Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
Description
DIALING SIMPLIFICATION SYSTEM FOR TELEPHONES
Today, there is a bigger quantity of telephones in a telephone
area, because there is a bigger quantity of apartments and also everyone
as one telephone at home.
There was a huge increase of telephones in each telephone area and
there is no more numbers available. The telephone number has six digits
and the telephone numbers reached the maxim number of 99 99 99. This
problem obliged a two changes in the national phone system.
One of the changes is that the user has to dial the local area
code, for a local phone call. So the user has to dial three digits of the
local area code and the six digits of the telephone number. Before this
changing of the national phone system, there was only need to dial the
local area code, for a call outside the telephone area.
Another changing was to divide one telephone area in two telephone
areas. So for each new telephone area, there will be one full sequence of
numbers till 99 99 99. There will be twice the quantity of telephone
numbers.
People at home or in the companies have a private telephone
directory, in which the local phone numbers are written without local
area code. The telephone numbers of others telephone areas are written
with there local area code. Also, when there are more telephone areas, it
means, small telephone areas. One person that stayed far away of other
telephone area, now can stay close.
People phone to places, that stages a few kilometres or even few
hundreds of meters. Now, this places belong to another telephone area.
For this daily telephone calls, the user has to dial the local area code.
Another changing iu the national telephone system is the
possibility, to make use of more then~one telephone company, however,
there is only one telephone wire.
The possibility of choosing two companies makes the price decrease,
because there is concurrence:
The user to make use of another company, has to dial an extra
prefix.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
2
If the user does not dial the extra prefix, because he forgot or he
is in hurry or because of to many digits, then the phone call goes to
another telephone company, where the prices are not the best ones. To use
another company, the user has to dial more digits to profit the economy
of the concurrence between two companies.
A local phone has now, the six standard digits, plus there of the
local area code and plus there more of the company prefix. That gives a
total of twelve digits.
Another complication for the user is that the companies change the
prices of telephone call during the day for concurrence reasons.
When making a phone call, the user has to check the hour of the day
and only then choose the more economic company.
The cellular phone, fax, and so on, are also affected, because when
the user makes a call, there are also the need to dial nine or twelve
digits instead of the standard six digits.
With just one cellular phone, fax, and so on, the user can have the
possibility to make use of a different telephone company, but for that he
has to dial more digits, It is the same case than a standard telephone.
There was also another change. The special wire for the cable
television, can be used also as a telephone wire.
This change obliges the user to have two telephones. The user has
to choose during the day, which telephone is more economic.
In the future, there is the possibility to make use of the
satellite or the wire of electricity as phone wires. The user will be
oblige to have three or four telephones, to be able to make the more
economic phone calls.
Another old problem, that it is increased, with more telephones
areas is the following one. One person that lives in the centre of a
telephone area, the daily calls are to that telephone area. One person
that lives in the board of the telephone area, will have people of his
relationship, in his telephone area, but also in the neighbour telephone
area.
For his daily calls, the user dials six digits for the local calls
and the calls to the neighbour area, he dials nine digits.
Nowadays due to concurrence between companies there is a continuos
change of the price of telephone calls. The user has difficult to keep
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
3
informed of the changing of prices.
The prior art is the applications US 5455858 of the Apple Computer,
the application US 5859901 of Henri Tz,ui, the application US 5859896 of
Howard Rosen and the application US 5764741 of Gideon Barak.
The application US 5455858 is about a telephone interface for a
computer, to improve to dial the different prefix, and telephone numbers,
considering where the computer is and to where the user is going to
phone.
The application US 5859901 is about a equipment, that only when the
telephone number does not have the prefix area, then the phone number is
studied, based in a data base. This data base has the calls usually made
by the user. If the number is there, the equipment can know if that
number is to the neighbour area or to the telephone area, where the
telephone is. Then adds or not a prefix.
The application US 5859896 is about a equipment, that when there is
an off-hook, it dials the local area code, and then the user dials the
standard number. After a few time, if the user does not dial any digit
then the equipment hang up and then off-hook. Them the user dials the
telephone number with another local area code.
The application US 5764741 is about a equipment that the user dials
a number. Then the equipment for that particularly call and talking in
attention the distance of the call, the foreseeable of the call, based in
a data with the history of the previous calls of the user and also with
different company cost.
This invention is to overcame the present prior of art.
It is an object of the present invention that the user does not
have to dial the local area code for a local phone call.
It is another object of this invention that the user does not have
to dial the prefix of other telephone companies, or any other prefix
independent of the hour of the day, to obtain more economic prices.
It is another object of the present invention, that if there are
several wires, the user does not need one telephone for each wire,
instead, the user has one telephone and he is able to use any of the
wires.
It is also another object of the present invention, that the user
does not have to dial the local area code, when he is calling to the
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
4
neighbour area. Instead he dials a short prefix.
It is another object of the present invention, to keep the
simplicity and speed in using the telephone. The user does not have to
spend time and get tired, to decide which of the prefix he has to dial,
specially in continuos telephone calls. If he has to dial the local area
code, or the prefix of a telephone company, or both. Taking also notice
of the different prices between companies during the day.
It is another object of the present invention, to study the
telephone number dial by the user and from that study, to know which of
the above conditions, it schould apply, if just one, several or any, with
the intention to keep simple the use of the telephone.
It is also another object of the present invention, that the user,
can receive information by the telephone wire, of the changing of price
of the telephone calls. With this invention it is possible to change
automatically the telephone companies, that are making the telephone call
or to warm the user of the new prices.
The drawings are the following.
Fig 1. Basic electronic scheme.
Fig 2. Scheme with the logic of analysis of the telephone calls.
Fig 3. Basis scheme with the study of each digit, as they are
dialled.
Fig 4. Outside looking of the equipment with the simplification
system for telephones. Top view.
Fig 5. Outside looking of the equipment with the simplification
system for telephones. Side view of the same equipment of figure 4.
Fig 6. Outside looking of the equipment with the simplification
system for telephones. Side view of another model.
Fig 7. Looking of the equipment with buttons, that allows to
choose between two phone companies.
Fig 8. Looking of the equipment with buttons, that allows to
choose between three companies.
Fig 9. Continuation of figure 3.
Fig 10. Logic scheme of analysis of telephone calls in the second
alternative.
