Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR HOSE STORAGE IN AN ARTICLE
HANDLING DEVICE
FILING NOTES: claim priority -5/23/00
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates generally to improvements in the design and
operation of article handling apparatus and in particular to hose storage and
retraction
techniques useful in the environment of article handling devices that use a
hose type
of article gripping mechanism.
2. Description of the Prior Art
Most prior art article handling mechanisms, more specifically referred to in
the
description of the present invention as being in the environment of a point-of
sale
(POS) article dispenser, rely on a multitude of motors, switches and solenoids
for
moving various portions of the handling mechanism, and handling of the
articles
themselves, such as packaged products. Most such machines require one motor,
switch and/or solenoid dedicated for each row, column or type of article or
package to
be handled or dispensed therefrom. Such machines generally suffer from
numerous
disadvantages, such as poor reliability due to mechanical failures, as well
known by
those skilled in this art.
US Patent 5,240,139 represents a significant improvement in article handling
devices. It describes the use of a negative air pressure lifter (i.e., article
pickup or
handling mechanism), which uses suction, i.e., a reduced or so-called
"negative" air
pressure created by a partial vacuum, for making a secure contact to an
article to be
retrieved by entering the open top of an article storage bin located in a
refrigerated
storage area of a vending machine. Although robotic, and specifically suction-
type
lifting mechanisms are in common use in factory settings, where space
limitations are
generally relaxed, their use in tight confines, such as an article vending
machine, has
not gained wide acceptance. Due to the greater reliability and versatility of
vending
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
machines of the type which utilizes suction technology for grasping and moving
selected articles, it would be desirable to develop new techniques and methods
for the
operation and control of such machines, as well as for other more generalized
article
handling mechanisms.
Hose storage is provided in the forenoted US Patent 5,240,139 by use of a
longitudinally compressible air hose having about a 3:1 compression ratio. One
end
of the hose is connected to a source of negative air pressure and another end
is
connected to an article pickup head. The use of a compressible hose is
satisfactory in
the environment of US Patent 5,240,139 since the freezer compartment only
occupies
the lower half of the interior of the vending machine, leaving the upper half
available
for the hose and its positioning mechanism. However, since the significant
part of the
expense of operating a vending machine business comprises servicing (i.e.
refilling)
of the vending machine with products, it would be desirable to be able to
provide
taller article storage bins, with or without a freezer compartment, in order
to
maximize the article storage volume within the interior of the vending machine
cabinet. . Prior art article dispensers typically use between 50 and 60
percent of their
available height for article storage.
Due to the above noted disadvantage, it would be desirable to decrease the
height requirement for the hose positioning mechanism. One such way would be
to
consider the use of a non compressible hose. A non compressible hose has the
advantage that it can be driven andlor guided by direct engagement with the
walls of
the hose, a much simpler technique as compared to the indirect hose
positioning
technique of the forenoted US patent 5,240,139. Additionally, a non
compressible
hose has the advantage of maintaining a constant length in spite of being
subjected to
changes in vacuum. Even furthermore, a non compressible hose has greater
structural
integrity and reduced leakage, as compared with for example telescopic tubing.
However, two serious problems are presented by the use of a non compressible
hose:
where can a sufficient length of the hose be stored in order that it's free
end can travel
the distance from the bottom of the hose positioning mechanism (a position
aligned
with the top of an article storage bin) to the bottom of the article storage
bin; and how
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
can it be simply and reliably be withdrawn and retracted to and from the
storage area
as needed?
PCT patent publication WO 99/12132 entitled VENDING MACHINE
discloses a vending machine having a folded articulated arm for positioning an
article
gripping suction hose into a freezer for retrieving articles to be dispensed.
The hose is
. non-compressible, and continuous from a base area located beneath the
articulated
arm to its free end, where it is coupled to an article pickup head. A linear
actuator and
arm mechanism located in the base area is used to drive the hose into and out
of the
base area, through the articulated arm and into the freezer compartment. The
hose
positioning arrangement of this PCT patent publication has a similar
disadvantage as
the forenoted US patent 5,240,139, in that a significant volume within the
vending
machine cabinet is required for the mechanism which positions the hose over
and into
the storage bins during a package dispensing cycle (i.e., a height almost
equal to the
height of the article storage bins themselves). Additionally, it is noted that
only a
relatively small length of hose is required to be stored, corresponding to the
amount of
hose required to move the article pickup head in the Z direction (i.e., into
and out of
the freezer), since a significant length of the hose is already stored in the
folded
articulated arm. Even furthermore, it is noted that this patent publication
teaches a
relatively complex mechanism fox hose positioning, storage and drive.
U.S. patent 3,977,037 entitled VACUUM CLEANER, US patent 4,212,421
entitled RETRIEVAL AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS, and
US patent 5,740,581 entitled FREESTANDING CENTRAL VACUUM SYSTEM,
are representative of a class of patents which disclose apparatus for
retrieving and
storing an elongated flexible/compressible element, such as an electrical cord
or hose.
Generally, after the flexible element is withdrawn from the storage area, a
"pinch
roller" arrangement is driven so as to retract the flexible element into the
hose storage
area. Unfortunately, due to the flexibility/compressible in the nature of the
flexible
element, it's retraction takes place in a relatively haphazard manner and may
become
entangled during a subsequent withdrawal of the element.
