Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 1 PCT/EP03/03669
80360pct.210
Medicaments containing betamimetic drugs and a novel anticholinesterase
drug
The present invention relates to novel pharmaceutical compositions based on
beta2 agonists with a long-lasting effect and salts of a new anticholinergic,
processes for preparing them and their use in the treatment of respiratory
complaints.
Description of the invention
The present invention relates to novel pharmaceutical compositions based on
beta2 agonists with a long-lasting effect and salts of a new anticholinergic
1,
processes for preparing them and their use in the treatment of respiratory
complaints.
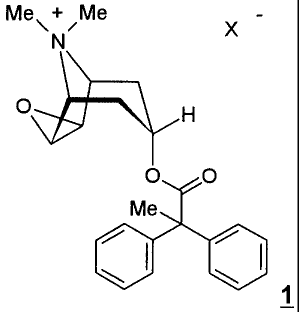
Within the scope of the present invention the anticholinergic agents used are
the
salts of formula 1
Met+~Me -
N X
O H
O O
Me
1
wherein
X - denotes an anion with a single negative charge, preferably an anion
selected from the group consisting of chloride, bromide, iodide,
sulphate, phosphate, methanesulphonate, nitrate, maleate, acetate,
citrate, fumarate, tartrate, oxalate, succinate, benzoate and p-
toluenesulphonate.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 2 PCT/EP03/03669
Preferably, the salts of formula 1 are used wherein
X - denotes an anion with a single negative charge selected from among
the chloride, bromide, 4-toluenesulphonate and methanesulphonate,
preferably bromide.
Most preferably, the salts of formula 1 are used wherein
X - denotes an anion with a single negative charge selected from among
the chloride, bromide and methanesulphonate, preferably bromide.
Particularly preferred according to the invention is the salt of formula 1
wherein
X - denotes bromide.
Anticholinergics may appropriately be used to treat a number of diseases.
Particular mention should be made, for example, of the treatment of asthma or
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). For treating these diseases WO
92/16528 proposes, for example, anticholinergics which have a scopine,
tropenol
or tropine basic structure.
The problem on which WO 92/16528 is based is the preparation of
anticholinergically active compounds which are characterised by their long-
lasting
activity. To solve this problem WO 92/16528 discloses inter alia benzilic acid
esters of scopine, tropenol or tropine.
For treating chronic diseases it is often desirable to prepare pharmaceutical
compositions with a longer-lasting effect. This will generally ensure that the
concentration of the active substance needed to achieve the therapeutic effect
is
present in the body for a longer period of time without the need for the
pharmaceutical composition to be administered repeatedly and all too
frequently.
Moreover, if an active substance is administered at longer intervals of time,
this
contributes to the feeling of well-being of the patient to a considerable
degree. It is
particularly desirable to provide a pharmaceutical composition which can be
used
to therapeutically good effect by administering it once a day (single dose). A
single application per day has the advantage that the patient can become
accustomed relatively quickly to the regular taking of the medicament at a
particular time of the day.
' ~ CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 3 PCT/EP03/03669
If it is to be used as a medicament for administration once a day, the active
substance which is to be given must meet particular requirements. First of
all, the
desired onset of the activity after the administration of the pharmaceutical
composition should occur relatively quickly and ideally the activity should
remain
as constant as possible over a fairly lengthy ensuing period. On the other
hand the
duration of activity of the pharmaceutical composition should not greatly
exceed a
period of about one day. Ideally, an active substance should have an activity
profile such that the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition which is
intended to be administered once a day and contains the active substance in
therapeutically appropriate doses can be properly controlled.
It has been found that the esters of scopine, tropenol or tropine disclosed in
WO
92/16528 do not meet these more stringent requirements. Because of their
extremely long duration of activity, significantly exceeding the period of
about one
day specified above, they cannot be used therapeutically in a single once-a-
day
dose. The salts of formula 1 however meet this requirement.
Surprisingly, an unexpectedly beneficial therapeutic effect, particularly a
synergistic effect can be observed in the treatment of inflammatory and/or
obstructive diseases of the respiratory tract if the anticholinergic of
formula 1 is
used with one or more betamimetics 2. In view of this synergistic effect the
pharmaceutical combinations according to the invention can be used in smaller
doses than would be the case with the individual compounds used in monotherapy
in the usual way. As a further positive aspect of the present invention,
unwanted
side effects such as may occur when beta2 agonists are administered, for
example, are thus reduced. Undesirable side effects in this context are, in
particular, the stimulant effects on the heart which are sometimes caused by
betamimetics, especially tachycardia, palpitations, angina-pectoris-like pain
and
arryhthmia.
The effects mentioned above may be observed both when the two active
substances are administered simultaneously in a single active substance
formulation and when they are administered successively in separate
formulations.
According to the invention, it is preferable to administer the two active
substance
ingredients simultaneously in a single formulation.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 4 PCT/EP03/03669
Within the scope of the present invention, any reference to the compound 1' is
to
be regarded as a reference to the pharmacologically active cation of the
following
formula contained in the salts 1
Mew+~Me
N
O H
O O
Me
1'.
In the pharmaceutical combinations mentioned above the active substances may
be combined in a single preparation or contained in two separate formulations.
Pharmaceutical compositions which contain the active substances 1 and 2 in a
single preparation are preferred according to the invention.
Salmeterol salts or forrnoterol salts are preferably used as the long-acting
betamimetics 2 according to the invention. Any reference to the term
betamimetics
2 also includes a reference to the relevant enantiomers or mixtures thereof.
Accordingly, any reference to the preferred compounds 2 according to the
invention, the salts of salmeterol and formoterol, also includes the relevant
enantiomeric salts of R-salmeterol, S-salmeterol, R,R-formoterol, S,S-
formoterol,
R,S-formoterol, S,R-formoterol and the mixtures thereof, while the
enantiomeric
salts of R-safmeterol and R,R-formoterol are of particular importance. The
compounds 2 may also be present according to the invention in the form of the
hydrates or solvates thereof.
The long-acting betamimetics 2 may also be the salts of the compounds of
formula 2a',
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 5 PCT/EP03/03669
OH
N R~
/ 3
HO R
HN
R R
O _2a'
wherein
R' and R2 which may be identical or different denote hydrogen or C~-C4-alkyl;
R3 and R4 which may be identical or different denote hydrogen, C~-C4-alkyl, -O-
C~-C4-alkyl,
- C~-C4-alkylene-O-C~-C4-alkyl or
R3 and R4 together denote one of the bridging groups
- C~-C4-alkylene- or -0-C~-C4-alkylene-O-.
Preferably, salts of the compounds of formula 2a' wherein
R' and R2 which may be identical or different denote hydrogen, methyl or
ethyl;
R3 and R4 which may be identical or different denote hydrogen, methyl, ethyl,
propyl, butyl, methoxy, ethoxy, methoxymethyl, or methoxyethyl, or
R3 and R4 together denote one of the bridging groups
propylene, butylene, -O-ethylene-O- or -O-propylene-O-
are used in the combinations according to the invention.
More preferably, salts of the compounds of formula 2a' wherein
R' and R2 which may be identical or different denote hydrogen or ethyl,
preferably hydrogen;
R3 and R4 which may be identical or different denote hydrogen, methyl, ethyl,
propyl, butyl or methyoxymethyl or
R3 and R4 together denote one of the bridging groups
butylene or -O-ethylene-0-
are used in the combinations according to the invention.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 6 PCT/EP03/03669
Most preferably, according to the invention, the salts of the following
compounds
of formula 2a' wherein
a) R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 denote ethyl; or
b) R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 denote methyl; or
c) R' and R2 denote ethyl and R3 and R4 denote hydrogen; or
d) R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 together denote butylene;
or
e) R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 together denote -O-
ethylene-O-; or
f) R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 denote tert.-butyl or
g) R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 denote iso-propyl; or
h) R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 denote methoxymethyl
are used in the combinations according to the invention
The compounds of formula 2a' are known from WO00/75114
Of the compounds mentioned above, the structure defined in a), wherein R' and
R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 denote ethyl, are exceptionally important in
the
pharmaceutical combinations according to the invention. The acid addition salt
of
this compound is hereinafter referred to as compound 2aa, while any reference
to
the free base of this compound is characterised by the designation 2aa'
according
to the following formula
H
N
Ethyl
HO
Ethyl
2aa'
In the pharmaceutical compositions according to the invention, the salts of
the
compounds of formula 2a' may be present in the form of their racemates,
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 7 PCT/EP03/03669
enantiomers or mixtures thereof. The separation of the enantiomers from the
racemates may be carried out using methods known in the art (e.g. by
chromatography on chiral phases, etc.) If the salts of the compounds of
formula
2a' are used in the form of their enantiomers, it is particularly preferable
to use the
enantiomers in the R configuration at the C-OH group.
The alkyl groups used, unless otherwise stated, are branched and unbranched
alkyl groups having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Examples include: methyl, ethyl,
propyl
or butyl. The groups methyl, ethyl, propyl or butyl may optionally also be
referred
to by the abbreviations Me, Et, Prop or Bu. Unless otherwise stated, the
definitions
propyl and butyl also include all possible isomeric forms of the groups in
question.
Thus, for example, propyl includes n-propyl and iso-propyl, butyl includes iso-
butyl,
sec. butyl and tert.-butyl, etc.
