Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
MEASURING AND INSTRUCTIONAL RULER
TECHNICAL FIELD
This invention concerns a ruler device for use in measuring distance, for
use in measuring and the construction of linear objects, for use during the
instruction of linear measurement, and for use as an instrument to demonstrate
the
relationship between a said unit of measure and fractional increments of said
standard unit of measure.
BACKGROUND ART
The concept of fractional increments of standard units of measure can be
1o demonstrated by abstract or mathematical approaches when accompanied by
visual indicia. The standard scale markings on a conventional ruler are not
easily
comprehended by children or persons. Young children and persons, especially
those with learning impediments, have difficulty with the perception of
fractional
increments of a said unit of measure on a conventional ruler. For example,
after
15 the concept of'/z", fourths of an inch, eighths of an inch have been
presented,
persons, especially young children, have difficulty with the perception of the
relationship between the-fractional incremental markings because the same
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
2
indicium can denote, for example, one-half inch, two-fourths, four eighths,
and
eight sixteenths of an inch.
Also because the fractional incremental markings on a standard ruler are
of the same color, it is difficult for the learner to distinguish the
markings.
Although the fractional incremental markings on a standard ruler may be of
gradually decreasing length which denote the decreasing size of the fractional
increment, the lines of one color are not easily described to the learner. For
example, when presenting the one inch mark, one states the longest lines are
the
inch marks. Then, when presenting the one-half inch mark, one states the next
l0 shorter lines are the one-half inch marks. Next, when presenting the one-
fourth
inch marks, the problem begins to present itself. If the instructor says the
shortest
lines are the one-fourth inch lines, the learner becomes confused. The term
"shorter" is now applied to more than one set of indicia. The problem becomes
even more severe when the instructor presents the eighth and 5 sixteenth inch
indicia.
U.S. Patent No. 4,614,042 to Maurer discloses an educational device for
use by children and persons having learning impediments or physical handicaps.
While the Maurer device provides a means for perceiving a fraction of an inch,
it
only shows a fraction of an inch as an extension of an inch at a given point
on the
2o device. It does not uniformly demonstrate the fractional increments
throughout
the entire length of the instrument. It also does not simultaneously
demonstrate
the relationship amongst the various fractional increments throughout the
entire
length of the device. Furthermore, it does not disclose the fact that the
incremental
markings denote multiple fractional increments of said standard unit of
measure.
Example: the one-half inch indicia is also the two-fourth, four-eighth and
eight-sixteenth inch indicia. The Maurer device, while demonstrating a
fractional
part of one inch, does not demonstrate the fractional parts of twelve inches
simultaneously. The Maurer device, while being a teaching aid for students, by
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
3
design, would preclude its wide-spread use as a measuring device for the
general
populace.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
This problem is alleviated with each of the fractional incremental indicia
being different colors, presented independently and then aligned on top of
each
other. Said standard unit of measure and the fractional increments thereof are
easily distinguished. It is accordingly an object of this invention to provide
a ruler
comprising functionally symbolic means to aid in the distinguishing of a said
standard unit of measure and its said fractional increments for wide-spread
use
1 o amongst students and the general populace.
It is another object of this invention to provide a ruler device for the
measuring of distance and objects and to use when drawing.
It is further an object of this invention to provide an educational tool
which will facilitate in the instruction for use of Conventional rulers.
15 It is still another object of this invention to provide a ruler of the
aforesaid
nature of sufficient construction and low cost that it may find wide-spread
use
amongst educators and persons.
These objects and advantages of this invention will be apparent from the
following description.
2o The above and other beneficial objects and advantages are accomplished
in accordance with the present invention by a measuring and instructional
ruler
comprised of
a base panel having a top surface, having a standard unit of measure
delineated thereon; and
25 at least one transparent sheet having fractional increments of said
standard
units of measure delineated thereon;
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
4
wherein said transparent sheet is positionable over said base panel so that
said delineated fractional increments of said standard unit of measure are
aligned
with said delineated unit of measure indicia to demonstrate the relationship
between said unit of measure and the fractional increments thereof.
