Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
ACTIVATORS OF SOLUBLE GUANYLATE CYCLASE
This invention relates to activators of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), to
their preparation and to their use.
Soluble guanylate cyclase is responsible for the enzymatic conversion of
S guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine-3',5'-monophosphate
(cGMP)
The enzyme is stimulated by NO binding to the enzyme.
sGC is responsible for numerous physiological processes including vascular
and non-vascular smooth muscle relaxation, peripheral and central
neurotransmission, platelet reactivity and phototransduction (Hobbs A.J.,
TiPS,
December 1997, Vol 18, p.484). Activators of sGC can therefore be expected to
have valuable therapeutic properties.
As explained above, NO is known as an activator of sGC. However, this
compound has a number of different physiological effects and its use in
activating
sGC therefore suffers from a myriad of side effects. There is therefore a need
for
selective activators of sGC.
3-(5'-hydroxymethyl-2'-furyl)-1-benzylindazole (YC-1) is a known NO
independent activator of sGC (Hobbs, A.J., TiPS, December 1997, Vol 18,
p.484).
However, the activation achieved is not high.
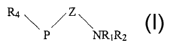
Accordingly, the present invention provides the use of a compound of the
formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, in the manufacture
of a
medicament for use in the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase
(~
P NR1R2
wherein:
- Rl and RZ are the same or different and each represent a C,-C6 alkyl
group, or R, and RZ together form a C3-C6 alkylene group;
- Z is a C,-C4 alkylene group;
- P is a direct bond or a moiety -X-, -Y-, -W-, -XY-, -YW- or -XYW-,
wherein:
- W is -O-, -S-, or -NR3, wherein R3 is hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl;
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-2-
Y is a moiety -U-V- wherein V is a direct bond or a C,-C6
alkylene group and U is -CS-, -CO-, -S(O)2- or -C(=NR)-
wherein R is hydrogen, hydroxy or C1-C6 alkyl;
X is -O- or -NR6- wherein R6 is hydrogen, C,-C6 alkyl, CZ-C6
alkenyl, CZ-C6 alkynyl, aryl or heteroaryl; and
R4 is C,-C6 alkyl, CZ-C6 alkenyl, Cz-C6 alkynyl, aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocyclyl, heterocyclyl, a group -R-A wherein R is -(C,-C6 alkyl)-,
-(CZ-C6 alkenyl)- or -(Cz-C6 alkynyl)- and A is aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocycyl or heterocyclyl, or R4 is a group -COR~~, -COzR~~, -S(O)ZR°
or -CONR~R~~ wherein R~ is hydrogen, C,-C6 alkyl, Cz-C6 alkenyl or
Cz-C~ alkynyl and R~~ is is aryl, heteroaryl, carbocyclyl or
heterocyclyl.
In the moiety P, the moiety -X-, when present, is attached to R4 and the
moiety W, when present, is attached to Z. In the moiety Y, the moiety V is
attached
to W or, if W is not present, to Z, and the moiety U is attached to X or, if X
is not
present, to R4.
As used herein, a C,-C6 alkyl group or moiety is a linear or branched alkyl
group or moiety. Suitable alkyl groups and moieties include CI-C4 alkyl groups
and
moieties, for example, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, i-propyl, n-butyl and t-butyl.
Methyl,
ethyl, n-propyl and t-butyl are preferred.
A C,-C6 alkyl group or moiety can be substituted or unsubstituted at any
position. Typically, it is unsubstituted or carries 1, 2 or 3 substituents.
Suitable
substituents include C,-C~ alkyl, C,-C6 alkylthio, C,-C6 alkoxy, C,-C6
haloalkyl, for
example -CF3 and -CCl3, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13,
halogen,
hydroxy, cyano, nitro, aryl, aryloxy, arylthio, heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy,
heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl,
carbocyclyloxy, carbocyclylthio, oxo, -NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are the same
or
different and are hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl, =NR, -COR, -CONR,R, -COZR, -NR,COR,
-NR,COZR, -NR,CONR,R, -S(O)zR and -S(O)ZNR,R wherein each R, can be the same
or different and represents hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl and each R can be the same
or
different and represents C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or
carbocyclyl, and
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-3-
-S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ and -O-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein each R~~~ can be the
same or
different and represents aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl.
Further, two
substituents on the same atom can, together with the atom to which they are
attached,
form a carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group.
Preferred substituents include oxo, halogen, C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, arylthio,
aryloxy, heteroaryl, heteroarylthio, heteroaryloxy and -NR~R~~, =N-R, -CONHR
and
-NHCOZR wherein R, R~ and R~~ are as defined above. Further, two preferred
substituents on the same carbon atom may, together with the atom to which they
are
attached, form a carbocyclyl group, preferably a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group.
More preferred substituents are oxo, halogen, for example chlorine and
fluorine, C~-C4 alkyl, for example methyl, ethyl or t-butyl, aryl, for example
phenyl,
-CONH-aryl, for example -CONH-phenyl, =N-aryl, for example =N-phenyl, -NH-
COZ-(C,-C4 alkyl), heteroarylthio, for example pyrimidinethio and -CO-aryl,
for
example -CO-phenyl. It is also preferred that two substituents on the same
carbon
atom may, together with the atom to which they are attached, form a C3-C6
cycloalkyl group.
As used herein, a CZ-C6 alkenyl group or moiety is a linear or branched
alkenyl group or moiety. Suitable alkenyl groups and moieties include CZ-C4
alkenyl
groups and moieties such as ethenyl, propenyl and butenyl groups and moieties.
Ethenyl and propenyl are preferred. A Cz-C6 alkenyl group or moiety may be
substituted or unsubstituted at any position.
A CZ-C~ alkenyl group is typically unsubstituted or carries 1, 2, 3 or 4
substituents. Preferably, it carries at least two substituents. Suitable
substituents
include oxo, C,-C6 alkyl, C,-C6 alkylthio, C,-C6 alkoxy, C~-C6 haloalkyl, for
example
-CF3 and -CC13, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13, halogen,
hydroxy, cyano, vitro, aryl, aryloxy, arylthio, heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy,
heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl,
carbocyclyloxy, carbocyclylthio, -NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are the same or
different
and are hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl, =N-R, -COR, -CONR,R, -COZR, -NR,COR,
-NR,COzR, -NR,CONR,R, -S(O)ZR and -S(O)ZNR,R wherein each R, can be the same
or different and represents hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl and each R can be the same
or
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-4-
different and represents C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or
carbocyclyl, and
-S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ and -O-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein each R~~~ can be the
same or
different and represents aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl.
Further, two
substituents on the same atom can, together with the atom to which they are
attached,
S form a carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group.
Preferred substituents include oxo, halogen, C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, arylthio,
aryloxy, heteroaryl, heteroarylthio, heteroaryloxy and -NR~R~~, =N-R, -CONHR
and
-NHCOZR wherein R, R~ and R~~ are as defined above. Further, two preferred
substituents on the same carbon atom may, together with the atom to which they
are
attached, form a carbocyclyl group, preferably a C3-C$ cycloalkyl group.
More preferred substituents are halogen, for example chlorine and fluorine,
C,-C4 alkyl, for example methyl, ethyl or t-butyl, aryl, for example phenyl,
heteroaryl, for example furanyl, -CONH-aryl, for example -CONH-phenyl, -NH-
COZ-(C,-C4 alkyl), -NH-CO-(C,-C4 allcyl), -NH-CO-aryl, for example -NH-CO-
phenyl, heteroarylthio, for example pyrimidinethio and -CO-aryl, for example -
CO-
phenyl. It is also preferred that two substituents on the same carbon atom
may,
together with the atom to which they are attached, form a C3-C8 cycloalkyl
group.
A CZ-C6 alkynyl group or moiety is typically an ethynyl, propynyl or butynyl
group or moiety. It may be substituted or unsubstituted at any position.
Typically, it
is unsubstituted or carnes 1 or 2 substituents. Suitable substituents include
C,-C6
alkyl, C,-C6 alkylthio, C,-C6 alkoxy, C,-C6 haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -
CCl3,
C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13, halogen, hydroxy, cyano,
nitro,
aryl, aryloxy, arylthio, heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy, heteroarylthio,
heterocyclyl,
heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl, carbocyclyloxy,
carbocyclylthio,
-NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are the same or different and 'are hydrogen or C,-
C6 alkyl, -
COR, -CONR,R, -COZR, -NR,COR, -NR,COZR, -NR,CONR,R, -S(O)ZR and
-S(O)ZNR,R wherein each R, can be the same or different and represents
hydrogen or
C,-C6 alkyl and each R can be the same or different and represents C,-C6
alkyl, aryl,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl, and -S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ and
-O-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein each R~~~ can be the same or different and
represents
aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl. Further, two substituents on
the same
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-5-
atom can, together with the atom to which they are attached, form a
carbocyclyl or
heterocyclyl group.
Preferred substituents include halogen, C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, arylthio, aryloxy,
heteroaryl, heteroarylthio, heteroaryloxy and -CONHR and -NHCOzR wherein R is
as defined above. Further, two preferred substituents on the same carbon atom
may,
together with the atom to which they are attached, form a carbocyclyl group,
preferably a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group.
More preferred substituents are halogen, for example chlorine and fluorine,
C,-C4 alkyl, for example methyl, ethyl or t-butyl, aryl, for example phenyl,
-CONH-aryl, for example -CONH-phenyl, -NFi-COZ-(C,-C4 alkyl), heteroarylthio,
for
example pyrimidinethio and -CO-aryl, for example -CO-phenyl. It is also
preferred
that two substituents on the same carbon atom may, together with the atom to
which
they are attached, form a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group.
A C,-C6 alkoxy group is typically a said C~-C6 alkyl group attached to an
1 S oxygen atom. A C,-C6 alkylthio group is typically a said C,-C6 alkyl group
attached
to a sulphur atom.
As used herein, a said alkylene group is a divalent alkyl moiety. It may be
unsubstituted or substituted at any position. Typically, it is unsubstituted
or
monosubstituted. Suitable substituents include halogen, for example chlorine
and
flourine, hydroxy, C,-C4 alkyl such as methyl and ethyl, C,-C4 alkoxy, for
example
methoxy, C~-C4 haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CC13 and C,-C4 haloalkoxy, for
example -OCF3 and -OCCl3. These substituents are typically themselves
unsubstituted.
A halogen is typically chlorine, fluorine, bromine or iodine. It is preferably
chlorine.
A haloalkyl or haloalkoxy group is typically a said alkyl or alkoxy group
substituted by one or more said halogen atoms. Typically, it is substituted by
l, 2 or
3 said halogen atoms. Preferred haloalkyl and haloalkoxy groups include
perhaloalkyl and perhaloalkoxy groups such as -CX3 and -OCX3 wherein X is a
said
halogen atom. Particularly preferred haloalkyl groups are CF3 and CC13.
Particularly
preferred haloalkoxy groups are -OCF3 and -OCCl3.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-6-
As used herein, an aryl group or moiety is typically a C6-CZO aryl group or
moiety. Suitable such aryl groups and moieties include phenyl, naphthyl and
pyrenyl. Phenyl and pyrenyl are preferred.
An aryl group or moiety may be substituted or unsubstituted at any position.
Typically, it is unsubstituted or carnes 1, 2, 3 or 4 substituents. Suitable
substituents
include C,-C6 alkyl, C,-C6 alkylthio, C,-C6 alkoxy, C,-C6 haloalkyl, for
example -CF3
and -CCl3, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13, halogen, cyano,
hydroxy, vitro, aryl, aryloxy, arylthio, heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy,
heteroarylthio,
heterocyclyl, heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl, carbocyclyloxy,
carbocyclylthio, -NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are the same or different and are
hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl, -COR, -CONR,R, -COzR, -NR,COR, -NR,COZR,
-NR,CONR, R, -S(O)zR and -S(O)ZNR,R wherein each R, can be the same or
different
and represents hydrogen or C,-C~ alkyl and each R can be the same or different
and
represents C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl, and -S-
(C,-C6
alkyl)-R~~~ and -O-(C1-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein each R~~~ can be the same or
different and
represents aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl.
Preferred substituents include C,-C6 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl,
C1-C6 alkoxy, for example methoxy, C,-C6 alkylthio, for example methylthio, C,-
C6
haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CC13, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and
-OCCl3, halogen, for example chlorine and fluorine, vitro, cyano, aryl, for
example
phenyl, aryloxy, for example phenyloxy, arylthio, for example phenylthio,
heteroaryl,
heteroaryloxy, heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, -NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are
the same
or different and are hydrogen or C,-C~ alkyl, -CONH-(C,-C6 alkyl),
-NHCONH-R wherein R is aryl, for example phenyl, or heteroaryl, -S(O)ZNHR~
wherein R~ is aryl, for example phenyl, or heteroaryl, -S-(C1-C6 alkyl)-R~~
wherein R~~
is aryl, for example phenyl, or heteroaryl and -COR~~~ wherein R~~~ is
heterocycyl,
heteroaryl or aryl.
Particularly preferred substituents are phenyl, in particular 4-phenyl,
phenoxy, in particular 2-phenoxy, phenylthio, halogen, -CF3, -CC13, vitro,
cyano,
-OCF3, -OCC13, C,-C4 alkyl, C,-C4 alkoxy, C,-C4 alkylthio, -CONH-(C,-C4
alkyl),
-CO-phenyl, -S(O)ZNH-phenyl, -S-(C~-C4 alkyl)-phenyl, -S-(C,-C4 alkyl)-
pyrazole,
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-S-(C,-C4 alkyl)-pyrimidine, -(C,-C4 alkyl)-NH-COz-(C,-C4 alkyl), thiazole, -
COR
wherein R is benzothiophenyl or ~i-carbolinyl and -NH-(CHZ)nNR'R" wherein n is
from 2~to 4 and R' and R" are the same or different and are C,-C4 alkyl.
An aryl group or moiety may be fused to a further said aryl group or to a
S carbocyclic, heterocyclic or heteroaryl group. For example, an aryl group
may be
fused to a pyridine ring to form a quinoline or isoquinoline group, or to a
furan ring.
It may also, for example, be fused to a cyclopropyl or cyclohexyl group or to
a
tetrahydrofuryl group, a 1,4-dioxolane group or a pyrimidone ring, for example
a 4-
pyrimidone ring.
As used herein, a carbocyclic group or moiety is a non-aromatic, saturated or
unsaturated carbocyclic group or moiety. Typically, it has from 3 to 10, for
example
from 3 to 8, carbon atoms. Preferably, it has from 3 to 8, for example 3 to 6,
carbon
atoms. Examples of suitable carbocyclic groups include cyclopropyl,
cyclobutyl,
cyclopentyl, cyclopentenyl, cyclopetadienyl, cyclohexyl, cyclohexenyl and
cyclooctanyl groups. Preferred carbocyclic groups include cyclohexyl,
cyclooctanyl
and cyclohexenyl groups.
A carbocyclic group or moiety may be unsubstituted or substituted at any
position. Typically, it carries up to 3 substituents. Suitable substituents
include oxo,
C,-C6 alkyl, C,-C6 alkylthio, C,-C6 alkoxy, C,-C6 haloalkyl, for example -CF3
and -
CC13, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCCl3, halogen, hydroxy, cyano,
nitro, aryl, aryloxy, arylthio, heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy, heteroarylthio,
heterocyclyl,
heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl, carbocyclyloxy,
carbocyclylthio, -
NR'R" wherein R' and R" are the same or different and are hydrogen or C,-C6
alkyl,
=NR, -COR, -CONR,R, -COZR, -NR,COR, -NR,COZR, ,
-NR,CONR,R, -S(O)ZR and -S(O)ZNR,R wherein each R, can be the same or
different
and represents hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl and each R can be the same or different
and
represents C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl, and
-S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R"' and -O-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R"' wherein each R"' can be the same
or
different and represents aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl.
