Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
PCT/DE 02/00031
-~ ~ TREATMENT SOLUTION FOR TAKING CARE OF WOUNDS AND
DRESSING MATERIAL TO BE USED TOGETHER WITH SAID
TREATMENT SOLUTION
This invention refers to a treatment solution according to the introductory
part of
patent claim 1 as well to a dressing material according to the introductory
part of claim
It is basically known that the healing of wounds can be improved by providing
a wet
milieu, especially by using a medium which assists the healing of wounds or at
least
includes a medium having a medicament, for example appyling a solution or a
gel. A
method used in practice nowadays is that the dressing material or a layer of
this
material comprising an absorbent material is soaked with the corresponding
solution
and that the dressing material then is applied onto the wound. With this
procedure the
way of handling is complicated and especially, when taking care of larger or
deeper
wounds and the necessity of changing the dressing material more often, special
educated or trained personal will be repuired.
It is an object of this invention to propose a treatment medium and a dressing
material
which together with a simplified application results in improving the healing
process
of wounds, especially improving the healing of chronic or post-operative
wounds.
This object is solved by a treatment solution according to the features of
patent claim
1. A dressing material used for taking care of wounds, especially for treating
chronic or
post-operative wounds by means of the treatment solution is prepared according
to
patent claim 7.
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
2
The dressing material according to the subject invention has the advantage
that in
addition to its simple way of use allows the caring of chronic wounds or post-
operative
wound healing in a wet milieu by using the treatment medium for improving the
healing of the wound, and, in addition thereto that the time period within
which the
dressing material is to be changed, is considerably increased. For example,
when using
the dressing material according to the invention it is possible to change the
dressing
only three days after the first treatment of the wound, which means at a time
at which
also a deep wound already is closed to such an extent that the danger of
infections is
considerably reduced. In view of the long time period the dressing material
can be
maintained applied to the wound, and this allows to keep the wound at rest,
which is
necessary for fast healing, especially within the first few days subsequent to
treating the
wound. This is possible because the chamber for the treatment medium is
provided
with at least one connector extending from the dressing material for refilling
and/or
renewing the treatment medium.
With the preferred embodiment of the invention characterised by a very
effective and
low-cost structure of the dressing material, the chamber is formed by at least
one
channel which is divided into several sections and/or windings across the
surface of the
treatment material. This channel preferably is at least one piece of hose.
Further embodiments of the invention are the subject matter of the subclaims.
In the
following the invention is described by embodiments together with the figures
of the
drawings which show:
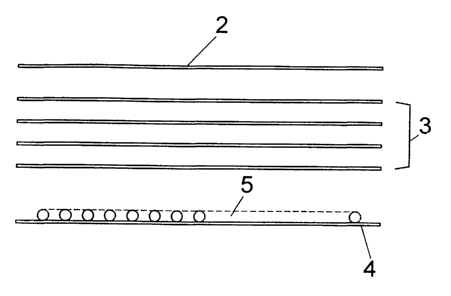
Figure 1 a schematic partial representation of the structure of layers of a
dressing
material according to the invention, whereby the individual layers which
are actually connected within the dressing material in view of better
understanding are shown separate from each other,in a type of an explosion
view,
figure 2 a simplified schematic representation/ top view of the material of
figure 1,
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
3
figures 4 - 7 different graphics showing the time slope of wound healings of
experiments on animals.
In the drawings the dressing material 1, which is suitable for taking care of
chronic
--wounds, however, also for taking care of open, deep wounds, is substantially
shown
as a multi-layer flat material, for example in the shape of a square or
rectangular
cutting.
The shown embodiment of the dressing material 1 comprises a first, outer
sterile layer
2 forming the coating to be applied onto the wound, and a perforated flat
material,
such as a perforated film or grid made of suitable plastics material, for
example of
PVC. The one-sheet outer layer 2 is followed by a layer 3 which is formed by
several
sheets of a sterile, absorbent air as well moisture permeable material, such
as a coarse
tissue or a non-woven material. With the embodiment according to this figure
layer 3
comprises several sheets of a sterile gauze, for example is made of four
sheets. The
surface of the other side or the outer side of the dressing material 1, which
when
actually used is the outer surface of the dressing material opposite to the
wound, is
formed by a layer 4, which is made from one sheet in the shown embodiment
consisting of a flat material or of a film, preferably a film of plastics
material. The layer
4 has semipermeable characteristics which means is permeable for air and gas,
however, is not permeable for liquid. At the inner side of layer 4 facing
layer 3 a
lumen or hose portion 5 is fastened which extends meander-type nearly across
the
entire surface of layer 4 and thus, across the entire surface of the dressing
material 1
and forms two ends or connectors 6, which are laterally extending from the
dressing
material 1, with the shown embodiment in such a manner that these ends 6
extend
away from each other at two opposing lateral sides 1' resp. 1 N of the
dressing material.
