Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
TITLE: APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR OPTIMALLY RECORDING
GEOGRAPHICAL POSITION DATA
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for optimally recording or
transmitting geographical position and events. In particular the present
invention
provides apparatus to determine position, time and speed of an object such as
a vehicle
and log data in accordance with changes in pre-determined parameters.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PRIOR ART
Recording or transmitting the position (latitude, longitude and possibly
altitude) and events that occur for an object is a useful exercise in many
scenarios in
business. There are many examples of systems that today record and or transmit
positional data, but they all suffer from the same problems. They do not
correctly choose
the positions that are to be stored or transmitted, so as to maximize the
level of useful
detail on a map but at the same time minimize the number of actual positions
used to do
this. Many systems currently base their logging on an interval (eg. every 60
seconds) or a
distance (eg. every 200m). When looking at this data on a map, very often
these points
don't show any new useful additional information or, which is worse they miss
out a
significant event like a turn or a big drop in speed.
The present invention is used to optimize exactly when these pieces of
information are recorded or transmitted. This then minimizes the memory
requirements if
these points are stored, or it minimizes time or cost if the information is
transmitted. In
addition, the usefulness of the information is maximized by making sure that
any
significant events are caught, like turning a corner or a large change in
speed.
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It is an object of the invention to provide a method to optimize exactly
when positional data is recorded or transmitted to minimize the memory
requirements if
the data is stored, or minimize time or cost if the data is transmitted.
It is a further object of the invention to provide a method to optimize
exactly when positional data is recorded or transmitted to ensure that any
significant
events are captured, like a change in direction arising from turning a corner
or a large
change in speed.
It is a further object of the invention to provide apparatus to determine
positional data associated with an object, compare new positional data with
existing data
to determine when positional data is recorded or transmitted.
Thus in accordance with the present invention there is provided apparatus
for optimally recording or transmitting positional data and events of an
object, said
apparatus including input means to continuously provide positional data to a
microprocessor and a memory device to store selected positional data wherein
the
microprocessor is programmed to compare new positional data from said input
means to
previously recorded log of positional data and creates a new log if the new
positional data
differs from the previously recorded log in accordance with pre-determined
parameters.
In a preferred embodiment for use with a vehicle, the input means to
continuously
provide positional data includes a GPS antenna and GPS engine and the
positional data
provided to the microprocessor includes the exact time, position and speed of
the vehicle.
No new information is recorded if the velocity vector of the vehicle has not
changed. The
velocity vector is determined by monitoring the speed and heading of the
vehicle. If these
do not change by more than a threshold then no logs are taken. In turn, if
these elements
change rapidly then the logs should be taken more frequently. Additional
events that are
of interest are also being monitored by other input means, then these could
trigger a log
even if there were no geographical reason to do so.
In another embodiment the present invention provides a system for
optimally recording or transmitting positional data and events of an object,
said system
having a processing unit on the object, said processing unit including input
means to
continuously provide positional data to a microprocessor and a memory device
to store
2
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
selected positional data wherein the microprocessor is programmed to compares
new
positional data from said input means to previously recorded log of positional
data and
creates a new log if the new positional data differs from the previously
recorded log in
accordance with pre-determined parameters and a base station programmed with
software
to extract, display, process and analyze the recorded data.
A further aspect of the present invention provides a method for optimally
recording or transmitting positional data and events of an object to optimize
exactly when
positional data is recorded or transmitted to minimize the memory requirements
if the
data is stored, or minimize time or cost if the data is transmitted and to
ensure that any
significant events are captured by continuously providing positional data to a
microprocessor from input means, said microprocessor compares new positional
data
from said input means to previously recorded log of positional data and
creates a new log
if the new positional data differs from the previously recorded log in
accordance with
pre-determined parameters.
Further features of the invention will be described or will become apparent
in the course of the following detailed description.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
In order that the invention may be more clearly understood, the preferred
embodiment thereof will now be described in detail by way of example, with
reference
to the accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a schematic illustration of a positional chart of a prior art
system that logs at
positional data for an object at regular time or distance intervals (prior
art).
Figure 2 is a schematic illustration of one embodiment of -apparatus according
to the
present invention for optimally recording or transmitting geographical
position and
events.
Figure 3 is a schematic illustration of a positional chart using the apparatus
of Figure 2
where the positional data for an object has been optimally recorded. .... Ll~
3
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
Referring to Figure 1 a schematic illustration of a positional chart of a
prior
art system that logs at positional data for an object at regular time or
distance intervals is
shown. The actual trip for the object is designated by line 1. The system logs
positional
data at regular intervals 3,4,5 from starting point 2 to end point 6.
Connecting points 2-6,
as shown by line 7, shows the apparent route of the object. The apparent route
7 does not
accurately reflect the actual trip 1.
