Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
TRANSMISSION POWER CONTROL METHOD AND SYSTEM
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a cellular
communications system, and more particularly to a
transmission power control technique in a base station.
2. Description of Related Art
In code division multiple access (CDMA) systems, soft
handover is a well-known technique where a mobile station
is simultaneously t;oIiiiTiuiaii:at:iiag witti mult.'i.ple base
stations, allowing hitless conne'ction switching by making
a connection to a new base station while maintaining a
connection to an old base station. Soft handover provides
diversity, which is a method of using independent fading
signals received on several transmission paths all
carrying the same message to,improve the reliability of
the transmission.
In the case of downlink (from base station to mobile
station) soft handover, however, multiple base stations
simultaneously transmit radio signals to the mobile
station, resulting in substantial interferences at
adjacent cells. As a technique of suppressing an increase
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
_ FQ5-499 2
in interference in the case of downlink soft handover, a
downlink transmission power control method has been
proposed by Furukawa (Technical Report of Institute of
Electronics, Information and Communication Engineers,
RCS97-218, February 1998, pp.40, Second chapter). An
outline of the downlink transmission power control method
will be described with reference to Figs. 1-4.
It is assumed that a mobile station is communicating
with multiple base stations for soft handover.
Referring to Fig. 1, a downlink signal from each of
the base stations is received at an antenna and is
transferred to a down converter 102 through a duplexer 101.
The down converter 102 converts the received radio-
frequency ( rf ) signal into a baseband signal and outputs
it to a pilot signal receiver 103. The pilot signal
receiver 103 detects a pilot signal from the received
baseband signal and measures the intensity or quality
thereof. A primary base station decision section 104
compares the intensity/quality measurements of the
received signals to determine a base station transmitting
a signal having the maximum intensity/quality as a primary
base station to communicate with. A base station selection
signal generator 105 generates a base station selection
signal from the identification number of the primary base
station. A control signal generator 10Ã generates control
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 3
signals including a transmission power control signal and
outputs the control signals to a combiner 107 together with
the base station selection signal received from the base
station selection signal generator 105.. The combiner 107
combines the control signals and the base station selection
signal with an uplink information signal to produce a
transmission signal. The transmission signal is
converted to an rf transmission signal by an up converter
108. The rf transmission signal is further amplified by
an rf amplifier 109 and then transmitted as an uplink signal
to the base stations through the duplexer 101. Each of the
base stations communicating with the mobile station
receives the uplink signal including the base station
selection signal from the mobile station.
Referring to Fig. 2, at each of the base stations
connected to the mobile station, the uplink signal is
received at an antenna and is transferred to a down
converter 202 through a duplexer 201. The down converter
202 converts the received rf uplink signal to a baseband
signal and outputs it to both a transmission power control
signal demodulator 203 and a base station selection signal
demodulator 204. The transmission power control signal
demodulator 203 demodulates the transmission power control
signal from the received baseband signal and outputs it
to a transmission power controller 205. The base station
selection signal demodulator 204 demodulates the base
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 4
station selection signal from the received baseband signal
and outputs it to a primary/non-primary base station mode
controller 206.
The transmission power controller 205 produces an
interim controlled transmission power value P1 depending
on the transmission power control signal inputted from the
transmission power control signal demodulator 203 and
outputs the interim controlled transmission power value
Pl to the primary/non-primary base station mode controller
206.
The primary/non-primary base station mode
controller 206 updates the interim controlled transmission
power value Pl depending on the base station selection
signal to produce a final controlled transmission power
value P2 and output it to a transmission controller 207.
The details of the primary/non-primary base station mode
controller 206 will be described later.
The transmission controller 207 receives a downlink
transmission signal and performs the output power control
such that the transmission power of the downlink
transmission signal is set to the final controlled
transmission power value P2. The power-controlled
downlink transmission signal is converted into radio
frequency by an up converter 208. The rf downlink
transmission signal is amplified by the rf amplifi er 209
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 5
and then transmitted to the mobile station through the
duplexer 201.
Referring to Fig. 3A, a transmission signal between
the mobile station and multiple base stations has a frame
structure. A frame 8-001 consists of Fn slots to which
consecutive numbers from 0 to Fn-1 are assigned,
respectively.
As described above, the mobile station transmits the
base station selection signal for soft handover to the base
stations which it is communicating with. The base station
selection signal is composed of a strin.g of bits
identifying each of the base stations. Since a plurality
of bits are used to form, a base station selection signal,
redundancy can be provided, resulting in reduced
transmission error due to noises and/or fading.
Hereinafter, a string of 8 bits identifying each of t h e
base stations is called "a base station selection code
word ". An example will be described with reference to Fig.
3B.
As shown in Fig. 3B, assuming that a base stati n
selection code word E-002 is "00001111" , each part of the
code word E-002 is assigned to the dedicated field E-001
of a different uplink slot E-003. In other words, the base
station selection code word E-002 is divided into 8 parts
(here, each part is one bit) and the respective 8 par t s
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 6
are transmitted by the dedicated fields E-001 of different
slots E-003. Here, a period of base station selection
control E-004 is 8 slots, each of which has the desiccated
field E-001 for storing a corresponding bit of the 8-bit
base station selection code word E-002. It is possible to
accommodate two or more bits of the base station selection
code word E-002. The larger the number of bits to be
accommodated, the shorter the period of base station
selection control E-004.
In the cellular system, each base station and each
mobile station measure intensities of pilot signals and
interference signals received from adjacent cells at
regular intervals in order to use them for handover control
and call admission control. In the case where a base
station performs the measuring of pilot signals and
interference signals, the uplink transmission of each
mobile station connected to the base station is temporarily
halted to allow the precise measuring of signals from
outside cells. Further, there are some cases where the
uplink transmission of a mobile station is halted during
communication so as to suppress uplink interference in the
case of packet transmission and no-voice transmission.
Conventional BS mode update
As described before, the primary/non-primary base
station mode controller 206 in each of the base stations
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 7
updates the interim controlled transmission power value
P1 depending on the base station selection code word E-002
to produce a final controlled transmission power value P2.
The conventional base station mode control is performed
as shown in Fig. 4.
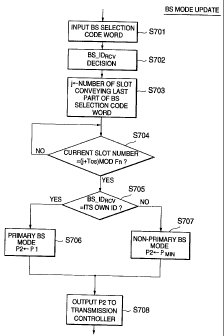
Referring to Fig. 4, the primary/non-primary base
station mode controller 206 inputs the base station
selection code word E-002 from the base station selection
signal demodulator 204 (step S401) and detects the base
station identification number BS_IDRSV from the base
station selection code word E-002 (step S402). Then, it
is determined whether the base station identification
number BS_IDRSV is identical to the identification number
ID of its own (step S403). If the base station
identification number BS_IDRSv is identical to the own
identification number ID (YES at step S403), then the final
controlled transmission power value P2 is set to the
interim controlled transmission power value P1 inputted
from the transmission power controller 205, that is, P2=P1
(primary base station mode), (step S404). If the base
station identification number BS_IDRSV is not identical to
the own identification number ID (NO at step S403), then
the final controlled transmission power value P2 is set
to a predetermined minimum transmission power value PMIN,
that is, P2= PMIN (non-primary base station mode), (step
S405). The predetermined minimum transmission power
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 8
value PMIN may be 0. The final controlled transmission
power value P2 is output to the transmission controller
207 (step S406).
