Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 PCT/DE01/04485
Description
Method for controlling a safety-critical railroad
operating process and device for carrying out said
method
The invention relates to a method according to the
preamble of patent claim 1, and to a device for
carrying out this method according to the preamble of
patent claim 12.
Railroad operating processes are processes which are
safety - critical because any malfunctions which happen
not to be detected in good time and whose effect on the
process is not prevented, can lead to considerable
damage to property and possibly also place people in
danger. For this reason, hitherto, devices which are
reliable in terms of signaling technology have been
used for controlling such processes, the objective of
said devices being to detect malfunctions both within
the process to be controlled and within the process
control system itself and to subsequently place the
process in a safe state, or leave it in such a state.
Such control systems which are reliable in terms of
signaling technology can be embodied in different
technologies, for example using relay technology or
electronic technology. In process control which is
reliable in terms of signal technology using computers,
hither to expensive special computers have been used
which process the waiting/queued processing orders on
two channels and continuously compare, by means of
signaling technology, processing sequences for
correspondence in terms of contents. Control
instructions which are produced are output to the
process elements of the process to be controlled only
if both processing channels have each arrived at the
same result; otherwise, the connection to the process
is interrupted, unless there
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 2 - PCT/DE01/04485
is at least one backup computer which can take over,
and actually takes over, the functions of the failed
computer.
The abovementioned functions of the reliable inputting
and outputting of data and the comparison of data with,
if appropriate, reliable shutting down of process
elements are brought about by the system software of
the reliable computers. In addition, the reliable
computers have hitherto also contained the railroad
administration-specific software for the actual process
control, for example the signaling cabin operations.
The railroad administration-specific software is
determined by the operating rules of the respective
railroad administration and it describes, for example,
the dependencies, predefined by it, of the setting and
release of the routes (Signal+Draht [Signal and Wire],
77 (1985) 12, pp. 259-265). The railroad
administration-specific software does not only differ
from railroad administration to railroad administration
but also at least partially from one piece of equipment
to another in the same railroad administration. This
means that the software which is to be loaded into a
computer which is reliable in terms of signaling
technology and runs on said computer differs from one
application case to another, it being necessary to
prove or make credible the freedom from faults of the
loaded software by means of a safety certificate for
each application case. As a result of the proliferation
of the system software and of the railroad
administration-specific software in each computer, this
leads to complex software packets which are difficult
to manage and which are time-consuming and costly to
produce and to test.
The object of the present invention is to disclose a
method for controlling a safety-critical railroad
operating process in accordance with the preamble of
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 2a - PCT/DE01/04485
patent claim 1 and whose programs, which are necessary
for the reliable
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/04?93? - 3 - PCT/DE01/04485
process control, are less costly to produce and which
makes it possible to react quickly and cost-effectively
to any changed requirements of a railroad operator with
respect to the process control system. The object of
the invention is also to disclose a device for carrying
out this method.
The invention achieves this object by means of the
features of claim 1 and/or of claim 12. The basic idea
of the invention consists in exporting the railroad
administration-specific software from the computer or
computers which are reliable in terms of signaling
technology to commercial computers which process the
data there at least twice in each case and test it
reliably for correspondence before outputting it to the
process in the computers which are reliable in terms of
signaling technology. The computers which are reliable
in terms of signaling technology have not only the
function of performing data comparison but essentially
also the function of reliably acquiring the incoming
messages and commands, and transmitting them to the
commercial computers as well as reliably acting on the
process elements and in the event of a fault
interrupting the connection to the process elements in
a way which is reliable in terms of signaling
technology.
Advantageous embodiments and developments of the method
according to the invention and the device according to
the invention are disclosed in the subclaims.
The invention is explained in more detail below with
reference to the exemplary embodiment illustrated in
the drawing, in which:
Figure 1 is a schematic view of the structure of the
device according to the invention for
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 3a - PCT/DE01/04485
controlling a safety - critical railroad operating
process and
Figure 2 shows the structure of a corresponding device
which is embodied according to the prior art.