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
German patent DE 2455673 by G. Lucas, published May 26, 1976 and entitled
VENDING MACHINE FOR ICE CREAM-USING SUCTION HEAD TO PICKUP
WRAPPED BLOCKS OF ICE CREAM FROM STACK IN REFRIGERATOR
discloses an ice cream vending machine wherein a movable carriage is mounted
inside a freezer and laterally positionable over the article storage bins. The
carriage
includes a drive mechanism for lowering an electric cord having a suction
motor at its
free end into the article storage bins for retrieving the ice cream packages.
This type
of positioning mechanism for an article handling device avoids the problem of
hose
storage by actually lowering the suction motor into the bin. It's is
particularly
disadvantageous since the repeated bending and flexing of the electric cord
can lead
to reliability/failure problems. Additionally, the diameter of the suction
motor places
severe limitations upon the dimensions of the article storage bins.
U.S. patent 5,957,326 entitled APPARATUS FOR RETRIEVING
RANDOMLY ORGANIZED ARTICLES, describes a vending apparatus including
carriage mounted for being laterally positionable over an article storage bin,
and
includes a drive mechanism for lowering into the storage bin a pickup head
having a
plurality of suction cups mounted thereon. Each suction cup is individually
connected
to a substantial length of hose which leads back to a manifold which supplies
suction
thereto. This type of positioning mechanism for an article handling device is
particularly disadvantageous since the plurality of suction hoses connected to
the
pickup head are not provided in a hose storage area, and instead are
coiled/dragged
beneath the carriage during its repositioning thereby protruding significantly
into a
space which could more advantageously being used for the storage of articles
to be
vended/dispensed.
US patent 4,725,186 entitled LIFT TRUCK WITH A VACUUM LOAD-
SUPPORTING ASSEMBLY discloses a fork-lift type of truck wherein the forks are
replaced by a vacuum pad assembly for adhering to and transporting a load. A
continuous pneumatic hose is provided between a vacuum pump located at the
rear
end of the truck and the vacuum pad assembly located at the front end of the
truck. In
order to accommodate movement of the vacuum pad assembly during handling of
the
load, a roller and tension assembly is used to form a tension loop in the hose
which is
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
intermediate the vacuum pump and the vacuum pad assembly. Although the
disclosed arrangement provides a means for preventing entanglements of the
hose
during its use for transporting articles, it is noted that the environment of
this patent
does not show or suggested a separate hose storage area, nor an enclosure for
storing
the articles to be handled.
It would be desirable to provide a storage area which uses less of the
interior
volume of the article storage enclosure for meeting the hose storage
requirements for
a hose type of article handling mechanism. Furthermore, it would be desirable
to
provide such a hose storage area in a relatively simple and reliable manner.
OBJECTS OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, one of the objects of the present invention is to provide new
techniques and methods for the design, operation and control of article
handling
mechanisms.
It is a further object of the present invention to provide new techniques and
methods for the design, operation and control of article handling mechanisms
of the
type that utilize computer-controlled electromechanical technology, and in the
illustrated embodiment a robotically positioned suction-type gripper, for
grasping and
moving a selected article from one area to another, such as from a storage
area to a
dispensing area.
It is also an object of the present invention to provide new techniques and
methods for such mechanisms, which improve the speed and accuracy of the
article
handling operation while still handling the articles to be dispensed in a
caxeful manner
so as to prevent any damage thereto.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The above objects are achieved in an illustrated embodiment of an article
handling apparatus embodied, for example, as a vending machine, including a
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
controllably positioned hose dispenser for retrieving articles from an article
storage
area. A hose is continuous from a first end located within a hose storage
area, where
the hose receives article securing energy (e.g., suction), to a second end
adapted to
secure to and extract a selected article from the storage area. A hose
positioning
mechanism coupled to the hose controllably positions the second end of the
hose so as
to be aligned with a given article stored in the storage area, for
controllably contacting
and extracting the selected article from the storage area, and controllably
positioning
the second end of the hose so as to transport the article to a dispensing
area. The hose
positioning mechanism imparts both a storage requirement and a retraction
requirement on the hose as a result of the controllable positioning. In
accordance with
the principles of the present invention a single hose storage axea is provided
in the
vending machine for meeting all of the hose storage and retraction
requirements.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention, the hose positioning
mechanism is used to withdraw the hose from the hose storage area, and the
hose
retraction requirements are met simply and reliably by the use of a retraction
mechanism comprising a "gravity-induced", i.e., passive, loop tensioner which
is
formed in the hose storage area.
In accordance with a further feature of the invention, the single hose storage
area is formed as a rectangular volume having a longitudinal axis which does
not
intersect the longitudinal axis of the article storage area, and in a
preferred
embodiment, is adjacent to and parallel with a longitudinal axis of the
article storage
area.
In one embodiment of the invention, the hose comprises a suction sustaining
air hose and the article securing energy comprises suction. In a further
embodiment
the hose can be solid or multi-stranded, and the article securing energy may
be
electrical or electromechanical, for operating an electromagnet or mechanical
claw
gripper, respectively.
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
FIG. 1 is a front perspective view of a vending machine constructed and
operating in accordance with the principles of the invention.
FIG.s 2 and 3 are front perspective views of the vending machine of FIG. 1,
with the front door opened, so as to illustrate the main mechanical and
electrical
components therein, as well as the hose storage area and retraction mechanism
constructed in accordance with the principles of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a functional block diagram illustrating the cooperation of the main
mechanical and electrical components in the vending machine of FIG. 1.