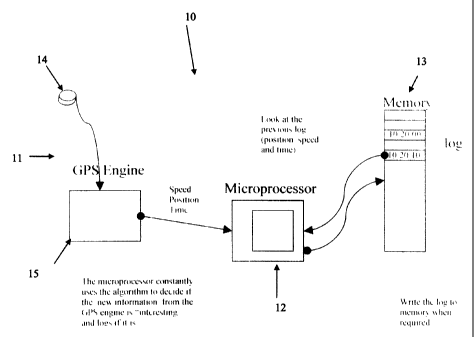
One embodiment of apparatus for optimally recording or transmitting
positional data and events of an object, preferably a vehicle, according to
the present
invention is generally indicated at 10. The apparatus 10 consists of input
means 11 to
continuously provide positional data to a microprocessor 12 and memory device
13 to
store selected positional data. The input means 11 to continuously provide
positional data
preferably includes a GPS antenna 14 and conventional GPS engine 15. The GPS
engine
15 delivers the positional data preferably the exact time, position and speed
of the object,
to microprocessor 12. Microprocessor 12 compares the new positional data to
the
previously recorded log of positional data to determine the time that has
elapsed since
that previous log, the change in speed and heading or other input triggers and
creates a
new log if the information is deemed to be "new and interesting" in accordance
with pre-
determined parameters. The pre-determined parameters preferably include harsh
braking,
excessive speed, change in heading at high speed, change in heading at low
speed,
change in speed, and time since last log. If the differences in positional
data are greater
than a pre-determined minimum, microprocessor 12 stores the positional data on
memory
device 13 for subsequent download or transmittal. If the differences in
positional data are
not greater than the pre-determined minimum, microprocessor 12 does not store
the new
positional data on memory device 13 thereby optimizing exactly when positional
data is
recorded to minimize the memory requirements if the data is stored, to
minimize the time
or cost when the data is transmitted and/or to ensure that any significant
events are
captured, like a change in direction arising from turning a corner or a large
change in
speed.
Figure 3 illustrates a schematic of a positional chart using the embodiment
of apparatus for optimally recording or transmitting positional data and
events of an
object I where the positional data for the object has been optimally recorded.
In this case
4
CA 02488030 2006-08-23
the actual trip for the object is designated by line 20. The system logs
positional data at starting
point 21, at point 22 where a change in speed is determined, point 23 where a
change of direction is
determined and end point 24. Connecting points 21-24, as shown by line 25,
shows the apparent
route of the object which reflects more accurately the actual trip 20 than the
prior art system
illustrated in FIG. 1 even though positional data is logged at fewer points.
In Figure 2 of the drawings, Microprocessor 12, in an embodiment, is
programmed to
compare and select position data to be recorded as follows:
// check valid GPS data against logging criteria
void ValidGPS(void)
{
unsigned long 1Temp;
unsigned char bDiff;
blnvalidCount = 0; /I reset invalid count
GPS.GPSData.bAux.gps_valid = 1; // valid flag
GPS.GPSData.bRecordType = GPS_RECORD;// log record type
// store valid vars
IValidDate = GPS.GPSData.IDateTime;
lValidLat.full = GPS.GPSData.lLat.full;
1ValidLong.full = GPS.GPSData.lLong.full;
// accident data check
if (GPS.GPSData.bSpeed > bMinAccSpeed)
bMemFlags.save_acc = 1;
if (bFlags3.valid_gps_restart)
{
if (bHarshBrake != 0)
{
if (bValidSpeed > GPS.GPSData.bSpeed)
{
bDiff = bValidSpeed - GPS.GPSData.bSpeed;
if (bDiffl bHarshBrake)
{
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason =
LOG_HARSH_BRAKE; // speeding start
bMemFlags.save_log = 1
}
5
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
f
}
}
bValidSpeed = GPS.GPSData.bSpeed;
bFlags3.valid_gps_restart = 1;
check log next valid flag - set on ign
if (bFlags3.log_next_valid)
{
if (bOptions0.beep_on_log 11 bFlags3.debug)
{
BUZZERON;
Delay 1 OKTCYx(250);
Delay l OKTCYx(250);
}
bFlags3.log_next_valid = 0;
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason = LOG_NEXT; // log first valid after
ign
bMemFlags.save_log = 1;
return;
}
if harsh braking occurred above then exit
if (bMemFlags.save_log)
return;
if (bOptions0.speeding)
{
// if not speeding
if (!bFlags2.speeding)
{
// and speeding occurs
if (GPS.GPSData.bSpeed > bSpeedingSpeed)
{
// start indicator and log
bFlags2.speeding = 1;
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason =
LOG_SPEEDING_START; // speeding start
bMemFlags.save_log = 1;
return;
}
}
6
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
else if speeding
else
{