In this manner, at each of the base stations
communicating with the mobile station, the transmission
power selectively switches on and off depending on the base
station selection code word E-002 received from the mobile
station. Accordingly, multiple base stations are
prevented f rom simultaneously transmitting the same signal
to a single mobile station and thereby interference to
adjacent cells is suppressed, resulting in improved
communication capacity.
1) Loss of BS selection signal
In the case where the uplink transmission of each
mobile station connected to the base station is temporarily
halted as described before, however, the base station
selection code word E-002 to be transmitted to the base
stations is punctured in part or in entirety as shown in
Fig. 3C.
More specifically, when the uplink transmission of
the mobile station is halted for an uplink transmission
puncturing period F-001 in the base station control period
E-004, the base station selection code word E-002 is
punctured in part and an incomplete code word F-002 is
received at the base stations. Such a partial or entire
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 9
loss of the base station selection code word E-002 results
in substantially reduced reliability on base station
selection control.
2) Variation in BS update timing
As described before, during the soft handover
operation, a plurality of base stations transmit the same
signal to a single mobile station. In this case, the
transmission timing of the signal is adjusted so that the
signals transmitted by the base stations arrive at the
mobile station within an acceptable time deviation. Since
propagation distances from the mobile station to the base
stations vary from base station to base station, the
respective transmission timings of the base stations are
different. On the other hand, the base stations also
receive the uplink signal from the mobile station at
different timings due to the different propagation
distances.
In the case where the respective transmission timings
of the downlink signals and the receiving timings of the
uplink signal including the base station selection signal
at the base stations are different as described above,
there are cases where actual BS mode update timings of the
base stations vary from base station to base station. The
details will be described hereinafter.
Referring to Fig. 5, a time slot is denoted by
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 10
reference symbol G-001 and each transmission signal has
a frame structure where 15 slots are numbered from 0 to
14. For simplicity, it is assumed that two base stations
1 and 2 transmit downlink transmission signals G-002 and
G-003 to the mobile station with the respective
transmission timings (propagation delays: Dl and D2)
adjusted so that the downlink transmission signals arrive
at the mobile station within an acceptable time deviation.
Accordingly, the mobile station receives the
downlink transmission signals G-002 as a downlink
reception signal G-004 from the base station 1 and, at the
approximately same time, receives the downlink
transmission signals G-003 as a downlink reception signal
G-005 from the base station 2.
The mobile station transmits an uplink transmission
signal G-006 to the base stations 1 and 2 a time period
of transmission timing offset TTR after the downlink
reception signals G-004 and G-005 have been received. As
described before, the uplink transmission signal G-006
includes the base station selection code word such that
respective parts of the base station selection code word
are conveyed in the dedicated fields as shown in Fig. 3B.
The base station 2 receives the uplink transmission
signal G-006 as an uplink reception signal G-007 with a
propagation delay time of D3 and the base station 1 receives
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 11
the uplink transmission signal G-006 as an uplink reception
signal G-008 with a propagation delay time of D4.
It is assumed that an entire base station selection
code word is received when the slot numbered 14 has been
received. In this case, the base station 2 starts the
primary/non-primary BS mode update operation as shown in
Fig. 4 when receiving the last part of the base station
selection code word stored in the dedicated field G-020
in the slot numbered 14 of the uplink reception signal G-007.
As shown in Fig. 5, the timing of receiving the last part
of the base station selection code word falls into the
subsequent slot numbered 0. Therefore, the actual
primary/non-primary mode update is performed at the
further subsequent slot G-017 numbered 1.
Similarly, the base station 1 starts the
primary/non-primary BS mode update operation as shown in
Fig. 4 when receiving the last part of the base station
selection code word stored in the dedicated field G-021
in the slot numbered 14 of the uplink reception signal G-008.
As shown in Fig. 5, the timing of receiving the last part
of the base station selection code word falls into the next
slot but one, that is numbered 1. Therefore, the actual
primary/non-primary mode update is performed at the
further next slot numbered 2.
In this manner, from the standpoint of the mobile
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
12
station, the primary base station update timing of the base
station 1 is the slot G-018 numbered 2 and that of the base
station 2 is the slot G-019 numbered 1. Since the BS
selection code word is transmitted during a period of base
station selection control, variations in BS mode update
timing may cause loss of a downlink signal. To avoid such
a signal loss, the mobile station needs an added circuit
for monitoring the BS mode update timing at all times.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
An object of the present invention is to provide a
transmission power control method and system allowing
stable and reliable signal transmission.
Another object of the present invention is to provide
a primary base station mode update method ensuring stable
and reliable operation in case of loss of a base station
selection signal.
Still another object of the present invention is to
provide a primary base station mode update method allowing
synchronization among the mode update timings of base
stations communicating with a mobile station.
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
13
According to one aspect of the present invention,
there is provided a method for controlling transmission
power of a downlink signal which is transmitted in frames
from a base station to a. mobile station depending on a base
station selection signal, wherein the mobile station selects
at least one primary base station among a plurality of base
stations which are connected to the mobile station for soft
handover to produce the base station selection signal
designating said at least one primary base station, wherein
an uplink signal including the base station selection signal
is transmitted in frames to the base stations, the method
comprising the steps of: at each of the base stations,
a) receiving the uplink signal including the base station
selection signal from the mobile station; b) determining a
transmission power update timing so that the downlink signal
received at the mobile station changes in transmission power
at a predetermined timirig synchronized with that of other
base stations; and c) when reaching the transmission power
update timing, setting the transmission power of the
downlink signal to a selected one of a normally controlled
level and a minimum level depending on the base station
selection signal, wherein each frame of the uplink signal
and the downlink signal is composed of a plurality of time
slots which are numbereci consecutively, wherein the
transmission power update timing in each of the base
stations is represented by a number of same time slot,
wherein the time slot number indicating the transmission
power update timing is determined by (j + Tos) mod Fn, where
j is number of a time slot indicating a last portion of the
base station selection signal, Tos is waiting time for
transmission power update, Fn is number of slots included in
one frame, and mod is ari operator whose result is the
remainder of a division operation.
