Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02428773 2003-05-15
SOLENOID VALVE
The invention relates to a solenoid valve for the closing of a seal seat which
is
located in the lift direction of the magnet armature and the sealing element.
In particular,
the invention relates to a regeneration valve for a fuel tank ventilation
arrangement in
motor vehicles.
BACKGROUND ART
The use of electromagnetic metering valves is generally known. The throughput
of such valves in both directions can be controlled by variation of the
pulsa~pause-ratio of
the electrical actuation. The magnet armature which during operation carries
out an
oscillating movement, is herefore pressed at variable time intervals against a
seal seat, or
lifted from the seal seat depending on the desired amount of input. At the end
face, the
magnet armature is provided with a seal seat elastomer. These valves generally
have to be
resistant to aggressive media and have to maintain their metering precision
over a large
temperature range. They Furthermore should not be noticeable acoustically and
able to be
manufactured at low cost. Solenoid valves are mostly used for this purpose
which permit
a fast movement of the sealing element and have a control frequency which is
at least 10
Hz. The mounting of the magnet armature is a special problem of these solenoid
valves,
which armature during operation achieves very high cycle rates but still
should have a
very high life expectancy.
CA 02428773 2003-05-15
DE 42 29 110 C 1 shows a regeneration valve in which the sealing element is
operated by an electrically driven magnet coil. Such regeneration valves have
proven
reliable in practice.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the invention to provide an improved supporting of the
magnet
armature in order to ensure a characteristic line band with tight tolerances
even after long
times of operation of the valve. Furthermore, it is an object to reduce large
throughput of
fuel vapors, which leads to an improved magnetic force-distance characteristic
curve.
Moreover, it is an object to improve the miero-metering behavior of the valve.
This is achieved in a solenoid valve in accordance with the invention by
supporting the magnet armature by two flat springs joined to the valve
housing. This
provides a friction free supporting of the magnet armature. Friction forces
which are
present with conventional guiding and supporting arrangements for the magnet
armature
in an armature sleeve or in hollow plates, are prevented with the construction
of the
invention. This results in an especially good force-distance characteristic
curve for the
magnet force to be used. Canting of the magnet armature is safely prevented by
positioning of the flat springs to both sides of the magnet armature. Wear of
the support
of the magnet armature is prevented and a good long-term behavior over the
whole
service life is achieved.
In a preferred embodiment, the flat springs are constructed as meander
springs.
CA 02428773 2003-05-15
For weight reduction, the magnet armature, is preferably of cylindrical shape.
The
sealing element is positioned at that end of the magnet armature which is
directed
towards the seal seat. It thereby covers the inner bore of the armature.
A high throughput of fuel vapor is made possible by shaping the magnet
armature
to concentrically surround the whole core with its upper edge. A larger feed
through can
thereby be realized. In an especially preferred embodiment of the solenoid
valve of the
invention, the magnet armature is coaxially surrounded by the pole plate. The
pole plate
is connected with the housing of the solenoid valve and the meander springs
are
preferably joined to both sides thereof. For that, the pole plate is provided
on both sides
with space protrusions to which the meander springs are mounted. The meander
springs
are pressed or welded onto the space protrusions. For reasons of manufacturing
technology and to facilitate mounting of the metal guide plate to the valve
housing, the
metal guide plate can be constructed to be reverse-symmetrical with respect to
the
meander springs, which means that the metal guide plate can be connected in
either
orientation with the meander springs and the valve housing, irrespective with
which side
is directed into the housing.
The sealing element is preferably made of a metallic supporting body provided
with perforations and an elastomeric sealing cover which is positively and/or
non-
positively connected with the supporting body. This allows for a very secure
connection
between the sealing cover and the supporting body. Furthermore, the supporting
body
facilitates the connection of the sealing element with the magnet armature.
The magnet
armature is preferably provided at its edge facing the seal seat with a
circumferential
indent into which the supporting body is pressed.
3
CA 02428773 2003-05-15
The embodiment in accordance with the invention of a magnet armature with
sealing element and flat springs can be especially advantageously used in a
regeneration
valve with a valve housing and a central Laval nozzle, the mouth of which
forms the seal
seat.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Preferred embodiments of the invention will now be further described by way of
example only and with reference to the attached drawings, wherein
Figure 1 is a longitudinal section through a preferred embodiment of a
solenaid
valve in accordance with the invention;
Figure 2 is an end view of the magnet armature with flat spring and pole plate
of
the valve shown in Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a side elevation of the magnet armature, the flat springs and the
pole
plate of the valve shown in Figure 1; and
Figure 4 is a cross-section through the magnet armature, the flat springs and
the
pole plate taken along line C-C' in Figure 2.
