Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
-1-
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
PROPELLANT EXTRUSION DIE
BAC~CGROUND OF THE TNVENTION
I. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates generally to the field
of propellant charges, particularly propellant charges
suited to be used in large or medium caliber projectile
ammunition which are made up of extruded perforated
stick-type propellant grains. More particularly, the
present invention relates to a propellant extrusion die
design that incorporates an array of perforation-forming
pins but that eliminates the need for a pin plate and
enables straight through propellant extrusion thereby
substantially eliminating flexing of the die pins. This
further enhances uniformity in perforation patterns
associated with extruded perforated stick-type propellant
shapes extruded through the die and the enhanced
uniformity reduces the amount of unburned propellant
slivers resulting at burnout. In addition, in accordance
with the present invention, dies can be manufactured with
pins of any desired cross sectional configuration and
thus they can procluce any desired perforation shapes in
the propellant stick grains. Certain shapes have been
found to significantly reduce propellant slivers
associated with multi-perf propellant burns.
II. Related Art
The success of all ammunition rounds depends greatly
upon the performance and reproducibility of the
performance of the associated propellant system. In this
regard, those skilled in the art have long sought to
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
-2-
control the mass rate of gas generation with predictable
progressive burns. Control of the burn has been enhanced
for certain types of munitions by the use of perforated
extruded stick propellant shapes packed into the munition
cartridge to be fired.
Almost all extruded gun propellants have
perforations parallel to the lengthwise dimension of the
extruded stick grains to provide ballistic progressivity
as the propellant burns. Depending on size and
IO application, stick propellants are normally processed
with 1, 7, 19 or even 37 or more perforations (perfs) to
enhance progressivity. Controlled progressivity is vital
to the performance required by modern gun systems.
Stick propellant is extruded through extrusion tools
IS in the form of extrusion dies which are designed to
produce an extrudate having the desired shape including
the internal voids associated with the perforations. The
physical shape, of course, is determined by the
requirements of the gun ammunition system. Extrusion
20 dies of the class described are provided with die pins
that are used to impart the perforations in the finished
propellant grains. Typically, 7 perf gun propellant
grains, for example, are provided with one central
perforation and a single row radial hexagonal pattern of
25 6 perforations surrounding the central perforation.
Other patterns including 19 perforations (a pattern of l.,
6, 12 perfs) and even 37 (a pattern of 1, 6, 12, 18
perfs) or more perforations are used in certain
propellant designs.
30 Particular limitations regarding the production of
stick-type propellant grains have resulted from
limitations associated with the extruding dies
themselves. Figures 1(a) and 1(b) depict top and cross
sectional views of a typical 2-piece prior art extrusion
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
-3-
die, generally at ~.0, which includes a die body 12 which
may be heat treated tool or stainless steel and a pin
plate 14 of the same material which nests in the die body
at the entrance to the die when it is assembled in place.
An orienting pin for the pin plate and matching recess in
the die body are shown at 15. The pin plate is provided
with an array of inlet passages 16 through which
propellant must be forced at high pressure (usually >
5000 psi) to be admitted to the die from a supply of
propellant to be extruded upstream of the die. An array
of 7 pins is shown at 18 forming a regular hexagon
surrounding a central pin. The pins themselves
designated as 20 are fixed to the pin plate as by being
press fit into the plate in openings at 22, the remainder
of the pin 20 being free and extending the length of the
die body 12. The die body 12 is rather wide at the top
or entrance to accommodate the pin plate and must be
provided with a transitional zone as at 24 which tapers
down to the size of the actual extrusion or agate area 26
which defines the cross sectional size of the stick.
Propellant entering the transitional zone 24 through
the openings or passages 16, as can be seen from the
drawings, is forced at high pressure to approach and
converge on the pin array 18 and thus the die pins 20
from the outside at an angle that approaches
perpendicular to the die pins 20. In the transitional
zone 24, the propellant flows nearly perpendicular to the
die pins 20 and this causes flexing of the die pins.
Prior die designs which processed a specific propellant
formulation and web size could make some allowances for
the predicted pin flexure. However, process variation
such as propellant solvent content (rheology),
temperature, extrusion rate, etc. cause unpredictable
variations in forces impinging the pins and, thus,
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
changes in the pin flexure.