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a device for controlling
transmission power of a downlink signal which is transmitted
in frames from a base station to a mobile station depending
on a base station selection signal, wherein the mobile
station selects at least one primary base station among a
plurality of base stations which are connected to the mobile
station for soft handover to produce the base station
selection signal designating said at least one primary base
station, wherein an uplink signal including the base station
selection signal is transmitted in frames to the base
stations, the device comprising: a receiver for receiving
the uplink signal including the base station selection
signal from the mobile station; and a controller for
controlling the transmission power of the downlink signal to
the mobile station by determining a transmission power
update tim_Lng so that the downlink signal received at the
mobile station changes in transmission power at a
predetermined timing synchronized with that of other base
stations; and when reaching the transmission power update
timing, setting the trar.Lsmission power of the downlink
signal to a selected one of a normally controlled level and
a minimum level dependirig on the base station selection
signal, wherein each frame of the uplink signal and the
downlink signal is composed of a plurality of time slots
which are numbered consecutively, wherein the transmission
power update timing in each of the base stations is
represented by a number of same time slot, wherein the time
slot number indicating the transmission power update timing
is determined by (j + Tos) mod Fn, where j is number of a
time slot indicating a last portion of the base station
selection signal, Tos is waiting time for transmission power
update, Fn is number of slots included in one frame, and
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14a
mod is an operator whose result is the remainder of a
division operation.
According to still another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a base-station selection
transmission power control method for controlling downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and the plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein the mobile station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base stations
receiving the base station identification, when the received
base station identification indicates the base station, the
base station sets its own state to a primary base station
state to normally perform the downlink transmission and,
when the received base station identification does not
indicate the base station, the base station sets the own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, wherein each of the
plurality of base stations updates its own state at a slot
number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identificat:ion is received from the mobile
station.
According to yet another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a base-station selection
transmission power control method for controlling downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14b
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and the plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein the mobile station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base stations
receiving the base station identification, when the received
base station identification does not indicate the base
station and the amount of loss of the received base station
identification does not exceed a threshold, the base station
sets its own state to a non-primary base station state to
halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise
the base station sets its own state to a primary base
station state to normally perform the downlink transmission,
and wherein each of the plurality of base stations updates
its own state at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos
is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of slots
included in a single frame), which is determined based on a
slot number j at which the base station identification is
received from the mobile station.
According to a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a base-station selection
transmissi_on power control method for controlling downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and the plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein at the mobile station and the plurality of
base stations, each frame of an uplink signal and a downlink
signal is divided on time axis into a plurality of slots
which are numbered consecutively, wherein downlink
transmission timing of each base station is adjusted so that
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14c
downlink reception timing at the mobile station synchronizes
to the downlink transmission timing, wherein the mobile
station selects one or more primary base station from the
plurality of base stations to generate the base station
identifica.tion and transmits the base station identification
to the plurality of base stations, wherein, at each of the
plurality of base stations receiving the base station
identification, when the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmissi.on, wherein each of the plurality of base stations
updates its own state at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn
(where Tos is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of
slots included in a single frame), which is determined based
on a slot number j at which the base station identification
is received from the mobile station.
According to yet a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a base-station selection
transmission power control method for controlling downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and the plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein at the mobile station and the plurality of
base stations, each frame of an uplink signal and a downlink
signal is divided on time axis into a plurality of slots
which are numbered consecutively, wherein downlink
transmission timing of each base station is adjusted so that
downlink reception timing at the mobile station synchronizes
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14d
to the dowrilink transmission timing, wherein the mobile
station selects one or more primary base station from the
plurality of base stations to generate the base station
identification and transmits the base station identification
to the plurality of base stations, wherein, at each of the
plurality of base stations receiving the base station
identification, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station and the
amount of loss of the received base station identification
does not exceed a threshold, the base station sets its own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise the base
station sets its own state to a primary base station state
to normally perform the downlink transmission, wherein each
of the plurality of base stations updates its own state at a
slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station.
According to still a further aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a base-station selection
transmission power control method for controlling downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and the plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, whe:rein the mobi:Le station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, 'wherein, at each of the plurality of base stations
receiving the base station identification, when the received
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14e
base station identification indicates the base station, the
base station sets its own state to a primary base station
state to normally perform the downlink transmission and,
when the received base station identification does not
indicate the base station, the base station sets the own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, wherein each of the
plurality of base stations updates its own state at a slot
number which is determir.ied based on a slot number at which
all of the plurality of base stations complete reception of
the base station identification from the mobile station,
thereby synchronizing update timing of the own state of each
base station, which is observed from the mobile station, in
a case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations.
According to another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a base-station selection
transmission power control method for controlling downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received f:rom the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and the plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, whe:rein the mobile station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, 'wherein, at each of the plurality of base stations
receiving the base statIon identification, when the received
base station identification does not indicate the base
station and the amount of loss of the received base station
identification does not exceed a threshold, the base station
sets its own state to a non-primary base station state to
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14f
halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise
the base station sets its own state to a primary base
station state to normal:ly perform the downlink transmission,
wherein each of the plurality of base stations updates its
own state at a slot number which is determined based on a
slot number at which all of the plurality of base stations
complete reception of the base station identification from
the mobile station, thereby synchronizing update timing of
the own state of each base station, which is observed from
the mobile station, in a case where the mobile station is at
different propagation distances away from respective ones of
the plurality of base stations.
According to yet another aspect of the present
invention, there is provided a base-station selection
transmission power cont:rol method for controlling downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and the plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein at the mobile station and the plurality of
base stations, each frame of an uplink signal and a downlink
signal is divided on time axis into a plurality of slots
which are numbered consecutively, wherein downlink
transmission timing of each base station is adjusted so that
downlink reception timing at the mobile station synchronizes
to the downlink transmission timing, wherein the mobile
station selects one or more primary base station from the
plurality of base stations to generate the base station
identification and transmits the base station identification
to the plurality of base stations, wherein, at each of the
plurality of base stations receiving the base station
identification, when the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14g
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the plurality of base stations
updates its own state at a slot number which is determined
based on a slot number at which all of the plurality of base
stations complete reception of the base station
identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchroniz_Lng update timing of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base-station
selection transmission power control method for controlling
downlink transmission from each of a plurality of base
stations to a mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein the
mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in a
soft handover state, wherein at the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations, each frame of an uplink signal
and a downlink signal is divided on time axis into a
plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively, wherein
downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14h
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station and the
amount of loss of the received base station identification
does not exceed a threshold, the base station sets its own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise the base
station sets its own state to a primary base station state
to normally perform the downlink transmission, wherein each
of the plurality of base stations updates its own state at a
slot number which is determined based on a slot number at
which all of the plurality of base stations complete
reception of the base station identification from the mobile
station, thereby synchronizing update timing of the own
state of each base station, which is observed from the
mobile station, in a case where the mobile station is at
different propagation distances away from respective ones of
the plural_Lty of base stations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein the mobil.e station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, wherein when the base station receives the base
station identification and the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14i
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, wherein the base station updates its own state
at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of
waiting slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single
frame), which is determined based on a slot number j at
which the base station identification is received from the
mobile station.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein the mobile station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, wherein when the base station receives the base
station identification which does not indicate the base
station and the amount of loss of the received base station
identification does not exceed a threshold, the base station
sets its own state to a non-primary base station state to
halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise
the base station sets the own state to a primary base
station state to normally perform the downlink transmission,
wherein the base station updates its own state at a slot
number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and :Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station.