Said ruler can be used to measure distance between two points, to measure
objects, or in the construction of a linear object. Said base panel may be
used
independently, or said transparent sheets may be positioned over said base
panel
so that delineated fractional increments of said unit of measure are aligned.
Said
ruler can then be used to measure distance, construct linear figures, and
measure
1o objects to said fractional increment of said unit of measure.
Said instructional ruler can be used as an educational tool to facilitate in
the instruction of use of conventional rulers. Said ruler can be utilized as a
demonstrational tool or as a measuring device in all circumstances which call
for
a measuring device such as elementary schools, technical schools, trade
schools,
15 prison, adult, and abilities educational programs or in any situation where
there is
a need for a ruler.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
For a fuller understanding of the nature and objects of this invention,
reference should be had to the following detailed description taken in
connection
2o with the accompanying drawings forming a part of this specification and in
which
similar numerals of reference indicate corresponding parts in all the figures
of the
drawings:
FIG. 1 is a top plan view embodiment of said base panel component of a
ruler of this invention.
25 FIGS. 2a-2e are top plan views of said base panel and four transparent
sheets which are positionable over the base panel so that standard unit of
measure
indicia are aligned with fractional incremental indicia of standard unit of
measure.
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
FIG. 3 is an exploded view of said ruler of this invention in operative
mode using the components of FIGS. l, 2b, 2c, 2d and 2e.
FIG. 4 is an alternative embodiment of said base panel from FIG. 1 and
said transparent sheet 2b from FIG. 2.
5 FIG. 5 is a top plan view of a further alternative embodiment of said base
panel from FIG. 1 and said transparent sheet 2d of FIG. 2.
FIG. 6 is an alternative exploded view of said ruler of this invention in
operative mode using the components of FIG. 1 and 2d from FIG. 2.
FIG. 7 is a perspective view of another embodiment of the present
invention.
BEST MODE OF CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Refernng to FIGS. 1-6, a ruler device of this invention is shown
comprised of a base panel 10 and multiple top sheets 11, 12, 13, 14, all
panels
being of substantially integral monolithic construction, the base panel having
been
fabricated of wood, cardboard, transparent or opaque plastic sheet stock, the
multiple top sheets having been fabricated of transparent plastic sheet stock.
Base
panel 10 having upper and lower faces 15 and 16, respectively, and having an
elongated rectangular perimeter bounded by parallel straight upper and lower
long
edges 17 and 18, respectively, and straight short leading and trailing edges
19 and
20, respectively. Said upper face of base panel is provided with numbered
linear
rulings 21 perpendicularly disposed to upper long edge 17 and defining said
standard unit of measure subdivision regions 22 having visual indicia
delineated
thereon.
In the illustrated embodiment, said standard units of measure are inch
units. In other embodiments, said standard units of measure may be metric.
In other embodiments, lower long edge 18 of said base panel 10 may be of
a curved configuration comprising one or more circular openings.
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
6
Referring to FIGS. 2a - 2e, top sheets 11, 12, 13, 14, having flat upper and
lower faces 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, respectively, have elongated
rectangular
perimeter bounded by parallel straight upper and lower long edges 31, 32, 33,
34,
35, 36, 37, 38, and straight short leading and trailing edges 39, 40, 41, 42,
43, 44,
45, 46, respectively.
Said upper face 23 of top sheet 11 is provided with solid linear rulings 47
perpendicularly disposed to upper long edge 31, and defining %z" wide
subdivision
regions 48.
Said upper face 25 of top sheet 12 is provided with solid linear rulings 49
perpendicularly disposed to upper long edge 33 and defining '/4" wide
subdivision
regions 50.
Said upper face 27 of top sheet 13 is provided with linear rulings 51
perpendicularly disposed to upper long edge 35 and defining 1/8" wide
subdivision regions 52.
