Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
1
D-2924
COMPOSITES USEFUL AS FENCE AND DECKING
COMPONENTS AND METHODS FOR PRODUCING SAME
Background of the Invention
The present invention generally relates to composites
and more specifically relates to composites useful as fence
components, decking components and the like, and methods
for producing same.
Traditionally, fences and decks have been made of
components fashioned from solid wood. Wood fences and
decks are often considered more aesthetically appealing
than those made of metal or cement, for example, wire
fences or cement block walls or decks. However,
construction of a wood fence or a wood deck is labor
intensive. Solid wood components are heavy and cumbersome.
In addition, maintenance of a wood fence or deck is
expensive. After a period of time, solid wood fence and
deck components will naturally begin to break down from
weather exposure and pest infestations. It is known that
this deterioration can be tempered by treating the fence or
deck with widely available weather resistant coatings,
paints, varnishes, finishes and the like. Unfortunately
however, it is often only a matter of time before such
treated fences or decks deteriorate requiring partial or
complete replacement. Many solid wood materials that are
suitable for fencing or decking are costly. In addition,
because of natural variations in wood, replacement of
individual components may result in an inconsistent, uneven
appearance to the fence or deck.
Plastic fence components have been developed as
alternatives or supplements to traditional, natural wood
fences. For example, Robbins, III, U.S. Patent No.
5,100,109 describes a method of constructing a fence by
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 2
providing a flexible, plastic, rollable fence -16oar4- that
can be unrol7_ed and fastened to sp&ced apart fence posts.
The flexible fence, b.oaxd is. made Ath height and width
dimensions simulating a standard woot-jen board and with a
length of 350 feet or more. Accordin~g to this patent, the
fence board is formed in a continuous e.xtrusion process of
a flexible thermoplastic material.
Collins U.S. Patent No. 5,404, 685, de scribes a wall or
fence made .in part of foamed pol-:ystyrene plastic
1ci components, more specifically, STYROF('.)AM@ polystyrene
plasti-c columz1s and panels. Construction.of a fence in
accordance with the Collins Patent requires multl-,ple steps.
For example, vw,all or fence stability is achieved by pouring
a reinforcing fillii~r; such as concrete, into a hollow of
the polystyrene plastic coiumns after the colum:.ns have been
secured to the ground. A hardP:1ed, Outer surf'ace of the
fence is achieved by applying an exterior tinis}:1, such as
stucco or special exterior paint, to the fence or wall
after the fence has been constructed.
There -still remains a need in the market today for
inexpensive, lightweight fencing and decking components and
fence and deck systems that are sturdy, weather resistant,
lightweight, and aesthetically appealing, and easy to
manufacture using simple manufacturing techniques.
Sununary of the invention
New composites, for example, useful in fence and deck
systems and fence and decking components, such as rails,
fence posts, fence slats, decking planks and the like, as
well as methods for producing same have been discovered.
The composites are easy to manufacture in a variety of
configurations using relatively inexpensive materials. In
addition, the composites are sturdy, lightweight and have
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 3
excellent weatherability properties. In addition, the
composites have many of the desirable properties of natural
wood fences and decks. For example, the composites, in the
form of fence and deck systems or fence and decking
components, of the invention can be made to have a wood-
like look and texture. However, unlike solid wood fences
and decks, the composites of the present invention
preferably are highly resistant to effects of weathering.
In a broad aspect of the invention, a layered
composite is provided, which can be formed, for example, as
a fence component or as a decking component.
The present composites, in general, comprise an outer
layer comprising present composites a first polymeric
material; a core layer, circumscribed by the outer layer
and comprising a second polymeric material; and an inner
layer, circumscribed by the core layer and comprising a
third polymeric material, wherein the inner layer defines
a hollow space. Preferably, the composites of the present
invention are in the form of a member having a length
defined along a longitudinal axis of the member. The
hollow space preferably extends along substantially the
entire length of the member. The core layer preferably is
substantially completely circumscribed by the outer layer
along substantially the entire length of the member and/or
the inner layer preferably is substantially completely
circumscribed by the core layer along substantially the
entire length of the member. The member may have any
suitable axial cross-section, such as circular,
rectangular, oval, an irregularly shaped cross-section and
the like. In one useful embodiment, the member has a
substantially rectangular, for example, an elongated
rectangular or square, axial cross-section, that is
perpendicular to the length or longitudinal axis of the
member.
