Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
Apparatus for Determining the Distance between Pupils
BACKGROUND OF THE iN~/ENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The invention relates to an apparatus as a component of a video
centering system for determining the distance between pupils for precisely
defining parameters relevant to the grinding of lenses to be mounted in the
sockets of spectacles or eyeglasses.
2. The Prior Art
!t is generally known that video systems are utilized for determining
parameters relevant to grinding lenses of spectacles which are based upon
producing a video photograph of a patient who is wearing the adjusted or
fitted
frame of his spectacles .
Thus, German patent specification DE 43 23 384 C2 describes a device
for measuring the parameters requisite for conforming optical lenses to the
frame
of spectacles, particularly the distance between the pupils and the height of
a
person's pupils relative to the spectacle frame. The device is provided with a
camera for taking a photograph of the head of the person wearing the spectacle
frame and for adjustment with respect to the head. Furthermore, the device is
provided with an electronic imaging unit for defining the parameters from the
photograph of the head at a predetermined measured distance between the
head and the camera. Within the camera, there is provided a coincidence range
Attorney Docket 040850-US -1-
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
finder with an optical system behind the objective of the camera for
separating
the photograph into four adjacent images or partial images such that the
correct
measuring distance is obtained if the images or partial images join into a
single
image.
This device in essence consists of a camera to be aimed by its operator
against a customer or patient with a follow-up optical system for determining
the
predetermined measured distance on the basis of a coincident distance
measurement. Such an arrangement suffers from two disadvantages, however:
It involves significant technical complexity to be made, and its manner of
operation is such that measurement errors cannot be excluded.
German patent specification DE 100 20 050 A1 discloses an apparatus
for, and a method of, defining the centering data for mounting lenses into
spectacle frames. It utilizes a camera and a centering rider with a light
source
which compels a patient to Rook into a previously determined direction.
Measurement data are read from a previously established centering foil, and
the
preferred light source is a laser pointer.
Another arrangement by which measuring the distance between the pupils
of a human eye may be carried out digitally, is disclosed by German patent
specification DE 100 05 801 A1. It proposes an examination frame for
measuring the distance between the pupils of the patient's eyes. The
examination frame consists of a lens support, a device for moving the lens
support along the frame in the direction of the patient's nose or temple. In
addition, the examination frame is provided with a source of electrical
current
and metal strips through which the current is flowing. By rotating the lens
supports, the level of current flowing through the metal conductor is
measured,
and the distance between the pupils of the eyes of a given patient may be
deduced from the measured current.
Attorney Docket 040650-US
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
Such an arrangement may be said to suffer from the drawback that for the
necessary corrective calculations, in particular the convergence or inward
rotation of the eyes at a short viewing distance, it relies upon a shooting
distance
between the patient and the recording camera stored in the given systems data.
In the event, the corrective calculations can be correct only to the extent
that the
stored values of shooting distances are adhered to during the exposures.
OBJECTS OF THE INVENTION
It is thus an object of the invention to provide an apparatus which serves
as a component of a video centering system for determining the distance
between the pupils for the exact or precise definition of parameters relevant
to
the grinding or fitting of lenses into spectacle frames and which
substantially
avoids the disadvantages of the prior art arrangements.
BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In the accomplishment of these and other objects, the invention provides
for an apparatus of the kind referred to for determining the distance between
the
pupils for exactly defining parameters relevant to the proper alignment of
optical
lenses to be mounted in the sockets of a spectacle frame, the apparatus being
an integral component of a video centering system provided with a camera, a
zooming device, a computer including monitor, and a calibrating device, in
which
the size of a subject is characterized by indicia on the calibration device
disposed in the plane of the lens to be mounted in the socket to be measured
and wherein the indicia recorded by the camera are transmitted to the computer
for determining the actual value of the shooting distance which forms the
basis of
a value representative of the distance between the pupils.
Other objects will in part be obvious and will in part appear hereinafter.
Attorney Docket 040650-US _3_
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
The invention is based on the general recognition that, as a precondition,
video systems useful for precisely determining all the parameters relevant to
grinding lenses into spectacle frames such that they match the wearer's pupils
function by a video photograph being taken of a patient with a frame of
spectacles adjusted for a proper fit. The photograph is then measured on a
monitor by software such that the position of the centers of the pupils of the
eyes
relative to the inner edges of the spectacle sockets are utilized as the
grinding
position of the lenses in the sockets of the spectacles to be made. The
requisite
corrective calculations and, more particularly, the convergence, are based
upon
values of the shooting distance between the patient and the recording camera
stored in the given system data.
In accordance with the invention, the apparatus for determining the
distance between the pupils is a component of a video centering system for
defining the parameters relevant to grinding or fitting lenses into spectacle
sockets. In a particularly advantageous embodiment of the invention, the
shooting distance between a calibration device and a camera is determined as
the value upon which the corrective calculations are based to derive the
actual
values of the distance between the pupils of a given patient.
A calibration device is mounted in the spectacle sockets such that it
coincides with the plane of the lens. The calibration device is provided with
two
indicia at a fixed, defined and known spacing from each other. The calibration
device is a component of the video centering system which is also equipped
with
a camera and a suitable zooming device as well as with a computer and a
monitor or video screen.
The image size of the patient, i.e. the size of the subject or distance
between the eyes of the patient is set on the monitor of the system by the
operator of the video centering system by continuous or stepless adjustment of
Attorney Docket 040650-US -4-
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
the focal length of the camera lens or zooming device, to a value relevant to
the
centering function.