Further, two
substituents on the same atom can, together with the atom to which they are
attached,
form a carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
_g_
Preferred substituents include oxo, C,-C6 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl,
C,-C6 alkoxy, for example methoxy, C,-C6 alkylthio, for example methylthio, C,-
C6
haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CCl3, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and
-OCC13, halogen, for example chlorine and fluorine, vitro, cyano, aryl, for
example
S phenyl, aryloxy, for example phenyloxy, arylthio, for example phenythio,
heteroaryl,
heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, -CONH-(C,-C6 alkyl), -NHCONH-R wherein R is
aryl,
for example phenyl, or heteroaryl, =NR~ wherein R~ is aryl, for example
phenyl, or
heteroaryl, -S(O)ZNHR~~ wherein R~~ is aryl, for example phenyl, or
heteroaryl,
-S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein R~~~ is aryl, for example phenyl, or heteroaryl,
and
-COR~~~~ wherein R~~~~ is heterocyclyl, heteroaryl or aryl.
Particularly preferred substituents are oxo, =N-aryl, for example =N-phenyl,
aryl, for example phenyl, and -CO-aryl, for example -CO-phenyl.
A carbocyclic group or moiety may be fused to a further carbocyclic group or
to an aryl, heteroaryl or heterocyclic group.
A heteroaryl group or moiety is typically a 5- to 10- membered aryl ring
containing at least one heteroatom, for example 1, 2 or 3 heteroatoms,
selected from
O, S and N. Preferably, the heteroaryl group or moiety is a 5- or 6- membered
ring.
Suitable heteroaryl groups and moieties include pyridyl, pyranyl, furanyl,
thienyl, pyrazolidinyl, pyrrolyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazinyl,
thiazolyl,
imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, isothiazolyl, isoxazolyl, furazanyl, triazolyl and
thiadiazolyl
groups. Pyridyl, pyrrolyl, thienyl, thiazolyl, furanyl, pyrazinyl and
1, 2, 3-thiadiazolyl groups are preferred.
A heteroaryl group or moiety may be unsubstituted or substituted at any
position. Typically, it is unsubstituted or carries up to three substituents.
Suitable
substituents include C~-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkylthio, C,-C6 alkoxy, C1-C6
haloalkyl, for
example -CF3 and -CC13, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13,
halogen,
hydroxy, cyano, vitro, aryl, aryloxy, arylthio, heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy,
heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl,
carbocyclyloxy, carbocyclylthio, -NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are the same or
different
and are hydrogen or C~-C6 alkyl, -COR, -CONR,R, -C02R, -NR,COR, -NR,COzR,
-NR,CONR,R, -S(O)zR and -S(O)ZNR,R wherein each R, can be the same or
different
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-9-
and represents hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl and each R can be the same or different
and
represents C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl, and
-S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ and -O-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein each R~~~ can be the
same or
different and represents aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl.
Preferred substituents include C,-C6 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl;
C,-C6 alkoxy, for example methoxy, C,-C6 alkylthio, for example methylthio, C,-
C6
haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CCl3, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and
-OCC13, halogen, for example chlorine, cyano, nitro, aryl, for example phenyl,
aryloxy, for example phenoxy, arylthio, for example phenylthio and
-O-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R, -S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R, -S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-CONH-R, -CO-R and
-CO-NH-R, wherein R is an aryl group, for example a phenyl group.
Particularly preferred substituents include phenyl, halogen, for example
chlorine, C,-C4 alkyl, for example methyl, -CF3, -CC13, -OCF3, -OCC13,
phenylthio,
phenoxy, -S-(C,-C4 alkyl)-CONH-phenyl, -S-(C,-C4 alkyl)-phenyl,
-O-(C,-C4 alkyl-phenyl, -CO-phenyl, cyano, C,-C4 alkylthio, nitro,
2,3-dihydrobenzafuranyl and -CO-NH-(1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydranaphthalen-8-yl).
A heteroaryl group may be fused to a said aryl or carbocyclic group or to a
further heteroaryl group or to a heterocyclic group. Examples of such fused
heteroaryl groups include quinolyl, indolyl, isoindolyl, benzothiophenyl,
imidazo[1,2-a]pyridyl and (3-carbolinyl groups.
As used herein, a heterocyclic group or moiety is a non-aromatic, saturated or
unsaturated cyclic group or moiety containing at least one, for example, one,
two or
three, heteroatoms selected from N, O and S. Typically, it is a 3- to 6-
membered
ring. Preferably, it is a 5- or 6- membered ring containing, as heteroatoms,
one or
two nitrogen atoms.
Suitable heterocyclic groups and moieties include pyrazolidinyl, piperidyl,
piperazinyl, pyrrolidinyl, pyrrolinyl, imidazolidinyl, imidazolinyl,
pyrazolinyl,
3,4-dihydro-2H-pyranyl, tetrahydropyrimidinyl (for example 1,2,3,4- or 1,4,5,6-
tetrahydrapyrimidinyl), 2-hydropyridinyl, 2-hydrothiazolyl,
tetrahydropyridinyl (for
example 1,2,5,6- or 2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridinyl) and tetrahydropyridazinyl,
for
example 3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridazinyl.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-10-
A heterocyclic group or moiety may be substituted or unsubstituted at any
position., Typically, it is unsubstituted or carnes 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5
substituents. Suitable
substituents include oxo, C,-C6 alkyl, C,-C6 alkylthio, C,-C6 alkoxy, C,-C6
haloalkyl,
for example -CF3 and -CC13, C,-C6 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCCl3,
halogen, hydroxy, cyano, vitro, aryl, aryloxy, arylthio, heteroaryl,
heteroaryloxy,
heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, heterocyclyloxy, heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl,
carbocyclyloxy, carbocyclylthio, -NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are the same or
different
and are hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl, =NR, -COR, -CONR,R, -COZR, -NR,COR,
-NR,COZR, -NR,CONR,R, -S(O)ZR and -S(O)zNR,R wherein each R, can be the same
or different and represents hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl and each R can be the same
or
different and represents C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or
carbocyclyl, and
-S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ and -O-(C~-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein each R~~~ can be the
same or
different and represents aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl.
Further, two
substituents on the same atom can, together with the atom to which they are
attached,
form a carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl group.
Preferred substituents include oxo, C,-C6 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl,
C,-C6 alkoxy, for example methoxy, C1-C6 alkylthio, for example methylthio, CI-
C6
haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CC13, C1-C~ haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and
-OCC13, halogen, for example chlorine and fluorine, vitro, cyano, aryl, for
example
phenyl, aryloxy, for example phenyloxy, arylthio, for example phenythio,
heteroaryl,
heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, -CONH-(Ci-C6 alkyl), -NHCONH-R wherein R is
aryl,
for example phenyl, or heteroaryl, =NR~ wherein R~ is aryl, for example
phenyl, or
heteroaryl, -S(O)zNHR~~ wherein R~~ is aryl, for example phenyl, or
heteroaryl,
-S-(C1-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ wherein R~~~ is aryl, for example phenyl, or heteroaryl,
and
-CORD°~ wherein R~~~~ is heterocyclyl, heteroaryl or aryl.
Particularly preferred substituents are oxo, =N-aryl, for example =N-Ph, aryl,
for example phenyl, halogen, C,-C4 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl, C,-C4
alkoxy, for example methoxy and ethoxy, C1-C4 haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and
-CC13 and C,-C4 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13.
Heterocyclic groups carrying one oxo substituent and up to 2, for example 0,
1 or 2, further substituents are particularly prefered.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-11-
A heterocyclic group or moiety may be fused to a further said heterocyclic
group or to a said carbocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl group. Typically, it is non-
fused or
is fused to a benzene ring or to an iodole group. Examples of such fused
heterocyclic
groups include chromanyl and chromonyl groups.
An aryloxy, heteroaryloxy, heterocyclyloxy or carbocyclyloxy group is
typically a said aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl group attached
to an
oxygen atom. An arylthio, heteroarylthio, heterocyclylthio or carbocyclylthio
group
is typically a said aryl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl group
attached to a
sulphur atom.
Typically, R~ and RZ are the same or different and represent methyl, ethyl,
propyl, n-butyl or t-butyl. Preferably the groups represented by R, and Rz are
unsubstituted or carry one or two substituents. Preferred substituents for R,
and RZ
include C1-C4 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl, CI-C4 alkoxy, for example
methoxy and ethoxy, halogen, for example chlorine, C~-C4haloalkyl, for example
-CF3 and -CC13 and C,-C4 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13. Typically,
these substituents are themselves unsubstituted.
More preferably, R, and RZ are methyl or Rl and RZ together form a
n-butylene group.
Z is methylene, ethylene, propylene or butylene and is preferably propylene.
Preferably Z is unsubstituted, monosubstituted or disubstituted. Preferred
substituents for Z include C,-C4 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl, Ci-C4
alkoxy,
for example methoxy and ethoxy, halogen, for example chlorine, C1-C4haloalkyl,
for
example -CF3 and -CC13 and C,-C4 haloalkoxy, for example -OCF3 and -OCC13.
Typically, these substituents are themselves unsubstituted. Particularly
preferred
substituents for Z are C1-C4 alkyl groups, in particular methyl groups. A
preferred
substituted alkylene group is 2,2-dimethylpropylene.
Typically, the moiety P is -Y-, -XY-, -YW- or -XYW-. Preferably, the
moiety P is -XYW- or -YW-. When P is -W- or is a direct bond,. R4 is typically
an
aryl, heteroaryl or heterocyclyl moiety and/or is typically substituted by an
aryl,
heteroaryl, heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl substituent.
Typically, W is -O- or -NR3. Typically, R3 is hydrogen or is methyl, ethyl,
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-12-
propyl, n-butyl or t-butyl. Preferably, R3 is unsubstituted or carries one or
two
substituents. Preferred substituents for R3 include C,-C4 alkyl, for example
methyl
and ethyl, C~-C4 alkoxy, for example methoxy and ethoxy, halogen, for example
chlorine, C,-C4 haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CCl3 and C1-C4 haloalkoxy,
for
example -OCF3 and -OCC13. Typically, these substituents are themselves
unsubstituted.
More preferably, R3 is hydrogen or methyl, most preferably hydrogen.
V is preferably a direct bond. U is preferably -CO-, -S(O)Z-, -C(=NH)- or
-C(=NOH)-, more preferably -CO-.
X is typically -NR~-. When X is a group -NR6-, R6 is typically C~-C4 alkyl,
for example methyl, ethyl, propyl, n-butyl and t-butyl, aryl, for example
phenyl, or
heteroaryl, for example pyridyl. Preferably, R6 is unsubstituted or carries 1,
2 or 3
substituents. Preferred substituents for R6 include C~-C4 alkyl, for example
methyl
and ethyl, C,-C4 alkoxy such as methoxy or ethoxy, halogen, for example
fluorine or
chlorine, C,-C4 haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CC13, C,-C4 haloalkoxy, for
example -OCF3 and -OCC13, cyano, vitro and -NR~R~~ wherein R~ and R~~ are the
same
or different and are hydrogen or C,-C4 alkyl. Typically, these substituents
are
themselves unsubstituted.
Preferably, X is -NH-.
Typically, the group R4 has up to 30 carbon atoms and up to 10 heteroatoms
selected from N, O and S. Preferably, it has up to 25 carbon atoms and up to 7
heteroatoms. Typically, the group R4 contains at least one, preferably at
least two,
aryl or heteroaryl rings.
Preferably, R4 is C,-C6 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, carbocyclyl, heterocyclyl,
-(C,-C6 alkyl)-aryl, -(C,-C6 alkyl)-heteroaryl or -COR~~, -COzR~~ or -CONR~R~~
wherein R~ is hydrogen or C~-C6 alkyl and R~~ is an aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocyclyl or
heteroaryl group.
Suitable substituents for the group R4 are oxo, C1-C6 alkyl, C~-C6 alkylthio,
C,-C6 alkoxy, C,-C6 haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CCl3, C,-C6 haloalkoxy,
for
example -OCF3 and -OCCl3, halogen, hydroxy, cyano, vitro, aryl, aryloxy,
arylthio,
heteroaryl, heteroaryloxy, heteroarylthio, heterocyclyl, heterocyclyloxy,
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-13-
heterocyclythio, carbocyclyl, carbocyclyloxy, carbocyclylthio, -NR~R~~ wherein
R~
and R~~ are the same or different and are hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl, =NR, -COR,
-CONR,R, -COZR, -NR,COR, -NR,COzR, -NR~CONR~R, -S(O)zR and -S(O)ZNR,R
wherein each R, can be the same or different and represents hydrogen or C1-C6
alkyl
and each R can be the same or different and represents C~-C6 alkyl, aryl,
heteroaryl,
heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl, and -S-(C,-C6 alkyl)-R~~~ and -O-(C~-C6 alkyl)-
R~~~
wherein each R~~~ can be the same or different and represents aryl,
heteroaryl,
heterocyclyl or carbocyclyl. Further, two substituents on the same atom can,
together
with the atom to which they are attached, form a carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl
group.
Substituents on the group R4 may be further substituted.
Typically, when P is a direct bond, -O- or -NH-, R4 is not a moiety (A) or
(B).
R.3 R.3
N (A) N
R,4 N R~4 ~ N. , R~ 1
I
R' I
wherein:
R', is: hydrogen, aryl, heteroaryl, 3- to 6- membered heterocyclyl, -(C,-C4
alkyl)-R
wherein R is aryl, heteroaryl or 3- to 6- membered heterocyclyl, C1-C4 alkyl,
-CONA'z, -COA" or -SOZA" wherein each A' is the same or different and is
selected from H, C,-C4 alkyl and aryl and each A" is the same or different
and is selected from C~-C4 alkyl and aryl; and
R'3 and R'4 are either:
(a) the same or different and selected from -COZA~wherein A~ is as
defined above, -CF3, -CC13, halogen, C,-C4 alkoxy, -(C,-C4 alkyl)-
aryl, -(C,-C4 alkyl)-heteroaryl, hydrogen, C,-C4 alkyl, C3-C6
carbocyclyl, 3- to 6- membered heterocyclyl, -SOZNA'z wherein A' is
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-14-
as defined above, and -CONZ,ZZ wherein Z, and Z2, which are the
same or different, represent H, C,-C4 alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, C3-C6
carbocyclyl, 3- to 6- membered heterocyclyl or -(C,-C4 alkyl)-R
wherein R is aryl, heteroaryl, 3- to 6- membered heterocyclyl or C3-C6
carbocyclyl, or Z, and Z2, together with the nitrogen atom to which
they are attached, denote a 5- or 6- membered N-containing
heterocyclic group; or
(b) different, one of R'3 and R'4 being aryl or heteroaryl and the other
being as defined above
or R', is as defined above and R'3 and R'4 together form the divalent group,
-(CH)4-, which group is optionally substituted.
Preferably, R4 is not a 3- or 5- pyrazole or a 3- indazole group when P is a
direct bond, -O- or -NH-. More preferably R4 is not a pyrazole or indazole
group
when P is a direct bond, -O- or -NH-. More typically, R4 is not a 3- or 5-
pyrazole or
a 3- indazole group or, more preferably, a pyrazole or indazole group when P
does
not contain the moiety U.
More preferably, when P is a direct bond, -O- or -NH- and R4 is a heteroaryl
group, R4 is a pyridyl, pyrimidyl, thiazolyl or thienyl group. R4 is typically
also a
pyridyl, pyrimidyl, thiazolyl or thienyl group when P does not contain the
moiety U
and R4 is a heteroaryl group. Suitable pyridyl, pyrimidyl, thiazolyl and
thienyl
groups include groups fused to a said aryl or said carbocyclic group or to a
said
heteroaryl or said heterocyclic group. In such compounds, R4 may be
substituted by
one or more of the groups mentioned above as appropriate substituents for R4.
