Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
1
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EXCAVATING SOIL MATERIAL
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to a method for excavating soil material below a water
surface by
means of a working appliance, which is installed on a floating body, in which
a flat soil
layer is crushed by lowering several times said working appliance and the
crushed soil
material is delivered to the water surface, during each lowering of the
working
appliance a zone is excavated from the soil layer which is approximately
perpendicular
to the water surface, in a first excavation step primary zones are excavated
in an offset
manner with respect to one another and between the primary zones soil material
remains in secondary zones, and in a second excavation step the secondary
zones are
removed. The invention also relates to an apparatus for excavating soil
material below a
water surface for performing the method according to the invention and having
a
working appliance for crushing soil material, a floating body, a lifting
mechanism with
which the working appliance can be lowered from the floating body onto the bed
and at
least one delivery line for delivering the crushed soil material to the water
surface.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
German published Patent Application No. DE 1 812 879 A discloses a method for
working the bed of watercourses, in which in an area of the watercourse bed to
be
worked, boreholes are made with a mutual spacing down to a predetermined depth
and
the parts left standing between these boreholes are also worked to a
predetermined
depth by means of a rotary tool. Boring devices with a rotating boring rod are
used for
making the boreholes.
It is also known to excavate underwater soil layers using excavating buckets
on a
conveying chain. However, this method is relatively imprecise and is not
particularly
efficient in the case of hard soil layers. Moreover, excavating with
excavating buckets
introduces much turbid matter into the water.
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
2
DE 2 310 769 A describes an apparatus for producing boreholes in the bed of
watercourses. This known apparatus has an excavating tool with shovels and
prospecting cutters which is rotated about a rotation axis substantially
parallel to the
direction of advance. The apparatus also has a suction pipe for sucking off
broken loose
soil material.
EP 0 819 819 Al discloses a method and an apparatus for removing rock samples
from
the ocean bed. A milling head with a roughly circular boring cross-section
bores in the
ocean bed from a ship and as a result punctiform sampling can take place.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The object of the invention is to provide a method and an apparatus permitting
a
planned and particularly economic excavation of even hard soil layers under
water.
In an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for the
excavation of
soil material below a water surface by means of a working appliance, which is
installed
on a floating body, in which a flat soil layer is crushed by lowering the
working
appliance several times and the crushed soil material is delivered to the
water surface,
one zone is excavated from the soil layer roughly perpendicular to the water
surface
during each lowering of the working appliance, in a first excavation step
primary zones
are excavated in an offset manner with respect to one another and between the
primary
zones soil material is left behind in secondary zones, and in a second
excavation step
the secondary zones are removed, whereby the working appliance is constituted
by a
milling device with a rectangular excavation cross-section, and the primary
zones and
secondary zones are arranged in an alternating sequence, having an overhead
appearance similar to that of a chessboard.
In a further aspect of the present invention, there is provided an apparatus
for the
excavation of soil material below a water surface, for performing the method
according
to any one of claims 1 to 9, having a working appliance for crushing soil
material, a
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
3
floating body, a lifting mechanism with which the working appliance can be
lowered to
the bed from the floating body and at least one delivery line for delivering
the crushed
soil material to the water surface, wherein the working appliance is a milling
device
with a rectangular excavation cross-section incorporating at least one milling
cutter.
From the method standpoint the object is achieved according to the invention
in that the
working appliance is constituted by a milling device having a rectangular
excavating
cross-section and in that the primary zones and secondary zones are arranged
in
chessboard-like manner or in a checkered formation.
A fundamental idea of the invention is that by lowering a soil-breaking and
crushing
device from a floating body the soil within an excavation zone can be removed
and the
removed material delivered to the floating body. As a result of repeated,
planned
lowering of the soil-removing and crushing device the soil is removed within
further
excavation zones. The desired soil layer can be efficiently excavated in that
in planned
manner a plurality of specific excavation zones are removed. This permits a
complete,
layerwise removal of a soil layer, even in the presence of hard rock. The
roughly
vertical lowering and direct conveying away of the crushed soil material
ensure that the
environment of the excavation site suffers to a greatly reduced extent.
In principle, numerous excavation sequences are possible when excavating a
flat soil
layer as a result of lowering the working appliance several times. Thus, in a
linear
excavation sequence e.g. the individual zones can directly follow on to one
another.
However, according to the invention, from the soil layer during each lowering
of the
working appliance one zone is excavated roughly perpendicular to the water
surface, in
a first excavation step initially primary zones are excavated offset with
respect to one
another and between the primary zones soil material is left behind in
secondary zones,
and the secondary zones are removed during the second excavation step. With
this
procedure, following the first excavation step soil walls or columns are left
behind in
the soil layer and can be used for guiding the working appliance. Thus, it is
possible to
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
4
largely eliminate the risk of running off centre of the working appliance and
the
intended vertical excavation direction can be maintained, which allows a
particularly
rapid and thorough excavation.
