Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02413009 2002-12-20
WO 02/04252 PCT/CA01/00995
HEADLINER AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a headliner for use with a motor vehicle
and, more particularly, to a headliner formed of multiple layers to provide
shape
stability and a method of manufacturing the same.
2. Description of the Related Art
Headliners are used with motor vehicles to provide a pleasing finish to the
interior of a vehicle compartment. Headliners also provide for sound
absorption
and insulation and accordingly increase the quality of environment in the
vehicle
compartment.
Headliners typically include a number of different layers of material.
Typically, they are formed of a foam or urethane core sprayed between two
reinforcing layers. The layers of material are assembled and then molded into
the
desired shape, normally the shape of the vehicle ceiling. Current urethane
headliners tend to warp shortly after dernolding and often retain the
distorted
shape permanently.
Therefore it is desirable to provide a mufti-layer headliner, and method of
manufacturing same, such that the headliner will retain its molded shaped and
not
warp after being removed from the mold.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention provides a headliner and method of making the same
that overcomes the problem of permanent warpage normally occurring shortly
after demold. According to one aspect of the invention a headliner is formed
of
top and bottom layers having a urethane matrix sprayed between the layers to
form the core. The headliner includes a separate scrim layer, a film layer,
and a
CA 02413009 2002-12-20
WO 02/04252 PCT/CA01/00995
chopped fiber material randomly distributed between the film layer and the
urethane core. In some instances, a binder material may be used to increase
adherence of the chopped fiber material to the film layer. The film layer is
perforated to allow for degassing of the urethane matrix.
According to another aspect of the invention a method is provided for
forming a headliner for an automotive vehicle. The method includes the steps
of
providing a top layer and bottom layer of laminated non-woven polypropylene
scrim and polyethylene film, providing a layer of fiberglass mat between the
top
and bottom layers, dispensing a urethane matrix onto the layer of fiberglass
mat between the top and bottom layers, and randomly dispersing a chopped fiber
material between at least one of the top and bottom layers and the urethane
matrix
to provide internal structural rigidity to the headliner.
Accordingly, the combination of the chopped fiber material and a non-
woven film provide a synergistic effect that eliminates headliner warpage. The
combination of stiffiiess and mechanical bond between the film layer and
chopped
fiber material randomly distributed between the film layer and urethane core
provides this effect.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Other features and advantages of the present invention will be readily
appreciated as the same becomes better understood after reading the subsequent
description when considered in connection with the accompanying drawings
wherein:
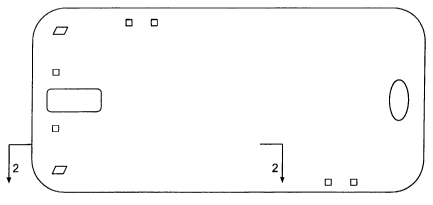
Fig. 1 is a top view of an automotive headliner according to the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is an enlarged partial cross-sectional view of the headliner of Fig. 1
taken along line 2-2 of Fig. 1;
Fig. 3 is a schematic side view of an apparatus using a method of forming
the headliner of the present invention with the press shown in the open
position;
and
2
CA 02413009 2002-12-20
WO 02/04252 PCT/CA01/00995
Fig. 4 is a schematic side view of an alternative embodiment of an
apparatus using a method of forming the headliner of the present invention
with
the press shown in the open position.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
Referring to Fig. 1, there is illustrated a headliner 10 of the present
invention. The headliner 10 conforms and fits to the ceiling of the passenger
compartment of a motor vehicle. The headliner 10 is formed as a laminate
including a top layer 12, a urethane core 14 and a bottom layer 16.
As shown in Fig. 2, each of the top and bottom layers 12, 16 include a non-
woven polypropylene scrim 18 and a polyethylene film 20 combined to form a
laminate 21. The non-woven polypropylene scrim 18 is preferably supplied by
weight, specifically, 0.1 to 2.0 ounces per square yard, while the
polyethylene film
is preferably 0.0005 to 0.003 inches thick.
15 The scrim 18 and film 20 are laminated by a combination of heat and
pressure through nip rolls. Nip rolls are a pair of opposed rollers having a
small
gap therebetween. The rollers are heated to a temperature of about 160 degrees
Fahrenheit and the scrim 18 and film 20 are run through the heated rollers to
create a bond and laminate the scrim 18 and film 20. The laminate 21 is then
20 perforated. Perforation of the laminate 21 allows air and gas to permeate
through
the laminate 21 during the step of forming the core 14.
The core 14 is formed from a layer of a fiberglass mat 42 embedded in a
urethane matrix of foam 44.