Preferred compounds of the invention are those in which X is -NR6- wherein
R6 is as defined above, and R4 is aryl or heteroaryl. In these preferred
compounds, P
is typically -XYW-. Y is typically -CO-. W is typically -NR3- wherein R3 is as
defined above. X is preferably -NH- and/or R4 is preferably phenyl, thienyl or
pyrazolyl.
In the above preferred compounds, when R4 is phenyl it is typically
substituted by a phenoxy group or by a phenylthio group, in particular a 2-
phenoxy
or 2-phenylthio group, or by a further phenyl group, in particular a 4-phenyl
group.
When R4 is thienyl or pyrazolyl, it is typically substituted by a phenyl or
phenylthio
group. These substituents may be unsubstituted or may be further substituted
at any
position. Typically, they are unsubstituted or carry one, two or three further
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-15-
substituents. Preferred further substituents include halogen, for example
chlorine and
fluorine, C,-C4 alkyl, for example methyl and ethyl, C~-C4 alkoxy, for example
methoxy and ethoxy, C,-C4 haloalkyl, for example -CF3 and -CCl3, and
-S(O)ZNH-phenyl. These further substituents are typically themselves
unsubstituted.
In the above preferred compounds of the invention, R4 is preferably
2-phenoxyphenyl, 2-fluoro-diphen-4-yl, 5-(4-chlorophenylthio)-thien-3-yl,
4-(4-fluorophenyl)-thien-2-yl, 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-
pyrazol-3-
yl Or -(C6Ha)-S-(C6Ha)-S(O)z-~-(C6H4O
Further preferred compounds of the invention are those in which P is -YW-
and R4 is an aryl, heterocyclyl or heteroaryl group. In these further
preferred
compounds, Y is typically -CO-. W is typically -NR3- wherein R3 is as defined
above. Further, R4 is preferably an oxo-substituted heterocyclic group such as
a
chromonyl group or is a pyrazolyl, thienyl, phenyl or indolyl group.
In the above further preferred compounds, R4 is typically unsubstituted or
substituted by one or more, for example, one, two or three substituents
selected from
C,-C6 alkyl, for example t-butyl, phenyl, thiazolyl, phenylthio, cyano, nitro,
CI-C6
alkylthio, for example i-propylthio, C1-C6 alkoxy, halogen such as chlorine
and
-S-(C,-C4 alkyl)-phenyl. These substituents may be unsubstituted or may be
substituted at any position. Typically, they are unsubstituted or carry one,
two or
three further substituents. Preferred further substituents include halogen,
for example
chlorine, C,-C4 haloalkyl, for example -CF3, phenyl and -S(O)2-NH-phenyl.
These
further substituents are typically themselves unsubstituted.
Additional preferred compounds of the invention are those in which P is -W-
or -YW- wherein Y is -CO- and W is -O-.
Particularly preferred compounds of the invention are compounds of formula
(h) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof,
(~
X N NR1R2
R3
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-16-
wherein:
- R, and RZ are the same or different and each represent a C,-C6 alkyl
group, or Rl and RZ together form an allcylene group having from 3 to
. 6 carbon atoms;
- Z is an alkylene group having from 2 to 4 carbon atoms;
- R3 is hydrogen or C,-C6 alkyl;
- Y is -CO- or -S(O)2-;
- X is a direct bond or -NR6- wherein R6 is hydrogen, C,-C6 alkyl, CZ-C6
alkenyl, CZ-C6 alkynyl, aryl or heteroaryl; and
- R4 is C,-C6 alkyl, CZ-C6 alkenyl, CZ-C6 alkynyl, aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocyclyl, heterocyclyl, a group -R-A wherein R is -(C,-C6 alkyl)-,
-(Cz-C6 alkenyl)- or -(CZ-C6 alkynyl)- and A is aryl, heteroaryl,
carbocycyl or heterocyclyl, or R4 is a group -CORD or -COZR~ wherein
1 S R~ is aryl, heteroaryl, carbocyclyl or heterocyclyl.
Further particularly preferred compounds of the invention are compounds of
formula (I~~), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof
O
RawX N~NR R (h/)
( i 2
R3
wherein R1 and RZ are methyl or together form a n-butylene group, R3 is
hydrogen or methyl, R4 is as defined in the formula (I) or in the formula (h)
and X is
a direct bond or is -NR6- wherein R6 is as defined above. Preferably, when X
in the
formula (h~) is -NR6-, R4 is as defined as in the above preferred compounds of
the
invention. Preferably, when X in the formula (I~~) is a direct bond, R4 is as
defined in
the above further preferred compounds of the invention.
The present invention includes pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the
compounds of the invention. Suitable salts include salts with pharmaceutically
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-17-
acceptable acids, both inorganic acids such as hydrochloric, sulphuric,
phosphoric,
diphosphoric, hydrobromic or nitric acid and organic acids such as citric,
fumaric,
malefic, malic, ascorbic, succininc, tartaric, benzoic, acetic,
methanesulphonic,
ethanesulphonic, benzenesulphonic or p-toluenesulphonic acid. Salts may also
be
formed with pharmaceutically acceptable bases such as alkali metal (eg sodium
or
potassium) and alkali earth metal (eg calcium or magnesium) hydroxides and
organic
bases such as alkyl amines, aralkyl amines or heterocyclic amines.
Particularly preferred compounds of the invention are:
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2-phenoxy-phenyl)-urea
1-[2-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-pyridin-3-yl]-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-pyren-1-ylmethyl-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[( 1 R,2R)-5-phenyl-2-( 1-phenyl-methanoyl)-
cyclohexyl]-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[2-(4-phenoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[3-methyl-5-(4-methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazol-5-
yl)-1-(4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-1 H-pyrazol-4-yl]-urea
2'-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid (4-
fluoro-phenyl)-amide
N-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-4-[3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-3-
phenyl-butyramide
1-[4-(4-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-thiophen-3-yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
urea
1-[2-(3,4-Dimethoxy-phenyl)-6-methyl-quinolin-4-yl]-3-(4-dimethylamino-
propyl)-urea
1-(6-Bromo-2-thiophen-3-yl-quinolin-4-yl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
1-[3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-4-cyano-5-isobutylsulfanyl-thiophen-2-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
1-[6-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-cyclohex-3-enyl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
urea
1-(2-Benzylsulfanyl-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
Z- {2-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-phenylsulfanyl} -N-phenyl-
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-18-
benzenesulfonamide
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2'-fluoro-biphenyl-4-yl)-urea
N-(3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-2- {3-[3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-pyridin-
2-ylsulfanyl}-acetamide
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3- {2-[ 1-(1-trifluoromethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-b-
carbolin-2-yl)-methanoyl]-phenyl}-urea
8-{2-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-phenylsulfanyl}-naphthalene-1-
carboxylic acid methylamide
1-[ 1-(3,4-Dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridin-3-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(3-oxo-I ,2,3-triphenyl-propyl)-urea
1-[5-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-1-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-1H pyrazol-3-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
1- {4-[4-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-thiazol-2-yl]-phenyl} -3-(3-dimethylamino-
. propyl)-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[5-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-thiophen-2-yl]-urea
1-[3-(4-tert-Butyl-benzyloxy)-thiophen-2-yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[4-(4-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl)-phenyl]-urea
1-[3-(3,4-Dichloro-benzylsulfanyl)-thiophen-2-yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-urea
1-[2-(5-Chloro-1-methyl-3-phenyl-1H pyrazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-phenyl]-
3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
1-[2-(4-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazolin-7-yl]-
3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3- {4-[4-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-pyrimidin-2-
ylsulfanylmethyl]-phenyl} -urea
1-(4-Bromophenyl)-3-(3-(1-pyrrolidinyl) propyl) urea
1-(4-Bromophenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-methyl-1-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
1-(3-Phenyl-5-methoxy phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-19-
3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
1-(3-Nitrophenyl)-1-benzyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
1-Benzyl-1-(4-methyl-3-pyridinyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
1-Methyl-1-(3,5-bistrifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)urea
1-(2-Phenacyl-4-chorophenyl)-1-methyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
1-(2-Chloro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) urea
1-(3-Fluoro-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) urea
1-(3-N-tent-butoxycarbonyl-benzylamino)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) urea
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[ 1-(4-fluorobenzoyl]-benzamide
2-[ 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
5-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-1-phenyl-1H pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
5-Chloro-3-phenyl-1H indole-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-(2-phenylsulfamoyl-phenylsulfanyl)-
benzamide
2-Benzylsulfanyl-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
6,8-Di-tert-butyl-4-oxo-4H chromene-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino
-propyl)-amide
3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-4-cyano-5-isobutylsulfanyl-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
4-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-3-nitro-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-(4-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl)-benzamide
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2-phenoxyphenyl)-urea
1-[4-(4-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-thiophen-3-yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)
-urea
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2'-fluoro-biphenyl-4-yl)-urea
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[ 1-(4-fluorobenzoyl]-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-phenoxy-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-phenoxy-benzamide
2-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-nicotinamide
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-20-
4'-n-Propyl-biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-methanoyl]-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-ami de
5-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-furan-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
2-[ 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
2-Phenyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-[ 1-(4-Chloro-3-nitrobenzoyl)]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-pyren-1-yl-acetamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(3-methyl-benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-
methanoyl]-benzamide
4-Chloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2-phenoxy-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(4-phenoxy-phenyl)-propionamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[ 1-( 1-trifluoromethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydro-b-
carbolin-2-yl)-methanoyl]-benzamide
1-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-1-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2- { 1-[(3-Dimethylamino-propylcarbamoyl)-methyl]-cyclopentyl} -N-(4-
trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-acetamide
8-[2-(3-Dimethylamino-propylcarbamoyl)-phenylsulfanyl]-naphthalene-1-
carboxylic acid methylamide
3-Methyl-5-(4-methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazol-5-yl)-1-(4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-
1H pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
6,8-Di-tert-butyl-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
2-(Furan-2-yl)-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
Biphenyl-2,2'-dicarboxylic acid 2'-[(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide]-2-[(4-
fluoro-phenyl)-amide]
3-Phenyl-pentanedioic acid (3-chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-amide (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-(3,4-Dimethoxy-phenyl)-6-methyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (3-
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-21-
dimethylamino-propyl)-ami de
6-Bromo-(2-thiophen-3-yl)-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-4-cyano-S-isobutylsulfanyl-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
4-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-3-nitro-benzamide
6-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-cyclohex-3-ene carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-(2-phenylsulfamoyl-phenylsulfanyl)-
benzamide
2'-Fluoro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-Benzylsulfanyl-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
Pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid 2-[(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide] 3-
[(5 , 6, 7, 8-tetrahydro-naphthal en-1-yl)-amide]
2-[(3,5-Dichloro-phenylcarbamoyl)-methylsulfanyl]-N-(3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-nicotinamide
2-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
2-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide
5-Chloro-1-(2,4-dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic
acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
1-(2,4-Dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
5-Chloro-1-(3,4-dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic
acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
1-(3,4-Dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
5-Chloro-1-(2,6-dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic
acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
1,1-Dimethyl-indan-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-22-
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[ 1-(4-ethyl-phenyl)-methanoyl]-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-phenyl)-butyramide
2-[3-(3,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-ureido]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4-triphenyl-butyramide
5-(4-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-(3-Chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2-ylsulfanyl)-3-methyl-3H imidazole-
4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-(2-Chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-[1,3]-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-(2,3-Dihydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-(2,3-Dichloro-phenyl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
4-[4-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-thiazol-2-yl]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
5-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide
4-Methyl-2-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
. 3-(4-tert-Butyl-benzyloxy)-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
4-Oxo-3-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3,4-dihydro-phthalazine-1-carboxylic
acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-4-oxo-4-phenyl-
butyramide
5-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-1-phenyl-1H pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-(4-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl)-benzamide
1-(2,4,5-Trichloro-phenylsulfonyl)-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
3-(3,4-Dichloro-benzylsulfanyl)-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (3-
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-23-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
5-Chloro-3-phenyl-1H indole-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(4-fluoro-benzyl)-1H indol-3-yl]-
acetamide
2-Phenyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-(7-ethyl-1H indol-3-yl)-4-oxo-4-phenyl-
butyramide
Phenyl-trifluoromethyl-thieno[3,2-b]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
3-(4-Nitro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenoxy)-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
2-(5-Chloro-1-methyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-N-(3-
1 S dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
2-(4-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline-7
-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-[4-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-pyrimidin-2
-ylsulfanylmethyl]-benzamide
1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylethylamido)-6-pyridone
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(3-N,N-dimethylpropylamido)-6-pyridone
1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylethylamido)-2-pyridone
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylethylamido)-2-pyridone
1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(N-[2,N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido])-2-pyridone
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(N-[2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido])-6-pyridone
5-chloro-1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido)-6
-pyridone
S-chloro-3-(2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido)-1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-6-
pyridone
5-chloro-1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-[N',N'-dimethylaminoethylamido])-2-
pyridone
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-24-
5-chloro-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)ethyl)amido-2-
pyridone
5-chloro-1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-3-N-(2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)ethyl)
amido-2-pyridone
1-benzyl-5-chloro-3-N-(2-[N',N'-dimethylamino]ethyl)carboXamido-6-
pyridone
5-chloro-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-[N',N'-dimethylamino]ethyl)carboxamido
-6-pyridone
4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)pyrrole-2-N-dimethylaminopropylcarboxamide
4-[(N-[3-(N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl)]carboxamido]-2-phenylthiazo1e
4-(N-(3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl)carboxamido)-2-(4-pyridinyl)thiazole
2-[4-(N-[3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl]carboxamido)phenyl-4-
(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)]thiazole
4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-[3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl]carboxamido)phenyl)
15. thiazole
1-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)-3-[N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)
carboxamido]-2 [ 1 H]-pyridone
N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-4-(3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy)
phenylsulfonamide
N 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-[3-chloro-5 -(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]
propanamide
3-(N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)carboxamido]-1-(4-trifluoromethylbenzy1))-2
[1H]-pyridone
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)urea
1-(3-(dimethylamino)-propyl)-3-phenylurea
N1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl]-N2-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]
ethanediamide
N4-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-c
arboxamide
N-[[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-N'-[3-(dimethyla
mino)propyl]urea
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-25-
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N'-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]urea
N-(3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propylamino)-propionamide
[3-(2-Ethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-yloxy)-propyl]-dimethyl-amine
8-(3-Dimethylamino-propoxy)-1,3,7-trimethyl-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