According to the invention the primary and secondary zones are arranged in a
chessboard-like manner, or from an overhead view, appear similar to that of a
chessboard. Such an arrangement can be easily produced. It is particularly
preferred for
the secondary zones to be smaller than the primary zones, because this allows
a
particularly reliable guidance of the working appliance. The cross-sectional
area of the
secondary zones is in particular dimensioned in such a way as to be smaller
than the
excavation area of the working appliance.
In principle, the primary zones and the secondary zones can be sunk to the
same depth.
However, preferably, the primary zones and secondary zones are sunk to a
different
depth. Should it prove necessary to subsequently excavate the soil layer to a
greater
depth in further excavation steps and following on to the second excavation
step, the
soil walls or columns left behind after said second excavation step can be
used for
guiding the working appliance in the following excavation steps.
During the excavation of the zones, the working appliance can be retained
solely by
gravity and its own mass moment of inertia in the working direction. However,
the
working appliance is preferably guided on a guide device, which is preferably
fixed in
the soil layer. If the guide device is provided during the excavation of the
secondary
zones, it can advantageously be fixed to the side walls of the columns left
behind
following the first excavation step.
According to the invention, the working appliance is guided by a leading tool.
The
leading tool can in particular be a milling cutter. A guidance with a guide
device or a
leading tool permits a particularly precise positioning of the working
appliance and
therefore a thorough excavation of the soil layer.
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
The inventive method can be used for the excavation of soil layers below any
natural
water surface such as lakes, rivers and oceans. A method according to the
invention
involves the water surface being artificially created by flooding an open-cast
mining
boiler. Such normally circular or oval pits are used in open-cast mining for
diamonds
5 along extinct volcanic vents. The conically downwardly narrowing pits must
have a
specific minimum diameter, so that the truck necessary for transporting the
excavated
material can be driven spirally along the pit edge. Thus, the starting
diameter of such
boilers establishes the attainable final depth. If excavatable material is
found below the
maximum reachable final depth, the boiler diameter must be increased in order
to reach
a greater final depth, which involves a very considerable material excavation.
As a
result of the inventive flooding of the bottom of the open-cast mining pit by
a height of
a few metres, it is possible to use the inventive method for the further
excavation of the
pit bottom. Thus, without changing the boiler wall, it is possible to
significantly
increase the final depth by up to 200 m or more.
Fundamentally the crushed soil material can be delivered to the water surface
by means
of a suction device, which can have a pump. However, in a preferred embodiment
soil
material delivery takes place by the feeding in of compressed air to the
crushed soil
material over a first line, the soil material being removed with the
compressed air by
means of a second line.
It is advantageous when performing the method according to the invention to
precisely
fix the position of the floating body on the water surface. This can e.g. take
place by an
active control of drives of the floating body through a position determination
system.
However, with particular preference the position of the floating body is set
by adjusting
the length of at least two cables, which link the floating body with the bank
or with
anchor points. This makes it possible to precisely fix the position, whilst
involving a
very limited energy expenditure. The anchor points can in particular be fitted
to the bed
below the water surface.
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
6
A further inventive method performance is characterized in that the crushed
soil
material is supplied to a separating or dressing plant for extracting mineral
resources.
The mineral resources can e.g. be diamonds or precious metals. In principle,
the
separating or dressing plant can be located on the floating body, on the bank
or on
another floating body. After passing through the separating or dressing plant
the
worthless part of the soil material can be delivered to a waste dump or
returned to the
excavation zones.
The crushed soil material can be delivered continuously from the floating body
to the
separating or dressing plant by means of a pump line, which can be constructed
in
floating manner in the water area. Alternatively there can be a transfer
station on the
bank, to which the crushed soil material is supplied by means of a pump line
and which
transfers said soil material to trucks, which transport it to the separating
or dressing
plant.
From the apparatus standpoint the object is achieved in that the working
appliance is a
milling device with a rectangular excavation cross-section and which
incorporates at
least one milling cutter.
The floating body of the apparatus according to the invention is preferably a
pontoon,
ship or boat and the floating body preferably has a drive, such as e.g. a
propeller.
Preferably the floating body incorporates at least two controllable cable
winches with
cables, which are fixed to the bank or to anchor points. This permits an
energy-
favourable, very precise positioning of the floating body.
According to the invention the working appliance is a milling device
incorporating at
least one milling cutter. A milling device permits a particularly efficient
excavation and
crushing of even very hard soil or ground material. The excavation cross-
section of the
milling device is, according to the invention, rectangular, because this
allows a
complete excavation of the soil layer. The milling cutter can be in the form
of so-called
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
7
trench wall cutters, in which the drive is located in a frame or support
between the
milling or cutting wheels and the crane suspension.
In a particularly preferred embodiment, at least one milling cutter has a
milling wheel
pair, which permits particularly efficient milling.
In order to increase the boring cross-section attainable during a single
lowering of the
working appliance, it is particularly preferable for there to be two parallel
milling
cutters. In principle, it is also possible to have three or more milling
cutters. It is
particularly preferred for the two milling cutters to be arranged in such a
way that the
milling wheel pairs are axially parallel. This permits a particularly simple
design and
construction of the milling device. The drive for the milling wheels is
preferably
hydraulic, but it is also possible to use other drives, e.g. of an electrical
or mechanical
nature.
