Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-1-
f (INDOL-3-YL)-CYCLOALKYLI-3-SUBSTITUTED AZETIDINES FOR THE
TREATMENT OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS
Field of the Invention
This invention relates to new N-(indolyl-cycloalkyl) azetidine derivatives
which are useful as pharmaceuticals for the treatment of diseases caused by
disorders
of the serotonin-affected neurological systems, such as depression and
anxiety.
Background of the Invention
Pharmaceuticals which enhance serotonergic neurotransmission are useful for
the treatment of many psychiatric disorders, including depression and anxiety.
The
first generation of non-selective serotonin-affecting drugs operated through a
variety
of physiological functions which endowed them with several side-effect
liabilities.
The more currently prescribed drugs, the selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake
inhibitors (SSRIs), act predominately by inhibiting 5-HT, which is released at
the
synapses, from being actively removed from the synaptic cleft via a
presynaptic
serotonin transport carrier.
The present invention relates to a new class of molecules which have the
ability to act at the 5-HT transporter. Such compounds are therefore
potentially
useful for the treatment of depression as well as other serotonin disorders.
Described in WO 95/20588 are compounds of general formula:
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-2-
W ~ (CH2)r
A NRRi
Wherein R and RI are each independently hydrogen or C,_a alkyl, or R and R,
are
linked to form an azetidine ring. These compounds are reported to have
activity at
the SH'T, receptor and be useful for the treatment of migraine, headache and
headache associated with vascular disorder.
Summary of the Invention
In accordance with this invention there is provided a group of compounds
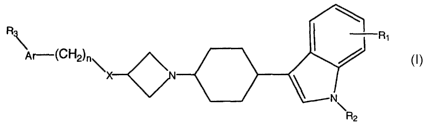
represented by the formula I:
Rs Ri
Ar-(CH2)n
I
wherein:
X is N-R, O, S(O)m;
m is an integer of 0 to 2;
n is an integer of 0 to 4;
Ar is an aryl group of 6 to 12 carbon atoms optionally substituted with 1 to 3
groups selected independently from R3, RQ and R5, or a heteroaryl group of 4
to 10
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-3-
carbon atoms optionally substituted with 1 to 3 selected independently from
R3, R,
and R~;
R and R~ are independently H, straight chain alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms,
branched alkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms,
alkoxycarbonyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, alkylcarbonyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
aminocarbonyl, or alkylaminocarbonyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms;
RI, R3, R4 and RS are independently H, straight chain alkyl of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms, branched alkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkyl of 3 to 8 carbon
atoms,
halogen, alkoxy group of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, haloalkyl of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms,
hydroxy, nitro, amino, sulfonyl, cyano, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl of 1 to 4
carbon
atoms, alkylcarbonyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, aminocarbonyl, or
alkylaminocarbonyl
of 1 to 4 carbon atoms;
and all crystalline forms or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
In a preferred aspect of this invention are provided compounds of formula I
wherein:
X is O, or NR;
n is an integer of 0 to 1;
Ar is an aryl group of 6 to 10 carbon atoms optionally substituted with 1 to 3
groups selected independently from R3, R~ and R5, or a heteroaryl group of 5
to 10
carbon atoms optionally substituted with 1 to 3 groups selected independently
from
R3, R; and R5;
R and R~ are independently H, straight chain alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
branched alkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms, or cycloalkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-4-
R~, R3, R~ and RS are independently H, straight chain alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon
atoms, branched alkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloalkyl of 3 to 6 carbon
atoms,
halogen, alkoxy of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, haloalkyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms,
hydroxy,
nitro, nitrite, amino, sulfonyl, cyano, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl of 1 to 4
carbon atoms,
alkylcarbonyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, aminocarbonyl, or alkylaminocarbonyl of
1 to 4
carbon atoms;
and all crystalline forms or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
In another preferred group of compounds of this invention:
X is S(O)m;
m is an integer of 0 to 2;
n is an integer of 0 or l;
Ar is an aryl group of 6 to 10 carbon atoms optionally substituted with 1 to 3
groups selected independently from R3, RQ and R5, or a heteroaryl group of 5
to 10
carbon atoms optionally substituted with 1 to 3 groups selected independently
from
R3, RQ and R5;
R and RZ are independently H, straight chain alkyl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms,
branched alkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms, or cycloalkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
R1, R3, R4 and RS are independently selected from H, straight chain alkyl of 1
to
6 carbon atoms, branched alkyl of 3 to 6 carbon atoms, cycloatkyl of 3 to 6
carbon
atoms, halogen, alkoxy of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, haloalkyl of 1 to 4 carbon
atoms,
hydroxy, nitro, nitrite, amino, sulfonyl, cyano, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyt of 1
to 4
carbon atoms, alkylcarbonyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms, aminocarbonyl, or
alkylaminocarbonyl of 1 to 4 carbon atoms;
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-5-
and all crystalline forms or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
A subset of these preferred compounds includes those in which X is S(O)m; m
is an integer from 0 to 2; and Ar is a phenyl ring optionally substituted by
from 1 to 3
groups independently selected from R3, R~ and R5, defined above.
