Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
I
a
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
WO 01!08487 PCTlEP00/07050
Combinations of herbicides and safeners
The invention relates to the technical field of the crop protection products,
in particular herbicidelantidote combinations (active substancelsafener
combinations) which are outstandingly suitable for the use against
competing harmful plants in crops of useful plants.
EP-A 436 680 discloses herbicidal active substances which control a broad
range of weeds and which, alone or as a mixture with other active
substances, can be employed [lacuna] of important weeds; the publication
not only describes what is known as the nonselective use jointly with
nonselective foliar-acting herbicides, but also mentions the possibility of
selective uses in crops which have been made tolerant to such active
substances by recombinant methods.
However, many of these active substances are not fully compatible with
(i.e. not sufficiently selective in) some important crop plants such as maize,
rice or cereals, so that their use is strictly limited. In certain crops, they
can
therefore not be employed, or at such low application rates that the desired
broad herbicidal efficacy towards harmful plants is not guaranteed.
Specifically, many of the abovementioned herbicides cannot be employed
sufficiently selectively against harmful plants in maize, rice, cereals or
some other crops.
To overcome these disadvantages, it is known to employ herbicidal active
substances in combination with a so-called safener or antidote. A safener
for the purpose of the invention is a compound or a mixture of compounds
which compensates for, or reduces, the phytotoxic properties of a herbicide
towards useful plants without substantially reducing the herbicidal action
against harmful plants.
The identification of a safener for a particular class of herbicides remains a
difficult task since the exact mechanisms by which a safener reduces the
harmful effect of herbicides are unknown. The fact that a compound in
combination with a particular herbicide acts as a safener allows no
conclusions as to whether such a compound also acts as a safener with
other classes of herbicide. Thus, it has emerged that, when using safeners
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
v
2
for protecting the useful plants from herbicide damage, the safeners may
still have a number of disadvantages in many cases. These are:
~ the safener reduces the action of the herbicides against the harmful
plants,
~ the useful-plant-protecting properties are insufficient,
~ in combination with a given herbicide, the spectrum of the useful
plants in which the safener/herbicide is to be used is insufficiently
wide,
~ a given safener may not be combined with a sufficiently large
number of herbicides.
It was an object of the present invention to identify herbicidal compositions
in which the selectivity of the abovementioned herbicides to important crop
plants is increased. Surprisingly, this object is achieved by the herbicidal
compositions of the present invention.
The invention therefore relates to a herbicidally active composition
comprising a mixture of
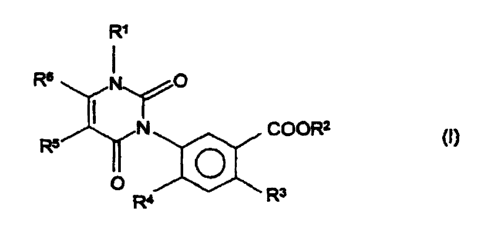
(A) a herbicidally effective amount of one or more compounds of the
formula (I)
R=
R6 ~ O
COORZ
0
Rs
R~
in which
R~ is hydrogen, C~-C4-alkyl, C3-C4-alkenyl, C3-C4-alkynyl or C~-C4-
haloalkyl,
R2 is hydrogen, C~-Cep-alkyl, C~-Cep-haloalkyl, Cg-Cep-aryl,
Cg-Cep-haloaryl, C~-Cg-alkylsulfonyl-C~-C4-alkyl, di(C~-Cg-
alkyl)phosphono-C~-C4-alkyl, tri(C~-Cg-alkyl)silyl-C~-C4alkyl),
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
' 3
C2-C7-alkanoyl-C~-C4-alkyl, carboxy-C~-C4-alkyl, (C~-Cg-
alkoxy)carbonyl-C~-C4-alkyl, {[C3-Cg(a-alkylalkylidene)]iminooxy-
(C~-Cg-alkoxy)carbonyl}-C~-C4-alk~rl, (C3-Cg-alkenyloxy)carbonyl-
C~-C4-alkyl, (C3-Cg-alkynyloxy)carbonyl-C~-C4-alkyl, (C3-Cg-
cycloalkyloxy)carbonyl-C~-C4-alkyl, phenoxy-C~-C4-alkyl, C3-Cg-
alkenyloxy-C~-C4-alkyl, C3-Cg-cycloalkenyloxy-C~-C4-alkyl, C5-Cg-
cycloalkenyl, Cg-Cg-bicycloalkyl, Cg-Cg-bicycloalkenyl, C2-C7-
cyanoalkyl or C3-Cg-alkynyloxy-C~-C4-alkyl,
R3 is hydrogen, halogen or cyano,
R4 is hydrogen or halogen,
R5 is hydrogen, halogen or C~-C4-alkyl, and
R6 is C~-C4-alkyl or C~-C4-haloalkyl, or R5 and R6 together form
trimethylene or tetramethylene,
and the corresponding enol ethers of the compound of the formula (I) in
which R~ is other than hydrogen and C~-C4-haloalkyl, and the salts of the
compound of the formula (I) in which R~ is hydrogen,
and
(B) an antidote-effective amount of one or more safeners.
Examples of radicals R2 are:
acetylmethyl, 2-acetylethyl, propionylmethyl, cyanomethyl, trimethyl-
silylmethyl, 2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl, 2-(methylsulfonyl)ethyl, methoxycarbonyl-
methyl, ethoxycarbonylmethyl, 1-(methoxycarbonyl)ethyl, 1-(ethoxy-
carbonyl)ethyl, 1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1-methylethyl, 2-(ethoxycarbonyl~1-
methylethyl, 1-(allyloxycarbonyl~1-methylethyl, isopropyl, 2-phenoxyethyl,
2-cyclohexenyl, 2-cyanoethyl, 2-norbornanyl, 5-norbomen-2-yl,
2-allyloxyethyl and 2-propargyloxyethyl.
If R~ is C3-C4-alkenyl, C3-C4-alkynyl or C~-C4-haloalkyl, then allyl,
propargyl and difluoromethyl are preferred in each case. If R6 is C~-C4-
haloalkyl, then trifluoromethyl and pentafluoroethyl are preferred.
A preferred group of compounds of the formula (I) are those in which R2 is
other than carboxy-C~-C4-alkyl, R5 is hydrogen, fluorine or C~-C4-alkyl and
R6 is C~-C4-alkyl or C~-C4-haloalkyl, and their enol ethers and salts.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
' 4
Also preferred are compounds of the formula (I) in which
R~ is C~-C4-alkyl, preferably methyl,
R2 is C2-C7-alkanoyl-C~-C4-alkyl, {C~-Cg-alkoxy)carbonyl-C~-C4-alkyl,
C~-C4-alkyl, {[C3-Cg-{a-alkylalkylidene)iminooxy-(C~-Cg-alkoxy~
carbonyl]-C~-C4-alkyl, (C3-Cg-alkenyloxy)carbonyl-C~-C4-alkyl,
(C3-Cg-alkynyloxy)carbonyl-C~-C4-alkyl or (C3-Cg-cycloalkyloxy)-
carbonyl-C~-C4-alkyl,
R3 is halogen, preferably chlorine or bromine, or cyano, preferably
chlorine,
R4 is hydrogen or fluorine, preferably hydrogen,
R5 is hydrogen, fluorine or methyl, preferably hydrogen, and
R6 is methyl, trifluoromethyl or pentafluoroethyl, preferably
trifluoromethyl.
Preferred compounds of the formula (I) are:
ethyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1 (2H~pyrimidinyl]-4-
fluorobenzoyloxy}-2-methylpropionate,
methyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1 (2H)-pyrimidinyl]-
4-fluorobenzoyloxy}-2-methylpropionate,
tert-butyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1 (2H)-
pyrimidinyl]-4-fluorobenzoyloxy}-2-methylpropionate,
ethyl 2-ethyl-2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-1 (2H~
pyrimidinyl]-4-fluorobenzoyloxy}propionate,
methyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-
1 (2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy}-2-methylpropionate,
isopropyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-
1 (2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy)propionate,
ethyl 2-ethyl-2-{2-ch I o ro-5-[3, 6-d i hyd ro-2, 6-d ioxo-3-m ethyl-4-trifl
a oro-
methyl-1-(2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy}propionate,
tert-butyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-
1 (2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy-2-methylpropionate,
allyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1 (2H~
pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy}-2-methylpropionate,
cyclo pe ntyl 2-{2-ch to ro-5-[3, 6-d i hyd ro-2, 6-d ioxo-3-methyl-4-trifl a
oromethyl-
1 (2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy}-2-methylpropionate,
ethyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2, 6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1-(2H)-
pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy}propionate,
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
ethyl 2-{2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1 (2H)-
pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy)-2-methylpropionate,
1-acetylethyl 2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-
1 (2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoate and
5 ethyl 3-{2-chloro-5-(3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1(2H)-
pyrimidinyl]benzoyloxy]butanoate.
Especially preferred compounds of the formula (I) are butafenacil ((I-1 ),
1,1-d i m ethyl-2-oxo-2-(2-pro pe n y1 oxy)ethyl 2-ch loro-5-[3, 6-d i h yd ro-
2, 6-
dioxo-3-methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1 (2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoate, CAS No.:
134 605-64-4)
and flupropacil ((I-2), 1-methylethyl 2-chloro-5-[3,6-dihydro-2,6-dioxo-3-
methyl-4-trifluoromethyl-1-(2H)-pyrimidinyl]benzoate, UCC-C4243).