The alkylene groups used, unless otherwise stated, are branched and unbranched
double-bonded alkyl bridges with 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Examples include:
methylene, ethylene, propylene or butylene.
The alkyloxy groups used (also known as -0-C~-C4-alkyl groups), unless
otherwise
stated, are branched and unbranched alkyl groups with 1 to 4 carbon atoms
which
are linked via an oxygen atom. The following may be mentioned, for example:
methyloxy, ethyloxy, propyloxy or butyloxy. The groups methyloxy, ethyloxy,
propyloxy or butyloxy may optionally also be referred to by the abbreviations
MeO,
EtO, PropO or BuO. Unless otherwise stated, the definitions propyloxy and
butyloxy also include all possible isomeric forms of the groups in question.
Thus,
for example, propyloxy includes n-propyloxy and iso-propyloxy, butyloxy
includes
iso-butyloxy, sec. butyloxy and tert.-butyloxy, etc. The word alkoxy may also
possibly be used within the scope of the present invention instead of the word
alkyloxy. The groups methyloxy, ethyloxy, propyloxy or butyloxy may optionally
also be referred to as methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy or butoxy.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 $ PCT/EP03/03669
The alkylene-alkyloxy groups used, unless otherwise stated, are branched and
unbranched double-bonded alkyl bridges with 1 to 4 carbon atoms which may be
mono-, di- or trisubstituted, preferably monosubstituted, by an alkyloxy
group.
Within the scope of the present invention any reference to compounds 2 should
be
taken to mean a reference to physiologically acceptable acid addition salts
thereof.
Examples of physiologically acceptable acid addition salts of the betamimetics
2
according to the invention are the pharmaceutically acceptable salts which are
selected from among the salts of hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid,
sulphuric
acid, phosphoric acid, methanesulphonic acid, acetic acid, fumaric acid,
succinic
acid, lactic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid, 1-hydroxy-2-
naphthalenecarboxylic acid,
4-phenylcinnamic acid, 5-(2.4-difluorophenyl)salicylic acid or malefic acid.
If
desired, mixtures of the abovementioned acids may also be used to prepare the
salts 2.
According to the invention, the salts of the betamimetics 2 selected from
among
the hydrochloride, hydrobromide, sulphate, phosphate, fumarate,
methanesulphonate, 4-phenylcinnamate, 5-(2.4-difluorophenyl)salicylate,
maleate
and xinafoate are preferred. Particularly preferred are the salts of 2 in the
case of
salmeterol selected from among the hydrochloride, sulphate, 4-phenylcinnamate,
5-(2.4-difluorophenyl)salicylate and xinafoate, of which the 4-
phenylcinnamate, 5-
(2.4-difluorophenyl)salicylate and especially xinafoate are particularly
important.
Particularly preferred are the salts of 2 in the case of formoterol selected
from the
hydrochloride, sulphate and fumarate, of which the hydrochloride and fumarate
are
particularly preferred. Of exceptional importance according to the invention
is
formoterol fumarate. Most preferably, the salts of 2 in the case of the
compound
2aa' are selected from among the hydrochloride and maleate, of which the
maleate is particularly preferred.
Where the present invention refers to betamimetics which are not in the form
of
salts, this is indicated by a reference to compounds 2'. For example, the
preferred
betamimetics 2' according to the invention which are not in salt form include
the
free base of formoterol, salmeterol or the compounds of formula 2a', whereas
the
particularly preferred compounds 2 according to the invention are salmeterol
xinafoate, formoterol fumarate or an acid addition salt 2a of a compound of
formula 2a'.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 g PCT/EP03/03669
Within the scope of the present invention the betamimetics 2 may possibly also
be
referred to as sympathomimetics or beta-2-agonists ((32-agonists). All these
terms
are to be regarded as interchangeable for the purposes of the present
invention.
In one aspect the present invention relates to the abovementioned
pharmaceutical
compositions which contain, in addition to therapeutically effective
quantities of 1
and 2, a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. In another aspect the present
invention relates to the abovementioned pharmaceutical compositions which do
not contain any pharmaceutically acceptable carrier in addition to
therapeutically
effective quantities of 1 and 2.
The present invention also relates to the use of therapeutically effective
quantities
of the salts 1 for preparing a pharmaceutical composition containing long-
acting
betamimetics 2 for treating inflammatory or obstructive diseases of the
respiratory
tract. Preferably, the present invention relates to the abovementioned use for
preparing a pharmaceutical composition for treating asthma or COPD.
Within the scope of the present invention the compounds 1 and 2 may be
administered simultaneously or successively, while it is preferable according
to the
invention to administer compounds 1 and 2 simultaneously.
The present invention further relates to the use of therapeutically effect
amounts of
salts 1 and long-acting betamimetics 2 for treating inflammatory or
obstructive
respiratory complaints, particularly asthma or COPD.
The proportions in which the active substances 1 and 2 may be used in the
active
substance combinations according to the invention are variable. Active
substances 1 and 2 may possibly be present in the form of their solvates or
hydrates. Depending on the choice of the compounds 1 and 2, the weight ratios
which may be used within the scope of the present invention vary on the basis
of
the different molecular weights of the various salt forms. Therefore, the
weight
ratios specified below were based on the cation 1' and the free bases _2' of
the
betamimetics salmeterol, formoterol and the compound 2aa' (= compound of
formula 2a wherein R' and R2 denote hydrogen and R3 and R4 denote ethyl) which
are preferred according to the invention.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 10 PCT/EP03/03669
The pharmaceutical combinations according to the invention may contain 1' and
2'
in the case of formoterol, for example, in ratios by weight ranging from 1:10
to
300:1, preferably from 1:5 to 200:1, preferably 1:3 to 150:1, more preferably
from
1: 2 to 100:1.
For example, without restricting the scope of the invention thereto, preferred
combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention may contain the cation _1'
and
formoterol 2' in the following weight ratios: 1:5, 1:4, 1:3, 1:2, 1:1, 2:1,
3:1, 4:1, 5:1,
6:1, 7:1, 8:1, 9:1, 10:1, 11:'1, 12:1, 13:1, 14:1, 15:1, 16:1, 17:1, 18:1,
19:1, 20:1,
21:1, 22:1, 23:1, 24:1, 25:1, 26:1, 27:1, 28:1, 29:1, 30:1, 31:1, 32:1, 33:1,
34:1,
35:1, 36:1, 37:1, 38:1, 39:1, 40:1, 41:1, 42:1, 43:1, 44:1, 45:1, 46:1, 47:1,
48:1,
49:1, 50:1, 51:1, 52:1, 53:1, 54:1, 55:1, 56:1, 57:1, 58:1, 59:1, 60:1, 61:1,
62:1,
63:1, 64:1, 65:1, 66:1, 67:1, 68:1, 69:1, 70:1, 71:1, 72:1, 73:1, 74:1, 75:1,
76:1,
77:1, 78:1, 79:1, 80:1, 81:1, 82:1, 83:1, 84:1, 85:1, 86:1, 87:1, 88:1, 89:1,
90:1,
91:1, 92:1, 93:1, 94:1, 95:1, 96:1, 97:1, 98:1, 99:1, 100:1.
The pharmaceutical compositions according to the invention containing the
combinations of 1 and 2 are normally administered so that the
pharmacologically
active cation 1' and formoterol 2' are present together in doses of 5 to
5000~,g,
preferably from 10 to 2000wg, more preferably from 15 to 1000~g, better still
from
20 to 800~g, preferably, according to the invention, from 30 to 600~.g,
preferably
from 40 to 500~,g.
For example, combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention contain a
quantity
of cation 1' and formoterol 2' such that the total dosage per single dose is
about
10Ng, 15pg, 20pg, 25pg, 30pg, 35Ng, 40Ng, 45Ng, 50pg, 55pg, 60pg, 65pg, 70pg,
75Ng, 80Ng, 85pg, 90pg, 95pg, 100pg, 105pg, 110pg, 115pg, 120Ng, 125Ng,
130pg, 135Ng, 140Ng, 145Ng, 150Ng, 155pg, 160pg, 165Ng, 170pg, 175Ng,
180Ng, 185pg, 190pg, 195pg, 200pg, 205pg, 210Ng, 215Ng, 220Ng, 225Ng,
230Ng, 235Ng, 240Ng, 245Ng, 250Ng, 255Ng, 260Ng, 265pg, 270Ng, 275pg,
280Ng, 285pg, 290pg, 295pg, 300pg, 305pg, 310Ng, 315pg, 320Ng, 325Ng,
330pg, 335pg, 340Ng, 345Ng, 350Ng, 355Ng, 360pg, 365pg, 370pg, 375Ng,
380Ng, 385pg, 390Ng, 395Ng, 400Ng, 405Ng, 410pg, 415pg, 420pg, 425Ng,
430Ng, 435Ng, 440Ng, 445pg, 450Ng, 455Ng, 460pg, 465pg, 470pg, 475Ng,
480Ng, 485pg, 490Ng, 495Ng, 500pg, 505Ng, 510pg, 515pg, 520pg, 525Ng,
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 11 PCT/EP03/03669
530pg, 535Ng, 540pg, 545Ng, 550Ng, 555pg, 560Ng, 565Ng, 570pg, 575pg,
580pg, 585Ng, 590pg, 595Ng, 600Ng or similar. It is clear to anyone skilled in
the
art that the suggested dosages per single dose specified above are not to be
regarded as being limited to the numerical values actually stated.