2-(3-Dimethylamino-propylamino)-isophthalonitrile
Dimethylamino-(3-methyl-benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-propan-1-one (HCl)
N-Benzo[ 1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl-N,N-dimethyl-propane-1,3-diamine
N,N-Dimethyl-N-(5-vitro-quinolin-8-yl)-propane-1,3-diamine
1-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
2-Amino-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-b enzamide
3-Phenyl-acrylic acid 3-dimethylamino-propyl ester
3,5-Dinitro-benzoic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl ester
[4-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-3H-thiazol-2-ylidene]-
phenyl-amine
3-Methyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid dimethylamino-dimethyl-propyl ester
N'-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-propane-1,3-diamine
[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-5-(4-vitro-phenyl)-3H-thiazol-2-ylidene]-
phenyl-amine
[3-(10,11-Dihydro-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-propyl]-dimethyl-
amine
2,3-Dimethyl-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl ester
N'-(3,4-Dinitro-5-pyridin-2-yl-thiophen-2-yl)-N,N-dimethyl-propane-1,3-
diamine
Cyclooctyl-dithiocarbamic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl ester (HCl)
N-(2,6-Difluoro-phenyl)-C-dimethylamino-acetamide
2-Acetylamino-3-(4-chloro-phenyl)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-acrylamide
N-[2-[5-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-furan-2-yl]-1-(3-dimethylamino-propyl
carbamoyl)-vinyl]-4-methyl-benzamide
2,6-Bis-(3-dimethylamino-propylamino)-3-vitro-benzonitrile
3 0 N-[2-(2,4-Dichloro-phenoxy)-phenyl]-N'-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
oxalamide
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-26-
3,5-Dichloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2,6-dimethoxy-benzamide
2-Dimethylaminomethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-naphthalen-1-one (HCl)
2-( { 1-[N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-
methanimidoyl}-amino)-6-fluoro-benzoic acid
S 2,4-Dichloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-N'-hydroxy-benzamidine
3-(3-Methyl-ureido)-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline-2-carboxylic acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
5-Bromo-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2-hydroxy-benzamide
N-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-6-(2-dimethylamino-ethylsulfanyl)-4-
trifluoromethyl-nicotinamide
1-(2,6-Dichloro-benzyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid
(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-amide
3-Amino-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline-2-carboxylic acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
Certain compounds of the invention are novel. Thus, the present invention
also provides a compound of the formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable
salt
thereof, in which Rl, RZ, Z, R3, Y, X and R4 are as defined above except for:
2-Benzylsulfanyl-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-phenoxy-benzamide
1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylethylamido)-6-pyridone
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(3-N,N-dimethylpropylamido)-6-pyridone
1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylethylamido)-2-pyridone
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylethylamido)-2-pyridone
1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(N-[2,N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido])-2-pyridone
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(N-[2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido])-6-pyridone
5-chloro-1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido)-6-
pyridone
5-chloro-3-(2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido)-1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-6-
pyridone
5-chloro-1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-[N',N'-dimethylaminoethylamido])-2-
pyridone
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-27-
S-chloro-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)ethyl)amido-2-
pyridone
5-chloro-1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-3-N-(2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)ethyl)
amido-2-pyridone
1-benzyl-5-chloro-3-N-(2-[N',N'-dimethylamino]ethyl)carboxamido-6-
pyridone
5-chloro-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-[N',N'-dimethylamino] ethyl)
carboxamido-6-pyridone
4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)pyrrole-2-N-dimethylaminopropylcarboxamide
4-[(N-[3-(N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl)]carboxamido]-2-phenylthiazo1e
4-(N-(3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl)carboxamido)-2-(4-pyridinyl)thiazole
2-[4-(N-[3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl]carboxamido)phenyl-4-
(3-trifluoromethylphenyl]thiazole
4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-[3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl]carboxamido)phenyl)
thiazole
1-(3,5-bis(trofluoromethyl)benzyl)-3-[N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)
carboxamido]-2 [ 1 H]-pyridone
N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-4-(3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy)
phenylsulfonamide
N1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-[3-chloro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]
propanamide
3-(N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)carboxamido]-1-(4-trifluoromethylbenzy1))-2
[ 1 H]-pyridone
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)urea
1-(3-(dimethylamino)-propyl)-3-phenylurea
N1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenyl]-N2-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]
ethanediamide
N4-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-c
arboxamide
N-[[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-S-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]-N'-[3-
(dimethylamino)propyl]urea
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-28-
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N'-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]urea
N-(3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propylamino)-propionamide
[3-(2-Ethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-yloxy)-propyl]-dimethyl-amine
8-(3-Dimethylamino-propoxy)-1,3,7-trimethyl-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
2-(3-Dimethylamino-propylamino)-isophthalonitrile
Dimethylamino-(3-methyl-benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-propan-1-one (HCl)
N-B enzo [ 1, 3 ] dioxol-5 -ylmethyl-N,N-dimethyl-prop ane-1, 3 -di amin a
N,N-Dimethyl-N-(5-vitro-quinolin-8-yl)-propane-1,3-diamine
1-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
2-Amino-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
3-Phenyl-acrylic acid 3-dimethylamino-propyl ester
3,5-Dinitro-benzoic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl ester
[4-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-3H-thiazol-2-ylidene]-
phenyl-amine
3-Methyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid dimethylamino-dimethyl-propyl ester
N'-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-propane-1,3-diamine
[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-5-(4-vitro-phenyl)-3H-thiazol-2-ylidene]-
phenyl-amine
[3-( 10,11-Dihydro-dibenzo [a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-propyl]-dimethyl-
amine
2,3-Dimethyl-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl ester
N'-(3,4-Dinitro-5-pyridin-2-yl-thiophen-2-yl)-N,N-dimethyl-propane-1,3-
diamine
Cyclooctyl-dithiocarbamic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl ester (HCl)
N-(2,6-Difluoro-phenyl)-C-dimethylamino-acetamide
2-Acetylamino-3-(4-chloro-phenyl)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-acrylamide
N-[2-[5-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-furan-2-yl]-1-(3-dimethylamino-
propylcarbamoyl)-vinyl]-4-methyl-benzamide
2,6-Bis-(3-dimethylamino-propylamino)-3-vitro-benzonitrile
N-[2-(2,4-Dichloro-phenoxy)-phenyl]-N'-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
oxalamide
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-29-
3,5-Dichloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2,6-dimethoxy-benzamide
2-Dimethylaminomethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-naphthalen-1-one (HCl)
2-( { 1-[N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl]-
methanimidoyl)-amino)-6-fluoro-benzoic acid
2,4-Dichloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-N'-hydroxy-benzamidine
3-(3-Methyl-ureido)-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline-2-carboxylic acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
5-Bromo-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2-hydroxy-benzamide
N-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-6-(2-dimethylamino-ethylsulfanyl)-4
trifluoromethyl-nicotinamide
1-(2,6-Dichloro-benzyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic acid
(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-amide
3-Amino-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline-2-carboxylic acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
Compounds of the invention in which P is -U-W- may be prepared by
reacting a compound of formula (II)
Z
/ \
W W R2
wherein Z, R~ and RZ are as defined above and W~ is a group WH wherein W
is as defined above, with a compound of formula (III)
R.a-~ (
wherein R4 is as defined above and U~ is a group -UL wherein U is as defined
above and L is a hydroxy group or a leaving group such as a halogen atom.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-3 0-
Compounds of formulae (II) and (III) are known compounds, or may be prepared
by
analogy with known methods.
Typically, the reaction takes place in the presence of a base such as
diisopropylethylamine or the equivalent polymer bound resin N,N
(diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), and a coupling agent
such
as O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
(HATI~. The reaction typically takes place in a solvent such as acetonitrile
at a
temperature of from 0 to 100 °C, preferably from 20 to 80 °C.
The work-up typically
involves the use of a sequestration enabling reagent such as
tetrafluorophthalic
anhydride and polymer bound scavenger resins to remove unwanted starting
materials. Such techniques are described in Parlow et al Tetrahedron Lett.,
1997, 38,
7959.
Compounds of the invention wherein P is -NH-CO-W- can be prepared by
reacting a compound of formula (II) above with a compound of formula (IV)
R4-N=C=O (IV)
wherein R4 is as defined above.
Typically, the reaction takes place in a hydrocarbon solvent such as toluene
at
a temperature of from 0 to 100 °C. The work-up typically involves the
use of a
sequestration enabling reagent such as tetrafluorophthalic anhydride and
polymer
bound scavenger resins to remove unwanted starting materials. The amides
thereby
prepared may be converted to the corresponding amidines by standard methods.
The compounds of formula (IV) may be prepared by techniques known in the
art. For example, they may be prepared by reacting a compound of formula (V)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-31-
O
(
R4 OH
wherein R4 is as defined above, with diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA), in
the presence of a base such as triethylamine. Typically, the reaction takes
place
under reflux, in a solvent such as toluene. Compounds of formula (V) are known
compounds or may be prepared by analogy with known methods.
Compounds of the invention wherein P is -X-U-W- wherein X, U and W are
as defined above can be prepared by reacting a compound of formula (II) above
with
a compound of formula (VI)
~~ ~U~
X L
wherein R4, X and U are as defined above and L is a hydroxy group or
leaving group such as a 4-nitro-phenoxy group. Typically, the reaction takes
place in
a hydrocarbon solvent such as tetrahydrofuran at a temperature of from 60 to
70 °C.
The work-up typically involves the use of a sequestration enabling reagent
such as
tetrafluorophthalic anhydride and polymer bound scavenger resins to remove
unwanted starting material.
The compounds of formula (VI) are known compounds or may be prepared
by analogy with known methods. For example, compounds of formula (VI) in which
U is -CO- can be prepared by reacting a compound of formula (VII)
(
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-32-
wherein R4 and X are as defined above, with a chloroformate, for example an
aromatic chloroformate such as 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate. Typically, the
reaction
takes place under reflux, in a solvent such as anhydrous THF. Further,
compounds of
formula (VI) in which U is -C-(=NH)- can, for example, be prepared from the
corresponding nitrite of formula R4-X-C=N, for example by reaction with
hydrochloric acid.
Compounds of the invention in which P is -X-Y- or -X-Y-W- and R4 is other
than -COR~~, -COzR~~, -S(O)zR~~ and -CONR~R~~ can be made by standard
techniques,
for example by reacting a compound of formula (VIII)
R4-X-H (VIII)
wherein R4 is other than -COR~~, -COzR~~, S(O)ZR~~ and -CONR~R~~ and X is as
defined above, with a compound of formula (IX)
L-Y-ZNR,Rz (IX)
wherein Y, Z, Rl and RZ are as defined above and L represents a hydroxy
group or a leaving group such as a halogen. The reaction is typically
conducted in
the presence of a base at from -78°C to the reflux temperature of the
solvent.
The compounds of formulae (VIII) and (IX) are known compounds or may be
prepared by analogy with known methods.
Compounds of the invention in which P is -X-U-W- and R4 is -COR~~,
-COZR~~, -S(O)zR~~ or -CONR~R~~ can be made in an analogous fashion by
reacting a
compound of formula (X)
R4X-U-L (X)
wherein R4, X and U are as defined above and L represents a hydroxy group
or a leaving group such as a halogen, with a compound of formula (XI)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-33-
HWZNR,RZ (XI)
wherein W, Z, R, and RZ are as defined above.
The compounds of formula (X) and (XI) are known compounds or may be
prepared by analogy with known methods.
Compounds in which P is X or W and R4 is other than -COR", -COZR",
-S(O)ZR" and -CONR'R" can be prepared, for example, by reacting a compound of
formula (XII)
R4-AH (XII)
wherein A is -X- or -W-, wherein X and W are as defined above and R4 is
other than -COR", -COzR", -S(O)ZR" and -CONR'R", with a compound of formula
(XIII)
L-Z-NR,RZ (XIII)
wherein Z, R, and Rz are as defined above and L is a leaving group such as a
triflate group or a halogen atom. The reaction can be conducted under standard
conditions. Typically, it takes place in the presence of a base in a solvent
such as
DMF.
The compounds of formula (XII) are known compounds or may be prepared
by analogy with known methods. The compounds of formula (XIII) are also known
compounds or may be prepared by analogy with known methods. For example, they
can be prepared from a corresponding compound of formula HO-Z-NR,Rz by
reaction with triflic anhydride or with PCIs.
Compounds of the invention in which P is X or W and R4 is -COR", -COZR",
-S(O)ZR" or CONR'R" can be prepared by reacting a compound of formula (IXV)
HA-Z-NR,RZ (IXV)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-34-
wherein A, Z, Rl and Rz are as defined above, with R4-L, wherein R4 is as
defined above and L is a hydroxy group or a leaving group, for example a
halogen.
The reaction can be conducted under standard conditions, such as those given
above
for the reaction of compounds of formulae (VIII) and (IX).
S Compounds of formula (IXV) and compounds of formula R4-L are known
compounds or may be prepared by analogy with known methods.
Compounds of the invention in which P is Y, Y is -CO- and R4 is aryl or
heteroaryl may be prepared, for example, by a Friedel-Crafts reaction between
a
compound of formula (XV)
R4-H (~)
wherein R4 is aryl or heteroaryl, and a compound of formula (XVI)
~NR1R2 (XVI)
L VZ
wherein L is a hydroxy group, a group OR wherein R is alkyl, or a halogen,
for example chlorine, and Z, V, R, and RZ are as defined above. The reaction
can be
performed under conventional conditions, in the presence of a catalyst such as
A1C13.
Examples of such reactions are described in section 1-15 of "Advanced Organic
Chemistry", 3'd Edition, by Jerry March.
The compounds of formulae (XV) and (XVI) are known compounds or may
be prepared by analogy with known methods.
Compounds in which P is -Y- or -XY- and in which X, Y and R4 are as
defined above may be prepared, for example, by reacting a compound of formula
(XVII)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-3 S-
Ra~Y~ L
wherein R4 is as defined above, Y~ is -U- or -X-U-, and L is a hydroxy group
or a leaving group, for example a halogen atom, with an organometallic
compound of
formula (XVIII)
M-B-NRIRZ (XVIII)
wherein B is -V-Z- wherein V and Z are as defined above, R1 and RZ are as
defined above and M is a metal-containing moiety such as Li or -MgX wherein X
is a
halogen atom such as bromine.
The reaction can be carried out under conventional conditions. Preferably, M
in the formula (XVIII) is Li. When M in the formula (XVIII) is -MgX, it may be
necessary to conduct the reaction at around -78 °C and to use a large
excess of the
compound of formula (XVII).
The compounds of formula (XVII) are known compounds or may be prepared
by analogy with known methods. The compounds of formula (XVIII) are also
known compounds or may be prepared by analogy with known methods. For
example, compounds of formula (XVIII) in which M is Li can be prepared by
reacting a corresponding compound of formula Br-B-NR1R2 with lithium or with
magnesium.
In some cases, it may be necessary to protect the -NR1R2 group during the
synthesis of the compounds of formula (XVIII) or during the reaction between
the
compounds of formulae (XVIII) and (XVII). This can be done by standard
techniques.
Compounds of the invention in which P is -Y-W- or -XYW-, wherein Y is -
UV- and -V- is -(C,-C6 alkyl)-, can be made, for example, by reacting a
compound of
formula (IXX)
R4 P-L (IXX)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-36-
wherein R4 and P are as defined above and L is a leaving group such as a
halogen atom or a triflate group, with a compound of formula (XX)
S HW-ZNRIRZ (XX)
wherein W, Z, R~ and Rz are as defined above. The reaction can be conducted
under conventional conditions. Typically, it is conducted in the presence of a
base.
If necessary, the NRiR2 group can be protected during the reaction by
conventional
means.
The compounds of formulae (IXX) and (XX) are knowN compounds, or may
be prepared by analogy with known methods. For example, the compounds of
formula (IXX) can be prepared by reacting a corresponding compound of formula
R4-P-OH with triflic anhydride or PCIs.
1 S Compounds in which P is a direct bond can be prepared by conventional
synthetic techniques.
A compound of the invention can, of course, be converted to a different
compound of the invention by standard functional group interconversions known
to
those of skill in the art. For example, a compound of the invention in which U
is
-CO- can be converted to a compound of the invention in which U is -C(=NR)- by
reaction with a compound of formula RNH2. Suitable such reactions are
described in
section 6-14 of "Advanced Organic Chemistry" 3~d Edition, by Jerry March.
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds of formula (I) may be
prepared by salifying a compound of formula (I) with an appropriate acid or
base.
The compounds of the invention are activators of sGC. They can be used as
selective sGC activators. A compound of the invention can therefore be used as
a
vasodilator or to inhibit platelet aggregation. It can be used for the
treatment or
prevention of peripheral vascular diseases such as hypertension, angina
pectoris,
arteriosclerosis, or for the treatment or prevention of glaucoma,
preeclampsia,
Raynaud's Syndrome, stroke or erectile dysfunction. Further, the compounds of
the
invention are effective in improving ocular blood flow. They can therefore be
used
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-3 7-
in the treatment and prevention of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). For
example, they can be used in the treatment and prevention of non-exudative or
exudative AMD. They can also be used in the treatment and prevention of
neovascular or non-neovascular AMD.
