Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 SELECTIVE ENCRYPTION TO ENABLE TRICK PLAY
2
3 COPYRIGHT NOTICE
4 A portion of the disclosure of this patent document contains material which
is
subject to copyright protection. The copyright owner has no objection to the
facsimile
6 reproduction of the patent document or the patent disclosure, as it appears
in the Patent
7 and Trademark Office patent file or records, but otherwise reserves all
copyright rights
8 whatsoever.
9 FIELD OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates generally to the field of encryption of digital video
content.
11 More particularly, this invention relates to use of selective encryption to
permit trick play
12 with digital video content.
13 BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
14 When digital video such as MPEG (Moving Pictures Expert Group) digital
video is
played back in various trick play modes, access to I frames or P frames is
generally
16 required. I frames and P frames contain information that can be used to
directly
17 represent an image, whereas images are created with B frames by referencing
and
18 modifying preceding and/or subsequent I frames and P frames. As an example,
when
19 playback is carried out at 2X or 4X speed, the playback algorithm jumps
from I frame to
I frame or P frame to P frame to speed up the presentation of the video frames
while
21 skipping certain frames.
22 Unfortunately, when content is encrypted using traditional encryption
techniques,
23 trick play becomes difficult or impossible since content has to be
decrypted in order to
24 find the I frames and/or P frames. In the case of unencrypted content,
these frames are
accessed by calculating an offset from the start of frame (SOF).
-1-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
2 The features of the invention believed to be novel are set forth with
particularity in
3 the appended claims. The invention itself however, both as to organization
and method
4 of operation, together with objects and advantages thereof, may be best
understood by
reference to the following detailed description of the invention, which
describes certain
6 exemplary embodiments of the invention, taken in conjunction with the
accompanying
7 drawings in which:
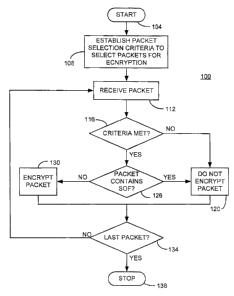
8 FIGURE 1 is a flow chart showing a selective encryption process and decoding
9 process consistent with certain embodiments of the present invention.
FIGURE 2 illustrates one embodiment of a selective encryption and decoding
11 process consistent with certain embodiments of the present invention.
12 FIGURE 3 illustrates another embodiment of a selective encryption and
decoding
13 process consistent with certain embodiments of the present invention.
14 FIGURE 4 is a programmed processor which can represent either an encryption
processor or a decoder consistent with certain embodiments of the present
invention.
-2-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
2 While this invention is susceptible of embodiment in many different forms,
3 there is shown in the drawings and will herein be described in detail
specific
4 embodiments, with the understanding that the present disclosure is to be
considered as an example of the principles of the invention and not intended
to limit
6 the invention to the specific embodiments shown and described. In the
description
7 below, like reference numerals are used to describe the same, similar or
8 corresponding parts in the several views of the drawings.
9 The terms "scramble" and "encrypt" and variations thereof are used
synonymously herein. The term "video" may be used herein to embrace not only
11 true visual information, but also in the conversational sense (e.g., "video
tape
12 recorder").to embrace not only video signals but associated audio and data.
The
13 present document generally uses the example of a "dual selective
encryption"
14 embodiment, but those skilled in the art will recognize that the present
invention
can be utilized to realize multiple partial encryption without departing from
the
16 invention. The terms "partial encryption" and "selective encryption" are
used
17 synonymously herein. Also, the terms "program" and "television program" and
18 similar terms can be interpreted in the normal conversational sense, as
well as a
19 meaning wherein the term means any segment of AN content that can be
displayed on a television set or similar monitor device. The term "legacy" as
used
21 herein refers to existing technology used for existing cable and satellite
systems.
22 The exemplary embodiments disclosed herein are decoded by a television Set-
Top
23 Box (STB), but it is contemplated that such technology will soon be
incorporated
24 within television receivers of all types whether housed in a separate
enclosure
alone or in conjunction with recording and/or playback equipment or
Conditional
26 Access (CA) decryption module or within a television set itself. The
present
27 document generally uses the example of a "dual partial encryption"
embodiment,
28 but those skilled in the art will recognize that the present invention can
be utilized
29 to realize multiple partial encryption without departing from the
invention.
-3-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 The related patents (US Patent Numbers: 7,336,787; 7,139,398; 7,124,303;
2 7,151,831; 7,127,619; 7,376,233; 7,302,059; 7,155,012; and, 7,292,690)
describe
3 inventions relating to various aspects of methods generally referred to
herein as partial
4 encryption or selective encryption. More particularly, systems are described
wherein
selected portions of a particular selection of digital content are encrypted
using two (or
6 more) encryption techniques while other portions of the content are left
unencrypted.
