Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-1-
METHOD FOR PACKAGING AND PACKAGING APPARATUS
The present invention relates to a method for packaging and a packaging
apparatus for
the packaging of, for example, food such as meat products. In particular, the
invention
relates to a method of packaging and an apparatus which utilize a feed of
packaging material
in tubing form which is slit and unfolded to be formed around a fed product.
Methods and apparatus for the packaging of products, for example, food and in
particular meat products, are broad ranging, various techniques being employed
depending
on the product which is to be packaged and the packaging material which is
being used.
Generally, conventional form, fill and seal packaging machines and processes
involve the
supply of packaging material in continuous sheet form, commonly referred to as
single wound
material. The sheet material is supplied having a width as required for the
wrapping process
in question. Generally, the width of the sheet material is up to about 700 mm.
The sheet
material may be produced in various ways including using extrusion techniques,
or via the
production of a tube of the material which is subsequently collapsed and slit
to provide two
flat sheets. These two methods have been traditionally used to supply sheet
material for use
in conventional form, fill and seal packaging practices.
The use of some types of plastic packaging materials may be somewhat limited
when
produced by conventional production methods due to limitations in the maximum
possible
widths of the flat sheets produced using these methods. In particular,
materials which are
necessarily extruded and blown into a vertical bubble to induce shrink
characteristics
generally suffer from pore bubble stability. That is, when the material in a
semi-molten
phase is inflated to a wider tube before the plastic sets, if the bubble is
not stable due to the
plastic properties and size of the bubble, then it may collapse ceasing
production of the
packaging material. Furthermore, and related to this, the accuracy and
tolerances of the final
packaging materials produced may be greatly affected using conventional
production methods
for flat sheet materials. More particularly, conventional processes of edge
slitting the
material to form two continuous flat sheets from a tube will produce flat
sheets with variable
width, the edges of which deviate quite markedly from a straight line.
The present invention advantageously provides a means for alleviating problems
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-2-
related to variation in width of a single wound packaging material. The
invention also
advantageously provides a method and apparatus which may be economically
viable in
reducing production costs for the packaging material being used, and allows
packaging
materials to be run at widths which are not conventionally available. Still
further, the
invention advantageously provides a method and apparatus which may
substantially avoid
contamination of the product-contact surface of the packaging material prior
to and during
packaging of the product.
According to the present invention there is provided a method for packaging
comprising the steps of
(i) continuously feeding a packaging material as tubing from a supply;
(ii) slitting and unfolding the tubing to form a flat web of the packaging
material;
(iii) forming the flat web of packaging material around a fed product and
longitudinally sealing the packaging material formed around the product; and
(iv) cutting and sealing the packaging material at one or both ends of the
product.
The fed product is, in accordance with conventional methods, generally fed as
individual, spaced units of product, the flat web of packaging material being
formed around
each of the units. Subsequently, in step (iv) the packaging material which is
formed and
sealed around the product is cut at a location between units of product and
sealed at one or
both ends of the unit. In some instances it will be preferable that the
packaging material be
sealed at only one end so that the product is left in an open-ended bag. This
will enable, if
necessary, the subsequent vacuum sealing of the product in the bag. As such,
in a particular
embodiment, in step (iv) the packaging material is cut and sealed at one end
of the product
and the packaged product is subsequently vacuum sealed.
The method according to the invention utilizes a feed of packaging material in
the
form of tubing. This is quite different from the conventional form, fill and
seal techniques
which involve the supply of a flat single wound sheet of material which
generally has been
produced by edge slitting of a tube of material to form two flat sheets. In
accordance with
the method of the invention, as the packaging material is fed in tubing form
and then slit and
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-3-
opened out, it will be recognised that the width of the opened tubing, that is
the flat web
referred to in step (ii), will be twice that of conventionally used single
wound material when
that material has been produced by slitting of a tube to form two flat sheets.
As such,
according to the invention, if tubing is supplied having a double web width of
up to about 550
mm, then the flat web formed by slitting and unfolding of the tubing will have
a width of up
to about 1100 mm. Such widths have generally been unavailable to date and, as
will be
recognised by those in the art, provide substantial advantages in the
packaging of larger
products.
The feeding of the packaging material in tubing form also removes costs
related to the
post-production conversion of conventional materials to flat continuous
sheeting, for example,
the edge slitting of a tube to form two flat sheets described above. The
supply of tubing also
means that the packaging material is not opened to the air prior to the
slitting and unfolding
of the tubing in step (ii) of the method. This fact substantially decreases
the chance of
contamination to the inner surface of the film which will form the inside or
product-contacting
surface of the packaging material.
