Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR OBTAINING MARKETING INFORMATION
Related Applications
This application is based on provisional applications,
serial number 60/135,208, filed May 21, 1999 serial number
60/138, 210, filed June 9, 1999; serial number 60/139, 947,
filed June 18, 1999; serial number 60/142,097, filed July
2, 1999; and serial number 60/163,299, filed November 3,
1999.
Background of the Invention
A great deal of time and effort goes into compiling
marketing information regarding individuals, groups,
regions and all sorts of demographic categories. This
information is generally obtained by surveying the targeted
subjects about their buying behavior or preferences. While
surveys produce reasonably accurate results, they are
costly and time consuming, and there is no guarantee of
accuracy. A reliable method of compiling information is
needed that both indicates a reliable preference for a
product and if an individual is still a potential buyer.
Such a method would be an extremely valuable tool for
marketers.
As the use of the Internet proliferates, marketing
efforts need to be focused more on an individual, so that
the individual can be targeted for specific advertising
with a reasonable expectation of a response. There is a
need therefore, for a means of obtaining information which
originates at the individual level.
One problem in obtaining product preference
1
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
information is its accuracy. Without any particular
incentive, a product preference survey will be fraught with
inaccuracies due .to the vagaries of the individuals
responding. An incentive is needed to promote an honest
response. It is a purpose of this invention, to have an
individual select a product preference in the context of a
possibility of winning the product.
It is a purpose of this invention to provide an
Internet user with an attractive mechanism for providing
product preference information which is accurate and
timely, while engaging in a pleasurable and potentially
rewarding activity.
Summary of the Invention
A game is provided for simultaneous play by a group of
users through a real-time interactive network set up on an
Internet web site. An Internet server is linked to one or
more game servers set up to offer a selection of games
that are playable on an interactive basis by individuals or
groups. The games are playable by multiple users at the
same time. The basic rules of the games presented may be
well known, such as bingo, poker, and other playing card
games. Each game employs a playing medium such as the
tablet in Bingo and the deck of cards in poker. Each
individual player sets up a specific reference table of
products, i.e., a product medium, selected from a hierarchy
of product categories and products, accessible by the game
server. The products are potential prizes that may be
awarded, in a sweepstakes style contest, upon winning the
game.
The game server provides a game algorithm, for
2
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/iJS00/13025
example, a matrix, designed to convert the standard game
symbols in the game medium, i.e. columns and numbers for
bingo or suits and cards for playing cards, to products in
the product medium. The product medium is used in the play
of the game. In addition the game server provides access
to the product lists in a hierarchy of categories and sub-
categories selectable by the player. Each game symbol of
a game will be correlated in some fashion with a product,
a category, or sub-category. In this manner, players may be
competing at the same game, but with entirely different
selected product symbol arrays. The incentive for making
product choices accurately reflecting preferences is the
possibility of winning, in a sweepstakes style contest, one
or more of the selected products during the course of
playing the game. During set up of the game or during
play, advertising geared to the individual's selections may
be presented to the player by the game server.
A database of product lists and associated advertising
and marketing graphics and text is maintained to provide
the information required by the player to generate the
product medium and to provide the information for targeted
advertising during the play of the game.
In the process of setting up a game, each player goes
through a hierarchical selection process in which he
selects one or more products, categories or sub-categories.
In completing the selection process, the player creates a
product preference profile that is tabulated and recorded
for each individual player. This information is compiled
for use in an individual player product preference profile
and/or extrapolated into larger, more generic, marketing
profiles. Using the player profile, advertisers are
provided with a medium to target individuals who have
3
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
preselected a product. Discounted products, specifically
selected to meet the personal preferences of each
individual player, may be offered directly during the game.
Product preference data obtained from the user's
selections may be mined, in a marketing sense, in a great
variety of ways. The advertiser is reasonably assured that
the player has accurately indicated his preferences and has
not yet purchased the specific item, because the player has
chosen the item in an attempt to win it.
In this manner, a system is devised which provides
games that use player prize preference selection to
determine and develop a database of consumer product
preferences. The selections are incorporated into the play
of the game, which is further designed to take advantage of
product promotion activities targeted to the player's
selected preferences. The player is allowed to compete
with other players in the same game using a symbol set
unique to each player, while the game algorithm converts
back and forth between the selected product symbol set of
the product medium to the standard symbol set of the game
medium. At the conclusion of a game, a winner is
established by rules predetermined for each game variation.
