Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
- 1 -
Method and device for language comprehension
The present invention relates to methods and devices
for comprehension of a language, particularly a modern
language other than the mother tongue and, in
particular, in order to.learn it.
It is already known how to understand a foreign
language by listening to statements recorded on disks
or on cassettes and by following their notation printed
in this language and also their translation into the
mother tongue in a booklet- When the listener pauses,
he finds it very difficult to relocate the statement in
the foreign language where he paused, as he has poor
mastery of the foreign language he wishes to learn. As
the listener necessarily has to pause-, the statements
he hears, and the notations he reads in the booklet,
are subdivided into lessons. Between the lessons, the
listener hears statements in the mother tongue enabling
him easily to recognize the point in the booklet where
he has to restart listening. These statements in the
mother tongue are in themselves useless for the
purposes of understanding the foreign language and take
up space in the statement-emitting device and also in
the booklet. Actual understanding of the language is
made difficult because the listener has to pay
attention not only to the sounds he is hearing and to
the notations he is seeing, but also to making a
connection between them, since the phonemes and the
notations are made to correspond by means of their
order of succession. The mental effort required for
this connection is to the detriment of the level of
attention required to understand the-language.
An attempt was made to solve this problem in German
patent application 4 013 070 by causing words to be
heard, for example in English, and by simultaneously
displaying both these English words and their
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
2 -
translation into German, simultaneity being marked, for
example, by the fact that the word just displayed and
its translation appear in bold.
The invention relates to a method and a device that
facilitate comprehension of the language, relieving the
listener not only of any effort of sequencing that is
not strictly necessary for the purpose pursued, but
also of a simultaneous-comprehension effort.
The subject of the invention is therefore a method for
enabling- a source language to be understood by a
listener mastering a target language, in which the
listener is played a statement consisting of a
succession of several contents, in the source language,
and is shown, simultaneously with listening to the
statement, a succession of notations marking the
succession of contents in the source language, showing
a notation marking a content only from the moment when
it is made possible for it to be heard, and a sequence
of inscriptions is shown in the target language
corresponding to the meaning of the entire statement,
characterized in that the entire series of inscriptions
is shown before the beginning of the statement.
By showing the inscription, prior to the start of the
statement, the listener is relieved of the
comprehension effort to be made at the same time as the
listening and notation-following effort. Experience
shows-that the mind takes precedence over the ear, and
that the listener will not truly pay attention to the
sound unless his mind is not taken up with seeking the
meaning at the time of hearing.
According to a highly preferred embodiment, for good
comprehension of the language, the contents are all
phonemes. Unlike the German document mentioned above,
words without phonic relevance are no longer displayed,
but notations corresponding to the phonemes themselves
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
- 3 -
are. One word in the source language, such as
"understand", will correspond to three distinct,
successive phonemes, such as "un" "der" "stand".
Simultaneity of listening to the phoneme and the
notation appearing now enables them to be associated
without effort and automatically.
In particular, it is possible to show the notation at
the same time as the corresponding phoneme is uttered
or to show it before the following phoneme is uttered.
Preferably, the notation marking the phoneme is shown
up until the moment when the statement is finished. The
listener does not have to follow any reference system,
which might, in the meantime, conceal notations. On the
screen where the succession of notations is displayed,
there is discrimination between the succession of
notations that are already apparent and the remainder
2.0 of the blank line where the following notations will
appear. It is also possible to use for this purpose
bold-accentuated or color-accentuated writing, an
accompanying light beam, a mask that is removed step by
step, or another graphic distinction as they appear.
According to one embodiment, simultaneously with the
hearing of the succession of phonemes, a series of
words in the target language is shown, each word in the
series of words in the target language corresponding to
a group of phonemes in the source language, a word
being shown only from the moment when the first phoneme
in the group of phonemes in the source language
corresponding to this word is played, one group
including one or more phonemes.
Preferably, the succession of notations of the phonemes
in a first line is shown superposed over a second line
in which the series of words is shown by aligning
vertically the first character of each notation of a
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
- 4 -
group of phonemes with the first character of the word
corresponding to this group of phonemes, the vertical
superposition of the first characters of each phoneme
and word greatly lessening the attention effort the
listener has to make.