In order to minimise variation in width of the flat web formed in step (ii),
in a
preferred embodiment during feeding of the tubing, the tubing is tracked to
ensure that it is
substantially centrally slit along its length. More particularly, the tubing
is advantageously
centrally slit along its upper or lower surfaces as illustrated in Diagram
2.2, although it may
be possible to slit the tubing material along one of its edges to form the
flat web as illustrated
in Diagram 2.1.
After the slitting and unfolding of the tubing to form the flat web, the flat
web of
packaging material is formed around the product which is to be packaged and is
longitudinally
sealed to substantially reform the tubing originally fed from the supply. Due
to the deviation
in width of the flat web, on longitudinal sealing to reform the tubing, it
will be recognised
that there will be at least some excess packaging material along the
longitudinal seal.
Therefore, in a preferred embodiment, prior to or during the longitudinal
sealing of the
packaging material in step (iii), the packaging material is trimmed along its
slit edges formed
in step (ii) to remove excess packaging material therefrom. This trimming of
the edge of the
film is completed by a knife or shearing apparatus. The trimming function
allows control of
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-4-
the amount of excess material outside the longitudinal seal as illustrated in
Diagram 3.1.
The cutting and sealing of the packaging material in step (iv), as discussed
above, may
include cutting and sealing at one end of the product and cutting and
optionally sealing at the
other end of the product depending on whether vacuum sealing of the packaged
product is
desirable. The cutting and sealing may be conducted by any suitable method,
such as using
conventional hot or cold sealing systems. According to one embodiment, the
cutting and
sealing of the packaging material is carried out by impulse sealing the
packaging material at
the end or ends of the product.
Vacuum packaging of the product would commonly involve evacuating the bag
through the open end then sealing. The final package would contain no gas
sealed inside with
the packaged item. This could be completed by a vacuum nozzle or a vacuum
chamber
system. The final seal could be in the form of a clip or heat seal weld.
According to another aspect of the invention there is provided a packaging
apparatus
comprising:
means for receiving packaging material continuously fed as tubing from a
supply, and slitting and unfolding the tubing to form a flat web of the
packaging material;
calendering means for receiving the flat web and tensioning the flat web;
forming means for receiving the tensioned flat web and forming the flat web
around a fed product;
sealing means for longitudinally sealing the packaging material formed around
the product; and
end sealing means for cutting and sealing the packaging material at one or
both
ends of the product.
The slitting and unfolding means receives the continuous feed of packaging
material
in tubing form and slits and unfolds the tubing to form the flat web of the
packaging material
for subsequent calendering and forming around a fed product.
The calendering means may include any means which is suitable for tensioning
the flat
web to supply the forming means. In a preferred embodiment, the calendering
means
comprises a pair of spring clamped rollers which are adapted to ensure that
the flat web is fed
to the forming means at a consistent tension and angle. This calendering
allows the apparatus
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-S_
to be started and stopped during operation without the feed tension changing.
The forming means may comprise any suitable means for forming the flat web
into
a tubular shape around the fed product as will be understood by those skilled
in the art. In
a preferred embodiment, the forming means comprises a forming shoe which forms
the flat
web around the fed product.
The sealing means for longitudinally sealing the packaging material formed
around
the product may include any suitable means for longitudinally sealing the
packaging material
to substantially reform the material into its original tubing form around the
fed product. The
longitudinal seal is typically formed by a combination of heat and pressure
which cause the
two layers of material to weld or bond together. It is preferable that this
joint is hermetic in
nature. The heat and pressure are supplied typically by heated rollers with
the film clamped
therebetween. Variations of this include heated bands, drag wires, ultra sonic
heating devices
clamping the layers of plastic material and applying heat. An alternative
method is to apply
a cold bonding adhesive agent to both faces which may then bond to each other
when pressure
is applied.
The end sealing means may comprise any suitable hot or cold sealing systems
which
employ adhesive and/or heat to facilitate sealing of the packaging material at
one or both ends
of the fed product. The configuration of the sealing means is selected to cut
and seal the
packaging material at one or both ends of the product and may be determined,
as discussed
above, on the basis of whether subsequent vacuum sealing of the packaged
product is
desirable. That is, the end sealing means may be selected to provide a single
seal adjacent
a transverse cut in the packaging material or may be selected to provide a
pair of seals which
straddle a transverse cut in the packaging material. It will be recognised
that the first of these
options will produce an open bag containing the fed product. In a preferred
embodiment,
the end sealing means comprises an impulse sealing device which includes at
least two
complimentary jaw members which clamp the packaging material to form a
transverse cut in
the packaging material, and which form a seal on one or both sides of the
formed transverse
cut.