Conditions attributable to down regulation of sGC can thus be alleviated.
Accordingly, the present invention also provides a compound of formula (I),
as defined above, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use in
the
treatment of the human or animal body, wherein R,, Rz, Z, R3, Y, X and RQ are
as
defined above.
The compounds of the invention may be administered in a variety of dosage
forms. Thus, they can be administered orally, for example as tablets, troches,
lozenges, aqueous or oily suspensions, dispersible powders or granules. The
compounds of the invention may also be administered parenterally, either
subcutaneously, intravenously, intramuscularly, intrasternally, transdermally
or by
infusion techniques. The compounds may also be administered as suppositories.
A compound of the invention is typically formulated for administration with a
pharmaceutically acceptable Garner or diluent. For example, solid oral forms
may
contain, together with the active compound, diluents, e.g. lactose, dextrose,
saccharose, cellulose, corn starch or potato starch; lubricants, e.g. silica,
talc, stearic
acid, magnesium or calcium stearate, and/or polyethylene glycols; binding
agents;
e.g. starches, arabic gums, gelatin, methylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose
or
polyvinyl pyrrolidone; disaggregating agents, e.g. starch, alginic acid,
alginates or
sodium starch glycolate; effervescing mixtures; dyestuffs; sweeteners; wetting
agents, such as lecithin, polysorbates, laurylsulphates; and, in general, non-
toxic and
pharmacologically inactive substances used in pharmaceutical formulations.
Such
pharmaceutical preparations may be manufactured in known manner, for example,
by
means of mixing, granulating, tabletting, sugar-coating, or film coating
processes.
Liquid dispersions for oral administration may be syrups, emulsions and
suspensions. The syrups may contain as. carriers, for example, saccharose or
saccharose with glycerine and/or mannitol and/or sorbitol.
Suspensions and emulsions may contain as carrier, for example a natural
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-3 8-
gum, agar, sodium alginte, pectin, methylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose, or
polyvinyl alcohol. The suspensions or solutions for intramuscular injections
may
contain, together with the active compound, a pharmaceutically acceptable
carrier,
e.g. sterile water, olive oil, ethyl oleate, glycols, e.g. propylene glycol,
and if desired,
a suitable amount of lidocaine hydrochloride.
Solutions for intravenous or infusions may contain as carrier, for example,
sterile water or preferably they may be in the form of sterile, aqueous,
isotonic saline
solutions.
A therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention is
administered to a patient. A typical daily dose is from about 0.1 to 50 mg per
kg of
body weight, according to the activity of the specific compound, the age,
weight and
conditions of the subject to be treated , the type and severity of the disease
and the
frequency and route of administration. Preferably, daily dosage levels are
from 5 mg
to2g.
The Examples which follow illustrate the invention. ,
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-39-
EXAMPLE S
The synthesis of some of the compounds of the invention is detailed below.
Examines 1 to 69
S The aryl acid (different for each reaction) (0.1 mmol), 3-(dimethylamino)-
propylamine (10 mg, 0.1 mmol), N, N (diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin
(PS-DIEA), (86.0 mg, 0.3 mmol, loading 3.5 mmol/g) and O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-
yI)-N, N, N, N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HATU) (38 mg, 0.1 mmol)
were shaken under nitrogen in anhydrous acetonitrile (4 mL) and heated to 50
°C for
S hours. After this time the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature.
Tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (65 mg, 0.3 mmol) was then added and the
reaction mixture was shaken under nitrogen for 18 hours. Macroporous
triethylammonium methylpolystyrene carbonate resin (MP-carbonate), (610 mg,
1.96
mmol, loading 3.18 mmol/g) was then added and the reaction mixture was shaken
under nitrogen for a further 48 hours. The reactions were then filtered
through filter
syringes into vials and washed with methanol. The solvent was removed on a
vacuum concentrator and each product was weighed and analysed by LC-MS.
This method was used to synthesise the following compounds. The
molecular weight, purity and yield of the compounds synthesised is shown in
Table
1.
Example No. Compound
1 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(4-fluorobenzoyl]-benzamide
(CFM2262)
2 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-phenoxy-benzamide
(CFM2263)
3 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-phenoxy-benzamide
(CFM2264)
4 2-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-nicotinamide
(CFM2265)
5 4'-n-Propyl-biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide (CFM2266)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-40-
6 2-[1-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-methanoyl]-cyclohexanecarboxylic
acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide(CFM2267)
7 5-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-furan-2-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2268)
8 2-[1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
(CFM2269)
9 2-Phenyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide (CFM2331)
10 2-[1-(4-Chloro-3-nitrobenzoyl)]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
benzamide (CFM2332)
11 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-pyren-1-yl-acetamide
(CFM2333)
12 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(3-methyl-benzo[b]thiophen-
2-yl)-methanoyl]-benzamide (CFM2320)
13 4-Chloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2-phenoxy-benzamide
(CFM2321)
14 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(4-phenoxy-phenyl)-
propionamide (CFM2322)
15 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(1-trifluoromethyl-1,3,4,9-
tetrahydro-b-carbolin-2-yl)-methanoyl]-benzamide
(CFM2334)
16 1-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-2,5-dimethyl-1-pyrrole-3-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2335)
17 2- { 1-[(3-Dimethylamino-propylcarbamoyl)-methyl]-
cyclopentyl}-N-(4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-acetamide
(CFM2336)
18 8-[2-(3-Dimethylamino-propylcarbamoyl)-phenylsulfanyl]-
naphthalene-1-carboxylic acid methylamide (CFM2337)
19 3-Methyl-5-(4-methyl-[1,2,3]thiadiazol-5-yl)-1-(4-
trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-1H pyrazole-4-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2338)
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-41-
20 6,8-Di-tert-butyl-4-oxo-4H chromene-2-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2339)
21 2-(Furan-2-yl)-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide (CFM2340)
22 Biphenyl-2,2'-dicarboxylic acid 2'-[(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide]-2-[(4-fluoro-phenyl)-amide] (CFM2342)
23 3-Phenyl-pentanedioic acid (3-chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-amide
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2343)
24 2-(3,4-Dimethoxy-phenyl)-6-methyl-quinoline-4-carboxylic
acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2344)
25 6-Bromo-(2-thiophen-3-yl)-quinoline-4-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2345)
26 3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-4-cyano-S-isobutylsulfanyl-thiophene-2-
carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM2346)
27 4-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-3-nitro-
benzamide (CFM2347)
28 6-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-cyclohex-3-ene carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2348)
29 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-(2-phenylsulfamoyl-
phenylsulfanyl)-benzamide(CFM2349)
30 2'-Fluoro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-carboxylic acid
(3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide (CFM2350)
31 2-Benzylsulfanyl-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide
(CFM23 51 )
32 Pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid 2-[(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide] 3-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-naphthalen-1-yl)-amide]
(CFM2352)
33 2-[(3,5-Dichloro-phenylcarbamoyl)-methylsulfanyl]-N-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-nicotinamide (CFM2432)
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-42-
34 2-(3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thiazole-4-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2368)
35 2-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid
(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2369)
36 5-Chloro-1-(2,4-dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-
carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM2370)
37 1-(2,4-Dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic
acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2371)
S 38 S-Chloro-1-(3,4-dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-
carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM2372)
39 1-(3,4-Dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-carboxylic
acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2373)
40 5-Chloro-1-(2,6-dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-3-
carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM2388)
41 1,1-Dimethyl-indan-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide (CFM2389)
42 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(4-ethyl-phenyl)-methanoyl]-
benzamide (CFM2390)
43 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-phenyl)-
butyramide (CFM2391 )
44 2-[3-(3,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-ureidoJ-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
benzamide (CFM2392)
45 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4-triphenyl-butyramide
(CFM2393)
46 5-(4-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-[1,2,3]thiadiazole-4-carboxylic
acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2394)
47 2-(3-Chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2-ylsulfanyl)-3-methyl-
3H imidazole-4-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM2395)
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-43-
48 2-(2-Chloro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-[1,3]-thiazole-4-
carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM2396)
49 2-(2,3-Dihydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic
acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2397)
50 2-(2,3-Dichloro-phenyl)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2398)
51 4-[4-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-thiazol-2-yl]-N-(3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-benzamide (CFM1899)
52 5-(4-Fluoro-phenyl)-thiophene-2-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2399)
53 4-Methyl-2-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-thiazole-5-carboxylic
acid
(3-dilnethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2400)
54 3-(4-tent-Butyl-benzyloxy)-thiophene-2-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2401 )
55 4-Oxo-3-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-3,4-dihydro-phthalazine-1-
carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM2402)
56 2-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-4-oxo-4-
phenyl-butyramide (CFM2403)
57 5-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-1-phenyl-1H pyrazole-3-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2404)
58 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-(4-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl)-
benzamide (CFM2405)
59 1-(2,4,5-Trichloro-phenylsulfonyl)-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic
acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2406)
60 3-(3,4-Dichloro-benzylsulfanyl)-thiophene-2-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2407)
61 5-Chloro-3-phenyl-1H indole-2-carboxylic acid
(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2408)
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-44-
62 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(4-fluoro-benzyl)-1H
indol-3-
yl]-acetamide (CFM2409)
63 2-Phenyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxylic
acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2410)
64 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-(7-ethyl-lI~ indol-3-yl)-4-oxo-4-
phenyl-butyramide (CFM2411)
65 Phenyl-trifluoromethyl-thieno[3,2-b]pyridine-2-carboxylic
acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2412)
66 3-(4-Nitro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenoxy)-thiophene-2-carboxylic
acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2428)
67 2-(5-Chloro-1-methyl-3-phenyl-1H pyrazol-4-ylmethylsulfanyl)-
N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide (CFM2429)
68 2-(4-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-
quinazoline-7-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
(CFM243 0)
69 N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-[4-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-
pyrimidin-2-ylsulfanylmethyl]-benzamide (CFM2431)
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-45-
Table 1
Example Molecular LC-MS Results % Yield % Yield
Weight Purity (mg)
1 328.22 62.1 25.5 40
2 298.22 86.6 23.7 41
3 298.22 86.1 32.1 55
4 333.64 96.6 33 51
5 324.3 100 35.1 55
6 395.17 60.1 33.5 43
7 340.18 95.7 14.2 21
g 344.68 58.5 25.2 37
12 380.35 90.5 32.2 43
13 332.67 73.8 24.5 38
14 326.28 96.1 21.2 33
9 333.27 94.0 22.6 35
10 389.68 94.4 43.8 57
11 344.3 44.0 46.1 68
15 472.35 96.2 50.9 >100
16 333.7 87.0 24.3 74
17 429.35 71.6 30.1 71
1 g 421.4 52.4 28.7 69
19 468.34 72.4 28.1 61
20 386.37 68.0 10.8 28
21 323.23 92.9 12.8 40
22 350.1 90.8 22.5 65
23 415.8 52.0 17 41
24 407.35 90.5 15.5 38
25 418.19 69.5 13.1 32
26 435.88 95.9 21.3 43
27 377.67 83.6 12.8 33
2g 355.15 59.0 16.8 48
29 469.46 72.9 21.9 74
30 300.24 93.1 11.5 35
31 328.31 63.4 16 34
32 381.32 57.0 17.1 45
34 357.24 97.3 14.1 40
35 323.68 96.9 17.7 55
36 416.57 94.1 10.1 25I
37 382.13 86.0 14 37
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-46-
38 416.57 88.9 12.8 31
39 382.13 64.5 10.3 27
40 416.57 100 22.6 55
41 274.24 97.4 12.3 45
42 338.28 89.0 16.7 50
43 290.28 81.6 15.7 55
44 409.15 91.9 12.1 30
45 414.38 41.0 18.8 47
46 356.73 86.6 20.3 58
47 421.71 79.9 14.3 34
48 391.68 90.9 25 72
49 331.27 91.2 24.5 20
50 358.13 34.2 16.3 75
52 306.24 96.4 18.3 44
53 371.26 97.4 27.6 60
54 374.38 94.8 75
55 418.26 96.7 26.2 71
56 372.73 34.4 21 51
57 382.73 100 19.9 54
58 365.34 100 26.3 69
59 442.63 96.6 16.2 45
60 403.23 100 27.8 63
61 355.71 100 19.9 50
62 367.71 100 8.9 25
63 322.25 54.6 26.2 66
64 405.38 97.8 21.2 53
65 407.3 100 11.5 50
66 417.24 79.5 19.7 48
442.85 59.7 5.1 12
68 444.82 32.7 18.9 43
69 436.41 86.3 23.6 55
33 441.22 40.3 18.2 42
Examples 70 to 99
The aryl acid (different for each reaction) (0.1 mmol) was stirred under
nitrogen in
anhydrous toluene (2 mL) and heated to 50 °C. Triethylamine (10 mg, 0.1
mmol)
dissolved in 1 mL of anhydrous toluene was then added. The temperature was
raised
to 80 °C and diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA), (27.0 mg, 0.1 mmol) was
added.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-47-
The reaction was kept at this temperature for 1 hour then cooled to room
temperature
while still stirnng under nitrogen.
3-(Dimethylamino)-propylamine (10 mg, 0.1 mmol) was added and the whole
mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. Tetrafluorophthalic
anhydride
(64.7 mg, 0.3 mmol) was added and the reaction stirred for a further 18 hours.
Following this 20 equivalents of macroporous triethylammonium
methylpolystyrene
carbonate resin (MP-carbonate), (610 mg, 1.96 mmol) was added and the
reactions
were stirred for another 24 hours. Each reaction was then filtered through
filter
syringes into vials and washed with methanol. The solvent was removed using a
vacuum concentrator and each product was weighed and analysed by LC-MS.
This method was used to synthesise the following compounds. The
molecular weight, purity and yield of the compounds synthesised is shown in
Table
2.
Examples Compounds
No.
70 1-(3-DimethyIamino-propyl)-3-(2-phenoxy-phenyl)-urea
(CFM2260)
71 1-[2-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-pyridin-3-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylaminopropyl)-urea (CFM2261 )
72 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-pyren-1-ylmethyl-urea
(CFM2317)
73 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[(1R,2R)-5-phenyl-2-(1-phenyl-
methanoyl)-cyclohexyl]-urea (CFM2318)
74 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[2-(4-phenoxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-
urea (CFM2319) .