Aryl, as used herein refers to single or multiple 6 to 12 membered aromatic
ring radicals including but not limited to phenyl, naphthalene, anthracene,
phenanthrene, indene and indacene, in some embodiments of the present
invention,
the aryl group may be substituted with one to three groups selected from R3,
R4 and
R5.
Heteroaryl as used herein refers to single or multiple 5 to 10 membered
aromatic ring radicals having from 1 to 3 hetero atoms independently selected
from
nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur, including, but not limited to, furan, thiophene,
pyrrole,
imidazole, oxazole, thiazole, isoxazole, pyrazole, isothiazole, oxadiazole,
triazole,
thiadiazole, quinolizine, quinoline, isoquinoline, cinnoline, phthalazine,
quinazoline,
quinoxaline, napthyridine, pteridine, pyridine, pyrazine, pyrimidine,
pyridazine,
pyran, triazine, indole, isoindole, indazole, indolizine, and isobenzofuran.
In some
embodiments of the present invention, the heteroaryl group is substituted with
one to
three groups selected from those of R3, R~ and R5.
Alkyl, whether used alone or as part of another group includes straight and
branched chain alkyl groups containing from 1 to 6 carbon atoms, for example,
methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, i-butyl and t-butyl are encompassed
by the
term alkyl. In alkyl-containing groups herein, such as alkylcarbonyl and
alkylaminocarbonyl groups, the number of carbon atoms listed refers to the
alkyl
group, itself, and not including the carbonyl carbon. In some embodiments of
the
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-6-
present invention alkyl may refer to substituted or unsubstituted alkyl. The
substituted alkyl groups in these compounds may be fully substituted, such as
with
perhalogenated compounds. Other alkyl groups in these definitions may be
substituted by from 1 to 3 substituents selected from halogen, hydroxy, CN,
NO2, or
NH3. The number of carbon number refers to carbon backbone and does not
include
carbon atoms of substituents such as alkoxy substitutions and the like.
Halogen is preferably fluoro, chloro, bromo or iodo.
Among the most preferred compounds of the present invention are:
{ 1-[cis-4-(5-Fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl)-2-methoxy-
phenyl
)amine;
{ 1-[trans-4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl)-2-methoxy-
phenyl)
amine;
3-{cis-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole-5
carbonitrile;
3-{ trans-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl }-1H-indole-5-
carbonitrile;
2-{ cis-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl }-1H-indole-5-
carbonitrile;
2-{trans-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole-5-;
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
_ '7 _
{ 1-[cis-4-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl }-(3-fluoro-
phenyl)-
arrune;
{ 1-[cis-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl }-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-
amine;
{1-[trans-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl}-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-
amine;
2-{ cis-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl }-1H-indole;
2-{ trans-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl }-1H-indole;
5-fluoro-3-{cis-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole ;
5-fluoro-3-{trans-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
;
5-fluoro-3-{cis-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole;
5-fluoro-3-{trans-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl }-1H-
indole;
3-{cis-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl }-1H-indole;
3-{trans-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl }-1H-indole;
6-fluoro-3-{cis-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexy1}-1H- indole;
6-fluoro-3-{trans-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-
indol;
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of one or more of these compounds.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
_g_
It is understood that the definition of the compounds of formula I, when R,
R,,
RZ or R3 contain asymmetric carbons, encompass all possible stereoisomers and
mixtures thereof which possess the activity discussed below. In particular, it
encompasses racemic modifications and any optical isomers which possess the
indicated activity. Optical isomers may be obtained in pure form by standard
separation techniques.
Pharmaceutically acceptable salts are those derived from such organic and
inorganic acids as: lactic, citric, acetic, tartaric, succinic, malefic,
malonic, oxalic,
fumaric, hydrochloric, hydrobromic, phosphoric, nitric, sulfuric,
methanesulfonic,
and similarly known acceptable acids. Where R, R1, R, or R; contain a carboxyl
group, salts of the compounds of this invention may be formed with bases such
as
alkali metals (Na, K, Li) or the alkaline earth metals (Ca or Mg).