7 By properly selecting the portions to be encrypted, the content can
effectively be
8 encrypted for use under multiple decryption systems without the necessity of
encryption
9 of the entire selection of content. In some embodiments, only a few percent
of data
overhead is needed to effectively encrypt the content using multiple
encryption systems.
11 This results in a cable or satellite system being able to utilize Set-top
boxes or other
12 implementations of conditional access (CA) receivers from multiple
manufacturers in a
13 single system - thus freeing the cable or satellite company to
competitively shop for
14 providers of Set-top boxes.
The present invention applies similar selective encryption techniques to the
16 problem of enabling trick play with encrypted digital video content. The
partial
17 encryption processes described in the above patents utilize any suitable
encryption
18 method. However, these encryption techniques are selectively applied to the
data
19 stream, rather than encrypting the entire data stream, using techniques
described in the
above-referenced patents. In general, but without the intent to be limiting,
the selective
21 encryption process utilizes intelligent selection of information to encrypt
so that the
22 entire program does not have to undergo dual encryption. By appropriate
selection of
23 data to encrypt, the program material can be effectively scrambled and
hidden from
24 those who desire to hack into the system and illegally recover commercial
content
without paying. MPEG (or similar format) data that are used to represent the
audio and
26 video data does so using a high degree of reliance on the redundancy of
information
27 from frame to frame. Certain data can be transmitted as "anchor" data
representing
28 chrominance and luminance data. That data is then often simply moved about
the
29 screen to generate subsequent frames by sending motion vectors that
describe the
movement of the block. Changes in the chrominance and luminance data are also
31 encoded as
-4-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 changes rather than a recoding of absolute anchor data. Thus, encryption of
this
2 anchor data, for example, or other key data can effectively render the video
un-
3 viewable.
4 In accordance with certain embodiments consistent with the present
invention, the selected video data to be encrypted may be any individual one-
or
6 combination of the following (described in greater detail in the above
patents):
7 video slice headers appearing in an active region of a video frame, data
8 representing an active region of a video frame, data in a star pattern
within the
9 video frame, data representing scene changes, I Frame packets, packets
containing motion vectors in a first P frame following an I Frame, packets
having
11 an intra_slice flag indicator set, packets having an intra_slice indicator
set, packets
12 containing an intra_coded macroblock, data for a slice containing an
intra_coded
13 macroblock, data from a first macroblock following the video slice
header,packets
14 containing video slice headers, anchor data, and P Frame data for
progressively
refreshed video data, data arranged in vertical and or horizontal moat
patterns on
16 the video frame, and any other selected data that renders the video and/or
audio
17 difficult to utilize. Several such techniques as well as others are
disclosed in the
18 above-referenced patents, any of which (or other techniques) can be
19 utilized with the present invention to encrypt only a portion of the
content, so long
as the packets containing the SOF header is not encrypted, as will be
explained
21 later.
22 Currently there is a problem with delivering content to a personal-video-
23 recorder (PVR) enabled set-top box is that to.enable trick play it must be
first
24 descrambled. If the content is downloaded "opportunistically" from a
carrousel at
night, then descrambling (and locally re-scrambling) the content can cause a
26 security problem. Keys used to locally re-scramble the content will not be
as
27 secure as those from the conditional access (CA) element. The content on
the hard
28 drive might be accessed without paying the appropriate viewing fees.
Ideally,
29 content delivered "opportunistically" or speculatively to a local drive of
a set-top box
would remain CA scrambled on the hard drive.
-5-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 In accordance with certain embodiments consistent with the present
2 invention, selective encryption is utilized to encrypt selective portions of
content, but
3 leaves the packets containing the SOF header in the clear (unencrypted). By
4 leaving the SOF header unencrypted, trick play circuits and algorithms can
operate
properly. The remainder of the content can be encrypted fully or selectively
6 according to any of the selective encryption schemes described in the
related
7 patents, or any other suitable selective encryption, content selection
criterion.
8 FIGURE 1 describes a process 100, in accord with certain embodiments
9 consistent with the present invention, starting at 104. A packet selection
criterion
is established at 108 for determining which packets are to be encrypted. Such
11 selection criterion can, for example, be established in accord with any of
the above-
12 referenced selective encryption selection criteria (including full
encryption of all
13 content except SOF header packets). Once the selection criterion is
established,
14 packets can be received at 112. If the packet does not meet the selection
criterion
at 116, then the packet is not encrypted at 120. If the packet does meet the
16 selection criterion at 116, then control passes to 126 where the packet is
examined
17 to determine if it contains the SOF header. If so, the packet is not
encrypted at
18 120. If not, the packet is encrypted at 130. Control passe from 120 or 130
to 134.