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14j
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received fr_om the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wher_ein at the mobile station and the plurality of
base stations, each frame of an uplink signal and a downlink
signal is divided on time axis into a plurality of slots
which are numbered consecutively, wherein downlink
transmission timing of each base station is adjusted so that
downlink reception timing at the mobile station synchronizes
to the downlink transmission timing, wherein the mobile
station selects one or more primary base station from the
plurality of base stations to generate the base station
identification and transmits the base station identification
to the plurality of base stations, wherein, when the base
station receives the base station identification and the
received base station identification indicates the base
station, the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission and, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station, the base
station sets the own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, wherein
the base station updates its own state at a slot number
(j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting slots and
Fn is number of slots included in a single frame), which is
determined based on a slot number j at which the base
station identification is received from the mobile station.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14k
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein at the mobile station and the plurality of
base stations, each frame of an uplink signal and a downlink
signal is divided on time axis into a plurality of slots
which are riumbered consecutively, wherein downlink
transmission timing of each base station is adjusted so that
downlink reception timing at the mobile station synchronizes
to the downlink transmission timing, wherein the mobile
station selects one or more primary base station from the
plurality of base stations to generate the base station
identification and transmits the base station identification
to the plurality of base stations, wherein, when the base
station receives the base station identification which does
not indicat:e the base station and the amount of loss of the
received base station identification does not exceed a
threshold, the base station sets its own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, and otherwise the base station sets the own
state to a primary base station state to normally perform
the downlink transmission, wherein the base station updates
its own state at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos
is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of slots
included in a single frame), which is determined based on a
slot number j at which the base station identification is
received from the mobile station.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station dependinci on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
141
state, wherein the mobile station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, wherein when the base station receives the base
station identification and the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, wherein the base station updates its own state
at a slot number which is determined based on a slot number
at which all of the plurality of base stations complete
reception c>f the base station identification from the mobile
station, thereby synchronizing update timing of the own
state of each base station, which is observed from the
mobile station, in a case where the mobile station is at
different propagation distances away from respective ones of
the plurality of base stations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein the mobile station selects one or more
primary base station from the plurality of base stations to
generate the base station identification and transmits the
base station identification to the plurality of base
stations, vvherein when the base station receives the base
station identification which does not indicate the base
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14m
station and the amount of loss of the received base station
identification does not exceed a threshold, the base station
sets its own state to a non-primary base station state to
halt or suppress the dow7:11link transmission, and otherwise
the base station sets the own state to a primary base
station state to normally perform the downlink transmission,
wherein the, base station updates its own state at a slot
number which is determined based on a slot number at which
all of the plurality of :base stations complete reception of
the base station identification from the mobile station,
thereby synchronizing update timing of the own state of each
base station, which is observed from the mobile station, in
a case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein at the mobile station and the plurality of
base stations, each frame of an uplink signal and a downlink
signal is divided on time axis into a plurality of slots
which are numbered consecutively, wherein downlink
transmission timing of each base station is adjusted so that
downlink reception timing at the mobile station synchronizes
to the downlink transmission timing, wherein the mobile
station selects one or more primary base station from the
plurality of base stations to generate the base station
identification and transmits the base station identification
to the plurality of base stations, wherein, when the base
station receives the base station identification and the
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14n
received base station identification indicates the base
station, the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission and, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station, the base
station sets the own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, wherein
the base station updates its own state at a slot number
which is determined based on a slot number at which all of
the plurality of base stations complete reception of the
base static>n identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchronizing update timing of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a base station for
controlling downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
and a plurality of base stations are in a soft handover
state, wherein at the mobile station and the plurality of
base stations, each frame of an uplink signal and a downlink
signal is divided on time axis into a plurality of slots
which are riumbered consecutively, wherein downlink
transmission timing of each base station is adjusted so that
downlink reception timirig at the mobile station synchronizes
to the downlink transmission timing, wherein the mobile
station selects one or more primary base station from the
plurality of base static>ns to generate the base station
identification and transmits the base station identification
to the plurality of base stations, wherein, when the base
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14o
station receives the base station identification which does
not indicate the base station and the amount of loss of the
received base station identification does not exceed a
threshold, the base station sets its own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, and otherwise the base station sets the own
state to a primary base station state to normally perform
the downlirik transmission, wherein the base station updates
its own state at a slot number which is determined based on
a slot number at which all of the plurality of base stations
complete reception of the base station identification from
the mobile station, thereby synchronizing update timing of
the own state of each base station, which is observed from
the mobile station, in a case where the mobile station is at
different propagation distances away from respective ones of
the plurality of base stations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission from the base station to the mobile
station depending on a base station identification received
from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations are in a soft handover state,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14p
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the plurality of base stations
sets its own update timing of updating its own state at a
slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission from the base station to the mobile
station depending on a base station identification received
from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations are in a soft handover state,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station and the
amount of :1oss of the received base station identification
does not exceed a threshold, the base station sets its own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise the base
station sets its own state to a primary base station state
to normally perform the downlink transmission, wherein each
of the plurality of base stations sets its own update timing
of updating its own stat:e at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14q
(where Tos is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of
slots included in a single frame), which is determined based
on a slot number j at which the base station identification
is received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile
station receives the downlink signal from the primary base
station which has updated its own state at the update
timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission from each of a plurality of base
stations to the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein the
mobile station and the :plurality of base stations are in a
soft handover state, wherein at the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations, each frame of an uplink signal
and a downlink signal is divided on time axis into a
plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively, wherein
downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14r
transmission, wherein each of the plurality of base stations
sets its own update timing of updating its own state at a
slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission from each of a plurality of base
stations to the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein the
mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in a
soft handover state, wherein at the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations, each frame of an uplink signal
and a downlink signal is divided on time axis into a
plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively, wherein
downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downli:nk reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station and the
amount of loss of the received base station identification
does not exceed a threshold, the base station sets its own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14s
suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise the base
station sets its own state to a primary base station state
to normally perform the downlink transmission, wherein each
of the plurality of base stations sets its own update timing
of updating its own state at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn
(where Tos is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of
slots included in a single frame), which is determined based
on a slot number j at which the base station identification
is received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile
station receives the downlink signal from the primary base
station which has updated its own state at the update
timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission from the base station to the mobile
station depending on a base station identification received
from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations are in a soft handover state,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the base stations sets its own
update timing of updating its own state at a slot number
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14t
which is determined based on a slot number at which all of
the plurality of base stations complete reception of the
base station identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchronizing update timing of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present irivention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission from the base station to the mobile
station depending on a base station identification received
from the mobile station., wherein the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations are in a soft handover state,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station and the
amount of loss of the received base station identification
does not exceed a threshold, the base station sets its own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise the base
station sets its own state to a primary base station state
to normally perform the downlink transmission, wherein each
of the base stations sets its own update timing of updating
its own state at a slot number which is determined based on