As mentioned previously, the compounds of formula I have been found to
have affinity for the 5-HT reuptake transporter. They are therefore useful in
the
treatment of diseases affected by disorders of the serotonin affected
neurological
systems, such as depression, anxiety, sleep disorders, sexual dysfunction,
alcohol and
cocaine addiction, cognition enhancement and related problems. The present
invention accordingly provides methods of treatment or prevention of these
maladies,
the methods comprising administering to a mammal, preferably a human, in need
thereof pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound of this invention, or
a
pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
This invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions which comprise
one or more compounds of this invention, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt
thereof, in combination or association with one or more pharmaceutically
acceptable
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-9-
carriers or excipients. The compositions are preferably adapted for oral or
subcutaneous administration. However, they may be adapted for other modes of
administration.
The compositions of the invention may be formulated with conventional
excipients, such as a filler, a disintegrating agent , a binder, a lubricant,
a flavoring
agent and the like. They are formulated in conventional manner, for example,
in a
manner similar to that use for known antihypertensive agents, diuretics and (3-
blocking agents.
Applicable solid carriers or excipients can include one or more substances
which may also act as flavoring agents, lubricants, solubilizers, suspending
agents,
fillers, glidants, compression aids, binders or tablet-disintergrating agents
or an
encapsulating material. In powders, the carrier is a finely divided solid
which is in
admixture with the finely divided active ingredient. In tablets, the active
ingredient is
mixed with a carrier having the necessary compression properties in suitable
proportions and compacted in the shape and size desired. The powders and
tablets
preferably contain up to 99% of the active ingredient. Suitable solid carriers
include,
for example, calcium phosphate, magnesium stearate, talc, sugars, lactose,
dextrin,
starch, gelatin, cellulose, methyl cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose,
polyvinylpyrrolidine, low melting waxes and ion exchange resins.
Liquid carriers may be used in preparing solutions, suspensions, emulsions,
syrups and elixirs. The active ingredient of this invention can be dissolved
or
suspended in a pharmaceutically acceptable liquid carrier such as water, an
organic
solvent, a mixture of both or pharmaceutically acceptable oils or fat. The
liquid
carrier can contain other suitable pharmaceutical additives such as
solubilizers,
emulsifiers, buffers, preservatives, sweeteners, flavoring agents, suspending
agents,
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-10-
thickening agents, colors, viscosity regulators, stabilizers or osmo-
regulators.
Suitable examples of liquid carriers for oral and parenteral administration
include
water (particularly containing additives as above e.g. cellulose derivatives,
preferably
sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution), alcohols (including monohydric
alcohols
and polyhydric alcohols e.g. glycols) and their derivatives, and oils (e.g.
fractionated
coconut oil and arachis oil). For parenteral administration the carrier can
also be an
oily ester such as ethyl oleate and isopropyl myristate. Sterile liquid
carriers are used
in sterile liquid form compositions for parenteral administration.
Liquid pharmaceutical compositions which are sterile solutions or suspensions
can be utilized by, for example, intramuscular, intraperitoneal or
subcutaneous
injection. Sterile solutions can also be administered intravenously. Oral
administration may be either liquid or solid composition form.
Preferably the pharmaceutical composition is in unit dosage form, e.g. as
tablets or capsules. In such form, the composition is sub-divided in unit dose
containing appropriate quantities of the active ingredient; the unit dosage
forms can
be packaged compositions, for example packeted powders, vials, ampoules,
prefilled
syringes or sachets containing liquids. The unit dosage form can be, for
example, a
capsule or tablet itself, or it can be the appropriate number of any such
compositions
in package form.
In order to obtain consistency of administration, it is preferred that a
composition of the invention is in the form of a pharmaceutically effective
unit dose.
Suitable unit dose forms include tablets, capsules and powders in sachets or
vials.
Such unit dose forms may contain from 0.1 to 100 mg of a compound of the
invention and preferably from 2 to 50 mg. Still further preferred unit dosage
forms
contain 5 to 25 mg of a compound of the present invention. The compounds of
the
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-11-
present invention can be administered orally at a dose range of about 0.01 to
100
mg/kg or preferably at a dose range of 0.1 to 10 mg/kg. Such compositions may
be
administered from 1 to 6 times a day, more usually from 1 to 4 times a day.
The following specific examples illustrate the synthetic procedures for the
preparation of intermediates and invention compounds and should not be
construed as
limiting the scope of this disclosure. Those skilled in the art of organic
synthesis may
be aware of still other routes to prepare compounds of this invention.
Reactants and
intermediates are either commercially available or can be prepared according
to
standard literature procedures.
In accordance with the present invention, compounds of formula I may be
prepared by Scheme I
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-12-
Scheme I
/~ Rs
v-i
X \NH R2
(2) NaBH(OAc)3, HOAc
DCE, 23°C, 12 hours
-R~
R- \
3
(I) R2
Thus, a compound of formula (2) is reacted with a compound of formula (3)
in the presence of a reducing reagent such as sodium triacetoxyborohydride,
and
acetic acid in a solvent such as dichloroethane at 23 °C to give a
compound of
formula I in accordance with the procedure described by Abdel-Magid, Carson,
Harris, Maryanoff and Shah in J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 3849.
