Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
1
Description
Warning device for a compressed air breathing apparatus
The invention relates to a warning device for a compressed air
breathing apparatus comprising a movement sensor and a sound
generator triggered by a microprocessor in the event of
motionlessness of the user, wherein a monometer can be connected
via a pressure line to an breathing tank of the compressed air
apparatus under pressure.
Warning devices of this type are conventionally switched on
manually by the device wearer before use. If the movement sensor
registers a motionlessness of the device wearer initially a
preliminary alarm is triggered for the user himself and after a
time delay a main alarm is triggered to summon aid from third
parties. Comfort, forgetfulness or sometimes even the disruptive
noises in the event of frequently occurring preliminary alarm
mean that the warning device is sometimes not switched on and
therefore the safety, but also the competence of the relevant
person is not guaranteed. To solve this problem as is known the
warning devices are designed with a Hall-effect switch which can
be switched via a key. The removed and centrally managed key
should facilitate control of the activation of the warning device
by third parties. This system is complex and does not provide
complete security in relation to the actual activation of the
warning device.
In the known warning devices for compressed air breathing
apparatus calculation and display of the remaining available time
of the compressed air breathing apparatus or of the device wearer
is also performed on the basis of the volume of the breathing
tank, so for compressed air breathing apparatus with different
capacities different or differently programmed warning devices
have to be used. The known warning devices are also designed for
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
2
specific warning thresholds which do not always satisfy the
existing requirements.
The object of the invention is therefore to disclose a warning
device of the type mentioned at the outset, the data of which can
be altered in accordance with the respective requirements for
sounding the alarm and is reliably switched on in the operational
state of the compressed air breathing apparatus and can be
variably and arbitrarily refitted in relation to fixing of the
remaining available time irrespective of the volume of the
respective breathing tank.
The object is achieved according to the invention by a warning
device for a compressed air breathing apparatus designed in
accordance with the features of claim 1.
An essential feature of the invention consists initially in that,
proceeding from the conventionally used mechanical manometers and
the electronic warning units equipped with a sound generator for
signalling a motionlessness of the user, the manometer and the
electronic system are combined in a unit and, more precisely, via
a pressure sensor incorporated into the compressed air supply in
the manometer, the electric signals of which processed in a
signal processing component are supplied to a microprocessor in
order to activate the electronic system and in particular the
movement sensor and the corresponding sound generator. The
warning device is consequently independent of the user in
operation as soon as the compressed air breathing apparatus is
used. Accidental or conscious non-commissioning of the warning
device is therefore reliably ruled out.
Furthermore, the pressure sensor also acts as a second pressure
measuring device independent of the manometer. The respective
pressure prevailing is digitally displayed on a display.
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
3
In conjunction with the microprocessor and the data input therein
the pressure sensor serves to activate the sound generator when
certain - graduated - pressure values in the breathing tank are
not attained. The user is pre-warned in good time and repeatedly
owing to the triggering of the acoustic signals, for example when
150 bar, 100 bar and 60 bar are reached.
A further function of the pressure sensor in conjunction with the
microprocessor and a clock integrated in the device finally
consists in, proceeding from the respective pressure prevailing
in the breathing tank and the repeated measurement of the drop in
pressure per unit of time i.e. the instantaneous air consumption
by the user, calculating the maximum remaining available time to
the device wearer and displaying this on the display at short
time intervals. This type of calculation of the remaining
available time based on the values transmitted by the pressure
sensor allows the warning device according to the invention to be
used for all tank sizes conventional in compressed air breathing
apparatuses.
An important feature of the invention of the electronic component
of the warning device also consists in the incorporation of an
infrared interface connected to the microprocessor for inputting
data into the microprocessor in order in this way to fix the
required alarm thresholds for pressure and temperature or also
the switching on of a Hall-effect switch for optional activation
of the electronic system via a key.
In an advantageous development of the invention the infrared
interface designed as an IR transceiver is coupled to a
telemetry, so the data can also be input from a central operation
point and the stored data can be read out from there.
Therefore, with the solution according to the invention a warning
device variable in its warning thresholds is provided which meets
the highest requirements in relation to the safety of the user
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
4
and can be used for all sizes of compressed air breathing
apparatus and can also be readily refitted as the conventional
manometer merely has to be changed for the warning device
according to the invention.
Further features and advantageous configurations emerge from the
sub-claims and the following description of an embodiment of the
present invention given by way of example.
An embodiment of the invention is described in more detail with
the aid of the drawings in the single figure of which a block
diagram of a warning device attachable to a compressed air
breathing apparatus is shown.