The, invention also relates to a device emitting a
statement composed of a succession of phonemes, a
screen, and means for displaying a succession of
notations on the screen, respectively marking the
phonemes in the succession of phonemes, means for
synchronizing the emitting device and the display means
so as to display the notations on the screen only as
the phonemes that they mark are emitted.
According to the invention, the display means comprise
means for placing a series of inscriptions in the form
of a series of electrical translation signals, and the
means for placing a series of inscriptions in the form
of a series of electrical translation signals are such
that the electrical translation signals appear before
the first phoneme is emitted.
According to one embodiment that is particularly simple
to implement, the emitting device comprises means for
placing the succession of phonemes in the form of a
phonetic electrical signal train, the display means
comprising means for placing the succession of
notations in the form of a script electrical signal
train, and the synchronizing means synchronizing the
phonetic electrical signals and the script electrical
signals, this synchronization being effected also in
respect of the electrical signals that a person skilled
in the art is well able to synchronize.
According to one embodiment, provision is made for
means synchronized by emitting device and display means
synchronized return synchronization means. The listener
may thus immediately listen again to a phoneme and see
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
-
its notation reappear at the same time (a word, a
sentence, a verse, a strophe and/or a paragraph).
Lastly, the invention relates to a display panel
5 including a first line of notations subdivided into
groups separated by first intervals, the first line
being superposed on a second line of a series of words
separated by second intervals, characterized in that
the first character in each group is in line with the
first character of a word, a first interval has a
length different than that of another first interval,
and a second interval has a length different than that
of another second interval. This panel may be produced
in advance and, associated with accentuation means,
revealed to the listener at the time of listening or be
produced, at the same time as listening takes place, on
a screen.
In the appended drawing, given solely by way of
example:
figure 1 is a block diagram of a. device according to
the invention; and
figure 2 illustrates the notations and words appearing
on the screen of the device.
The device according to the invention comprises a.
database 1 in which a statement composed of a
succession of phonemes in electrical form is memorized.
This database 1 is connected by a line 2 to a
loudspeaker 3 in which the phonetic electrical signals
from the database 1 are converted into sounds. The
device also comprises a database 4 memorizing a
succession of notations corresponding to the succession
of phonemes and presented in the form of a script
electrical signal train conveyed by a line 5 to a
synchronizing device 6 that conveys them via a line 7,
with interposition of a transducer 8, reconverting the
electrical signals into script signals at a screen 9 on
which the notations corresponding to the phonemes are
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
- 6 -
displayed. A line 10 connects the database 1 to the
synchronizing device 6 such that a notation
corresponding to a phoneme appears on the screen 9 only
when the phoneme is emitted by the loudspeaker 3.
The device also comprises a database 11 in which
translation electrical signals conveyed by a line 12
and, via a transducer 13, to the screen 9 are
memorized. However, unlike the signals emitted from the
database 4, which appear on the screen only as the
corresponding phonemes are heard, the inscriptions
corresponding to the translation electrical signals
appear at the same time on the screen just before the
appearance of the first phoneme of the statement.
Provision is also made for a return device 14
synchronized for the emitting device and for the
display means of the script electrical signals
controlled by a control unit 15 and arranged such that
it causes all or some of the most recent phonemes to be
reheard and deletes the corresponding notations that
appeared on the screen.
In a database 16, a series of words corresponding to a
word-by-word translation of the succession of phonemes
is memorized.. The electrical signals corresponding to
this series are conveyed by a line 17 to the
synchronizing device 6, which synchronizes them, first
character of one group of phonemes with.first character
of a word, before conveying them to the screen 9 via a
line 18 after passage via a transducer 19.
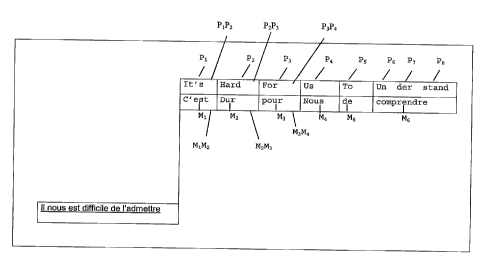
The time chart in figure 2 illustrates the invention.
The panel comprises a third line, starting from the
top, hence the lowest line, in which a formal
translation may be read, namely "It is difficult for us
to understand", all of this translation appearing
before the two other lines appear on the screen.
