Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
Window Frames
The present invention relates to frames for windows and glazed doors.
S Existing window frames can be manufactured using various metals. Aluminium
is
widely used since it has the advantages that only a relatively small thickness
is required,
that it can be used in tubular sections and that thermal breaks can be easily
provided.
Cold formed steel can also be used; narrow gauge material is bent into shape
and thermal
breaks can also be provided.
Existing window frames made from hot rolled steel, including stainless steel,
have no
provision for a thermal break.
The present invention seeks to provide a window frame having a high thermal
1S performance. The present invention also seeks to provide a window frame
which
supplies a wide range of options for the materials of the inner and outer
faces of the
frame which are visible after installation.
EP 008S77S discloses windows and door frames with a thermally insulating
member
between two metal profile elements. However, the metal profile elements have a
relatively complicated cross-section since they define channels for
accommodating
retaining means for glazing units.
According to the present invention, there is provided a window frame having a
cross-
2S section with a central portion of a thermally-insulating material with
sections of a
different material attached to the inner face and to the outer face of the
central portion,
characterised in that the central portion has one or more channels for
accommodating
retaining means for a glazing unit.
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
2
An advantage of the above arrangement is that the inner and outer sections can
have a
simple cross-section and can be easily and relatively cheaply produced, e.g.
by rolling.
Such a frame is also easy to assemble.
The central portion is preferably an extruded or pultruded section of glass
fibre-
reinforced polyester or phenolic resin profile material. This means it is
relatively easy to
manufacture the central portion with all the projections and channels required
to
accommodate glazing units, beads and hardware fixings.
The central portion may be hollow and may comprise a plurality, e.g. three, of
hollow
channels .
The inner and outer sections axe preferably of stainless steel or carbon
steel.
Alternatively, they may be of aluminium, wood or PVC U. The inner section on a
window frame may be of the same material as, or a different material from, the
material
of the outer section on the same window frame.
The inner and outer exterior may incorporate U-shapes which fit over the end
regions of
the central portion. The ends of the U-shapes may be separated by gaps from
the end
regions of the central portion.
Preferred embodiments of the present invention will now be described, by way
of
example only, with reference to the accompanying drawings, of which:
Figure 1 shows an exploded cross-sectional view on an enlarged scale of a
fixed light
window frame in accordance with a first embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 2 shows the embodiment of Figure I after assembly;
Figures 3 and 4 show fixed light window frames with modified facia sections.
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
3
Figure 5 shows an exploded cross-sectional view on an enlarged scale of an
opening
window frame within an outer fixed window frame in accordance with a second
embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 6 shows the embodiment of Figure 5 after assembly;
Figures 7 and 8 show opening window frames with modified facia sections;
Figure 9 shows a view corresponding to Figure 5 of the parts of a glaze in,
open out
window frame in accordance with a third embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 10 shows a view corresponding to Figure 5 of the parts of a glaze in,
open in
window frame in accordance with a fourth embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 11 shows a view corresponding to Figure 1 of a glaze in, fixed light
window
frame in accordance with a fifth embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 12 shows a cross-section view of a glaze in fixed light window frame
according to
a sixth embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 13 shows view corresponding to Figure 12 of a glaze in open in
arrangement in
accordance with a seventh embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 14 shows a view corresponding to Figure 12 of a glaze in open out
arrangement
in accordance with an eighth embodiment of the present invention; and
Figure 15 shows a cross-sectional view of a glaze in open out window frame
arrangement
according to a ninth embodiment of the present invention.
Preferred dimensions in mm are given in the Figures.
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
4
Referring to the drawings, Figure 1 shows three parts of a window-frame
section 100,
namely a central portion 10 and inner and outer portions 20 and 30. Preferred
dimensions of the various parts of portions 10, 20 and 30 are given in
millimetres in
Figure 1.
Central portion 10 is made of a thermally-insulating synthetic material such
as a glass-
reinforced profile of polyester/phenolic resin material. It is of extruded or
pultruded
material and is manufactured with the various projections and channels
necessary to
accommodate the glazing units and beads and to fit in the surrounding aperture
in a
building wall. Portion 10 has an inner face part 11 with ends 12, 14 which are
angled at
20° in the manner of a dove-tail joint. Similarly, outer face part 16
has angled ends 17
and 19.