19 At 134, if the last packet has not been encountered, the next packet is
received at
112. If the last packet has been received at 134, the process stops at 138.
21 Thus, in accord with one embodiment consistent with the invention, a
22 method of selectively encrypting. digital video content, involves receiving
a plurality
23 of packets containing the digital video content; selecting certain of the
packets for
24 encryption according to a selection criterion, wherein the selected packets
exclude
certain packets containing start of frame (SOF) headers; encrypting the
selected
26 packets; and retaining the packets containing the SOF headers unencrypted
to
27 form selectively encrypted digital video content.
28 A method of decoding selectively encrypted digital video content,
consistent
29 with certain embodiments, involves receiving the selectively encrypted
digital video
content, wherein the selectively encrypted digital video content has
unencrypted
-6-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 packets containing start of frame (SOF) headers; calculating offsets for at
least one
2 of I frames and P frames from the SOF headers; and storing the calculated
offsets
3 as an offset table. The offset table can be accessed to enable trick play of
the
4 selectively encrypted digital video content by, identifying the location of
I and/or P
frames.
6 A selective encryption encoder for selective encryption of digital video
7 content, consistent with certain embodiments of the present invention
receives a
8 plurality of packets containing the digital video content. A programmed
processor
9 selects certain of the packets for encryption according to a selection
criterion,
wherein the selected packets exclude packets containing start of frame (SOF)
11 headers. An encrypter encrypts the selected packets while retaining the
packets
12 containing the SOF headers unencrypted to form selectively encrypted
digital video
13 content. The selectively encrypted content can then be stored on an
electronic
14 storage medium and/or transmitted to a receiver such as a television Set-
top box.
In certain embodiments consistent with the present invention, all of the
16 packets containing SOF headers can be left encrypted. However, this should
not
17 be considered limiting since in other embodiments only certain of the
packets
18 containing SOF headers might be left unencrypted, while others are
encrypted. By
19 way of example, and not limitation, I frames may generally be the more
important
frames containing SOF headers to have in the clear. Thus, some or all of the
21 packets containing I frame SOF headers may be passed in the clear while
other
22 packets containing SOF headers may be encrypted. For example, B and/or P
23 frame packets containing SOF headers, in many instances may be encrypted
freely
24 while I frame packets containing SOF headers are kept in the clear. Many
variations with various advantages may be contemplated by those skilled in the
art
26 upon consideration of this teaching.
27 FIGURE 2 depicts an embodiment of this process wherein a clear stream
28 of data 204 is converted to a selectively encrypted stream of data 208.
Clear
29 stream 204 contains a sequence of packets each having program identifier
(PID)
A. Packets 212 and 214 contain SOF headers, while packets 218, 220, 222, 224
-7-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 and 226 contain other information that forms a part of the video data
stream. As
2 a part of the encryption process of this example, all packets except those
3 containing SOF headers are encrypted. Thus, packets 212 and 214 are
transferred
4 directly to the. selectively encrypted stream 208. Packets 218, 220, 222,
224 and
226 are encrypted to produce encrypted packets 238, 240, 242, 244 and 246,
6 respectively. At the decoder (e.g., in a television Set-top box (STB)), the
fact that
7 the SOF headers are unencrypted enables calculation of offsets for trick
play at
8 240. These offsets can then be stored in a local trick play offset table at
254 to
9 enable rapid access to the proper I and/or P frames, and thus produce trick
play.
FIGURE 3 depicts an embodiment of this process wherein a clear stream
11 of data 304 is converted to a selectively encrypted stream of data 308. In
this
12 example, the selective encryption selection criterion is one that only
partially
13 encrypts packets not containing SOF headers. Clear stream 304 contains a
14 sequence of packets each having program identifier (PID) A. Packets 312 and
314
contain SOF headers, while packets 318, 320, 322, 324 and 326 contain other
16 information forming part of the stream of video. As a part of the
encryption process
17 of this example, only certain of the packets containing information other
than the
18 SOF header are encrypted. As illustrated, packets 312 and 314 are
transferred
19 directly to the selectively encrypted stream 308. Packets 318, 322 and 326
are
encrypted to produce encrypted packets 338, 342 and 346, respectively. At the
21 decoder (e.g., in a television STB), the fact that the SOF headers are
unencrypted
22 enables calculation of offsets for trick play at 340. These offsets can
then be stored
23 in a local trick play offset table at 354 to enable rapid access to the
proper I and/or
24 P frames, and thus produce trick play.
When selectively encrypted digital video content is created as streams 208
26 or 308, the selectively encrypted digital video content can.then be stored
on an
27 electronic storage medium or transmitted to one or more recipients (e.g.,
by
28 downloading, streaming or broadcast by a cable or satellite content
provider to
29 subscriber's Set-top boxes serving as receivers and decoders.