In one especially advantageous embodiment of the
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 4
invention, the composite is structured in the form of a
fence building component or a fence component, for example,
the composite may be in the form of a fence post or a fence
rail or the like. Moreover, in accordance with the present
invention, a fencing system is provided including a
plurality of fence components, for example, a plurality of
fence posts and a plurality of fence rails, wherein each of
the fence components, e.g., each of the fence posts and
fence rails, comprise a composite described herein.
In another useful embodiment, the composite is
structured in the form of a deck building component or a
decking component, for example, the composite may be in the
form of a decking plank or the like. A deck system or
decking system is provided in accordance with the present
invention including a plurality of decking components, for
example, a plurality of decking planks, wherein each of the
decking components, e.g., each of the decking planks,
comprise a composite described herein.
Each one of the first, second and third polymeric
materials of the composite layers preferably comprises a
thermal plastic polymeric material. In one embodiment of
the invention, at least two of the first, second and third
polymeric materials have different chemical compositions.
Preferably, the outer layer is made of a weatherable,
thermal plastic polymeric material. The outer layer
advantageously is substantially solid. As used herein, the
term "weatherable" refers to the ability or property of a
material to effectively withstand the conditions of an out-
of-doors environment for a long period of time, for
example, at least about five years and preferably at least
about seven years or longer. Specific examples of polymers
which can be used as the outer layer include, without
limitation, polyvinylchloride, acrylonitrile/styrene/
acrylic polymeric materials, and the like and mixtures or
combinations thereof.
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 5
Preferably, the second material comprises a solid
thermal plastic polymeric material or a thermal plastic
polymeric material foam or combinations thereof, and an
effective amount of a filler. Suitable polymeric materials
for the core layer include, without limitation,
polyvinylchloride, acrylonitrile/styrene/acrylic polymeric
materials, acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene polymeric
materials, and the like and mixtures or combinations
thereof. Any suitable filler component may be present in
any of the layers of the present composites. Such filler
component or components preferably are effective to add
bulk and/or strength and/or reinforcement and/or stability
to the layer and/or composite. Examples of useful filler
components include, without limitation, wood, mica, talc,
calcium carbonate, graphite or carbon, for example, in the
form of particles, such as fibers, and the like and
mixtures thereof. A filler component is particularly
advantageous in the core layer, while the inner layer
and/or outer layer preferably and substantially free of
filler component. Preferably, the filler component of the
core layer material comprises a wood component such as,
but not limited to, wood particles, for example, wood
shavings, wood chips, wood flour and the like and mixtures
thereof. This use of a wood component advantageously
provides a effective filler without unduly increasing the
weight or cost of the composite.
The inner layer is circumscribed by the core layer and
defines or bounds the hollow space of the composite. The
inner layer can be made of a thermal plastic material which
need not be weatherable, but preferably is effectively
impact resistant. The inner layer is preferably
substantially solid. Examples of materials that are
suitable as the third polymeric material include, without
limitation, polyvinylchloride, acrylonitrile/butadiene/
styrene polymeric materials and the like and mixtures or
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 6
combinations thereof.
Advantageously, the composites in accordance with the
invention can be produced using a single coextrusion
process using a suitable feedblock, pipehead and forming
die assembly. The methods, in accordance with the present
invention, for producing such composites comprise providing
the desired materials, in an extrudable state, for the
outer layer, the core layer and the inner layer, and
passing the materials, by means of or through, three
coextruders, into a feedblock/pipehead assembly to produce
a material form having a radially layered, annular cross-
section, for example, a substantially circular cylindrical
axial cross-section. This material form is passed through
a shaper die and is reconfigured thereby to produce or form
a hollow, layered composite having a desired cross-section,
for example, a square, elongated rectangle or other desired
cross-section shape. Composites can be formed, e.g. cut,
into different lengths and configurations to be useful as
fence components, for example, rails and posts.
Any and all features described herein and combinations
of such features are included within the scope of the
present invention provided that the features of any such
combination are not mutually inconsistent.
These and other features, aspects and advantages of
the present invention will become apparent hereinafter,
particularly when considered in conjunction with the
following claims and detailed description in which like
parts bear like reference numerals.