Fig 11. Outside looking of the equipment with the simplification
system for telephones for the second alternative.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
Fig 12. Outside looking of the equipment similar to the one of
figure 11, but more simple.
Fig 13. Interface for the computer.
Fig 14. Basic scheme of analysis of messages.
Fig. 15 Continuation of figure 14.
The change of the national telephone system, has already happened
in same countries and it is going to happen in others countries. This
invention is going to be explained With the change that already happened
in Spain.
In one first stage, there is a exemplification in what consisted
the change of national telephone system. In a second stage, what kind of
real problems that change makes to the user. In the last stage, how this
invention is going to handle these problems.
For a local call, the user has to dial also the local area code.
In a phone call in the telephone area of Burgos, that has the local
area code 947, the user has to dial the following.
The telephone number 54 36 79, has to be dialled 947 54 36 79.
In some areas of Spain, but not in all of them, even for local
calls, there are more than one company, usually two. For the phone call
to be made by another company, it is necessary to dial a extra prefix. It
will be necessary to dial 050 947 54 36 79.
In this example, it is supposed that the other company has the
pref i.x 050.
In same regions there are two telephone wires. It is necessary one
telephone equipment for each wire. During the day, depending the hour,
the user chooses one phone or the other in function of the more economic.
There are telephone numbers that did not changed. It is the case of
special numbers, like information 003 or 1003, or repair 004, and so on.
This numbers are very short, with three or four digits.
To phone to another telephone area, it was already necessary, to
dial the local area code of that area.
To phone to 46 54 67 of the telephone area of Santander, from
another area, it was necessary to dial 942 54 36 79. The local area code
of Santander is 942.
To make this phone call, but making use of another company, it is
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
6
necessary to dial an extra prefix. It should be necessary to dial 050 942
54 36 79.
To call to a cellular phone, there is also the possibility to make
use of another company and for that is necessary to dial an extra prefix.
For this calls, if there are another phone wire, it will be
necessary to make use of a second telephone.
There are other phone numbers, with ten digits. There are special
phone numbers, that begin by the prefix 0800 or 0641, and so on.
In some regions of Spain this phone call can be made by another
company.
The change of national system originates five different kinds of
telephone calls, that have to be distinguish by the simplification system
for telephones.
There is another kind of telephone call. When a phone call is to
another telephone area. Instead of dialling the neighbour area code, the
user dials a short prefix.
The six different kinds of telephone calls that the simplification
system for the telephones has to discern, are the following.
Kind one are the local phone calls where is necessary to dial the
local area code. In some regions of Spain is possible that the phone
calls are made by another company.. For that the user has to dial one more
prefix. In some regions is possible to choose between two phone wires.
Kind two is when a direct connection to the standard phone wire. It
is a phone call for information, repair, and so on.
Kind three are phone calls for another telephone area, or
international, or cellular telephone. For this phone calls, it is
possible to use another company. For that is necessary to dial one more
prefix. In some regions is possible to choose between two wires.
Kind four are telephone numbers with ten digits, in which the
first four digits are standard, like 0800 and so on.
The others six digits are always different, and are the ones who
identifies each telephone subscriber. Depending the region and the
evolution of the telephone system, there are two possible options.
For this numbers, there is only one company to make the phone call,
or there are two companies. In the option, that there are two companies,
the user has to dial one extra prefix. So the user has to dial three
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
7
digits of the company prefix, and then ten of the phone number. A total
of thirteen digits.
In some regions there is also the possibility to choose between two
phone wires.
Kind five is a safety option. The user dials a local phone number,
but with the local area code. It is a direct call to the telephone wire.
Kind six are the calls for the neighbour area. With the increasing
of the telephones areas, the user, could stay with one or even two
telephones areas, near where he lives. In his daily calls, instead of six
digits, the user has to dial nine digits, and if he wants to use another
company, three more. A total of twelve digits.
However, it was mentioned five different kinds of phone calls, it
can happen that due to differences, from one region or from one country
to another country, or the evolution of the telephone system, it carves
out more or different kinds of phone calls.
In the telephone area of Madrid, the telephone numbers have seven
digits and the local area code two digits.
That gives a total of nine digits, like the others telephone areas.
The logical scheme of the simplification system for telephones has to be
adapted to the specifies of each area. Same areas have phone numbers
always with six digits, others areas with always seven digits, and so on.
Others telephone areas the quantity of digits is not fixed.
In some countries the special prefix 0800, can have not six more
digits, but seven, or any other quantity of digits.
In one country is the prefix 0800, but in another country this
prefix correspond another number, and so on.
The logical scheme of the simplification system for telephone
should be adapted for the specific characteristics of each telephone area
or each region or country and to develop with the changing of the
telephone national or regional system, so in that way it keeps simple, to
use the phone.
To handle this six different kinds of calls, the simplification
system for telephones works in this way.
The basic electronic system of the simplification system for
telephones is in figure one.
The dial (1) of the telephone.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
8
The logical analysis system (2). That can be a microprocessor, or a
CPU, or any electronic component.
To count the digits (5).
A clock (6).
One relay (7) that is going to connect one wire or the other wire.
In this figure, it is represented two wires. However, it is possible more
wires and of different kinds.
The phone wires (8) and (9).
Besides this components, it is also need a electronic component to
dial the digits to the wire.
The memory (3) has the prefix of another telephone company and the
prefix of the local area code where is the telephone, and so on. This
prefixes are going to be add to the number dial (1).
The memory (4), has others numbers or prefixes characteristics of
each country. For instance the numbers of information 003, the emergency
112, and so on. Also the international prefix 00, and the prefix 0800,
and others prefixes.
In Portugal, all the local area code begin by zero. In Spain they
begin by nine, as it can be seem in the table one. This situation is
similar in other countries. For Spain, the memory (3) has the number
nine, as data. In this example, the two memories are separated, but they
can be together. In both situations the functioning is similar.
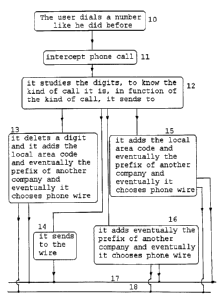
The simplification system for telephones has to analyse the
telephone number and to know which of the six different kinds of phone
calls are. For doing this, it uses a logical scheme to analyse the phone
number. This logical scheme is in figure two.