As discussed above in relation to the method according to the invention, when
the
apparatus is in use, the flat web formed by slitting and unfolding of the
tubing of packaging
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-6-
material will include some deviation in width. Therefore, in a preferred
embodiment, the
packaging apparatus preferably further comprises means for trimming excess
packaging
material from the flat web of packaging material to advantageously ensure that
a longitudinal
seal is formed along the length of the packaging material formed around the
product which
is a neat fm seal.
The packaging apparatus also preferably further comprises means to facilitate
center
tracking of the tube to ensure that it is slit centrally along its length by
the slitting and
unfolding means.
In order to completely automate the packaging apparatus according to the
invention,
it is preferred that the apparatus further comprise sensing means for auto-
positioning of a
product and successive products for end sealing. That is, preferably a sensing
means is
provided to sense when a product is in position for end sealing at which stage
the conveyance
of the product is stopped and an end seal formed or the sealing mechanism
travels with the
product forming a seal without halting the conveyance of the product. After
completing the
transverse seal, the sealing mechanism travels in the reverse direction to
prepare for the
following seal. By controlling the spacing of the product with respect to each
other, the
package or bag length can be controlled. In a preferred embodiment, the
sensing is generally
completed by optical sensors which detect the leading and trailing edge of the
products. This
is the method used in determining spacing of respective products and the final
position of the
transverse seal.
The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the
accompanying diagrams in which:
Diagram 1.1 illustrates a conventional form, fill and seal packaging
apparatus;
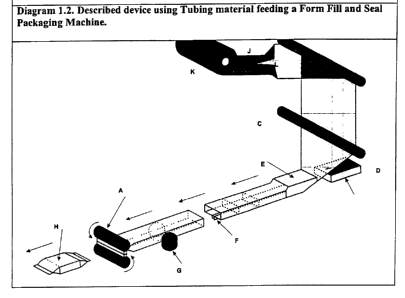
Diagram 1.2 illustrates an embodiment of the form, fill and seal packaging
apparatus
according to the invention;
Diagram 2.1 illustrates the slitting and unfolding of the fed tubing material
by slitting
one edge thereof;
Diagram 2.2 illustrates the slitting and unfolding of the tubing material by
slitting
centrally on one face thereof;
Diagram 3.1 illustrates the trimming of excess edge material;
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
Diagram 4.1 illustrates the configuration of the packaging apparatus of the
invention;
and
Diagram 5.1 illustrates the transverse sealing sequence used in accordance
with
embodiments of the invention.
Referring to Diagram 1.1, a conventional form, fill and seal packaging
apparatus feeds
a single wound material from a roll (B). The film is unwound from the roll (B)
and fed into
the apparatus by a passive or powered unwind mechanism. Calendering of the
unwound film
is conducted in a calendering zone (C) where the material is adapted to ensure
that it is
supplied to the feed area of the apparatus at a consistent tension and angle.
Product to be packaged (D) is fed by a conveyor belt under the web of material
to a
forming device (E), commonly referred to as a forming box or forming shoe. The
forming
device (E) wraps the flat web of material around the incoming product (D) so
that the flat web
of material forms a tubular shape around the product. The material, when
wrapped around
the incoming product (D) may be folded in a manner which facilitates the
production of a
longitudinal seal. This may be achieved, for example, by forming a fin (F) or
a lap in the
material.
After wrapping of the flat web of material around the incoming product (D), a
longitudinal seal is made in the material by a longitudinal sealing device (G)
to seal the two
edges of the wrapped material together to form a complete tube.
When the complete tube is formed around the product, an end sealing device (A)
is
used to seal the tube and cut the tube between successive products (D) to form
a finished
packaged product (H).
As discussed earlier, these conventional form, fill and seal packaging
apparatuses are
limited due to the limitations in the maximum possible widths of the flat
sheets fed from the
roll (B).
The invention, however, as illustrated in Diagram 1.2, feeds a tubing material
(J) from
a roll (K) of packaging material in an integral tubing form. In this case, the
apparatus is
provided with a slitting and unfolding device (L) which makes a continuous cut
in the tubing
material (J) and folds or forms the cut tubing material into a flat sheet. The
slitting and
unfolding device uses a set of geometric plates and frames to ensure the
alignment of the
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
_g_
material does not vary in the process.
As will be seen in Diagram 1.2, the following calendering of the slit and
unfolded
material is achieved by a pair of sprung clamped rollers in a calendering zone
(C). The
remaining packaging of the product (D) by a forming device (E), longitudinal
sealing device
(G) and end sealing device (A) may be conducted in line with conventional
methods.
