Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02487777 2004-11-17
-1-
TITLE OF THE INVENTION
High Performance Telecommunications Cable
FILED OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a high performance telecommunications cable.
In particular the present invention relates to a staggered asymmetric cross
web
as well as a cable design including a rod wound around the cable core
improving PSANEXT.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The introduction of a new IEEE proposal for 10G (Gigabit per second)
transmission speeds over copper cable has spearheaded the development of
new copper Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cable designs capable to perform
at this speed.
As known in the art, such UTP cables typically consist of four twisted pairs
of
conductors each having a different twist lay. In many installations, a number
of
UTP cables are arranged in cable runs such that they run side by side in
parallel. In particular, in order to simplify the installation of UTP cables
in cable
runs, EMC conduit, patch bays or the like, a number of UTP cables are often
bound together using twist ties or tape or the like. A major technical
difficulty in
such installations is the electromagnetic interference between the twisted
pair
conductors of a "victim" cable and the twisted pair conductors of other cables
in
the vicinity of the victim cable (the "offending" cables). This
electromagnetic
interference is enhanced by the fact that, in 10G systems which require all
twisted pairs of the UTP cable to support the high speed transmission, all
conductors in a first cable are the "victims" of the twisted pair conductors
of all
CA 02487777 2004-11-17
-2-
other cables surrounding that first cable. These like pairs, having the same
twisting lay, act as inductive coils that generate electromagnetic
interference
into the conductors of the victim cable. The electromagnetic interference
generated by each of the offending cables into the victim cable is generally
. known in the art as Alien Cross Talk or ANEXT. The calculated overall effect
of
the ANEXT into the victim cable is the Power Sum ANEXT or PSANEXT.
Alien NEXT and PSANEXT are important parameters to minimise as network
cards are not able to compensate for noise external to the UTP cable to which
it is connected. As a result active systems at receiving and the emitting end
of
10G Local Area Networks are able to cancel internal Cross Talk or NEXT but
cannot do the same with ANEXT. This is also due to some degree to the much
higher amount of calculations involved (24 emitting pairs in ANEXT
calculations
vs. 3 emitting pairs in NEXT calculations).
In order to reduce the PSANEXT to the required IEEE draft specification
requirement of 60 dB at 100 MHz cable designers are obliged to manipulate the
few basic parameters that play a leading role in the generation of
electromagnetic interference between cables, namely:
~ Geometry: 1) The distance between pairs, longitudinally, in adjacent cables,
2) The axial X-Y asymmetry of the pairs a cable cross-section and 3) The
thickness of the jacket; and
~ balance: improved balance of the twisted pairs and of the overall cable is
known to reduce emission of electromagnetic interference and increase the
immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Currently, the only commercial design of a 10G incorporates a design that
creates an asymmetry on the Y-axis with a special asymmetric cross web that
separates the four (4) pairs in the cable (Fig. 1). This cable incorporates
pairs
CA 02487777 2004-11-17
-3-
with very short twisting lays and stranding lay that are known to enhance the
balance of the twisting lays.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
To address the above and other drawbacks of the prior art there is disclosed a
telecommunications cable comprising four twisted pairs of conductors, a cross
web separating the four twisted pairs, the cross web comprised of a centre
dividing strip and first and second cross dividing strips attached
longitudinally
along the centre dividing strip and on opposite sides thereof and a cable
jacket
covering the cross web and the twisted pairs. The point of attachment of the
first dividing strip is closer to a first edge of the centre dividing strip
than a point
of attachment of the second dividing strip.
There is also disclosed a communications cable comprising four twisted pairs
of conductors, a cross web separating the twisted pairs, the cross web
comprised of a centre dividing strip and first and second cross dividing
strips
attached longitudinally along the centre dividing strip and on opposite sides
thereof, a longitudinal rod wound around the cross web and the twisted pairs
along a length of the cable and a cable jacket covering the cross web and the
twisted pairs.
Furthermore, there is disclosed a telecommunications cable comprising four
twisted pairs of conductors, a cross web separating the four twisted pairs,
the
cross web having an X shaped cross section comprised of first and second
transverse arms and a cable jacket covering the cross web and the twisted
pairs. A thickness of the first transverse arm is greater than a thickness of
the
second transverse arm.