a slot number at which all of the plurality of base stations
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14u
complete reception of the base station identification from
the mobile station, thereby synchronizing update timing of
the own state of each base station, which is observed from
the mobile station, in a case where the mobile station is at
different propagation distances away from respective ones of
the plurality of base stations, wherein the mobile station
receives the downlink signal from the primary base station
which has updated its own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission from each of a plurality of base
stations to the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein the
mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in a
soft handover state, wherein at the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations, each frame of an uplink signal
and a downlink signal is divided on time axis into a
plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively, wherein
downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14v
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the base stations sets its own
update timing of updating its own state indicative of a
primary base station or a non-primary base station at a slot
number which is determined based on a slot number at which
all of the plurality of base stations complete reception of
the base station identification from the mobile station,
thereby synchronizing update timing of the own state of each
base station, which is observed from the mobile station, in
a case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a mobile station for
causing each of a plurality of base stations to control
downlink transmission f:rom each of a plurality of base
stations to the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein the
mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in a
soft handover state, wherein at the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations, each frame of an uplink signal
and a downlink signal is divided on time axis into a
plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively, wherein
downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14w
station identification, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station and the
amount of loss of the received base station identification
does not exceed a threshold, the base station sets its own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise the base
station sets its own state to a primary base station state
to normally perform the downlink transmission, wherein each
of the base stations sets its own update timing of updating
its own state indicative of a primary base station or a non-
primary base station at a slot number which is determined
based on a slot number at which all of the plurality of base
stations complete reception of the base station
identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchronizing update tiining of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein each of the base stations
controls downlink transmission from the base station to the
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
selects one or more primary base station from the plurality
of base stations to generate the base station identification
and transmits the base station identification to the
plurality of base stations, wherein when the base station
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14x
receives the base station identification and the received
base station identification indicates the base station, the
base station sets its own state to a primary base station
state to normally perform the downlink transmission and,
when the received base station identification does not
indicate the base station, the base station sets the own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, wherein the base station
updates its own state at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn
(where Tos is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of
slots included in a single frame), which is determined based
on a slot number j at which the base station identification
is received from the mobile station.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft haridover state, wherein each of the base stations
controls downlink transmission from the base station to the
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
selects orie or more primary base station from the plurality
of base stations to generate the base station identification
and transmits the base station identification to the
plurality of base stations, wherein when the base station
receives the base station identification which does not
indicate the base station and the amount of loss of the
received base station identification does not exceed a
threshold, the base station sets its own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, and otherwise the base station sets the own
state to a primary base station state to normally perform
the downlink transmission, wherein the base station updates
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14y
its own state at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos
is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of slots
included in a single frame), which is determined based on a
slot number j at which the base station identification is
received from the mobile station.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein each of the base stations
controls downlink transmission from the base station to the
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein at the mobile
station and the plurality of base stations, each frame of an
uplink signal and a downlink signal is divided on time axis
into a plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively,
wherein downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
when the base station receives the base station
identification and the received base station identification
indicates the base station, the base station sets its own
state to a primary base station state to normally perform
the downlink transmission and, when the received base
station identification does not indicate the base station,
the base station sets the own state to a non-primary base
station state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission,
wherein the base station updates its own state at a slot
number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14z
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a p:lurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein each of the base stations
controls downlink transmission from the base station to the
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein at the mobile
station and the plurality of base stations, each frame of an
uplink signal and a downlink signal is divided on time axis
into a plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively,
wherein downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
when the base station receives the base station
identification which does not indicate the base station and
the amount of loss of the received base station
identification does not exceed a threshold, the base station
sets its own state to a non-primary base station state to
halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise
the base station sets the own state to a primary base
station state to normally perform the downlink transmission,
wherein the base station updates its own state at a slot
number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14aa
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein each of the base stations
controls downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station dependinq on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
selects one or more primary base station from the plurality
of base stations to generate the base station identification
and transmits the base station identification to the
plurality of base stations, wherein when the base station
receives the base station identification and the received
base station identification indicates the base station, the
base station sets its own state to a primary base station
state to normally perform the downlink transmission and,
when the received base Station identification does not
indicate the base station, the base station sets the own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, wherein the base station
updates its own state at a slot number which is determined
based on a slot number at which all of the plurality of base
stations complete reception of the base station
identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchronizing update timing of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations.
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14bb
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile stat:ion; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein each of the base stations
controls downlink transmission from the base station to a
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received fr_om the mobile station, wherein the mobile station
selects one or more primary base station from the plurality
of base stations to generate the base station identification
and transmits the base station identification to the
plurality of base stations, wherein when the base station
receives the base station identification which does not
indicate the base station and the amount of loss of the
received base station identification does not exceed a
threshold, the base stat.ion sets its own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, and otherwise the base station sets the own
state to a primary base station state to normally perform
the downlink transmission, wherein the base station updates
its own state at a slot number which is determined based on
a slot number at which all of the plurality of base stations
complete reception of the base station identification from
the mobile station, thereby synchronizing update timing of
the own state of each base station, which is observed from
the mobile station, in a case where the mobile station is at
different propagation distances away from respective ones of
the plurality of base st:ations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present in-vention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein each of the base stations
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14cc
controls downlink transmission from the base station to the
mobile station depending on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein at the mobile
station and the plurality of base stations, each frame of an
uplink signal and a downlink signal is divided on time axis
into a plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively,
wherein downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
when the base station receives the base station
identification and the received base station identification
indicates the base station, the base station sets its own
state to a primary base station state to normally perform
the downlink transmission and, when the received base
station identification does not indicate the base station,
the base station sets the own state to a non-primary base
station state to halt o:r suppress the downlink transmission,
wherein the base station updates its own state at a slot
number which is determined based on a slot number at which
all of the plurality of base stations complete reception of
the base station identification from the mobile station,
thereby synchronizing update timing of the own state of each
base station, which is observed from the mobile station, in
a case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14dd
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein each of the base stations
controls downlink transmission from the base station to the
mobile station dependinc{ on a base station identification
received from the mobile station, wherein at the mobile
station and the plurality of base stations, each frame of an
uplink signal and a dowrilink signal is divided on time axis
into a plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively,
wherein downlink transmi_ssion timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlirik reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identificat:ion and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
when the base station receives the base station
identification which does not indicate the base station and
the amount of loss of the received base station
identification does not exceed a threshold, the base station
sets its own state to a non-primary base station state to
halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise
the base station sets the own state to a primary base
station state to normally perform the downlink transmission,
wherein the base station updates its own state at a slot
number which is determined based on a slot number at which
all of the plurality of base stations complete reception of
the base station identification from the mobile station,
thereby synchronizing update timing of the own state of each
base station, which is observed from the mobile station, in
a case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations.