It should study all the numbers dialled, to know what kind of phone
call it is. Then it should take the measures in accordance with the kind
of call, to get one telephone number correct for the national telephone
system and also the more economic company.
In figure three, there is the study of each digits as they are
dial.
To exemplifying how the simplification system for telephones works,
it is going to suppose the following situations. In the memory (3) there
is the prefix 050, of a telephone company, that makes a better price for
local calls, long distance calls and international calls. There is also
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
4
the number nine, that is the first digit of all the local area code of
Spain, as it can be seen in table one.
For the phone calls of kind one.
In the memory (3) there is also the local area code, for example
947. The logical system of analysis (2) studies the number. It compares
the digits of this number with the digits of the prefix in the memories
(3) and (4). If it does not detect any characteristic prefix or the nine
as first digit, that means, the telephone number does not have any
pref ix.
The logical system of analysis based on the value of the memory (3)
adds the prefix 947 to the number dialled and only then sends to the wire
phone (8).
All the five kind of calls have a characteristic prefix, expect
this one.
If there is not one of the following prefixes has to be a local
phone. The nine for a call to another area, the 00 for an international
call, and so on. However there is a special number, that does not go by
this rule and it is going to be analysed later.
The kind one calls, corresponds in figure two, to the items 10, 11,
12, 15, 17 or 18. In figure three to the items 19, 22, 23, 24, 26, 28 or
29.
In figure three, like in figure nine, mentioned ahead, when there
is the expression "has nine" or "has one", it means that the first digit
of the telephone number, it is a nine or an one.
The simplification system for telephones allows speed and facility,
when one person has to phone.
It can happen, that for local calls, there are two or even more
companies in concurrence.
In some countries there are only two companies, but in other
countries, there are three or four. In some countries the quantity of
telephone companies is limited by the government.
In the previous call, if the user wants that the call is made by
another company, it should add two prefix, the 050 and the 947. The total
number is 050 947 70 59 54.
There is the possibility that the user has two phone wires. So
after adding the local area code, the relay (7), will be activated and
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
the phone call will be send to the another wire.
The simplification system for telephones has to have the previous
instruction from the user, to add the prefix of other company.
Depending on the change of the phone call prices the user activates
the equipment to add or not the prefix 050, or he does not activate and
it is not add this prefix.
Forward, it is going to exemplify, how the user adds or not the
prefix of another company.
The special number does not go by the previous rule, are the
following. It is the local phone numbers, with six digits, but that begin
by nine, for instance 97 51 24.
This phone number does not have prefix, but begins by nine. The
logical system of analysis will suppose, that is a phone number with
pref ix.
The logical system of analysis with the counter (5) will count the
quantity the digits. After, have been dialled six digits and waiting some
time, for instance half second, if the user has not dialled another
digit, so it can be deduce that it is a local call.
In figure three corresponds to the items 19, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28
or 29.
In the Madrid telephone area, the numbers have seven digits, so it
will count till the seven digit. The simplification system for telephones
will be adapted for each area with regard of the quantity of digits in
the phone number.
Another way to handle this problem is to compare the first three
digits, with the local area code. If they are not equal, it is necessary
to compare with all the local area code of Spain. If it is not equal to
any, it is a local call. But if they are equal, it should check, if they
are more then six digits and only them, it could conclude, that it is a
phone call to another telephone area. If it is exactly six digits, it
could conclude, it is a local call.
For the study above mention, all the prefixes, should be in the
memory (3).
This solution can be expensive in a electronic system. However in
computers, to have all the prefix in the memory, it is not expensive and
allows a faster study of the number dial.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
11
Kind two is the phone calls to information, and so on.
The logical system of analysis (2), connected with the data of the
memory (4), it cheeks if there are two aeros. That is the international
prefix. Then is dialled the digit three, so the logical system of
analysis (2), connected with the clock (6) waits a few time and for it is
not dial any other digit, so it is conclude that it is a complete number
and then it sends to the wire phone.
In Portugal, the information number is 118.
Each country has his own special numbers, but normally of three or
four digits. For this numbers is always necessary to wait sometime, to
check if it is a short number or not.
To count the time, it is possible to use the clock (6) or any other
system that counts time.
In figure two, it corresponds to the items 10, 11, 12, 14,17.
In figure three, it corresponds to the items 19, 20, 21, 28.
In this example there is ,lust one wire (28). That it is the more
standard situation. However there is the possibility to exist several
wires. In this case, the logical of analysis (2) should be adapted for
this, and in the item (14), should have the option to choose between one
of the several wires.
The simplification system for telephones should be adapted for the
characteristics of this short number, for each region or for each
country.
Kind three, it is for phone calls for another telephone area,
normally denominated long distance calls and the international calls and
the calls for cellular phone.
The prefix that are going to identify each phone call are the
following ones. For international call the 00, for long distance call the
nine, and for a cellular phone company, for example the 936.
In countries where the local area code does not begin by the same
digit, the memories (4) should have all the local area code.
When one person dials (1) a telephone number for another telephone
area, for instance 956 60 74 95. Then the logical system of analysis (2)
with the memory (3) compares the first digit, and it checks a telephone
number that begins with the digit nine.
Then the logical system of analysis (2) with the counter (5),
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
12
counts if there are more then six digits. If both conditions are
accomplish, it is a phone call to another telephone- area.
The logical system of analysis (2) should eventually add the prefix
050 or activate the relay (7), to send to another telephone wire (9) and
not for the standard wire (8).
In the figure two, it corresponds, to the items 10, 11, 12, 16, 17
or 18. In the figure three to the items 19, 22, 23 ,24, 25, 27, 28 or 29.
For an international call or a call to a cellular phone, it is a
similar study and reaction of the previous call.
The international call should begin always for 00. The logical
system of analysis (2) connected with the memory (4), checks two zeros as
first digits. That means, that it is perhaps a international call. After
the user dials the fourth digit. That means, it is not a special number
of kind two. To count the digits, it is used the counter (5). Then it
will be add eventually before the 00, the prefix of another company or
eventually activate the relay (7), to send to another telephone wire (9),
and not the standard wire (8).