Description of the Drawing
The invention is described in more detail below with
reference to the Drawing, in which:
Figure 1 is a block diagram of the system of this
invention
Figure 2 is a block diagram of the game server
architecture of this invention;
4
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
Figure 3 is a block diagram of the basic process of
this invention;
Figure 4 is an information flow diagram depicting the
operation of the game Bingo as adapted to this
invention;
Figure 5 is a chart of the steps used in playing the
game of Bingo according to this invention;
Figures 6a, 6b, and 6c are illustrations of possible
menu screens for use in playing Bingo or cards
according to this invention; and
Figure 7 is a table illustrating a possible algorithm
for converting a game medium to a product medium.
Detailed Description of the Invention
The system of this invention is shown in figure 1 and
consists of a game server 1, which is accessible by a
player through multiple Internet servers 4. The Internet
server 4 is accessible in a known manner through a player
interface 2 connected through a communications network 3.
The game server 1 is constructed to be compatible with a
wide variety of Internet, intranet, or extranet servers,
but could conceivably be accessible directly by the player
interface, depending on the communications network and
protocols available. Although this invention is described
in the context of an Internet application, it could be
adapted for use on an intranet, extranet or other types of
networks which employ basic Internet protocols.
5
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
An example of processor architecture which may be
employed to construct Game server 1 is shown in figure 2.
As shown, game server 1 is constructed with a group of
game server processor packages 17, 18, and 19 to control
game play and related activities. These processors are
redundant units which are available for a player depending
on the amount of traffic at the site at any time. They are
designed to accommodate maximum projected traffic. Each of
the game servers 17, 18, and 19 have access to a network
file system 20 which provides all of the product data
including ads, images, and multimedia presentations if
desired. Graphics from the file system 20 are accessible
through a separate graphics server 16.
Traffic routers 11, 12, and 13 provide the gateway to
the web site on which the sweepstakes style games are
available. Traffic router 12 handles the basic
interaction for player browsing, registration, and log
activities over a normal speed link, through web site
server 14. Through router 12, a potential player may
access the site information data storage unit 21 to obtain
general information about the site and the activities
available. A data administration server 15 keeps track of
the on going activities of the site for example: the number
of hits, game status, and other indications of traffic
volume and quality. The personal and generic marketing
information provide by the player's product selections is
stored in additional storage media. In this manner,
specific data storage unit is provided to segregate the
data compiled, for example storage media 21 may provide
site information, storage media 22 would keep track of on
going play, and storage media 23 would track the number of
hits and other site activities parameters. In addition
generic marketing information may be held in storage medium
6
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/iJS00/13025
9 and player specific information in storage medium 8.
Actual game play would be handled through traffic
router 11 over a high speed link to the Internet server.
The gateway can take a variety of forms and be accessed
through other sites by hypertext or other link. Another
high speed link would be provided through traffic router 13
which is designed to facilitate multimedia viewing.
Appropriate log-on menus provide means to identify the
player and allow him or her to select a particular game.
The log-on process will require basic information about the
player to allow compilation of the player data into general
marketing information. Specific information with respect to
the products selected by the players, interests and
preferences will be compiled and stored in a subjective
player database 8, while objective data, extrapolated from
the subjective data, may be compiled and stored in a
general market database 9, shown in figure 1. As shown in
the more general illustration of figure 1, these data are
accessible by the Game Server 1 to provide targeted
advertising and product offerings. The structure of the
databases 8 and 9 may be combined or vary depending on the
processors and software employed.
As described above, game server 1 may consist of a
series of interconnected processors 14 - 19 which are
selectively operated by associated software to allow the
user to play a selected game . Game servers 17 - 19 are
processors which provides the software required for
interactive game play by multiple players and the
algorithms required to set up the product medium for each
game. The game function will be according to the known
rules of the game adapted for interactive computer use.
7
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
Each game will have a game medium for example: bingo
tablets, playing cards, and the like. In addition a
product medium will be generated from the players
selection. The game medium will vary depending on the game
and consist of a set of game symbols used in the play of
the game, i.e. the column headings and numbers of Bingo and
the suits and cards of playing card games.
A game algorithm will be designed to correlate the
symbols of the game medium with the symbols of the product
medium and convert from one to the other, as required by
the play of the game. In some instances, only a look up
table or matrix will be necessary as an algorithm to
translate a particular game medium. The game algorithm
substitutes products for game symbols in the game medium.
Game software data storage unit 7 will form part of each
game server and will contain the structure of the game
medium, including the related symbol set and an algorithm
for translating the game medium into a product medium,
containing the product symbol set. In addition game process
software is supplied to allow the game servers to direct
the play of the game to its designed conclusion.