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
l4ee
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a pl.urality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of: base stations to control downlink
transmission from the base station to the mobile station
depending on a base station identification received from the
mobile station, wherein the mobile station selects one or
more prima:ry base station from the plurality of base
stations to generate the base station identification and
transmits the base station identification to the plurality
of base stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base
stations receiving the base station identification, when the
received base station identification indicates the base
station, the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission and, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station, the base
station sets the own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, wherein
each of the plurality of base stations sets its own update
timing of updating its own state at a slot number (j + Tos)
mod Fn (where Tos is nurnber of waiting slots and Fn is
number of slots included in a single frame), which is
determined based on a slot number j at which the base
station identification is received from the mobile station,
wherein the mobile stat_Lon receives the downlink signal from
the primary base station which has updated its own state at
the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a p:lurality of base stations, wherein
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14ff
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of base stations to control downlink
transmission from the base station to the mobile station
depending on a base station identification received from the
mobile station, wherein the mobile station selects one or
more primary base station from the plurality of base
stations to generate the base station identification and
transmits the base station identification to the plurality
of base stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base
stations receiving the base station identification, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station and the amount of loss of the received base
station identification does not exceed a threshold, the base
station sets its own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and
otherwise the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the plurality of base stations
sets its own update timing of updating its own state at a
slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station, wherein the mo:bile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of base stations to control downlink
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14gg
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to
the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein the
mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in a
soft handover state, wherein at the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations, each frame of an uplink signal
and a downlink signal is divided on time axis into a
plurality of slots whicrL are numbered consecutively,
wherein downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station synchronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification indicates the base station, the base station
sets its own state to a primary base station state to
normally perform the downlink transmission and, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station, the base station sets the own state to a non-
primary base station state to halt or suppress the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the plurality of base stations
sets its own update timing of updating its own state at a
slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn (where Tos is number of waiting
slots and Fn is number of slots included in a single frame),
which is determined based on a slot number j at which the
base station identification is received from the mobile
station, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14hh
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of base stations to control downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to
the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein the
mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in a
soft handover state, wherein at the mobile station and the
plurality of base stations, each frame of an uplink signal
and a downlink signal is divided on time axis into a
plurality of slots which are numbered consecutively,
wherein downlink transmission timing of each base station is
adjusted so that downlink reception timing at the mobile
station syrichronizes to the downlink transmission timing,
wherein the mobile station selects one or more primary base
station from the plurality of base stations to generate the
base station identification and transmits the base station
identification to the plurality of base stations, wherein,
at each of the plurality of base stations receiving the base
station identification, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station and the
amount of loss of the received base station identification
does not exceed a threshold, the base station sets its own
state to a non-primary base station state to halt or
suppress the downlink transmission, and otherwise the base
station sets its own state to a primary base station state
to normally perform the downlink transmission, wherein each
of the plurality of base stations sets its own update timing
of updating its own state at a slot number (j + Tos) mod Fn
(where Tos is number of waiting slots and Fn is number of
slots included in a single frame), which is determined based
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
l4ii
on a slot number j at which the base station identification
is received from the mobile station, wherein the mobile
station receives the downlink signal from the primary base
station which has updated its own state at the update
timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there: is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of base stations to control downlink
transmission from the base station to the mobile station
depending on a base station identification received from the
mobile station, wherein the mobile station selects one or
more primary base station from the plurality of base
stations to generate the base station identification and
transmits the base station identification to the plurality
of base stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base
stations receiving the base station identification, when the
received base station identification indicates the base
station, the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission and, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station, the base
station sets the own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, wherein
each of the base stations sets its own update timing of
updating its own state at a slot number which is determined
based on a slot number at which all of the plurality of base
stations complete recept:ion of the base station
identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchronizing update timing of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
l4jj
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a p:Lurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of base stations to control downlink
transmission from the base station to the mobile station
depending on a base station identification received from the
mobile station, wherein the mobile station selects one or
more primary base station from the plurality of base
stations to generate the base station identification and
transmits the base station identification to the plurality
of base stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base
stations receiving the base station identification, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station and the amount of loss of the received base
station identification does not exceed a threshold, the base
station sets its own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and
otherwise the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the base stations sets its own
update timing of updating its own state at a slot number
which is determined based on a slot number at which all of
the plurality of base stations complete reception of the
base station identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchronizing update timing of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14kk
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of base stations to control downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to
the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein at
the mobile station and the plurality of base stations, each
frame of an uplink signal and a downlink signal is divided
on time axis into a plurality of slots which are numbered
consecutively, wherein downlink transmission timing of each
base station is adjusted so that downlink reception timing
at the mobile station synchronizes to the downlink
transmission timing, wherein the mobile station selects one
or more primary base station from the plurality of base
stations to generate the base station identification and
transmits the base station identification to the plurality
of base stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base
stations receiving the base station identification, when the
received base station identification indicates the base
station, the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission and, when the received base station
identification does not indicate the base station, the base
station sets the own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, wherein
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
1411
each of the base stations sets its own update timing of
updating its own state indicative of a primary base station
or a non-primary base station at a slot number which is
determined based on a slot number at which all of the
plurality of base stations complete reception of the base
station identification from the mobile station, thereby
synchronizing update timing of the own state of each base
station, which is observed from the mobile station, in a
case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
According to still yet another aspect of the
present invention, there is provided a system comprising: a
mobile station; and a plurality of base stations, wherein
the mobile station and t:lie plurality of base stations are in
a soft handover state, wherein the mobile station causes
each of the plurality of base stations to control downlink
transmission from each of a plurality of base stations to
the mobile station depending on a base station
identification received from the mobile station, wherein at
the mobile station and t:he plurality of base stations, each
frame of an. uplink signal and a downlink signal is divided
on time axis into a plurality of slots which are numbered
consecutively, wherein downlink transmission timing of each
base station is adjusted so that downlink reception timing
at the mobile station synchronizes to the downlink
transmission timing, wherein the mobile station selects one
or more primary base station from the plurality of base
stations to generate the base station identification and
transmits the base station identification to the plurality
of base stations, wherein, at each of the plurality of base
CA 02452165 2007-06-07
75372-35D
14mm
stations receiving the base station identification, when the
received base station identification does not indicate the
base station and the amount of loss of the received base
station identification does not exceed a threshold, the base
station sets its own state to a non-primary base station
state to halt or suppress the downlink transmission, and
otherwise the base station sets its own state to a primary
base station state to normally perform the downlink
transmission, wherein each of the base stations sets its own
update timing of updating its own state indicative of a
primary base station or a non-primary base station at a slot
number which is determined based on a slot number at which
all of the plurality of base stations complete reception of
the base station identification from the mobile station,
thereby synchronizing update timing of the own state of each
base station, which is observed from the mobile station, in
a case where the mobile station is at different propagation
distances away from respective ones of the plurality of base
stations, wherein the mobile station receives the downlink
signal from the primary base station which has updated its
own state at the update timing.