In Spain, the national telephone system for an international call,
obliges the user after dialling the prefix 00, to wait, till the user
listen a specific sound and only then the user dials the rest of the
digits.
The specific sound is a electric wave. This electric wave is
changed to sound, to be understood by the user.
The logical system of analysis (2) should take attention to this.
So it should dial the first digits, waiting for the electric wave and
only then the logical system of analysis (2) dials the others digits.
It can happen others situations, when the user has to wait for a
signal of confirmation. For example, to confirm to use another telephone
company or any other kind of telephone call. The simplification system
for telephones should be adapted for this confirmations, or any others
that it will exist in the future.
It can happen that the signal of confirmation of another company,
take a long time to be emitted, because there is an overcharge of phone
calls. The simplification system for telephones warms the user that it is
waiting for the confirmation, and after a few seconds automatically, hang
up and make the call with another company. This can be done not
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
13
automatically, but only after a confirmation of the user.
However this can be a option.
If there are two companies for international, long distance and
cellular phone calls, the price of phone calls can change for example
every week due to concurrence. So it can happen that one week the price
is better in one company and in the next week in another company.
Ihie to this change of prices, the user can activate the
simplification system for telephones, for one week, or one month, or one
day to use one company and in the next week, month or day to use another
company.
In the figure four there is the equipment (30) with the
simplification system for telephones, adapted to a telephone (31). It is
a top view.
In figure five the same equipment, but in a side view.
In figure six the simplification system for telephones but with a
different external (32) looking. In this example the equipment is
intercalate in the phone wire (33), that already existed.
This equipment can have different external looking.
In figure seven, it can be seen the bottoms with detailed. In this
case with two options. The button (34) allows to choose between two local
phone companies. In the position, 1 there will be add only the local area
code. In the position 2, there will be add the company prefix and the
local area code. The button (35), allows to choose between two companies
to phone calls of kind three. In the position 1, it will not be add any
prefix and in the position 2, it will be add the prefix of another
telephone company.
If there are more than two companies, for example three or four,
the situation will be similar.
If there are two companies, one without prefix, other with the
prefix 050 and another one with the prefix 075. It should have a button
with three positions.
In the figure eight, it can be seem in detail the buttons for three
companies. It is a similar situation of the figure seven, only with one
more option. In this example, the position 3 of the button, that means
the prefix 075.
The simplification system for telephones can be incorporated in the
telephone itself, or fax itself, or any other communication equipment.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
14
That equipment should have buttons for the user to choose which company
he wants.
Any of this communication equipment can have a different or more
complete kind of buttons. In the figure eleven, it is showed a more
sophisticated to select between companies.
For the calls to a cellular phone, it is a similar study of the
international calls. Each cellular phone company has a prefix that
identifies that company. When it is dialled one of this prefixes, then
counts the number of digits. When the user dials the seven digit, that
means a phone call to a cellular phone.
The prefix of a cellular phone is 936. When the simplification
system for telephones checks the prefix 936, it counts the number of
digits. If it is more that six digits, then it adds or not a prefix, or
activates or not the relay to send to another wire, if there is more then
one wire.
In figure two, it correspond to the items 10, 11, 12, 16, 17 or 18.
In the figure three are the items 19, 22, 23, 25, 27, 28 or 29.
In figure three, in the item 23, when it is written "has 936 or
others", it means to check if there is the prefix 936 in the first three
digits of the telephone number, or to check if there is the prefix of
another cellular phone company in the first three digits of the telephone
numbers.
In kind four, there are calls with the prefix 0800.
In this situation, the logical system of analysis (2), compares
that prefix with the date in the memory (4). If it is equal, then the
logical system of analysis (2) with the counter (5), counts the digits.
When it notices more then six digits, it is sure, it is a telephone
number with the prefix 0800. Then it adds or not the prefix of another
company, or makes the option to use another phone wire.
In the figure two, it corresponds to the items 10, 11, 12, 16, 17
or 18.
In figure three, it correspond to the items 19, 22, 25, 27, 28 or
29.
In the figure three, in the item 22, when it is written "has 0800",
that means, the first four digits are 0800.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
This solution is also for other special prefix like 0641, and so
on.
This special prefix can be different in each country. In the Madrid
telephone area, the telephone numbers have seven digits. The count of the
~a~gits should detect more then seven digits.
In all the previous situations, it has been mentioned to add prefix
in a certain order, but the prefix can be add in any order.
Instead of the complete number have this order 050 947 70 59 54. It
can be first the local area code and then the company prefix. The number
will stay like this 947 050 70 59 54. The prefixes can have any relative
position between themselves and also between the telephone number.
It can also happen, that others wires of communication, like for
instance, the cable television, that it is necessary to add a prefix. The
simplification system for telephones, should also handle this problem.
Kind five, is the safeguard call. If the user dials (1) the
telephone number, with his local area code, it should happen the
following. The logic system of analysis (2), compares the first digit
with the digit in the memory (3) and finds that the first digit is nine.
Then it counts the number of digits. If it is more then six, then it
cheeks, if the first three digits are equal to the local area code, that
is the memory (3). If there are the same, then should add eventually a
prefix of another company and to choose the wire. If it was only dialled
six digits, it is a local call, without local area code.
In figure two, it corresponds to the items 10, 11, 12, 16, 17 or
18. In the figure three, it corresponds to the items 19, 22, 23, 24. In
the figure nine, there is the alteration to the figure three, to handle
this kind of phone calls. Following the item 24, are the items 25, 37,
38, 28 or 29.
This problem can also happen with other phone calls. Like the
number with local area code and with the prefix of another company, and
so on.
This five kind of call, can be a option. If the simplification
system for telephones adds a local area code to a number already with the
local area code, then the national telephone system does not make the
call, because there are too many digits and it will send a warning sound.
Kind six, it is when the user lives near another telephone area,
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
16
and he has to phone daily to that area. That means, that the user has to
dial the local area code and eventually also the prefix of another
company.
To handle this situation, there are several possible solutions.
To have a prefix that identifies another area, for example the
number one. The user to call the phone 45 67 34, of the telephone area
948, instead of dialling 948 45 67 34, he would dial 1 45 67 34.
When is dialled (1), the number one, the logical system of analysis
(2), compares with the memories (3) and detects this prefix. Then it
should count (5) if there are seven digits.