Inner frame portion 20 has a thickness of 2mm and is of stainless steel
prepared from a
solid shape by means of a hot rolling and cold drawing process. It has a
channel 21
which has angled ends 22, 24 and is arranged to slide on to face part 11 of
portion 10 to
be fixedly attached thereto.
Outer frame portion 30 also has a thickness of 2mm and is made of the same
material as
portion 20. It, too, has a channel 31 with angled ends 32, 34 which engage
with the ends
17, 19 of face part 16 to fixedly attach portion 30 to portion 10.
The assembled window-frame section is shown in Figure 2. To form a frame,
lengths of
the composite section are connected at the corners by welding or by means of
adhesive or
mechanical fixings.
The above described window frame has numerous advantages. For example, the
material of portion 10 gives considerable strength to the window frame.
Moreover, all
the projections and channels are provided on the portion 10, so that the steel
sections 20
and 30 have shapes which are simple to produce by rolling. A thermal break is
provided
by portion 10, while allowing the window to have the internal and external
appearance of
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
S
stainless steel which is attractive and does not corrode. Alternatively, it
can be readily
coated with polyester powder. Moreover, the steel sections are relatively
narrow, so that
the window has good sight-lines.
S Use of such window frames also provides greater flexibility in shape and
finish. For
example, the portions 20 and 30 may be of any desired material such as carbon
steel,
aluminium or another metal or alloy, wood, plastics material such as PVC, and
the
portions on a single frame may be of a different material and/or colour.
Various modifications may be made to the above-described embodiment to cater
for
different applications. For example, Figure 3 shows a fixed window frame with
a longer
outer portion 40 instead of portion 30. Alternatively, as shown in Figure 4, a
longer
outer portion 40 is combined with an inverted portion 30 on the inside instead
of portion
20.
1S
Portions 20, 30 and 40 may be arranged to snap onto faces 11 and 16 of portion
10
rather than to slide thereon.
The window frame section can also be used in opening windows as illustrated in
Figures
S to 8 which show open out vents. Figure S shows the parts of a fixed window
frame
section 400 and a relatively movable window frame section 500. In similar
fashion to
window frame section 100 of Figure 1, section 400 comprises a thermally-
insulating
central portion 410 and inner and outer stainless steel portions 20 and 30.
Section S00
also comprises a thermally-insulating portions S 10 and two stainless steel
portions 30.
2S Again the central portions 410, S10 and manufactured with all the shaped
projections to
receive the glazing units and the seals and to engage the surrounding aperture
in the
building wall.
Figure 6 shows the assembled window frame sections 400, S00 of Figure S in
their
installed disposition.
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
6
Modified assemblies are possible, e.g. Figure 7 shows an opening window-frame
in
which the steel portion 30 of section 400 is replaced by a longer outer
portion 40.
Alternatively in the modification of Figure 8, section 400 is further modified
in that it
has a longer inner portion 30 instead of portion 20.
In general, the same modifications may be made to the window frame sections of
Figure
5 to 8 as mentioned in connection with Figures 1 to 4.
For all the described embodiments, the dimensions axe given only as examples
preferred
thickness of the portions 20, 30 and 40 lie in the range l.Smm to 3mm and the
preferred
angles of the ends 12, 14, 17, 19, 22, 24, 32, 34 lie within the range of 15
° to 30° .
The various embodiments of the invention permit a flexible design process. It
will be
noted that only three differently-shaped steel portions 20, 30 and 40 are
required to
provide a wide range of options. If windows of a different thickness are
required, e.g. to
increase the separation of the glazing sheets, it is relatively simple to vary
the size of the
extruded/pultruded portion 10, 410, 510.
Window frames with a large range of portions 20, 30, 40 of different materials
and
colours may be supplied to a site, to permit the finish to be selected as Iate
as possible in
the design process.
Glazed doors may also be provided with similar frame sections.