The safeners (B) are preferably selected from the group consisting of:
a) compounds of the formulae (II) to (IV),
O
(R~s~ ,
w" N
(R~y~, / I / ~ n
R'8
O T/C~ ~RZo
O
R~
R2~~ N
\ R~
(1v)
where the symbols and indices having the following meanings:
n' is a natural number from 0 to 5, preferably 0 to 3;
T is a (C~ or C2)-alkanediyl chain which is unsubstituted or
substituted by one or two (C~-C4)alkyl radicals or by ((C~-C3)-
alkoxy]carbonyl;
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
6
W is an unsubstituted or substituted divalent heterocyclic radical
selected from the group consisting of the partially unsaturated
or aromatic five-ringed heterocycles having 1 to 3 hetero ring
atoms of the type N or O, the ring containing at least one
nitrogen atom and not more than one oxygen atom, preferably
a radical selected from the group consisting of (W1) to (UU4),
N . N . N -(CH2)m,
~N ' ,'N ' ~N
~= N
R2~ ~ R~ R2e Rzs O' N
COORS
(V111 ) (~) M~) (
m' is0or1;
R17, R19 are identical or different halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl,
(C~-C4)alkoxy, nitro or (C~-C4)haloalkyl;
R~8, R2~ are identical or different OR24, SR24 or
NR24R25 or a
saturated or unsaturated 3- to 7-membered heterocycle
having
at least one nitrogen atom and up to 3 hetero
atoms, preferably
from the group consisting of O and S, which
heterocycle is
linked to the carbonyl group in (II) or (III)
via the nitrogen atom
and which is unsubstituted or substituted by
radicals selected
from the group consisting of (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy
or
optionally substituted phenyl, preferably a
radical of the formula
OR24, NHR25 or N(CH3)2, in particular of the
fomula OR24;
R24 is hydrogen or an unsubstituted or substituted
aliphatic
hydrocarbon radical, preferably having in total
1 to 18 carbon
atoms;
R25 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-Cg)alkoxy or
substituted or
unsubstituted phenyl;
R26 is hydrogen, (C~-C$)alkyl, (C~-Cg)haloalkyl,
(C~-C4)alkoxy-
(C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-Cg)hydroxyalkyl, (C3-C~2)cycloalkyl
or tri-
(C~-C4)-alkylsilyl;
R27, R28, R29 are identical or different hydrogen,
(C~-Cg)alkyl,
(C~-Cg)haloalkyl, (C3-C~2)cycloalkyl or substituted
or
unsubstituted phenyl;
R2~ is (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C2-C4)alkenyl,
(C2-Cq,~
haloalkenyl, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl, preferably dichloromethyl;
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
7
R22, R23 is identical or different hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl,
(C2-C4)alkenyl, (C2-C4)alkynyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C2-C4)-
haloalkenyl, (C~-C4)alkylcarbamoyl-(C~-C4)alkyl, (C2-C4)-
alkenylcarbamoyl-{C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy-{C~-C4)alkyl,
dioxolanyl-(C~-C4)alkyl, thiazolyl, furyl, furylalkyl, thienyl,
piperidyl, substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, or R22 and R23
together form a substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic ring,
preferably an oxazolidine, thiazolidine, piperidine, morpholine,
hexahydropyrimidine or benzoxazine ring;
b) one or more compounds from the group:
1,8-naphthalic anhydride,
methyl diphenylmethoxyacetate,
cyanomethoxyimino(phenyl)acetonitrile (cyometrinil),
1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethoxyimino(phenyl)acetonitrile (oxabetrinil),
4'-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroacetophenone O-1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyloxime
(fluxofenim),
4,6-dichloro-2-phenylpyrimidine (fenclorim),
benzyl-2-chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylate (flurazole),
2-dichloromethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolane (MG-191),
N-(4-methylphenyl)-N'-{1-methyl-1-phenylethyl)urea (dymron),
1-[4-(N-2-methoxybenzoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-3-methylurea,
1-[4-(N-2-methoxybenzoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-3,3-dimethylurea,
1-[4-(N-4,5-dimethylbenzoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-3-methylurea,
1-[4-(N-naphthoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-3,3-dimethylurea,
(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid (2,4-D),
(4-chlorophenoxy)acetic acid,
(R,Sr2-(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)propionic acid (mecoprop),
4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid (2,4-DB),
(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)acetic acid (MCPA),
4-(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)butyric acid,
4-(4-chlorophenoxy)butyric acid,
3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid (dicamba),
1-(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl 3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoate
(lactidichlor)
and their salts and esters, preferably (C~-Cg);
c) N-acylsulfonamides of the formula (V) and their salts,
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
8
R31 R33
~R34~m
~N ~ ~ S-N .
II o N)
0
(R32~n
where
R3~ is hydrogen, a hydrocarbon radical, a hydrocarbon oxy radical, a
5 hydrocarbon thio radical or a heterocyclyl radical, which is preferably
attached via a carbon atom, each of the last-mentioned 4 radicals
being unsubstituted or substituted by one or more identical or
different radicals selected from the group consisting of halogen,
cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl, formyl, carboxamide,
10 sulfonamide and radicals of the formula -Za-Ra ,
each hydrocarbon moiety preferably having 1 to 20 carbon atoms
and a carbon-containing radical R3~ inclusive of substituents
preferably having 1 to 30 carbon atoms;
R3~ is hydrogen or (C~-C4)alkyl, preferably hydrogen, or
15 R3~ and R3~ together with the group of the formula -CO-N- are the radical
of a 3- to 8-membered saturated or unsaturated ring;
R32 is identical or different halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl,
carboxyl, formyl, CONH2, S02NH2 or a radical of the formula
-Zb-Rb
20 R33 is hydrogen or (C~-C4)alkyl, preferably H;
R34 is identical or different halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl,
carboxyl, CHO, CONH2, S02NH2 or a radical of the formula -Z~-R~;
Ra is a hydrocarbon radical or a heterocyclyl radical, each of the two
last-mentioned radicals being unsubstituted or substituted by one or
25 more identical or different radicals selected from the group
consisting of halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl, mono- and di
[(C~-C4)alkyl]amino, or is an alkyl radical in which more than one,
preferably 2 or 3, nonadjacent CH2 groups are each replaced by an
oxygen atom;
30 Rb,R~ identical or different are a hydrocarbon radical or a heterocyclyl
radical, each of the two last-mentioned radicals being unsubstituted
or substituted by one or more identical or different radicals selected
from the group consisting of halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl,
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
9
phosphoryl, halo(C~-C4)alkoxy, mono- and di[(C~-C4)alkyl]amino, or
are an alkyl radical in which more than one, preferably 2 or 3,
nonadjacent CH2 groups are each replaced by an oxygen atom;
Za is a divalent group of the formula -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CS-, -CO-O-,
-CO-S-, -O-CO-, -S-CO-, -SO-, -S02-, -NR*-, -CO-NR*-, -NR*-CO-,
-S02-NR*- or -NR*-S02-, the bond shown on the right of the divalent
group in question being the bond to the radical Ra and the R* in the
last-mentioned 5 radicals independently of one another being in
each case H, (C~-C4)alkyl or halo(C~-C4)alkyl;
Zb,Z~ independently of one another are a direct bond or a divalent group of
the formula -O-, -S-, -CO-, -CS-, -CO-O-, -CO-S-, -O-CO-, -S-CO-,
-SO-, -S02-, -NR*-, -S02-NR*-, -NR*-S02-, -CO-NR*- or -NR*-CO-,
the bond shown on the right of the divalent group in question being
the bond to the radical Rb or R~, respectively, and the R* in the last-
mentioned 5 radicals independently of one another being in each
case H, (C~-C4)alkyi or halo(C~-C4)alkyl;
n is an integer from 0 to 4, preferably 0, 1 or 2, in particular 0 or 1, and
m is an integer from 0 to 5, preferably 0, 1, 2 or 3, in particular 0, 1 or
2.
d) Acylsulfamoylbenzamides of the formula (VI), if appropriate in salt
form,
Rs~ O
_ O O
y ~R~°)m (V~)
R's I X
O
~Rs~) R3e
where
X3 is CH or N;
R35 is hydrogen, heterocyclyl or a hydrocarbon radical, the two last-
mentioned radicals optionally being substituted by one or more,
identical or different radicals selected from the group consisting of
halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl, CHO, CONH2,
S02NH2 and Za-Ra ;
R36 is hydrogen, hydroxyl, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C2-Cg)alkenyl, (C2-Cg)alkynyl,
(C~-Cg)alkoxy, (C2-Cg)alkenyloxy, the five last-mentioned radicals
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
optionally being substituted by one or more identical or different
radicals selected from the group consisting of halogen, hydroxyl,
(C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy and (C~-C4)alkylthio, or
R35 and R36 together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached are
5 a 3- to 8-membered saturated or unsaturated ring;
R37 is halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl, CHO, CONH2,
SOZNH2 or Zb-Rb;
R38 is hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C2-C4)alkenyl or (C2-C4)alkynyl;
R39 is halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl, carboxyl, phosphoryl,
10 CHO, CONH2, S02NH2 or Z~-R~;
a
R is a (C2-C2p)alkyl radical whose carbon chain is interrupted once or
more by oxygen atoms, or is heterocyclyl or a hydrocarbon radical,
the two last-mentioned radicals optionally being substituted by one
or more, identical or different radicals selected from the group
consisting of halogen, cyano, vitro, amino, hydroxyl, mono- and
di[(C~-C4)alkyl]amino;
Rb, R~ identical or different are a (C2-C2p)alkyl radical whose carbon chain
is interrupted once or more by oxygen atoms, or are heterocyclyl or
a hydrocarbon radical, the two last-mentioned radicals optionally
being substituted by one or more, identical or different radicals
selected from the group consisting of halogen, cyano, vitro, amino,
hydroxyl, phosphoryl, (C~-C4)haloalkoxy, mono- and di[(C~-C4)-
alkyl]amino;
Za is a divalent unit selected from the group consisting of O, S, CO, CS,
C(O)O, C(O)S, SO, S02, NRd, C(O)NRd or S02NRd;
Zb, Z~ identical or different are a direct bond or a divalent unit selected
from
the group consisting of O, S, CO, CS, C(O)O, C(O)S, SO, S02,
NRd, S02NRd or C(O)NRd;
Rd is hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl or (~~-C4)haloalkyl;
n is an integer from 0 to 4, and
m in the event that X is CH, is an integer from 0 to 5 and, in the event
that X is N, an integer from 0 to 4;
e) compounds of the formula (VII),
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
11
Rao
Q'
I
Ray
(VII)
(~2
Ra2
where the symbols and indices have the following meanings:
R4~ is H, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkyl substituted by (C~-C4)alkyl-X4 or
(C~-C4)haloalkyl-X4, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, N02, CN, -COO-R43, NR244,
S02NR245 or CONR246;
R4~ is H, halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, CF3, (C~-C4)alkoxy or (C~-C4)halo-
alkoxy;
R42 is H, halogen or (C~-C4)alkyl;
Q~, Q2, E, G are identical or different, -O-, -S-, -CR247-, -CO-, NR48- or a
group of the formula (VIII),
~C=CH-O-CR2~-(CO)-A VIII)
with the proviso that
a) at least one of the groups Q~, Q2, E, G is a carbonyl group, that
exactly one of this group is a radical of the formula (VIII) and that the
group of the formula (VIII) is adjacent to a carbonyl group, and
Vii) two adjacent groups Q~, Q2, E and G cannot simultaneously be
oxygen;
Ra is identical or different H or (C~-Cg)alkyl or the two radicals Ra
together are (C2-Cg)alkylene;
A is Rb -Y3- or -N 8249;
X4 is -O- or -S(O)p-;
Y3 is -O- or -S-;
Rb is H, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-Cg)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy(C~-Cg)alkyl,
(C3-Cg)alkenyloxy(C~-Cg)alkyl, or phenyl(C~-Cg)alkyl, the phenyl
ring optionally being substituted by halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, CF3,
methoxy or methyl-S(O)p; (C3-Cg)alkenyl, (C3-Cs)haloalkenyl,
phenyl(C3-Cg)alkenyl, (C3-Cg)alkynyl, phenyl(C3-Cg)alkynyl,
oxetanyl, furfuryl, tetrahydrofuryl;
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
12
R43 is H or (C~-C4)alkyl;
R44 is identical or different H, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkylcarbonyl or the
two radicals R44 together are (C4-C5)alkylene;
R45, R46 are independently of one another in each case identical or
different H, (C~-C4)alkyl, or the two radicals R45 andlor R46 together
are (C4-C5)alkylene, it being possible for one CH2 group to be
replaced by O or S or by one or two CH2 groups to be replaced by
_NRc_
Rc is H or (C~-Cg)alkyl;
R4~ is identical or different H, (C~-Cg)alkyl or the two radicals R4~
together are (C2-Cg)alkyiene;
R48 is H, (C~-Cg)alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, or benzyl
which is unsubstituted or substituted on the phenyl ring;
R49 is identical or different H, (C~-Cg)alkyl, phenyl, phenyl(C~-Cg)alkyl, it
being possible for a phenyl ring to be substituted by F, CI, Br, N02,
CN, OCH3, (C~-C4)alkyl or CH3S02_; or is (C~-C4)alkoxy
(C~-Cg)alkyl, (C3-C6)alkenyl, (C3-Cg)alkynyl, (C3-Cg)cycloalkyl or
two radicals R49 together are (C4-C5)alkylene, it being possible for
one CH2 group to be replaced by O or S or for one or two CH2
groups to be replaced by -NRd-;
Rd is H or (C~-C4)alkyl;
m" is 0 or 1 and
p is 0, 1 or 2;
inclusive of the stereoisomers and of the salts conventionally used in
agriculture.
