Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
1
TILT AND SWIVEL CHAIR AND MECHANISM THEREFOR
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to chairs, and more particularly, to chairs capable of
tilting and
swiveling.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
An occupant of a chair, such as an office chair, does not remain stationary
throughout
the course of the day. The occupant is frequently required to change position,
whether
to move the occupant's spatial position on the floor, or to rotate to face
sideward or
rearward, or to reach for an object positioned away from the occupant.
To an extent, modern desk chairs address these mobility concerns by providing
caster
wheels on the base (allowing spatial positioning) and by providing a swivel
means
immediately below the seat part of the chair (allowing the occupant to face in
different
directions). However, chair designers have had difficulty addressing the reach
concern
without compromising the comfort or safety of the occupant.
The ability to move in place while seated is also an ergonomic issue. Certain
recent
seating improvements have allowed the occupant to tilt in various directions.
This
moderate degree of mobility is considered important to improve circulation and
accommodate the natural "restlessness" of the body, even while seated. Even in
stationary chairs, occupants tend to shift their body weight, by leaning from
side-to-side
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
2
and back-and-forth. Stress on the spine and ischia and reduced blood flow to
the legs
can result if such natural shifting movement is not accommodated in the chair.
While many chairs provide rearward tilting of the seat pan or seat back (or
both} to allow
the occupant to partially recline, tilting the entire chair at the base more
closely mimics
the natural shifting movements of the body, using the ankles as a pivot point.
The base
tilt also allows the occupant's feet to stabilize the chair. However, there is
a concern
that, in rearward or, especially, in rear-sideward tilting, the occupant may
lose control,
tilting back (and to the side) too far for the occupant to correct, which may
result in the
occupant either tipping the chair or falling off the seat, which may lead to
injury. It would
be beneficial to allow base tilting of the chair in circumscribed degrees to
reduce the
likelihood of rear-sideward spills.
Such tilting should be accommodated as an additional feature in harmony with
other
normal functions of a chair, such as swiveling and spring-based "bouncing".
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
According to a first aspect of the invention, a chair is provided comprising a
seat, a base
and an elongate structure. Preferably, the base has legs that extend to the
floor. The
base defines a longitudinal axis. Preferably, the elongate structure is
connected to the
seat at a first end, and to the base, and extends through the base to
terminate at a
second end. The elongate structure comprises a pillar assembly, an outer cover
housing a portion of the pillar assembly, a tilt ring, and a base portion. The
pillar
assembly is connected to the seat at the first end. The tilt ring preferably
engages in
part a lower portion of the outer cover. The base portion is preferably
connected to the
tilt ring and base. The base portion preferably comprises a bearing assembly.
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
3
The chair allows tilting and swivelling movements. To permit tilting, the
pillar assembly
and outer cover are preferably tiltable in any direction against the tilt ring
to tilt the seat.
When tilting force is applied to the seat, the seat is moved from an axial
orientation with
respect to the longitudinal axis of the base. When such tilting force is
relieved, the tilt
ring returns the pillar assembly and outer cover to axial orientation. To
permit swivelling
or rotating the seat, the pillar assembly, the outer cover, and the tilt ring
are preferably
swivellable at the bearing assembly.
Preferably, the base portion comprises a keyhole delimiter that defines a
keyhole. The
bottom end of the pillar assembly engages the keyhole, which limits the
degrees of tilt
permitted. The keyhole may be shaped:
~ to permit a greater rearward tilt range than frontward tilt range;
~ to permit a greater sideward tilt range than rear-sideward tilt range;
~ to permit less rear-sideward tilting than any other direction;
~ to encourage rear-sideward tilting toward rearward tilting;
~ substantially symmetrically from side-to-side and substantially
asymmetrically
from back-to-front (meaning that the sides of the keyhole are approximately
equidistant from dead-center, whereas the back and front are different
distances
from dead-center).
Preferably, the chair further comprises a clocking system. The clocking system
allows
the swivelling parts, namely the pillar assembly, the outer cover, the tilt
ring and the tilt
delimiter, to swivel together. This allows the orientation of the keyhole to
be maintained
in the course of rotating the seat.
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
' 4
The bearing assembly preferably comprises at least one race bearing,
preferably a pair
of race bearings. The first race bearing is preferably positioned in an upper
portion of
the base portion, while the second race bearing is preferably positioned in a
lower
portion of the base portion. The bearing assembly assists the swivelling of
the chair.
Preferably, the chair is capable of swivelling in tilted and untilted modes.
For tilting, the tilt ring preferably comprises a flexible ring capable of
elastic displacement
when tilting force is applied.