The hose portion S, which forms a channel for receiving and distributing a
treatment
medium, especially an aqueous treatment medium, is designed along its length
extending within the treatment material 1, which means between layers 3 and 4,
in
such a manner that a finely divided discharge of the treatment medium within
the hose
portion 5 into the layer 3 will be possible. For this purpose the hose portion
5 is finely
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
4
such a manner that a finely divided discharge of the treatment medium within
the hose
portion 5 into the layer 3 will be possible. For this purpose the hose portion
5 is finely
perforated. The protruding ends 6 preferably are formed by a hose length each
which is
without such perforations.
The individual layers 2, 3 and 4 with the hose portion 5 provided between
layers 3 and
4 are connected with each other in a suitable manner, for example along the
edge of
the dressing material 1 and/or dotlike also within the dressing material 1.
In use the dressing material 1 with layer 2 is applied onto the wound to be
taken care
of and then is fastened along the edges by means of an adhesive tape 7 or in
any other
manner. In order to obtain improved healing of the wound in a wet milieu a
solution
suitable for wound treatment is supplied via end 6, for example through the
upper end
in figure 2, over a time period within which this solution is discharged at
the other end
or connector 6, and thus the entire chamber formed by the hose portion 5 is
filled with
said treatment solution. Subsequent thereto, both ends 6 are closed, for
example by
means of a suitable plug. The treatment solution leaving the hose portion 5 is
finely
divided across the entire surface of the dressing material and accordingly,
also across
the entire wound area. The solution within the hose portion 5 is renewed and
substituted several times a day, f.e. two times a day.
By means of the dressing material according to the invention the wound is kept
occlusive and wet in an optimum manner so that a substantially improved
healing
result for the wound will be obtained. The special advantage of the dressing
material
according to the invention is to be seen in that changing the dressing only
will be
required after several days, for example every three days only, so that also
changing
the dressing material for the first time generally is required after a time
period, within
which even a deep open wound has improved to such an extent that the danger of
an
additional infection by changing the dressing can be basically excluded. In
view of the
long time interval between applying a dressing material and the first change
of said
dressing material, especially also the resting of the wound required for the
initial
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
healing process within the first days subsequent to taking care of the wound
is
guaranted. The dressing material according to the subject invention also
combines the
advantages of healing the wound in a wet milieu with the advantage of a
healing
process of a long-period rest of the wound, which assists the healing process,
especially within the first few days, considerably.
Figure 3 as a further embodiment of the invention shows a schematic view and
in cross
section a dressing material 1 a which is again made of a plurality of layers,
and also
serves the improved healing of the wound in a wet milieu. The dressing
material 1~
comprises a lower layer 10 with which this material is applied onto the wound.
This
layer 10 which forms the sterile coating on the wound, is made up by a sterile
perforated flat material, such as a perforated or grid-like film of suitable
plastics
material, for example PVC or silicon.
Upon layer 10 a layer 11 is provided, which serves as a distributor layer for
the
treatment liquid, and is made of a sterile soft and absorbent material, such
as gaze or a
non-woven material (vleece). On the surface of layer 10 opposite to layer 11
another
layer 12 is provided, which includes the liquid treatment medium in capsulated
form
so that by opening and breaking the layer 12 resp. the capsules there, the
treatment
medium is distributed over layer 11 to the underside of the distributor
material, and
thus is discharged to the wound area. Above layer 12 a cover layer 13 is
provided
which is made of semipermeable flat material, which means a flat material
which is not
permeable or substantially impermeable for the liquid treatment medium,
however, is
permeable for air and gas.
As shown in Figure 3 the cover layer 13 covers the dressing material 1a or
alternatively
the various layers and sheets of said dressing material also laterally, and is
provided
with a non-irritant adhesive coating 14 on the edge thereof, which is arranged
at the
level of the underside of layer 10. By using a withdrawable cover layer 15 the
dressing
material 1~ is closed in a sterile manner at that side on which it is applied
to a wound.
Layer 15 when being used on a wound is removed.
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
6
In use of the dressing material subsequent to removing the cover or protective
layer 15
with the then exposed layer 10 is applied onto the wound and is bonded around
the
wound by means of an adhesive layer 14. By breaking the layer 12 the capsuled
treatment liquid then is released.
Preferably, the dressing material 1 a is designed so that when changing the
dressing the
layer 10 of the dressing is separated from the adjacent layer 11, and the
layer 10 is
maintained on the wound so that the wound still can rest and thus, the healing
process
is not influenced by changing the dressing. When changing the dressing the
freshly
used dressing material then is equivalent to the dressing material 1~,
however, without
the layer 10, which means the structure is so that in addition to the
protective layer 15
also the layer 10 can be removed from the dressing material 1~, if necessary.
As a treatment medium a solution is used which for example comprises an
aqueous
solution of zinc and iron, besides of distillated water and sulphuric acid,
namely 10 -
100 mg Zn and 6,5 - 65 mg Fe, for example 15 - 45 mg Zn and 10 -30 mg Fe per
litre
solution, whereby the share of sulphuric acid is chosen so that a pH-value
between 2,5
and 3,5, preferably 2,8, is obtained. With a preferred embodiment a 95 - 97%
sulphuric acid is used. The distillated water is double distillated water
according to
DAB 10. As raw materials for example ZnCl2 and FeS04, about 20 - 209 mg ZnClz
and
32 - 325 mg FeS04 per litre solution are suitable.