Brief Description of the Drawings
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of a portion of layered
composite in accordance with the present invention.
Fig. la is a cross sectional view of the layered
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 7
composite taken generally across line la-la of Fig. 1.
Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view of an apparatus
useful for producing a layered composite in accordance with
the present invention.
Figs. 3a and 3b are cross sectional views of the
apparatus taken generally lines 3a-3a and 3b-3b of Fig. 2,
respectively.
Figs 4-7 show perspective views of different cross-
section shapes of composites in accordance with the present
invention.
Fig. 8 shows a fencing system in accordance with one
embodiment of the invention.
Detailed Description
Turning now to Fig. 1, a lightweight, durable,
weatherable layered composite member in accordance with the
present invention is shown generally at 10. The composite
10 is useful as a construction element when assembled
together with other similar composite members in accordance
with the invention. For example, the composite member 10
may be used as a fence post or fence rail in a complete
fencing system or as a decking plank in a complete decking
system.
Turning now as well to Fig. la, a portion of the
composite member 10 is shown in cross sectional view. The
composite member 10 generally comprises a weatherable outer
"skin" layer 12 comprising a first polymeric material, a
core layer 14 circumscribed by the outer layer 12 and
comprising a second polymeric material, and an inner layer
16 circumscribed by the core layer and comprising a third
polymeric material. The inner layer 16 defines a hollow
space 20. Preferably, at least two of the first, second and
third polymeric materials have different chemical
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 8
compositions as will be described in detail hereinafter.
The composite member 10 has a length 19 along a
longitudinal axis 21, and the hollow space 20 extends along
substantially the entire length 19 of the member 10. As
shown in Fig. 1, the member 10 may have a rectangular cross
section perpendicular to the longitudinal axis 21, although
other cross sectional shapes are possible, depending upon
the particular application of the composite member 10. In
one particularly useful embodiment of the invention, the
composite member 10 is in the form of a fence component,
such as a rail or post for example.
Although not shown in detail, preferably the core
layer 14 is, circumscribed by the outer layer 12 along
substantially the entire length 19 of the member 10 and the
inner layer 16 is, circumscribed by the core layer 14 along
substantially the entire length 19 of the member 10.
As will be described hereinafter, the composite member
10 preferably is formed using a single coextrusion process
by introducing each of the first, second and third
polymeric materials, in extrudable form, into a different
extrusion pathway of a single extruder/feedblock/pipehead
assembly. Advantageously, the layers 12, 14, 16 of the
composite member 10 are bonded together, during the
extrusion process, and thus are held together without the
aid of glues, adhesives, bonding agents or the like. To
this extent at least, the first, second and third polymeric
materials can be said to be compatible. Put another way,
the first, second and third polymeric materials are
selected to be effectively bonded together without the need
of glues, adhesives, bonding agents and the like.
Preferably, the outer layer 12 is comprised of a
relatively thin layer of solid "weatherable" polymeric
material. Suitable weatherable materials for the outer
layer 12 include, without limitation, thermal plastic
polymeric materials, such as polyvinylchloride,
CA 02473737 2008-07-18
9
acrylonitrile/styrene/acrylic ("ASA") polymeric materials
and the like, and mixtures, combinations or alloys thereof.
The presently useful ASA polymeric materials can be made
using any suitable methodology. See, for example, Hughes
U.S. Patent 5,883,191; Yu et al U.S. Patent 3,944,631;
Aliberto et al. U.S. Patent 4,517,339; Ting U.S. Patent
4,731,414; Ting U.S. Patent 4,831,079; and Moringa et al.
U.S. Patent 4,151,226. Such ASA polymeric materials may be
physical blends or mixtures of styrene/acrylonitrile
copolymers and acrylic polymers and copolymers;
acrylonitrile/styrene/acrylic terpolymers, interpolymers
including styrene-based units, acrylonitrile-based units
and acrylic-based units, and the like and mixtures and
combinations thereof.