Herbicidally effective amount means, for the purposes of the invention, an
amount of one or more herbicides which is suitable for adversely affecting
plant growth.
Antidote-effective amount means, for the purposes of the invention, an
amount of one or more safeners which is suitable for at least partially
counteracting the phytotoxic effect of a herbicide or herbicide mixture on a
useful plant.
Unless specifically defined otherwise, the following definitions generally
apply to the radicals in formulae (I) to (VIII) and the subsequent formulae.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
13
The radicals alkyl, alkoxy, haloalkyl, haloalkoxy, alkylamino and alkylthio
and the corresponding unsaturated and/or substituted radicals in the
carbon skeleton can each be straight-chain or branched.
Alkyl radicals, also in the composite meanings such as alkoxy, haloalkyl
and the like, preferably have 1 to 4 carbon atoms and are, for example,
methyl, ethyl, n- or i-propyl, n-, i-, t- or 2-butyl. Alkenyl and alkynyl
radicals
have the meaning of the unsaturated radicals which are possible and which
correspond to the alkyl radicals; alkenyl is, for example, allyl, 1-methylprop-
2-en-1-yl, 2-methylprop-2-en-1-yl, but-2-en-1-yl, but-3-en-1-yl, 1-methylbut
3-en-1-yl and 1-methylbut-2-en-1-yl. Alkynyl is, for example, propargyl, but
2-in-1-yl, but-3-in-1-yl, 1-methylbut-3-in-1-yl. "(C~-C4)-Alkyl" is the
abbreviation for alkyl having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; this also applies
analogously to other general definitions' of radicals whose ranges of the
possible number of carbon atoms is given in brackets.
Cycloalkyl is preferably a cyclic alkyl radical having 3 to 8, preferably 3 to
7,
especially preferably 3 to 6, carbon atoms, for example cyclopropyl,
cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl. Cycloalkenyl and cycloalkynyl
denote corresponding unsaturated compounds.
Halogen is fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine. Haloalkyl, haloalkenyl and
haloalkynyl are alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl which are partially or fully
substituted by halogen, preferably fluorine, chlorine and/or bromine, in
particular by fluorine or chlorine, for example CF3, CHF2, CH2F, CF3CF2,
CH2FCHCI, CCIg, CHCI2, CH2CH2CI. Haloalkoxy is, for example, OCF3,
OCHF2, OCH2F, CF3CF20, OCH2CF3 and OCH2CH2CI. This also applies
analogously to other halogen-substituted radicals.
A hydrocarbon radical can be an aromatic or an aliphatic hydrocarbon
radical, an aliphatic hydrocarbon radical generally being a straight-chain or
branched saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon radical, preferably having
1 to 18, especially preferably 1 to 12, carbon atoms, for example alkyl,
alkenyl or alkynyl.
An aliphatic hydrocarbon radical preferably means alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl
having up to 12 carbon atoms; this also applies analogously to an aliphatic
hydrocarbon radical in a hydrocarbonoxy radical.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
14
Aryl is generally a mono-, bi- or polycyclic aromatic system having
preferably 6-20 carbon atoms, by preference 6 to 14 carbon atoms,
especially preferably 6 to 10 carbon atoms, for example phenyl, naphthyl,
tetrahydronaphthyl, indenyl, indanyl, pentalenyl and fluorenyl, especially
preferably phenyl.
A heterocyclic ring, heterocyclic radical or heterocyclyl denotes a mono-, bi
or polycyclic ring system which is saturated, unsaturated andlor aromatic
and has one or more, preferably 1 to 4, hetero atoms, preferably selected
from the group consisting of N, S and O.
Preferred are saturated heterocycles having 3 to 7 ring atoms and one or
two hetero atoms selected from the group consisting of N, O and S,
chalcogens not being adjacent. Especially preferred are monocyclic rings
having 3 to 7 ring atoms and one hetero atom selected from the group
consisting of N, O and S, and also morpholine, dioxolane, piperazine,
imidazoline and oxazolidine. Very especially preferred saturated
heterocycles are oxirane, pyrrolidone, morpholine and tetrahydrofuran.
Also preferred are partially unsaturated heterocycles having 5 to 7 ring
atoms and one or two hetero atoms selected from the group consisting of
N, O and S. Especially preferred are partially unsaturated heterocycles
having 5 to 6 ring atoms and one hetero atom selected from the group
consisting of N, O and S. Very especially preferred partially unsaturated
heterocycles are pyrazoline, imidazoline and isoxazoline.
Also preferred is heteroaryl, e.g. mono- or bicyclic aromatic heterocycles
having 5 to 6 ring atoms which contain one to four hetero atoms selected
from the group consisting of N, O, S, chalcogens not being adjacent.
Especially preferred are monocyclic aromatic heterocycles having 5 to 6
ring atoms and containing a hetero atom selected from the group consisting
of N, O and S, and also pyrimidine, pyrazine, pyridazine, oxazole, thiazole,
thiadiazole, oxadiazole, pyrazole, triazole and isoxazole.
Very especially preferred are pyrazole, thiazole, triazole and furan.
Substituted radicals such as substituted hydrocarbon radicals, for example
substituted alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl such as phenyl and arylalkyl such as
benzyl, or substituted heterocyclyl, are a substituted radical derived from
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
the unsubstituted skeleton, the substituents preferably being one or more,
preferably 1, 2 or 3, in the case of CI and F also up to the maximum
possible number of, substituents selected from the group consisting of
halogen, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, alkylthio, hydroxyl, amino, vitro, carboxyl,
5 cyano, azido, alkoxycarbonyl, alkylcarbonyl, formyl, carbamoyl, mono- and
dialkylaminocarbonyl, substituted amino such as acylamino, mono- and
dialkylamino and alkylsulfinyl, haloalkylsulfinyl, alkylsulfonyl,
haloalkylsulfonyl and, in the case of cyclic radicals, also alkyl and
haloalkyl,
and unsaturated aliphatic substituents corresponding to the
10 abovementioned saturated hydrocarbon-containing substituents, preferably
alkenyl, alkynyl, alkenyloxy, alkynyloxy. In the case of radicals with carbon
atoms, those having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, in particular 1 or 2 carbon atoms,
are preferred. Preferred are, as a rule, substitutents selected from the
group consisting of halogen, for example~fluorine or chlorine, (C~-C4)alkyl,
15 preferably methyl or ethyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, preferably trifluoromethyl,
(C~-Cq.)alkoxy, preferably methoxy or ethoxy, (C~-C4)haloalkoxy, vitro and
cyano. Especially preferred are the substituents methyl, methoxy and
chlorine.
Mono- or disubstituted amino denotes a chemically stable radical selected
from the group consisting of the substituted amino radicals which are N-
substituted, for example, by one or two identical or different radicals
selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, acyl and aryl, preferably
monoalkylamino, dialkylamino, acylamino, arylamino, N-alkyl-N-arylamino
and N-heterocycles. Alkyl radicals having 1 to 4 carbon atoms are
preferred. Aryl is preferably phenyl. Substituted aryl is in this case
preferably substituted phenyl. As far as acyl is concerned, the definition
given further below applies, preferably (C~-C4)alkanoyl. This also applies
analogously to substituted hydroxylamino or hydrazino.
Optionally substituted phenyl is, preferably, phenyl which is unsubstituted
or mono- or polysubstituted, preferably up to trisubstituted, in the case of
halogen such as CI and F also up to pentasubstituted, by identical or
different radicals selected from the group consisting of (C~-C4)alkyl,
(C~-C4)alkoxy, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkoxy and vitro, for example
o-, m- and p-tolyl, dimethylphenyls, 2-, 3- and 4-chlorophenyl, 2-, 3- and
4-trifluoro- and -trichlorophenyl, 2,4-, 3,5-, 2,5- and 2,3-dichlorophenyl, o-
,
m- and p-methoxyphenyl.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
16
An acyl radical denotes the radical of an organic acid preferably having up
to 6 carbon atoms, for example the radical of a carboxylic acid and radicals
of acids derived therefrom such as of thiocarboxylic acid, optionally N-
substituted iminocarboxylic acids, or the radical of carbonic monoesters,
optionally N-substituted carbamic acids, sulfonic acids, sulfinic acids,
phosphoric acids, phosphinic acids. Acyl is, for example, formyl,
alkylcarbonyl such as (C~-C4-alkyl)carbonyl, phenylcarbonyl, it being
possible for the phenyl ring to be substituted, for example as indicated
above for phenyl, or alkyloxycarbonyl, phenyloxycarbonyl,
benzyloxycarbonyl, alkylsulfonyl, alkylsulfinyl or N-alkyl-1-iminoalkyl.