In the following a sample for the composition of the treatment solution is
given:
One litre solution comprises
Aqua bidestillata DAB 10 980 g
FeS04 0,097 g
ZnCL2 0,063 g
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
7
the remaining is sulphuric acid 95 - 97% with a share until a pH-value of 2,8
is
obtained.
In view of the low pH-value of the treatment medium said medium does not only
result
-in an acid and thus optimum wound milieu. Based on the acid milieu especially
the
metabolism improving the healing process is also stimulated. Furthermore, the
treament medium by means of the acid in combination with the iron constituents
also
operates microbacteriostatically, which means that a milieu is generated which
prevents the growth of germs and batteries, and acts repulsive on them so that
inflammations caused by germs entering the wound and developing there will be
effectively prevented.
The forementioned treatment medium (solution) is especially suitable in
connection
with the dressing material 1 resp. 1~ for treating or taking care of chronic
wounds and
burnings, as has been determined by experiments with animals. Experiments have
been made with pigs by using the treatment medium described above with a
constituent of 30 mg zinc and 20 mg iron per litre solution (in the following
0,003°/°
solution), with a comparable solution which only included 10 mg zinc and about
7 mg
iron per litre solution (in the following 0,01 °/° solution)
with a comparable solution
including 100 mg zinc and 66 mg iron per litre solution (in the following
0,001 °I°
solution). By means of a further comparative series of experiments the healing
process
has been tested using known processes of taking care of wounds.
The results of said experiments on burnings are, as generally acknowledged,
also
relevant for the effectivity of taking care of chronic wounds, such as
decubitus, ulcus
cruris wound healing defects in connection with diabetes mellitus, etc.
The results are shown in the graphs according to Figures 4, 5, 6 and 7, namely
in
Figure 4 for the 0,001 % solution, in Figure 5 for the 0,01 % solution, in
Figure 6 for the
0,003% solution, and in Figure 7 for a wound positioned just in open air. The
Figures
show that the best healing success has been obtained with the 0,003% solution.
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
8
The above-described treatment medium (solution) ~Iso can be used especially in
connection with the dressing material 1 or 1~, for treating post-operative
wounds, and
improves the healing process considerably, as has been proven by experiments
with
-pigs. So far, animal experiments on pigs have been made with the above-
described
treatment medium and the dressing material 1. These experiments have shown
that
compared with the healing of wounds at ambient air a substantially faster
healing
process (reducing the healing process to about five days) and a substantial
reduction in
the formation of scars has been obtained.
Within Figure 2 reference numeral 16 characterises an indicator which with the
shown
embodiment comprises a substrate or strips of flat material provided with an
indicator
material, which in case that the dressing material becomes dry, so that the
moisture of
said dressing material 1 in use will be reduced below a predetermined value;
changes
its colour. The indicator 16 is integrated into the dressing material 1 in
such a manner
that it is visible if the dressing material 1 is applied. With the shown
embodiment the
indicator 16 is provided underneath that layer which finishes the dressing
material at
the side opposite to the wound, which means with the dressing material 1
between
layer 4 and layer 5, and with the dressing material 1~ underneath layer 13.
Suitable materials for indicators change their colour dependent on the
moisture are
known to the expert. Basically, an indicator material is suitable for the
subject
invention, which dependent on the pH-value changes it's colour because if the
dressing material runs dry the pH-value changes.
In addition or instead of the indicator 16 which indicates if the dressing
material runs
dry, an indicator can be integrated into the dressing material 1 or 1a, which
indicator is
based on a possibly increased microbial contamination of the dressing material
so that
the dressing material can be changed in time. Also this indicator is formed
according to
indicator 16 and preferably is provided so that it is visible from the
dressing applied to
the patient, and consists of a carrier material which is provided with a
substance
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
9
altering it s colour with an increased microbial load or contamination, for
example also
by altering its pH-value.
Basically, there is also the possibility to position a corresponding indicator
16 at that
'side of the dressing material facing the wound, which indicator indicates the
moisture
content of the dressing and/or the microbial condition of the dressing.
Above, the invention has been described in connection with embodiments.
However,
numerous alterations and revisions will be possible without leaving the idea
on which
the subject invention is based.
CA 02435069 2003-07-17
Reference List
1, 1a dressing material
1', 1 " peripheral edge
2 layer from sterile, perforated flat material made from
plastics,
such as PVC applied to the wound
3 protective layer made of a sterile soft and absorbent
material,
for
example gauze
4 layer of a semi-permeable material
5 ~ hose portion
6 hose end or connector
7 adhesive tape
10, 11 layer
12 sheet
13 coverlayer
14 adhesive coating
coverlayer
16 indicator