The core layer 14 preferably is comprised of the
second polymeric material and an effective amount of a
filler. The core layer 14 may include a wood component, in
the form of wood particles 15, in an effective amount as a
filler. The core layer 14 may comprise any suitable second
polymeric material selected from, for example, without
limitation, polyvinylchloride,
acrylonitrile/styrene/acrylic (ASA) polymeric materials,
acrylonitrile/ butadiene/styrene ("ABS") polymeric
materials, and mixtures, combinations and alloys thereof,
and a filler component, preferably a wood component, in an
amount effective as a filler in the composition. Suitable
ASA/filler compositions and methods for making such
compositions are described in Hughes, U. S. Patent No.
6,133,349.
The second polymeric material may be solid or a
polymeric foam material and is present in the core layer 14
in an amount in the range of about 15% to about 90% or
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 10
about 95% or about 99.5% of the total weight of the core
layer. The filler component preferably is present in the
core layer 14 in an amount in the range of about 0.5% or
about 50 or about 10% to about 60% or about 70% or about
85% based on total weight of the core layer.
Although the wood component may be present in any
suitable form, it is preferred that the wood be present as
wood particles, such as wood chips, wood flakes, sawdust,
wood flour, and the like and mixtures thereof. More
preferably, such particles have a size in the range of
about 40 to about 200 U.S. mesh, still more preferably,
about 50 to about 150 U.S. mesh.
More preferably, the second polymeric material making
up the core layer 14 is produced using straightforward
physical mixing or blending methods, and without one or
more complex polymerization steps being required. Control
of the make-up and physical properties of such physically
blended ASA polymeric material is more easily achieved than
with compositions involving one or more polymerizations.
Suitable physical blending methods are described in Hughes
U.S. Patent No. 5,883,191.
Although the filler component of the core layer
material preferably comprises wood particles, it is to be
appreciated that other fillers may be included as
alternatives or in addition to the wood component. For
example, the filler material may comprise carbon fibers,
organic materials or other known filler materials. Wood is
a preferred filler component because it is lightweight,
strong, readily obtainable, and relatively inexpensive.
Furthermore, in addition to the filler, the composition may
contain effective amounts of one or more additional agents,
such as pigments, processing aides, lubricants,
antioxidants and stabilizers such as ultraviolet light and
thermal stabilizers, and the like.
In one embodiment of the present invention, the core
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 11
layer 14 comprises a composition of a substantially uniform
blend of an uncrossed-linked acrylonitrile/styrene
copolymer, for example, a linear uncross-linked
acrylonitrile/styrene copolymer, an acrylate copolymer,
such as a cross-linked alkyl acrylate/graft (meth)acrylate
copolymer, and filler, for example, wood component
particles.
Very useful results are obtained with the wood
component being selected from pine wood, woods softer then
pine wood, such as fir wood and the like, and mixtures
thereof. The wood component may also include a wood which
is harder than pine wood, such as oak wood, walnut wood,
hickory wood, maple wood and the like and mixtures thereof.
One very useful combination is a wood component which
includes a first wood at least as soft as pine wood and a
second wood harder than pine wood. In this embodiment, the
first wood preferably is present as a major amount, that is
at least 50% of the total wood present, while the
relatively hard wood is present in a minor amount, that is
less than 50% of the total wood present. The wood
component may, and preferably does, act to reinforce the
present compositions.
In a particularly useful embodiment the present
invention, the wood-filled compositions forming the core
layer 14 include an increased amount of lubricant relative
to the amount of lubricant included in a similar
composition without the filler, e.g., wood. Such increased
amount of lubricant is effective in facilitating forming a
substantially uniform physical blend of the components of
the composition, particularly, since the filler, e.g.,
wood, being employed is often relatively dry and/or
relatively incompatible with the copolymer components of
the compositions. The amount of lubricant used preferably
increases as the amount of filler particles increases. The
amount of lubricant used may vary widely depending on the
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 12
specific lubricant employed. The amount of lubricant
employed may be in a range of about 0.10 or about 0.5% to
about 2% or about 5%, by weight of the total composition.
Methods for forming a wood-filled composition useful
in the present composites, comprise providing an uncross-
linked acrylonitrile/styrene copolymer; providing a cross-
linked alkyl acrylate/graft (meth)acrylate copolymer;
providing filler component particles and forming a
substantially uniform physical blend of these two
copolymers and the filler particles. This physical blend
preferably is substantially free of cross-linked
acrylonitrile/styrene copolymer.