Fluctuations of
about ~ 2.5 fig, particularly in the decimal range, are also included, as will
be
apparent to the skilled man. In these dosage ranges, the active substances 1'
and
2' may be present in the weight ratios given above.
For example, without restricting the scope of the invention thereto, the
combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention may contain a quantity of
cation 1' and formoterol 2' such that, for each single dose, 8.3pg of 1' and
2.5pg
of 2', 8.3Ng of 1' and 4.9pg of 2', 8.3pg of 1' and 9.8Ng of 2', 8.3Ng of 1'
and
14,7pg of 2', 8.3pg of 1' and 19.6Ng of 2', 8.3Ng of 1' and 24.4pg of 2',
16.5pg of 1'
and 2.5pg of 2', 16.5pg of 1' and 4.9Ng of 2', 16.5Ng of 1' and 9.8Ng of 2',
16.5Ng
of 1' and 14.7pg of 2', 16.5Ng of 1' and 19.6pg of 2', 16.5Ng of 1' and 24.4Ng
of 2',
33.ONg of 1' and 2.5pg of 2', 33.ONg of 1' and 4.9Ng of 2', 33.Opg of 1' and
9.8Ng
of 2', 33.ONg of 1' and 14.7pg of 2', 33.ONg of 1' and 19.6Ng of 2', 33.ONg of
1' and
24.4pg of 2', 49.5Ng of 1' and 2.5pg of 2', 49.5pg of 1' and 4.9Ng of 2',
49.5Ng of 1'
and 9.8pg of 2', 49.5pg of 1' and 14.7Ng of 2', 49.5Ng of 1' and 19.6Ng of 2',
49.5Ng of 1' and 24.4Ng of 2', 82.6pg of 1' and 2.5pg of 2', 82.6pg of 1' and
4.9pg
of 2', 82.6pg of 1' and 9.8pg of 2', 82.6Ng of 1' and 14.7Ng of 2', 82.6Ng of
1' and
19.6pg of 2', 82.6Ng of 1' and 24.4Ng of 2', 165.1 Ng of 1' and 2.5pg of 2',
165.1 pg
of 1' and 4.9pg of 2', 165.1 pg of 1' and 9.8pg of 2', 165.1 pg of 1' and
14.7pg of 2',
165.1 Ng of 1' and 19.6pg of 2', 165.1 Ng of 1' and 24.4Ng of 2', 206.4pg of
1' and
2.5Ng of 2', 206.4pg of 1' and 4.9Ng of 2', 206.4Ng of 1' and 9.8pg of 2',
206.4Ng
of 1' and 14.7Ng of 2', 206.4Ng of 1' and 19.6Ng of 2', 206.4pg of 1' and
24.4pg of
2', 412.8Ng of 1' and 2.5pg of 2', 412.8Ng of 1' and 4.9~rg of 2', 412.8Ng of
1' and
9.8Ng of 2', 412.8pg of 1' and 14.7pg of 2', 412.8pg of 1' and 19.6Ng of 2',
412.8Ng of 1' and 24.4Ng of 2' are present.
If the active substance combination in which the bromide is used as the salt 1
and
in which 2 denotes formoterol fumarate is used as the preferred combination of
1
and 2 according to the invention, the quantities of active substance 1' and 2'
adrninistered per single dose mentioned by way of example correspond to the
following quantities of 1 and 2 administered per single dose: 10pg of 1 and
2.9Ng
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 12 PCTlEP03/03669
of 2, 10Ng of 1 and 5.7Ng of 2, 10pg of 1 and 11.5pg of 2, 10pg of 1 and
17.2Ng of
2, 10Ng of 1 and 22.9Ng of 2, 10pg of 1 and 28.5Ng of 2, 20pg of 1 and 2.9pg
of 2,
20pg of 1 and 5.7Ng of 2, 20pg of 1 and 11.5pg of 2, 20Ng of 1 and 17.2Ng of
2,
20pg of 1 and 22.9Ng of 2, 20Ng of 1 and 28.5pg of 2, 40Ng of 1 and 2.9pg of
2,
40Ng of 1 and 5.7pg of 2, 40pg of 1 and 11.5Ng of 2, 40pg of 1 and 17.2pg of
2,
40Ng of 1 and 22.9Ng of 2, 40pg of 1 and 28.5pg of 2, 60pg of 1 and 2.9pg of
2,
60pg of 1 and 5.7Ng of 2, 60pg of 1 and 11.5Ng of 2, 60Ng of 1 and 17.2Ng of
2,
60Ng of 1 and 22.9pg of 2, 60pg of 1 and 28.5pg of 2, 100pg of 1 and 2.9Ng of
2,
1OONg of 1 and 5.7Ng of 2, 1OOpg of 1 and 11.5pg of 2, 1OOpg of 1 and 17.2pg
of
2, 100Ng of 1 and 22.9Ng of 2, 100Ng of 1 and 28.5Ng of 2, 200pg of 1 and
2.9Ng
of 2, 200pg of 1 and 5.7Ng of 2, 200pg of 1 and 11.5Ng of 2, 200pg of 1 and
17.2pg of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 22.9Ng of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 28.5Ng of 2, 250Ng of
1
and 2.9pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 5.7pg of 2, 250pg of 1 and 11.5pg of 2, 250Ng
of 1
and 17.2pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 22.9Ng of 2, 250pg of 1 and 28.5pg of 2, 500Ng
of
1 and 2.9Ng of 2, 500pg of 1 and 5.7pg of 2, 500pg of 1 and 11.5pg of 2, 500pg
of
1 and 17.2pg of 2, 500Ng of 1 and 22.9pg of 2, 500Ng of 1 and 28.5Ng of 2.
If the active substance combination in which 2 denotes formoterol fumarate
dihydrate and the salt 1 is bromide is used as a preferred combination of 1
and 2
according to the invention, the quantities of active substance 1' and 2'
administered per single dose mentioned by way of example correspond to the
following quantities of 1 and 2 administered per single dose: 10Ng of 1 and
3pg of
2, 10Ng of 1 and 6Ng of 2, 10Ng of 1 and 12Ng of 2, 10Ng of 1 and 18pg of 2,
10pg
of 1 and 24Ng of 2, 10pg of 1 and 30Ng of 2, 20pg of 1 and 3Ng of 2, 20pg of 1
and
6pg of 2, 20Ng of 1 and 12Ng of 2, 20pg of 1 and 18Ng of 2, 20Ng of 1 and 24pg
of
2, 20Ng of 1 and 30pg of 2, 40pg of 1 and 3pg of 2, 40Ng of 1 and 6pg of 2,
40pg
of 1 and 12Ng of 2, 40pg of 1 and 18Ng of 2, 40Ng of 1 and 24pg of 2, 40Ng of
1
and 30Ng of 2, 60pg of 1 and 3Ng of 2, 60pg of 1 and 6pg of 2, 60Ng of 1 and
12Ng
of 2, 60Ng of 1 and 18pg of 2, 60pg of 1 and 24Ng of 2, 60Ng of 1 and 30Ng of
2,
100Ng of 1 and 3pg of 2, 100Ng of 1 and 6pg of 2, 100Ng of 1 and 12pg of 2,
100pg of 1 and 18Ng of 2, 100Ng of 1 and 24pg of 2, 100pg of 1 and 30pg of 2,
200Ng of 1 and 3pg of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 6Ng of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 12Ng of 2,
200pg of 1 and 18Ng of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 24pg of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 30pg of 2,
250Ng of 1 and 3pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 6pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 12pg of 2,
250Ng of 1 and 18pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 24pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 30Ng of 2,
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03!087097 13 PCT/EP03/03669
500Ng of 1 and 3Ng of 2, 500pg of 1 and 6pg of 2, 500Ng of 1 and 12Ng of 2,
500Ng of 1 and 18pg of 2, 500Ng of 1 and 24Ng of 2, 500pg of 1 and 30pg of 2.
The active substance combinations according to the invention may contain 1'
and
2' , in the case of salmeterol, for example, in ratios by weight in the range
from
about 1:30 to 400:1, preferably 1:25 to 200:1, preferably 1:20 to 100:1, more
preferably from 1:15 to 50:1.
For example, without i~~tricting the scope of the invention thereto, preferred
combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention may contain the cation 1'
and
salmeterol 2' in the following ratios by weight: 1:15, 1:14, 1:13, 1:12, 1:11,
1:10,
1:9,1:8,1:7,1:6,1:5,1:4,1:3,1:2,1:1,2:1,3:1,4:1,5:1,6:1,7:1,8:1,9:1,10:1,
11:1, 12:1, 13:1, 14:1, 15:1, 16:1, 17:1, 18:1, 19:1, 20:1, 21:1, 22:1, 23:1,
24:1,
25:1, 26:1, 27:1, 28:1, 29:1, 30:1, 31:1, 32:1, 33:1, 34:1, 35:1.
The pharmaceutical compositions according to the invention containing the
combinations of 1 and 2 are usually administered so that the cation 1' and
salmeterol 2' are present together in dosages of 5 to 5000pg, preferably from
10
to 2000pg, more preferably from 15 to 1000pg, even more preferably from 20 to
800Ng, and preferably according to the invention from 30 to 750Ng, preferably
from
40 to 700Ng per single dose.