The chair may also have "spring" or "bounce" movement. The pillar assembly may
further comprise a spring system to allow the springing or bouncing movement
of the
seat. The spring system preferably has starting and ending positions along a
second
longitudinal axis defined by the pillar assembly and the outer cover of the
structure.
Preferably, the spring "system" comprises two elements: a cylinder and a
spring. The
cylinder may be a pneumatic cylinder. The spring may be a coil spring, such as
a
variable rate coil spring. The spring system is preferably integrated with the
pillar
assembly, which may be understood as a "spring pillar assembly".
As optional features of the chair, the seat may include a back, and the base
may include
wheels on the legs.
The foregoing are examples of certain aspects of the present invention. Many
other
embodiments are also possible and will become apparent to those skilled in the
art from
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
a review of the detailed description of certain preferred embodiments of the
present
invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FIGURES
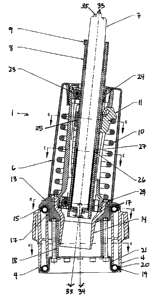
5 Fig. 1 shows an exploded view of the mechanism, according to the preferred
embodiment.
Fig. 2 shows an assembled view of the mechanism in Fig. 1, with outer cover 6
shown,
but with legs 5 truncated.
Figs. 3A-3F show assembly diagrams of the mechanism (in section) in the
preferred
order of assembly:
~ 3A: First stage assembly
~ 3B: Second stage assembly
~ 3C: Third stage assembly
~ 3D: Fourth stage assembly
~ 3E: Fifth stage assembly
~ 3F: Sixth stage assembly (completed)
Fig. 4 shows a detailed view of the base 4 and bearing components (in
section).
Fig. 5 shows a sectional view of the mechanism 1 in tilt orientation.
Fig. 6A shows a detailed view of area 32 of the cross-section shown in Fig.
7C.
Fig. 6B shows a detailed view of area 30 of the cross-section shown in Fig.
7B.
Fig. 6C shows a detailed view of area 31 of the cross-section shown in Fig.
7D.
Fig. 7A shows a cross-section through line H-H of Fig. 5, showing keyhole ring
18.
Fig. 7B shows a cross-section through line G-G of Fig. 5, showing coil spring
10 and
spring locator 11.
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
6
Fig. 7C shows a cross-section through line E-E of Fig. 5, showing central post
12
features.
Fig. 7D shows a cross-section through line B-B of Fig. 5, showing roller 23'
and roller
holder 24'.
Fig. 8A shows a front perspective view of the coil spring 10 and base 4
components.
Fig. 8B shows a sectional view of the coil spring 10 and base 4 components in
Fig. 8,
also showing roller 23'.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The invention provides a tilting and swiveling chair. The mechanism 1 is
intended for
use in a chair, especially a chair of the type commonly used in offices
(having a seat and
seat back, the seat being positioned over a column, the column terminating in
a
branched base with legs). The mechanism 1 is preferably an elongate structure,
which
takes the place of the seat column. As shown in Figs. 1 and 2, the elongate
structure
has two ends 2, 3. The first end 2 is connected to the seat, preferably by
means of a
tapered fit, and the second end 3 extends through the base 4 to terminate
slightly above
the floor. Advantageously, the legs 5 may include wheels, such as conventional
office
chair casters (not shown).
The mechanism 1 allows three basic occupant motions:
~ swiveling;
~ bouncing (i.e. longitudinal travel); and
~ tilting
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
7
The mechanism 1 is adapted to perform all of the above motions. In addition,
the
mechanism comprises means for limiting the amount of tilt permitted
(independent of
swivel). The functional aspects of the mechanism 1 are now described.
Swivel Motion
The mechanism 1 allows swiveling with respect to the base 4. A bearing ring
(such as a
race bearing) is provided to facilitate the swiveling by reducing friction
between
swivelling and non-swivelling parts of the mechanism 1. Preferably, as shown
in Fig. 4,
a pair of bearing rings 16, 20 is provided, one each at upper and lower ends
of the base
4.
The mechanism 1 swivels at the bearing rings 16, 20 while the base 4 remains
stationary. The mechanism 1 is preferably capable of swiveling in tilted (as
shown in
Fig. 5) or untilted state (as shown in Fig. 2). The bearing rings 16, 20
reduce friction to
facilitate smooth rotation of the mechanism about the axis 34 defined by the
base 4.
The mechanism 1 is preferably constructed so that the swiveling parts turn
together (at
the same rate of rotation and to the same degree). Rotation is transferred
between
adjacent parts by means of clocking and locating features. As shown in Figs.