At the time of the exposure, in addition to the image information (pixel),
the actual value of the focal length (zoom factor) of the camera lens is also
transmitted to the computer.
Thus, in accordance with the invention, there exists a fixed image scale
relatianship between the imaging size of the subject on the image plane of the
camera and the imaging size on the monitor of the computer. Hence, there also
exists a relationship between the size of the subject and the size of its
image on
the monitor, which depends upon the values of focal length of the camera lens
and the distance of the subject from the camera.
In accordance with the invention, the size of the image of the subject on
the monitor of the computer is determined by evaluation software either by the
operator of the video centering system or automatically. The focal length of
the
camera fens at the time of the exposure as weft as the original size of the
subject
are known. Thus, the distance between the subject and the camera, i.e. the
shooting distance, is determined by previously determined parametric or field
functions specific to the camera. The shooting distance forms the basis of the
corrective calculations of the convergence. It is thus the basis for
determining
the actually required or correct value of the distance between the pupils of
the
eyes of the patient.
DESCRIPTION OF THE SEVERAL DRAWINGS
The novel features which are considered to be characteristic of the
invention are set forth with particularity in the appended claims. The
invention
itself, however, in respect of its structure, construction and lay-out as well
as
Attorney Docket 040650-US _5-
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
manufacturing techniques, together with other objects and advantages thereof,
will be best understood from the following description of preferred
embodiments
when read in connection with the appended drawings, in which:
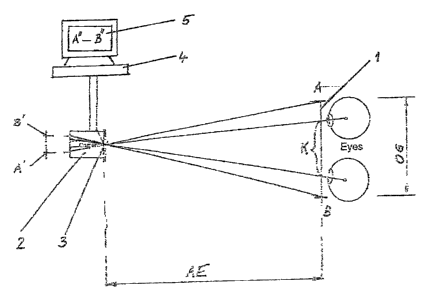
Fig. 1 schematically depicts the complete apparatus;
Fig. 2 schematically depicts the complete apparatus with the determined actual
values of the distance between pupils following a measurement.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The complete video centering system for precisely defining the
parameters relevant to grinding or fitting lenses into spectacle sockets of
which
the apparatus for determining the distance between pupils forms an integral
component, may be seen in Fig. 1.
The video centering system consists of a calibration unit 1, a camera 2
including a zooming device 3 as well as of a computer 4 and a monitor 5
associated therewith.
The meaning of the reference characters used in Figs. 1 and 2 is as
follows:
A; B indicia;
K convergence, i.e. the converged orientation of the eyes;
AE shooting distance;
OG size of the subject;
P the correct position of the eyes I distance between pupils.
A calibration device 1 is placed into the socket of the spectacles to be
measured of the patient to coincide with the plane of the lens of the
spectacle.
The calibration device 1 is provided with two indicia A; B which are spaced
from
Attorney Docket 040650-US _6_
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
each other by a fixed, defined, and known distance and which define the size
OG of the subject.
A mirror image labeled A' and B' in Fig. 1 is taken with the camera 2 and
the zooming device 3 thereof. The camera 2 is connected to the computer 4 and
its monitor 5 so that the indicia A' and B' may bet transmitted to it and
rendered
visible on the monitor 5. On the screen of the monitor 5, these parameters are
presented by indicia A" and B".
In addition to, and simultaneously with, the transmission of indicia A' and
B' from the camera 2 to the monitor 5, the zoom position of the lens of the
camera 2 is also transmitted to the computer 4 and the monitor 5.
The image of the subject size OG of the patient is adjusted on the monitor
to a value relevant to the centering function, by continuous or stepless
adjustment of the focal length of the zooming device 3, by the operator of the
video centering system. In addition to the image data, the actual value of the
focal length of the zooming device 3 is also transmitted to the computer 4 at
the
time of the exposure. A fixed image scale relationship exists between the size
OG of the image, shown here as indicia A' and B', on the focal plane of the
camera 2 and the image size of the subject on the monitor 5 as shown by
indicia
A"and B".
Thus, there also exists a relationship depending upon the values of the
zooming device 3 of the camera 2 relative to the distance of the subject from
the
camera 2, between the size OG of the subject shown by indicia A and B and the
image size of the subject on the monitor 5 shown by indicia A" and B". As
shown
in Fig. 1, the size OG of the subject is displayed on the calibration device 1
by
indicia A and B. The converged orientation of the eyes I pupils at the time of
taking the exposure is shown by reference character K. The distance between
Attorney Docket 040650-US
CA 02479064 2004-08-25
the calibration device 1 and the camera 2 represents the shooting distance AE.
The image size of the object on the monitor 5 is determined with suitable
software either by the operator of the system or automatically, as shown by
indicia A" and B" in Figs. 1 and 2. The zooming position of the camera 2 at
the
time of the exposure is known as is the original size OG of the subject
depicted
by indicia A and B on the calibration device 1. The precise shooting distance
AE
is defined by taking these known values into account. The precise shooting
distance AE then forms the basis upon which the correct positional values of
the
pupils of the eyes of a patient, shown in Fig. 2 by reference character P, is
determined. In this manner the parameters are established which are relevant
to
the grinding of lenses such that when mounted in the sockets of a spectacle
they
are properly aligned with the pupils of a patient.
Attorney Docket 040650-US _g_