Note: Claims are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
-37-
WHAT IS CLAIMED IS:
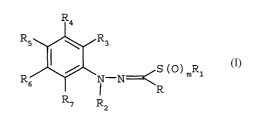
1. A compound of formula I
Image
wherein
R is hydrogen,
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C3-C6cycloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4-alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
phenyl optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
-38-
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups;
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogens,
C1-C6alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x,
phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
-39-
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
with the proviso that when R is phenyl, then m must be 1
or 2;
R1 is R12;
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
hydroxy,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12.
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4 haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
-40-
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkenyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
-41-
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkynyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
-42-
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
-43-
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
R2 is hydrogen or C1-C4alkyl;
R3, R4, R5, R6,and R7 are each independently hydrogen,
halogen, CN, NO2, C1-C6alkyl, C1-
C6haloalkyl, C1-C6alkoxy, C1-C6haloalkoxy,
or phenyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y, NO2
or CN groups,
with the proviso that at least one of R3, R4, R5, R6 or
R7 must be phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy, (C1-
C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x, NO2 or CN
groups;
x and y are each independently 0, 1 or 2;
m is an integer of 0, 1 or 2;
-44-
R8, R9 and R10 are each independently hydrogen or C1-
C4alkyl;
R11 is NR13 R14,
Image
R12 is Image
R13, R14, and R15 are each independently hydrogen or C1-
C4alkyl;
R16 is hydrogen, halogen or C1-C4 alkyl;
X is O, S or NR15;
r is an integer of 0 or 1;
p and q are each independently an integer of 0, 1, 2, or
3 with the proviso that only one of p, q, or r can
be 0 and with the further proviso that the sum of p
+ q + r must be 4, 5 or 6; and
x is an integer of 0, 1 or 2; or
the acid addition salts thereof.
2. The compound according to Claim 1 wherein
R3 and R7 are each independently H or C1-C6alkoxy; and R4
and R6 are each independently H or phenyl optionally
substituted with one or more halogen, C1-C4haloalkoxy, or
C1-C4haloalkyl groups.
-45-
3. The compound according to Claim 2 wherein R
is C1-C6alkyl or C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted
with one to three halogens.
4. The compound according to Claim 2, S-methyl-
2,2-dimethylthiopropionate, 2-(4-methoxy-3-biphenylyl)-
hydrazone; the S-oxide thereof; the S,S-dioxide thereof;
or the acid addition salt thereof.
5. A method for the control of insect or
acarid pests which comprises contacting said pests, their
food supply, habitat or breeding grounds with a
pesticidally effective amount of a compound of formula I
Image
wherein R is hydrogen,
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C3-C6cycloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4-alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
phenyl optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
-46-
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups;
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogens,
C1-C6alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x,
phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
-47-
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
with the proviso that when R is phenyl, then m must be 1
or 2;
R1 is R12;
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
hydroxy,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
-48-
C1-C4 haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkenyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
-49-
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkynyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
-50-
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
-51-
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
R2 is hydrogen or C1-C4alkyl;
R3, R4, R5, R6,and R7 are each independently hydrogen,
halogen, CN, NO2, C1-C6alkyl, C1-
C6haloalkyl, C1-C6alkoxy, C1-C6haloalkoxy,
or phenyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y, NO2
or CN groups,
-52-
with the proviso that at least one of R3, R4, R5, R6 or
R7 must be phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy, (C1-
C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x, NO2 or CN
groups;
6. The method according to Claim 5 wherein
said pests are acarid pests.
7. The method according to Claim 5 having a
formula I compound wherein R3 and R7 are each
independently H or C1-C6alkoxy; and R4 and R6 are each
independently H or phenyl optionally substituted with one
or more halogen, C1-C4haloalkoxy, or C1-C4haloalkyl
groups.
8. The method according to Claim 7 having a
formula I compound wherein R is C1-C6alkyl or C3-
C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one to three
halogens.
9. The method according to Claim 7 having the
formula I compound, S-methyl-2,2-dimethylthiopropionate,
2-(4-methoxy-3-biphenylyl)-hydrazone; the S-oxide
thereof; the S,S-dioxide thereof and the acid addition
salt thereof.
10. A method for the protection of growing or
harvested plants from attack or infestation by insect or
acarid pests which comprises applying to the foliage of
the plants, or to the soil or water in which they are
-53-
growing, a pesticidally effective amount of a compound of
formula I
Image
wherein
R is hydrogen,
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C3-C6cycloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4-alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
phenyl optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
-54-
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups;
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogens,
C1-C6alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x,
phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
-55-
with the proviso that when R is phenyl, then m must be 1
or 2;
R1 i s R12;
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
hydroxy,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4 haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
-56-
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkenyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11
R12
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
-57-
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkynyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
-58-
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
-59-
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
R2 is hydrogen or C1-C4alkyl;
R3, R4, R5, R6,and R7 are each independently hydrogen,
halogen, CN, NO2, C1-C6alkyl, C1-
C6haloalkyl, C1-C6alkoxy, C1-C6haloalkoxy,
or phenyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y, NO2
or CN groups,
with the proviso that at least one of R3, R4, R5, R6 or
R7 must be phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy, (C1-
C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x, NO2 or CN
groups;
11. The method according to claim 10 wherein
said pests are acarid pests.