The simplification system for telephones deletes the first digit
and adds the necessary prefix and chooses if possible, one of the wires,
like in the kind three phone calls.
The prefix is not fixed, it can be any other number, or a signal,
like for example * that are in same phones. That prefix has to be
previously determined. In same regions, has to be the prefix * or a
special button.
In the telephone area of Madrid, the numbers have seven digits. In
a neighbour area the telephone area have six digits. If from Madrid, the
user dials the prefix 1 to another area, it stays a telephone number with
seven digits.
The simplification system for telephones counts seven digits and
can not know, if it is a local phone call or a phone call to another
area.
In this particular situation the prefix, has to be special, but not
a number. Another option, it is to have a special button.
It can have this prefix or the activation of the button in any
relative position of the telephone number.
In figure two, it correspond to the items 10, 11, 12, 13, 17 or 18.
In figure three, it corresponds to the items 19, 22, 23, 24. It continues
in figure nine, with the items 24, 36, 39, 40, 28 or 29.
Another way to handle this problem, is that the prefix number is
any number.
The counter (5) detects seven digits. It will delete the prefix.
The prefix could be in the begin or in the end or any other relative
position of the telephone number. There was always the obligation, that
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
17
the prefix lays in the same position. The relative position has to be
determined and so the user dials the prefix in the same position.
If the user is in a telephone area near to two phone areas, there
will be two fixed prefixes.
To handle this problem, counting the digits is not enough. It is
necessary to have the prefix 1 to the telephone area 943 and the prefix
5, to the telephone area 948.
The simplification system for telephones when detects the first
digit 1 or 5, begins to count the number of digits. If it counts seven
digits confirms that it is a call to another area.
It deletes the prefix and it will add the necessary prefix and if
possible choose the wire.
In figure three, there is the study for groups of two or three
digits. However the logical system of analysis (2) can begin to study
immediately in the first digit. Beginning to add prefixes and send the
call to the telephone wire, before the all the digit has been dialled.
For same numbers, it has to wait for all the number to be dial, to get
sure what kind of phone call. If the number dialled is 08 54 17 and
studying immediately for the first digit. In figure three, it will be the
following.
In the item 19 will be standard, but in the item 22, when is
dialled the third digit, it will go to the item 24, without waiting for
the four digit.
Every phone area has his own characteristic local area code. This
local area code has to be in memory. The simplification system for
telephones has to be build for each telephone area or can be adapted for
each telephone area.
In same countries, in one telephone area, the telephone numbers,
can have four, five or six digits and they have not compulsorily the same
quantity of digits.
The simplification system for telephones should be adapted to this
situation. Instead of having the counter of digits, it has a counter of
time.
The counter of digits, the short prefix and the counter of time,
should work in conjugation in a way to detect what kind of telephone
number it is.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
18
In figure three, in the item 25, instead of a counting of digits,
it will have a counting of time. After a few time, if it is not dial any
more digit, it will go from the item 25 to the item 26. But if it is
dial, it will go to the item 27.
This counter of time, can be the continuos reading of the clock (6)
by the logical system of analysis (2). It can be any other way of
counting time.
This simplification system for telephones is explain in electronic
circuit, but it can be built in any other way. It can be used for
switchboard, computerise telephone, cellular phone, fax, wireless
telephone, equipment of sending e-mail messages, public phones, a
computer with modem or with any other equipment or any other equipment of
communication that exits today or it will exist in the future.
Due to the evolution or changing of the national phone system it
can change the prefix of the phone companies.
To avoid to buy a new equipment, the memories (3) and (4) can be
changed by a new ones, updated.
This memories can be a electronic component, as a memory eprom.
In this kind of memory it is possible to rewrite the data.
If there is a change in the prefix, it will be only necessary to
rewrite the memory eprom. This rewrite can be made directly or with an
outside equipment. This memory can be assemble in a plate. This plate can
be dissembled from the equipment and taken to a shop to be rewritten.
Instead of having a eprom memory, it can have a prom memory. This
memory does not allow to be rewritten. It will be necessary to buy a new
equipment. However the first equipment had cost less.
Instead of memories prom and eprom, it can be any other kind of
memories.
The concepts showed are in large meaning. Perhaps, there is one
country or one region, that for local calls, there is 5ust one company,
but it is necessary to add the prefix of that company to the phone
number. However to phone to other telephone area or international call,
there are two phone companies.
Another possibility is to have one wire to local calls
and another wire for long distance calls. For international calls, the
first wire, but with additional prefix.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
19
There are several possible combinations, between several prefixes
or other kind of prefixes, in one telephone wire, and also with other
telephone wire, eventually with his own specify prefix. There are also
the possibility of the communication by satellite or by the electrical
wire, or any other way, material or system of communication, that exist
today or it will exist in the future. There are different national or
regional telephone system, that the simplification system for telephones
or any communication equipment, shall be adapted to allow a simple and
economic use .
Perhaps there are countries, where the changing of the national
telephone system, is slight different.
For the local calls is not necessary to add the local area code,
but if the user wants another company, he has to add the prefix of
another telephone company. All of the others changes are the same.
The simplification system for telephones, will be adapted to this
system. In the figure 2, the item 15 will be different. In this item, it
will be add, if necessary, only the prefix of another company. The others
items stay the same. In the figure 3, the item 26, should add if
necessary the prefix of another company.
Other possible change, it is to have two or more phone companies
and the first digit of the local area code, is not the number nine.
Instead of the nine, to have one digit, that is the prefix of each
phone company.
In Spain all the local area code begin by the number nine and the
other two digits are different in relation with each telephone area. One
possible change, it is instead of the local area code 948 of Burgos, to
have two possible local area codes.
Instead of the fixed digit nine, there is one digit that correspond
to the phone company, the user wants.
For example, the phone company named A has the prefix 4. The phone
company named B has the prefix 5.
The user to phone to the number 74 53 69 of his telephone area, has
two possibilities.
One possibility is to dial 448 74 53 69 and the other possibility
is to dial 548 74 53 69.
In the first possibility, the call is made by the company A and in
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
the second possibility, the call is made by the company B.
This situation is similar, to the previous one. The user has also
~o dial the local area code for local calls, nevertheless with the
~~bligation to choose a telephone company.