The formulae (I) to (VIII) also encompass all stereoisomers whose atoms
have the same topological linkage, and mixtures of these stereoisomers.
Such compounds contain one or more asymmetric carbon atoms or else
double bonds which are not especially mentioned in the formulae. The
possible stereoisomers which are defined by their specific spatial form,
such as enantiomers, diastereomers, Z- and E-isomers, may be obtained
by customary methods from stereoisomer mixtures or else be prepared by
stereoselective reactions in combination with the use of stereochemically
pure starting materials.
Herbicides of the formula (I) are disclosed, for example, in EP-A-436 680,
which contains extensive information on preparation processes and starting
materials and mentions preferred compounds. This publication is referred
to expressly and it is incorporated herein by reference. The compounds of
the formula (II) are disclosed, for example, in EP-A-0 333 131
(ZA-89/1960), EP-A-0 269 806 (US-A-4,891,057), EP-A-0 346 620
(AU-A-89134951 ), EP-A-0 174 562, EP-A-0 346 620 (UVO-A-91/08 202),
WO-A-91/07 874 or WO-A 95/07 897 (ZA 9417120) and in the literature
cited therein or can be prepared by or analogously to the processes
described therein. The compounds of the formula (III) are disclosed in
EP-A-0 086 750, EP-A-0 94349 (US-A-4,902,340), EP-A-0 191736
(US-A-4,881,966) and EP-A-0 492 366 and in the literature cited therein or
can be prepared by or analogously to the processes described therein.
Some compounds are furthermore described in EP-A-0 582 198.
The compounds of the formula (IV) are disclosed in a large number of
patent applications, for example US-A-4,021,224 and US-A-4,021,229.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
17
Compounds of group B(b) are furthermore known from CN-A-87/102 789,
EP-A-365484 and from "The Pesticide Manual", The British Crop Protection
Council and the Royal Society of Chemistry, 11th edition, Farnham 1997.
The compounds of group B (c) are described in WO-A-97145016, those of
group B (d) in German Patent Application 197 42 951.3, and those of group
B (e) in WO-A 98/13 361.
The cited publications contain extensive information on preparation
processes and starting materials and mention preferred compounds. These
publications are referred to expressly and they are incorporated herein by
reference.
Preferred herbicidelsafener combinations are those which comprise
safeners of the formula (II) andlor (III) in which the symbols and indices
have the following meanings:
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-C~g)alkyl, (C3-C~2)cycloalkyl, (C2-Cg)alkenyl and
(C2-C~g)alkynyl, it being possible for the carbon-containing groups
tRoSO a substituted by one or more, preferably up to three, radicals
R5~ is identical or different halogen, hydroxyl, (C~-Cg)alkoxy,
(C~-Cg)alkylthio, (C2-Cg)alkenylthio, (C2-Cg)alkynylthio, (C2-Cg)
alkenyloxy, (C2-Cg)alkynyloxy, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl, (C3-C7)cyclo
alkoxy, cyano, mono- and di(C~-C4)alkyl)amino, carboxyl,
(C~-Cg)alkoxycarbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkenyloxycarbonyl, (C~-Cg)alkyl-
thiocarbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkynyloxycarbonyl, (C~-Cg)alkylcarbonyl,
(C2-Cg)alkenylcarbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkynylcarbonyl, 1-(hydroxyimino~
(C~-Cg)alkyl, 1-[(C~-C4)alkylimino](C~-C4)alkyl, 1-[(C~-C4)alkoxy-
imino](C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-Cg)alkylcarbonylamino, (C2-Cg)alkenyl-
carbonylamino, (C2-Cg)alkynylcarbonylamino, aminocarbonyl,
(C~-Cg)alkylaminocarbonyl, di-(C~-Cg)alkylaminocarbonyl, (C2-Cg)-
alkenylaminocarbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkynylaminocarbonyl, (C~-Cg)alkoxy-
carbonylamino, (C~-Cg)alkylaminocarbonylamino, (C~-Cg)alkyl-
carbonyloxy, which is unsubstituted or substituted by R~~,
(C2-Cg)alkenylcarbonyloxy, (C2-Cg)alkynylcarbonyloxy, (C~-Cg~
alkylsulfonyl, phenyl, phenyl(C~-Cg)alkoxy, phenyl(C~-Cg)alkoxy-
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
18
carbonyl, phenoxy, phenoxy(C~-Cg)alkoxy, phenoxy(C~-Cg)alkoxy-
carbonyl, phenylcarbonyloxy, phenylcarbonylamino, phenyl(C~-Cg)-
alkylcarbonylamino, it being possible for the last-mentioned 9
radicals to be unsubstituted or mono- or polysubstituted in the
phenyl ring, preferably up to trisubstituted, by radicals R52; SiR'3,
-O-SiR'3, R'3Si-(C~-Cg)alkoxy, -CO-O-NR'2, -O-N=CR'2, -N=CR'2,
-O-NR'2, -NR'2, CH(OR')2, -O-(CH2)m-CH(OR')2, -CR"'(OR')2, -O-
(CH2)mCR"'(OR")2 or by R"O-CHR"'CHCOR"-{C~-Cg)alkoxy,
R5~ is identical or different halogen, nitro, (C~-C4)alkoxy and phenyl
which is unsubstituted or substituted by one or more, preferably up
to three, radicals RS~;
R52 is identical or different halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy,
(C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkoxy or nitro;
R' is identical or different hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, phenyl which is
unsubstituted or substituted by one or more, preferably up to three,
radicals R52, or two radicals R' together form a (C2-Cg)alkanediyl
chain;
R" is identical or different (C~-C4)alkyl or two radicals R" together form
a (C2-Cg)alkanediyl chain;
R"' is hydrogen or (C~-C4)alkyl;
m is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6.
Especially preferred are herbicidelsafener combinations according to the
invention comprising safener of the formula (II) and/or (III) where the
symbols and indices have the following meanings:
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl or (C3-C7)cycloalkyl, the abovementioned
carbon-containing radicals being unsubstituted or mono- or
polysubstituted by halogen or mono- or disubstituted, preferably
monosubstituted, by radicals R5o ,
R5o is identical or different hydroxyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy, carboxyl,
(C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkenyloxycarbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkynyl-
oxycarbonyl, 1-{hydroxyimino)(C~-C4)alkyl, 1-[(C~-C4)alkylimino]-
(C~-C4)alkyl and 1-[(C~-C4)alkoxyimino](C~-C4)alkyl; -SiR'g,
-O-N=CR'2, -N=CR'2, -NR'2, and -O-NR'2, in which R' is identical or
different hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl or, as a pair, a (C4-C5)alkanediyl
chain,
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
' 19
R27, R28, R29 are identical or different hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl,
(C~-Cg)haloalkyl, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl or phenyl which is unsubstituted
or substituted by one or more radicals selected from the group
consisting of halogen, cyano, nitro, amino, mono- and
di[(C~-C4)alkyl]amino, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy,
(C~-C4)haloalkoxy, (C~-C4)alkylthio and (C~-C4)alkylsulfonyl;
R26 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-Cg)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy)(C~-C4)-
alkyl, (C~-Cg)hydroxyalkyl, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl or tri(C~-C4)alkylsilyl,
R~~, R~9 are identical or different hydrogen, halogen, methyl, ethyl,
methoxy, ethoxy, (C~ or C2)haloalkyl, preferably hydrogen, halogen
or (C~ or C2)haloalkyl.
Very especially preferred safeners are those in which the symbols and
indices in formula (II) have the following meanings:
R~~ is halogen, nitro or (C~-C4)haloalkyl;
n' is 0, 1, 2 or 3;
R~8 is a radical of the formula OR24,
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl or {C3-C7)cycloalkyl, the above carbon
containing radicals being unsubstituted or mono- or polysubstituted,
preferably up to trisubstituted, by identical or different halogen
radicals or up to disubstituted, preferably monosubstituted by
identical or different radicals selected from the group consisting of
hydroxyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy, (C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkenyloxy-
carbonyl, (C2-Cg)alkynyloxycarbonyl, 1-(hydroxyimino)(C~-C4)alkyl,
1-[(C~-C4)alkylimino)(C~-C4)alkyl, 1-[(C~-C4)alkoxyimino](C~-C4)-
alkyl and radicals of the formulae -SiR'3, -O-N=R'2, -N=CR'2, -NR'2
and -O-NR'2, the radicals R' in the abovementioned formulae being
identical or different hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl or, in pairs, (C4 or
C5)alkanediyl;
R27, R28, R29 are identical or different hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl,
(C~-Cg)haloalkyl, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl or phenyl which is unsubstituted
or substituted by one or more radicals selected from the group
consisting of halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy, nitro,
(C~-C4)haloalkyl and (C~-C4)haloalkoxy, and
R26 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-Cs)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy-(C~-C4~
alkyl, (C~-Cg)hydroxyalkyl, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl or tri(C~-C4)alkylsilyl.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
Very especially preferred safeners are also those of the formula (III) in
which the symbols and indices have the following meanings:
R~9 is halogen or (C~-C4)haloalkyl;
n' is 0, 1, 2 or 3, where (R~9)n' is preferably 5-CI ;
5 R2~ is a radical of the formula OR24;
T is CH2 or CH(COO-(C~-C3-alkyl)) and
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-Cg)haloalkyi or (C~-C4)alkoxy-
(C~-C4)alkyl, preferably (C~-Cg)alkyl.
10 Particularly preferred are the safeners of the formula (II) in which the
symbols and indices have the following meanings:
W is (V1I1 );
R~7 is halogen or (C~-CZ)haloalkyl;
n' is 0, 1, 2 or 3, (R~~)~~ preferably being 2,4-CI2;
15 R~8 is a radical of the formula OR24;
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)hydroxyalkyl,
(C3-C~)cycloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy(C~-C4)alkyl or tri(C~-C2)alkylsilyl,
preferably (C~-C4)alkyl;
R27 is hydrogen, (C~-C$)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl or (C3-C7)cycloalkyl,
20 preferably hydrogen or (C~-C4)alkyl, and
R26 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)hydroxyalkyl,
(C3-C7)cycloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy(C~-C4)alkyl or tri(C~-C2)alkylsilyl,
preferably hydrogen or (C~-C4)alkyl.