For example, combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention contain an
amount of 1' and salmeterol 2' such that the total dosage per single dose is
about
15pg, 20pg, 25pg, 30pg, 35pg, 40pg, 45Ng, 50Ng, 55Ng, 60pg, 65Ng, 70Ng, 75pg,
80pg, 85Ng, 90Ng, 95Ng, 100pg, 105Ng, 110Ng, 115pg, 120pg, 125Ng, 130Ng,
135Ng, 140Ng, 145Ng, 150Ng, 155pg, 160pg, 165Ng, 170Ng, 175Ng, 180Ng,
185Ng, 190~tg, 195Ng, 200pg, 205Ng, 210pg, 215Ng, 220pg, 225Ng, 230Ng,
235Ng, 240Ng, 245pg, 250Ng, 255Ng, 260Ng, 265Ng, 270pg, 275pg, 280Ng,
285Ng, 290Ng, 295Ng, 300Ng, 305Ng, 310Ng, 315Ng, 320Ng, 325Ng, 330Ng,
335Ng, 340Ng, 345Ng, 350pg, 355pg, 360pg, 365pg, 370pg, 375Ng, 380pg,
385Ng, 390Ng, 395Ng, 400pg, 405Ng, 410pg, 415Ng, 420Ng, 425pg, 430Ng,
435pg, 440Ng, 445Ng, 450pg, 455Ng, 460pg, 465Ng, 470Ng, 475pg, 480pg,
485Ng, 490Ng, 495pg, 500pg, 505pg, 510Ng, 515pg, 520pg, 525pg, 530Ng,
535Ng, 540Ng, 545Ng, 550Ng, 555Ng, 560Ng, 565Ng, 570pg, 575Ng, 580Ng,
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 14 PCT/EP03/03669
585pg, 590pg, 595pg, 600Ng, 605pg, 610pg, 615pg, 620Ng, 625pg, 630Ng,
635pg, 640pg, 645Ng, 650pg, 655Ng, 660pg, 665pg, 670Ng, 675pg, 680Ng,
685Ng, 690pg, 695Ng, 700pg or similar. It is clear to anyone skilled in the
art that
the suggested dosages per single dose specified above are not to be regarded
as
being limited to the numerical values actually stated. Fluctuations of about ~
2.5
~,g, particularly in the decimal range, are also included, as will be apparent
to the
skilled man. In these dosage ranges, the active substances 1' and 2' may be
present in the weight ratios given above.
For example, without restricting the scope of the invention thereto, the
combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention may contain a quantity of
cation 1' and salmeterol 2' such that, for each single dose, 8.3pg of 1' and
12.5Ng
of 2', 8.3Ng of 1' and 25Ng of 2', 8.3pg of 1' and 50pg of 2', 8.3Ng of 1' and
75pg of
2', 8.3Ng of 1' and 100pg of 2', 8.3Ng of 1' and 200Ng of 2', 16.5Ng of 1' and
12.5pg of 2', 16.5Ng of 1' and 25pg of 2', 16.5pg of 1' and 50pg of 2', 16.5pg
of 1'
and 75Ng of 2', 16.5Ng of 1' and 100Ng of 2', 16.5Ng of 1' and 200Ng of 2',
33.ONg
of 1' and 12.5pg of 2', 33.Opg of 1' and 25pg of 2', 33.ONg of 1' and 50Ng of
2',
33.Opg of 1' and 75pg of 2', 33.Opg of 1' and 100pg of 2', 33.ONg of 1' and
200Ng
of 2', 49.5Ng of 1' and 12.5Ng of 2', 49.5Ng of 1' and 25pg of 2', 49.5pg of
1' and
50Ng of 2', 49.5pg of 1' and 75pg of 2', 49.5pg of 1' and 100pg of 2', 49.5Ng
of 1'
and 200Ng of 2', 82.6pg of 1' and 12.5Ng of 2', 82.6Ng of 1' and 25pg of 2',
82.6pg
of 1' and 50pg of 2', 82.6Ng of 1' and 75pg of 2', 82.6pg of 1' and 100pg of
2',
82.6pg of 1' and 200pg of 2', 165.1 Ng of 1' and 12.5Ng of 2', 165.1 pg of 1'
and
25Ng of 2', 165.1 pg of 1' and 50Ng of 2', 165.1 Ng of 1' and 75pg of 2',
165.1 Ng of
1' and 100pg of 2', 165.1 pg of 1' and 200Ng of 2', 206.4Ng of 1' and 12.5pg
of 2',
206.4Ng of 1' and 25pg of 2', 206.4pg of 1' and 50pg of 2', 206.4pg of 1' and
75pg
of 2', 206.4Ng of 1' and 100pg of 2', 206.4Ng of 1' and 200Ng of 2', 412.8Ng
of 1'
and 12.5pg of 2', 412.8pg of 1' and 25Ng of 2', 412.8Ng of 1' and 50Ng of 2',
412.8Ng of 1' and 75pg of 2', 412.8pg of 1' and 100Ng of 2', 412.8pg of 1' and
200pg of 2' are present, for example.
If a combination of active substances wherein the bromide is used as the salt
1
and 2 denotes salmeterol xinafoate is used as the preferred combination of 1
and
2 according to the invention, the amounts of active substances 1' and 2'
administered per single dose as specified hereinbefore correspond to the
following
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 15 PCT/EP03/03669
amounts of 1 and 2 administered per single dose: 10pg of 1 and 18.2Ng of 2,
10pg
of 1 and 36.3Ng of 2, 10pg of 1 and 72.6pg of 2, 10Ng of 1 and 108.9Ng of 2, 1
Opg
of 1 and 145.2pg of 2, l0pg of 1 and 290.4pg of 2, 20Ng of 1 and 18.2pg of 2,
20Ng of 1 and 36.3Ng of 2, 20Ng of 1 and 72.6Ng of 2, 20pg of 1 and 108.9pg of
2,
20Ng of 1 and 145.2pg of 2, 20pg of 1 and 290.4pg of 2, 40Ng of 1 and 18.2Ng
of
2, 40Ng of 1 and 36.3pg of 2, 40pg of 1 and 72.6pg of 2, 40pg of 1 and 108.9pg
of
2, 40Ng of 1 and 145.2pg of 2, 40pg of 1 and 290.4Ng of 2, 60pg of 1 and
18.2Ng
of 2, 60pg of 1 and 36.3Ng of 2, 60pg of 1 and 72.6pg of 2, 60pg of 1 and
108.9pg
of 2, 60Ng of 1 and 145.2Ng of 2, 60pg of 1 and"290.4Ng of 2, 100pg of 1 and
18.2Ng of 2, 100pg of 1 and 36.3pg of 2, 100pg of 1 and 72.6pg of 2, 100pg of
1
and 108.9pg of 2, 100pg of 1 and 145.2Ng of 2, 100Ng of 1 and 290.4pg of 2,
200Ng of 1 and 18.2Ng of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 36.3pg of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 72.6pg
of
2, 200Ng of 1 and 108.9pg of 2, 200Ng of 1 and 145.2Ng of 2, 200pg of 1 and
290.4pg of 2, 250pg of 1 and 18.2Ng of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 36.3Ng of 2, 250Ng of
1
and 72.6pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 108.9pg of 2, 250Ng of 1 and 145.2Ng of 2,
250pg
of 1 and 290.4Ng of 2, 500pg of 1 and 18.2Ng of 2, 500pg of 1 and 36.3Ng of 2,
500pg of 1 and 72.6pg of 2, 500pg of 1 and 108.9Ng of 2, 500Ng of 1 and
145.2pg
of 2, 500Ng of 1 and 290.4Ng of 2.
The quantities of active substance in the pharmaceutical combinations
according
to the invention which are administered per single dose can be calculated
analogously if instead of the salmeterol xinafoate the compounds 2 salmeterol-
4-
phenylcinnamic acid salt (4-phenylcinnamate) and salmeterol-5-(2,4-
difluorophenyl)salicylic acid salt (5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)salicylate) which
are also
preferably used according to the invention are used.
The combinations of active substances according to the invention may captain
1'
and 2aa' in weight ratios which are in the range from about 1:30 to 400:1,
preferably 1:25 to 200:1, preferably 1:20 to 100:1, more preferably from 1:15
to
50:1.
For example, and without restricting the scope of the invention thereto,
preferred
combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention may contain the ration 1'
and
the compound 2aa' in the following ratios by weight: 1:15, 1:14, 1:13, 1:12,
1:11,
1:10,1:9,1:8,1:7,1:6,1:5,1:4,1:3,1:2,1:1,2:1,3:1,4:1,5:1,6:1,7:1,8:1,9:1,
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 16 PCT/EP03/03669
10:1, 11:1, 12:1, 13:1, 14:1, 15:1, 16:1, 17:1, 18:1, 19:1, 20:1, 21:1, 22:1,
23:1,
24:1, 25:1, 26:1, 27:1, 28:1, 29:1, 30:1, 31:1, 32:1, 33:1, 34:1, 35:1.
The pharmaceutical compositions according to the invention containing the
combinations of 1 and 2 are usually administered so that each single dose
contains the cation 1' and the compound 2aa' together in doses of from 5 to
5000Ng, preferably from 10 to 2000Ng, more preferably from 15 to 1000Ng, even
more preferably from 20 to 800Ng, preferably, according to the invention, from
30
to 750Ng, preferably from 40 to 700Ng.