-8-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 Thus, certain embodiments of the present invention keep the SOF header
2 packets in the clear. This allows commercially available decoder chips such
as the
3 model number 7030 manufactured and sold by Broadcom Corporation to calculate
4 the byte offset to I, P and B frames. For trick play operation, the offset
allows a
decoder (e.g., a Set-top box) to display, for example, every second I Frame or
fourth
6 I frame without decoding other content. While the SOF headers are not
encrypted,
7 the rest of the content does not need to be completely encrypted, as
described
8 above.
9 The processes above can be carried out on any suitable programmed
general purpose processor operating as a server/encoder such as that depicted
as
11 computer 400 of FIGURE 4. Computer 400 can represent either an encryption
12 processor or a decoder depending upon programming. Computer 400 has one or
13 more central processor units (CPU) 410 with one or more associated buses
414
14 used to connect the central processor unit 410 to. Random Access Memory 418
and Non-Volatile Memory 422 in a known manner. Output devices 426, such as
16 a display and printer, may be provided in order to display and/or print
output for the
17 use of the MSO or user as well as to provide a user interface such as
a.Graphical
18 User Interface (GUI). Similarly, input devices such as keyboard, mouse and
19 removable media readers 430 may be provided for the input of information by
the
operator. Computer 400 also may incorporate internal and/or external attached
21 disc or other mass storage 434 (e.g., disc and/or optical storage) for
storing.large
22 amounts of information including, but not limited to, the operating system,
23 encryption processes (for the encryption encoder), or offset calculation
and local
24 offset table if computer 400 is used as a decoder (e.g., forming a part of
a television
STB). The Computer system 400 also has an interface 438 for connection to the
26 cable system if present at the MSO. While depicted as a single computer,
the
27 digital content provider may utilize multiple linked computers to carry out
the
28 functions described herein.
29 Those skilled in the art will recognize that the present invention has been
described in terms of exemplary embodiments based upon use of a programmed
-9-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 processor (e.g., computer 400). However, the invention should not be so
limited,
2 since the present invention could be implemented using hardware component
3 equivalents such as special purpose hardware and/or dedicated processors
which
4 are equivalents to the invention as described and claimed. Similarly,
general
purpose computers, microprocessor based computers, micro-controllers, optical
6 computers, analog computers, dedicated processors and/or dedicated hard
wired
7 logic may be used to construct alternative equivalent embodiments of the
present
8 invention. Moreover, although the present invention has been described in
terms
9 of a general purpose personal computer providing a playback mechanism, the
playback can be carried on a dedicated machine without departing from the
present
11 invention.
12 Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the program steps and
associated
13 data used to implement the embodiments described above can be implemented
14 using disc storage as well as other forms of storage such as for example
Read
Only Memory (ROM) devices, Random Access Memory (RAM) devices; optical
16 storage elements, magnetic storage elements, magneto-optical storage
elements,
17 flash memory, core memory and/or other equivalent storage technologies
without
18 departing from the present invention. Such alternative storage devices
should be
19 considered equivalents.
The present invention, as described in embodiments herein, is implemented
21 using a programmed processor executing programming instructions that are
22 broadly described above form that can be stored on any suitable electronic
storage
23 medium or transmitted over any suitable electronic communication medium or
24 otherwise be present in any computer readable or propagation medium.
However,
those skilled in the art will appreciate that the processes described above
can be
26 implemented in any number of variations and in many suitable programming
27 languages without departing from the present invention. For example, the
order of
28 certain operations carried out can often be varied, additional operations
can be
29 added or operations can be deleted without departing from the invention.
Error
trapping can be added and/or enhanced and variations can be made in user
-10-
CA 02437025 2010-08-18
1 interface and information presentation without departing from the present
invention.
2 Such variations are contemplated and considered equivalent.
3 Software code and/or data embodying certain aspects of the present
4 invention may be present in any computer readable medium, transmission
medium, storage medium or propagation medium including, but not limited to,
6 electronic storage devices such as those described above, as well as carrier
7 waves, electronic signals, data structures (e.g., trees, linked lists,
tables, packets,
8 frames, etc.) optical signals, propagated signals, broadcast signals,
transmission
9 media (e.g., circuit connection, cable, twisted pair, fiber optic cables,
waveguides,
antennas, etc.) and other media that stores, carries or passes the code and/or
data.
11 Such media may either store the software code and/or data or serve to
transport
12 the code and/or data from one location to another. In the present exemplary
13 embodiments, MPEG compliant packets, slices, tables and other data
structures
14 are used, but this should not be considered limiting since other data
structures can
similarly be used without departing from the present invention.
16 While the invention has been described in conjunction with specific
17 embodiments, it is evident that many alternatives, modifications,
permutations and
18 variations will become apparent to those skilled in the art in light of the
foregoing
19 description. Accordingly, it is intended that the present invention embrace
all such
alternatives, modifications and variations as fall within the scope of the
appended
21 claims.
22
-11-