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
7 -
The first line, that which is the highest on the
screen, notes a succession of phonemes in the source
language, in this case English. In the case in point,
there are eight phonemes P,_ to P8. It will be noted most
S - particularly that the word "understand" in English
corresponds to the three successive, distinct phonemes
P6, P7 and P8. Each phoneme is separated from the
phoneme that follows it by an interval denoted, for the
interval separating the phoneme P1 and the phoneme P2,
"interval P1P2", for the interval separating the phoneme
P2 and the phoneme P3, "interval P2P3", etc.
In the second line, just below the first line, there is
a series of words in the target language, in this case
French, each word in the series of words corresponding
to a group of phonemes. The word M1 "c'est" corresponds
to the phoneme P1, the word M2 "dur" corresponds to the
phoneme P2, and so on for the phonemes P3, P4, P5 and
the words M3, M4 , M5, but the word M6 corresponds to the
group of three phonemes P6, P7 and P8.
The intervals between the words are denoted in the same
manner as in the first line by M1M2 for the interval
between the word M1 and the word M2, M2M3 for the
interval between the word M2 and the word M3, etc.
The first character of P1, namely I is aligned
vertically with the first character of the word M1,
namely C. The interval P1P2 is equal to the interval
M1M2. The first character H of P2 is aligned vertically
with the first character D of M2. However, as M2 has one
character less than the notation corresponding to the
phoneme P2, and as the first character of P3, namely F,
is aligned vertically with the first character P of M3,
the interval M7M3 is longer than the interval M1M2. As
the number of characters of the notation of P3 is
smaller than the number of characters of the word M3,
the notation P4 is offset to a greater extent, and P3P4
is longer than P2P3. Certain intervals between the
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
8
notations are longer than the minimum interval. Certain
intervals between the words, for example P2P3, are
longer than the minimum interval.
Alignment takes place in the following manner:
Step 1 Enumeration of the letters and/or signs
corresponding to one phoneme or to several phonemes
constituting a word in the source language.
The number of these words and/or of these signs
constitutes an "Original Value Unit, Line 1" (UVO1).
Step 2 Enumeration of the letters and/or signs
corresponding to the words of the target language
chosen to represent the "word-by-word" translation of
the corresponding words in the source language.
,The number of these words and/or of these signs
constitutes an "Original Value Unit, Line 2" (UVO2).
Step 3 Joining-up, in the form of binomials, of the
UVOls and UVO2s that correspond.
Step 4 Creation, if appropriate, of "Equivalent Value"
(VE) if UVO1 # UVO2.
In this- case: addition to the smallest value (either
UVO1 if < UVO2, or UVO2 if < UVO1) of as much blank
space as corresponds to a letter or to a sign as is
necessary to create an Equivalent Value, VE, equal to
the highest value: (either UVO1 if > UVO2, or UVO2 if
> UVO1) such that either UVO1 = VE or UVO2 = VE.
CA 02473155 2011-07-25
9 '
Illustration:
It's hard for us to understand
I I I I I_I I_I I I I I
WO( UVO1 UVOI UVO( 001 UVOI
I I I I ( I
VEI VEI VEI
C'est dur pour nous de comprendre
I I I t I I. I I II 1
UV02 UVO2 UV02 UVO2 U_V02 UV02
I I
VE2
Binomial number 1: "It's" and "C'est": UVO1 of "It's" _
4, UVO1 of "C'est" = 5, hence VE1 of value 5 replaces
UVO1.
Binomial number 2: "hard" and "dur": UVO1 of "hard"
4, UVO2 of "dur" = 3, hence VE2 of value 4 replaces
UV02.
Binomial number 3: "for" and "pour": UVO1 of "for" = 2,
UVO2 of "pour" = 4, hence VE1 of value 4 replaces UVO1.
Binomial number 4: "us" and "nous": UVO1 of "us" = 2,
UVO2 of. "nous" = 4, hence VE1 (of value 4) replaces
UVO1.
Binomial number 5: "to" and "de": UVO1 of "to" = 2,
UVO2 of "de" = 2, hence no readjustment.
Binomial number 6: "understand" and "comprendre": UVO1
of "understand" = 10, UV02 of "comprendre" = 10, hence
no readjustment.