In accordance with the present invention, compounds of formula (3) may be
prepared by Scheme II.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-13-
Scheme II
0
I
KOH, MeOH, 65°C
R~ ~4) ~ 5 v
2 Ri ( ) R
2
H2, 5% P~
H CI
EtOH, 2~ THF/H2C
R1 W) R2 R1 ~s) v
R2
Thus a compound of formula (4) is reacted with 1,4-cyclohexanedione
monoethylene ketal, potassium hydroxide in methanol at 65 °C to give
compounds of
formula (5) as described by Wustrow et al. in J. Med. ChenZ. 1997, 40, 250.
Hydrogenation to a compound of formula (6) can be realized by treatment in
suitable
solvents such as an alcohol, but not limited to ethanol with H, and 5% Pd/C.
Hydrolysis to a compound of formula (3) can be carried out using 1N HCl in a
1:1
mixture of THF and water.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
- 14-
In accordance with the present invention, compounds of formula (2) may be
prepared by Scheme III.
Scheme III
CH3S02C1/
OH TEA/CH2C1' oSO2CH3
(7)
XH
Rs
s II R3
HCOOH4/10% Pd/C
MeOH
Thus, a compound of formula (7) is prepared by reaction of N-benzhydryl-3-
hydroxyazetidine with methanesulfonyl chloride and triethylamine in a solvent
such
as dichloromethane. Compound (7) is reacted with a compound of formula (9) in
the
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-15-
presence of a base such as potassium carbonate in a solvent such as
acetonitrile to
yield a compound of formula (8). Deprotection of the azetidine nitrogen with
ammonium formate in an alcoholic solvent such as methanol yields a compound of
formula (2).
Compounds of formula (2) where X is NR are prepared according to scheme
IV. Standard N-alkylation methods may be used to convert a compound of formula
(9) where R is hydrogen to a compound of formula (9) where R is alkyl.
Scheme IV
R
~H
NH 1 ) HCOOC2H5
R3 ~ 2) LAH ~ R3
I
/ (9) R = alkyl
R=H
1-(Diphenylmethyl)-3-
methane sulfonyl azetidinE
R3
R
HN~\
HCOONH ,~/4
10% Pd/C >
(2)
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-16-
While the reaction schemes above show intermediates substituted only by R3
groups, the presence of optional RQ and RS groups in these compounds is
understood.
The present invention further provides a compound of the invention for use as
an active therapeutic substance. Compounds of formula I are of particular use
in the
treatment of diseases affected by disorders of the serotonin.
The present invention further provides a method of treating depression and
anxiety in mammals including man, which comprises administering to the
afflicted
mammal an effective amount of a compound or a pharmaceutical composition of
the
invention.
The following examples are presented to illustrate rather than limit the
present
invention.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-17-
Examples
The 5-HT transporter affinity of the compounds of this invention was
established in accordance with standard pharmaceutically accepted test
procedures
with representative compounds as follows:
Rat Brain 3H-Paroxetine Binding Assay (RB 5HT Transporter):
The following assay was used to determine a compound's affinity for the 5-
HT transporter.
A protocol similar to that used by Cheetham et. al. (Neuropharmacol.. 1993,
32, 737) was used. Briefly, frontal cortical membranes prepared from male S.D.
rats
were incubated with 3H-paroxetine (0.1 nM) for 60 min. at 25 °C. All
tubes also
contained either vehicle, test compound (one to eight concentrations), or a
saturating
concentration of fluoxetine (10 ~.M) to define specific binding. All reactions
are
terminated by the addition of ice cold Tris buffer followed by rapid
filtration using a
Tom Tech filtration device to separate bound from free 3H-paroxetine. Bound
radioactivity was quantitated using a Wallac 1205 Beta Plate~ counter.
Nonlinear
regression analysis was used to determine ICso values which were converted to
K;
values using the method of Cheng and Prusoff (Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22,
3099):
ICso
- _____________
K. -
Radioligand concentration/(1+KD)
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
- 18-
Inhibition of 'H-5-HT Uptake by cells Possessing the Human 5-HT Transporter
(HC
SHT Transporter):
A human carcinoma cell line (Jar cells) possessing low endogenous levels of
the 5-HT-transporter are seeded into 96 well plates and treated with
staurosporine at
least 18 h prior to assay. [Staurosporine greatly increases the expression of
the 5-HT-
transporter.] On the day of assay, vehicle, excess of fluoxetine, or test
compound is
added to various wells on the plate. All wells then receive 'H-5-HT and are
incubated
at 37 °C for 5 min. The wells are then washed with ice cold 50 mM Tris
HCl (pH
7.4) buffer and aspirated to remove free 3H-5-HT. 25 ~,1 of 0.25 M NaOH is
then
added to each well to lyse the cells and 75 p1 scintillation cocktail
(MicroscintTM 20)
added prior to quantitation on a Packard TopCount machine. Tubes with vehicle
represent total possible uptake, radioactivity counted in tubes with
fluoxetine
represent nonspecific binding/uptake and is subtracted from the total possible
uptake
to give total possible specific uptake. This nonspecific binding (usual low in
number)
is then subtracted from the counts obtained in wells with various test
compounds (or
different concentrations of test drug) to give specific uptake in the presence
of drug.