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 4 - PCT/DEOlj04485
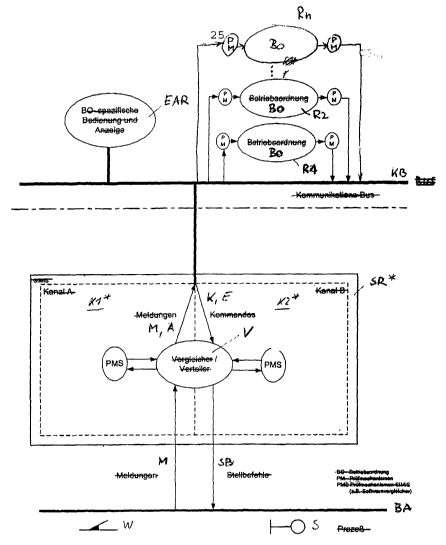
Figure 2 shows a known computer SR which is reliable in
terms of signaling technology, for executing a process
by means of preferably identical processing programs in
two independent processing channels K1, K2. The
reliable computer SR stands for any desired number of
computers which are reliable in terms of signaling
technology; their number is determined essentially by
the magnitude of the process to be controlled. The
process to be controlled is a railroad operating
process with which a railroad system BA is to be acted
on. As representatives for the process elements of the
railroad system, a railroad switch W and a signal S are
indicated in the drawing. The control and the
monitoring of the process elements is carried out by
means of control and monitoring circuits which have
been developed for that purpose, which are not
explicitly illustrated in the drawing and via which
control instructions SB are output by the reliable
computer SR to the process elements and messages M are
input into the reliable computer from said process
elements.
The computer SR which is reliable in terms of signaling
technology outputs the messages M transmitted to it by
the process to an input and display computer EAR via a
communications bus KB. Said input and display computer
EAR serves, inter alia, for monitoring the railroad
operating process according to representation rules
defined in the respective railroad operating rules; it
is preferably embodied as a computer which is process-
protected in terms of signaling technology. Using the
input and display computer EAR, the commands K for
controlling the railroad operating process are also
generated and transmitted to the computer SR which is
reliable in terms of signaling technology. The
inputting can be carried out here by an operator, for
example a stationmaster, or else by means of an
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 4a - PCT/DE01/04485
automatic system, for example for automatic points
changing or the transit mode.
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 5 - PCT/DE01/04485
The messages and commands are processed in the computer
which is reliable in terms of signaling technology, on
two channels in accordance with the conditions and
dependencies which are defined in the respective
operating rules of a railroad operator. The data,
addresses and control signals which are respectively
present on the buses of the two processing systems are
continuously compared with one another in a way which
is reliable in terms of signaling technology in order
to be able to detect immediately any discrepancies.
Test programs ensure that the input/output register of
the reliable computer and its program memories and main
memories as well as its address registers are checked
within predefined minimum time periods to determine
whether their memories can assume either the one state
or the other. Any malfunctions are thus detected in an
event-controlled or time-controlled fashion and lead to
the external equipment being reliably shut down:
control instructions to railroad switches can then no
longer be output and the signals go to the Stop
setting.
By virtue of the fact that the conditions and
dependencies which are predefined by the respective
operating rules of a railroad administration and are
represented in the drawing by elliptical place markers
B0, are stored in the program memories of the reliable
computer SR and mixed up with the system software, the
software which is stored in the reliable computers in
order to control the railroad operating process is
individual software which is very complex and
extraordinarily costly both to produce and test.