Said upper face 29 of top sheet 14 is provided with linear rulings 53
perpendicularly disposed to upper long edge 37 and defining 1/16" subdivision
regions 54.
In the embodiment shown in FIGS. 2a - 2e, the linear rulings 21, 47, 49,
51, 53 on upper faces 15, 23, 25, 27, 29, respectively, define said
subdivision
2o regions of 1" (9),1/2" (48), 1/4" (50), 1/8" (52), 1/16" (54),
respectively. In other
embodiments, the linear rulings may define subdivision regions of decimeter,
centimeter, and millimeter. The linear rulings may also define tenths and
hundredths of an inch.
In another embodiment, the base panel may have units of a first standard
unit of measure delineated thereon and a transparent sheet will have units of
a
second standard of measure delineated thereon to demonstrate the relationship
between the first and second standard units of measure. This embodiment may be
employed to demonstrate the relationship between, for example, an English
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
7
measurement, such as an inch, and a metric measurement, such as a decimeter.
Inches and fractional inches may thereby be converted to their metric
equivalents.
Additional transparent sheets may be provided delineated with fractional
increments of either the first or second unit of measure so that the
relationship
between either the fractional increments of the first unit of measure and the
second unit of measure or the fractional increments of the second unit of
measure
and the first unit of measure may be demonstrated. For example, additional
transparent sheets delineated with fractional units of an inch and a decimeter
(i.e.,
centimeters and millimeters) can be used to demonstrate the relationship
between
l0 the metric and English units and their respective fractional units.
Said linear markings 21, 47, 49, 51, 53 are of sequentially decreased
length corresponding to said standard unit of measure and its fractional
increment
thereof. Linear marking 21 being the longest in length. Linear marking 47
being
shorter than linear marking 21. Linear marking 49 being shorter than linear
marking 47. Linear marking 51 being shorter than marking 49. Linear marker 53
being shorter than linear marking 51.
Linear markings in other embodiments will be of sequentially decreased
length corresponding to said standard unit of measure and fractional
increments
thereof.
2o Said linear markings 21, 47, 49, 51, 53 are preferably of clearly distinct
variant colors. Linear markings 21 are of one color, clearly distinguishable
from
said colors of linear markings 47, 49, 51 and 53. Linear markings 47 are of
another different color clearly distinguishable from said colors of linear
markings
21, 49, 51 and 53. Linear markings 49 are of still another different color
clearly
distinguishable from said colors of linear markings 21, 47, 51 and 53. Linear
markings 51 are of a further different color clearly distinguishable from said
color
of linear markings 21, 47, 49 and 53. Linear markings 53 are of one further
different color clearly distinguishable from said color of linear markings 21,
47,
49 and S 1.
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
8
Said standard unit of measure subdivision regions will be delineated
within linear markings 47, 49, 51, 53 of said transparent sheets 11, 12, 13,
14 by
means of a thicker linear marking of same length and color as said linear
markings on said transparent sheets.
In other embodiments, said linear markings of said unit of measure and
fractional increments thereof may be of distinct variant color and thickness,
and
clearly distinguishable from each of said other linear markings comprised in
said
embodiment.
Said transparent sheets are positionable over said base panel so that said
l0 delineated fractional increments of said unit of measure may be aligned
with said
delineated unit of measure to demonstrate the relationship between unit of
measure and the fractional increments thereof.
Said base panel 10 and said base panel sheets 11, 12, 13, 14 may be
secured by means of rivets, ring binders, conventional book binding, heat
laminating, living hinge, snaps, veto binding, velcro, repositionable
adhesive, or
any other means by which two or more parts of an item can be bound. Said base
panel 10 and said transparent sheets 11, 12, 13, 14 may not be bound. Said
base
panel 10 may be used independently or in conjunction with said transparent
sheets
11, 12, 13, 14 in any various combinations.