75 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[3-methyl-5-(4-methyl-
[ 1,2,3]thiadiazol-5-yl)-1-(4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-1
H-
pyrazol-4-yl]-urea (CFM2353)
76 2'-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-biphenyl-2-carboxylic
acid (4-fluoro-phenyl)-amide (CFM2354)
77 N-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-phenyl)-4-[3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
ureido]-3-phenyl-butyramide (CFM2355)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-48-
78 1-[4-(4-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-thiophen-3-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2356)
79 1-[2-(3,4-Dimethoxy-phenyl)-6-methyl-quinolin-4-yl]-3-(4-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2357)
80 1-(6-Bromo-2-thiophen-3-yl-quinolin-4-yl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-urea (CFM2358)
81 1-[3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-4-cyano-5-isobutylsulfanyl-thiophen-2-
yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2359)
82 1-[6-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-cyclohex-3-enyl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2360)
83 1-(2-Benzylsulfanyl-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
(CFM2361 )
84 2-{2-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-phenylsulfanyl}-N-
phenyl-benzenesulfonamide (CFM2362)
85 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2'-fluoro-biphenyl-4-yl)-urea
(CFM2363)
86 N-(3,S-Dichloro-phenyl)-2-{3-[3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
ureido]-pyridin-2-ylsulfanyl}-acetamide (CFM2364)
87 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3- {2-[ 1-( 1-trifluoromethyl-1,3,4,9-
tetrahydro-b-carbolin-2-yl)-methanoyl]-phenyl}-urea
(CFM2366)
88 8-{2-[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-ureido]-phenylsulfanyl}-
naphthalene-1-carboxylic acid methylamide (CFM2367)
89 1-[ 1-(3,4-Dichloro-benzyl)-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridin-3-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2413)
90 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(3-oxo-1,2,3-triphenyl-propyl)-
urea (CFM2414)
91 1-[5-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-1-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-1H
pyrazol-3-
yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM241
S)
92 1- {4-[4-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-thiazol-2-yl]-phenyl}
-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2416)
93 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[5-(4-fluoro-phenyl)-thiophen-2-
yl]-urea (CFM2417)
94 1-[3-(4-tent-Butyl-benzyloxy)-thiophen-2-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2418)
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-49-
95 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-[4-(4-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl)-
phenyl]-urea (CFM2419)
96 1-[3-(3,4-Dichloro-benzylsulfanyl)-thiophen-2-yl]-3-(3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-urea (CFM2420)
97 1-[2-(S-Chloro-1-methyl-3-phenyl-1H pyrazol-4-
ylinethylsulfanyl)-phenyl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
(CFM2433)
98 1-[2-(4-Chloro-benzylsulfanyl)-3-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-
quinazolin-7-yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
(CFM2434)
99 1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-{4-[4-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-
pyrimidin-2-ylsulfanylmethyl]-phenyl}-urea
(CFM2435)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-5 0-
Table 2
ExampleMolecular Weight LC-MS Results % Yield % Yield
of Product Product (mg)
70 313.22 57.53 51 83.06
71 348.64 56.3 41.4 60.6
72 359.3 58.85 108.7 >100
73 407.38 42.59 75.1 94.1
74 341.28 54.28 52.1 77.9
87 487.35 53.05 29.4 61.44
88 436.4 53.98 63.6 >100
75 483.34 42 41.8 87.45
76 434.34 76.93 26 60.48
77 430.8 31.66 34.5 80.98
78 369.76 74.31 36.3 99.18
79 422.35 26.75 36.7 87.79
80 433.19 69.82 32.4 75.55
81 450.88 32 27.3 61.31
82 370.15 38.84 29.1 79.42
83 343.31 100 32.2 94.46
84 484.46 36.4 15.8 32.94
85 315.21 56.84 23.3 74.68
86 456.22 38.85 58.6 >100
89 397.13 ~ 32.11 46.1 >100
90 429.38 35.0 51.0 >100
91 466.62 51.18 45.7 98.6
92 414.78 70.68 65.8 >100
93 321.24 48.83 20.5 65.12
94 389.38 44.0 41.8 >100
95 380.34 49.46 33.5 89.88
96 418.23 27.0 32.8 80
97 457.85 52.98 47.1 >100
98 459.82 60.47 65.9 >100
99 451.41 55.72 19.9 44.53
Example 100
1-(4-Bromophenyl)-3-(3-(1-pyrrolidinyl) propyl) urea (CFM2138)
4-Nitrophenyl chloroformate (87.0 mg, 0.436 mmol), 4-bromoaniline (50.0 mg,
0.29
mmol) and triethylamine (44.0 mg, 0.436 mmol) were refluxed under nitrogen in
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-51-
anhydrous THF (20 mL) for 18 hours. After this time 1-(3-aminopropyl)
pyrrolidine
(55.O mg, 0.436 mmol) was added and the whole reaction mixture was refluxed
for a
further 2 hours.
The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and tetrafluorophthalic
anhydride (191.0 mg, 0.87 mmol) was added. The reaction was stirred at room
temperature under nitrogen for 1 hour, then 6 equivalents of tris-(2-
aminoethyl)amine
polystyrene resin (PS-trisamine), (500 mg, 1.74 mmol, loading 3.5 mmol/g) was
added and the reaction stirred for 2 hours. Following this 20 equivalents of
Dowex
AG1 resin (OH- form) (1.68 g, 5.8 mmol, loading 3.45 mmol/g) was added and the
mixture was stirred for 18 hours at room temperature.
It should be noted that the Cl~ form of the resin was converted to the OH-
form by washing with 20 volumes of 1M NaOH solution, followed by distilled
water
until the washings are neutral. Another 20 equivalents of the resin was added
after
this time and the reaction was stirred for a further 2 hours. The reaction
mixture was
then filtered and the solvent removed using a vacuum concentrator.
Example 101
1-(4-Bromophenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea (CFM2134)
Prepared as in Example 100 using 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (77.2 mg, 0.38
mmol), 4-bromoaniline (30.0 mg, 0.174 mmol) and triethylamine (38.8 mg, 0.38
mmol) to form the intermediate followed by 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine (26.6
mg, 0.26 mmol) to form the desired product. Work-up as in Example 100. The
crude product was purified by flash chromatography using MeOH/CHC13 (40:60).
Example 102
3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-methyl-1-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea (CFM2139)
Prepared as in Example 100 using 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (87.0 mg, 0.436
mmol), 4-bromoaniline (50.0 mg, 0.29 mmol) and triethylamine (44.0 mg, 0.436
mmol) refluxed for 5 hours in anhydrous THF (20mL) to form the intermediate.
Then N,N,N-trimethyl-1,3-propanediamine (50.5 mg, 0.436 mmol) was added and
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-52-
the reaction mixture refluxed for 18 hours to form the title compound. Work-up
as in
Example 100.
Example 103
1-(3-Phenyl-5-methoxy phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea (CFM2148)
Prepared as in Example 100 using 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (45.5 mg, 0.226
mmol), S-phenyl-o-anisidine (30.0 mg, 0.1 S 1 mmol) and triethylamine (22.8
mg,
0.226 mmol) refluxed in anhydrous THF (20 mL) for 18 hours to form the
intermediate followed by 3-(dimethylamino)-propylamine (23.1 mg, 0.226 mmol)
and refluxed for a further 5 hours to form the title compound. Work-up as in
Example 100.
Example 104
3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea (CFM2200)
Prepared as in Example 100 using 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (830 mg, 4.12
mmol),
4-chloroaniline (350 mg, 2.75 mmol) and triethylamine (416 mg, 4.12 mmol)
refluxed for 7 hours in anhydrous THF (30mL) to form the intermediate. Then
N,N,N'-trimethyl-1,3-propanediamine (478 mg, 4.12 mmol) was added and the
reaction mixture refluxed for 18 hours to form the title compound. Work-up as
in
Example 100.
Example 105
1-(3-Nitrophenyl)-1-benzyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea (CFM2270)
Prepared as in Example 100 using 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (66.0 mg, 0.328
mmol), N-benzyl-3-nitroaniline (50.0 mg, 0.219 mmol) and triethylamine (33.0
mg,
0.328 mmol) refluxed in anhydrous THF (20 mL) for 6 hours to form the
intermediate followed by 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine (44.6 mg, 0.438 mmol)
and
refluxed for a further 36 hours to form the title compound. Work-up as in
Example
100.
Example 106
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-53-
1-Benzyl-1-(4-methyl-3-pyridinyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea (CFM2271)
Prepared as in Example 100 using 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (76.0 mg, 0.378
mmol), 2-benzylamino-4-methyl-pyridine (50.0 mg, 0.25 mmol) and triethylamine
(38.0 mg, 0.378 mmol) refluxed in anhydrous THF (20 mL) for 5 hours to form
the
intermediate followed by 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine (38.0 mg, 0.378 mmol)
and
refluxed for a further 18 hours to form the desired product. Work-up as in
Example
100. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography using a gradient
from
to 50 % MeOH (in CHC13) to give the title compound.
10 Example 107
1-Methyl-1-(3,5-bistrifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)urea
(CFM2311)
Prepared as in Example 100 using 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (62.0 mg, 0.308
mmol), N-methyl-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)aniline (50.0 mg, 0.206 mmol) and
triethylamine (31.0 mg, 0.308 mmol) refluxed in anhydrous THF (20 mL) for 5
hours
to form the intermediate followed by 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine (31.5 mg,
0.308
mmol) and refluxed for a further 18 hours to form the desired product. Work-up
as
in Example 100. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography using a
gradient from 10 to 40 % MeOH (in CHC13) to give the title compound.
Example 108
1-(2-Phenacyl-4-chorophenyl)-1-methyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) urea
(CFM2310)
4-Nitrophenyl chloroformate (61.5 mg, 0.31 mmol), 5-chloro-2-(methylamino)-
benzophenone (50.0 mg, 0.20 mmol) and triethylamine (30.80 mg, 0.31 mmol) were
refluxed for 5 hours in anhydrous THF (20 mL) as in Example 100 to form the
intermediate. Then 3-(dimethylamino)-propylamine (32.0 mg, 0.31 mmol) was
added and the mixture was refluxed for a further 5 hours to form the desired
product.
Work-up as in Example 100. The crude product was purified by flash
chromatography using a gradient from 10 - 40% MeOH (in CHC13) to give the
title
compound.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-54-
Example 109
1-(2-Chloro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) urea
(CFM2421 )
4-Nitrophenyl chloroformate (77.0 mg, 0.39 mmol), 4-amino-3-chloro-
benzotrifluoride (50.0 mg, 0.26 mmol) and triethylamine (38.0 mg, 0.39 mmol)
were
refluxed for 18 hours in anhydrous THF (20 mL) as in Example 100 to form the
intermediate. Then 3-(dimethylamino)-propylamine (38.0 mg, 0.39 mmol) was
added and the mixture was refluxed for a further 5 hours to form the desired
product.
Work-up as in Example 100. The crude product was purified by flash
chromatography using a gradient from 10 - 40% MeOH (in CHC13) to give the
title
compound.
Example 110
1-(3-Fluoro-5-tri~luoromethylphenyl)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) urea
(CFM2422)
4-Nitrophenyl chloroformate (84.0 mg, 4.19 mmol), 3-amino-5-
fluorobenzotrifluoride (50.0 mg, 0.28 mmol) and triethylamine (42.0 mg, 4.19
mmol) were refluxed for 18 hours in anhydrous THF (20 mL) as in Example 100 to
form the intermediate. Then 3-(dimethylamino)-propylamine (42.0 mg, 4.19 mmol)
was added and the mixture was refluxed for a further 5 hours to form the
desired
product. Work-up as in Example 100. The crude product was purified by flash
chromatography using a gradient from 10 - 40% MeOH (in CHC13) to give the
title
compound.
Example 111
1-(3-N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-benzylamino)-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) urea
CFM2374
4-Nitrophenyl chloroformate (3.13 g, 15.54 mmol), 3-amino-1-(N-tert-butoxy-
carbonyl)benzylamine (2.30 g, 10.36 mmol) and triethylamine (1.56 g, 15.54
mmol)
was refluxed for 18 hours in anhydrous THF (100 mL) as in Example 100 to form
the intermediate. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine (1.58 g, 15.54 mmol) was
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-5 5-
added and the mixture was refluxed for a further 5 hours to form the desired
product.
Work-up same as in Example 100. The crude product was purified by flash
chromatography using a gradient from 10 - 40% MeOH (in CHCI3) to give the
title
compound.
Example 112
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-[1-(4-fluorobenzoyl]-benzamide (CFM2262)
2-(4-Fluorobenzoyl)benzoic acid (1.25 g, 5.12 mmol), N,N (diisopropyl)amino-
methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (4.30 g,15.36 mmol), and O-(7-
azabenzotriazol-1-
yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HATU) (1.95 g, 5.12 mmol)
was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (50 mL) at room temperature under
nitrogen for 5
minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine (0.52 g, 5.12 mmol) was added and
the
temperature was taken up to 50 °C and the mixture was left to stir at
this temperature for
18 hours. The mixture was allowed to cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride
(3.40 g,
15.36 mmol) was added and the mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. To the
mixture
was added water (5 mL) and the solvent was removed on a vacuum concentrator.
The
crude product was purified by flash chromatography using a gradient from 5 to
10%
MeOH (in CHC13) and the title compound was isolated as a white solid 0.36 g,
22
yield (mp 84 - 85 °C).
Example 113
2-(1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl]-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide (CFM 2269)
2-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-benzoic acid (1.25 g, 4.80 mmol), N,N (diisopropyl)amino-
methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (4.00 g, 14.38 mmol), and O-(7-
azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HATU)
(1.82 g, 4.80 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (50 mL) at room
temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine
(0.50 g, 4.80 mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C
and the
mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was
allowed to
cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (3.20 g, 14.40 mmol) was added and the
mixture was left to stir for 5 hours. The workup and purification was the same
as
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-56-
described in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a white solid
0.68g,
41 % yield (mp 108-110 °C).
Example 114
5-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-1-phenyl-1H pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide (CFM2404)
5-(4-Chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid (1.10 g, 4.09 mmol),
N,N (diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (3.40g, 12.27 mmol),
and O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
(HATU) (1.56 g, 4.09 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (SO mL) at
room
temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine
(0.42 g, 4.09 mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C
and the
mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was
allowed to
cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (2.70 g, 12.27 mmol) was added and the
mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. ' The workup and purification was the
same
as described in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a white solid
0.62g, 44 % yield (mp 165 °C).
Example 115
5-Chloro-3-phenyl-1H indole-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-
amide (CFM2408)
5-Chloro-3-phenyl-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid (1.00 g, 3.68 mmol), N,N
(diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (3.00 g, 11.04 mmol),
and
O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
(HATU) (1.49 g, 3.68 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (SO mL) at
room
temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine
(0.38 g, 3.68 mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C
and the
mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was
allowed to
cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (2.43 g, 11.00 mmol) was added and the
mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. The workup and purification was the
same
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-5 7-
as described in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a white solid
0.24
g, 18.5 % yield (mp 143-144 °C).
Example 116
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-2-(2-phenylsulfamoyl-phenylsulfanyl)-
benzamide(CFM2349)
2-(2-Phenylsulfamoyl-phenylsulfanyl)-benzoic acid (1.10 g, 2.60 mmol), N,N
(diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (2.18g, 7.78 mmol), and
O-
(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HATU)
(0.98 g, 2.6 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (50 mL) at room
temperature
under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine (0.26 g, 2.60
mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C and the
mixture was left
to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was allowed to cool and
tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (1.70 g, 7.78 mmol) was added and the mixture
was
allowed to stir for 5 hours. The workup and purification was the same as
described
in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a white solid (0.1 g, 9 %),
(mp
75-76 °C).
Example 117
2-Benzylsulfanyl-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide (CFM2351)
2-Benzylsulfanyl-benzoic acid (1.00 g, 4.09 mmol), N,N (diisopropyl)amino-
methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (3.40 g, 12.27 mmol), and O-(7-
azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HATU)
(1.55 g, 4.09 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (50 mL) at room
temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine
(0.42 g, 4.09 mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C
and the
mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was
allowed to
cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (2.60 g, 12.27 mmol) was added and the
mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. The workup and purification was the
same
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-58-
as described in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a white solid
0.41 g, 30.5 % yield (mp 85-86 °C).
Example 118
6,8-Di-tert-butyl-4-oxo-4H chromene-2-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-
propyl)-amide (CFM2339)
6,8-Di-tert-butyl-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylic acid (1.00 g, 3.31 mmol), N,N
(diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (2.78 g, 9.93 mmol), and
O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
(HATU) (1.25 g, 3.31 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (50 mL) at
room
temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine
(0.34 g, 3.31 mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C
and the
mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was
allowed to
cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (2.18 g, 9.93 mmol) was added and the
mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. The workup and purification was the
same
as described in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a white solid
(0.26g) in 20 % yield (mp 135-136 °C).
