Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
AN INFORMATION FILLING STATION FACILITATING WIRELESS ACCESS
OF DATA CONTENT OR EVENT-RELATED INFORMATION VIA A
PORTABLE DEVICE OR OTHER COMPUTER-BASED DEVICES AT PRE-
DEFINED LOCATIONS
PRIORITY INFORMATION
This application claims priority from U.S. serial number 10/180,521 filed June
27,
2002 entitled "An Information Filling Station Facilitating Wireless Transfer
of Data
Content to a Portable Device or Other Pre-Defined Locations" and U.S. serial
number
10/180,516 filed June 27, 2002 entitled "A System and Method for Wirelessly
Transacting
Access to a Set of Events and Associated Digital Content/Products", which are
hereby
incorporated by reference.
TECHNICAL FIELD
The present invention relates generally to the field of digital content
providers.
More specifically, the present invention is related to wireless access of data
content or
event-related information via a portable device or other computer-based
devices at pre-
defined locations.
BACKGROUND ART
Websites such as Fandango.comTM and MovieTickets.comTM allow users to view
movie trailers, movie reviews, and movie schedules. Users are also able to
purchase
tickets online at these websites, wherein the purchased tickets can be picked
up at the box
office prior to the movie by using a form of ID (such as the credit card that
was used to
make the reservation) or a transaction confirmation number.
Figure 1 illustrates a general prior art method 100 associated with purchasing
movie tickets at a location other than the movie theater. The two common
scenarios
associated with such prior art methods include allowing users to purchase
tickets either
over the Internet or over a telephone. In the first scenario, users access a
website (such as
Fandango.com or MovieTickets.com) 102 over a network (such as the Internet) to
request
movie related information. In the second scenario, users access a
communication center
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
2
over a telephone and access movie related information 104. Steps 106 through
112 of
Figure 1 illustrate steps common to both scenarios.
In step 106, users identify a theater of interest, a movie of interest playing
in the
theater of interest, and a convenient showtime for the movie of interest.
Next, in step 108,
users select a method of payment (usually a charge card) and perform a
financial
transaction for purchasing tickets for the movie of interest. Upon successful
completion of
the financial transaction, a confirmation number and instructions regarding
how and where
to collect the tickets are provided to the user.
In one instance, users are instructed to collect the tickets at a kiosk
located at the
movie theater of interest. Upon arrival at the kiosk, the user is either
instructed to insert
the charge card 108 that was used to make the financial transaction for
purchasing the
tickets or is instructed to enter the confirmation number. Upon
authentication, the kiosk
prints out the tickets for the movie of interest I10, which are then collected
by the user.
Although the above-mentioned first scenario is convenient for ordering movie
tickets, it requires users to have access to a computer that is capable of
being connected to
a network such as the Internet (via a network interface device communicating
with a
hub/router or a modem). The second scenario, on the other hand, restricts
users to use an
aural interface implemented in conjunction with a telephone.
One of the problems associated with the first scenario is the necessity of a
router/hub or a telephone line to be physically nearby, so that a physical
connection can be
made. One alternative in prior art communication systems 'has been to use
wireless
network devices (such as a wireless network interface card) that can access
the router/hub
without a physical connection.
One popular method of implementing a wireless connection is based upon the
IEEE
802.11 standard. 802.11 refers to a family of specifications developed by the
Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for wireless local area network
(LAN)
technology. 802.11 specifies an over-the-air interface between a wireless
client and a base
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
3
station or between two wireless clients. There are several specifications in
the 802.11
family, some of which are described below:
~ 802.11 - applies to wireless LANs providing 1 or 2 Mbps transmission in
the 2.4 GHz band using either frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
or direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS).
~ 802.11a - an extension to 802.11 that applies to wireless local area
networks (LANs) and provides up to 54 Mbps in the 5 GHz band. 802.11a
uses an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing encoding scheme rather
than FHSS or DSSS.
~ 802.1 lb - This is also referred to as 802.11 High rate or Wi-Fi (for
wireless
fidelity) and was formed as a ratification to the original 802.11 standard,
allowing wireless functionality comparable to the Ethernet. This is an
extension to 802.11 that applies to wireless LANs and provides 11 Mbps
transmission (with fallback to 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps) in the 2.4 GHz band.
Transmission in the 802.1 lb standard is accomplished via DSSS.
~ 802.1 lg - applies to wireless LANs and provides 20+ Mbps in the 2.4 GHz
band.
The most popular of the above standards is the 802.1 lb. One problem
associated
with this standard is that the signal strength fades away as a function of
distance and, as a
result, the data rate falls back to 5.5, 2, or 1 Mbps, depending on the
distance from the Wi-
Fi router/hub and the strength of the signal.