Specific uptake is then expressed as a % of control values and is analyzed
using
nonlinear regression analysis (Prizm) to determine ICSo values. If the
compound is
active at inhibiting 5-HT uptake, its counts will be close to that obtained
with
fluoxetine.
Results from these two assays are presented below in Table I.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-19-
Table I
Compound n RB SHT TransporterHC SHT Transporter
K; (nM) ICSO (nM)
Example 1 15.0 962
1 a
Example 1 17.0 591
1b
Example 1 16.0 336.50
2a
Example 1 48.0 282
2b
Example 1 2.38 91
3a
Example 1 11.0 232
3b
Example 1 18.0 6390
4
Example 1 124 -
Sa
Example 1 34.0 -
Sb
Example 1 120.0 -
6a
Example 1 - -
6b
Example 1 257 -
7a
Example 1 68 6000
7b
Example 1 24.0 6000
8a
Example 1 45.0 1500
8b
Example 1 275.0 -
9a
Example 1 455.0 -
9b
Example 1 190 -
10a
Example 1 73 4600
lOb
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-20-
Example la
{ 1-[cis-4-(5-Fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl)-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-
amine
Step 1
4-(5-Fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohex-3-ene-ethylene ketal
5-Fluoroindole (4.96, 0.036 mol), 1,4-cyclohexanedione monoethylene ketal
(7.17 g, 0.046 mol) and potassium hydroxide (6 g, 0.043 mol) were heated to
reflux
in 70 mI, of methanol for 6 h. The reaction was cooled and the product was
isolated
by filtration and washed with water to give 8.59 g (86%) of product as a white
solid:
mp 153-155°C.
Step 2
4-(5-Fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone ethylene ketal
A mixture of 4-(5-fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohex-3-en-ethylene ketal (8.5 g)
and 10% palladium on carbon (2.72 g) in ethanol (200 mL) was hydrogenated for
5 h.
The catalyst was filtered off and the solvent was removed under vacuum.
Chromatography (methanol-methylene chloride) afforded 7.55 g (82 %) of product
as
a white solid: mp 183-185°C.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-21-
Step 3
4-(5-Fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone
A solution of 4-(5-fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone ethylene ketal (2.8 g,
mmol) in 2 L of 1:l tetrahydrofuran-hydrochloric acid (1N) was allowed to stir
at
10 room temperature for 16 h. The solvent was evaporated under vacuum. The
crude
product was dissolved in ethyl acetate, washed with 1N sodium hydroxide (3 x
150
mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered.
Chromatography (40% ethyl acetate/hexanes) afforded 2.1 g (91 %) of product as
a
yellow solid: mp 112-114°C.
Step 4
1-(Diphenylmethyl)-3-methane sulfonyl azetidine
To a cold solution of 34 g (0.142 mol) of 1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-
hydroxyazetidine in 200 mL of CHZCIZ was added 30 mL (212 mol) of
triethylamine.
To the cold mixture a solution of 19.5 g (0.171 mol) of methanesulfonyl
chloride in
50 mL of CHZC12 was added dropwise. The reaction was stirred at room
temperature
for 2 h. Water was added and the methylene chloride was removed under vacuo.
The
product was extracted with ether, the combined extracts were dried over
anhydrous
sodium sulfate, and filtered to yield 36 g of product. 'H NMR (300 MHz, CDC13)
8
2.98 (s, 3H), 3.21 (m, 2H), 3.66 (m, 2H), 4.39 (s, 3H), 5.10 (m, 1H), 7.22 (m,
2H),
7.27 (m, 4H), 7.38 (m, 4H).
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-22-
Step 5
(1-Benzhydryl-azetidin-3-yl)-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-amine
To a solution of 4.1 g (0.033 mol) of o-anisidine in 20 mL DMF, 4.6 g (0.033
mol) of K,C03 was added, followed by 9.5g (0.030 mol) of 1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-
methane sulfonyl azetidine. The reaction was heated at 80 °C for 5 h.