Variation in propellant die pin flexure has been
ultimately manifested in variation of key physical
dimensions such as web size and web difference
(difference between inner and outer web thicknesses which
are designed to be equal) in the perforated stick grains.
While modifications have been made to the dies in an
effort to reduce pin stress such as rounding the
transition zone and utilizing fewer, larger openings in
the pin plate, they have only met with partial successes
and there remains a long-felt need to improve perforated
stick grain propellant extrusion dies.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In accordance with the present invention, there is
provided a new extrusion die design that solves many
problems enumerated above by allowing for secure
placement of the die pins without a pin plate. The
result is a straight-through die design that eliminates
the disadvantages of using a pin plate and reduces
inconsistencies in extruded propellant caused by pin
flexure.
The present invention provides an extrusion die for
use in producing perforated stick-type propellant which
includes a die body having a central passage extending
through the body, the passage having an open tapered
entry cavity and an open lattice webbing structure within
the body of the die spanning the central die passage.
The strut members of the open lattice webbing structure
extend parallel to the central die passage and divide but
provide very little obstruction to the passage of
material being extruded. An array of die pins for
imparting perforations in material forced through the
central passage includes pins each having a fixed end
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
-5-
fixed to the lattice structure and a free end extending
parallel to the passage beyond the lattice structure such
that the material being extruded flows parallel to and
around the pins.
The die of the invention may be formed as unitary
structures from a die blank utilizing both conventional
machining and electron discharge machining (EDM)
techniques. Thus, after the outside of the blank is
machined and holes are drilled in the blank corresponding
to openings in the lattice structure, EDM may be used to
cut out the lattice web, together with the desired array
of pins with great accuracy. The pins may be formed at
the time the open lattice web is machined, or they may be
separately fabricated and attached as by press fitting
into recesses provided in the open lattice webbing
itself. If separate pins are to be inserted, a slightly
thicker webbing is used.
The preferred material of construction for the
extrusion die of the invention is precipitation hardened
stainless steel, possibly 15-5 PH or 17-4 PH stainless
steel. Separately manufactured pins may be constructed
of hardened tool steel. The die passage surrounding the
vicinity of the pins preferably may be slightly tapered
in accordance with reforming the propellant stick after
it becomes segmented when it encompasses the open lattice
web structure.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In the drawings, wherein like reference characters
depict like parts throughout the same:
Figure 1(a) is a top view of a prior art propellant
extrusion die showing the top of the die pin and
indicating the central pin pattern;
Figure 1(b) is an elevational view partially in
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
-6-
section of the extrusion die of Figure 1(a);
Figure 2 is a top view of an extrusion die
fabricated in accordance with the present invention;
Figure 3 is an elevational view partially in section
of the extrusion die of Figure 2, taken along lines 3--3
of Figure 2;
Figure 4 is an elevational sectional view taken
substantially along lines 4--4 of Figure 2;
Figure 5 is a greatly enlarged view showing one pin
detail of an extrusion die fabricated in accordance with
the invention;
Figure 6 is a greatly enlarged top perspective view
of the die constructed in accordance with the invention;
and
Figure 7 is a greatly enlarged bottom perspective
view of the die of Figure 6 showing the area of pins as
integral with lattice webbing struts in the area of free
length of the pins.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The extrusion die of the present invention will now
be described with respect to a specific embodiment,
however, the descriptions contained herein are intended
to present examples of embodiments of the invention and
examples of methods of making the embodiments of the
invention and are not meant to be limiting with regard to
the scope of the invention in any manner. In this
regard, an important aspect of the invention involves the
provision of a straight-through extrusion arrangement
which eliminates the need for propellant to encounter the
perforation pins from the side. By enabling extrusion
directly into the web, alI propellant motion is
substantially parallel to the pins which is beneficial
both to product quality and pin life.
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
_7_
Figures 2-4 depict one embodiment of the extrusion
die of the invention which is depicted generally by the
reference character 40. The die may be of a single piece
unitary construction and includes an upstream or die body
entry opening 44 which is generally tapered at an acute
angle narrowing down to the entry of the main body or
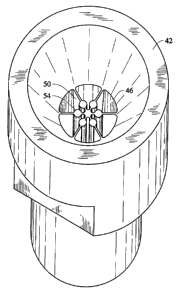
agate section of the die 46 which contains the open
lattice webbing which includes a center 48 and a series
of relatively thin radial struts connecting the center
with the inner wall of the die as at 50 which form the
open lattice webbing structure through which the extruded
propellant passes during the extrusion process. Each of
the webbing struts 50 includes an enlarged, .raised shaped
area as at 52 (see also Figures 6 and 7) that is in the
shape of and at the radial location of a perforation pin
54. The pins 54 preferentially end a short distance
before the end of the die to prevent pin damage. A minor
recess may be machined into the bottom of the die as at
56, if desired.