Additionally, there is disclosed a telecommunications cable comprising four
CA 02487777 2004-11-17
-4-
twisted pairs of conductors, a cross web separating the four twisted pairs and
a
cable jacket covering the cross web and the twisted pairs. The cable jacket
has
a thickness which varies along a length of the cable.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Figure 1 is a cross section of a prior art cross web;
Figure 2 is a cross section of a cable in accordance with an illustrative
embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 3 is a cross section of a cable in accordance with an alternative
illustrative embodiment of the present invention;
Figure 4 is a cross section of a cable in accordance with a second alternative
illustrative embodiment of the present invention; and
Figure 5 is a cross section of a cable in accordance with a third alternative
illustrative embodiment of the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE ILLUSTRATIVE EMBODIMENTS
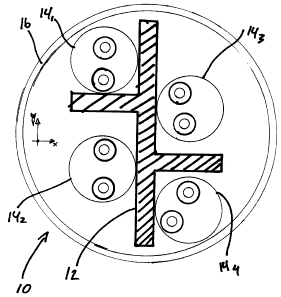
Referring now to Figure 2, a cable, generally referred to using the numeral
10,
is disclosed. The cable 10 includes a cross web 12 comprised of a centre
dividing strip 14, a first cross dividing strip 16 and second cross dividing
strip
18, attached longitudinally along the centre dividing strip 14 and on opposite
sides thereof for maintaining a prescribed separating between finristed pairs
20~, 20z, 203, 204 and a cable jacket 22 covering the cross web 12 and twisted
pairs as in 20. The point of attachment 24 of the first dividing strip is
closer to a
first edge 26 of the centre dividing strip than a point of attachment of the
CA 02487777 2004-11-17
-5-
second dividing strip 28. The cross web 12 improves the geometry of the cable
by creating an asymmetry on both X and Y-axis that translates into a
hellicoidal
pattern of the pairs in the Z direction, i.e. along the length of the cable
10.
In order to measure the Alien NEXT, and therefore the effects particular cable
configurations have on PSANEXT, a test scenario comprised of one victim
cable as in 10 surrounded by six (6) other offending cables was used. A test
scenario comprising seven (7) cables comprising the asymmetrical cross web
12 as discussed hereinabove was found to reduce PSANEXT of both the victim
cable and the offending cables.
Referring now to Figure 3, in an alternative illustrative embodiment of the
present invention, and in order to further improve PSANEXT reduction, the four
twisted pairs of conductors as in 20 are separated by a cross web as in 12 and
wound with a round rod 30 (or filler material). The assembly is covered in a
cable jacket 22. Illustratively, the round rod 30 is manufactured from a non-
conductive dielectric material such as plastic, or the like, in either a solid
or
stranded form.
Referring to Figure 4, a second alternative illustrative embodiment of the
present invention, where a cable 10 comprised of four (4) twisted pairs of
conductors as in 20 is surrounded by a cable jacket 22 and separated by an
alternative asymmetric cross web 12, is disclosed. The alternative cross web
12 is of an asymmetric design where the transverse arms 32 and 34 of the
cross section of the X shaped cross web 12 are of different thickness D and
D'.
In such cable designs, the incorporation of the round rod 30 (or filler
material)
of Figure 3 does not appear to provide the same level of reduction of
PSANEXT. Apparently, the incorporation of the round rod 30 (or filler
material)
improves PSANEXT mitigation by increasing the distance between the victim
cable and the six offending cables.
CA 02487777 2004-11-17
-6-
Referring now to Figure 5, further improvements in PSANEXT can be obtained
by positioning the twisted pairs 20 with the pairs with the longest twist lays
(indicated by the reference numeral 20') closest to the centre 36 of the
offset
cross web 12. In doing so, the distance between the pairs of twisted pairs
with
longer twist lays of adjacent cables is increased along the length of the
cable,
and is greater than that of the two shorter lays. As mentioned above, longer
lays are known to have less balance and therefore introduce more PSANEXT
in the victim cable.
Additional improvements in PSANEXT reduction may be obtained by
longitudinally randomising the twist lays and the strand lay of the core in a
gang
mode. Thus the randomisation is performed simultaneously on all the pairs in
order to maintain the internal twist lays ratios intact. This latter
requirement is
imperative for maintaining adequate internal cable NEXT parameters. One way
to effect the randomisation of the twist lays is by changing the strand lay
randomly along the length of the cable. This method affects both the strand
lay
and the twist lay, albeit to a lesser degree.
The randomisation of twist lays, the strand lay, or both serve to mitigate
PSANEXT on a victim cable by eliminating the repetition inherent in the like
pairs along the cable length.
A similar effect is obtained by randomising the lay of the round filler around
the
cable core. Such randomisation reduces the nesting between adjacent cables
and, consequently, further increase the distance between the victim cable and
the six offending cables.
A substitute to the stranded rod would be an asymmetric jacket extruded with
an especially designed rotating jacket and jacketing tools.
CA 02487777 2004-11-17
-7-
The incorporation of the stranded round rod (or filler) and also the offset
cross
web contributes to a lowering of the overall rigidity of the cable due to a
reduction in the mechanical rigidity of the assembly, thereby providing for a
more pliant or flexible cable. The same cannot be said in regards to a design
such as those disclosed in Figures 1 and 4.
In addition, the introduction of the round filler between the jacket and the
core
reduces the overall attenuation due to increased air space in the cable. In
another preferred enhancement of the above disclosure, the cable jacket is
striated in the inner surface in contact with the cable core in order to also
reduce the overall attenuation of the cable. This is achieved by the creation
of
additional air space between the cable core and the jacket.
Although the present invention has been described hereinabove by way of an
illustrative embodiment thereof, this embodiment can be modified at will
without
departing from the spirit and nature of the subject invention.