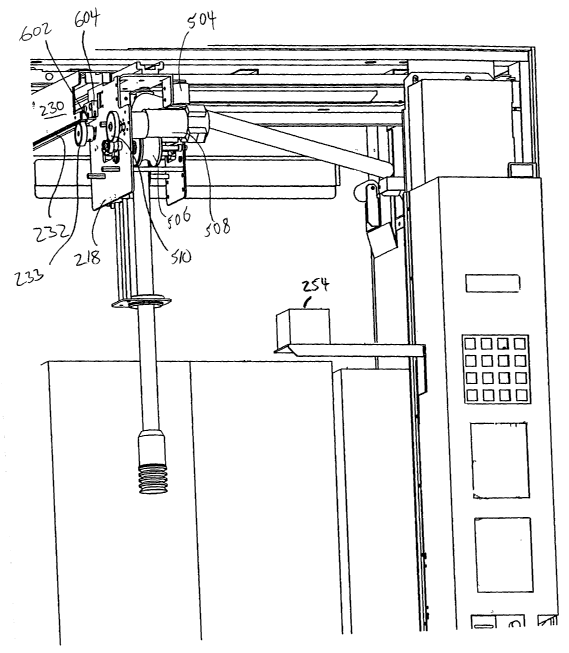
FIG.s 5 and 6 illustrate a right and left perspective view, respectively, of
the
hose positioning mechanism shown in FIG.s 2 and 3.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS OF THE
INVENTION
FIG. 1 illustrates an environment for the invention described herein, in the
form of an article dispenser, such as a point-of sale (POS) dispenser.
Although
throughout the following description, reference is made to implementation of
the
invention in a vending machine environment, it is intended that the term
"vending
machine", and in fact the environment for the present invention, include more
general
purpose article handling, retrieval and/or dispensing apparatus, as well as
POS
equipment. Such equipment, if embodied as a portable device may comprise and
be
about the size of a traditional vending machine or as large as a tractor-
pulled trailer,
and if embodied as a non-portable device may comprise and be embodied as an
automated dispensing room or an area located in a permanent structure, such as
in a
building (aboveground or underground, and with or without interior walls or an
enclosing cabinet). Furthermore, it is intended that the term "articles" or
"products"
include in at least some of the embodiments of the invention described herein,
not
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
'only goods, but also services and/or information, in either a permanent or
temporal
form.
Accordingly, FIG. 1 illustrates a perspective view of a vending machine 10,
comprising one embodiment for an apparatus which is constructed and operates
according to the present invention. Vending machine 10 includes a main cabinet
12
and a front door 14 mounted on a hinge 16 for providing access to the interior
of the
vending machine for servicing (refilling it with articles, maintenance, etc.).
Note, in a
further vending machine embodiment, a service door or port could be positioned
anywhere on or as a part of cabinet 12. In FIG. 1, front door 14 is shown in a
closed
position, forming an enclosure with main cabinet 12, within which various
components of vending machine 10 are housed, as explained in more detail
below.
Front door 14 includes a convex-shaped section 18 adjacent a flat section 20;
however, these particular shapes are not necessary to the invention. The
convex-
shaped section 18 comprises a translucent plastic display panel 18, which
typically
has brand name andlor logo graphics displayed thereon, and may even include
graphics which illustrate the individual articles that are vendible by vending
machine
10, as well as the price and/or selection information for the articles. Panel
18 is
typically back-light using fluorescent bulbs, not shown.
A customer retrieval area 22 is formed in the panel 18 on door 14 so that
articles stored therein can be discharged to a user of vending machine 10.
Various user interface features are mounted on flat section 20 of door 14. A
customer display 24 may be a conventional fluorescent or LED display panel for
displaying various items of information to a user of machine 10, such as
feedback to
the user of the selection made, the amount tended, and if the product is sold
out or
being vended. For accepting payments, a bill acceptor slot 26 accepts paper
money
into a conventional bill acceptor mechanism (mounted inside machine 10 so as
to
have its user interface portion extend through an aligned opening in flat
section 20)
for purchasing articles or for making change. A coin insertion slot 28 accepts
coins
into a conventional coin changer (also mounted inside machine 10 so as to have
its
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
user interface portion extend through an aligned opening in flat section 20)
for
purchasing articles or fox making change. A coin return actuator 30 comprises
a
conventional push-button mechanism for activating a coin return portion of the
coin
changer mechanism which, upon actuation returns coins inserted by the current
user,
to a coin return well 32. The coin return portion of the coin changer
mechanism also
provides change to the coin return well 32 either in response to the
purchasing of
articles or for making change for paper money or larger coins. A credit/debit
card slot
34 accepts a plastic credit/debit card inserted into a conventional card
reader
mechanism (also mounted inside machine 10 so as to have its user interface
portion
extend through an aligned opening in flat section 20) for allowing a user to
pay for
purchases via credit/debit cards. A door lock mechanism 36 enables front door
14 to
be secured so that it cannot be opened without a key. For allowing user
selections,
display panel 18 may include graphics, as noted above, which indicates the
various
articles vendible by the machine, as well as their associated price and unique
selection
number. Alternatively, flat section 20 could include a group of graphic
article
displays and their associated price. A conventional keypad push-button
mechanism 38
is provided for enabling a user to select a desired article from vending
machine 10.