Water was
added and the product was extracted with ether. The organic phase was dried
and the
solvent was removed under vacuo. The residue was filtered through silica gel,
starting with 100% methylene chloride, then 25% ethyl acetate/hexane to give
1.5 g
of the desired product: mp 75-77 °C. 'H NMR (300 MHz, CDC13) 8 2.89
(dd, 2H),
3.70 (dd, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 4.13 (m, 1H), 4.40 (m, 1H), 4.38 (s,lH), 6.42
(dd,lH),
6.69 (dd, 1H), 6.79 (m, 2H), 7.20 (m, 2H), 7.26 (m, 4H), 7.42 (m, 4H); MS (ES)
m/z
(relative intensity): 345 (M'+H).
Elemental analysis for C23HZQN20
Calculated: C, 80.20; H, 7.02; N, 8.13
Found: C, 80.53; H, 7.17; N, 8.13.
Step 6
Azetidin-3-yl-(2-methoxy-phenyl- amine)
A solution of 2.0 g of (1-benzhydryl-azetidin-3-yl)-(2-methoxyphenyl)-amine
in 30 mL of methanol was added to a suspension of 10°lo Pd/C in
methanol. 4.0 g of
ammonium formate was added portion wise and the reaction was heated under
reflux
for 2 h. The mixture was cooled, filtered over celite, the filtrate was
evaporated. The
residue was triturated with CHZCI=, and filtered. The filtrate was evaporated
to give
0.840 g of the desired product.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-23-
Step 7
{ 1-[cis-4-(5-Fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl)-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-amine
To a solution of 0.170 g of (1-benzhydryl-azetidin-3-yl)-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-
amine in 10 mL of CHZCI" was added 4-(5-fluoro-1-H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone
followed by 0.420 g of sodium triacetoxyborohydride. The reaction was stirred
at
room temperature overnight. It was quenched with 1N NaOH, and the product was
extracted with ether. The organic phase was washed with water and dried over
magnesium sulfate. The product was filtered through 150 mL of silica gel using
50%
ethyl acetate/hexanes, 75% ethyl acetate/hexanes, and finally 100% ethyl
acetate to
give 0.150 g of the desired product: mp 158-160 °C. 'H NMR (300 MHz,
CDCI3) 8
1.50-1.94 (m, 8H), 2.28 (m, 1H), 2.84-2.90 (m, 2H), 3.80-3.85 (m, 5H), 4.08-
4.14
(m, 1H), 4.38 (m, 1H), 6.51-6.68 (dd, 1H), 6.69-6.91 (m, 4H), 7.07 (d, 1H),
7.24-
7.28 (m, 2H), 8.02 (s, 1H); MS (ES) m/z (relative intensity): 394 (M++H).
Example 1b
{ 1-[trans-4-(5-Fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl)-2-methoxy-
phenyl)-amine
F
~~ WI
N N
NH
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-24-
The trans isomer of the compound of Example la was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as an off white solid (0.045 g): mp 73-76 °C. MS
(ES) m/z
(relative intensity): 394 (M++H).
Example 2a
3-(cis-4-[3-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole-5-
carbonitrile
Step 1
4-(5-Cyano-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohex-3-ene-ethylene ketal
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example la,
Step 1 except that 5-cyanoindole was used in place of 5-fluoroindole. Yield:
50%;
mp 158-160 °C.
Step 2
4-(5-Cyano-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone ethylene ketal
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example la,
Step 2, using 4-(5-cyano-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohex-3-ene-ethylene ketal. Yield:
95%;
mp 153-155 °C.
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-25-
Step 3
3-(4-Oxo-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole-5-carbonitrile
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 1,
Step 3, except that 4-(5-cyano-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone ethylene ketal was
used.
Yield: 81%; mp 162-164 °C.
Step 4
1-Benzhydryl- 3-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidine
To a solution of 3.9 g (0.035 mol) of 3-fluorophenol in 250 mL of
acetonitrile, was added 6.3 g (0.045 mol) of KZC03 followed by 12.25 g (0.039
mol)
of 1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-methane sulfonyl azetidine, prepared according to the
procedure of Example la, Step 4. The reaction mixture was heated at 75
°C for 18 h.
The solvent was removed under vacuo, and the residue was taken up in a mixture
of
ether and water. The aqueous layer was extracted with ether, the combined
extracts
were dried over magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under vacuo.
The
product was filtered through 500 mL of silica gel, eluted with 50%
CHzCl2/hexane
then 15% ethyl acetate/hexane to give 3.4 g of the title compound: mp 81-82
°C. 'H
NMR (300 MHz, CDC13) 8 3.17 (dd, 2H), 3.72 (dd, 2H), 4.46 (s, 1H), 4.77 (m,
1H),
6.48 (dd, 1H), 6.53 (dd, 1H), 6.63 (m, 1H), 7.22 (m, 3H), 7.29 (m, 4H), 7.31
(dd,
4H); MS (ES) m/z (relative intensity): 334 (M++H).