For example, combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention contain an
amount of 1' and 2aa' such that the total dosage per single dose is about
15Ng,
20N9, 25Ng, 30Ng, 35N9~ 40N9, 45N9~ 50N9~ 55N9~ 60Ng~ 65Ng, 70Ng, 75N9~ 80Ng,
85Ng, 90Ng, 95Ng, 100Ng, 105Ng, 110Ng, 115Ng, 120Ng, 125Ng, 130Ng, 135Ng,
140Ng, 145Ng, 150Ng, 155Ng, 160Ng, 165Ng, 170Ng, 175Ng, 180Ng, 185Ng,
190Ng, 195Ng, 200Ng, 205Ng, 210Ng, 215Ng, 220Ng, 225Ng, 230Ng, 235Ng,
240Ng, 245Ng, 250Ng, 255Ng, 260Ng, 265Ng, 270Ng, 275Ng, 280Ng, 285Ng,
290Ng, 295Ng, 300Ng, 305Ng, 310Ng, 315Ng, 320Ng, 325Ng, 330Ng, 335Ng,
340Ng, 345Ng, 350Ng, 355Ng, 360Ng, 365Ng, 370Ng, 375Ng, 380Ng, 385Ng,
390Ng, 395Ng, 400Ng, 405Ng, 410Ng, 415Ng, 420Ng, 425Ng, 430Ng, 435Ng,
440Ng, 445Ng, 450Ng, 455Ng, 460Ng, 465Ng, 470Ng, 475Ng, 480Ng, 485Ng,
490Ng, 495Ng, 500Ng, 505Ng, 510Ng, 515Ng, 520Ng, 525Ng, 530Ng, 535Ng,
540Ng, 545Ng, 550Ng, 555Ng, 560Ng, 565Ng, 570Ng, 575Ng, 580Ng, 585Ng,
590Ng, 595Ng, 600Ng, 605Ng, 610Ng, 615Ng, 620Ng, 625Ng, 630Ng, 635Ng,
640Ng, 645Ng, 650Ng, 655Ng, 660Ng, 665Ng, 670Ng, 675Ng, 680Ng, 685Ng,
690Ng, 695Ng, 700Ng or similar. It is clear to anyone skilled in the art that
the
suggested dosages per single dose specified above are not to be regarded as
being limited to the numerical values actually stated. Fluctuations of about t
2.5
~,g, particularly in the decimal range, are also included, as will be apparent
to the
skilled man. In these dosage ranges, the active substances _1' and 2aa' may be
present in the weight ratios given above.
For example, and without restricting the scope of the invention thereto, the
combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention may contain an amount of
cation 1' and 2aa' such that each single dose contains, for example, 8.3Ng of
1'
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 17 PCT/EP03/03669
and 12.5pg of 2aa', 8.3pg of 1' and 25Ng of 2aa', 8.3pg of 1' and 50pg of
2aa',
8.3Ng of 1' and 75pg of 2aa', 8.3Ng of 1' and 100Ng of 2aa', 8.3pg of 1' and
200Ng
of 2aa', 16.5pg of 1' and 12.5Ng of 2aa', 16.5pg of 1' and 25pg of 2aa',
16.5Ng of
1' and 50Ng of 2aa', 16.5pg of 1' and 75Ng of 2aa', 16.5Ng of 1' and 100Ng of
2aa',
16.5pg of 1' and 200Ng of 2aa', 33.ONg of 1' and 12.5Ng of 2aa', 33.Opg of 1'
and
25pg of 2aa', 33.0Ng of 1' and 50Ng of 2aa', 33.Opg of 1' and 75pg of 2aa',
33.Opg
of 1' and 100pg of 2aa', 33.Opg of 1' and 200pg of 2aa', 49.5pg of 1' and
12.5Ng of
2aa', 49.5Ng of 1' and 25Ng of 2aa', 49.5Ng of 1' and 50Ng of 2aa', 49.5pg of
1'
and 75pg of 2aa', 49.5pg of 1' and 1 OONg of 2aa', 49.5pg of 1' and 200N~of
2aa',
82.6Ng of 1' and 12.5Ng of 2aa', 82.6Ng of 1' and 25Ng of 2aa', 82.6pg of 1'
and
50Ng of 2aa', 82.6pg of 1' and 75Ng of 2aa', 82.6Ng of 1' and 100Ng of 2aa',
82.6pg of 1' and 200Ng of 2aa', 165.1 pg of 1' and 12.5pg of 2aa', 165.1 Ng of
1'
and 25pg of 2aa', 165.1 Ng of 1' and 50Ng of 2aa', 165.1 Ng of 1' and 75pg of
2aa',
165.1 pg of 1' and 1 OONg of 2aa', 165.1 pg of 1' and 200Ng of 2aa', 206.4Ng
of 1'
and 12.5Ng of 2aa', 206.4Ng of 1' and 25Ng of 2aa', 206.4Ng of 1' and 50Ng of
2aa', 206.4Ng of 1' and 75Ng of 2aa', 206.4Ng of 1' and 100pg of 2aa', 206.4Ng
of
1' and 200Ng of 2aa', 412.8pg of 1' and 12.5pg of 2aa', 412.8Ng of 1' and 25Ng
of
2aa', 412.8pg of 1' and 50Ng of 2aa', 412.8pg of 1' and 75pg of 2aa', 412.8pg
of 1'
and 100Ng of 2aa', 412.8~rg of 1' and 200pg of 2aa'.
If the active substance combination wherein the salt 1 is the bromide and the
salt
2aa is the maleate of the compound 2aa' is used as the preferred combination
of 1
and 2 according to the invention, the quantities of active substances 1' and
2aa'
administered per single dose as specified above by way of example correspond
to
the following amounts of 1 and 2aa administered per single dose:
10pg of 1 and 16.2pg of 2aa, 10pg of 1 and 32.4Ng of 2aa, 10pg of 1 and 64.8Ng
of 2aa, 10pg of 1 and 97.2pg of 2aa, 10pg of 1 and 129.6pg of 2aa, 10Ng of 1
and
259.2pg of 2aa, 20pg of 1 and 16.2Ng of 2aa, 20pg of 1 and 32.4pg of 2aa, 20pg
of 1 and 64.8Ng of 2aa, 20Ng of 1 and 97.2pg of 2aa, 20pg of 1 and 129.6Ng of
2aa, 20Ng of 1 and 259.2Ng of 2aa, 40Ng of 1 and 16.2Ng of 2aa,
40Ng of 1 and 32.4pg of 2aa, 40Ng of 1 and 64.8Ng of 2aa, 40pg of 1 and 97.2Ng
of 2aa, 40Ng of 1 and 129.6Ng of 2aa, 40Ng of 1 and 259.2Ng of 2aa, 60Ng of 1
and 16.2Ng of 2aa, 60pg of 1 and 32.4pg of 2aa, 60pg of 1 and 64.8Ng of 2aa,
60Ng of 1 and 97.2pg of 2aa, 60pg of 1 and 129.6pg of 2aa, 60pg of 1 and
259.2Ng of 2aa, 100Ng of 1 and 16.2Ng of 2aa, 100pg of 1 and 32.4Ng of 2aa,
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 1$ PCT/EP03/03669
1 OOpg of 1 and 64.8Ng of 2aa, 100Ng of 1 and 97.2Ng of 2aa, 100pg of _1 and
129.6Ng of 2aa, 100Ng of 1 and 259.2pg of 2aa, 200pg of 1 and 16.2pg of 2aa,
200pg of 1 and 32.4Ng of 2aa, 200Ng of 1 and 64.8Ng of 2aa, 200pg of 1 and
97.2Ng of 2aa, 200pg of 1 and 129.6pg of 2aa, 200Ng of 1 and 259.2pg of 2aa,
250Ng of 1 and 16.2pg of 2aa, 250Ng of 1 and 32.4Ng of 2aa, 250pg of 1 and
64.8pg of 2aa, 250Ng of 1 and 97.2Ng of 2aa, 250pg of 1 and 129.6pg of 2aa,
250Ng of 1 and 259.2pg of 2aa, 500pg of 1 and 16.2pg of 2aa, 500Ng of _1 and
32.4pg of 2aa, 500pg of 1 and 64.8Ng of 2aa, 500pg of 1 and 97.2Ng of 2aa,
500Ng of 1 and 129.6Ng of 2aa, 500pg of 1 and 259.2pg of 2aa.
The active substance combinations of 1 and 2 according to the invention are
preferably administered by inhalation. For this purpose, ingredients 1 and 2
have
to be made available in forms suitable for inhalation. Inhalable preparations
according to the invention include inhalable powders, propellant-containing
metered dose aerosols or propellant-free inhalable solutions. Inhalable
powders
according to the invention containing the combination of active substances 1
and 2
may consist of the active substances on their own or of a mixture of the
active
substances with physiologically acceptable excipients. Within the scope of the
present invention, the term carrier may optionally be used instead of the term
excipient. Within the scope of the present invention, the term propellant-free
inhalable solutions also includes concentrates or sterile inhalable solutions
ready
for use. The preparations according to the invention may contain the
combination
of active substances 1 and 2 either together in one formulation or in two
separate
formulations. These formulations which may be used within the scope of the
present invention are described in more detail in the next part of the
specification.