DETAILED DESCRIPT10N OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
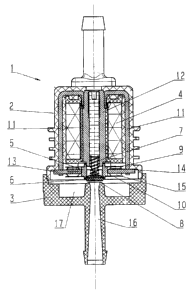
Figure 1 illustrates in longitudinal section a solenoid valve which allows a
high
activation frequency. The solenoid valve 1 includes an upper housing portion 2
and a
lower housing portion 3. An electromagnet 4 with a pole core 12 is inserted in
the upper
portion 2. The pole core 12 cooperates with the magnet armature 5 which is
provided
with a sealing element 6. The sealing element ti is forced by a bring 7,
position and
4
CA 02428773 2003-05-15
centrally in the electric magnet onto the seal seat 8 which is located in the
lower housing
portion 3. However, an embodiment without spring 7 in which only the flat
springs !~ and
force the seal element 6 onto the seal seat 8 is also possible and
advantageous for
some applications. The magnet armature 5 is held by the flat springs 9 and 10,
which are
constructed as meander springs. A pole plate 13 is mounted to the magnetic
yoke 11 of
the electromagnet 4, which pole plate simultaneously functions as a mount for
the magnet
armature 5. However, contact between magnet armature S and the pole plate 13
is not
provided. The pole plate 13 is provided on its upper and lower surfaces with
space
protrusions 14 and I S to which the meander springs 9 and 10 are fastened. The
two
housing portions, upper portion 2 and lower portion 3 are connected with one
another.
The Laval nozzle 1 b is positioned centrally in the lower housing portion 3
and the intake
of the nozzle forms the seal seat 8. The medium flowing through the valve
enters into the
annular chamber 17 of the lower valve potion 3 and exits through the Laval
nozzle 16.
Figure 2 shows an end view of the pole plate l3 with the meander spring 10
mounted thereto and the magnet armature 5 held by the meander spring 10. The
underside of the sealing element 6 is visible. The pole plate 13 is provided
with two
opposite tabs 19 and 20 by which it is mounted to the magnetic yoke 11.
Openings 2l are
provided in the pole plate 13 for insertion of complementary pins 21 on the
magnetic
yoke 11. The meander spring 10 is provided with three spring legs 22. It is at
its inner
edge 23 pressed or welded onto the magnetic armature 5. The meander spring 10
is also
connected with the protrusions 14 at the point of connection 24 for the spring
legs 22.
The protrusions 1 S located below the pole plate 13 are shown in broken lines.
The
meander spring 9 located below the pole plate 13 is pressed onto these
protrusions 15.
5
CA 02428773 2003-05-15
The protrusions 15 are revers-symmetrical to the protrusions 14, which means
the pole
plate 13 can be used with either side facing up.
Figure 3 illustrates in side view the pole plate 13 with the meander springs 9
and
and the magnet armature 5 with the sealing element 6. Three space protrusions
14 are
visible and two oppositely positioned space protrusions 15.
Figure 4 shows a cross-section through Figure 2 taken along line C-C. The
magnet armature 5 is held in relation to the pole plate 13 by the meander
springs 9 and
10. The pole plate 13 is for this purpose provided with the space protrusions
14 and 15.
As is apparent from the lower portion of the Figure, the protrusions 14 and 15
were
manufactured by stamping parts of the pole plate 13. The sealing element 6 is
inserted
into the cylindrical magnet arnlature ~. The sealing element 6 consists of the
metallic
supporting body 30, which is provided with a perforation, the elastomeric
sealing layer
31 on both sides of the supporting body 30, and the stop 32. The spring 7 is
placed onto
the central pin 18 on the sealing element 6. During the vulcanization process
for
application of the sealing layer 31 and the stop 32, the elastomer flows
through the
perforation in the supporting body 13 so that a non-positive connection is
achieved
between the supporting body 30 and the elastomeric seal seat 31 or the stop
32. However,
a positive connection between the supporting body 30 and the sealing layer 31
achieved,
for example, by vulcanizing the elastomeric directly onto the supporting body,
is also
possible. The circumferential edge 33 of the supporting body 30 is inserted
into a circular
groove 34 in the magnet armature 5 for connection of the sealing element 6
with the
magnet armature 5. The end 35 of the magnet armature 5 which is directed
towards the
pole core 12 is conically shaped on its inner surface 36 and suwounds the
lower edge of
6
CA 02428773 2003-05-15
the pole core 12 which is of complementary shape. This construction and
arrangement of
the magnet armature 5 and the pole core 12 provides a high flow through in the
open
position of the valve 1.
7