Also particularly preferred are herbicidal compositions comprising a safener
of the formula (II) where the symbols and indices have the following
meanings:
W is (W2);
R~7 is halogen or (C~-C2)haloalkyl;
n' is 0, 1, 2 or 3, (R~ 7)~~ preferably being 2,4-CI2;
R~8 is a radical of the formula OR24;
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)hydroxyalkyl,
(C3-C7)cycloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy~C~-C4-alkyl or tri(C~-C2)alkylsilyl,
preferably (C~-C4)alkyl, and
R27 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl or
phenyl, preferably hydrogen or (C~-C4)alkyl.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
21
Also particularly preferred are safeners of the formula (II) where the
symbols and indices have the following meanings:
W is (1N3); '
R~7 is halogen or (C~-C2)haloalkyl;
n' is 0, 1, 2 or 3, (R~~)n~ preferably being 2,4-CI2;
R~$ is a radical of the formula OR24;
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)hydroxyalkyl,
(C3-C7)cycloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy(C~-C4)alkyl or tri(C~-C2)alkylsilyl,
preferably (C~-C4)alkyl, and
R28 is (C~-Cg)alkyl or (C~-C4)haloalkyl, preferably C~-haloalkyl.
Also particularly preferred are safeners of the formula (II) where the
symbols and indices have the following meanings:
W is (V1/4);
R~7 is halogen, nitro, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C2)haloalkyl, preferably CF3 or
(C~-C4}alkoxy;
n' is 0, 1, 2 or 3;
m' is0or1;
R~$ is a radical of the formula OR24 ;
R24 is hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, carboxy(C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy-
carbonyl(C~-C4)alkyl, preferably (C~-C4}alkoxy-CO-CHZ-,
(C~-C4)alkoxy-CO-C(CH3}H-, HO-CO-CH2- or HO-CO-C(CH3)H-,
and
R29 is hydrogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C3-C7)cycloalkyl or
phenyl which is unsubstituted or substituted by one or more radicals
selected from the group consisting of halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl,
(C~-C4)haloalkyl, vitro, cyano and (C~-C4)alkoxy.
The following groups of compounds are particularly suitable as safeners for
the herbicidal active substances of the formula (I):
a) compounds of the dichlorophenylpyrazoline-3-carboxylic acid , type
(i.e. of the formula (II), where W' = W1 and (R~7}~~ = 2,4-CI2),
preferably compounds such as ethyl 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-
(ethoxycarbonyl)-5-methyl-2-pyrazoline-3-carboxylate (II-1,
mefenpyr-diethyl), and related compounds as they are described in
WO-A 91/07874;
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
22
b) dichlorophenylpyrazolecarboxylic acid derivatives (i.e. of the formula
(II), where W = (V112) and (R~7)~~ = 2,4-CI2), preferably compounds
such as ethyl 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-methylpyrazole-3-carboxylate
(II-2), ethyl 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-isopropylpyrazole-3-carboxylate
(II-3), ethyl 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(1,1-dimethylethyl)pyrazole-3-
carboxylate (II-4.), ethyl 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-phenyipyrazole-3-
carboxylate (II-5) and related compounds as they are described in
EP-A-0 333 131 and EP-A-0 269 806.
c) Compounds of the triazolecarboxylic acid type (i.e. of the formula
(II), where W = (Vlf3) and (R~7)n~ = 2,4-CI2), preferably compounds
such as fenchlorazol-ethyl, i.e. ethyl 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl~
5-trichloromethyl-(1 H)-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylate (II-6), and related
compounds (see EP-A-0 174 562 and EP-A-0 346 620);
d) compounds of the 5-benzyl- or 5 phenyl-2-isoxazoline-3-carboxylic
acid type or the 5,5-diphenyl-2-isoxazoline-3-carboxylic acid type
(where W - (UV4)), preferably compounds such as ethyl
5-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-2-isoxazoline-3-carboxylate (II-7) or ethyl
5-phenyl-2-isoxazoline-3-carboxylate (II-8) and related compounds
as they are described in WO-A-91108202, or of the ethyl
5,5-Biphenyl-2-isoxazolinecarboxylate type (II-9, isoxadifen-ethyl),
the n-propyl 5,5-Biphenyl-2-isoxazolinecarboxylate type (II-10) or the
ethyl 5-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-phenyl-2-isoxazoline-3-carboxylate type
(I I-11 ), as they are described in WO-A-95/07897.
e) Compounds of the 8-quinolinoxyacetic acid type, for example those
of the formula (III), where (R~9)~~ = 5-CI, R2~ = OR24 and T = CH2,
preferably the compounds
1-methylhexyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-1, cloquintocet-
mexyl),
1,3-dimethylbut-1-yl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-2),
4-allyloxy-butyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-3),
1-allyloxyprop-2-yl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-4),
ethyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-5),
methyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-6),
allyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-7),
2-(2-pro~ylideneiminoxy)-1-ethyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate
(III-8),
2-oxoprop-1-yl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)acetate (III-9)
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
23
and related compounds as they are described in EP-A-0 860 750,
EP-A-0 094 349 and EP-A-0 191 736 or EP-A-0 492 366.
f) Compounds of the (5-chloro-8-quinolinox~)malonic acid type, i.e. of
the formula (III), where {R~9)~~ = 5-CI, R ~= OR24, T = -CH(COO-
alkyl)-, preferably the compounds diethyl (5-chloro-8-
quinolinoxy)malonate, diallyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)malonate,
methyl ethyl (5-chloro-8-quinolinoxy)malonate and related
compounds as they are described in EP-A-0 582 198.
g) compounds of the dichloroacetamide type, i.e. of the formula (IV),
preferably:
N,N-diallyl-2,2-dichloroacetamide (dichlormid, disclosed in
US-A 4,137,070),
4-dichloroacetyl-3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-2H-1,4-benzoxazine (IV-1,
benoxacor, disclosed in EP 0 149 974),
N~,N2-diallyl-N2-dichloroacetylglycinamide (DKA-24, disclosed in
H U 2143821 ),
4-dichloroacetyl-1-oxa-4-aza-spiro[4,5]decane (AD-67),
2,2-dichloro-N-(1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethyl)-N-(2-propenyl)acetamide
(PPG-1292),
3-dichloroacetyl-2,2,5-trimethyloxazolidine,
3-dichloroacetyl-2,2-dimethyl-5-phenyloxazolidine,
3-dichloroacetyl-2,2-dimethyl-5-(2-thienyl)oxazolidine,
3-dichloroacetyl-5-{2-furanyl)-2,2-dimethyloxazolidine (furilazole,
MON 13900),
1-dichloroacetylhexahydro-3,3,8a-trimethylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-
6(2H~one (dicyclonon, BAS 145138),
h) compounds of group B{b), preferably
1,8-naphthalic anhydride,
methyl diphenylmethoxyacetate,
cyanomethoxyimino(phenyl)acetonitrile (cyometrinil),
1,3-dioxolan-2-ylmethoxyimino(phenyl)acetonitrile (oxabetrinil),
4'-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroacetophenone O-1,3-dioxolan-2-
ylmethyloxime (fluxofenim),
4,6-dichloro-2-phenylpyrimidine (fenclorim),
benzyl 2-chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylate
(flurazole),
2-dichloromethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxolan (MG-191 ),
N-{4-methylphenyl)-N'-(1-methyl-1-phenylethyl)urea (dymron),
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
24
1-[4-(N-2-methoxybenzoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-3-methylurea,
1-[4-(N-2-methoxybenzoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-3,3-dimethylurea,
1-[4-(N-4,5-dimethylbenzoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-3-methylurea,
1-[4-(N-naphthoylsulfamoyl)phenyl)-3,3-dimethylurea,
(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid (h-1, 2,4-D),
(4-chlorophenoxy)acetic acid,
(R,S)-2-(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)propionic acid (h-2, mecoprop),
4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid (2,4-DB),
(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)acetic acid (h-3, MCPA),
4-(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)butyric acid,
4-(4-chlorophenoxy)butyric acid,
3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid (dicamba),
1-(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl 3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoate
(lactidichlor) '
and their salts and esters, preferably (C~-Cg).
Furthermore preferred as safeners are compounds of the formula (V) or
their salts, where
R3~ is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C3-Cg)cycloalkyl, furanyl or thienyl, it
being possible for each of the last-mentioned 4 radicals to be
unsubstituted or substituted by one or more substituents selected
from the group consisting of halogen, (Ct-C4)alkoxy, halo(C~-Cg~
alkoxy and (C~-C4)alkylthio and, in the case of cyclic radicals, also
(C~-C4)alkyl and (C~-C4)haloalkyl,
R3~ is hydrogen,
R32 is halogen, halo(C~-C4)alkyl, halo(C~-C4)alkoxy, (C~-C4)alkyl,
(C~-C4)alkoxy, (C~-C4)alkylsulfonyl, (C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl or
(C~-C4)alkylcarbonyl,
preferably halogen, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, such as trifluoromethyl,
(C~-C4)alkoxy, halo(C~-C4)alkoxy, (C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl or
(C~-C4)alkylsulfonyl,
R33 is hydrogen,
R~ is halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, halo(C~-C4)alkyl, halo(C~-C4)alkoxy,
(C3-C6)cycloalkyl, phenyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy, cyano, (C~-C4)alkylthio,
(C~-C4)alkylsulfinyl, (C~-C4)alkylsulfonyl, (C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl or
(C~-C4)alkylcarbonyl,
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
preferably halogen, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, such as
trifluoromethyl, halo(C~-C4)alkoxy, (C~-C4)alkoxy or (C~-C4)-
alkylthio,
n is 0, 1 or 2 and
5 m is 1 or 2.
