, obesity, glucose intolerance, leptin resistance,
insulin resistance, or diseases in which insulin resistance is the underlying
pathophysiological mechanism comprising administering a polymorphic Form
selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of L-
arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in claims 1-12 or a
pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30 in combination/
concomittant with HMG CoA reductase inhibitors or fibrates or nicotinic acid
or
cholestyramine or colestipol or probucol which may be administered together or
within such a period as to act synergistically together to a patient in need
thereof.
36. A method according to claim 35, wherein the disease is type II diabetes,
impaired
glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to Syndrome X such as
49
hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery
disease
and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal diseases including
glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome, hypertensive
nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to endothelial
cell
activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), useful as aldose
reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in dementia and
treating
diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, myotonic
dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma and cancer.
37. A method according to claim 35 for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of
disorders related to Syndrome X, which comprises administering a polymorphic
Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of
L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in claims 1-12 in
combination with HMG CoA reductase inhibitors or fibrates or nicotinic acid or
cholestyramine or colestipol or probucol which may be administered together or
within such a period as to act synergistically together.
38. A method of reducing plasma glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol,
LDL,
VLDL and free fatty acids in the plasma, which comprises administering a
polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form
I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in claims 1-12 or a
pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30 in combination/
concomittant with HMG CoA reductase inhibitors or fibrates or nicotinic acid
or
cholestyramine or colestipol or probucol which may be administered together or
within such a period as to act synergistically together to a patient in need
thereof.
39. A method according to claim 35 for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of
disorders related to Syndrome X, which comprises administering to a patient in
need thereof an agonist of PPARa and/or PPARy of formula (I) as claimed in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition according to claim 13 or 30 and
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, fibrates, nicotinic acid, cholestyramine,
colestipol or probucol or their combination within such a period as to act
synergistically.
50
40. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
for preventing or treating hyperlipidemia, hypercholesteremia, hyperglycemia,
osteoporosis, obesity, glucose intolerance, leptin resistance, insulin
resistance, or
diseases in which insulin resistance is the underlying pathophysiological
mechanism.
41. Use of a polymorphic Form according to claim 40, wherein the disease is
type II
diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to
Syndrome X such as hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia,
coronary artery disease and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal
diseases
including glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome,
hypertensive nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to
endothelial cell activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS),
useful as aldose reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in
dementia and treating diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel
diseases, myotonic dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma or
cancer.
42. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
for reducing plasma glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL, VLDL and
free fatty acids in the plasma.
43. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
in combination/concomittant with HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, fibrates,
nicotinic acid, cholestyramine, colestipol or probucol which may be
administered
together or within such a period as to act synergistically together for
preventing
or treating hyperlipidemia, hypercholesteremia, hyperglycemia, osteoporosis,
51
obesity, glucose intolerance, leptin resistance, insulin resistance, or
diseases in
which insulin resistance is the underlying pathophysiological mechanism to a
patient in need thereof.
44. Use of a polymorphic Form according to claim 43, wherein the disease is
type II
diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to
Syndrome X such as hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia,
coronary artery disease and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal
diseases
including glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome,
hypertensive nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to
endothelial cell activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS),
useful as aldose reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in
dementia and treating diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel
diseases, myotonic dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma or
cancer.
45. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
in combination/concomittant with HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, fibrates,
nicotinic acid, cholestyramine, colestipol or probucol for reducing plasma
glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL, VLDL or free fatty acids in
the
plasma.
46. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
for preparing a medicament for preventing or treating hyperlipidemia,
hypercholesteremia, hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, obesity, glucose intolerance,
leptin resistance, insulin resistance, or diseases in which insulin resistance
is the
underlying pathophysiological mechanism.
47. Use of a polymorphic form according to claim 37, wherein the disease is
type II
diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to
Syndrome X such as hyper-tension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia,
52
coronary artery disease and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal
diseases
including glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome,
hypertensive nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to
endothelial cell activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS),
useful as aldose reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in
dementia and treating diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel
diseases, myotonic dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma or
cancer.
48. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
for preparing a medicament for reducing plasma glucose, triglycerides, total
cholesterol, LDL, VLDL and free fatty acids in the plasma.
49. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
for preparing a medicament in combination/concomittant with HMG CoA
reductase inhibitors, fibrates, nicotinic acid, cholestyramirie, colestipol or
probucol for preventing or treating hyperlipemia, hypercholesteremia,
hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, obesity, glucose intolerance, leptin resistance,
insulin resistance, or diseases in which insulin resistance is the underlying
pathophysiological mechanism.
50. Use of a polymorphic form according to claim 49, wherein the disease is
type II
diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to
Syndrome X such as hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia,
coronary artery disease and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal
diseases
including glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome,
hypertensive nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to
endothelial cell activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS),
useful as aldose reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in
53
dementia and treating diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel
diseases, myotonic dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma or
cancer.
51. Use of a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of
polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30
for preparing a medicament in combination/concomittant with HMG CoA
reductase inhibitors, fibrates, nicotinic acid, cholestyramine, colestipol or
probucol for reducing plasma glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL,
VLDL or free fatty acids in the plasma.
52. A medicine for preventing or treating hyperlipidemia, hypercholesteremia,
hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, obesity, glucose intolerance, leptin resistance,
insulin resistance, or diseases in which insulin resistance is the underlying
pathophysiological mechanism comprising administering an effective amount of
a polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic
Form I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-
yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in
claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and
30.
53. A medicine according to claim 52, wherein the disease is type II diabetes,
impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to Syndrome X
such
as hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery
disease
and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal diseases including
glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome, hypertensive
nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to endothelial
cell
activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), useful as aldose
reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in dementia and
treating
diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, myotonic
dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma or cancer.
54. A medicine for reducing plasma glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol,
LDL,
VLDL and free fatty acids in the plasma comprising an effective amount of a
polymorphic Form selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form
I and X of L-arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
54
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in claims 1-12 or a
pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30.
55. A medicine for preventing or treating hyperlipidemia, hypercholesteremia,
hyperglycemia, osteoporosis, obesity, glucose intolerance, leptin resistance,
insulin resistance, or diseases in which insulin resistance is the underlying
pathophysiological mechanism comprising a polymorphic Form selected from
Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of L-arginine salt of
(2S)
3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-ethoxypropanoic acid, having the
formula I as defined in claims 1-12 or a pharmaceutical composition as claimed
in claims 13, 28 and 30 and HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, fibrates, nicotinic
acid, cholestyramine, colestipol or probucol.
56. A medicine according to claim 55, wherein the disease is type II diabetes,
impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidaemia, disorders related to Syndrome X
such
as hypertension, obesity, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery
disease
and other cardiovascular disorders, certain renal diseases including
glomerulonephritis, glomerulosclerosis, nephrotic syndrome, hypertensive
nephrosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, disorders related to endothelial
cell
activation, psoriasis, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), useful as aldose
reductase inhibitors, for improving cognitive functions in dementia and
treating
diabetic complications, osteoporosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, myotonic
dystrophy, pancreatitis, arteriosclerosis, xanthoma or cancer.
57. A medicine for reducing plasma glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol,
LDL,
VLDL and free fatty acids in the plasma, which comprises a polymorphic Form
selected from Form I to XI or a mixture of polymorphic Form I and X of L-
arginine salt of (2S) 3-[4-[2-(phenoxazin-10-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-
ethoxypropanoic acid, having the formula I as defined in claims 1-12 or a
pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claims 13, 28 and 30 and HMG CoA
reductase inhibitors, fibrates, nicotinic acid, cholestyramine, colestipol or
probucol.