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-26-
Step 6
3-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidine
A solution of 2.50 g of 1-benzhydryl-3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidine in 10
mL of THF was added to a suspension of 10% Pd/C in methanol. Ammonium
formate (4.6g) were added portion wise and the reaction was heated under
reflux for
3 h. The mixture was cooled, filtered through celite, and the filtrate was
concentrated. The residue was triturated with CH~C12 and filtered. The
filtrate was
concentrated to give 0.840 g of the desired product.
Step 7
3-(cis-4-[3-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole-5-
carbonitrile
To a solution of 0.170 g of 3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidine in 10 mL of
CHzCl2 was added 0.180 g of 3-(4-oxo-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole-5-carbonitrile
followed
by 0.420 g of sodium triacetoxyborohydride. The reaction was stirred at room
temperature overnight. It was quenched with 1N NaOH and the product was
extracted with ether. The organic phase was washed with water, dried over
magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated. The product was filtered
through 150
mL of silica gel using 50% ethyl acetate/hexane, 75% ethyl acetate/hexane and
finally
100% ethyl acetate to give 0.095 g of the desired product: mp 187-190
°C. 'H NMR
(300 MHz, CDCl3) 8 1.51-1.65 (m, 2H), 1.69-1.75 (m, 4H), 1.77-1.90 (m, 2H),
2.45
(m, 1H), 2.90 (m, 1H), 3.03 (dd, 2H), 3.81 (dd, 2H), 4.77 (m, 1H), 6.53-6.59
(m,
2H), 6.66 (m, 1H), 7.13-7.22 (m, 2H), 7.39 (dd, 2H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 8.28 (s,
1H); MS
(ES) m/z (relative intensity): 390 (M++H).
Elemental analysis for Cz4HZ4FN3O
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-27-
Calculated: C, 74.01; H, 6.21; N, 10.79
Found: C, 73.95; H, 6.24; N, 10.45.
Example 2b
3-(trans-4-[3-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole-5-
carbonitrile
N
NH
The trans isomer of the compound of Example 2a was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as a white solid (0.037 g): mp 186-192 °C. 'H
NMR (300
MHz, CDC13) 8 1.98-1.33 (m, 2H), 1.45-1.49 (m, 2H), 1.95-1.99 (m, 2H), 2.14-
2.23
(m, 3H), 2.73-2.83 (m,lH), 3.17 (dd, 2H), 3.89 (dd, 2H), 4.78 (m, 1H), 6.48-
6.70 (m,
3H), 7.06 (d, 1H), 7.18-7.24 (m, 2H), 7.40 (dd, 2H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 8.23 (s,
1H); MS
(ES) m/z (relative intensity): 390 (M++H).
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-28-
Example 3a
2-{cis-4-[3-(3-Methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole-5
carbonitrile
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2a,
using m-methoxy-phenol in Step 5, and 3-(4-oxo-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole-5-
carbonitrile in Step 7. mp 126-127 °C. MS (ES) m/z (relative
intensity): 402
(M++H).
Example 3b
2-{trans-4-[3-(3-Methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole-5-
carbonitrile
N
~~~ill
H3C0 ~ O 'N ~ NH
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-29-
The trans isomer of the compound of Example 3a was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as a white solid (O.OSSg ): mp 58-62 °C. MS (ES)
m/z
(relative intensity): 402 (M'+H).
Example 4
{1-[cis-4-(5-Fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl}-(3-fluoro-
phenyl)-
amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example la,
Step 5 using m-fluoroaniline: mp 67-70 °C. MS (ES) m/z (relative
intensity): 382
(M++H).
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-30-
Example Sa
{ 1-[cis-4-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl}-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 1 a,
using 3-(4-oxo-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole in Step 7: mp 67-70 °C. MS (ES)
m/z
(relative intensity): 382 (M'+H).
Example Sb
{1-[trans-4-(1H-Indol-3-yl)-cyclohexyl]-azetidin-3-yl}-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-
amine
H3C N ~N ~~ ~nl
\ NH
The trans isomer of the compound of Example Sa was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as an off white solid (0.045 g): mp 73-76 °C. MS
(ES) m/z
(relative intensity): 394 (M'+H).
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-31-
Example 6a
2-{cis-4-[3-(3-Methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
O
H3C0
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2a,
using m-methoxy-phenol in Step 5, and 3-(4-oxo-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole in Step
7:
mp 126-127 °C. MS (ES) m/z (relative intensity): 383 (M++H).
Elemental analysis for Cz3H2~F,NZOZ
Calculated: C, 72.23; H, 6.33; N, 7.32
Found: C, 72.43; H, 5.88; N, 7.07.