Furthermore preferred are safeners of the formula (VI), in which
X3 is CH;
R35 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C3-Cg)cycloalkyl, (CZ-Cg)alkenyl,
10 (C5-Cg)cycloalkenyl, phenyl or 3- to 6-membered heterocyclyl
having up to three hetero atoms selected from the group consisting
of nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur, it being possible for the six last
mentioned radicals to be optionally substituted by one or more
identical or different substituents selected from the group consisting
15 of halogen, (C~-Cg)alkoxy, (C~-Cg)haloalkoxy, (C~-C2)alkylsulfinyl,
(C~-C2)alkylsulfonyl, (C3-Cg)cycloalkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl,
(C~-C4)alkylcarbonyl and phenyl and, in the case of cyclic radicals,
also (C~-C4)alkyl and (C~-C4)haloalkyl;
R36 is hydrogen, (C~-Cg)alkyl, (C2-Cg)alkenyl, (C2-Cg)alkynyl, it being
20 possible for the three last-mentioned radicals optionally to be
substituted by one or more, identical or different substituents
selected from the group consisting of halogen, hydroxyl,
(C~-C4)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy and (C~-C4)alkylthio;
R37 is halogen, (C~-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkoxy, vitro, (C~-C4)alkyl,
25 (C~-C4)alkoxy, (C~-C4)alkylsulfonyl, (C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl or
(C~-C4)alkylcarbonyl;
R3$ is hydrogen;
R39 is halogen, vitro, (C~-C4)alkyl, (C1-C4)haloalkyl, (C~-C4)haloalkoxy,
(C3-Cg)cycloalkyl, phenyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy, cyano, (C1-C4)alkylthio,
(C~-C4)alkylsulfinyl, (C~-C4)alkylsulfonyl, (C~-C4)alkoxycarbonyl or
(C~-C4)alkylcarbonyl;
n is 0, 1 or 2 and
m is 1 or 2.
Especially preferred amongst the safeners of the formula (VII) are the sub-
groups which follow:
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
26
- compounds in which R4$ and R49 are H, (C~-Cg)alkyl, phenyl,
phenyl(C~-Cg)alkyl, (C~-C4)alkoxy-(C~-Cg)alkyl, (C3-Cg)alkenyl or
(C3-C6)alkynyl, it being possible for phenyl rings to be substituted by
F, CI, Br, N02, CN, OCH3, (C~-C4)alkyl or CH3-S02-;
- compounds in which Ra is H;
- compounds in which A is Rb-Y;
- compounds in which E is O;
- compounds in which Q~ is CR247;
- compounds in which R47 is H;
- compounds in which m" is 1 and E is O or S;
- compounds in which m" = 0;
- compounds in which R4~ to R~ are H, m" is 1, E is O , Q~ is CR247
and A is Rb-Y, in particular those where R4~ is H, Rb is CH3 and Y is
O;
- compounds in which Q~ is CR24~ and m" equals 0, in particular
those in which R~ and R47 are H and A is Rb-Y3 where Rb is
preferably methyl and Y is preferably O.
Examples of preferred combinations of herbicidal active substances (A)
and safeners (B) are: (I-1 ) + (II-1 ), (I-1 ) + (II-9), (I-1 ) + (III-1 ), (I-
1 ) + (IV-1 ),
(I-1 ) + (h-1 ), (I-1 ) + (h-2), (I-1 ) + (h-3), (I-2) + (II-1 ), (I-2) + (1I-
9), (I-2) +
(III-1 ), (I-2) + (1V-1 ), (I-2) + (h-1 ), (I-2) + (h-2) and (I-2) + (h-3).
The safeners (antidotes) of the formulae (II) - (VII) and the compounds of
group (b), for example safeners of the preferred groups a) to h), reduce or
prevent phytotoxic effects which may occur when using the herbicidal
active substances of the formula (I) in crops of useful plants without
substantially affecting the efficacy of these herbicidal active substances
against harmful plants. This allows the field of application of conventional
crop protection products to be widened quite considerably and to be
extended to, for example, crops such as wheat, barley, maize, rice and
other crops in which use of the herbicides was hitherto impossible, or only
limited, that is to say at low rates and with a restricted spectrum.
The herbicidal active substances and the mentioned safeners can be
applied together (as a readymix or by the tank mix method) or in
succession in any desired sequence. The weight ratio of safener:herbicidal
active substance may vary within wide limits and lies preferably in the
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
27
range of from 1:100 to 100:1, in particular 1:10 to 10:1. The optimum
amounts of herbicidal active substance and safener which are used in each
case depend on the type of the herbicidal.active substance used or on the
safener used and on the species of the crop stand to be treated and can be
determined in each individual case by simple routine preliminary
experiments.
The main fields of application for the combinations according to the
invention are, in particular, maize and cereal crops (for example, wheat,
rye, barley, oats), rice, sorghum, cotton and soybeans, preferably cereals,
rice and maize.
Depending on their properties, the safeners contained in the herbicidal
composition according to the invention can be used for pretreating the seed
of a crop plant (seed dressing), or be incorporated into the seed furrows
prior to sowing or applied together with the herbicide before or after plant
emergence. The pre-emergence treatment includes not only treatment of
the area under cultivation prior to sowing and treatment of the areas under
cultivation where the seeds have been planted but the plants have not yet
emerged. The joint application together with the herbicide is preferred. To
this end, tank mixes or readymixes may be employed.
The application rates of safener required may vary within wide limits
depending on indication and herbicidal active substance used and are
generally in the range of from 0.001 to 5 kg, preferably 0.005 to 0.5 kg, of
active substance per hectare.
The present invention furthermore relates to a method of controlling
harmful plants in plant crops, which comprises applying a herbicidalty
effective amount of a herbicidally effective composition according to the
invention to the harmful plants, crop plants, plant seeds or the area on
which the plants grow. In this context, the antidote-effective amount of one
or more safeners, preferably of one or more, in particular one, compound of
the formula (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (VII) and/or from among group B(b),
can
be applied to the plants, plant seeds or the area on which the plants grow
before, after or simultaneously with the herbicidally active substances) of
the formula (I).
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
28
The herbicidelsafener combination according to the invention may also be
employed for controlling harmful plants in crops of genetically engineered
plants which are either known or still to be developed. As a rule, the
transgenic plants are distinguished by particular, advantageous properties,
for example by resistance to certain crop protection agents, resistance to
plant diseases or pathogens causing plant diseases such as particular
insects or microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria or viruses. Other
particular properties relate, for example, to the harvested material in terms
of quantity, quality, storing properties, composition and specific
constituents. Thus, there are known transgenic plants with an increased
starch content or with an altered starch quality, or those where the
harvested material has a different fatty acid composition.
The use of the combinations according. to the invention in economically
important transgenic crops of useful plants and ornamentals, for example
cereals (for example wheat, barley, rye, oats), sorghum and millet, rice,
cassava and maize, or else crops of sugar beet, cotton, soya, oilseed rape,
potatoes, tomatoes, peas and other vegetables.
When the combinations according to the invention are applied in transgenic
crops, effects on harmful plants to be observed in other crops are
frequently accompanied by effects which are specific for application in the
transgenic crop in question, for example an altered or specifically widened
weed spectrum which can be controlled, altered application rates which
may be used, preferably good compatibility with the herbicides to which the
transgenic crop is resistant, and altered growth and yield of the transgenic
crop plants.
The invention therefore also relates to the use of the herbicidally active
composition according to the invention for controlling harmful plants in
transgenic crop plants or crop plants that have tolerance owing to
selection-based breeding.
The safeners, preferably of the formulae (II) - (VII) andlor of group B(b),
and the abovementioned herbicidal active substances of the formula (I) can
be formulated in various ways, either jointly or separately, depending on
the biological andJor chemico-physical parameters specified. Examples of
possible formulations which are suitable are:
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
29
Wettable powders (V11P), emulsifiable concentrates (EC), water-soluble
powders (SP), water-soluble concentrates (SL), concentrated emulsions
(BW) such as oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions, sprayable solutions or
emulsions, capsule suspensions (CS), oil- or water-based dispersions
(SC), suspoemulsions, suspension concentrates, dusts (DP), oil-miscible
solutions (0L), seed-treatment products, granules (GR) in the form of
microgranules, spray granules, coated granules and adsorption granules,
granules for soil application or broadcasting, water-soluble granules (SG),
water-dispersible granules (V11G), ULV formulations, microcapsules and
waxes.
These individual formulation types are known in principle and described, for
example, in: Winnacker-Kuchler, "Chemische Technologie" [Chemical
Technology], Volume 7, C. Hauser Verlag Munich, 4t" Edition 1986; Wade
van Valkenburg, "Pesticide Formulations", Marcel Dekker N.Y., 1973; K.
Martens, "Spray Drying Handbook", 3rd Edition 1979, G. Goodwin Ltd.
London.
The formulation auxiliaries which may be required, such as inert materials,
surfactants, solvents and other additives are also known and described, for
example, in: Watkins, "Handbook of Insecticide Dust Diluents and
Carriers", 2nd Ed., Darland Books, Caldwell N.J., H.v. Olphen, "Introduction
to Clay Colloid Chemistry"; 2nd Ed., J. Wiley & Sons, N.Y.; C. Marsden,
"Solvents Guide"; 2nd Ed., Interscience, N.Y. 1963; McCutcheon's
"Detergents and Emulsifiers Annual", MC Publ. Corp., Ridgewood N.J.;
Sisley and Wood, "Encyclopedia of Surface Active Agents", Chem. Publ.
Co. Inc., N.Y. 1964; Schonfeldt, "Grenzfl~chenaktive Athylenoxidaddukte"
[Surface-Active Ethylene Oxide Adducts], Wiss. Verlagsgesell., Stuttgart
1976; Winnacker-Kuchler, "Chemische Technologie" [Chemical
Technology], Volume 7, C. Hauser Verlag Munich, 4t" Edition 1986.
Based on these formulations, it is also possible to prepare combinations
with other agrochemical active substances, for example with substances
which act as crop protection agents, such as insecticides, acaricides,
herbicides, fungicides, and also with safeners, fertilizers and/or growth
regulators, for example in the form of a readymix or tank mix.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
Wettable powders are preparations which are uniformly dispersible in water
and which, besides the active substance, also comprise ionic and/or
nonionic surfactants (wetting agents, dispersants), for example
polyoxyethylated alkylphenols, polyoxyethylated fatty alcohols,
5 polyoxyethylated fatty amines, fatty alcohol polyglycol ether sulfates,
alkanesulfonates, alkylbenzenesulfonates, sodium lignosulfonate, sodium
2,2'-dinaphthylmethane-6,6'-disulfonate, sodium dibutylnaphthalenesulfon-
ate, or else sodium oleoylmethyltaurinate, in addition to a diluent or inert
substance. To prepare the wettable powders, the active substances, for
10 example the herbicidally active substances andlor the safeners are ground
finely, for example in customary apparatus such as hammer mills, blower
mills and air jet mills, and simultaneously or subsequently mixed with the
formulation auxiliaries.