In the device according to the invention (illustrated
in Figure 1) for controlling a railroad operating
process there is also at least one computer SR* which
is reliable in terms of signaling technology and has
two processing channels Kl* and K2* which are preferably
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 5a - PCT/DE01/04485
both structured and operated identically. The function
of said computer SR* is,
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 6 - PCT/DE01/04485
similarly to the conventional computer SR which is
reliable in terms of signaling technology, to reliably
acquire, and feed to the processing means, all the
messages M and commands K which are fed to it. In
addition, its function is to output control
instructions SB, produced reliably in terms of
signaling technology, to the process elements W, S of
the respective railroad equipment BA and to ensure that
the outputting of such control instructions is
prohibited, in a way which is reliable in terms of
signaling technology, in the event of a fault. The
processing of the conditions and dependencies, defined
by the respective railroad operating rules BO, for
controlling and monitoring the railroad operating
process does not take place, in contrast to the prior
art, in the computer or computers SR* which is/are
reliable in terms of signaling technology but rather in
commercial computers R1, R2, ... Rn in which the
equipment-specific data for controlling the railroad
operating process is also stored; the computers R1, R2
are representative of one or more computer pairs, each
computer also being able to belong to more than one
pair; three computer pairs can therefore be formed from
three computers. They each carry out processing orders
A fed to them by the reliable computer SR*
independently of the respective other computer in
accordance with the conditions and dependencies defined
for the process control in the respective railroad
operating rules BO. The two computers of each
commercial computer pair R1, R2 transmit their working
results to the computer SR* which is reliable in terms
of signaling technology, the chronologically first
computer R1 or R2 bringing about a waiting point with
time monitoring, at which point the system waits for
the working result of the other computer or computers,
or in the event of the time being exceeded a fault
procedure is carried out. Test mechanisms PM for the
plausibility of the messages fed to the commercial
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 6a - PCT/DE01/04485
computer pairs Rl, R2, and of the signatures of the
outputs and memory areas produced by them are indicated
schematically in Figure 1. The commands K which are fed
to the reliable computer SR* via the input and display
computer
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 7 - PCT/DE01/04485
EAR are converted by said computer SR* into processing
orders A and transferred to the commercial computers
R1, R2 in the form of telegrams; they bring about the
processing therein in accordance with the conditions
and dependencies of the respective railroad operating
rules B0.
Tn the event of program points which provide for the
programs to be further processed only after a
predefined waiting time being reached by the commercial
computers during the processing of the railroad
administration-specific software by said computers, the
computer which is reliable in terms of signaling
technology ensures, in response to a corresponding
request by the commercial computers, synchronization of
the processing programs of the commercial computers for
further processing of the programs after the expiry of
the waiting time. For example, after the expiry of a
waiting time of several seconds a sensor message which
is determined by the commercial computers will be read
in and evaluated.
The processing results E which are determined by the
commercial computer pair R1, R2 are fed as telegrams to
the computer SR* which is reliable in terms of
signaling technology, distributed there between the two
processing channels K1*, K2* in a way which is reliable
in terms of signaling technology and compared for
correspondence in a way which is reliable in terms of
signaling technology. The function block V represents
in the drawing the reliable distribution of messages
and the reliable comparison of the results produced by
the commercial computers R1, R2, the programs which
relate to the above being stored as system software in
said function block V. The test mechanisms PMS of the
computer which is reliable in terms of signaling
technology are embodied in a way which is reliable in
terms of signaling technology, in contrast to the test
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 7a - PCT/DE01/04485
mechanisms PM of the commercial computers R1, R2.
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 8 - PCT/DE01/04485
The particular advantage of the device according to the
invention in comparison with a corresponding device
embodied according to the prior art is that only the
functions of the reliable inputting and outputting and
of the reliable data comparison are to be implemented
in the computer which is reliable in terms of signaling
technology, and this is done independently of the
requirements and conditions respectively defined by the
operating rules of the individual railroad
administrations. In this way, not only is the system
software which runs in the reliable computer or
reliable computers simple and easy to manage but it is
also the same for all application cases, that is to say
no longer has to be produced newly from case to case
and subjected to approval testing. The railroad
administration-specific software which is determined by
the different operating rules of the individual
railroad administrations runs in the commercial
computers. Its interaction with the system software of
the reliable computers does not need to be tested.
Instead, all that is necessary is to comply with the
specified interface between the computer which is
reliable in terms of signaling technology and the
commercial computer and to test the functionality of
the actual railroad administration-specific software
which is to be implemented in the commercial computers,
i.e. to test whether certain inputs actually lead to
certain outputs. This functionality testing takes place
separately from the testing of the system software and
is, in contrast to the prior art, no longer integrated
into the system software of the reliable computers,
which is itself also easier to manage than in the prior
art.