Returning to the discussion of Figure l, a computer equipped with a wireless
network interface card can be conveniently used to order movie tickets, but
the computer
has to operate within a certain radius for it to be functional. Thus, if one
were outside their
residence or outside the optimal radius, they would have to use a telephone,
as described in
the second scenario, to order the movie tickets. But, as mentioned earlier,
this is a pure
aural interface which lacks the ease of a visual interface. Furthermore, prior
art systems
implementing functionality similar to that of Figure 1 do not offer content
that can be
directly downloaded wirelessly onto a portable device not operatively linked
to the
Internet.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
4
Data content providers presently push a myriad of data content (such as e-
mail, data
files, multimedia files, etc.) to various portable devices (such as personal
computers,
laptops, personal digital assistant (PDA), etc.). Some of the limitations
associated with
prior art systems in the transfer of such data content include limitations in
the size of the
data content to be transferred and limitations associated with the
transmission rate as
defined by the networks over which the data content is to be transferred.
Figure 2 illustrates another prior art scenario 200 wherein one or more data
content
providers 202, 204, 206 push data content over a network 208 onto a proxy
server 210
which, in turn, interacts with a portable device over a narrow bandwidth
network 212.
Data content providers include various services such as accessing: e-mail,
data files,
multimedia files, and other miscellaneous information services. Users access
such data
content via various portable devices, including: wireless phones 214, PDA 216,
pagers
218, etc. The narrow bandwidth networks 212 over which the end device and the
proxy
server interact include broadcast networks, cellular networks, and satellite-
based networks.
Although some networks such as some satellite-based networks are promoted as
wide
bandwidth networks, it should be noted that only a portion of the bandwidth
associated
with such networks is allocated for the purposes of personalized data content
transmission,
thereby limiting the size of data content that can be transferred in a given
time period.
It should be noted that, for simplification purposes, only one network cloud
is
shown facilitating the interaction between the various content providers and
the proxy
server (network 208) and between the proxy server and the portable device
(network 212),
but such interactions can occur over one or more networks.
As mentioned earlier, a customer's access to such data content today is
limited by
the information content (size) and network speed (rate) by which the
information can be
delivered to the device. Certain services are typically only one-way, i.e.,
radio broadcast
and satellite services. On the other hand, e-mail and data file delivery,
while two-way, is
limited to very narrow bandwidths, which restrict the type and quantity of
information that
can be delivered to the customer's portable device.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
Thus, the prior art systems fail to provide for a fast and efficient way to
facilitate
the interaction between the content providers and the portable devices.
Additionally, the
prior ant fails to disclose a system wherein content providers push data
content over a
broadband network to information filling stations at various physical
locations accessible
5 by portable devices (associated with mobile users) that wirelessly transact,
access, and
receive data content from the information filling station.
The following references provide a general description of digital content
providers
that allow digital content to be downloaded.
The U.S. patent to Schulhof et al. (5,572,442), assigned to Information
Highway Media Corporation, provides a system for distributing subscription and
on-
demand audio programming. Disclosed is a system for downloading digital audio
data
onto a portable audio storage medium and listening to it at a desired time.
The portable
audio storage medium is capable of high-speed data transfer that can be
downloaded from
such systems as a television cable system, satellite, or fiber optic telephone
linlc.
The published U.S. patent application to Tsukamoto (2001/0013120A1),
assigned to NEC Corporation, provides for a digital contents rental system.
Disclosed is a
process that consists of a customer visiting the store with a portable storage
unit, such as a
magnetic disk. The user may then choose from a plurality of digital content
and download
desired content onto his/her storage medium.
The published U.S. patent application to Ekkel (2001/0037360A1), assigned
to I~oninklijke Philips Electronics N.V., provides for a data service at a
transit terminal.
Disclosed is a system that provides information content to a user at a
repository. While a
consumer is traveling, a data service offers information availability that can
be downloaded
by the user to a storage device and viewed offline. Using a mobile storage
medium, such
as a memory card or a magnetic disk, the individual may use the highly
customizable
service to download electronic information content from a host repository or
server.
The published U.S. patent application to Sibley (2001/0039662A1), assigned to
Hughes Electronics Corporation, provides for a digital over-the-air
communication system
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
6
for use with digital terrestrial broadcasting system. Disclosed is a system
for distributing
electrical content using digital over-the-air communication. The process
consists of a
network operation center uplinking electronic content packages to a satellite,
a broadcast
center receiving the electronic content from the satellite, and a user device
receiving the
digital content via a digital channel generated by the broadcast center.
The published U.S. patent application to Ramachandran et al.
(2001/0044747A1), assigned to Diebold, Incorporated, provides a system and
method for
dispensing digital information from an automated transaction machine.
Disclosed is a
service that offers digital content information to a user through an automated
transaction
machine.
Whatever the precise merits, features, and advantages of the above-cited
references,
none of them achieve or fulfills the benefits of the present invention.