Alternatively, push-button mechanism 40 could include individual push buttons
for
each article selection, as well as an associated price display; and even
furthermore, a
user operated touch screen could replace pushbutton mechanism 40 and display
24.
Although not shown in Figure 1, machine 10 also includes a conventional
telecommunications component that can be used for authenticating credit card
purchases, as well as other uses relating to machine control and reporting the
inventory and operational status of machine 10 to a remote location, as more
fully
described later on. Although vending machine 10 is illustrated to include the
above
described user interface components, in a more minimal embodiment of the
invention,
most, if not all, of these user interface components could be omitted, and the
dispenser could in fact be controlled from a remote location, with or without
a local
payment system.
FIG. 2 is a front perspective view of the vending machine of FIG. l, with the
front door open, so as to illustrate the main mechanical and electrical
components
therein. FIG. 3 is a somewhat idealized version of the main components of the
article
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
handling mechanism portion of vending machine 10, and is useful for
understanding
its general operation. Note, some portions of vending machine 10 are shown in
these
FIGURES cut away in order to better illustrate the interior components.
Referring first to FIG 2, it is noted that the right portion of the front of
cabinet
12 includes a vertically mounted support panel 202 which is used for mounting
most
of the user interface components. More specifically, a hinged mounting bracket
204
is mounted on panel 202 and aligned with an opening in door 14 so that the
user
interface components, such as the selection button keypad 40, coin insertion
slot 30,
bill acceptor slot 28, coin return 32, and customer display 24, are all
accessible to the
user from the front side of door 14. Mounted on the interior of front door 14
axe two
fluorescent bulb light sources (which are behind protective covers 206. Other
numbers of light sources can be used) which emit light for backlighting panel
18. A
ballast 208 for the fluorescent bulbs and a product delivery chute 210. Note,
the
product delivery chute 210 is unconventional in that it is extremely tall, and
therefore
serves as a security measure to prevent unauthorized access into the machine
by
insertion of an arm or other grasping mechanism into the customer retrieval
area 22
from outside the machine. In typical prior art vending machines, a swinging
security
door is usually found at the top of chute 210, which swings into a vandal
blocking
position when the customer pushes in the swinging door at the entrance to the
product
retrieval axea 8. In a further embodiment of vending machine 10, such a
security door
could be used in conjunction with product delivery chute 210, especially if
chute 210
is not as tall as the one illustrated in Figure 2 and also if the product
retrieval area 8 is
located higher up on machine 10. Mounted behind hinged mounting bracket 204 is
a
conventional bill acceptor mechanism for causing paper money inserted into
bill
acceptor slot 28 to be drawn into vending machine 10, a conventional coin
changer
supplies coins to coin return slot 34 and is located behind panel, a coin
guide guides
inserted coins into the coin changer, and a conventional bill validator
ascertains
proper insertion of paper money into bill acceptor slot 28 .
A control board 212 comprises a printed circuit board on which circuitry is
formed and to which integrated circuit chips are attached. Control board 212
includes
a microprocessor that is electrically connected to various sensors, motors,
the above
to
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
described user interface elements, as well as other devices within vending
machW a
10, to control the operation of vending machine 10 as described herein. When
reference is made in this description to performance of specified functions by
control
board 212, it is to be understood that these functions are controlled by the
microprocessor and the associated circuitry formed on control board 212. A
power
supply 214 is mounted on panel 202 and supplies power for the electrical
components
of vending machine 10.
Referring now also to FIG 3, it is apparent that the bulk of the interior of
cabinet 12 is available as an article storage area 215. In the illustrated
embodiment, a
plurality of vertically aligned article storage bins 216 are arranged on the
interior floor
217 of cabinet 12, for storing articles 223 to be vended by machine 10. In a
refrigerated environment for the present invention the bins could be arranged
to sit on
a shelf positioned above the refrigeration system. An opened-top container 219
can
be dimensioned to hold a plurality of article storage bins 216 therein, and
used to
facilitate their simultaneous handling (i.e., removal and installation) of the
plurality of
bins 216 from article storage area 215.
An opened-top container 219 can be dimensioned to hold a plurality of article
storage bins 216 therein, and used, for example to facilitate the simultaneous
handling
(i.e., removal ,installation and transportation) of the plurality of bins 216
into/out of
the article storage area 215. Container 219 also facilitates rapid and
accurate
positioning of a plurality of the article storage bins into the storage area
of the article
handling apparatus. A carriage 218 (which may be more generally referred to as
an
X-Y or planar positioning mechanism) is coupled to the interior topside of
cabinet 12
and adapted for being controllably positioned by the control board portion 212
of
machine 10, to a location centered over (so as to be aligned with) the open
top-end of
a selected one of article storage bins 216.