To determine if it is a local call, it is necessary to count the
number of digits. After the user has dialled the six digit and after a
short time for example 1/4 of a second, if no more digit is dialled, it
could be concluded, that is a local call.
The simplification system for telephones should add the local area
code like before, and also the prefix of the phone company.
A phone call to another telephone area is not possible to detect,
by the first digit, the number nine. To know if it is a phone call to
another area, it is necessary to count the number of digits. The user
will dial, six digits of the telephone number and two more of the local
area code. A totally of eight digits.
When the user dials the seven digit, it is confirmed, that it is a
call to another area.
This example is generic. If the simplification system for
telephones is equipped to detect a phone call to a neighbour area, then
it has to be the eight digit. The seven digit will indicate a phone call
to the neighbour area.
If in a telephone area, the quantity of digits in a telephone
number, is not the same, then the solution has to be different. It will
be necessary a special prefix or to have a special button, or to count
the time to determine, when the user finishes to dial.
Another solution is to have in the memory all the local area code
and by comparison to detect which phone calls are long distance calls.
Another possible change of the national telephone system is not to
' dial any prefix of a phone company. The number will be 48 74 53 64,
without the first digit, but with the local area code.
In this case the phone call will be made by a third company.
Also this situation could be handled by the simplification system
for telephones and the user only dials 74 53 64 and it will be add the
prefix 48.
Not all the telephone areas of Spain have two wires of
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
21
communication. The possibility to choose between two or more wires is a
option.
The logical scheme of the figure three and nine, are not limited.
It is possible to have another logical scheme, but with equal results.
The logical schemes of the figure three and nine are with relation
to the national Spain telephone system and does not take in attention,
the characteristics of some regions or telephone areas of Spain. One
telephone area with telephone numbers with seven digits, or to have two
wires of communications, obliges in each case a different logical scheme.
The simplification system for telephones should be built, in
attention to all this different characteristic. Also any other different
telephone characteristic of others countries. The evolution or any change
or more quantity of phone companies, obliges a different logical scheme
of the figure three and nine.
To handle all this present variation and future variation the
simplification system for telephones should be built for each case, with
a unique relation between comparing digits, counting digits, counting
time, and then the simplification system for telephones is able to study
the number dialled and to know what kind of number is, and then it should
add or not the necessaries prefixes and to choose the wire of
communication. Always, with the goal to keep simple and economic the use
of the phone.
The telephone companies can have different prices during the day.
The simplification system for telephones can have a internal clock
(6) to be able to economise with the change of price during the day.
The user defines previously in the clock (6) the hour of the day,
when the call begins to be made by another company. When it arrives that
time, automatically, when it is dialled a number, it is heard a warning
sound. The user changes the position of the button, that chooses the
company, for instance (34) or (35), and so on. Then the phone call is
made by another company. Because it was changed the position of the
button, it stops to emit the warming sound, next time the user dials a
number.
Another way of operating is when it arrives the time defined before
by the user, then the equipment changes automatically the position of the
button, that chooses the company, for instance (34) or (35), and so on.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
22
The user can due to the pre-selection of the buttons, that the local
phones made by a company for the long distance call another company. He
can also choose another wire and also take in account the hour of the
day. In this way, it is possible to program the simplification system for
telephones.
Perhaps, there is one company, that the calls are lower price, but
the quality of sotmd is not very good. The user, can make a selection of
the company, taking in account the two paraments and not just the
economic one.
It can happen, that the user is interested, to have the
company A for local calls and the company B for long distance calls and
the company C for international calls.
To handle all this options, the logical scheme is slight different
to the figure 3. The "yes" of the item 21, it will not go to the item 27,
but to another one similar to the 27. In this similar one, it will add a
prefix. The item 27, it will stay the same for the others conditions.
It will be necessary one more button, to select one more prefix.
The equipment with the simplification system for telephones can be
more sophisticated. It can have a liquid crystal display (LCD) with
buttons interplay with the data in the display. In this way, there is a
more visual and interaction programming with the data. This equipment can
handle more companies and in a easy way.
It was explained a simplification system for telephones to handle
the six different kinds of calls. However it is possible another
solution. It is a second alternative.
It also simplifies the use of the telephone. It is more economic,
but less practical.
The first alternative is for people in offices or people that makes
a lot of calls.
There are people that makes few calls and the majority of them are
local calls.
Because the majority of the calls are local ones, they do not spend
time thinking what kind of phone call is.
For economic reasons, it can be interested another alternative
equipment. This equipment is described as followed.
There are six different kinds of calls, to be study by the
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
23
simplification system for telephones. If the equipment has not the
logical syqtem of analysis (2), the user has to decide between three
conditions.
In figure ten, there is the new logic scheme related with the
switch on of the buttons.
Condition one and the button (41) is switch on, that means, it will
add the local area code and eventually the prefix of other phone company,
or to use another wire.
It is for local calls, that before it was necessary to dial the
local area code.
Condition two and the button (42) is switch on, that means, it will
add the prefix of other company or to use another wire.
It is for phone calls for other telephone area, international
calls, cellular phone calls and calls for special prefix 0800, and so on.
Condition three and the button (43) is switch on, that means the
phone calls go directly to the wire. It is for calls for information,
emergency, and so on.
In figure eleven, it can be seen an equipment with three buttons.
The user has to take the decision, what kind of call it is. Then
the user switches on, one of the buttons (44), (45), (46) and so it will
be add one or several prefix, or it will be not add any prefix.
For each call is not necessary to switch on one of the buttons.
Once the button is switch on, it remains fixed till it is switch
on, another button.
This equipment is for people that makes few calls and the majority
of them are local calls. So there is no need to switch on continually the
buttons. The majority of the time, the local call button will stay
activated.
To call attention, the button (46) of the figure eleven has a
different colour of the others buttons, or it is bigger than the others,
or another shape.
In an accident situation, a person can stay nervous and she does
not remember, that she has to switch on the button before it makes the
call.
The emergency number is 112 and it is a direct call to the wire,
without need of an extra prefix.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
24
Eventually, the equipment can have the word EMERGENCY written near
to this button.
Another possibility, it is the equipment to have a logical system
to detect the number 112 and independently of the button activated, it
sends the phone call to the wire.