A) Inhalable powder containing the combinations of active substances 1 and
2 according to the invention:
The inhalable powders according to the invention may contain 1 and 2 either on
their own or in admixture with suitable physiologically acceptable excipients.
If the active substances 1 and 2 are present in admixture with physiologically
acceptable excipients, the following physiologically acceptable excipients may
be
used to prepare these inhalable powders according to the invention:
monosaccharides (e.g. glucose or arabinose), disaccharides (e.g. lactose,
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 1 g PCT/EP03/03669
saccharose, maltose), oligo- and polysaccharides (e.g. dextran), polyalcohols
(e.g.
sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol), salts (e.g. sodium chloride, calcium carbonate)
or
mixtures of these excipients with one another. Preferably, mono- or
disaccharides
are used, while the use of lactose or glucose is preferred, particularly, but
not
exclusively, in the form of their hydrates.
Within the scope of the inhalable powders according to the invention the
excipients
have a maximum average particle size of up to 250pm, preferably between 10 and
150Nm, most preferably between 15 and 80Nm. It may sometimes seem
appropriate to add finer excipient fractions with an average particle size of
1 to
9Nm to the excipient mentioned above. These finer excipients are also selected
from the group of possible excipients listed hereinbefore. Finally, in order
to
prepare the inhalable powders according to the invention, micronised active
substance 1 and 2, preferably with an average particle size of 0.5 to 10pm,
more
preferably from 1 to 6p,m, is added to the excipient mixture. Processes for
producing the inhalable powders according to the invention by grinding and
micronising and by finally mixing the ingredients together are known from the
prior
art. The inhalable powders according to the invention may be prepared and
administered either in the form of a single powder mixture which contains both
1
and 2 or in the form of separate inhalable powders which contain only 1 or 2.
The inhalable powders according to the invention may be administered using
inhalers known from the prior art. Inhalable powders according to the
invention
which contain one or more physiologically acceptable excipients in addition to
1
and 2 may be administered, for example, by means of inhalers which deliver a
single dose from a supply using a measuring chamber as described in
US 4570630A, or by other means as described in DE 36 25 685 A. The inhalable
powders according to the invention which contain 1 and 2 optionally in
conjunction
with a physiologically acceptable excipient may be administered, for example,
using the inhaler known by the name Turbuhaler~ or using inhalers as disclosed
for example in EP 237507 A. Preferably, the inhalable powders according to the
invention which contain physiologically acceptable excipient in addition to 1
and 2
are packed into capsules (to produce so-called inhalettes) which are used in
inhalers as described, for example, in WO 94/28958.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 2Q PCT/EP03/03669
A particularly preferred inhaler for using the pharmaceutical combination
according
to the invention in inhalettes is shown in Figure 1.
This inhaler (Handyhaler) for inhaling powdered pharmaceutical compositions
from
capsules is characterised by a housing 1 containing two windows 2, a deck 3 in
which there are air inlet ports and which is provided with a screen 5 secured
via a
screen housing 4, an inhalation chamber 6 connected to the deck 3 on which
there
is a push button 9 provided with two sharpened pins 7 and movable counter to a
spring 8, and a mouthpiece 12 which is connected to the housing 1, the deck 3
and a cover 11 via a spindle 10 to enable it to be flipped open or shut, as
well as
airholes 13 for adjusting the flow resistance.
If the inhalable powders according to the invention are packed into capsules
(inhalers) for the preferred use described above, the quantities packed into
each
capsule should be 1 to 30mg per capsule. These capsules contain, according to
the invention, either together or separately, the doses of _1 or _1' and _2 or
_2'
mentioned hereinbefore for each single dose.
B) Propellant gas-driven inhalation aerosols containing the combinations of
active substances 1 and 2:
Inhalation aerosols containing propellant gas according to the invention may
contain substances 1 and 2 dissolved in the propellant gas or in dispersed
form. _1
and 2 may be present in separate formulations or in a single preparation, in
which
1 and 2 are either both dissolved, both dispersed or only one component is
dissolved and the other is dispersed. The propellant gases which may be used
to
prepare the inhalation aerosols according to the invention are known from the
prior
art. Suitable propellant gases are selected from among hydrocarbons such as
n-propane, n-butane or isobutane and halohydrocarbons such as fluorinated
derivatives of methane, ethane, propane, butane, cyclopropane or cyclobutane.
The propellant gases mentioned above may be used on their own or in mixtures
thereof. Particularly preferred propellant gases are halogenated alkane
derivatives selected from TG11, TG12, TG134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane) and
TG227 (1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane) and mixtures thereof, of which the
propellant gases TG134a, TG227 and mixtures thereof are preferred.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 21 PCT/EP03/03669
The propellant-driven inhalation aerosols according to the invention may also
contain other ingredients such as co-solvents, stabilisers, surfactants,
antioxidants, lubricants and pH adjusters. All these ingredients are known in
the
art.
The inhalation aerosols containing propellant gas according to the invention
may
contain up to 5 wt.-% of active substance 1 and/or 2. Aerosols according to
the
invention contain, for example, 0.002 to 5 wt.-%, 0.01 to 3 wt.-%, 0.015 to 2
wt.-%,
0.1 to 2 wt.-%, 0.5 to 2 wt.-% or 0.5 to 1 wt.-% of active substance 1 and/or
2.
If the active substances 1 and/or 2 are present in dispersed form, the
particles of
active substance preferably have an average particle size of up to 10~,m,
preferably from 0.1 to 6~m, more preferably from 1 to 5~,m.
The propellant-driven inhalation aerosols according to the invention mentioned
above may be administered using inhalers known in the art (MDIs = metered dose
inhalers). Accordingly, in another aspect, the present invention relates to
pharmaceutical compositions in the form of propellant-driven aerosols as
hereinbefore described combined with one or more inhalers suitable for
administering these aerosols. In addition, the present invention relates to
inhalers
which are characterised in that they contain the propellant gas-containing
aerosols
described above according to the invention. The present invention also relates
to
cartridges fitted with a suitable valve which can be used in a suitable
inhaler and
which contain one of the above-mentioned propellant gas-containing inhalation
aerosols according to the invention. Suitable cartridges and methods of
filling
these cartridges with the inhalable aerosols containing propellant gas
according to
the invention are known from the prior art.
C) Propellant-free inhalable solutions or suspensions containing the
combinations of active substances 1 and 2 according to the invention:
Propellant-free inhalable solutions and suspensions according to the invention
contain, for example, aqueous or alcoholic, preferably ethanolic solvents,
optionally ethanolic solvents mixed with aqueous solvents. If
aqueous/ethanolic
solvent mixtures are used the relative proportion of ethanol compared with
water
is not limited but preferably the maximum is up to 70 percent by volume, more
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 22 PCT/EP03/03669
particularly up to 60 percent by volume of ethanol. The remainder of the
volume is
made up of water. The solutions or suspensions containing 1 and 2, separately
or
together, are adjusted to a pH of 2 to 7, preferably 2 to 5, using suitable
acids.
The pH may be adjusted using acids selected from inorganic or organic acids.
Examples of particularly suitable inorganic acids include hydrochloric acid,
hydrobromic acid, nitric acid, sulphuric acid and/or phosphoric acid. Examples
of
particularly suitable organic acids include ascorbic acid, citric acid, malic
acid,
tartaric acid, malefic acid, succinic acid, fumaric acid, acetic acid, formic
acid
and/or propionic acid etc. Preferred inorganic acids are hydrochloric and
sulphuric
acids. It is also possible to use the acids which have already formed an acid
addition salt with one of the active substances. Of the organic acids,
ascorbic
acid, fumaric acid and citric acid are preferred. If desired, mixtures of the
above
acids may be used, particularly in the case of acids which have other
properties in
addition to their acidifying qualities, e.g. as flavourings, antioxidants or
complexing
agents, such as citric acid or ascorbic acid, for example. According to the
invention, it is particularly preferred to use hydrochloric acid to adjust the
pH.
According to the invention, the addition of editic acid (EDTA) or one of the
known
salts thereof, sodium editate, as stabiliser or complexing agent is
unnecessary in
the present formulation. Other embodiments may contain this compound or these
compounds. In a preferred embodiment the content based on sodium editate is
less than 100mg/100m1, preferably less than 50mg/100 ml, more preferably less
than 20mg/100 ml. Generally, inhalable solutions in which the content of
sodium
editate is from 0 to 10mg/100m1 are preferred.
Co-solvents and/or other excipients may be added to the propellant-free
inhalable
solutions according to the invention. Preferred co-solvents are those which
contain hydroxyl groups or other polar groups, e.g. alcohols - particularly
isopropyl
alcohol, glycols - particularly propyleneglycol, polyethyleneglycol,
polypropyleneglycol, glycolether, glycerol, polyoxyethylene alcohols and
polyoxyethylene fatty acid esters. The terms excipients and additives in this
context denote any pharmacologically acceptable substance which is not an
active
substance but which can be formulated with the active substance or substances
in
the pharmacologically suitable solvent in order to improve the qualitative
properties of the active substance formulation. Preferably, these substances
have
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 23 PCT/EP03/03669
no pharmacological effect or, in connection with the desired therapy, no
appreciable or at least no undesirable pharmacological effect. The excipients
and
additives include, for example, surtactants such as soya lecithin, oleic acid,
sorbitan esters, such as polysorbates, polyvinylpyrrolidone, other
stabilisers,
complexing agents, antioxidants and/or preservatives which guarantee or
prolong
the shelf life of the finished pharmaceutical formulation, flavourings,
vitamins
and/or other additives known in the art. The additives also include
pharmacologically acceptable salts such as sodium chloride as isotonic agents.