15 Emulsifiable concentrates are prepared, for example, by dissolving the
active substance, for example the herbicidal active substance and/or the
safener, in an organic solvent, such as butanol, cyclohexanone,
dimethylformamide, xylene or else higher-boiling hydrocarbons such as
aromatics, saturated or unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons or alicyclic
20 hydrocarbons, or mixtures of the organic solvents with the addition of one
or more ionic andlor nonionic surfactants (emulsifiers). Examples of
substances which can be used as emulsifiers are: calcium
(Cg-C~g)alkylarylsulfonates such as calcium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, or
nonionic emulsifiers such as fatty acid polyglycol esters, (C2-C~g)alkylaryl
25 polyglycol ethers, fatty alcohol polyglycol ethers, propylene
oxidelethylene
oxide condensates, alkyl polyethers, sorbitan esters, for example sorbitan
fatty acid esters or polyoxyethylene sorbitan esters, for example
polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid esters.
30 Dusts are generally obtained by grinding the active substance, for example
the herbicidal active substance andlor the safener, with finely distributed
solid substances, for example talc, natural clays such as kaolin, bentonite
and pyrophyllite, or diatomaceous earth.
Suspension concentrates can be water- or oil-based. They can be
prepared, for example, by wet grinding using commercially available bead
mills with or without an addition of surfactants, for example those which
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
31
have already been mentioned above in the case of the other formulation
types.
Emulsions, for example oil-in-water emulsions (EW), can be prepared, for
example, by means of stirrers, colloid mills andlor static mixers using
aqueous organic solvents in the presence or absence of surfactants which
have already been mentioned above, for example, in the case of the other
formulation types.
Granules can be prepared either by spraying the active substance, for
example the herbicidal active substance andlor the safener, onto
adsorptive, granulated inert material or by applying active substance
concentrates to the surface of carriers such as sand, kaolinites or
granulated inert material with the aid of binders, for example polyvinyl
alcohol, sodium polyacrylate or else mineral oils. Suitable active
substances can also be granulated in the manner which is conventional for
the preparation of fertilizer granules, if desired as a mixture with
fertilizers.
As a rule, water-dispersible granules are prepared by the customary
processes such as spray drying, fluidized bed granulation, disk granulation,
mixing with high-speed mixers, and extrusion without solid inert material.
For the preparation of disk, fluidized-bed, extruder and spray granules see,
for example, processes in "Spray-Drying Handbook" 3"° Ed. 1979, G.
Goodwin Ltd., London; J.E. Browning, "Agglomeration", Chemical and
Engineering 1967, pages 147 et seq.; "ferry's Chemical Engineer's
Handbook", 5t" Ed., McGraw-Hill, New York 1973, p. 8-57.
For further details on the formulation of crop protection products see, for
example, G.C. Klingman, "Weed Control as a Science", John Wiley and
Sons, Inc., New York, 1961, pages 81-96 and J.D. Freyer, S.A. Evans,
"Weed Control Handbook", 5~' Ed., Blackwell Scientific Publications,
Oxford, 1968, pages 101-103.
As a rule, the agrochemical formulations comprise 0.1 to 99% by weight, in
particular 0.1 to 95% by weight, of active substances, for example safener
active substances (B), preferably of the formula (II) - (VII) andlor from
among group B(b), or herbicidal active substances of the formula (I), or of
the herbicide/safener active substance mixture according to the invention,
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
32
comprising compounds of the formula (I) and safener active substances
(B), preferably compounds of the formula (II) - (VII) andlor from among
group B(b), and 1 to 99.9% by weight, in particular 5 to 99.8% by weight, of
a solid or liquid additive and 0 to 25% by weight, in particular 0.1 to 25% by
weight, of a surfactant.
In wettable powders, the active substance concentration is, for example,
approximately 10 to 90% by weight, the remainder to 100% by weight being
composed of customary formulation components. In the case of
emulsifiable concentrates, the concentration of active substance is
approximately 1 to 80% by weight. Formulations in the form of dusts
comprise 1 to 20% by weight of active substance, sprayable solutions
comprise approximately 0.2 to 20% by weight of active substance. In the
case of granules, such as water-dispersible granules, the active substance
content depends partly on whether the active compound is in liquid or solid
form. The active substance content of the water-dispersible granules is, for
example, between 10 and 90% by weight.
Besides this the abovementioned formulations of active substances may
comprise, if appropriate, the adhesives, wetting agents, dispersants,
emulsifiers, penetrants, preservatives, antifreeze agents, solvents, fillers,
carriers, colorants, antifoams, evaporation inhibitors and pH and viscosity
regulators which are customary in each case.
Components which can be used in combination with the mixtures according
to the invention in mixed formulations or in tank mixes are, for example,
known active substances as they are described, for example, in Weed
Research 26, 441-445 (1986), or "The Pesticide Manual", 10t" edition, The
British Crop Protection Council, 1994, and the literature cited therein.
Examples of active substances which may be mentioned as herbicides
which are known from the literature and which can be combined with the
mixtures according to the invention are the following (note: either the
common names in accordance with the International Organization for
Standardization (ISO) or the chemical names, if appropriate together with a
customary code number, of the compounds are given):
acetochlor; acifluorfen; aclonifen; AKH 7088, i.e. [[[1-[5-[2-chloro-4-
(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitrophenyl]-2-methoxyethylidene]amino]oxy]-
acetic acid and its methyl ester; alachlor; alloxydim; ametryn;
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
33
amidosulfuron; amitrol; AMS, i.e. ammonium sulfamate; anilofos; asulam;
atrazine; azafenidine (DPX-R6447), azimsulfurone (DPX-A8947);
aziprotryn; barban; BAS 516 H, i.e. 5-fluoro-2-phenyl-4H-3,1-benzoxazin-4-
one; benazolin; benfluralin; benfuresate; bensulfuron-methyl; bensulide;
bentazone; benzofluor; benzoylprop-ethyl; benzthiazuron; bialaphos;
bifenox; bispyribac-sodium (KIH-2023), bromacil; bromobutide;
bromofenoxim; bromoxynil; bromuron; buminafos; busoxinone; butachlor;
butamifos; butenachlor; buthidazole; butralin; butroxydim (ICI-0500),
butylate; cafenstrole (CH-900); carbetamide; cafentrazone; CDAA, i.e.
2-chloro-N,N-di-2-propenylacetamide; CDEC, i.e. 2-chloroallyl diethyldithio-
carbamate; chlomethoxyfen; chloramben; chloransulam-methyl (XDE-565),
chlorazifop-butyl, chlorbromuron; chlorbufam; chlorfenac; chlorflurecol-
methyl; chloridazon; chlorimuron ethyl; chlornitrofen; chlorotoluron;
chloroxuron; chlorpropham; chlorsulfuron; chlorthal-dimethyl; chlorthiamid;
cinidon-ethyl, cinmethylin; cinosulfuron; clethodim; clodinafop and its ester
derivatives (e.g. clodinafop-propargyl); clomazone; clomeprop;
cloproxydim; clopyralid; cumyluron (JC 940); cyanazine; cycloate;
cyclosulfamuron (AC 014); cycloxydim; cycluron; cyhalofop and its ester
derivatives {e.g. butyl ester, DEH-112); cyperquat; cyprazine; cyprazole;
2,4-DB; dalapon; desmedipham; desmetryn; di-allate; dicamba; dichlobenil;
dichlorprop; diclofop and its esters such as diclofop-methyl; diclosulam
(XDE-564), diethatyl; difenoxuron; difenzoquat; diflufenican; diflufenzopyr-
sodium (SAN-835H), dimefuron; dimethachlor; dimethametryn;
dimethenamid (SAN-582H); dimethazone, 5-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl-
carbamoylsulfamoyl)-1-(2-pyridyl)-pyrazole-4-carboxylate (NC-330);
triaziflam (IDH-1105); clomazon; dimethipin; dimetrasulfuron, dinitramine;
dinoseb; dinoterb; diphenamid; dipropetryn; diquat; dithiopyr; diuron;
DNOC; eglinazine-ethyl; EL 177, i.e. 5-cyano-1-(1,1-dimethylethyl~N-
methyl-1 H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide; endothal; epoprodan (MK-243), EPTC;
esprocarb; ethalfluralin; ethametsulfuron-methyl; ethidimuron; ethiozin;
ethofumesate; F5231, i.e. N-[2-chloro-4-fluoro-5-[4-(3-fluorpropyl)-4,5-
dihydro-5-oxo-1H-tetrazol-1-yl]phenyl]ethanesulfonamide; ethoxyfen and its
esters (e.g. ethyl ester, HN-252); ethoxysulfuron (disclosed in EP 342569)
etobenzanid (NW 52); 3-(4-ethoxy-6-ethyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-1-(2,3-dihydro-
1,1-dioxo-2-methylbenzo[b]thiophene-7-sulfonyl)urea (EP-A 079 683); 3-(4-
ethyl-6-methoxy-1,3, 5-triazin-2-yl)-1-(2,3-dihydro-1,1-dioxo-2-
methylbenzo[b]thiophene-7-sulfonyl)urea (EP-A 079 683); fenoprop;
fenoxan, fenoxaprop and fenoxaprop-P and their esters, e.g. fenoxaprop-P-
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
34
ethyl and fenoxaprop-ethyl; fenoxydim; fenuron; flamprop-methyl;
flazasulfuron; flufenacet (BAY-FOE-5043), fluazifop and fluazifop-P,
florasulam (DE-570) and their esters, e.g. fluazifop-butyl and fluazifop-P-
butyl; fluchloralin; flumetsulam; flumeturon; flumiclorac and their esters
(e.g. pentyl ester, S-23031 ); flumioxazin (S-482); flumipropyn; flupoxam
(KNW-739); fluorodifen; fluoroglycofen-ethyl; flupropacil CUBIC-4243);
flupyrsulfuron-methyl sodium (DPX-KE459), fluridone; flurochloridone;
fluroxypyr; flurtamone; fluthiacet-methyl (KIH-9201 ), fomesafen; fosamine;
furyloxyfen; glufosinate; glyphosate; halosafen; halosulfuron and its esters
(e.g. methyl ester, NC-319); haloxyfop and its esters; haloxyfop-P (= R-
haloxyfop) and its esters; hexazinone; imazamethabenz-methyl; imazamox
(AC-299263), imazapyr; imazaquin and salts such as the ammonium salt;