The equipment has other buttons (47) and (48), that allow to choose
which company the user wants. The button (47) has four positions, that
allows to choose between four companies. The button (48) is similar to
the button (47), but it is for long distance calls and international
calls and to cellular phone calls.
In the figure eleven, the user chose in the button (47) the company
one, for local calls. For other kind of calls the user chose in the
button (48), the company four. When the user activates the button (44),
is the company one that it will make the phone call.
If the user wants another company, he changes in the button (47),
for example company three. When the user makes a phone call, and if the
button (44) is activated, the phone call will be made by the company
three. The same relation between the button (48) and the button (45).
Some countries only have two companies in concurrence. In figure
twelve, it can be seem an equipment that it is only possibly to choose
between two companies (54) and (55).
The buttons (47) and (48) instead of having four positions, they
can have three or five or any other quantity of positions. The quantity
of positions, it is in function of the quantity of companies in
concurrence and the economic profit of the user to have a equipment to
select between so many companies.
The telephone number has six digits. Now the user to get profit of
the concurrence has to dial twelve digits. To dial so many digits is a
limitation to concurrence. It is important to have the more economic
equipment for the user and so the user can save money with the
concurrence between telephone companies.
There is also another equipment, in which the companies, that the
user selects in the buttons (47) and (48) can be changed with the
buttons (49) and (50).
If there is a great change in the prices, this equipment gives the
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
possibility to change the four companies, that the user selects in the
daily calls.
The equipment can have a four button for calls for the neighbour
Telephone area. When the user switch on this button, it will add to the
number dialled, the following. The neighbour local area code and
eventually the prefix of another company or to choose another wire. If
the user lives near two telephone areas, the equipment could have two
buttons.
For the same problem, there is another option. The user dials one
more digit. The equipment has a counter of digits. When it detects one
more digit, it deletes this digit and adds the necessary prefix an choose
the wire if necessary. This counter of digit can have the possibility to
detect the signal * or any other signal, in the same way as the first
alternative.
It can have a five button, to select between two or more wires.
Instead of the five button, this option can be integrated in the
buttons (47) and (48). This buttons would select between companies and
also between wires.
It is possible that in a country, there are two companies for local
calls, but for long distance calls, four companies. The equipment will
have the following configuration. In the figure twelve, it will keep the
button (54), but instead of the button (55), there will be the button
(48) of the figure eleven.
This possibility, like the one of changing throw the buttons (49)
and (50), which companies to select, they both apply to the first
alternative.
It can be interested to have one button for long distance calls and
another button for international calls.
There was mentioned different equipment combinations, but there are
others possible combinations. The quantity of buttons (44), (45), (46)
and the quantity of options (47), (48) and to have or not the buttons
(49), (50) gives different possible equipment combinations.
In this alternative like in the first one, the equipment is able to
wait for the electric sign of confirmation and only then, the equipment
will dial the rest of the digits.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
26
This equipment can have a simple clock (52) or one with
programming.
When changed the hour, a simple clock, every time the user dials a
number, makes a warning sound. The user will switch off the button (51)
that it will stop the sound. The clock can be programmed for different
hours of the day and so can handle differences of prices during the day.
A programming clock will change automatically the prefix company.
For a long distance call, the equipment till 18 hours will add the prefix
050. After 18 hours automatically, it will add the prefix of another
company.
The user should had programmed in the button (53), that hour. The
clock can be programmed for two or more different hours of the day. For
instance, one at 18 hours and the other at 21 hours.
There are countries or regions that have just one wire of
communications. There are people that do not leave near another telephone
area. Some countries only have two companies in concurrence, others
countries have more companies. Due to all this different conditions, this
equipment can be built in several ways.
This equipment can be an independent one, or to be part of the
telephone itself, or part of any other communication equipment. It would
be a more economic telephone models, than the ones of the first
alternative.
The phone calls made by the computer have the same solution as the
first alternative.
The logical scheme of the phone calls are the same of the first
alternative as also the operation of the simplification system for the
telephones.
In the figure thirteen there is the interface.
For a local call the user, only dials the number, without any
prefix. In a long distance call, the user dials the number with the local
area code, of that area. Z~e user has not to worry to separate any prefix
or code, from the telephone number. For the other phone calls, it is the
same as mentioned in the first alternative.
Instead of the electronic components, the simplification
system for the telephones uses the CPU the ROM and the RAM of the
computer.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
27
The user types the number with the keyboard, or the mouse or the
user dictates, and the number will be written in (57).
The computer can write in (59) the telephone number that it is dial
to the wire. This for information of the user or for eventually
confirmation by the user.
In this way, the simplification system for telephones will keep
simple the use of the computer as a communication system. The user would
not worry, with any prefix. The simplification system for telephones will
choose and dial the necessary prefix to that particularly call, and to
choose wire.
The user when needs to phone to the neighbour area, instead of
typing one more number, it could switch on the button (58). This button
has the name of "another area". If the user lives near to two neighbour
areas, it would have two buttons.
If the user takes the computer to another telephone area, then the
user activates the option "computer another area" (60). The user will
indicate the new area, and the simplification system for telephones will
operate taking in account, that the computer is in a new telephone area.
The option (56) has the name "change prefiA'. This option allows to
survey the phone companies and prices that are used. The user can also
change the companies that make the phone calls.
The interface can have more options, for example a map with the
prefix of the several telephone areas.
The interface is not rigid, it can have other graphic look and to
have more options. The figure thirteen is only to exemplify the concepts
of the simplification system for telephones.
The computer or any other computerised system with a modem or any
other outfit can use the simplification system for telephones. It can
also be used by other outfit directly or indirectly to the wire.
When it is mentioned the telephone wire, that is not restricted to
this wire. It can be any other Wire of communication, that already exist
or it will exist in the future.
The simplification system for telephones can be used in connections
by Internet, to send e-mail mensage, or fax throw the computer, and so
on.
For the first and the second alternative, the simplification system
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
28
for telephones adds local area code and company prefix but also others
prefixes.
Some countries can have a national telephone system, or
certain areas or regions or any others, that oblige the user to dial
today or in the future other kind of prefixes.
For instance a personal identification code and for the first and
second alternative, the simplification system for telephones could dial
this code. This personal identification code will be related with the
components, that has the simplification system for telephones.