The type and style of player interface 2 depends to
some extent on the medium of the communications network,
for example, a cellular phone would be used in a cellular
system or a cable controller in a cable system. At the
present, it is anticipated that the player interface will
most likely consist of a personal computer, set up in a
well known fashion, to connect to the Internet through a
modem connected to land lines. There are many systems
competing to provide Internet access including: telephone
landline systems, digital subscriber lines, cable networks,
cellular networks and others. Whatever communications
system 3 is employed, it will have little effect in the
8
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
basic operation of this invention, except perhaps in speed
of interactive play. For the purpose of illustration, it
is assumed that the communications system used is the
standard telephone line access to the Internet by a modem
connected to a personnel computer.
A product database 6 of figure 1 will be stored in
data storage unit 20 of figure 2 and is created to supply
product information to the processor for selection by the
player. The database 6 will contain a hierarchy of
categories, subcategories, and specific products, which
will be available for selection by the player for insertion
into his personal product medium. The availability of
products will vary from game to game. The product database
6 may also contain supplemental information relating to the
products, including advertising and marketing information,
product offerings and links for access by the game server
1 or processor 5 during the play of the game. This allows
the game server 1 to provide targeted advertising and
product offerings based on the particular preferences
contained in player database 7.
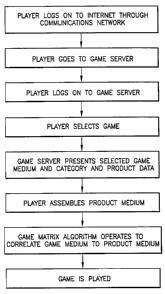
As shown in the process diagram of figure 3, the
player will access the website, at which the game server 1
is available, by first logging on to his or her Internet
server 4 through player interface 2. As stated above, this
may be accomplished in many ways and the future holds many
more possibilities, but for the purpose of illustration, it
is assumed that the game server 1 is accessed in the
currently standard manner through a modem and over a
telephone land line connection. As is common today, each
Internet server has its individual log on procedure and
medium for exploring the Internet and providing access to
various web sites. The web site of game server 1 may be
9
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
entered through hypertext displayed in targeted
advertising, through selection of the domain name, or other
mechanisms for Internet navigation.
Upon entering the game server web site, the player
will be prompted by a menu and advised how to select the
various paths available. Initially a player identifier
file must be created to allow the player to reuse the site
with convenient regularity. The player identifier file
will also provide the needed linkage to allow marketing
data to be compiled directly from the player's activities
in the site. Since it is likely that the customer specific
data will be very useful in broader marketing efforts,
sufficient information needs to be provided to assess the
demographics of groups of customers according to selected
marketing categories. The game server menu will,
therefore, necessarily include a simple form into which the
required information will be inserted by the player.
After the player file is generated, it is saved in
player database 8 and the player is ready to select a game.
The process of game selection will again be menu driven as
shown in figures 6a, b, and c and contain access to
information about game play. In order to provide an
incentive for the player to participate in a straight
forward manner, the rules and rewards of winning a
particular game will be promoted during the game selection
process.
Once a game is selected, a set of game symbols will be
displayed which comprises the game medium, as shown for
Bingo in figures 4 and 5 . This will further illustrate
how the game is to be played and the potential rewards.
Next it is necessary that the product medium be
constructed. To do this, the player must select a
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
preference for a particular product by reviewing the
product hierarchy contained in product database 6. The
selection may be made at any point in the hierarchy
consistent with the game medium. During the selection of a
set of product symbols by the player, access will be
provided to more detailed product information and
advertising in product database 6 to aid in the selection
process.
Once the product medium is generated, it is stored in
the player database 8 for future reference and
manipulation. The game will then progress to a conclusion
according to its particular rules and process software.
Each game will be different and because of the game
algorithm, which converts an individual's product medium
into a game medium, multiple players may be playing at the
same time using the same game medium, but completely
different product mediums.
To accommodate the volume of traffic and facilitate
technical control, upon making a choice of games, the
player will be assigned to a section consisting of other
players for the same game. Each section will be for a
particular type of game, i.e. poker, bingo, etc. A minimum
number of players will be predetermined for each section to
contain the odds at a reasonable level.
The term sweepstakes is used in a broad sense to refer
to any contest, other than gambling, in which a winner is
selected in a generally random manner, other than just
winning a particular game on the game server 1. Depending
on the nature of the prizes, the game could be set up to
award prizes simply by winning the game played. The key
factor is to generate an incentive for players to
11
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
participate by providing the opportunity to win prizes
which the player selects in advance.
The invention will now be illustrated with reference
to particular games adapted for the purpose. One game that
is particularly adaptable is bingo.