and get to reset speed
if (GPS.GPSData.bSpeed <= bResetSpeed)
{
BUZZER OFF; // just in case
// stop indicator and log
bFlags2.speeding = 0;
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason =
LOG_SPEEDING_STOP; // speeding stopped
bMemFlags.save_log = 1;
return;
}
}
}
// change in heading at hi speed
if (GPS.GPSData.bSpeed > bHiDeltaHeadMinSpeed)
{
if ((GPS.GPSData.bHeading < 37) && (bLastHeading > 113))
{
bDiff = GPS.GPSData.bHeading + (150 - bLastHeading);
}
else if ((bLastHeading < 37) && (GPS.GPSData.bHeading > 113))
{
bDiff = bLastHeading + (150 - GPS.GPSData.bHeading);
}
else if (GPS.GPSData.bHeading > bLastHeading)
{
bDiff = GPS.GPSData.bHeading - bLastHeading;
}
else
{
bDiff = bLastHeading - GPS.GPSData.bHeading;
}
if (bDiff > bHiDeltaHead)
{
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason = LOG_HEADING;
change in heading
bMemFlags.save_log = 1;
return;
}
7
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
}
change in heading at low speed
else if (GPS.GPSData.bSpeed > bDeltaHeadingMinSpeed)
{
if ((GPS.GPSData.bHeading < 37) && (bLastHeading > 113))
{
bDiff = GPS.GPSData.bHeading + (150 - bLastHeading);
}
else if ((bLastHeading < 37) && (GPS.GPSData.bHeading > 113))
{
bDiff = bLastHeading + (150 - GPS.GPSData.bHeading);
}
else if (GPS.GPSData.bHeading > bLastHeading)
{
bDiff = GPS.GPSData.bHeading - bLastHeading;
}
else
{
bDiff = bLastHeading - GPS.GPSData.bHeading;
}
if (bDiff > bDeltaHeading)
{
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason = LOG_HEADING;
change in heading
bMenzFlags.save_log = 1;
return;
}
}
// change in speed
if (GPS.GPSData.bSpeed > bDeltaSpeedMinSpeed)
{
if (GPS.GPSData.bSpeed > bLastSpeed)
bDiff=GPS.GPSData.bSpeed - bLastSpeed;
else
bDiff=bLastSpeed - GPS.GPSData.bSpeed;
if (bDiff > bDeltaSpeed)
{
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason =LOG_SPEED; // change in
speed
bMemFlags.save_log = 1;
8
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
return;
}
}
time since last log
if (GPS.GPSData.lDateTime - ILastDate > iMinLogTime.full)
{
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason = LOG_TIME; time elapsed
bMemFlags.save_log = 1;
return;
}
if (bOptions0.log_valid)
{
GPS.GPSData.bLogReason = LOG_ALL; // log all valid
option set
bMemFlags.save_log = 1;
return;
In an embodiment the microprocessor 12, GPS engine 15 and optionally the
memory device 13 to store selected positional data are provided in an in-
vehicle
processing unit which is in a sealed housing. In lieu of the memory device 13
being
included in the vehicle processing unit, a separate portable memory device
(such as
memory stick, disc or key can be provided). Appropriate wiring harness would
be
provided to easily connect the in-vehicle processing unit containing the
microprocessor
12, and GPS engine 15 to the vehicle electrics, GPS antenna 14 and other
inputs or
outputs including memory device 13.
In another embodiment, the present invention provides a system which
includes a base station piece programmed with software to extract, display,
process and
analyze the recorded vehicle data. Where a portable memory device 13 is used
in
conjunction with the in-vehicle processing unit, data maybe "extracted" from
the portable
memory device or directly from the vehicle via a wireless connection such as
900MHz
radio or through a GSM/GPRS/Internet communication medium or other like method
and
transmitted to the base station.
The additional inputs can include an identification key to identify
individual drivers or vehicles or permit updating or modification of the
software in the
9
CA 02488030 2004-12-07
microprocessor unit 12 to set parameters on which the system is customized to
compare
and log data.
The base station and its software can be used as noted above to view trip
data on a map, produce activity reports including list of trips, speed
profile, auxiliary
usage and the like. In addition the software can be customized to set rules
for determining
when a log point should be recorded by monitoring data such as speed, stop
time,
auxiliary useage or vehicle position relative to prescribed zones such as
customer
locations.
Having illustrated and described a preferred embodiment of the invention
and certain possible modifications thereto, it should be apparent to those of
ordinary skill
in the art that the invention permits of further modification in arrangement
and detail. All
such modifications are covered by the scope of the invention.