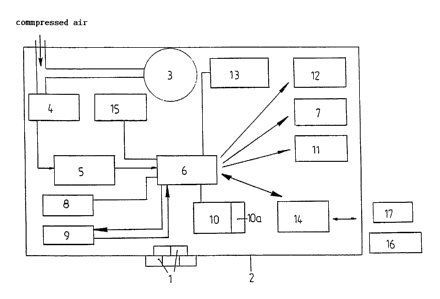
The warning device consists of a robust housing 2 comprising
function keys 1 and in which a mechanical tube spring manometer 3
for analogue pressure display and an electronic measuring and
warning unit are integrated. The electronic unit comprises a
pressure sensor 4 formed, for example, from a diaphragm provided
with a wire strain gauge loaded, like the manometer 3 directly by
the compressed air in an breathing tank (not shown). The
compressed air sensor 4 is connected via a signal processing
component 5 to a microprocessor 6 and a display 7. In this way
the pressure in the breathing tank is measured both mechanically
and electronically and is displayed in analogue form on the one
hand and digitally on the other. Even if a measuring unit fails
there is always the measured value of the other unit as warning
signal.
A temperature sensor 8, a movement sensor 9 and a real time clock
connected to the microprocessor 6 are also housed in the
housing 2. An LED status display 11 and a sound generator 12 are
also connected to the microprocessor 6. All current consumers 11
of the electronic system are supplied by a battery 13 with the
necessary energy. The real time clock 10 also has an auxiliary
battery 10a so the function of the clock is not impaired in the
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
event of an interruption to the energy supply, for example upon a
battery change.
As soon as the compressed air breathing apparatus is activated
with the breathing tank valve open (not shown) there is a
pressure at the pressure sensor 4 and the electronic unit of the
warning device is automatically activated, i.e. without any
action on the device wearer's part by the electrical signals
produced as a result and in conjunction with the signal
processing component and supplied to the microprocessor 6, in
order to trigger an alarm at the sound generator 12 when a
certain pressure in the breathing tank shown on the display 7 is
not attained, when a specific temperature detected by the
temperature sensor is exceeded or when the movement sensor 9
reacts via the microprocessor.
The pressure is displayed on the display 7 at the start of
initial operation of the compressed air breathing apparatus or of
the warning device.
The respective maximum remaining available time is shown on the
display 7 in the following period. This time remaining to the
user until the air available in the breathing tank is fully
consumed is calculated on the basis of the respective - actual -
pressure in the breathing tank and the air breathed by the user
in a specific unit of time measured using the real time clock.
The instantaneous air consumption per unit of time (instantaneous
breathing) is remeasured every 30 seconds in order to display the
respective remaining available time to the device wearer in this
time interval. This type of calculation of the remaining
available time on the basis of the pressure and of the drop in
pressure per unit of time allows the warning device to be used
irrespective of the size of the respective breathing tank, so any
compressed air breathing apparatus can be refitted with the
warning device.
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
6
The microprocessor 6 connected to the movement sensor 9 and the
real time clock 10 is programmed in such a way that upon
motionlessness of the device wearer, i.e. when the movement
sensor reacts, a pre-alarm is initially triggered and at a
certain interval a main alarm is triggered at the sound emitter
12. The microprocessor 6 can also induce the emission of an
acoustic alarm via the sound generator 12 at a certain pressure
of, for example 60 bar, or also at a plurality of different
pressures, for example at 60 bar, 100 bar and 150 bar. The
temperature value for triggering the temperature alarm can also
be adjusted via the microprocessor or the preliminary alarm can
be switched off upon the reaction of the movement sensor 9.
To read in certain data from pressure and temperature values and
the time intervals or instances for setting the alarm triggering
via a PC 17 with data stored therein, an IR transceiver 14
(infrared interface) is integrated in the warning device via
which the respectively desired data can be read into the
microprocessor 6. The instantaneous data available from the
warning device can equally be read out via the IR transceiver 14.
As can be seen from the drawing the warning device also has a
Hall-effect switch 15 with a key, by the removal of which the
warning device can also be activated via the microprocessor 6.
The Hall-effect switch 15 is activated via the IR transceiver 14,
the function of the pressure sensor~of commissioning the warning
device 5 no longer existing in this case, but the pressure gauge
continues to retain its function of determining pressure and of
determining the drop in pressure per unit of time in conjunction
with the time measurement for triggering specific pressure alarms
or for calculating the remaining available time.
The drawing also indicates with the reference numeral 16 a
telemetry connected to the infrared interface via which the data
of the warning device can be ascertained by radio by an external
operational control centre or specific data can also be read into
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
7
the device in this way. It is therefore possible to control the
deployment of the device wearer via the interface in the warning
device and to initiate necessary measures, for example trigger
the main alarm as a demand to leave the region of deployment.
The described warning device represents only one embodiment of
the invention described by way of example and not limiting the
subject of the application. Numerous modifications in relation to
the specific design of the warning device and its individual
components are possible in the context of the basic idea of the
invention consisting in the combination according to the
invention of a manometer with a pressure sensor and the
electrical signals therefore supplied to a microprocessor for
commissioning the warning device, calculating the remaining
available time and triggering an alarm as a function of specific
pressure and temperature details which can be read in via an IR
transceiver and time details as warning thresholds.
CA 02379697 2002-O1-25
8
List of reference numerals
1 function keys
2 housing
3 tube spring manometer
4 pressure sensor
signal processing component
6 microprocessor
7 display
8 temperature sensor
9 movement sensor
real time clock
10a auxiliary battery
11 LED status display
12 sound generator
13 battery
14 IR transceiver (infrared interface)
Hall-effect switch
16 telemetry
17 PC