5, 6A and
7D, a clocking bushing 26 is preferably provided between the pneumatic
cylinder 7 and
the cylinder extruded tube 8. The bushing 26 preferably has a tab-in-groove
fit with the
cylinder extruded tube 8. The bushing 26 has the function of transferring
swivel motion
to the bearing rings 16, 20.
The outer cover 6 preferably rotates with its interior parts, as shown in Fig.
5. The
cylinder extruded tube 8 threads to a predetermined stop to align the parts to
a rubber tilt
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
ring 13. Furthermore, the tilt ring 13, bottom post 14 and bearing cup 17
align with the
keyhole delimiter ring 18. As shown in Fig. 5, pneumatic cylinder T contains a
locating
feature 35 to align the seat (not shown) attached at the first end 2.
Bounce Motion
In addition to swivel motion, the mechanism 1 preferably allows "bounce"
motion along
the longitudinal axis 33 defined by the tilting parts of the mechanism 1.
Preferably, two
parts supply the bounce action: the cylinder extruded tube 8 and the coil
spring 10. The
bounce moves the seat up and down to provide increased comfort and support and
aid
spinal alignment. The longitudinal axis 33 moves in unison with the axis of
the
occupant's spine (i.e. the occupant's center of gravity moves with the chair).
This has
the effect of reducing gravitational pressure on the occupant's spine.
The cylinder extruded tube 8 preferably moves up and down within the central
post 12,
assisted by upper and lower rollers 23, 23'.
As shown in Fig. 5, the coil spring 10 is preferably acted upon by a spring
locator 11.
The coil spring 10 may be a variable rate coil spring that compresses variably
with the
occupant's weight (i.e. compression becomes progressively more difficult as
load is
applied).
In operation, the pneumatic cylinder 7, the cylinder extruded tube 8 and the
coil spring
10 are activated in series when weight (load) is applied to the seat part (not
shown).
Downward pressure on the pneumatic cylinder 7 and the cylinder extruded tube 8
causes the spring locator 11 (which is attached to the extruded tube 8 via
flange 25,
shown in detail in Fig. 6B) to compress the coil spring 10. Both the cylinder
extruded
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
9
tube 8 and the coil spring 10 act to return the chair seat to preset "normal"
height when
the seat is not under load. The outer cover 6, the base 4 and the tilt ring 13
are not
affected by the bounce.
The height of the seat can also be adjusted by extending or compressing the
pneumatic
cylinder 7 inside the tube 8. The height of the seat, set by the pneumatic
adjustment,
does not affect the bounce range of the cylinder extruded tube 8, which
operates
independently. A preferred range of bounce travel is approximately 3 inches.
Means
may optionally be provided to adjust the bounce resistance or to permit a + or
- range of
travel (not shown).
Tilting
As shown in Fig. 5, the mechanism 1 (in loaded or unloaded state) allows
tilting. At rest,
the axis 33 of the tilting parts of the mechanism 1 is substantially co-linear
with the axis
34 of the base 4. When tilt pressure is applied from the seat, certain parts
of the
mechanism tilt while the base 4 remains stationary. The cylinder 7, the tube
8, the coil
spring 10, the outer cover 6, the central post 12, and bottom post 14 all tilt
together with
their internal parts. The lower shoulders of the outer cover 6 (housing the
central post
12, cylinder 7, tube 8, and coil spring 10) and the attached bottom post 14
bear upon a
flexible tilt ring 13. The flexible ring 13 and bearing cup 17 remain
stationary with the
base 4, however the flexible material of the ring 13 elastically displaces to
accommodate
the tilting parts.
The flexible tilt ring 13 has several functions. it cushions and supports the
outer cover 6
and bottom post 14 when tilted. The ring 13 provides resistance against
tilting, and
resistance will increase depending on load. The ring 13 may be made of rubber
or
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
synthetic rubber, or similar elastic material, such as silicone. The skilled
person will
appreciate that the shore hardness of the flexible material used in the ring
can be
adjusted to modify the resistance. The ring 13 also gently restores the
tilting parts of the
mechanism 1 back into vertical alignment with the base 4 when the tilt
pressure is
5 removed. The ring 13 flexibly bonds the bottom post 14 to the bearing cup
17.
Tilt Delimiter
To control the degree of tilting, a keyhole delimiter ring 18 is preferably
provided in the
base 4 of the mechanism 1. As shown in Fig. 7A, the shape of the interior of
the keyhole
10 ring 18 is preferably slightly eccentric. The aperture of the keyhole
delimiter ring 18
preferably has a broader "Back" portion and a narrower "Front" portion.