Although vertical (Z-axis) alignment of the article storage bins 216 is shown,
non-vertical, i.e., slanted or even horizontal (X or Y axis) alignment may
also be
possible (such as found in the well know glass front vending machines of the
type
using a "spiral wire" type of dispensing apparatus). In the event of
substantially
11
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
horizontal alignment of the storage bins, the planar positioning mechanism
will be
appropriate changed so as to position carriage 218 for movement in the X/Z or
Y/Z
plane. In fact, a curvilinear plane, such as a cylinder, is also considered to
be within
the scope of the present invention. The combination of substantially
horizontally
aligned stacks of products with a robotically controlled article transport
mechanism
which moves in a vertical plane adjacent to dispensing ends of the stacks of
products,
is known, for example in US patent 6,230,930 issued May 15, 2001 and entitled
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR VENDING PRODUCTS, and in US patent
publication US 2001/0000609 published May 3, 2001. Use of a curvilinear plane
for
article transport is known, for example in the videocassette vending art,
wherein the
videocassette's are stacked in an outwardly facing manner in a central storage
carousel, and a robotic gripper encircles the carousel. Furthermore, although
article
storage bins 216 are shown to be an ambient environment, bins 216 could in
fact the
positioned in a refrigerated environment, such as a freezer located in the
bottom of
storage area 217, and the article transport mechanism enter the bins from a
top
opening the freezer, such as shown and described in the forenoted U.S. patent
5,240,139. Alternatively, in the event the refrigerated environment is of the
type
including a substantially horizontal alignment of the storage bins, a
vertically oriented
opening could be used to provide access to the dispensing end of the article
storage
bins.
In the environment of the present invention, an air hose 220 is used to
provide
an "article securing force" which facilitates securing, grasping and
releasing, i.e.,
handling, by an article pickup head 224 of the articles 223 stored in bins
216. In
accordance with one aspect of the present invention, air hose 220 is
continuous from a
point before it's exit from a hose storage area 222 over orthogonally
positioned rollers
213, to its free end 221. Free end 221 includes a weighted portion 225 in
combination
with a bellows extension tip portion 227. Depending upon the physical
characteristics
of the articles to be dispensed, article pickup head 224 may comprise only the
weighted portion 225, or this portion in combination with a fitting
specifically
adapted to the type of packages to be dispensed, such as the bellows tip 227
or a
compliant tip without a weight. Hose 220 has one end coupled to a source of
negative
air pressure, i.e., suction, which source of suction comprises in the
preferred
12
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
embodiment a blower motor 226, and a free end couplea to the article pickup
heaa
224. In the present invention, the word continuous is intended to mean a hose
which
is connected and acts between it's end points, in order to accomplish the
functions
required by it, as a unitary/single hose. An air hose portion 235 provides
suction from
blower motor 226 to one port of an air junction box 229, while continuous hose
220 is
connected to a second port of air junction box 229. Air junction box 229,
included at
a top portion of hose storage area 222, includes an airflow sensor and vacuum
breaker
assembly. The airflow sensor is used to develop a signal which is applied to
the
controller of the vending machine and is representative of the airflow through
air hose
220. The vacuum breaker assembly is used to quickly bring the air pressure in
hose
220 to the ambient pressure, thereby facilitating a "quick-release" of an
article
transported by the article pickup head, into the dispensing chute 210. It is
noted that a
quick release of the products does not have to occur at the top of dispensing
chute
210, and in the event that it is desirable to avoid subjecting the article to
forces which
result from jarring or dropping, the article pickup head could proceed to the
bottom of
the dispensing chute 210 before providing the quick release of the article. In
one
embodiment, the airflow sensor arrangement may comprises a two-part switch, a
first
part includes a reed switch mounted on a top portion of box 229, and a second
part
includes a magnet mounted at the free end of a swinging arm mounted inside box
229.
As the arm swings inside box 229 due to changes in airflow, the switch is
"toggled",
thereby indicating changes in airflow. The use of this airflow signal will be
described
in greater detail later.
In the environment of the present invention, as shown generally in FIG 3, and
more specifically in Figures 5 and 6, a novel hose positioning arrangement is
provided
for aligning carriage 218 with a selected one of bins 216. This alignment is
accomplished in the front/back (Y) direction using a front/back linear slide
228
(shown in a cut away view) mounted to an "L" shaped front/back beam 230 so
that
carriage 218 can be controllably positioned therealong using slide 228. A
bottom
edge portion of beam 230 includes a rack portion 232 and carriage 218 includes
an
electric motor 233 that drives a gear (633 of Fig. 6) which engages rack
portion 232.
Application of forward and reverse motor control signals from control board
212 to
motor 233 causes carriage 218 to be driven in the front/back directions.
Alignment of
13
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
carriage 218 in the leftlright (X) direction is accomplished in a similar
manner, using
a leftlright linear slide 234 which slidably couples the top side of
frontlback beam 230
to the underside of each of spaced apart left/right beams 236a and 236b. Beams
236a
and 236b are rigidly attached to the inside top portion of cabinet 12. A rack
238, also
rigidly attached to the top inside portion of cabinet 12 and in parallel with
beams 236,
is engaged by a gear 240 driven by a reversible motor 243 mounted near the
inside
corner of beam 230. Application of forward and reverse motor control signals
from
control board 212 to motor 243 causes a rotation of gear 240 and a
corresponding
movement of beam 230, and hence carriage 2I 8, in the Ieft/right (X)
directions.
As shown in FIG.'s 2 and 3, as an article 223 is moved by pickup head 224
along its way from a storage bin 216 to chute 210, it is positioned past an
article
identification (ID) device 254 mounted within cabinet 12. A specific type of
article
ID device is not required for the present invention, and depending upon system
constraints, such a device may comprise, for example, a bar code scanner or
other
optical image/pattern recognition system, or even a non-optical system, such
as a
radio frequency identification (RFID), or magnetic-based system mounted within
cabinet 12. for uniquely identifying and confirming that the article being
dispensed is
in fact the article that was selected. The construction operation of such
article
identification devices are well known to those of ordinary skill in this
technology, and
therefore further description in this regard is not necessary.