The amount of loss of the base station selection
signal may be a number of erroneously received bits in the
base station selection Signal. The amount of loss of the
base station selection signal may be a ratio of a punctured
length to a length of the base station selection signal.
The threshold may vary depending on a length of the base
station selection signal. The threshold may vary depending
on the length of the base station selection signal.
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 15
Each frame of the uplink signal and the downlink
signal may be composed of a plurality of time slots which
are numbered consecutively, wherein the transmission power
update timing in each of the base stations is represented
by a number of same time slot.
The time slot number indicating the transmission
power update timing may be determined by delaying a
receiving time of the base station selection signal by an
amount of time determined so that the downlink signal
received at the mobile station changes in transmission
power at same timing.
The time slot number indicating the transmission
power update timing is preferably determined by
(j + Tos) mod Fn,
where j is number of a time slot indicating a last portion
of the base station selection signal, Tos is waiting time
for transmission power update, Fn is number of slots
included in one frame, and mod is an operator whose result
is the remainder of a division operation.
The waiting time Tos may vary depending on a
propagation delay between the base station and the mobile
station. The waiting time Tos may vary depending on the
time slot number J.
As described above, according to the present
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 16
invention, when the amount of loss of a base station
selection signal received from a mobile station exceeds
a predetermined level, the base station mode does not
reduce the transmission power of the downlink signal
regardless of whether the base station selection signal
instructs the base station itself to be the primary base
station or not. Therefore, base station selection error
due to a low-reliable base station selection signal can
be avoided. Especially, in the case where a base station
is designated as the primary base station, it is avoided
that the base station erroneously reduces or switches off
the transmission power.
Further, since the update timings of the base
stations are in synchronization with each other in the
downlink signal received at the mobile station, loss of
a downlink signal caused by loss of synchronism can be
avoided without the need of an added circuit for monitoring
the mode update timing at the mobile station.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a configuration
of a mobile station in a mobile communications system;
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 17
Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram showing a configuration
of a base station in the mobile communications system;
Fig. 3A is a diagram showing a frame format of an
uplink signal transmitted from a mobile station to a base
station;
Fig. 3B is a diagram showing the frame format of an
uplink signal for explaining a method of transmitting a
base-station selection signal;
Fig. 3C is a diagram showing the frame format of an
uplink signal for explaining an uplink transmission stop
period;
Fig. 4 is a flow chart showing a conventional method
of updating the primary/non-primary base station mode;
Fig. 5 is a time chart showing the base-station mode
update timing in the conventional method;
Fig. 6 is a flow chart showing a method of updating
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 18
the primary/non-primary base station mode according to a
first embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 7 is a flow chart showing a method of updating
the primary/non-primary base station mode according to a
second embodiment of the present invention;
Fig. 8 is a time chart showing the base-station mode
update timing according to the second embodiment; and
Fig. 9 is a flow chart showing a method of updating
the primary/non-primary base station mode according to a
third embodiment of the present invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The preferred embodiments of the present invention
will be described in detail with reference to Figs. 6-
9. Each of the embodiments will be described as a control
operation of the primary/non-primary base station mode
controller 206 at a base station, which may be implemented
by a control program running on a program-controlled
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 19
processor in the primary/non-primary base station mode
controller 206.
As described before, the primary/non-primary base
station mode controller 206 in each of the base stations
updates the interim controlled transmission power value
P1 depending on the base station selection code word E-002
to produce a final controlled transmission power value P2.
FIRST EMBODIMENT
Referring to Fig. 6, a first embodiment of the present
invention controls the transmission power taking into
consideration the amount of loss of a base station
selection signal or code word.
More specifically, the primary/non-primary base
station mode controller 206 inputs the base station
selection code word from the base station selection signal
demodulator 204 (step S601) and measures the amount of loss
of the base station selection code, word (step S602 ). The
amount of loss of the base station selection code word may
be the number of punctured bits as shown in Fig. 3C or the
ratio of the number of punctured bits to the number of all
bits of the base station selection code word. Hereafter,
the amount of loss of the base station selection code word
is denoted by Lcw-
Subsequently, it is determined whether the amount
of loss of the base station selection code word, Lcw, is
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 20
greater than a threshold LTH (step S603). The threshold
LTH may vary depending on the length of the base station
selection code word.
If LCw > LTH (YES at step S603), then it is determined
that the demodulated base station selection code word is
not sufficiently reliable and the final controlled
transmission power value P2 is set to the interim
controlled transmission power value P1 inputted from the
transmission power controller 205, that is, P2=P1 (primary
base station mode), (step S604). In other words, the
transmission power is not suppressed regardless of whether
the base station itself is the primary base station or not.
If LcW is equal to or lower than LTH (NO at step S603),
then the base station identification number BS_IDRSV is
detected from the base station selection code word (step
S605). Then, it is determined whether the base station
identification number BS_IDRSV is identical to the
identification number ID of its own (step S606).
If the base station identification number BS_IDRSV is
identical to the own identification number ID (YES at step
S606), then the final controlled transmission power value
P2 is set to the interim controlled transmission power
value P1, that is, P2=P1 (primary base station mode) , (step
S604 ). If the base station identification number BS_IDRSv
is not identical to the own identification number ID (NO
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 21
at step S606), then the final controlled transmission power
value P2 is set to a predetermined minimum transmission
power value PMZN, that is, P2= PI=N (non-primary base station
mode), (step S607). The predetermined minimum
transmission power value PM=N may be 0. The final
controlled transmission power value P2 is output to the
transmission controller 207 (step S608).
Alternatively, if the base station identification
number BS_IDRSõ is not identical to the own identification
number ID (NO at step S606), it may be further determined
whether the reception quality of the base station selection
code word satisfies a predetermined level. If the
reception quality does not satisfy the predetermined level,
then it is determined that the demodulated base station
selection code word is not sufficiently reliable, and the
final controlled transmission power value P2 may be set
to the interim controlled transmission power value P1 (step
S604).
As described above, in the case where the amount of
loss of the base station selection code word is greater
than the threshold, in other words, where the demodulated
base station selection code word is not sufficiently
reliable, the transmission power is iiot suppressed
regardless of whether the base station itself is designated
as the primary base station or not.