Figure 5 shows a greatly enlarged alternate pin
detail in which a circular hexagonal array of
substantially trapezoidal shaped pins 70 are machined as
integral extensions of the lattice webbing struts 50 and
the center pin 72 is a round press fit, separately
manufactured pin. Note that the inner and outer bases of
the trapezoidal pin are indicated by and are co-incident
with concentric circles 74 and 76, at least the outer,
longer base of each trapezoid being of an arcuate shape
to coincide with the round outer dimension of propellant
extruded through the subject die.
The trapezoid is one non-round shape that has been
used to greatly enhance burn progressivity (by
elimination of slivers) in certain propellant sticks.
Figures 6 and 7 show greatly enlarged top and bottom
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
_g_
perspective views of an embodiment of the invention which
utilizes 7 round pins to create a 7-perf extruded stick.
Figure 7, particularly, depicts the free ends of the pins
extending beyond the open lattice webbing struts 50. As
can be seen from the figures, and particularly, Figure 4,
the area of the open lattice webbing between its
beginning at 58 and ending at 60 is tapered. The taper
is normally between about 9° and 11°, but may be varied as
desired. The taper slightly constricts the propellant
that has been segmented in moving past the struts 50 of
the open lattice webbing of the die so that it more
readily re-forms a single stick in the lower or exit die
area 62. The area 62, of course, is in the area of the
free length of the pins 54. It should be noted that very
little movement of the propellant is required in the
direction perpendicular to the pins during the extrusion
process.
The dies 40 can be made from a single piece of
stainless steel first machined using conventional
machining techniques where possible to achieve the
desired outer surface and inner entry taper, and if
desired, an outlet recess. In the case of a 7-perf
system, 6 holes are then drilled in the blank
corresponding to the void areas between the webbing
struts and an EDM device using a wire cutout system is
utilized to make the web and, if,desired, the pins so
that the entire device is integral with the original
blank. This technique allows highly accurate web and pin
structures to be produced. As indicated before, the
material of the die blank is preferably heat treated
stainless steel as it must be a material which is
corrosive resistant when exposed to various propellant
compositions, caustic cleanout material and other
materials associated with processing the propellant. Such
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
-9-
techniques are known and can create webs or pins of any
desired shape or thickness.
While this -Technique has been found quite
successful, the applicants contemplate that other hybrid
techniques might also be employed. For example, the
center pin is typically manufactured separately and press
fit into a central tapered opening as shown at 64 in
Figure 4. In addition, the radially distributed pins of
any desired shape may be fabricated separately and added
to the web after other machining is completed. This
requires slightly enlarged shaped areas for receiving
pins as at 52 to be created on the struts of the web and
press fit or other techniques employed to implant the
pins such as that described for the center pin.
The straight-through extrusion die enables great
improvements to be achieved in geometric stability of the
pin pattern. Using the techniques of the present
invention, pin flexure associated with the extrusion
process has been reduced by 75-80o from conventional
dies. Variations in the web thickness of propellant
extruded through the dies have been greatly improved
(reduced), i.e., from about 7.Oo, which has been commonly
encountered with prior dies, to 40 or less utilizing the
dies of the present invention. The dies of the present
invention may achieve a web uniformity variance as little
as 2-3o in some cases. In addition, in. recent extrusion
tests, dies in accordance with the present invention have
experienced a first pass yield of 900 or greater of
usable material versus no more than 80o with prior
conventional dies.
This invention has been described herein in
considerable detail in order to comply with the patent
statutes and to provide those skilled in the art with the
information needed to apply the novel principles and to
CA 02471095 2004-07-08
-10-
construct new such specialized comb>onents as are
required. However, it is to be understood that the
invention can be carried out by specifically different
devices and that the various modifications, both as to
the equivalent details and operating pracedures can be
accomplished without departing from the scope of the
invention itself.