("Front" and
"Back" refer to the occupant's facing direction. Note, however, that the
"Back" portion of
the aperture governs the occupant's forward tilt motions, while the narrower
"Front"
portion of the aperture governs the occupant's backward tilt motions.) Sloped
edges are
preferably provided between the front and back portions. The keyhole ring 18
circumscribes where the bottom post 14 (connected with the other tilting parts
of the
mechanism) may tilt. Front and front-sideward tilt movements are least
restricted (to
allow reaching motions). Rearward motions are permitted, but rear-sideward
motions
are nudged into rearward direction to permit relaxation tilt postures, while
preventing
rear-sideward spills. Preferably, the keyhole delimiter ring permits
approximately 7°
forward tilt, 10° backward tilt, 7° sideward tilt, and 5°
rear-sideward tilt.
The keyhole delimiter ring 18 preferably moves with the swiveling of the
chair, so that
the frontward orientation is maintained relative to the occupant in the seat.
The function
of the keyhole delimiter ring 18 is not affected by downward motion of the
cylinder
extruded tube 8 and coil spring 10.
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
11
Construction and Materials
Looking at Figs. 1-4, the preferred construction of the mechanism 1 will now
be
described. In particular, Figs. 3A-3F illustrate the assembly of the
mechanism, step by
step.
Beginning at Fig. 3A, the central post 12 is provided, which consists of the
main internal
support member for the mechanism 1. The central post 12 is a hollow, tapered
body
having a wide top section tapering to a narrower mid-section, broadening again
at the
bottom. The bottom section is preferably provided with a threaded exterior
portion
adapted for threaded connection to the bottom post 14, as shown in Figs. 3C
and 8B.
The central post is preferably constructed of cast aluminum.
As shown in Figs. 3A and 8B, the central post 12 houses the lower rollers 23'
in roller
holders 24'. There are preferably 3 rollers arranged as shown in Fig. 7D.
Upper rollers
23 in roller holders 24 are also housed in the central post 12, as shown in
Fig. 3B. The
upper and lower rollers 23, 23' are preferably constructed of a roller tube
positioned over
a dowel pin 28 as shown in Fig. 6C.
As shown in Fig. 5, the clocking bushing finer 27 is snapped on to the
clocking bushing
26 on the pneumatic cylinder 7. This assembly is next installed in the
cylinder extruded
tube 8 (sandwiching upper bushing 9, which is used to guide the cylinder 7 and
reduce
friction). The flange 25 is slid on the tube 8 and rotated 180° to lock
the flange 25 in
place. The tube 8 is positioned within the cavity defined in the central post
12 and
supported within rollers 23. The cylinder 7 and tube 8 extend from the top of
the
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
12
mechanism 1 to a point within the base 4. The spring locators 11 are attached
to flange
25.
As shown in Fig. 3C, the central post 12 is threadably connected to a
permanently-
bonded assembly consisting of the flexible tilt ring 13 and bottom post 14 and
bearing
cup 17. As shown in Fig. 8A, a set screw 29 is screwed to the central post 12
to prevent
unthreading of the threaded parts. As shown in Fig. 3D, the coil spring 10
sits atop the
top part of the bottom post 14.
As shown in Fig. 5, the bearing cups 17, 21 sandwich the keyhole delimiter
ring 18. The
bearings 16, 20 are preloaded due to the height of the keyhole delimiter 18.
This
sandwich has the effect of reducing the side-to-side "play", while maintaining
the ability
to swivel independently of the base 4.
The keyhole ring 18 is preferably constructed of aluminum. The sandwich is
preferably
held together using socket head cap screws 22 (also shown in Figs. 1 and 5).
An outer cover 6 caps the coil spring 10 and central post 12, as shown in Fig.
3F. The
outer cover 6 is preferably of translucent polypropylene, to allow the coil
spring to be
visible by the occupant. The cover 6 is preferably attached using molded snap
clips.
The base 4 preferably includes branched legs 5 as shown in Fig. 1. Wheels may
be
provided (not shown).
CA 02488519 2004-11-25
13
The foregoing description illustrates only certain preferred embodiments of
the invention.
The invention is not limited to the foregoing examples. That is, persons
skilled in the art
will appreciate and understand that modifications and variations are, or will
be, possible
to utilize and carry out the teachings of the invention described herein.
Accordingly, all
suitable modifications, variations and equivalents may be resorted to, and
such
modifications, variations and equivalents are intended to fall within the
scope of the
invention as described and within the scope of the claims.