Example 119
3-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-4-cyano-5-isobutylsulfanyl-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid (3-
dimethylamino-propyl)-amide (CFM2346)
3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-cyano-S-isobutylsulfanyl-thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
(1.00 g,
2.84 mmol), N,N (diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (2.37 g,
8.53 mmol), and O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium
hexafluorophosphate (HATU) (1.08g, 2.84 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous
acetonitrile (50 mL) at room temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-
(dimethylamino)propylamine (0.3 g, 2.84 mmol) was added and the temperature
was
taken up to 50 °C and the mixture was left to stir at this temperature
for 18 hours.
The mixture was allowed to cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (1.87 g,
8.52
mmol) was added and the mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. The workup
and
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-59-
purification was the same as described in Example 112. The title compound was
isolated as a white oil/solid 0.3 g, 24 % yield.
Example 120
4-(4-Chloro-phenoxy)-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-3-vitro-benzamide
(CFM2347)
4--(4-Chlorophenoxy)-3-vitro-benzoic acid (1.00 g, 3.40 mmol), N, N
(diisopropyl)amino-methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (2.84 g, 10.20 mmol),
and
O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
(HATU) (1.29 g, 3.40 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (50 mL) at
room
temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine
(0.35 g, 3.40 mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C
and the
mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was
allowed to
cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (2.24 g, 10.20 mmol) was added and the
mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. The workup and purification was the
same
as described in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a yellow solid
(0.6
g) in 46.5% yield (mp 165-167 °C.
Example 121
N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-4-(4-phenyl-thiazol-2-yl)-benzamide (CFM2405)
4-(4-Phenyl-thiazol-2-yl)-benzoic acid (1.38 g, 4.91 mmol), N,N
(diisopropyl)amino-
methylpolystyrene resin (PS-DIEA), (3.84 g, 14.70 mmol), and O-(7-
azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N,N tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HATU)
(1.87 g, 4.91 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetonitrile (SO mL) at room
temperature under nitrogen for 5 minutes. Then 3-(dimethylamino)propylamine
(0.50 g, 4.91 mmol) was added and the temperature was taken up to 50 °C
and the
mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 18 hours. The mixture was
allowed to
cool and tetrafluorophthalic anhydride (3.24 g, 14.70 mmol) was added and the
mixture was allowed to stir for 5 hours. The workup and purification was the
same
as described in Example 112. The title compound was isolated as a white solid
(1.18
g) in 66% yield (mp 204-205 °C).
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-60-
Example 122
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2-phenoxyphenyl)-urea (CFM2260)
2-Phenoxybenzoic acid (1.50 g, 7.00 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous toluene (50
mL) at 50 °C under nitrogen. To this mixture was added triethylamine
(0.71 g, 7.00
mmol) and the temperature was increased to 80 °C at which stage
diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA) (1.92 g, 7.00 mmol) was added and the mixture
was left to stir at this temperature for 5 hours. After this period 3-
(dimethylamino)propylamine (0.71 g, 7.00 mmol) was added and the mixture was
left to stir at 80 °C overnight under nitrogen. The solvent was removed
on a vacuum
concentrator The residue was taken up in chloroform (100 mL) and washed with
1M
sodium hydroxide (2 x 50 mL). The organic fraction was washed with saturated
sodium chloride solution and then dried (NazS04). The solvent was removed on a
vacuum concentrator. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography
using a gradient from 5 to 10% MeOH (in CHC13) and the title compound was
isolated as a white solid (1.00 g ) in 46% yield (mp 126- 128 °C).
Example 123
1-[4-(4-Chloro-phenylsulfanyl)-thiophen-3-yl]-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea
(CFM2356)
4-(4-Chlorophenylsulfanyl)-thiophene-3-carboxylic acid (1.30 g, 4.80 mmol) was
stirred in anhydrous toluene (50 mL) at 50 °C under nitrogen. To this
mixture was
added triethylamine (0.48 g, 4.80 mmol) and the temperature was increased to
80 °C
at which stage diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA) (1.32 g, 4.80 mmol) was added
and
the mixture was left to stir at this temperature for 5 hours. After this
period 3-
(dimethylamino)propylamine (0.48 g, 4.80 mmol) was added and the mixture was
left to stir at 80 °C overnight under nitrogen. The solvent was removed
on a vacuum
concentrator. The residue was taken up in chloroform (100 mL) and washed with
1M sodium hydroxide (2 x 50 mL). The organic fraction was washed with
saturated
sodium chloride solution and then dried (Na2S04). The solvent was removed on a
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-61-
vacuum concentrator. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography
using a gradient from 5 to 10% MeOH (in CHCl3) and the title compound was
isolated as a white solid (0.50 g ) in 28% yield (mp 125-126 °C).
Example 124
1-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-(2'-fluoro-biphenyl-4-yl)-urea (CFM2363)
2-Fluoro-biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid (1.00 g, 4.63 mmol) was stirred in
anhydrous
toluene (50 mL) at 50 °C under nitrogen. To this mixture was added
triethylamine
(0.47 g, 4.63 mmol) and the temperature was increased to 80 °C at which
stage
diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA) (1.27 g, 4.63 mmol) was added and the mixture
was left to stir at this temperature for 5 hours. After this period 3-
(dimethylamino)propylamine (0.48 g, 4.63 mmol) was added and the mixture was
left to stir at 80 °C overnight under nitrogen. The solvent was removed
on a vacuum
concentrator. The residue was taken up in chloroform (100 mL) and washed with'
1M sodium hydroxide (2 x 50 mL). The organic fraction was washed with
saturated
sodium chloride solution and then dried (Na2S04). The solvent was removed on a
vacuum concentrator. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography
using a gradient from S to 10% MeOH (in CHCl3) and the title compound was
isolated as a orange oil (0.50 g ) in 34% yield.
Physical data for some of the compounds synthesised in the Examples is
given in Table 3.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-62-
TABLE 3: Physical Data
Example 'H NMR 8, CDC13, 300 MHz MS mp yield
101 7.28 (d, 2H, J= 8.7 Hz), 7.17(APCI) 73%
(d, 2H, J= 9.0 Hz), 302
3.22 (q, 2H, J= 5.9 Hz), 2.31[M+2H]'
(t, 2H, J= 6.2 Hz),
2.12 (s, 6H), 1.58 (quintet,
2H, J= 6.2 Hz)
100 7.31 - 7.27 (m, 2H), 7.16
- 7.19 (m, 2H), 3.26 (q, (APCI) 69%
328
2H, J = 6.0 Hz), 2.52 (t, [M+2H]+
2H, J = 6.4 Hz), 2.46 -
2.44 (m, 4H); 1.72 - 1.68
(m, 4H), 1.64 (t, 2H, J
= 6.2 Hz)
102 CD30D 7.37 (d, 2H, J= 9.0 (FAB) 314 85%
Hz), 7.29 (d, 2H, J= M+
8.7 Hz), 3.41 (t, 2H, J =
6.4 Hz), 2.95 (s, 3H),
2.37 (t, 2H, J = 6.9 Hz),
2.29 (s, 6H), 1.81
(quintet, 2H, J= 6.7 Hz)
103 8.31 (d, IH, J= 2.26 Hz), (FAB) 328 85%
7.62, (t, 2H, J= 7.16
Hz), 7.41 (t, 2H, J = 6.41 [M+1H]+
Hz), 7.33 - 7.29 (m,
1 H), 7.25 (dd, 1 H, J = 2.5
Hz, J = 8.5 Hz), 6.94
(d, 1 H, J = 8.67 Hz), 3.92
(s, 3H), 3.40 (q, 2H, J
= 5.9 Hz), 2.39 (q, 2H, J=
6.7 Hz), 2.18 (s, 6H),
1.74 - 1.65 (m, 2H)
104 9.86 (br s, IH), 7.26 (d, (FAB) 270 31%
2H, J= 9.0 Hz), 7.12 (d,
2H, J= 9.0 Hz), 3.31 (t, 2H, [M+1H]+
J= 5.8 Hz), 2.83 (s,
3H), 2.32 (t, 2H, J= 5.8 Hz),
2.22 (s, 6H), 1.69
(quintet, 2H, J= 5.8 Hz)
105 8.04 - 8.00 (m, 1H), 7.95 (EI) 356 26%
- 7.91 (m, IH), 7.45 - M+
7.35 (m, 2H), 7.25 - 7.I4
(m, 5H), 6.49 (br s, IH),
4.85 (s, 2H), 3.29 (m, 2H),
2.24 (t, 2H, J = 5.7
Hz), 1.81 (s, 6H), 1.54 (q,
2H, J= 5.7 Hz)
IO 106 acetone-d~ 8.42 (d, 1H, J= (APCI) 37%
4.9 Hz), 7.53 - 7.41 327
(m, 5H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 7.06 [M+1H]+
(d, 1H, J= 5.3 Hz),
5.48 (s, 2H), 3.68 (m, 2H),
3.04 (brs, 2H), 2.76 (s,
6H), 2.45 (s, 3H), 2.19 (m,
2H)
108 7.43 (d, 1H, J= 2.26 Hz), (APCI) 30%
7.31 - 7.15 (m, 7H), 374
6.72 (d, IH, J= 9.05 Hz), [M+1H]+
3.76 - 3.69 (m, 1H),
3.32 (s, 3H), 3.33 - 3.30
(m, 1H), 2.60 - 2.40 (m,
2H), 2.19 (brs, 6H), 1.78
- 1.63 (m, 2H)
107 7.68 (s, 2H), 7.63 (s, 1H), (APCI) 33%
6.77 (br s, 1H), 3.35 - 372
3.31 (m, 2H), 3.28 (s, 3H), [M+1H]+
2.64 - 2.52 (m, 2H),
2.23 (br s, 6H), I.80 - I.68
(m, 2H)
111 7.47 - 7.43 (m,2H), 7.35 (t, (FAB) 351 83%
1H, J= 7.9Hz), 7.06
(d, 1H, J= 7.53 Hz), 4.38 [M+1H]+
(d, 2H, J= 5.27 Hz),
4.05 - 3.85 (br s, 3H), 3.50
- 3.40 (m, 2H), 2.80
(t, 2H, J= 6.6 Hz), 2.56 (s,
6H), 1.92 (t, 2H, J=
6.2 Hz), 1.59 (s, 9H)
109 8.36 (d, 1H, J= 8.67 Hz), (EI) 323 24%
7.69 (s, 1H), 7.53 (d, M+
IH, J= 8.29 Hz), 3.08 (t,
2H, J= 7.73 Hz),
2.80 (s, 6H), 1.94 (2H, t,
J= 7.35 Hz), 1.31 (t,
2H, J = 7.16 Hz)
110 7.56 (br s, 1H), 7.51 (br (FAB) 308 35%
s, 1H), 6.97 (br d, 1H, J
= 8.29 Hz), 3.26 (t, 2H, J= [M+IH]+
6.78 Hz), 2.62 (t,
2H, J= 7.73 Hz), 2.44 (s,
6H), 1.79 (t, 2H, J=
7.53 Hz)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-63-
112 7.81 (d, IH, J = 6.41 Hz), EI 328 84- 44%
7.64 - 7.52 (m, 2H), [M]+
7.48 - 7.39 (m, 2H), 7.29 85C
(d, 1H, J = 6.78 Hz),
7.10 (t, 2H, J = 8.86 Hz),
3.65 - 3.56 (m, 1H),
3.21 - 3.11(m, 1H), 2.92 (t,
2H, J = 7.54 Hz),
2.69(s, 6H), 1.93 - 1.76 (m,
2H)
113 7.81 (d, 1H, J= 6.78 Hz), (APCI) 108- 41%
7.63 - 7.52 (m, 2H), 345
7.38 (s, 4H), 7.29 (d, 1H, [M]+ I 10C
J= 6.78 Hz), 3.65 - 3.56
(quintet, 1H, J= 7.06 Hz),
3.20 - 3.10 (quintet,
1H, J= 7.06 Hz), 2.92 (t,
2H, J= 7.35 Hz), 2.68
(s, 6H), 1.93 - 1.77 (m, 2H)
114 7.45 - 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.37 (APCI) 165C 44%
- 7.32 (m, 3H), 7.23 (d, 383 M+
2H, J = 8.67, Hz), 7.02 (s,
1 H), 3.50 (t, 2H, J =
6.40 Hz), 3.20 (t, 2H, J=
7.73, Hz), 2.91 (s, 6H),
2.08 - 1.99 (quintet, 2H,
J = 7.25 Hz)
115 7.57 - 7.38 (m, 7H), 7.22 (FAB) 356 143- 18.5
(dd, 1H, J = 8.67 Hz, J
= 1.89 Hz), 3.29 (t, 2H, J= [M]+ 144C
6.78 Hz), 2.19 (t, 2H,
J= 7.53 Hz), 2.16 (s, 6H),
1.60 (quintet, 2H, J=
7.25 Hz)
$ 116 8.02 (dd, 1H, J= 7.73 Hz, (APCI) 75- 9%
J= 1.7 Hz), 7.50 (dd, 470
1 H, J = 7.54 Hz, J = 1.51 [M]+ 76C
Hz), 7.41 - 7.11 (m,
9H), 7.01 (t, 2H, J = 6.97
Hz), 3.36 (t, 2H, J =
6.78 Hz), 2.42 (t, 2H, J =
7.91 Hz), 2.21 (s, 6H),
1.74 (quintet, 2H, J= 7.25
Hz)
117 7.43 - 7.20 (m, 9H), 4.16 (APCI) 85- 30.5
(s, 2H), 3.36 (t, 2H, J= 329 M+
6.78 Hz), 2.45 (t, 2H, J =
7.73 Hz), 86C
2.23 (s, 6H),
1.79 (quintet, 2H, J= 7.35
Hz)
118 8.05 (d, 1H, J = 2.64 Hz), (APCI) 135- 20%
7.89 (d, 1H, J= 2.26 387
Hz), 7.88 (s, 1H), 3.47 (t, [M]+ 136C
2H, J= 6.78 Hz), 2.44
(t, 2H, J = 7.72 Hz), 2.27
(s, 6H), 1.84 (quintet,
2H, J= 7.34 Hz), 1.57 (s,
9H), 1.39 (s, 9H)
119 7.54 (d, 2H, J = 8.66 Hz), (APCI) 24%
7.45 (d, 2H, J = 8.67 436
Hz), 3.20 (t, 2H, J = 6.79 [M]+
Hz), 3.07 (d, 2H, J =
7.15 Hz), 2.17 (s, 3H), 2.,14
(t, 2H, J = 7.92 Hz),
2.05 - 1.92 (m, 1H), 1.56
(quintet, 2H, J = 7.44
Hz), 1.09 (d, 6H, J = 6.78
Hz)
120 (CDCl3) 8.50 (d, 1H, J = 2.26(APCI) mp 46.5
Hz), 8.08 (dd, J 378
= 8.66 Hz, J= 2.26 Hz), 7.31 [M]+ 165-
(d, 2H, J= 9.04
Hz), 6.96 (d, 2H, J= 8.66 167C
Hz), 6.91 (s, 1H),
3.56 (q, 2H, J= 5.91 Hz),
3.07 (t, 2H, J= 6.60
Hz), 2.79 (s, 6H), 2.11 (quintet,
2H, J= 6.03
Hz)
121 8.16 (d, 2H, J= 8.67 Hz), (APCI) mp 66%
8.04 (d, 2H, J= 7.16 366
Hz ), 7.97 (d, 2H, J= 8.67 [M] 204-
Hz), 7.90 (s, 1H),
7.46 (t, 2H, J= 7.35 Hz), 205C
7.37 (d, 1H, J= 7.53
Hz), 3.50 (t, 2H, J= 6.78
Hz), 3.03 (t, 2H, J=
7.54 Hz), 2,77 (s, 6H), 2.00
(quintet, 2H, J=
7.07 Hz)
122 8.06 (dd, 1H, J= 8.11 Hz, (FAB) 314 mp 44%
J= 1.7 Hz), 7.34 (t, (M
2H, J= 8.11 Hz), 7.12 - 7.05 + H)+ 126-
(m, 2H), 6.98 -
6.91 (m, 3H), 6.82 (dd, 1H, 128C
J= 8.29 Hz, J=
1.51 Hz), 3.19 (t, 2H, J =
6.78 Hz), 2.26 (s, 6H),
1.73 - 1.63 (quintet, 2H,
J = 7.25 Hz)
SUBSTITUTE SHEET (RULE 26)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-64-
123 7.72 (d, 2H, J= 3.39 Hz), (FAB) 370 mp 28%
7.57 (d, 2H, J= 3.76 M+
Hz), 7.24 (d, 2H, J= 8.66 125-
Hz), 6.99 (d, 2H, J=
8.67 Hz), 3.16 (t, 2H, J= 126C
6.59 Hz), 2.32 (t, 2H,
J= 7.72 Hz), 2.22 (s, 6H),
1.64 (quintet, 2H, J=
7.25 Hz)
124 7.44 (bs, 4H), 7.31 - 7.11 (APCI) 35-
(m, 4H), 3.25 (t, 2H, J 316
= 6.78 Hz), 2.44 (t, 2H, J= [M+1H]+ 4%
7.72 Hz), 2.29 (s,
6H), 1.79 - I.69 (quintet,
2H, J= 7.25 Hz)
Activity Example 1
Compounds of the invention were assayed to determine their ability to
activate sGC. The assay employed was an enzyme immunoassay to measure changes
in cGMP. To perform the assay recombinant soluble Guanylate cyclase was added
to
1.1 mg/ml IBMX, 2.6 mg/ml GTP, 667 nM DeaNO and the test compound (10~M).