Article ID device 254 is mounted within cabinet 12 at a relatively fixed
location, the mounting being such that some controlled movement in the
orientation
of article ID device 254 may be facilitated, in order to help ensure a good
"view" of
the article being transported, and a high confidence of the transported
articles being
identified. One way to provide such controlled movement for ID device 254
would
be to mount it on a piezoelectric substrate, and control board 212 could
provide a
voltage to the substrate so as to shift the "view" of ID device 254. It is
noted that by
using an appropriately positioned article ID device 254, only a single article
ID device
254 is needed. This is particularly useful for a robotic type dispenser, since
the
robotic apparatus can controllably position, and re-position if necessary, the
article in
14
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
the vicinity of the article ID device 254, thereby helping ensure a reliable
ID of the
article.
Note that although carriage assembly 218 only moves in a single plane, it is
responsible for precisely positioning pickup head 224 in each of the X, Y and
Z
directions. More specifically, as shown in FIG.s 5 and 6, carriage 218
includes a
roller arrangement 502 which comprises three orthogonally positioned rollers
504 at
the point where hose 220 enters carriage 21 &, for redirecting the movement of
hose
220 from a substantially horizontal direction along the top interior portion
of machine
10 (i.e., in the X,Y direction), to a direction perpendicular thereto (i.e.,
in the Z
direction). Movement of carriage 218 will hot only move the free end 221 of
hose
220 so that it can be axially aligned with a selected one of bins 216, but it
will also
automatically withdraw hose 220 from the hose storage area 222. Thereafter, a
hose
drive mechanism which may comprise a set of conventionally operated "pinch
rollers"506 driven by a reversible motor 508 via gear set 510 which are used
for
driving pickup head 224 into/out of the selected bin 216 in order to retrieve
articles
stored therein.. In the illustrated embodiment the hose drive mechanism is
mounted
in carriage 218, but in a further embodiment motor 508/rollers 506, or some
other
drive mechanism, such as the articulated arm shown from the forenoted PCT
publication WO 99/12132, could be mounted so as to act somewhere else along
the
length of hose 220.
This arrangement, where hose 220 travels in the same X,Y plane that carriage
218 travels, facilitates a compact hose positioning and drive mechanism
embodiment
for the present invention. Furthermore, since movement of the carriage is
responsible
for supplying most of the force needed to withdraw hose 220 from storage area
222"
the Z drive motor is only needed to drive the hose for causing its free end to
travel
into/out of bins 216 for article retrieval. It is noted that the pinch rollers
506 should
comprise a soft rubber material so as to provide a good friction contact to
hose 220,
and if the hose 220 is corrugated, rollers 506 could have
corresponding/matching
corrugations. In the illustrated embodiment, it has been determined that two
drive
rollers are not needed, and accordingly only one of the pinch rollers is
driven by
motor 508, while a spring (514) is used to urge the other roller towards the
driven
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
roller, thereby pinching and driving hose 220 therebetween. rurttiermore wrien
using
corrugated hose, in some applications it may be possible to replace pinch
rollers 506
with a linear screw mechanism adjacent hose 220, for driving the hose.
In the vending machine environment, having a compact hose positioning and
drive mechanism is significant. Consider a cabinet having a height of 72
inches: a
prior art hose positioning mechanism, such as provided by the forenoted US
patent
5,240,139 or the PCT patent publication WO 99/12132 typically occupied
approximately 40 percent of the height dimension inside the cabinet, thereby
leaving
60 percent or less for the storage of articles to be vended. With the
arrangement of
the present invention the hose positioning and drive mechanism comprises less
than
25 percent of the interior height of the enclosure, a very desirable result.
Additionally, it is noted that the compact hose positioning and drive
mechanism of the
present invention is extraordinary in that in the illustrated embodiment it
occupies
approximately only 15 percent of the interior height of the enclosure. What is
even
more remarkable is that this very compact hose positioning and drive mechanism
can
position the free end of the hose into alignment with a bin of articles, and
then have
the ability to drive the hose all way to the bottom of the bin. In the present
invention
the hose is able to be driven a distance which is greater than three times the
height of
the hose positioning mechanism and in fact, in the illustrated embodiment the
hose is
driven approximately five times the height of the hose positioning mechanism.
A bin holder 260, shown in FIG. 2, comprising a pair of rectangular brackets
secured in a spaced manner to opposed interior side walls of cabinet 12, is
used to
maintain the bins situated therebetween in a predetermined position relative
to the
interior of the vending machine cabinet. This is required in view of the pre-
programming of control board 212 which controls the robotic structure for
retrieving a
selected article from one a selected one of bins 216.
As previously noted, since hose 220 is formed of a continuous material from
its connection to the source of suction at one end to the pickup head 224 at
its other
end, means are necessary for providing hose storage and/or retraction during
travel of
16
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
the pickup head 224 in the X, Y and Z directions, as appropriate during the
article
dispensing operations.
As shown in Fig. 3, placing an interior wall 246 parallel and adjacent to an
exterior wall 248 of cabinet 12 is used to form the hose storage area 222
there
between. Hose storage area 222 has a cross-sectional area which is slightly
greater
than the cross-sectional area of the hose loop formed therein. Walls 246 and
248 are
shown partially cut-away so as to illustrate a gravity feed self retracting
loop
tensioner/ retraction mechanism 250 formed in hose 220. Loop tensioner 250 is
constrained for movement within hose storage area 222, and made somewhat self
retracting by comprising a rolling weight 252 having a groove 253 along its
periphery
in order to provide constant centering of the weight within hose storage area
222 and
for providing a constant, passive "loop forming" tension on hose 220.
