Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02434992 2012-03-13
=
1 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING AN ADAPTABLE
2 SECURITY LEVEL IN AN ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION
3
4 BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
6 FIELD OF THE INVENTION
7 [0001] The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for
providing an adaptable
8 security level in an electronic communication.
9
DESCRIPTION OF THE PRIOR ART
11 [0002] In electronic communications, it is often necessary to
prevent an eavesdropper from
12 intercepting message. It is also desirable to have an indication of the
authenticity of a message,
13 that is a verifiable identification of the sender. These goals are
usually achieved through the use
14 of cryptography. Private key cryptography requires sharing a secret key
prior to initating
communications. Public key cryptography is generally preferred as it does not
require such a
16 shared secret key. Instead, each correspondent has a key pair including
a private key and a public
17 key. The public key may be provided by any convenient means, and does
not need to be kept
18 secret.
19 [0003] There are many variations in cryptographic algorithms, and
various parameters that
determine the precise implementation. In standards for wireless
communications, it has been
21 customary to set these parameters in advance for each frame type.
However, this approach limits
22 the flexibility of the parameters.
23 [0004] When one device is communicating with several other
devices, it will often need to
24 establish separate parameters for each communication.
[0005] It is an object of the present invention to obviate or mitigate the
above disadvantages.
26
27 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
28 100061 In accordance with one aspect, there is provided a method
performed by a
29 communication device and computer readable storage medium comprising
instructions for
1
CA 02434992 2012-03-13
1 preparing a plurality of frames, each frame having a header and data; and
on a frame-by-
2 frame basis, the communication device processing each individual frame
by: determining
3 a security level for that individual frame, the security level indicating
whether to provide
4 encryption for the individual frame and whether to provide authenticity
for the individual
frame, thereby allowing different frames to utilize different security levels
to adapt to the
6 nature of respective frames on the frame-by-frame basis; and based on the
security level,
7 including security level data in the header of that individual frame, the
security level data
8 indicating whether encryption is being used for the individual frame and
whether
9 authenticity is being used for the individual frame; and the
communication device
providing the plurality of frames for transmission to a recipient. In
accordance with
11 another aspect, there is provided a method performed by a communication
device and
12 computer readable storage medium comprising instructions for receiving a
plurality of
13 frames, each frame having a header and associated data, the header of
each individual
14 frame including security level data that indicate for that individual
frame whether
encryption has been provided for the individual frame and whether authenticity
has been
16 provided for the individual frame, such that different frames can
utilize different security
17 levels to adapt to the nature of respective frames on a frame-by-frame
basis; for each
18 frame, the communication device: identifying a security level for the
frame based on the
19 security level data in the header of the frame; checking the security
level against
predetermined security requirements for the communication device; and
rejecting the
21 frame if the security level does not meet the predetermined security
requirements.
22212935.1 lA
CA 02434992 2012-03-13
1
2
3
4 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0007] These and other features of the preferred embodiments of the
invention will become
6 more apparent in the following detailed description in which reference is
made to the appended
7 drawings wherein:
8 [0008] Figure 1 is a schematic representation of a communication
system;
9 [0009] Figure 2 is a schematic representation of an information
frame exchanged in the
communication system of Figure 1;
11 [0010] Figure 3 is a schematic representation of a frame control
portion of the frame of
12 Figure 2;
13 [0011] Figure 4 is a schematic representation of a method performed
by a sender in Figure 1;
14 [0012] Figure 5 is a schematic representation of a method performed
by a recipient in Figure
1.
16
17 DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
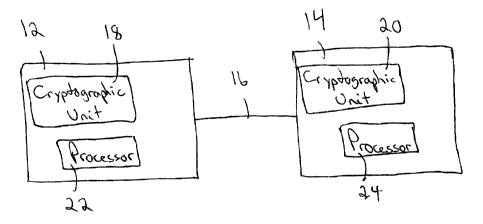
18 [0013] Referring to Figure 1, a communication system 10 includes a
pair of correspondents
19 12, 14 connected by a communication link 16. Each correspondent 12, 14
includes a respective
cryptographic unit 18, 20.
21 [0014] Each correspondent 12, 14 can include a processor 22, 24.