Figure 9 shows a window frame section 90 in accordance with third embodiment
of the
present invention comprising a fixed frame section 91 and a relatively movable
frame
section 92. Figure 10 shows a window frame section 80 in accordance with a
fourth
embodiment of the present invention comprising a fixed frame section 81 and a
relatively
movable frame section 82. Again the frame sections comprise thermally-
insulating
central portions and inner and outer stainless steel sections 61, 62, 63. The
sections 61,
62, 63 and the central portions are attached by pushing them together so that
projections
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
7
64 enter grooves 65. They are then secured with adhesive. At the corners of
the frames,
the various components are secured together by pinning.
In a modification, frame section 81 serves for a fixed light window.
Figure 11 shows a fixed light window frame section 50 in accordance with a
fifth
embodiment of the present invention comprising a thermally-insulating central
portion 55
and stainless steel portions 51, 52. The portions 51, 52 are attached to the
central
portion by arrow-head protrusions 57, which enter slots 58.
The features and modifications of the embodiments of Figures 9 to 11 may be
exchanged
with those of Figures 1 to 8 as appropriate.
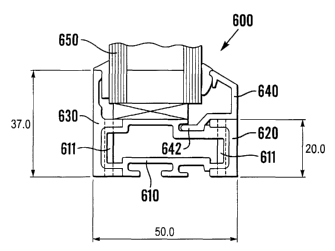
Figure 12 shows a glaze in fixed light frame section 600 comprising a central
portion 610
of insulting material and inner and outer steel portions 620, 630. A bead 640
fits into
one of the channels formed in portion 610 to assist in retaining a glazing
unit 650. The
portions 620, 630 comprise U-shapes for fitting snugly over the inner and
outer end
regions of central portion 610. They are assembled simply by being pushed on.
To
ensure that portions 620, 630 remain permanently attached to central portion,
a hole is
made extending completely through the arms of the U-shapes and the end region
of
portion 610, and a mechanical retaining pin 6I I is then driven into the hole.
These holes
are provided at the ends of each side of the window frame and also at a
central region of
each side.
Since central portion 610 is hollow, it requires less material for the same
rigidity and is
lighter. In addition, pins 611 prevent unauthorised removal of the inner and
outer
portions 620, 630.
Figures 13 and 14 respectively show open in and open out arrangements 660,670
employing similar frame components to Figure 12, but using central portions
612, 613,
CA 02421361 2003-03-05
WO 02/20930 PCT/GBO1/03997
8
614 and 615 having differing cross-sectional shapes. The embodiment of Figure
14 also
incorporates an outer portion 631 of a different shape.
Figure 15 shows a glaze in open out frame section 700 comprising insulating
central
portions 710, 712 with respective inner and outer steel portions 720, 731 and
730, 720.
As with the embodiments of Figures 12 to 14, the inner and outer portions are
attached
to the central portions by mechanical retaining pins 711. The sections 710,
712 each
comprise three separate enclosed channels 744, 745, 746. An operating handle
770 is
also provided.
It will be noted that in this embodiment, the arms of the U-shapes of the
portions 720,
730, 731 overhang the end regions of the central portions to form gaps 755.
This means
that there is a reduced area of contact between the central portions and the
steel portions
as compared to the previous embodiments, leading to improved thermal
performance.
It will also be noted that the end 742 of bead 740 is bent back, into the
adjacent gap 755,
in the form of a U-shape. This contrasts with the corresponding arm 642 of the
bead 640
of the preceding embodiment.
The embodiment of Figure 15 shares the advantages of the previous embodiments
and
has additional advantages. In addition, its thermal performance is improved by
having a
central portion with three longitudinal hollow sections 744, 745, 746, which
reduces
thermal conduction between inside and outside the window and which also
reduces the
effects of thermal convection within the central portion. The reduced areas of
contact
between the end regions of the central portion and the inner and outer
portions also serve
to reduce thermal conduction. Bending back the arm 742 of bead 740 also
reduces the
amount by which bead 740 extends across the width of the window and thus also
serves
to reduce unwanted transfer of heat.
The features of the various embodiments described above may be combined or
interchanged as desired.