The production of the railroad administration-specific
software does not necessarily have to take place at the
manufacturer of the computers which are reliable in
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 8a - PCT/DE01/04485
terms of signaling technology, who is responsible for
the safety of the processing events in terms of
signaling technology. Instead, it is possible to
allocate orders for the production of the programs for
the
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 9 - PCT/DE01/04485
commercial computers to qualified engineering offices
or the like which have to reconcile the software
produced by them with the respective railroad
administration and, for example, an approval authority
such as the Eisenbahnbundesamt (German Federal Railroad
Office). This makes it possible to adapt the programs
for controlling and monitoring a safety - critical
railroad operating process to the respective conditions
very much more quickly and economically than hitherto
without having to make any compromises in terms of
safety as a result.
In the exemplary embodiment illustrated above, the
commercial computers Rl, R2 stand for one or more
double computer systems or computer systems provided
with redundant computers in whose individual computers
in each case identical programs for processing the
conditions and dependencies predefined by the
respective railroad operating rules are to run, in
which case preferably either only specific sub-
functions of the operating rules are to be implemented
in each case by the individual commercial computers or
else only specific parts of the railroad equipment are
to be acted on in each case. However, the arrangement
can also be configured such that the commercial
computers R1, R2 are each individual computers in which
the programs, determined by the operating rules of a
railroad administration, of the railroad
administration-specific software are processed
repeatedly, and at least twice in succession,
independently of one another. The railroad
administration-specific software which is necessary for
this can be configured in different ways or else can be
identical in terms of contents for both processing
procedures.
For the transmission of the results produced by the
commercial computers to the computer or computers which
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 9a - PCT/DE01/04485
is/are reliable in terms of signaling technology, a
data transmission which is preferably not reliable in
terms of signaling technology
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 10 - PCT/DE01/04485
is preferably used, during which transmission either
the results which are produced on two channels either
serially or in parallel are transmitted to the reliable
computer or computers on two channels, or else said
results are transmitted twice in succession over just
one channel. A second or third redundant channel
increases the availability. Any data falsifications on
the transmission path from the commercial computers to
the computers which are reliable in terms of signaling
technology, and vice versa, can be detected in the
receiving computer by a signature which is entered by
the dispatching computer and which encodes the telegram
contents by means of a computing rule. During the
serial transmission of data to the reliable computers,
the data is provided with identifiers which make it
possible for the computers which are reliable in terms
of signaling technology to detect whether the
transmitted data is current and actually originates
from different computer channels of the commercial
computers and/or whether it is the result is of
different processing procedures; during the
transmission of data over separate buses, the computers
which are reliable in terms of signaling technology can
detect, from the data transmitted to them via one bus
or the other, whether or not this data also actually
originates from the one computer or the other of a
commercial computer pair.
In an advantageous embodiment of the invention, the
commercial computer or computers can be embodied as
what are referred to as operating console computers, by
means of which the commands from a railroad employee or
from an automatic system can be output for execution to
the railroad operating process and the acknowledgements
of the railroad operating process can be displayed. In
the operating console computers, the programs for
inputting and displaying commands and messages and the
programs via which the process elements are controlled
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - l0a - PCT/DE01/04485
in accordance with the railroad operating rules then
run independently of one another. The programs for the
CA 02467972 2004-05-20
WO 03/047937 - 11 - PCT/DE01/04485
inputting of commands and the displaying of the process
events can also be combined with the programs for
process control, such as are respectively predefined by
the railroad operating rules.
The computer or computers which are reliable in terms
of signaling technology can also be embodied as an m of
n computer system in which the decision as to whether
control instructions, and if so which control
instructions, are to be output to the process can be
taken by majority decision by at least two intact
computers.
The outputting of the control instructions to the
process takes place on two channels; each computer has
the possibility of preventing the outputting of control
instructions when processing errors are detected.
The method according to the invention and the device
according to the invention can be used advantageously
for all safety - critical railroad operating processes.
Such an application can be, for example, the reliable
control of a railroad operation by a signal cabin or
else also, for example, the reliable control of a
railroad crossing, of an axle counting system or of
track-mounted and vehicle-mounted equipment of a
continuous automatic train control system (LZB).