Each processor may be
22 coupled to a display and to user input devices, such as a keyboard,
mouse, or other suitable
23 devices. If the display is touch sensitive, then the display itself can
be employed as the user
24 input device. A computer readable storage medium is coupled to each
processor 22, 24 for
providing instructions to the processor 22, 24 to instruct and/or configure
processor 22, 24 to
26 perform steps or algorithms related to the operation of each
correspondent 12, 14, as further
27 explained below. The computer readable medium can include hardware
and/or software such as,
28 by way of example only, magnetic disks, magnetic tape, optically
readable medium such as CD
29 ROM's, and semi-conductor memory such as PCMCIA cards. In each case, the
medium may
2
McCarthy Tetrault LLP TDO-RED #8199673 v. I
CA 02434992 2003-07-07
1 take the form of a portable item such as a small disk, floppy diskette,
cassette, or it may take the
2 form of a relatively large or immobile item such as hard disk drive,
solid state memory card, or
3 RAM provided in a support system. It should be noted that the above
listed example mediums
4 can be used either alone or in combination.
[0015] Referring to Figure 2, a frame used in communications between the
correspondents
6 12, 14 is shown generally by the numeral 30. The frame 30 includes a
header 32 and data 34. The
7 header 32 includes information about the source and destination of the
frame 30 and is used for
8 processing frames. The header 32 may contain other control information as
will be understood
9 by those skilled in the art.
[0016] Referring to Figure 3, the header 32 also contains frame control
bits 33. The frame
11 control bits 33 include security bits 35, 36, and 37. Security bit 35
indicates whether encryption
12 is on or off. Security bits 36 and 37 together indicate the integrity
level, such as 0, 32, 64, or 128
13 bits. It will be recognized that providing security bits in each frame
allows the security level to
14 be modified on a frame-by-frame basis rather than on the basis of a pair
of correspondents,
therefore providing greater flexibility in organizing communications.
16 [0017] In order to provide security, certain minimum security
levels may be used. These
17 levels should be decided upon among all of the correspondents through an
agreed-upon rule.
18 This rule may be either static or dynamic.
19 [0018] In operation, the correspondent 12 performs the steps
shown in Figure 4 by the
numeral 100 to send information to the correspondent 14. First, the
correspondent 12 prepares
21 data and a header at step 102. Then it selects the security level at
step 104. The security level is
22 determined by considering the minimum security level required by the
recipient, the nature of the
23 recipient, and the kind of data being transmitted. If the security level
includes encryption, then
24 the correspondent 12 encrypts the data at step 106. If the security
level includes authentication,
then the correspondent 12 signs the data at step 108. Then the correspondent
12 includes bits
26 indicating the security level in the frame control at step 110. The
correspondent 12 then sends the
27 frame to the correspondent 14.
28 [0019] Upon receiving the frame, the correspondent 14 performs
the steps shown in Figure 5
29 by the numeral 120. The correspondent 14 first receives the frame at
step 122. It then extracts the
3
McCarthy Tetrault LLP TDO-RED #8199673 v 1
CA 02434992 2012-03-13
1 security bits at step 124. If the security bits indicate encryption, then
the correspondent 14
2 decrypts the data at step 126. If the security bits indicate
authentication, then the correspondent
3 14 verifies the signature at step 126. Finally, the correspondent 14
checks the security level to
4 ensure it meets predetermined minimum requirements. If either the
encryption or authentication
fails, or if the security level does not meet the minimum requirements, then
the correspondent 14
6 rejects the message.
7 [0020] It will be recognized that providing security bits and an
adjustable security level
8 provides flexibility in protecting each frame of the communication. It is
therefore possible for the
9 sender to decided which frames should be encrypted but not authenticated.
Since authentication
typically increases the length of a message, this provides a savings in
constrained environments
11 when bandwidth is at a premium.
12 [0021] In a further embodiment, the correspondent 12 wishes to send
the same message to
13 multiple recipients 14 with varying minimum security requirements. In
this case, the
14 correspondent 12 chooses a security level high enough to meet all of the
requirements. The
correspondent 12 then proceeds as in Figure 4 to assemble and send a message
with the security
16 level. The message will be accepted by each recipient since it meets
each of their minimum
17 requirements. It will be recognized that this embodiment provides
greater efficiency than
18 separately dealing with each recipient's requirements.
19 [0022] In another embodiment, a different number of security bits
are used. The actual
number of bits is not limited to any one value, but rather may be
predetermined for any given
21 application. The security bits should indicate the algorithm parameters.
They may be used to
22 determine the length of a key as 40 bits or 128 bits, the version of a
key to be used, or any other
23 parameters of the encryption system.
24 [0023] Although the invention has been described with reference to
certain specific
embodiments, various modifications thereof will be apparent to those skilled
in the art without
26 departing from the scope of the claims appended hereto.
27
28
4