The substantially uniform blend formed preferably
includes at least about 30% by weight, based on the total
weight of the copolymers present, of the uncross- linked
acrylonitrile/styrene copolymer and at least about 5% by
weight, based on the total weight of the copolymers
present, of the cross-linked alkyl acrylate/graft
(meth)acrylate copolymer and an amount of filler component
particles effective as a filler in the final composition.
More preferably, the uncross-linked acrylonitrile/styrene
copolymer is present in an amount in a range of about 30%
to about 95% by weight based on the total weight of the
copolymer and the cross-linked alkyl acrylate/graft
(meth) acrylate copolymer is present in an amount in a range
of about 5% to about 70o by weight based on the total
weight of the copolymers. It is preferred that, during the
forming step, substantially no polymerization occurs.
The inner layer 16, which bounds the generally
central, hollow space 20 of the composite member 10, can be
made of any suitable thermal plastic material, preferably
a solid thermal plastic material, which need not be
weatherable, but preferably is effectively impact resistant
for providing strength during fence assembly and/or use.
Examples of polymeric materials that are useful for
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 13
inclusion in the inner layer 16, include, without
limitation, polyvinylchloride, acrylonitrile/
butadiene/styrene polymeric materials, and the like and
mixtures, alloys or combinations thereof.
Referring now to Fig. 2, the composite member 10 (not
shown in Fig. 2) can be produced using co-extrusion
techniques. Useful coextrusion assemblies, for producing
a layered, extruded composite having a radially stratified
annular form are disclosed in Rosenbaum U.S. Patents Nos.
4,125,585 and 4,208,175, the disclosure of both of which
are incorporated herein in their entireties by reference.
For example, as shown schematically, a single
extruder/feedblock/pipehead assembly 40, comprising a
coextrusion feedblock 42 adapted to be fed by three
extruders 46a, 46b, 46c is shown. Each extruder 46a, 46b,
46c defines a separate extruder pathway 47a, 47b, and 47c,
respectively. Each of the compositions (i.e. the first
polymeric material, second polymeric material and third
polymeric material) is introduced into a different one of
the extruder pathways 47a, 47b, and 47c and extruded to
yield a radially layered, substantially circular
cylindrical form. This form is then reshaped to a desired
axial cross section and cut to a desired length.
More specifically, the wood-filled core layer
material, preferably along with a conventional polymeric
material blowing agent, such as sodium bicarbonate,
azodicarbonamide and the like, is fed into inlet 56a of
first extruder 46a. The outer layer material and the inner
layer material are fed into coextruder inlets 56b and 56c
respectively. The coextrusion feedblock 42 is operable to
produce a circular cylindrical form of inner layer
material, core material and outer layer material at zone
58. This cylindrical form is fed directly into an inlet 60
of a pipehead forming die 62, connected to the feedblock
42, as shown. The assembly 40 produces an annular, or
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 14
pipe-shaped form of the composite materials 12, 14, 16 at
zone 64 which is substantially free of radial and
circumferential maldistributions, as shown in cross section
in Fig. 3a.
Turning back to Fig. 2, the form is then passed
through another forming die, or shaping die, 70 connected
to the pipehead die 62, which shapes and compresses the
form to produce a composite of indefinite length having the
desired axial cross-sectional shape. See cross-sectional
view in Fig. 3b.
The shaped form extruded from the assembly 40 is then
cut to a length suitable for the desired application. In
addition, the composite may be produced to have wall or
layer thicknesses suitable for the desired application.
These thicknesses can vary widely.
For a typical application, the composite member 10
preferably has a composite wall thickness (radial
thickness) in a range of about 0.06 inches to about 1.7
inches, for example, a thickness of about 0.1 inches to
about 0.6 inches. The core layer 14 preferably has a
thickness (radical thickness) in a range of about 0.04
inches to about 0.9 inches, and the outer layer and the
inner layer each, independently, preferably has a thickness
(radical thickness) in a range of about 0.01 inches to
about 0.4 or about 0.7 inches.
For purposes of example only, various cross-sectional
shapes of layered, hollow composites in accordance with the
present invention are shown in Figs. 4-7, and a simplified
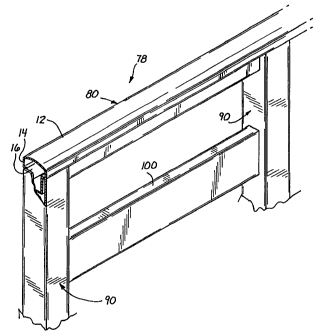
illustration of a fencing system 78 is shown in Fig. 8.