The preferred excipients include antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, for
example,
provided that it has not already been used to adjust the pH, vitamin A,
vitamin E,
tocopherols and similar vitamins and provitamins occurring in the human body.
Preservatives may be used to protect the formulation from contamination with
pathogens. Suitable preservatives are those which are known in the art,
particularly cetyl pyridinium chloride, benzalkonium chloride or benzoic acid
or
benzoates such as sodium benzoate in the concentration known from the prior
art.
The preservatives mentioned above are preferably present in concentrations of
up
to 50mg/100m1, more preferably between 5 and 20mg/100m1.
Preferred formulations contain, in addition to the solvent water and the
combination of active substances 1 and 2, only benzalkonium chloride and
sodium
editate. In another preferred embodiment, no sodium editate is present.
The propellant-free inhalable solutions according to the invention are
administered
in particular using inhalers of the kind which are capable of nebulising a
small
amount of a liquid formulation in the therapeutic dose within a few seconds to
produce an aerosol suitable for therapeutic inhalation. Within the scope of
the
present invention, preferred inhalers are those in which a quantity of less
than
100~L, preferably less than 50~L, more preferably between 20 and 30~L of
active
substance solution can be nebulised in preferably one spray action to form an
aerosol with an average particle size of less than 20~,m, preferably less than
10~m, in such a way that the inhalable part of the aerosol corresponds to the
therapeutically effective quantity.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 24 PCT/EP03/03669
An apparatus of this kind for propellant-free delivery of a metered quantity
of a
liquid pharmaceutical composition for inhalation is described for example in
International Patent Application WO 91/14468 and also in WO 97/12687 (cf. in
particular Figures 6a and 6b). The nebulisers (devices) described therein are
known by the name Respimat~.
This nebuliser (Respimat~) can advantageously be used to produce the inhalable
aerosols according to the invention containing the combination of active
substances 1 and 2. Because of its cylindrical shape and handy size of less
than
9 to 15 cm long and 2 to 4 cm wide, this device can be carried at all times by
the
patient. The nebuliser sprays a defined volume of pharmaceutical formulation
using high pressures through small nozzles so as to produce inhalable
aerosols.
The preferred atomiser essentially consists of an upper housing part, a pump
housing, a nozzle, a locking mechanism, a spring housing, a spring and a
storage
container, characterised by
- a pump housing which is secured in the upper housing part and which
comprises at one end a nozzle body with the nozzle or nozzle arrangement,
- a hollow plunger with valve body,
- a power takeoff flange in which the hollow plunger is secured and which is
located in the upper housing part,
- a locking mechanism situated in the upper housing part,
- a spring housing with the spring contained therein, which is rotatably
mounted on the upper housing part by means of a rotary bearing,
- a lower housing part which is fitted onto the spring housing in the axial
direction.
The hollow plunger with valve body corresponds to a device disclosed in
WO 97/12687. It projects partially into the cylinder of the pump housing and
is
axially movable within the cylinder. Reference is made in particular to
Figures 1 to
4, especially Figure 3, and the relevant parts of the description. The hollow
plunger with valve body exerts a pressure of 5 to 60 Mpa (about 50 to 600
bar),
preferably 10 to 60 Mpa (about 100 to 600 bar) on the fluid, the measured
amount
of active substance solution, at its high pressure end at the moment when the
spring is actuated. Volumes of 10 to 50 microlitres are preferred, while
volumes of
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
W0 03/087097 25 PCT/EP03/03669
to 20 microlitres are particularly preferred and a volume of 15 microlitres
per
spray is most particularly preferred.
The valve body is preferably mounted at the end of the hollow plunger facing
the
5 valve body.
The nozzle in the nozzle body is preferably microstructured, i.e. produced by
microtechnology. Microstructured nozzle bodies are disclosed for example in
WO-94107607; reference is hereby made to the contents of this specification,
10 particularly Figure 1 therein and the associated description.
The nozzle body consists for example of two sheets of glass and/or silicon
firmly
joined together, at least one of which has one or more microstructured
channels
which connect the nozzle inlet end to the nozzle outlet end. At the nozzle
outlet
end there is at least one round or non-round opening 2 to 10 microns deep and
5
to 15 microns wide, the depth preferably being 4.5 to 6.5 microns while the
length
is preferably 7 to 9 microns.
In the case of a plurality of nozzle openings, preferably two, the directions
of
spraying of the nozzles in the nozzle body may extend parallel to one another
or
may be inclined relative to one another in the direction of the nozzle
opening. In a
nozzle body with at least two nozzle openings at the outlet end the directions
of
spraying may be at an angle of 20 to 160° to one another, preferably 60
to 150°,
most preferably 80 to 100°. The nozzle openings are preferably arranged
at a
spacing of 10 to 200 microns, more preferably at a spacing of 10 to 100
microns,
most preferably 30 to 70 microns. Spacings of 50 microns are most preferred.
The directions of spraying will therefore meet in the vicinity of the nozzle
openings.
The liquid pharmaceutical preparation strikes the nozzle body with an entry
pressure of up to 600 bar, preferably 200 to 300 bar, and is atomised into an
inhalable aerosol through the nozzle openings. The preferred particle or
droplet
sizes of the aerosol are up to 20 microns, preferably 3 to 10 microns.
The locking mechanism contains a spring, preferably a cylindrical helical
compression spring, as a store for the mechanical energy. The spring acts on
the
power takeoff flange as an actuating member the movement of which is
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 26 PCT/EP03/03669
determined by the position of a locking member. The travel of the power
takeoff
flange is precisely limited by an upper and lower stop. The spring is
preferably
biased, via a power step-up gear, e.g. a helical thrust gear, by an external
torque
which is produced when the upper housing part is rotated counter to the spring
housing in the lower housing part. In this case, the upper housing part and
the
power takeoff flange have a single or multiple V-shaped gear.
The locking member with engaging locking surfaces is arranged in a ring around
the power takeoff flange. It consists, for example, of a ring of-plastic or
metal
which is inherently radially elastically deformable. The ring is arranged in a
plane
at right angles to the atomiser axis. After the biasing of the spring, the
locking
surfaces of the locking member move into the path of the power takeoff flange
and
prevent the spring from relaxing. The locking member is actuated by means of a
button. The actuating button is connected or coupled to the locking member. In
order to actuate the locking mechanism, the actuating button is moved parallel
to
the annular plane, preferably into the atomiser; this causes the deformable
ring to
deform in the annular plane. Details of the construction of the locking
mechanism
are given in WO 97/20590.
The lower housing part is pushed axially over the spring housing and covers
the
mounting, the drive of the spindle and the storage container for the fluid.
When the atomiser is actuated the upper housing part is rotated relative to
the
lower housing part, the lower housing part taking the spring housing with it.
The
spring is thereby compressed and biased by means of the helical thrust gear
and
the locking mechanism engages automatically. The angle of rotation is
preferably
a whole-number fraction of 360 degrees, e.g. 180 degrees. At the same time as
the spring is biased, the power takeoff part in the upper housing part is
moved
along by a given distance, the hollow plunger is withdrawn inside the cylinder
in
the pump housing, as a result of which some of the fluid is sucked out of the
storage container and into the high pressure chamber in front of the nozzle.
If desired, a number of exchangeable storage containers which contain the
fluid to
be atomised may be pushed into the atomiser one after another and used in
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 27 PCT/EP03/03669
succession. The storage container contains the aqueous aerosol preparation
according to the invention.
The atomising process is initiated by pressing gently on the actuating button.
As a
result, the locking mechanism opens up the path for the power takeoff member.
The biased spring pushes the plunger into the cylinder of the pump housing.
The
fluid leaves the nozzle of the atomiser in atomised form.
Further details of construction are disclosed in PCT Applications WO 97/12683
and WO 97/20590, to which reference is hereby made.
The components of the atomiser (nebuliser) are made of a material which is
suitable for its purpose. The housing of the atomiser and, if its operation
permits,
other parts as well, are preferably made of plastics, e.g. by injection
moulding. For
medicinal purposes, physiologically safe materials are used.
Figures 2a/b attached to this patent application, which are identical to
Figures 6a/b
of WO 97/12687, show the nebuliser (Respimat~) which can advantageously be
used for inhaling the aqueous aerosol preparations according to the invention.
Figure 2a shows a longitudinal section through the atomiser with the spring
biased
while Figure 2b shows a longitudinal section through the atomiser with the
spring
relaxed.
The upper housing part (51 ) contains the pump housing (52) on the end of
which
is mounted the holder (53) for the atomiser nozzle. In the holder is the
nozzle
body (54) and a filter (55). The hollow plunger (57) fixed in the power
takeoff
flange (56) of the locking mechanism projects partially into the cylinder of
the
pump housing. At its end the hollow plunger carries the valve body (58). The
hollow plunger is sealed off by means of the seal (59). Inside the upper
housing
part is the stop (60) on which the power takeoff flange abuts when the spring
is
relaxed. On the power takeoff flange is the stop (61 ) on which the power
takeoff
flange abuts when the spring is biased. After the biasing of the spring the
locking
member (62) moves between the stop (61 ) and a support (63) in the upper
housing part. The actuating button (64) is connected to the locking member.