The two milling cutters are preferably mounted so as to be displaceable
relative to one
another. In the case of transverse displaceability, this makes possible a
sliding apart,
thereby giving access to the inner milling wheels, which is advantageous from
the
maintenance standpoint. Access for changing the inner milling wheels can also
be made
possible in that the two milling cutters are constructed so as to be at least
partly
separable from one another. In the case of vertical displaceability it is
possible with
displaceably mounted milling cutters to use in a mutual movement of the two
cutters
one leading cutter for guiding the entire milling device.
A particularly precise guidance of the working appliance during sinking can be
achieved in a particularly preferred embodiment in that the working appliance
has a
guide frame, which can be fitted to one or more sides of the working
appliance. It is
particularly preferred to provide on the floating body a boring rig for fixing
the guide
frame on the milling base. Fixing can take place by means of a soil auger or
other fixing
means.
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
8
An apparatus according to the invention is further developed in that the
working
appliance can be moved by a lifting mechanism in a plane parallel to the water
surface
relative to the floating body. This permits a particularly precise positioning
of the
working appliance.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
The invention is described in exemplified manner hereinafter relative to the
attached
drawings, wherein show:
Fig. 1 A side view of an apparatus according to the invention for the
excavation of soil
material.
Fig. 2 A plan view of an apparatus according to the invention for excavating
soil
material.
Fig. 3 A plan view of an apparatus according to the invention for the
excavation of soil
material whilst also showing the watercourse bed for illustrating the method
according to the invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figs. 1 and 2 show a pontoon as the floating body 10 floating on a water
surface 7. To
the pontoon is fitted a working appliance 20, which comprises a frame 21 and a
bottom
positioned milling cutter 22. By means of a lifting mechanism the working
appliance 20
can be lowered and then raised again through an opening 11, known as a moon
pool.
The lifting mechanism comprises supporting cables 45, 45', which are connected
by
means of guide pulleys 38, 38' to supporting cable winches 46, 46'. The guide
pulleys
38, 38' are mounted on a crane frame 30, which has ajib 32. The crane frame 30
also
has a hydraulic cylinder 31 permitting an adjustment of the position of the
working
appliance 20.
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
9
To the working appliance 20 are supplied supply hoses or lines 41, 41' and 43
through
which crushed soil material is delivered and compressed air and hydraulic
fluid
supplied and removed. The supply hoses 41 and 41' run over guide pulleys 36
from
working appliance 20 to drums 42, 42'. The supply hose 43 passes over guide
pulleys
37, 37' to drum 44. On lowering or raising the working appliance 20, a
corresponding
length of the supply hoses 41, 41' and 43 is unwound or wound onto the drums
42, 42'
and 44.
Cable winches 16, 16', 16" and 16"' are marginally fitted to the four corners
on the
pontoon. Said cable winches are used for the planned shortening or lengthening
of the
cables, which are connected to the bank and/or anchor points, so that the
pontoon
position can be precisely moved and fixed. The pontoon also carries diesel
hydraulic
units 13, 13' and a cabin 14 for the operating personnel.
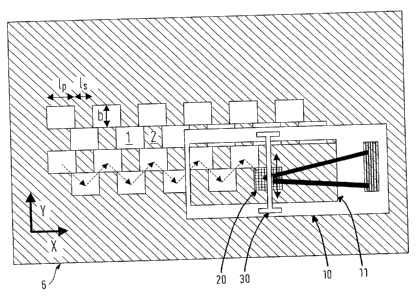
A method according to the invention for the excavation of a soil or ground
layer is
illustrated in Fig. 3, which diagrammatically shows an apparatus according to
the
invention and the watercourse bed 6 below it during the excavation of primary
zones in
a first excavation step. The pontoon is moved in one direction and by repeated
lowering
of the working appliance 20 the soil within the primary zones 1 is worked to a
depth of
approximately 15 metres. Soil material in the form of columns is left between
the
primary zones 1 in secondary zones 2. The primary zones e.g. have a length
(lp) of 3.2
metres and the secondary zones a length (15) of 2 metres, both zones having a
width (b)
of 3 metres.
The excavation sequence during one pass of the pontoon in the X-direction is
illustrated
by the broken line arrows. In order to bring about this excavation sequence
the working
appliance 20 can be alternately moved in the Y-direction by the crane frame
30. As a
result of the excavation sequence shown, at the end of the first excavation
step, there is
a chessboard-like arrangement of the primary zones 1 and between them smaller,
secondary zones 2. These secondary zones 2 are removed in a following
operation,
CA 02438634 2007-04-30
during which the pontoon can move in the X or Y-direction, by the lowering of
the
working appliance 20. In the case of use under extreme weather conditions, the
entire
pontoon or only the crane with the supply means and the moon pool can be
protectively
housed, particularly being covered by a dome or a casing.
5