More specifically, Fig. 4 shows a rail extrusion
component 80 which can be used as an upper rail of a
fencing system 78 in accordance with the invention. As
shown, the rail extrusion component 80 includes a cross-
sectional shape, perpendicular to a longitudinal axis, that
includes a somewhat rounded, widened upper portion 82
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 15
relative to a rectangular, more narrow lower portion 84.
Fig. 5 shows a post extrusion component 90 having a square
cross-sectional shape perpendicular to a longitudinal axis
thereof, and Fig. 6 shows an alternative rail extrusion
component 100 having an elongated rectangular shape. The
components can be formed to any convenient length depending
upon the particular fencing application desired.
Fig. 7 shows a preferred decking plank component 110
having an elongated, generally rectangular shape and having
a slightly sloping upper outer surface 111, which
facilitates water run-off when the decking plank 110 is
combined with other such planks to form a generally
horizontally positioned deck. To illustrate the extent of
this sloping, the composite 110 may be about 5.5 inches
wide, from surface A to surface B. The wall thickness of
composite 110 is about 0.3 inches. The height of composite
110 at the center line 113 is about 1.0625 inches and at
surfaces A and B is about 1.00 inches. This difference
results in the sloping of upper outer surface 111. A
plurality of planks 110 can be secured together, for
example, on wooden crossbars, to form a completed deck.
In addition, the thin outer layer 12 of the composite
member and components 10, 80, 90, 100, 110 in accordance
with the invention can be painted with any suitable weather
resistant paint, finish or varnish to achieve a desired
appearance. Moreover, the wood particles in the core layer
material can be selected so as to produce a desired look
and/or texture to the finished product. It will be
appreciated that, as with other fencing components, the
composites in accordance with the present invention may
include cut-out portions, brackets, fasteners and the like
(not shown) for facilitating assembly of a complete fencing
system.
A process for manufacturing a layered composite is
also provided by the present invention. The process
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 16
generally comprises the steps of providing the materials
described hereinabove, in flowable or extrudable form, and
forming a cylindrical flow of the materials, reshaping the
cylindrical flow into a desired cross sectional shape to
achieve a composite having substantially uniform layers
surrounding a generally central hollow space, and cutting
the reshaped flow into a desired length.
For example, the forming step includes introducing the
polymer materials, which will make up the outer layer and
inner layer, and the wood-filled polymer material which
will make up the core layer, into an extruder assembly
while the materials are in an extrudable form. For
example, the outer layer and inner layer materials may be
subjected to elevated temperatures and/or pressures prior
to being introduced into the extruder assembly.
The wood-filled thermal plastic material is provided
in an extrudable form by subjecting a mixture of, for
example, acrylonitrile/styrene/acrylic polymeric material
and wood particles, to conditions effective to produce a
substantially uniform, flowable or extrudable composition.
Such conditions are described in detail in incorporated
Hughes U.S. patent No. 6,133,349, and can generally include
for example, elevated temperature conditions, elevated
pressure conditions, shear or mixing conditions and
combinations thereof. The substantially uniform
composition is then introduced in a suitable coextrusion
assembly along with the outer layer and inner layer
materials, and formed by suitable connecting shapers or
dies, into useful shapes and configurations as described
hereinabove. It is preferable that, during the forming
step, substantially no polymerization occurs. The
composite can be subjected to any post-processing steps,
such as texturing, painting and the like as may be
desirable. Advantageously, the layered composites in
accordance with the present invention do not require any
CA 02473737 2004-07-16
WO 03/061951 PCT/US02/01477
D-2924 17
mechanical means to secure the layers together. The co-
extrusion process described hereinabove causes the layers
to bond together without the aid of adhesives, glue,
bonding agents or the like.
Multiple composites, such as various fence post and
fence rail configurations, in accordance with the
invention, may be packaged together and sold as a fencing
system kit.
While this invention has been described with respect
to various specific examples and embodiments, it is to be
understood that the invention is not limited thereto and
that it can be variously practiced within the scope of the
following claims.