The
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 2$ PCT/EP03/03669
upper housing part ends in the mouthpiece (65) and is sealed off by means of
the
protective cover (66) which can be placed thereon.
The spring housing (67) with compression spring (68) is rotatably mounted on
the
upper housing part by means of the snap-in lugs (69) and rotary bearing. The
lower housing part (70) is pushed over the spring housing. Inside the spring
housing is the exchangeable storage container (71 ) for the fluid (72) which
is to be
atomised. The storage container is sealed off by the stopper (73) through
which
the hollow plunger projects into the storage container and is immersed at its
end in
the fluid (supply of active substance solution).
The spindle (74) for the mechanical counter is mounted in the covering of the
spring housing. At the end of the spindle facing the upper housing part is the
drive
pinion (75). The slider (76) sits on the spindle.
The nebuliser described above is suitable for nebulising the aerosol
preparations
according to the invention to produce an aerosol suitable for inhalation.
If the formulation according to the invention is nebulised using the method
described above (Respimat~) the quantity delivered should correspond to a
defined quantity with a tolerance of not more than 25%, preferably 20% of this
amount in at least 97%, preferably at least 98% of all operations of the
inhaler
(spray actuations). Preferably, between 5 and 30 mg of formulation, most
preferably between 5 and 20 mg of formulation are delivered as a defined mass
on
each actuation.
However, the formulation according to the invention may also be nebulised by
means of inhalers other than those described above, e.g. jet stream inhalers
or
other stationary nebulisers.
Accordingly, in a further aspect, the invention relates to pharmaceutical
formulations in the form of propellant-free inhalable solutions or suspensions
as
described above combined with a device suitable for administering these
formulations, preferably in conjunction with the Respimat~. Preferably, the
invention relates to propellant-free inhalable solutions or suspensions
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 2g PCT/EP03/03669
characterised by the combination of active substances 1 and 2 according to the
invention in conjunction with the device known by the name Respimat~. In
addition, the present invention relates to the above-mentioned devices for
inhalation, preferably the Respimat~, characterised in that they contain the
propellant-free inhalable solutions or suspensions according to the invention
as
described hereinbefore.
According to the invention, inhalable solutions which contain the active
substances
1 and 2 in a single preparation are preferred. The term "single preparation"
also
includes preparations which contain the two ingredients 1 and 2 in two-chamber
cartridges, as disclosed for example in WO 00/23037. Reference is hereby made
to this publication in its entirety.
The propellant-free inhalable solutions or suspensions according to the
invention
may take the form of concentrates or sterile inhalable solutions or
suspensions
ready for use, as well as the above-mentioned solutions and suspensions
designed for use in a Respimat~. Formulations ready for use may be produced
from the concentrates, for example, by the addition of isotonic saline
solutions.
Sterile formulations ready for use may be administered using energy-operated
free-standing or portable nebulisers which produce inhalable aerosols by means
of
ultrasound or compressed air by the Venturi principle or other principles.
Accordingly, in another aspect, the present invention relates to
pharmaceutical
compositions in the form of propellant-free inhalable solutions or suspensions
as
described hereinbefore which take the form of concentrates or sterile
formulations
ready for use, combined with a device suitable for administering these
solutions,
characterised in that the device is an energy-operated free-standing or
portable
nebuliser which produces inhalable aerosols by means of ultrasound or
compressed air by the Venturi principle or other methods.
The Examples which follow serve to illustrate the present invention in more
detail
without restricting the scope of the invention to the following embodiments by
way
of example.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 3p PCT/EP03103669
First, the preparation of compounds 1 and 2 used within the scope of the
present
invention which are not known in the art will be described.
1 ) Preparation of the compounds of formula 1:
1.a.: 2,2-Diphenylpropionic acid chloride:
52.08g (0.33 mol) of oxalyl chloride are slowly added dropwise at 20°C
to a
suspension of 25.0 g (0.11 mol) of 2,2-diphenylpropionic acid, 100 ml of
dichloromethane and 4 drops of dimethylformamide. The mixture is stirred for 1
h
at 20°C and 0.5 h at 50°C. The solvent is distilled off and the
residue remaining is
used in the next step without any further purification.
1.b.: scopine 2,2-diphenylpropionate:
The residue obtained from step 1.a. is dissolved in 100 ml of dichloromethane
and
at 40°C a solution of 51.45 g (0.33 mol) of scopine in 200 ml of
dichloromethane is
added dropwise thereto. The resulting suspension is stirred for 24 h at
40°C, then
the precipitate formed is suction filtered and the filtrate is extracted first
with water,
then with aqueous hydrochloric acid. The combined aqueous phases are made
alkaline with aqueous sodium carbonate solution, extracted with
dichloromethane,
the organic phase is dried over Na2SOa, evaporated to dryness and the
hydrochloride is precipitated from the residue. The product is purified by
recrystallisation from acetonitrile.
Yield: 20.85 g (= 47 % of theory)
DC: Rf value: 0.24 (eluant: sec. butanollformic acidlwater 75:15:10);
m. p.: 203-204°C.
1.c: sco~pine 2 2-diphenylpropionate methobromide
11.98 g (0.033 mol) of the compound of step 1.b, 210 rnl of acetonitrile, 70
ml of
dichloromethane and 20.16 g (0.1 mol) of 46.92 % bromomethane in acetonitrile
are combined at 20°C and left to stand for 3 days. The solution is
evaporated to
dryness and the residue is recrystallised from isopropanol.
Yield: 11.34 g (= 75 % of theory); m.p.: 208-209°C.
C24H28N03xBr (458.4);
Elemental analysis: calculated: C (62.89) H (6.16) N (3.06)
found: C (62.85) H (6.12) N (3.07).
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 31 PCT/EP03/03669
The salts 1 wherein X- denotes an anion with a single negative charge other
than
bromide may be obtained in a manner similar to step 1.3.
2.) Preparation of the compounds of formula 2:
2.1: Salmeterol-4-phenylcinnamate salt 2b:
HO /
HO \ I N ~O /
OH H~ H
'OOC /
1.35 g (6 mmol) of 4-phenylcinnamic acid are dissolved by refluxing in 75 mL
of
ethyl acetate. To this solution is added a warm solution of 2.5 g (6 mmol) of
salmeterol in 25 mL of ethyl acetate. The solution is allowed to cool and
stirred for
16 h at room temperature. The suspension is filtered, the precipitate is
washed
with ethyl acetate and tert.-butylmethylether and dried in vacuo at 25-
30°C. 47 g
of the title compound are obtained as a colourless solid. Melting point:
109°C;
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 32 PCT/EP03/03669
2.2.: Salmeterol-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)salicylate salt 2c:
HO
HO ~ ~ N O
OH H H
OOC
HO ~ ~ / \ F
F
30 g of salmeterol are dissolved by refluxing in 300 mL of ethyl acetate. 18.3
g of
5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)salicylic acid (Diflunisal) are added to this solution.
The
solution is allowed to cool to ambient temperature. The suspension is filtered
off,
the precipitate is washed with ethyl acetate and dried in vacuo at
35°C. 46 g of the
title salt are obtained as a colourless solid.
Melting point: 104°C
The following examples of formulations, which may be obtained analogously to
methods known in the art, serve to illustrate the present invention more fully
without restricting it to the contents of these examples.
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 33 PCT/EP03/03669
Examples of Formulations
A) Inhalable powders:
1)
2)
3)
4)
Ingredients Ng per capsule
1
1'-brom ide 200
Formoterol fumarate dihydrate 12
Lactose 24788
Total 25000
Ingredients Ng per capsule
1'-brom ide 100
Salmeterol xinafoate 50
Lactose 12350
Total 12500
Ingredients Ng per capsule
1'-brom ide 200
Salmeterol xinafoate 50
Lactose 12250
Total 12500
Ingredients Ng per capsule
1'-brom ide 200
Formoterol fumarate dihydrate 24
Lactose 24776
Total 25000
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 34 PCT/EP03/03669
5)
6)
7)
8)
,. Ingredients " erg per capsule
1'-brom ide 100
2b 50
Lactose 12350
Total 12500
Ingredients pg~ per capsule
1'-brom ide 200
2c 50
Lactose 12250
Total 12500
Ingredients Ng per capsule
1'-brom ide 100
2aa' maleate salt 65
Lactose 12335
Total 12500
Ingredients erg per capsule
~~~
1'-brom ide 200
2aa' maleate salt 65
Lactose 12235
Total 12500
CA 02481468 2004-10-05
WO 03/087097 35 PCT/EP03/03669
B~ Propellant-containing inhalable aerosols:
1 ) Suspension aerosol:
Ingredients % by weight
1'-brom ide 0.020
Salmeterol xinafoate 0.066
Soya lecithin 0.2
TG 11 : TG12 = 2:3 ad 100
2) Suspension aerosol:
Ingredients % by weight
1'-brom ide 0.039
Salmeterol xinafoate 0.033
Absolute ethanol 0.5
Isopropyl myristate 0.1
TG 227 ad 100