A chopped fiberglass roving 22 is randomly distributed between the film
20 of the top layer 12 and the core 14. In one embodiment of the invention,
the
chopped fiberglass roving 22 is randomly distributed on the film 20. When the
chopped fiberglass roving 22 is distributed on the film 20 prior to forming
the
substrate; i.e. when the laminate 21 includes the chopped fiberglass roving
22, a
binder material 24 is also distributed on the film 20 and operates to adhere
the
chopped fiberglass roving 22 to the film 20. The binder material 24 may be
3
CA 02413009 2002-12-20
WO 02/04252 PCT/CA01/00995
distributed on the film 20 along with the chopped fiberglass roving 22. The
binder
material 24 is a polyester powder adhesive that can be purchased from Bostick
of
Middleton, Massachusetts. When used, the binder material 24 is applied by
weight, specifically, 1 to 20 percent, by means of a shaker box that
distributes at
random a specific amount of the adhesive. The weight of the chopped fiberglass
roving 22 determines the amount of binder 24 required; e.g., 40 grams per
square
meter requires 5 grams of powder adhesive or approximately 12 percent by
weight. The fiberglass roving 22 is formed of fiberglass strands having a
diameter
of .03 inches chopped into two-inch lengths. As set forth above, the chopped
fiberglass is randomly distributed on either the polyethylene film 20 or the
urethane core 14 at a density of 5 to150 grams per square meter. It should be
appreciate that the fiberglass roving 22 may alternatively be randomly
distributed
between the polyethylene film 20 of the bottom layer 16 and the core 14 or
between both the top and bottom layers 12, 16 and the core 14.
Turning now to Fig. 3, there is shown an apparatus for use with the method
for forming the headliner panel 10. The apparatus includes a forming tool or
die
30 shown with an upper platen 32 attached to a press head 34 and a lower
platen
36 attached to a press bed 3~. The laminate 21 forms both the top 12 and
bottom
16 layers of the headliner 10 and is supplied as a rolled good from supply
rollers
40, 41. The fiberglass mat 42 is supplied as a rolled good from supply roller
4~.
During the manufacturing process, as the glass mat 42 is rolled or pulled into
the
forming tool 30, the urethane matrix 44 is sprayed onto the glass mat 42 by a
urethane spray head 46. Next, the chopped fiberglass roving 22 is distributed
from a hopper 50 onto the urethane matrix 44, after which the entire assembly
including the top layer 12, chopped fiberglass roving 22, urethane matrix 44,
glass
mat 42, and bottom layer 16 are placed in the forming tool 30 which operates,
through a molding cycle, to form the headliner 10. In this method or process,
no
binder 24 is used. If required, additional glass or other fibers can be added
as
rolled goods prior to spraying the urethane matrix 44. Also, additional
chopped
fiber materials such as jute, sisal, or hemp may be used in place of the
chopped
4
CA 02413009 2002-12-20
WO 02/04252 PCT/CA01/00995
fiberglass roving 22.
Turning now to Fig. 4, an alternative embodiment of an apparatus and
method for manufacturing a headliner 10 is shown.' Again, a forming tool or
die
30 receives the headliner 10 components from a plurality of supply rollers.
The
lower or bottom layer 16 is the laminate 21 supplied as a rolled good drawn
from
supply roller 40. A fiberglass mat 42 is also supplied from a supply roll 48.
Once
again, prior to the molding process, a urethane matrix 44 is deposited on the
fiberglass mat 42 by a urethane spray head 46. The top layer 12 includes the
laminate 21 with the chopped fiberglass roving 22 already secured thereto by a
binder material 24. The top layer 12 is supplied as a rolled good from a
supply
roller 52.
Accordingly, the chopped fiberglass roving 22 gives internal structure to
the headliner 10 as the urethane matrix 44 adheres to the chopped fiberglass
roving 22 to prevent the headliner 10 from warping after shaping and molding
in
the forming tool 30. It should be understood that the film 20, while
perforated to
allow the air and gas to escape therethrough, provides a barrier that prevents
the
urethane matrix 44 from leaking through to the outer surface of the headliner
10.
Finally, the scrim 18 provides an anti-squeak and smooth surface quality to
the
outer surface of the headliner 10.
Pursuant to the present invention, the chopped fiber material combines
with the polypropylene non-woven material and polyethylene film to prevent
warpage in headliners and similar products. As disclosed herein, various
chopped
fiber materials may be used. The invention teaches inline random distribution
of
the chopped fiber material during introduction directly onto the urethane
matrix.
Alternatively, the chopped fiber material is randomly distributed on and
attached
to the polypropylene non-woven material and polyethylene film laminate by a
binder material prior to layering with the urethane matrix.
The present invention has been described in an illustrative manner. It is to
be understood that the terminology, which has been used, is intended to be in
the
nature of words of description rather than of limitation.
5
CA 02413009 2002-12-20
WO 02/04252 PCT/CA01/00995
Many modifications and variations of the present invention are possible in
light of the above teachings. Therefore, within the scope of the appended
claims,
the present invention may be practiced other than as specifically described.
6