A general process for playing Bingo in accordance with
this invention is shown in figures 4 and 5. In the
traditional game of bingo, the game medium is the Bingo
card or tablet on which numbers are arranged randomly in
columns and rows with the columns identified by one of the
letters B,I,N,G,O, as shown in figures 4 and 5. There is a
universe of numbers used in the game medium ranging from
the lowest number in the first column to the highest number
in the last column. Normally, there are five columns with
fifteen numbers assigned to each column; therefore, the
game medium will consist of a set selected from the overall
field of 75 numbers, running from 1 to 75. The first
column is assigned the field of 1 through 15; the second
column is assigned the field from 16 through 30; and so on,
until the fifth column which is assigned the field of 61
through 75. Typically, the product medium, i.e., the card
is five columns of five rows each. Although the first
column consists of the 15 numbers, 1 through 15, only a
subset of five of these numbers are displayed on the card
in the first column. This process is repeated for each
column in order to make a complete bingo card. By
constructing bingo cards in this manner, there are hundreds
of millions of potential combinations and permutations of
cards. Once the card in determined, this product medium is
ready for a game to be played.
During the play of the game, numbers are called and
12
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
the player marks any spots on his card that contains that
number. The winner is the first player achieving a
predetermined pattern from the numbers called during the
course of the game. Other variations may be played with
any number of columns and rows, and with a different size
field of numbers from which to construct the cards.
Bingo is adapted, according to this invention, by
substituting a set of symbols representing products for the
traditional set of numbers displayed in each spot on the
bingo card. Similarly, the traditional column headings of
"B, I, N, G, & O" can be replaced by categories of
products. The game can be designed for play with any
number of columns and rows, with or without freespaces.
In order to generate a product oriented medium, the
game medium, i.e. the bingo card, containing a set of
numbers, is converted to a product medium with the
traditional numbers replaced by a set of product symbols
selected by the player. The column headings would be
replaced by categories of products, thereby structuring the
hierarchy of the selection process. To accomplish the
conversion, a game algorithm is devised for making the
conversion. For example, using the traditional bingo card
format of five columns of five rows, the first column, or
"B" column, can be chosen from a field of 15 products
within a category which are assigned numbers from 1 through
15 by the player or automatically by selection of a
category. A second field of 15 products are chosen for the
second column, or "I" column, and are assigned the fifteen
numbers from 16 to 30. The process continues until the
available numbers are replaced by products. From each
field five products are chosen to be displayed in the spots
on the bingo card. The game processor would operate in
13
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
accordance with the game algorithm to convert back and
forth from the game medium to the product medium as the
game progresses. In the context of the game Bingo, the
algorithm is a simple look up table, as shown in figures 6c
and 7, in which the columns of the game card are correlated
to categories and the set of numbers for the game medium
are correlated to the set of selected product symbols for
the product medium.
As shown in the example of figure 7, the "B" heading
of the first column could be converted to the word "CARS"
and the set of numbers in the first column could be
associated with, i.e. substituted for or used with 15 names
or images ("symbols") of different models of cars. The
first column of the bingo card would then consist of the
appropriate number of spots filled with the names or images
of cars chosen by the player or chosen at random. In a five
by five bingo card, there would be five car "symbols"
filling the first column. The Bingo game algorithm would
convert the numbers to product symbols and back as shown.
A similar conversion table would be utilized for each
column and column heading selected by the player. A
formula for assigning numbers to the products in each
category selected for a particular column would read as
follows:
Each "symbol" in each category is assigned a unique
number (X) in its field of 1, 2, ......, n where n is the total
number of "symbols" in each category. To determine that
"symbols" number (N) in the universe, you would use the
following formula:
N = X + (C-1) *n, where C is the number of the
14
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
column to which the category is assigned.
In the most common five column, five row game of bingo
with a universe of 75 numbers, the first product in the
category assigned to third column would have a range number
of 1 and a number in the universe computed as follows:
N = 1 + (3-1) 15 = 31; where C=3, n=15, and X=1.
The game algorithm would enable a player to select
from a variety of categories and place those categories in
whichever column he/she prefers. It also enables the
player to select the products that will make up his unique
card. Since the content of the product medium is selected
according to each players preference, each of the players
will play with diverse sets of product symbols and
categories while the game algorithm converts each of the
product mediums back to the game medium, the universal
bingo game card. The players therefore, compete in the
same game with different cards. For example, player X may
have designated his first column to be "Cars" with the Ford
Taurus being equated to the number "1" in the algorithm for
this card and player Y may have designated the first column
to be "Jewelry" with an opal ring being equated to the
number "1" in the algorithm for her card. During the play
of the game, if the number "1" is chosen, determined by a
random number generator or manual draw, player X would be
shown the product symbol for the Ford Taurus and player Y
would be shown the product symbol for opal ring. Each
would appropriately mark their cards in the appropriate
square of the product medium. To facilitate the play of
the game, the number may be shown in conjunction with the
appropriate product symbol on the product card. If one or
neither have chosen the product symbol correlating to the
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
randomly selected number, the square on the product medium
would not be marked, since it would not be displayed on
their bingo cards.