2o In use, said base panel as shown in FIG. 1 may and can be presented
independently. The user positions object on zero line indicia (denoted with
visual
indicia A in FIG. l, B as in FIG. 4), then measures to the nearest whole
standard
unit of measure. Said transparent sheet 11 can/may then be positioned over
said
base panel 10 as shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, so that said fractional linear
markings
on said transparent sheet and said standard unit of measure linear markings on
said base panel are aligned beginning with zero line indicia A on base panel
10
and zero line indicia on transparent sheet 11. User positions object on zero
line
indicia and measures to nearest fractional increment of said standard unit of
measure.
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
9
This procedure may/can be repeated until user has positioned Said
transparent sheets 12, 13, 14 over said base panel 10 and said transparent
sheet
11, as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6.
The standard unit of measure need not be a linear unit of measure. For
example, the base panel may be delineated with standard units of time (such as
hours), volume (such as gallons or liters) or incremental angular units of
measure.
One or more transparent sheets can then be delineated with fractional units of
time (such as half hours, quarter-hours or minutes), volume (cups, pints,
quarts,
half gallons or deciliters), or angular units of measure.
1o For volume, when the base panel is delineated with gallons, one or more
transparent sheets may be delineated with metric units such as liters and
deciliters
to demonstrate how gallons can be converted to metric equivalents. Additional
transparent sheets may be delineated with fractional units of gallons to
demonstrate how cups, pints, quarts and half gallons are related, and how
these
units can be converted to metric equivalents. Alternatively, the base panel
can be
delineated with metric units such as liters with the transparent sheets
delineated
with English units and fractional units thereof for purposes of conversion,
with
additional transparent sheets delineated in fractions of liters to demonstrate
the
relationship to liters and for comparison to the English units.
2o For angular measurement, the base panel can represent a 180°
semicircle,
preferably in the form of a protractor, with transparent sheets delineated in
fractional units thereof, such as single degrees and units of ten degrees. A
transparent sheet may be delineated in radians to demonstrate the relationship
between degrees and radians. Alternatively, the base panel can represent a
180°
semicircle delineated in single degrees and units of ten degrees typically
found on
a protractor, and the transparent sheets may then be delineated in
trigonometric
functions such as sine, cosine, tangent and the like, to demonstrate the
relationship between the trigonometric functions as a function of angle size,
and
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
to permit the rapid and accurate determination of trigonometric functions for
any
given angle.
For measurement of time, the base panel can be circular and represent a
clock face with the familiar twelve hourly delineations. A transparent sheet
may
5 be delineated in five-minute units to demonstrate how the twelve
delineations
simultaneously represent hours and minutes. Other transparent sheets may be
employed delineated in half and quarter-hours to demonstrate these fractional
relationships.
FIGS. 1 and 2a-a thus may also represent a ruler delineated with units of
1 o volume. Linear rulings 21 of base panel 10 may define gallons, with linear
rulings 47 of top sheet 11 representing half gallons, linear rulings 49 of top
sheet
12 representing quarts, linear rulings 51 of top sheet 13 representing pints
and
linear rulings 35 of top sheet 14 representing cups. Alternatively, linear
rulings
51 and 53 may be delineated to represent liters and deciliters.
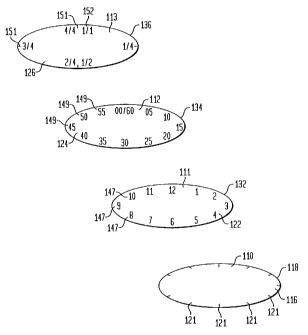
FIG. 7 depicts a clock face 110 having a circular perimeter bounded by
edge 118. The face 116 of base panel 110 is provided with linear rulings 121
perpendicularly disposed to edge 118 and delineating the familiar twelve
markings that simultaneously represent hours and minutes. Top sheets 111, 112,
113 have circular perimeters bounded by edges 132, 134, 136, respectively.