Referring to Diagrams 2.1 and 2.2, the slitting and unfolding device generally
comprises a back unfolding plate (1.1) and a front unfolding plate (1.2).
In Diagram 2.1, the tubing material is slit along one edge thereof by the
slitting and
unfolding device. In this regard, the raw tubing material (A) is fed into the
device and slit
at an edge slitting point (B). Following slitting of the tubing material, the
back layer (C) of
the film folds to travel 90° from the original infeed path, and the
front layer (D) of the film
travels in a direct path. The back layer of the film travelling at 90°
from the original infed
path (E) travels between the front unfolding plate (1.2) and the back
unfolding plate (1.1)
until it is folded to travel at 180° (F) from the original infed path.
Following this operation,
a final single web of film (G) exits the slitting and unfolding device at
180° from the original
infed path of the tubing material.
It should be noted that the angle (H) of the back and front unfolding plates
(1.1, 1.2)
are identical angles between 30 ° and 60 ° .
The slitting and unfolding device illustrated in diagram 2.2 utilizes the
central slitting
of the tubing material (A).
In this case, a central slitting point (B) is provided on the back face of the
tubing
material (A). The back layer of the slit filin (C) is then folded to travel at
90° from the
original infeed path. The front layer (D) of the film travels in a direct
path. As was the case
in Diagram 2.1, the back layer of film travelling at 90° from the
original infeed path (E)
passes between the front unfolding plate (1.2) and the back unfolding plate
(1.1). The back
layer of the film is then folded to travel at 180° (F) from the
original infeed path. The final
single web of film (G) exits the slitting and unfolding device at 180°
from the original infeed
path of the tubing (A).
As was the case in Diagram 2.1, the angles (H) provided by the plates are
identical
angles between 30 ° and 60 ° .
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-9-
Referring to Diagram 3.1, excess material (E) is advantageously trimmed from
the
packaging material at a point (C), and a longitudinal seal (D) applied to the
trimmed material
to complete the tube. This procedure advantageously removes inconsistent edges
(B) of the
packaging material generally present due to inconsistencies and variations
during the
manufacture of the tubing material.
A further illustration of the packaging apparatus according to the invention
is provided
in Diagram 4.1. As illustrated in this diagram, the tubing material is unwound
from a roll
(B) and slit and unfolded using a slitting and unfolding device (C). The slit
and unfolded
material is then fed as a single web to a tensioning and feeding calender (D)
and then onto
a forming or folding box (E). After forming or folding of the single web
material by the
forming or folding box (E) product (A) is fed into the formed material and an
edged trimming
device (F) used to trim the edges of the material. Following this, a
longitudinal sealing
device (G) is used to seal the material to form a complete tube. Scrap or edge
trim material
is removed by a suitable waste removal device (H).
1 S Sealing of the formed tubing material about the product (A) is conducted
by means
of a pair of transverse sealing jaws (J) which are mounted for complementary
movement
towards each other. These jaws may either form a pair of transverse seals and
cut the tubing
material between the pair of seals, or may seal only one side of the tubing
material and cut
the material adjacent the seal. In the first case, the product (A) is
completely enclosed as the
final package (L), whereas in the second instance the product (A) is conveyed
out of the
apparatus in an open bag as the final package (L).
In any event, the product (A) is conveyed by means of a main transport
conveyor belt
(K), and the packaging of the product (A) controlled by a machine control
panel (M).
As previously discussed, the apparatus preferably includes sensors (not shown)
which
determine the position of the product (A) relative to the sealing jaws (J) so
as to determine
operation of the sealing jaws (J) to seal between subsequent products (A).
The transverse sealing sequence is better illustrated in Diagram 5.1. The
sequence
includes the lowering of the jaws (A, B) toward the material (C) until the
jaws are in a closed
position. In this position, sealing means (D) on each jaw (A, B) form a pair
of longitudinal
seals in the material (C). Simultaneously, a blade (E) forms a cut in the
material between the
pair of seals formed by the sealing means (D). The sealing means (D) may
include
CA 02384009 2002-03-04
WO 01/17853 PCT/AU00/01062
-10-
conventional means such as thermal bands.
Throughout this specification and the claims which follow, unless the context
requires
otherwise, the word "comprise", and variations such as "comprises" and
"comprising", will
be understood to imply the inclusion of a stated integer or group of integers
or steps but not
the exclusion of any other integer or group of integers or steps.
Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the invention described herein
is
susceptible to variations and modifications other than those specifically
described. It is to be
understood that the invention includes all such variations and modifications.
The invention
also includes all of the steps, features, compositions and compounds referred
to or indicated
in this specification, individually or collectively, and any and all
combinations of any two or
more of said steps or features.