Example 6b
2-{trans-4-[3-(3-Methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
~~~iii
N
H3C0 NH
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-32-
The trans isomer of the compound of Example 6a was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as an off white solid: mp 52-57 °C. MS (ES) m/z
(relative
intensity): 383 (M++H).
Example 7a
5-Fluoro-3-{cis-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
F
O
F
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2a,
Step 7 using 4-(5-fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone: mp 119-125 °C.
MS (ES)
m/z (relative intensity): 383 (M++H).
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-33-
Example 7b
5-Fluoro-3-{trans-4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
F
~ n11
NH
The trans isomer of the compound of Example 7a was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as an off white solid: mp 52-57 °C. MS (ES) m/z
(relative
intensity): 395 (M'+H).
Example 8a
5-Fluoro-3-{cis-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
H3C0
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2a,
using m-methoxy-phenol in Step 5, and 4-(5-fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone
in
Step 7: mp 125-127 °C. MS (ES) m/z (relative intensity): 395
(M++H).
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-34-
Example 8b
5-Fluoro-3-{trans-4-[3-(3-methoxy-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-
indole
F
O ~N .~nII \
H3C0 ~ NH
The trans isomer of the compound of Example 8a was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as a white solid (0.055 g): mp 59-63 °C. MS (ES)
m/z
(relative intensity): 395 (M++H).
Elemental analysis for CZaH2,FN~OZ
Calculated: C, 73.07; H, 6.90; N, 7.10
Found: C, 72.98; H, 7.32; N, 6.51.
Example 9a
3-{4-[3-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
O
F
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-35-
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2a,
using 3-(4-oxo-cyclohexyl)-1H-indole in Step 7: mp 114-117 °C. MS (ES)
m/z
(relative intensity): 365 (M++H).
Example 9b
3-{4-[3-(3-Fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
~~~il
NH
The trans isomer of the compound of Example 9a was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as a white solid (0.055 g): mp 146-148 °C. MS
(ES) m/z
(relative intensity): 365 (M'+H).
Example 10a
6-Fluoro-3-{4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
y
F
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-36-
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Example 2a,
using 4-(5-fluoro-1H-3-indolyl)-cyclohexanone in step 7: mp 117-123 °C.
MS (ES)
m/z (relative intensity): 383 (M++H).
Elemental analysis for CZ3H24F2N0
Calculated: C, 72.23; H, 6.33; N, 7.32
Found: C, 72.19; H, 6.49; N, 7.13.
Example lOb
6-Fluoro-3-{4-[3-(3-fluoro-phenoxy)-azetidin-1-yl]-cyclohexyl}-1H-indole
F
O 'N ~.y I
F ~ ~ NH
The trans isomer of the compound of Example 10a was isolated at the same
time as the cis isomer as a white solid: mp 111-114 °C. MS (ES) m/z
(relative
intensity): 383 (M++H).
Example 11
N-methyl o-Anisidine
~Hs
NH
OCH3
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-37-
A solution of 12.3 g of o-anisidine in 50 mL of ethyl formate was heated
under reflux for 6 h. Excess ethyl formate was removed under vacuo. The
residue
was washed with ether to give 10.0 g of N-formyl o-anisidine.
To a cold solution of 9.0 g of N-formyl o-anisidine in 50 mL of THF was
added 66 mL of a 1M solution of LAH in THF dropwise at 0 °C. After
complete
addition the reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for one h. The
reaction was then
quenched with ethyl acetate, then with a saturated solution of NHQCI. The
mixture
was extracted with ether, the combined extracts were dried over magnesium
sulfate,
and the solvent was removed to give 6.0 g of product. 'H NMR (300 MHz, CDC13)
8
2.85 (s, 3H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 4.16 (s, 1H), 6.61 (dd, 1H), 6.69 (m, 1H), 6.75
(dd, 1H),
6.87 (m, 1H).
Example 12
(1-Benzhydryl-azetidin-3-yl)-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-methyl-amine
CH3 OCH3
N
To a solution of 0.65 g of N-methyl o-anisidine in 15 mL of acetonitrile, was
added 0.280g of KzC03, followed by 0.650g of 1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-methane
sulfonyl azetidine. The reaction mixture was heated at 80 °C for 1 h
then at 50 °C
overnight. Water was added and the mixture was extracted with ether. The
organic
phase was dried and the solvent was removed under vacuo. The product was
filtered
through 100 mL of silica gel, eluting with 15% ethyl acetate/hexanes then 25%
ethyl
CA 02390531 2002-05-08
WO 01/34598 PCT/US00/29954
-38-
acetate/hexanes to give 0.200 g of the desired product: mp 91-95 °C. MS
(ES) m/z
(relative intensity): 356 (M++H).
Elemental analysis for CZ~Hz6NZ0
Calculated: C, 80.41; H, 7.31; N, 7.81
Found: C, 80.57; H, 7.39; N, 7.69.