The capacity to add this personal code is the user who gives the
data or it is made in factory.
For doing this, the logical system of analysis, the memories and
the counter of digits and the counter of time, they all shall be
actualised as also the co-ordination between all of them.
In this way the simplification system for telephones can keep with
the evolution of the telephone and differences between countries,
regions, areas, with the goal to keep simple the use of the telephone,
computer, and others communication equipments.
The logic scheme of figure three for the first alternative and the
logical scheme of figure ten for the second alternative should be adapted
to more or different prefixes.
Also both logical schemes should be adapted, if it is necessary to
wait for a confirmation with a electric wave, after has been dial a
prefix or code or several prefixes or codes.
Another problem it is the continuos changing of the prices. The
user has to be continued informed, to save in the phone calls.
The user can receive a message with the changes of prices. This
message has special characteristics. One of the characteristic is to have
a special code to be identify by the simplification system for
telephones.
Another characteristic is to have a normalised message, that it
allows to be understood and with interaction with the simplification
system for telephones.
This message should have standard characteristic. In this way it
can be send by any telephone company and the user with just one
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
29
equipment, can understand and studied all the messages, send by
differents companies.
If the new prices of a company are study by a department of the
government or by a independent company, then it will only send the
message, if the prices are real better. The only thing to be confirmed,
if the user has subscription in that company.
If the message is send by a company, it should be always checked.
The first check is if the user has subscription. Another check, if the
price of that company is better then the prices of the actual company.
The logical scheme is in figure fourteen and continuous in the
figure fifteen.
The item 61 receives the message.
The item 62 checks if there are subscription. If there are not, it
sends to the item 72, to stop analyse. If there are, then it sends to the
item 63.
In the item 63 checks the type of call that shall be study. If it
is a local call, a long distance call, international call, and so on.
The item 64 identifies in the message the new cost and the hour of
the day, that begins that price. The new cost is given to the variable A
and the time to the variable hl.
In the item 65, the cost of the call is given to the variable B and
the hour of the day to the variable h2. This values are the ones been
used in this moment.
The item 66, cheeks if the two hours of the day are identical. For
that it compares hl with h2. If they are not identical then it sends to
the item 67, for the user came to a decision.
If they are identical, it goes to the item 68, that will compare
the price in the variable A, with the price in the variable B.
If the price A is not better, it goes to the item 73. In this item,
it checks if all the message has been studied. If it has not, it sends to
the item 62. If it has, it stops the analyse.
If the price is better it goes to the item 69: In this item,
cheeks, if it is necessary confirmation of the user to change the
company.
If it is necessary confirmation, it goes to the item 70. When the
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
user makes a phone call, he will be warmed with a sound or in any other
way.
If it is not necessary confirmation, it goes to the item 71. In
this item makes the alteration of the company.
Independent of the confirmation in the item 70, it goes to the item
73. The item 71 after the change and the item 67, they both go to the
item 73.
In the item 73 will continue the study of the message or it will
stop the study of analysis if all the message has been studied.
If it continues, them it will send to the item 62, to study another
type of call.
In the item 66 if the hour of the day are not equal, it could not
wait for the confirmation of the user, but to continue the study of the
prices.
For exemplifying, the following values. Two companies A and B with
the same price, during the day. The company A reduces the price after the
18 hours, and this new price is kept during the night. The company B
reduces the price after 19 hours, and this new price is kept during the
night. However the new price of the company B is better than the new
price of the company A.
The phone calls during the day are made by the company B. After 18
hours, the phone calls will be made by the company A and after 19 hours
again by the company B.
In the item 62 it could have another option. If the user has not a
subscription, it could continue and make the study of the price. This
study could include the result, taking in consideration, the cost of a
new subscription and also the saving on the phone calls. Considering the
average of the calls in the previous month.
Both alternatives can have this study of analysis. If the equipment
. has a liquid crystal display (LCD) or the interface of figure 13, can
show all the results. The simple equipment can have a light sign or any
other way to warm the user of a message. Then the user will contact the
company.
This message analysis can be an independent equipment, without the
other part of the simplification system for telephones. That is for a
country, where there was not the telephone national change. This message
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
31
telephones can be integrated in a telephone, or in other mean of
communication.
The logical analysis of the message in figure fourteen and fifteen,
are not rigid. In this example it took in consideration several premises,
like price and the hour of the day. But it can take any others, like the
quality of sound, and so on. It could exist a department of the
government that can analysis the quality of sound. It can take in account
any other premise that exist today or it will exist in the future.
This premises should be normalised, for the logical scheme of
figure 14 and 15, will be able to analysis, the message complete and
fair.
It can also have another logic scheme, with identical results.
Perhaps there are other kind of prefixes, that the simplification
system for telephones, for the first and second alternative also has to
handle.
There are countries, that inside the telephone area, it is divided
in small telephone areas. That telephone area is just one city, and it
has a local area code. It can also be a region with several cities and
countrside. But in each quarter the telephone number, begins by one or
two or three specific digits, of that quarter. It is similar to the
postcode in a city.
With this mini local area code is possible to know more exactly,
where the telephone is and where the user is phoning to. In that way, it
is possible to know the distance in kilometre between the two phones.
It would be also possible, to know the distance between two phones,
even they are in different telephone areas.
The companies can have different prices, regarding the distance,
and not just only the telephone areas and the international calls, and so
on.
The simplification system for telephones can have in the memories
(3) and (4), this mini local area code and to choose the company, taking
in attention the distance, even inside the telephone area.
Any other circumstance, that it will make different prices between
telephone companies, that exist today or it will exist in the future,
then the simplification system for telephones, should be adapted, to
obtain the more economic and easy phone calls.
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02385756 2002-03-22
WO 00/22799 PCT/PT99/00016
32
TABLE ONE Local area code
Telephone Local area
area
Telephone
Local
area code area code
Alicanante 96 Madrid 91
Badaioz 924 Oviedo 95
Barcelona 93 P. Maiorca 971
Bilbau 94 Palmas 928
Burgos 947 Pamplona 948
Cl3ceres 927 Salamanca 923
Cadiz 956 San. de Compostela 981
Corunha 981 San Sebastian 943
Gijon 98 Santander 942
Huelva 959 Sta. Cruz Tenerife 922
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)