The pattern necessary to win is presented before the
beginning of the game. As numbers are drawn by the random
number generator, they are converted to the appropriate
product symbol via the game algorithm. They are then
displayed for the players in their product medium form.
While the game is underway, the player views his tablet
and highlights the appropriate spot. The winner of the
game is the first player to achieve the predesignated
pattern and signal "bingo".
As the player opens the menu for the bingo game that
he has selected, a series of preferences must be made to
fill out a set of products in which the player is
interested in winning. The player chooses category,
subcategory, and product symbols to generate a product
preference database for the game of bingo from which the
product medium for each player is selected.
From the illustration of the use of the process and
apparatus of this invention in the context of a game of
bingo, it is observed that the subject invention provides
a methodology for delivering advertising, appropriate to
the individual audience, after gathering preference data
directly from the individual. Player preference data
obtained from one of the several games available on the
game server 1, provides an accurate mechanism for
monitoring consumer preference. By permitting the consumer
to choose prizes that will be awarded as part of a
competitive game situation, the consumer indicates that he
or she would like to win that product and, in all
16
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
likelihood, that, they do not already have the product.
Over time, the data on prize choices permits the
compilation of preference vectors based on comparative
preferences among potential prizes. With this
information, from the player database, opportunities arise
during the set up, play and between game interludes for
directing advertising to the player, targeted to the stated
preferences.
Another embodiment of this invention adapts the use of
playing cards for the purpose of encouraging a player to
volunteer product preference data. Decks of playing cards
have been around for centuries. During that time, hundreds
of card games have been invented which use decks of cards
in one form or another. Variations on the playing card
deck include, but are not limited to, the standard poker or
bridge deck of 52 cards with 13 cards in each of four
suits: the 48 card pinochle deck with two each of nine
through ace in each suits the 32 card euchre or skat deck
with one each of 7 through ace in each suit: and the 64
card bezique deck which is essentially a double euchre deck.
Through the process and apparatus of this invention,
any card game can become both a promotional event for
advertisers and an opportunity to win sweepstakes prizes
for players of those games. With this invention, everyone
with access to a game can be both entertained and compete
for prizes. Everyone can play and everyone can be an
actual contestant with an opportunity to win the prizes
offered.
The game medium of games using playing cards consists
of the suits and cards themselves . The suits of playing
cards are associated either at random, by player selection,
17
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/US00/13025
or by advertiser selection with classes or categories of
products such as CDs, videos, movie passes, restaurant gift
certificates, books, books on tape, cosmetics, etc. For
example, CDs may be associated with spades, books with
hearts, cosmetics with clubs, and videos with diamonds.
Each of the thirteen cards of the standard deck can be
specific products in each of the categories. The product
and category list are stored in the product database 6 and
are accessible to the game processor 5 and Game server 1.
The player may select the category and product, just the
product, or it may be presented by an advertiser. Once the
associations are made, a game algorithm is constructed
that is unique to that particular deck of playing cards.
The game algorithm converts the game medium, the playing
cards, to the product medium similar to the process used in
the bingo version of this invention of bingo. An example
of a game of solitaire using a CD related product medium is
shown in figure 6b.
In order to add variety to the playing of the games
according to this invention, the game server 1, through one
of its processors, such as data administration server 15,
is programmed to keep track of the number of games played
on a particular product medium in storage medium 23. After
a predetermined number of repetitions, the player may be
prompted to consider different categories of products.
This can also be done automatically to test the player' s
preferences in other categories of products.
As an illustration, after a predetermined cumulative
number of cards are played in consecutive games, the game
software can call for a replacement deck. In selecting
the replacement deck, (either by player choice, random
selection, or advertiser selection) categories, previously
18
CA 02371984 2001-11-07
WO 00/72205 PCT/~1500/13025
used in association with suits for that particular player,
are no longer available, thereby avoiding additional
repetitions of an advertiser's product promotion to that
particular player. If categories are player selected, the
categories available to that player might no longer show
the categories he had previously chosen.
According to the above, a unique method of obtaining
an honest, straight forward, statement of product
preference by an individual is provided. The process is
incentivised for the player by providing product selection
from a list, which are potential prizes to be won in a
sweepstakes style contest. It should be understood that
the system and method may be implemented in a wide variety
of configurations, styles and media and variations may be
used within the boundaries of the invention as described
in the claims.
19