The mixture was then incubated at room temperature for 10 minutes. Compounds
were formulated in DMSO diluted in Tris HCl (pH 7.4) buffer and with a final
DMSO concentration of <0.5%.
To determine the amount of cGMP produced, the BiotrakTM cGMP enzyme
immunoassay system commercially available from AmershamTM was used.
The assay is based on the competition between unlabelled cGMP and a fixed
quantity of peroxidase labelled cGMP for a limited amount of cGMP specific
antibody. The peroxidase ligand that is bound to the antibody is immobilised
on
precoated microtitre wells. The amount of labelled cGMP is determind using a
one
pot stabilised substrate. The concentration of unlabelled cGMP in a sample is
determined by interpolation from a standard curve.
The results are shown in Tables 4 to 7. The results shown in Tables 6 and 7
relate to commercially available compounds.
Activi , Example 2
The ability of the compounds of the invention to inhibit platelet aggregation
was also determined. ICSO values were measured as set out below.
Materials
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-65-
Prostacyclin (PGIz ; ICN Pharmaceuticals, Oxford) in Tris (O.OSM, pH 9),
Sodium citrate solution, Tyrodes solution without calcium (140mM NaCI; 3mM
KCI; l2mM NaHC03; 0.4mM NaHZP04.H20; 2mM MgC12.6H20; 0.1% Glucose)
contains O.OSM Hepes, pH7.4. Collagen (collagenreagent Horm, Nycomed
S Arzneimittel GmbH, Munchen).
PGIZ dissolved in Tris buffer (O.OSM, pH9). Test compounds dissolved in
DMSO (at lOmM) and subsequent dilutions made in Tyrodes; final assay
concentration of DMSO did not exceed 0.1% (which is without effect on platelet
reactivity).
Platelet Preparation
Platelets prepared according to Vagas, J.R., Radomski, M. and Moncada, S.
The use of prostacyclin in the separation from plasma and washing of human
1 S platelets. PROSTAGLANDINS 1982; 23:6:929-945.
Briefly, fresh human blood was collected into tubes contaiung 1:9 sodium
citrate (3.I5%) and centrifuged immediately at 260g for 20 minutes to separate
the
red cells from the platelet rich plasma (PRP). The PRP was decanted and PGIZ
(0.3 ~g/mI) was added. The PRP was then centrifuged at 180g for 1 Omins to
sediment
the remaining red and white cells. The resulting PRP was decanted into new
tubes,
PGIZ (0.15~g/ml) added and centrifuged at 950 g for 10 mins to sediment the
platelets. The resultant platelet poor plasma (PPP) was discarded and the
platelet
pellet was resuspended in an equal volume of Tyrodes buffer by gently
pipetting up
and down. The suspension was centrifuged at 870 g for l Omins at 4 °C.
The
supernatant was discarded and the platelet pellet was resuspended in an equal
volume
of Tyrodes buffer as before. The platelets were counted (using a Coulter
Counter
model T540 (address)) and normalised to 250,OOOcells/pl using Tyrodes. The
resultant suspension was placed on ice for approximately 1 hour until use.
Platelet Assays
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-66-
Platelet aggregation was monitored using either a Chrono-Log model 560-CA
dual channel ormodel 570-4S four channel aggregometer (Chrono-Log Corp.,
Havertown, PA). Aggregation was analysed by using 0.5 mL aliquots of the
platelet
suspension at 37 °C using % light transmittance.
For each sample, baseline reading was established for a 3 min period,
followed by addition oftest compound or buffer. An ECso dose of collagen was
added 1 min later and the response measured 3 min after addition of collagen.
Data Analysis
The amplitude of each aggregatory response, normalised to the collagen
control, was used to plot dose-response curves. The concentration of drug that
inhibited collagen-induced platelet aggregation by SO% (ICS) was calculated
from
the dose-response curves.
The results are shown in Tables 4 to 7. The results shown in Tables 6 and 7
relate to
commercially available compounds.
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-67-
Table 4
ICSO for Inhibition
1 st Test cGMP. Change with of
xample I ~.M cpd (NO Platelet Aggregation
Donor Present), % of DEANO response(~M)
70 153.79 4
71 136.37 10+
72 135.49
73 143.35
74 158.0
75 163.88 10+
76 303.25 6
77 284.9 8
78 303.77 4
79 218.24 I O+
80 244.87 6.5
81 230.49 4.5
82 224.57
83 314.64 6
84 408.17 3.5
85 358.65 2
86 358.65 10+
87 336.16 10+
88 377.13 10+
89 10+
90 6
91 2.5
92 5
93 4
94 10+
95 10+
96 10+
97 9.5
98 IO+
99 5
101 199.21
100 135.7
102 273.17
103 ~ __ _ 8
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-68-
ICSO for Inhibition
1 st Test cGMP Change with 1 of
xample p,M cpd (NO Platelet Aggregation
Donor Present), % of DEANO response(pM)
104 10
105 181.53
106 137.91
108 129.29
107 125.26
111 476.39 10+
109 7
110 10+
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-69-
Table 5
ICSO for Inhibition
1st Test cGMP Change with 1mM of Platelet
xample cpd (NO Aggregation
Donor Present), % of DEANO response(pM)
1 93.33 3.5
2 145.84 6
3 132.77 10+
4 ~ 184.86 7
5 134.99 5
6 131.66 8
7 178.03
8 125.15 2
12 128.76
13 169.14
14 166.45
9 153.88 10+
I O 157.53 6
11 174.75 6
15 201.95 6
16 282.88 6.5
17 173.64 6
18 201.95 10+
19 209.14 10+
20 459.96 5
21 250.98 10+
22 186.32
23 225.46
24 249.76
25 142.96
26 299.44 1.5
27 338.6 6
28 144.71
29 256.76 3.5
30 201.33
31 353.4 1.5
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-70-
ICso for Inhibition
1 st Test cGMP Change with 1mM of Platelet
xample cpd (NO Aggregation
Donor Present), % of DEANO response(pM)
32 151.68 10+
34 322.81 6
35 363.36 10+
36 296.59 10+
37 337.89 10+
38 295.16 10+
39 312.4 10+
40 418.37 10+
41 455.13 10+
42 181.88 8
43 215.41 10+
44 457.39 10+
45 218.66 5
46 10+
47 10+
48 10+
49 10+
50 10+
52 10+
53 9
54 5
55 7
56 6.5
57 3
58 3
59 10+
60 7.5
61 1.5
62 7
63 9.5
64 10+
65 10+
33 7
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-71-
Table 6
Compound 1 st Test ICSO for
cGMP
Change with ~ibition
1 ~M of
cpd (NO DonorPlatelet
Present), Aggregation
% of
DEANO response(~.M)
1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N- 156.75
dimethylethylamido)-6-pyridone (CFM1882)
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(3-N,N- 421.09 20
dimethylpropylamido)-6-pyridone (CFM1883)
1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-207.03
dimethylethylamido)-2-pyridone (CFM1884)
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N- 194.38
dimethylethylamido)-2-pyridone (CFM1885)
1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(N-[2,N,N- 204.61
dimethylaminoethylamido])-2-pyridone
(CFM1886)
1-(2,6-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(N-[2-N,N- 154.78
dimethylaminoethylamido])-6-pyridone
(CFM 1887)
5-chloro-1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-(2-N,N-140.94
dimethylaminoethylamido)-6-pyridone
(CFM 1888)
5-chloro-3-(2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamido)-1-135.6
(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-6-pyridone
(CFM1889)
5-chloro-1-(3,4-dichlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-[N',N'-202.02
dimethylaminoethylamido])-2-pyridone
(CFM1890)
5-chloro-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-(N',N'-170.53
dimethylamino)ethyl)amido-2-pyridone
(CFM 1891 )
5-chloro-1-(3-trifluoromethylbenzyl)-3-N-164.85
(2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)ethyl)amido-2-pyridone
(CFM1892)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-72-
Compound 1 st Test ICso for
cGMP
Change with b~ibition
1 ~M of
cpd (NO DonorPlatelet
Present), Aggregation
% of
DEANO response(p,M)
1-benzyl-5-chloro-3-N-(2-[N',N'-dimethylamino]148.43
ethyl)carboxamido-6-pyridone (CFM1893)
5-chloro-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-3-N-(2-[N',N'-144.32
dimethylamino] ethyl)carboxamido-6-pyridone
(CFM1894)
4-(2,4-dichlorobenzoyl)pyrrole-2-N-360.01
dimethylaminopropylcarboxamide (CFM1985)
4-[(N-[3-(N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl)]334.25 10
carboxamido]-2-phenylthiazole (CFM1896)
4-(N-(3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl) 296.23
carboxamido)-2-(4-pyridinyl)thiazole
(CFM1897)
2-[4-(N-[3-N',N'-dimethylaminopropyl]269.18 1.5
carboxamido)phenyl-4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl]
thiazole (CF1898)
4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-[3-N',N'- 233.13 1.5
dimethylaminopropyl]carboxamido)phenyl)
1-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)-3-[N-(2-149.33
dimethylaminoethyl)carboxamido]-2
[ 1 H]-
pyridone (CFM 1900)
N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-4-(3-chloro-5-191.9
trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyloxy)phenylsulfonamide
(CFM 1901 )
N1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-3-[3-chloro-5-309.73
(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]propanamide
(CFM1902)
3-(N-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)carboxamido]-1-169.35
(4-trifluoromethylbenzyl))-2 [ 1
H]-pyridone
(CFM1905)
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)urea266.6
(CFM1917)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-73-
Compound 1 st Test ICso for
cGMP
Change with In~bition
1 ~M of
cpd (NO DonorPlatelet
Present), Aggregation
% of
DEANO response(~,M)
1-(3-(dimethylamino)-propyl)-3-phenylurea281.16
(CFM1918)
N1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)phenylJ-N2-[3-207.01
(dimethylamino)propylJethanediamide
(CFM1935)
N4-[3-(dimethylamino)propylJ-3-(2,6-142.14
dichlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-
carboxamide (CFM1936)
N-[[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4334.47
-ylJcarbonylJ-N'-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]urea
(CFM l 93 7)
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N'-[3-dimethylaminopropylJ299.26
urea (CFM1938)
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-74-
Table 7
1 st Test cGMP
Change with
1 mM
Compound cpd (NO Donor
Present), %
of
DEANO response
N-(3,5-Dichloro-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propylamino)p174.42
ropionamide
[3-(2-Ethyl-6-methyl-pyridin-3-yloxy)-propyl]-dimethyl188.03
-amine
8-(3-Dimethylamino-propoxy)-1,3,7-trimethyl-3,7-dihydro191.65
-purine-2,6-dione
2-(3-Dimethylamino-propylamino)-isophthalonitrile213.04
Dimethyl amino-(3-methyl-benzo [b] thiophen-2-yl)-propan-1279.3 3
-one (HCl)
N-B enzo [ 1,3 ]dioxo 1-5-ylmethyl-N,N-dimethyl-propane-1,3184.90
-di amine
N,N-Dimethyl-N-(5-nitro-quinolin-8-yl)-propane-1,3219.03
-diamine
1-(4-Chloro-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-urea421.21
2-Amino-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-benzamide363.98
3-Phenyl-acrylic acid 3-dimethylamino-propyl298.89
ester
3,5-Dinitro-benzoic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl141.22
ester
[4-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-3-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-3204.10
H-thiazol
-2-ylidene]-phenyl-amine
3-Methyl-benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid dimethylamino197.46
-dimethyl-propyl ester
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-75-
N'-(2-Chloro-4-vitro-phenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-propane-1,3161.70
-di amine
[3-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-5-(4-vitro-phenyl)-3H-thiazol157.02
-2-ylidene]-phenyl-amine
[3-(10,11-Dihydro-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)150.39
-propyl]-dimethyl-amine
2,3-Dimethyl-1H-indole-5-carboxylic acid 217.3
2-dimethylamino
-ethyl ester
N'-(3,4-Dinitro-5-pyridin-2-yl-thiophen-2-yl)-N,N-dimethyl282.12
-propane-1,3-diamine
Cyclooctyl-dithiocarbamic acid 2-dimethylamino-ethyl185.31
ester
(HCl)
N-(2,6-Difluoro-phenyl)-C-dimethylamino-acetamide168:99
2-Acetylamino-3-(4-chloro-phenyl)-N-(3-dimethylamino142.31
-propyl)-acrylamide
N-[2-[5-(4-Bromo-phenyl)-furan-2-yl]-1-(3-dimethylamino163.49
-propylcarbamoyl)-vinyl]-4-methyl-benzamide
2,6-Bis-(3-dimethylamino-propylamino)-3-vitro-benzonitrile167.75
N-[2-(2,4-Dichloro-phenoxy)-phenyl]-N'-(3-dimethylamino328.31
-propyl)-oxalamide
3,5-Dichloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2,6-dimethoxy193.93
-benzamide
2-Dimethylaminomethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-naphthalen-1175.73
-one (HCl)
2-( { 1-[N-(3-Dimethylamino-propyl)-3-trifluoromethyl231.40
-phenyl]-methanimidoyl}-amino)-6-fluoro-benzoic
acid
CA 02389773 2002-05-03
WO 01/32604 PCT/GB00/04249
-76-
2,4-Dichloro-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-N'-hydroxy212.83
-benzamidine
3-(3-Methyl-ureido)-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline-2305.22
-carboxylic acid (3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
5-Bromo-N-(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-2-hydroxy-benzamide258.28
N-(2,4-Dichloro-phenyl)-6-(2-dimethylamino-ethylsulfanyl)162.85
-4-trifluoromethyl-nicotinamide
1-(2,6-Dichloro-benzyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-pyridine-3149.44
-carboxylic acid (2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-amide
3-Amino-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-quinazoline-2-carboxylic230.76
acid
(3-dimethylamino-propyl)-amide
20