imazethamethapyr; imazethapyr; imazosulfuron; iodosulfuron (methyl-4-
iodo-2-[3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)ureidosulfonyl]-benzoate,
sodium salt, WO 92/13845); ioxynil; isocarbamid; isopropalin; isoproturon;
isouron; isoxaben; isoxapyrifop; karbutilate; lactofen; lenacil; linuron;
MCPA; MCPB; mecoprop; mefenacet; mefluidid; metamitron; metazachlor;
methabenzthiazuron; metham; methazole; methoxyphenone;
methyldymron; metobenzuron, methyl-2-[3-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-
yl)ureidosulfonyl]-4-methanesulfonamidomethylbenzoate (WO 95110507);
methobenzuron; metobromuron; metolachlor; S-metolachlor, metosulam
(XRD 511 ); metoxuron; metribuzin; metsulfuron-methyl; MH; molinate;
monalide; monocarbamide dihydrogensulfate; monolinuron; monuron;
MT 128, i.e. 6-chloro-N-(3-chloro-2-propenyl)-5-methyl-N-phenyl-3-
pyridazinamine; MT 5950, i.e. N-[3-chloro-4-(1-methylethyl)phenyl]-2-
methylpentanamide; N,N-dimethyl-2-[3-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-
yl)ureidosulfonyl]-4-formylaminobenzamide (WO 95/01344); naproanilide;
napropamide; naptalam; NC 310, i.e. 4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)-1-methyl-5-
benzyloxypyrazole; neburon; nicosulfuron; nipyraclofen; nitralin; nitrofen;
nitrofluorfen; norflurazon; orbencarb; oryzalin; oxadiargyl (RP-020630);
oxadiazon; oxaziclomefone (MY-100), oxyfluorfen; oxasulfuron (CGA-
277476), paraquat; pebulate; pendimethalin; pentoxazone (KPP-314),
perfluidone; phenisopham; phenmedipham; picloram; piperophos;
piributicarb; pirifenop-butyl; pretilachlor; primisulfuron-methyl; procyazine;
prodiamine; profluralin; proglinazine-ethyl; prometon; prometryn;
propachlor; propanil; propaquizafop and its esters; propazine; propham;
propisochlor; propyzamide; prosulfalin; prosulfocarb; prosulfuron (CGA-
152005); prynachlor; pyraflufen-ethyl (ET-751 ), pyrazon; pyrazosulfuron-
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
ethyl; pyrazoxyfen; pyribenzoxim, pyridate; pyriminobac-methyl (KIH-6127),
pyrithiobac (KIH-2031 ); pyroxofop and its esters (e.g. propargyl ester);
quinclorac; quinmerac; quinofop and its ester derivatives, quizalofop and
quizalofop-P and their ester derivatives e.g. quizalofop-ethyl; quizalofop-P-
5 tefuryl and -ethyl; renriduron; rimsulfuron (DPX-E 9636); S 275, i.e. 2-
[4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-{2-propynyloxy)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-2H-indazole;
secbumeton; sethoxydim; siduron; simazine; simetryn; SN 106279, i.e. 2-
[[7-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-naphthalenyl]oxy]-propanoic acid
and its methyl ester; sulfentrazon (FMC-97285, F-6285); sulfazuron;
10 sulfometuron-methyl; sulfosate (ICI-A0224); sulfosulfuron (MON-37500),
TCA; tebutam (GCP-5544); tebuthiuron; tepraloxydim (BAS-620H), terbacil;
terbucarb; terbuchlor; terbumeton; terbuthylazine; terbutryn; TFH 450, i.e.
N,N-diethyl-3-[(2-ethyl-6-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-1 H-1,2,4-triazole-1-
carboxamide; thenylchlor (NSK-850); thiazafluron; thiazopyr (Mon-13200);
15 thidiazimin (SN-124085); thifensulfuron-methyl; thiobencarb; thiocarbazil;
tralkoxydim; tri-allate; triasulfuron; triazofenamide; tribenuron-methyl;
triclopyr; tridiphane; trietazine; trifluralin; triflusulfuron and esters
(e.g.
methyl ester, DPX-66037); trimeturon; tsitodef; vernolate; WL 110547, i.e.
5-phenoxy-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1 H-tetrazole; UBH-509; D-489; LS
20 82-556; KPP-300; KPP-421, MT-146, NC-324; KH-218; DPX-N8189;
DOWCO-535; DK-8910; V-53482; PP-600; MBH-001.
For use, the formulations which are in commercially available form are, if
desired, diluted in the customary manner, for example using water in the
25 case of wettable powders, emulsifiable concentrates, dispersions and
water-dispersible granules. Preparations in the form of dusts, soil granules,
granules for broadcasting and sprayable solutions are usually not diluted
any further with other inert substances prior to use.
30 The necessary application rate of the herbicides of the formula (I) varies
with the external conditions such as, inter alia, temperature, humidity and
the nature of the herbicide used. It may be varied within wide limits, for
example between 0.001 and 10.0 kglha or more of herbicide, but it is
preferably between 0.005 and 5 kglha.
The examples which follow are intended to illustrate the invention:
A. Formulation Examples
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
. ~ 36
a) A dust is obtained by mixing 10 parts by weight of a herbicidal active
ingredient of the formula (I) or of a compound of the formula (II) -
(VII) andlor from amongst group. (b) or of an active substance
mixture of a herbicidal active substance of the formula (I) and a
safener of the formula (II) - (VII) andlor from amongst group B(b)
and 90 parts by weight of talc as inert substance and comminuting
the mixture in a hammer mill.
b) A wettable powder which is readily dispersible in water is obtained
by mixing 25 parts by weight of a herbicidal active ingredient of the
formula (I) or of a compound of the formula (II) - (VII) andlor from the
group B(b) or of an active substance mixture of a herbicidal active
substance of the formula (I) and a safener of the formula (II) - (VII)
andlor from amongst group B(b), 64 parts by weight of kaolin-
containing quartz as inert material, 10 parts by weight of potassium
lignosulfonate and 1 part by weight of sodium oleoylmethyltaurinate
as wetter and dispersant and grinding the mixture in a pinned-disk
mill.
c) A concentrate which is readily dispersible or suspendible in water is
obtained by mixing 20 parts by weight of a herbicidal active
ingredient of the formula (I) or of a compound of the formula (II) -
{VII) and/or from amongst group B(b) or of an active substance
mixture of a herbicidal active substance of the formula (I) and a
safener of the formula (II) - (VII) andlor from amongst group B(b),
6 parts by weight of alkylphenol polyglycol ether (~Triton X 207),
3 parts by weight of isotridecanol polyglycol ether (8 EO) and
71 parts by weight of paraffinic mineral oil (boiling range, for
example, approx. 255 to above 277°C) and grinding the mixture in a
ball mil to a fineness of below 5 microns.
d) An emulsifiable concentrate is obtained from 15 parts by weight of a
herbicidal active ingredient of formula (I) or of a compound of the
formula (II) - (VII) andlor from amongst group B(b) or of an active
substance mixture of a herbicidal active substance of the formula (I)
and a safener of the formula (11) - (VII) and/or from amongst group
B(b), 75 parts by weight of cyclohexanone as solvent and 10 parts
by weight of ethoxylated nonylphenol as emulsifier.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
37
e) Water-dispersible granules are obtained by mixing
75 parts by weight of a herbicidal active ingredient of formula (I) or
of a compound of the formula (II) - (VII) andlor
from amongst the group B(b) or of an active
substance mixture of a herbicidal active
substance of the formula (I) and a safener of the
formula (II) - (VII) andlor from amongst group
B(b)
" of calcium lignosulfonate
10 5 " of sodium lauryl sulfate,
3 " of polyvinyl alcohol and
7 " of kaolin,
grinding the mixture on a pinned-disk mill and granulating the
powder in a fluidized bed by spraying on water as the granulation
liquid.
f) Water-dispersible granules are also obtained by homogenizing and
precomminuting, on a colloid mill,
parts) by weight of a herbicidal active ingredient of formula (I) or
20 of a compound of the formula (11) - (VII) and/or
from amongst group B(b) or of an active
substance mixture of a herbicidal active
substance of the formula (I) and a safener of the
formula (II) - (VII) and/or from amongst group
25 B(b)
5 " of sodium 2,2'-dinaphthylmethane-6,6'-
disulfonate
2 " of sodium oleoylmethyltaurinate,
1 " of polyvinyl alcohol,
17 " of calcium carbonate and
50 " of water,
subsequently grinding the mixture on a bead mill and atomizing and
drying the resulting suspension in a spray tower by means of a
single-substance nozzle.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
38
Biological Examples
1. Scoring the damage
The damage to the plants is assessed visually in comparison with control
plants on a scale of 0-100%:
0% - no noticeable effect in comparison with the untreated plant,
100% - treated plant dies.
2. Post-emergence herbicide action
Seeds of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous weed plants and of crop
plants are placed in sandy loam soil in plastic pots, covered with soil and
grown in the greenhouse under good growth conditions.
Three weeks after sowing, the test plants are treated in the 3-4 leaf stage.
The individual active substances according to the invention which are
formulated as emulsion concentrates are sprayed onto the green parts of
the plants individually or as mixtures in various dosages at a water
application rate of 300 I/ha (converted) and, after the test plants have been
left in the greenhouse for 3 weeks under ideal growth conditions, the effect
of the products was scored visually by comparison with untreated controls.
The results are given in Table 1, which follows.
CA 02378840 2002-02-O1
39
Table 1:
Active substances Dose Damage (%)
g a.s.lha Wheat Barley
(I-1 ) 100 40 30
(I-1 ) 50 25 20
{I_1 ) 25 15 10
(I-1 ) + (I I-1 ) 100+100 15 10
(I-1 ) + (II-1 ) 50+50 5 0
{I-1 ) + (II-1 ) 25+25 0 0
(I-1 ) + (III-1 ) 100+100 ' 15 15
(I-1 ) + (III-1 ) 50+50 10 10
(I-1 ) + (III-1 ) 25+25 0 5
(I-1 ) + (II-9) 50+50 10 10
Abbreviations: g
a.s.lha = g of active
substance per hectare
The terms (I-1 (III-1 ) and (II-9) are explained
), (II-1 ), in the description.
As shown in the examples, the invention
the combinations of
according to
herbicides and safeners
are capable of substantially
reducing damage
to
crop plants such cereals as compared with
as the use of the individual
herbicides without
safener.