-60-
12. The method according to Claim 10 wherein
the compound of formula I is applied in a concentration
of about 10 ppm to 10,000 ppm.
13. The method according to Claim 10 wherein
the compound of formula I is applied in a concentration
in about 100 ppm to 5,000 ppm.
14. A composition for controlling insect or
acarid pests which comprises an agriculturally acceptable
carrier and a pesticidally effective amount of a compound
of formula I
Image
wherein
R is hydrogen,
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C3-C6cycloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4-alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
phenyl optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
-61-
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups;
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogens,
C1-C6alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x,
phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
-62-
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
with the proviso that when R is phenyl, then m must be 1
or 2;
R1 is R12 ;
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
hydroxy,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
-63-
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4 haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkenyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
-64-
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkynyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
-65-
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
-66-
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
R2 is hydrogen or C1-C4alkyl;
R3, R4, R5, R6,and R7 are each independently hydrogen,
halogen, CN, NO2, C1-C6alkyl, C1-
C6haloalkyl, C1-C6alkoxy, C1-C6haloalkoxy,
or phenyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y, NO2
or CN groups,
-67-
with the proviso that at least one of R3, R4, R5, R6 or
R7 must be phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy, (C1-
C4alkyl)SO x, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x, NO2 or CN
groups;
15. The composition according to Claim 14 wherein
R3 and R7 are each independently H or C1-C6alkoxy; and R4
and R6 are each independently H or phenyl optionally
substituted with one or more halogen, C1-C4haloalkoxy, or
C1-C4haloalkyl groups.
16. The composition according to Claim 14 wherein R
is C1-C6alkyl or C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted
with one to three halogens.
17. The composition according to Claim 15 wherein
the compound of formula I is 5-methyl-2,2-
dimethylthiopro-pinnate(4-methoxy-3-biphenylyl)hydrazone;
the S-oxide thereof; the S,S-dioxide thereof; or the acid
addition salt thereof.
18. A process for the preparation of a compound of
formula I
Image
wherein
-68-
R is hydrogen,
C1-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C3-C6cycloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4-alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
phenyl optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C2-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO y,
NO2 or CN groups;
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogens,
C1-C6alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
-69-
(C1-C4haloalkyl)SO x,
phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
phenoxy optionally substituted with one to
three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
with the proviso that when R is phenyl, then m must be 1
or 2;
R1 is R12;
C2-C10alkyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
hydroxy,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
-70-
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4 haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkenyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
-71-
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
C2-C10alkynyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
-72-
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups; or
C3-C12cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one or
more halogen,
hydroxy,
C1-C4alkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SO x,
CONR8R9,
CO2R10,
R11,
R12,
-73-
C3-C6cycloalkyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
Cl-C4halo-alkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
N02 or CN groups,
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
Cl-C4haloalkoxy,
N02 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
Cl-C4alkyl,
Cl-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
NO2 or CN groups;
phenyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
Cl-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
Cl-C4haloalkoxy,
N02 or CN groups, or
pyridyl optionally substituted with one or more
halogen,
C1-C4alkyl,
C1-C4haloalkyl,
C1-C4alkoxy,
-74-
C1-C4haloalkoxy,
N02 or CN groups;
R2 is hydrogen or C1-C4alkyl;
R3, R4, R5, R6,and R7 are each independently hydrogen,
halogen, CN, N02, C1-C6alkyl, C1-
C6haloalkyl, C1-C6alkoxy, C1-C6haloalkoxy,
or phenyl optionally substituted with one
to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy,
(C1-C4alkyl)SOx, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SOy, N02
or CN groups,
with the proviso that at least one of R3, R4, R5, R6 or
R7 must be phenyl optionally substituted with
one to three halogen, C1-C4alkyl, C1-
C4haloalkyl, C1-C4alkoxy, C1-C4haloalkoxy, (C1-
C4alkyl)SOx, (C1-C4haloalkyl)SOx, N02 or CN
groups;
x and y are each independently 0, 1 or 2;
m is an integer of 0 , 1 or 2 ;
R8,R9 and R10 are each independently hydrogen or C1-
C4alkyl;
R11 is NR13 R14'
Image
R12 is
-75-
R13, R14, and R15 and are each independently hydrogen or
C1-C4alkyl;
R16 is hydrogen, halogen or C1-C4 alkyl;
X is O, S or NR15;
r is an integer of 0 or 1;
p and q are each independently an integer of 0, 1, 2, or
3 with the proviso that only one of p, q, or r can
be 0 and with the further proviso that the sum of p
+ q + r must be 4, 5 or 6; and
x is an integer of 0, 1 or 2;
which process comprises reacting a compound of formula II
Image
wherein Xl is halogen and R, R2 , R3 , R4 , R5 , R6 ; and R7 are
as hereinbefore defined, with at least one molar
equivalent of a mercaptan of formula III
HS-R1
(III)
wherein R1 is as hereinbefore defined,
in the presence of a base, optionally in the presence of a
solvent, to form the compound of formula I wherein m is 0,
optionally reacting the compound of formula I wherein m is 0
with one or more molar equivalents of an oxidizing reagent
to form a compound of formula I wherein m is 1 or 2.