Furthermore,
centering of the grooved rolling weight 252 within hose storage area 222
results in
centering of hose 220, thereby preventing hose 220 from rubbing with the walls
of
hose storage area 222 during X, Y and Z repositioning of pickup head 224. In
order
to prevent binding of hose 220, rolling weight 252 is dimensioned so as to be
slightly
larger than the diameter of hose 220 and the width dimension of hose storage
area 222
is dimensioned to be only slightly larger than the width dimension of rolling
weight
252. The specific amount of weight used for rolling weight 252 is a matter of
design
choice, and depends upon various factors, such as the weight of the articles
to be
moved, the strength of the motors used to drive the hose in the Z direction,
etc. In a
further embodiment, it may be desirable to couple weight 252 to a lower
portion of
cabinet 12 using a spring, for adding fut-ther tension to loop tensioner 250.
It is also noted that this gravity-based retraction/ hose storage technique
meets
the storage requirements needed for both the X and Y movements of carriage 218
(left/right and front/back), as well as for the Z movement of pickup head 224.
Of
course this gravity-based retraction/ hose storage technique would work
equivalently
well in an embodiment wherein the robotic hose positioning mechanism used a
rotary
type device (R, 0), an articulated arm, telescoping or scissor system, or
other
technique. Furthermore, the illustrated gravity-based retraction/ hose storage
technique is not necessary for some embodiments of the present invention, and
in fact
17
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
a fully or partially motorized retraction technique could also be used.
Furthermore, in
other embodiments, it may be desirable to place hose storage area at another
location,
such as parallel to the top or rear portion of cabinet 12. In the event it is
in the top
portion of cabinet 12, the passive, gravity based retraction described above
would not
be appropriate, and instead an active system would be needed, such as one with
a
motorized retractor.
Even furthermore, although only a single storage area 215, hose 220 and
carriage 218 are shown in the illustrated embodiment, the invention described
herein
could also be used in a dispensing apparatuslarticle handler of the type
having
multiple storage areas and/or robotic article handling mechanisms, such as two
robotic
mechanisms (vertically or horizontally positioned) each one serving, for
example, a
different storage area (such as one being refrigerated and one being non-
refrigerated,
or one being oriented for vertical storage of products and the other one for
horizontal).
In this case a separate hose, hose positioning mechanism and hose storage area
may
be required, although they may possibly share a single source of suction
(e.g., blower
motor 226), airflow sensor and vacuum breaker. Alternatively, a single hose,
hose
positioning mechanism and hose storage area could be used in a further
embodiment
where the single hose services more than one article storage area. Each
robotic article
handling mechanism could have its own article ID device, or they could share a
single
article ID device.
In the embodiment illustrated herein, blower motor 226 provides a relatively
high volume of airflow but a relatively modest negative air pressure. As a
matter of
design choice, blower motor 226 could comprise a vacuum pump, so as to provide
a
much more substantial degree of negative air pressure, but, due to size and
cost
limitations, a correspondingly reduced amount of airflow. In this latter case,
the
diameter of the air hose 220 would be reduced from the diameter illustrated in
FIG's 2
and 3, which may be particularly important in some applications of the present
invention . The illustrated embodiment is particularly useful for picking up
flexible
packages since a momentary or even sustained leak in the coupling to the
packaging
to the article will generally not result in dropping of the package, while at
the same
time offering extreme versatility due to the ability to pick up a wide variety
of shaped
18
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
obj ects of varying weight and size. In the event that blower motor 226
comprises a
vacuum pump, it could be used alone or in combination with a storage tank
coupled to
the suction hose via a valve and air hose, in order to provide a greater
volume of
airflow. Alternatively a compressor could be used in combination with a
venturi
device to create a vacuum.
Alternative embodiments for the robotic hose positioning mechanism
described above are contemplated to be within the scope of the present
inventions.
For example, instead of using a combination of left/right slides 234 and
support
beams 236a and 236b, a roller/guide rail combination could be used. Support
beams
236a and 236b may comprise a support plate having two outwardly facing, i.e.,
opposed, L-shaped rails, along its edges. The function of slides 234 could be
accomplished by fixing a pair of brackets to opposed ends of beam 230, each
bracket
including a pair of spaced apart and inwardly facing rollers which engage and
follow
the opposed rails on the support plate. Furthermore, the spaced apart and
inwardly
facing rollers could each comprise a set of rollers positioned to be angled 90
degrees
with respect to each another, so as to engage or follow the two orthogonal
surfaces of
the L-shaped rails. Such arrangement may result in a coupling of carriage 218
to
beam 230 which needs less adjustment for proper operation. Furthermore, as
previously noted, the event of substantially horizontal alignment of the
storage bins,
the robotic hose positioning mechanism can position carriage 218 for movement
in a
vertical plane which is substantially flat (i.e., in the X/Z or Y/Z plane) or
in fact a
vertical curvilinear plane. Additionally, as previously noted, in some aspects
of the
invention, it may be desirable for the robotic hose positioning mechanism to
include a
rotary device (R, ~) of the type including an I beam of fixed length (or
telescopic
sections), for establishing the "R" movement of the gripper/pickup head, which
pivots
for establishing the "0" movement. Alternatively, in other environments for
the
invention the robotic hose positioning mechanism may include an articulated
arm or
scissor system, or other technique.