2o Upper face 122 of top sheet 111 is provided with numerical indicia 147
demonstrating the hours of the day that correspond to each marking. The upper
face 124 of top sheet 112 is provided with numerical indicia 149 demonstrating
the minutes of the hour represented by each marking. Upper face 126 of top
sheet
113 is provided with linear rulings 151 perpendicularly disposed to edge 136
and
defining quarter-hours subdivision regions identified by fractional indicia
152.
Alternatively, the device of FIG. 7 can be employed to demonstrate the
relationship between units of angular measurement and trigonometric functions.
In this embodiment of the invention, the face 116 of base panel 110 is
provided
with linear rulings 121 perpendicularly disposed to edge 118 and defining the
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
11
degrees of a circle. Numerical indicia identify the degree value corresponding
to
each linear marking is also included. Upper face 122 of sheet 111 is provided
with numerical indicia depicting the radian values corresponding to the degree
values depicted on the face of the base panel. Upper face 124 of sheet 112 is
provided with numerical indicia depicting sine values corresponding to the
degree
values depicted on the face of the base panel. Upper face 126 of sheet 113 is
provided with numerical indicia depicting cosine values corresponding to the
degree values depicted on the face of the base panel.
This embodiment is also a useful device for teaching principles of vector
l0 calculus. A half version of this embodiment, from zero to 180 °, is
useful in
teaching the use of a protractor and the relationship of trigonometric
functions to
angles on the protractor.
Still yet another application for this embodiment of the invention is in the
teaching of basic principles of navigation and direction. As in the previous
embodiment, the face 116 of base panel 110 is provided with numbered linear
rulings 121 perpendicularly disposed to edge 118 and defining the degrees of a
circle with numerical indicia depicting the degree value for each linear
ruling.
Upper face 122 of sheet 111 is provided with linear rulings perpendicularly
disposed to edge 132 at 0°, 90°, 180° and 270° of
the circle and delineated with
indicia identifying north, south, east and west. Upper face 124 of top sheet
112 is
provided with linear rulings perpendicularly disposed to edge 134 and defining
subdivisions of the linear markings of top sheet 111 corresponding to the
compass
points northeast, southeast, northwest and southwest. Indicia on the face 124
of
top sheet 112 identifies each intermediate compass point. Upper face 126 of
sheet
113 is provided with linear rulings perpendicularly disposed to edge 136 and
further subdividing the subdivisions of face 124 of sheet 112 at points
corresponding to intermediate compass points such as north-northeast, east-
northeast, east-southeast and so forth. The face 126 of sheet 113 is also
provided
with indicia identifying the foregoing compass points.
CA 02450716 2003-12-12
WO 02/101324 PCT/USO1/40928
12
This embodiment of the present invention is useful in also teaching the
degrees of a circle corresponding to compass points, as well as the degrees of
a
circle between compass points, so that a student can readily understand the
degree
of a turn required to change direction of travel from first compass point to a
second compass point.
This embodiment of the present invention may be modified to demonstrate
fractional relationships by employing a base panel with no linear rulings or
indicia and replacing the linear rulings of each top sheet with pie chart-type
fractions of the base panel. One top sheet may depict a half "slice," another
top
to sheet may depict one or more quarter "slices," including a depiction of how
the
half "slice" may be divided into quarter "slices," another top sheet may
depict one
or more eighth "slices," including a depiction of how each quarter "slice" may
be
divided into eighth "slices," and so forth.
The present invention includes methods by which relationships between
units of volume, units of time and units of angular measurement may be
demonstrated and taught with the devices of the present invention. The present
invention also includes methods by which vector calculus and navigation may be
demonstrated and taught using the devices of the present invention.
The foregoing description of the preferred embodiments should be taken
2o as illustrating, rather than as limiting, the present invention as defined
by the
claims. As will be readily appreciated, numerous variations and combinations
of
the features set forth above can be utilized without departing from the
present
invention as set forth in the claims. Such variations are not regarded as a
departure from the spirit and scope of the invention, and all such
modifications
are intended to be included within the scope of the following claims.