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 22
SECOND EMBODIMENT
Referring to Fig. 7, a second embodiment of the
present invention controls the BS mode update timing so
that synchronization among the primary/non-primary mode
update timings of base stations is achieved.
More specifically, the primary/non-primary base
station mode controller 206 inputs the base station
selection code word from the base station selection signal
demodulator 204 (step S701) and detects the base station
identification number BS_IDRSV from the base station
selection code word E-002 (step S702). Then, variable i
is set to the number of a current slot and. variable j is
set to the number of a slot conveying the last part of the
base station selection code word (step S703). Thereafter,
it is determined whether the following equation (1) is
satisfied (step S704):
i = (j + Tos) mod Fn (1),
where Tos is waiting time for mode update, Fn is the number
of slots included in one frame, and X mod Y is an operator
whose result is the remainder of a division operation (X/Y) .
In other words, the base station mode updating operation
is not performed until the current slot reaches a slot
numbered (j + Tos) mod Fn.
When the equation (1) is satisfied (YES at step S704 ),
it is determined whether the base station identification
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 23
number BS_IDRSV is identical to the identification number
ID of its own (step S705). If the base station
identification number BS_IDRSV is identical to the own
identification number ID (YES at step S705) , then the final
controlled transmission power value P2 is set to the
interim controlled transmission power value P1 inputted
from the transmission power controller 205, that is, P2=P1
(primary base station mode), (step S706). If the base
station identification number BS_IDRSV is not identical to
the own identification number ID (NO at step S705), then
the final controlled transmission power value P2 is set
to a predetermined minimum transmission power value PMir,,
that is, P2= P,N (non-primary base station mode), (step
S707). The predetermined minimum transmission power
value PMIN may be 0. The final controlled transmission
power value P2 is output to the transmission controller
207 (step S708).
Alternatively, if the base station identification
number BS_IDRSV is not identical to the own identification
number ID (NO at step S705), it may be further determined
whether the reception quality of the base station selection
code word satisfies a predetermined level. If the
reception quality does not satisfy the predetermined level,
then it is determined that the demodulated base station
selection code word is not sufficiently reliable, and the
final controlled transmission power value P2 may be set
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 24
to the interim controlled transmission power value P1 (step
S706).
Referring to Fig. 8, a time slot is denoted by
reference symbol J-001 and each transmission signal has
a frame structure where Fn (=15) slots are numbered from
0 to 14. For simplicity, it is assumed that two base
stations 1 and 2 transmit downlink transmission signals
J-002 and J-003 to the mobile station with the respective
transmission timings (propagation delays: Dl and D2)
adjusted so that the downlink transmission signals arrive
at the mobile station within an acceptable time deviation.
Accordingly, the mobile station receives the
downlink transmission signals J-002 as a downlink
reception signal J-004 from the base station 1 and at the
approximately same time, receives the downlink
transmission signals J-003 as a downlink reception signal
J-005 from the base station 2.
The mobile station transmits an uplink transmission
signal J-006 to the base stations 1 and 2 a time period
of transmission timing offset TTR after the downlink
reception signals J-004 and J-005 have been received. As
described before, the uplink transmission signal J-006
includes the base station selection code word such that
respective parts of the base station selection code word
are conveyed in the dedicated fields as shown in Fig. 3B.
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 25
The base station 2 receives the uplink transmission
signal J-006 as an uplink reception signal J-007 with a
propagation delay time of D3 and the base station 1 receives
the uplink transmission signal J-006 as an uplink reception
signal J-008 with a propagation delay time of D4.
It is assumed that an entire base station selection
code word is received when the slot numbered 14 has been
received, that is, j= 14, and the mode update waiting time
Tos is set to 3, Fn = 15. In this case, (j + Tos) mod Fn
= 2. Therefore, the base station 1 performs the actual mode
update at the slot J-017 numbered 2. Similarly, the base
station 1 also performs the actual mode update at the slot
J-017 numbered 2.
In this manner, from the standpoint of the mobile
station, the primary base station update timing of the base
station 1 is in synchronization with that of the base
station 2.
It is preferable that the waiting time Tos is as short
as possible to achieve high-speed mode switching. Since
the propagation delay and processing delay in a base
station may vary, it is possible to make the waiting time
Tos variable during communication.
Further, the waiting time Tos may be varied depending
on the number j of the slot conveying the last part of the
base station selection code word. In this case, the
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 26
primary base station mode update timing at the mobile
station can be set to a desired timing.
THIRD EMBODIMENT
Referring to Fig. 9, a third embodiment of the present
invention is a combination of the first and second
embodiments. Steps S901-S905 are the same as the steps
S701-S705 of Fig. 7, respectively. If the base station
identification number BS_IDRSV is identical to the own
identification number ID (YES at step S905), then it is
determined whether the amount of loss of the base station
selection code word, LcW, is greater than a threshold LTH
(step S906).
If Lcw > LTH (YES at step S906), then it is determined
that the demodulated base station selection code word is
not sufficiently reliable and the final controlled
transmission power value P2 is set to the interim
controlled transmission power value P1 inputted from the
transmission power controller 205, that is, P2=P1 (primary
base station mode), (step S604). In other words, the
transmission power is not suppressed regardless of whether
the base station itself is the primary base station or not.
If LcW is equal to or lower than LTF, (NO at step S906),
then the final controlled transmission power value P2 is
set to a predetermined minimum transmission power value
PMIN I that is, P2= PMIN (non-primary base station mode ) (step
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 27
S908). The final controlled transmission power value P2
is output to the transmission controller 207 (step S909).
Alternatively, if the base station identification
number PS_IDRSV is not identical to the own identification
number ID (NO at step S905), it may be further determined
whether the reception quality of the base station selection
code word satisfies a predetermined level. If the
reception quality does not satisfy the predetermined level,
then it is determined that the demodulated base station
selection code word is not sufficientlv reliable, and the
final controlled transmission power value P2 may be set
to the interim controlled transmission power value Pl (step
S907).
As described above, according to the present
invention, when the amount of loss of a. base station
selection signal received from a mobile station exceeds
a predetermined level due to an uplink puncturing operation
of the mobile station, the base station mode is set to the
primary mode regardless of whether the base station
selection signal instructs the base station itself to be
the primary base station or not. Therefore, such a
decision error that the base station is erroneously set
to the non-primary base station mode due to reception error
can be effectively eliminated, resulting in stable and
reliable quality of a downlink signal from the base station
CA 02452165 2003-12-30
FQ5-499 28
to the mobile station.
Further, since the update timings of the base
stations are in synchronization with each other in the
downlink signal received at the mobile station, loss of
a downlink signal caused by loss of synchronism can be
avoided without the need of an added circuit for monitoring
the mode update timing at the mobile station.