19
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
FIG. 4 illustrates a functional block diagram of the general operation of the
various aspects of the invention described herein, as embodied in an article
dispenser
of the type comprising, for example, vending maclune 10. A control system 400
including a microprocessor 402 and associated memory circuits 404, is
constructed on
control board 212. Control system 400 may also include the electronic parts of
other
portions of vending machine 10, as appropriate. Memory circuits 404 include
ROM
for storage of operating programs (embedded software, as well known, for
accomplishing the described herein control of vending machine 10), as well as
RAM
cache for temporary storage of operational data during system operation as
well as
other data as may be needed. Control system 400 is responsive to user
operation of
the user payment and selection system 406 (including the coin and bill
mechanism 28
and 30 and the selection buttons 40 of FIG. 1) for operating the user
interface and
article handling apparatus of vending machine 10 so as to dispense the axticle
desired
by a user. More specifically, upon proper payment for a selection made by the
user
using payment and selection system 406, control system 400 operates the X/Y
(left/right and front/back) drive motors 233 and 243 so as to position pickup
head 224
to be in alignment with a bin 216 which holds the article selected by the
user. Control
system 400 then engages a hose drive motor 508 (Z-motor) mounted within and
carried by carriage 218, so that hose 220 is driven in a direction towards the
top
article in the aligned bin. At an appropriate time before head 224 contacts
the article
to be removed (and in an embodiment of the invention where cabinet 12 does not
include refrigerated air, an appropriate time may be just before head 224
enters bin
216, but if the air is refrigerated, just before contact with the desired
article is
expected, in order to minimize removal of refrigerated air), control system
400
activates blower motor 226 so as to provide lifting suction at pickup head
224. Upon
position sensors 412 determining that pickup head 224 has contacted and become
secured to the desired article, control system 400 causes hose drive motor 410
to
reverse its direction so as to retract hose 220 from the aligned bin 216 and
thereby lift
out from the bin 216 the selected article. Carriage 218 is then driven to a
position in
alignment with the article delivery chute 210.
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
Upon sensors 412 sensing alignment of carriage 218 with chute 210 (in this
case sensor 412 may comprise a reed switch mounted on a front wall of the
cabinet,
and a magnet mounted at a leading edge of carriage 218), control system 400
turns off
blower motor 226 and the resulting loss of vacuum causes the selected article
to drop
into the customer retrieval area 22. As previously noted, in the event that
the articles
are so fragile that they should not be dropped or subjected to such impact
forces, hose
220 can be driven to the bottom of chute 210 before the article is released.
It is noted that position sensor 412 may include the airflow sensor of
junction
box 229, or in a further embodiment, comprise a mechanically operated plunger-
type
position sensor associated with pickup head 224. Even furthermore, position
sensors
412 may also include a xeed switch mounted on a front wall of the cabinet, and
a
magnet mounted at a leading edge of carriage 218.
In accordance with a further aspect of the present invention, since the
control
system keeps track of the movement of hose 220 and carriage 218(for example,
by
sensing pulses from a shaft encoder or other distance measuring device on each
of
their respective drive motors), the signal generated by the airflow sensor at
the time
carriage 218 reaches the virtual home can also be used as a check to ensure
that
control system 400 accurately counted the motor drive pulses, and can re-
calibrate the
positioning system based on the virtual home, if necessary.
A communication system 414 is connected to control system 400 so as to
provide article inventory and vending machine operation information to a
remote
location, as well as to allow for control of the operation of the vending
machine from
a remote location. In this regard, communication system 414 may include a
connection to means for making a wire-line and/or wireless transceiver
interface
through which a communication link with a remote computer can be established.
Additionally, the communication system 414 may communicate with a plurality of
other similarly connected vending machines in the same general area and
communicate therewith using the wire-line interface ox wireless communication.
Even furthermore, communication system 414 can provide for communication with
multiple vending machines andlor a local server/controller, in a local site
along a
21
CA 02410053 2002-11-20
WO 01/91071 PCT/USO1/16846
LAN (local area network), LAWN (a local area wireless network) or a WAN (wide
area network). The remote computer may comprise a database which receives
and/or
accumulates the operational data from one or more vending machines, which data
is
then accessible (via, e.g., the Internet, using a wired or wireless
connection) using
appropriate encryption, to others, such as route drivers, machine operators,
machine
owners, product suppliers, etc. Furthermore, the remote site may give feedback
to the
vending machines, such as authorization information, which can control its
operation,
such as allow its continued operation.
While this invention has been particularly shown and described with
references to preferred embodiments thereof, it will be understood by those
skilled in
the art that various changes in form and details may be made therein without
departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the
appended
claims. In fact, many such changes are already noted in this description.
Those
skilled in the art will recognize, or be able to ascertain using no more than
routine
experimentation, many equivalents to the specific embodiments of the invention
described specifically herein.
For example, although a suction providing air hose 220 has been disclosed in
the described preferred embodiments, in fact a solid element having a gripper
at its
free and, such as a mechanically operated claw (or an electromagnetic device
or even
a self contained suction generator), could also be used. Such equivalents are
intended
to be encompassed in the scope of the appended claims..
22