DISCLOSURE OF INVENTION
The present invention provides for one or more information filling stations
(IFS)
located at one or more physical locations accessible by mobile users who
wirelessly
communicate with the IFS via a portable device that is in close proximity to
the IFS. Users
are able to wirelessly communicate with the IFS and request diverse data
content such as:
multimedia files, WWW data, real-time and interactive games, e-mail (with or
without
attachments), electronic newspapers, news and sports information, traffic and
weather
information, e-books, interactive messaging, and/or data files. Additionally,
the portable
devices are also capable of facilitating point-of sale purchases and
electronic funds
transfers. Furthermore, users are able to use their portable device (which is
either a stand-
alone device or a device integrated with an automobile) to selectively
transfer data content
onto various locations such as, but not limited to, a portable device, a PC
located at home,
a PC located at work, etc. The IFS performs such data content transfers only
after
authenticating users (via a smart card or a virtual private networlc setup)
via their portable
device.
Upon such authentication, the IFS receives one or more content requests and
identifies any content in such requests that is protected (e.g., copyrighted
materials) using,
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
7
for example, Digital Rights Management (DRM) models. Next, the availability
and
pricing information of the requested content (including any fees payable to
content
providers with respect to DRM-protected content) is extracted from one or more
databases
and transmitted onto the portable device, wherein it is rendered.
Optionally, one or more advertisements are also transmitted via the IFS for
promoting one or more products, wherein the advertisements either provide for
or indicate
a location for accessing pricing information related to the advertised
products.
Subsequently, instructions identifying content of interest, any products of
interest, and
routing instructions (identifying locations for selectively transferring each
of the content of
interest and any of the products of interest) are received by the IFS. Upon
reception of
these instructions, the IFS identifies pricing associated with the products of
interest and
performs a financial transaction based upon any pricing information associated
with the
content of interest and the products of interest. Lastly, a payment
arrangement is made
with the content providers for any identified fees that are payable with
respect to the
protected content, and the IFS selectively sends to the identified locations
corresponding
content of interest and any products of interest.
In the preferred embodiment, the mobile device is either carried in or
integrated
with an automobile, and the wireless communication between the mobile device
and the
IFS is based upon the IEEE 802.1 Ib protocol.
In one specific embodiment, the system and method of the present invention
provide for an architecture comprising an information filling station (IFS)
and a portable
device interacting with the IFS over a wireless network. One or more content
providers are
able to push data content related to events (such as movies) over a network
onto the IFS
which, in turn, transmits any requested event related content to the portable
computer-
based device. Furthermore, the portable device is able to wirelessly interact
with the IFS
to perform financial transactions for purchasing tickets (direct purchase
tickets or via
auction-based ticket purchase), digital entertainment content of interest, and
event related
products.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
g
In another embodiment, the IFS is placed at or near a theater, theater lobby
or ticlcet
stand. Alternatively, many of the functions described herein can also be
implemented in a
hub at a location remote from a theater such as a generic information filling
station.
The portable device can be any of, but not limited to, the following: a
laptop, a
pen-based computer, a personal digital assistant (PDA), a wireless phone
capable of
displaying digital entertainment content, or a pager capable of displaying
digital
entertainment content. The data content can be any of, but not limited to, the
following:
trailers, reviews (text, audio, and video), showtimes, ticket availability,
prices, director's
comments, text of dialogue, auction information related to tickets for movies
of interest,
pushed advertisements, movie related products, digital movie content, movie
soundtrack,
food/snack information, feedback information, or chatroom related information.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
Figure 1 illustrates a prior art method associated with purchasing movie
tickets at a
location other than the movie theater.
Figure 2 illustrates a prior art scenario wherein one or more data content
providers
push data content onto one or more portable devices via a proxy server.
Figure 3 illustrates a general architecture associated with the preferred
embodiment
of the present invention.
Figure 4 illustrates various categories of service that the IFS of the present
invention is capable of delivering.
Figure 5 illustrates various categories of service offered under the service
delivery
category.
Figure 6 illustrates various information services that are deliverable by the
IFS of
the present invention.
Figure 7 illustrates various telematic services associated with the present
invention.
Figure S illustrates the various advertising and promotional services
associated with
the present invention.
Figure 9 illustrates various modes of authentication of the portable device.
Figure 10 illustrates vehicle or device authentication via a virtual private
networlc
(VPN).
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
9
Figures I la-l lb collectively illustrate the present invention's method for
selectively routing data content based upon a wireless interaction between a
portable
device and an information filling station (IFS).
Figures 12a and 12b collectively illustrate the interaction between various
wireless
clients and the IFS core network.
Figure 13 illustrates a non-exhaustive group of the various interactions that
are
possible between a portable computer-based device and the information filling
station
(IFS).
Figure 14 illustrates system interaction in the preferred embodiment between
the
IFS and the portable device.
Figure 15 illustrates a method of the present invention as implemented between
an
IFS and a portable device.
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT INVENTION
While this invention is illustrated and described in a preferred embodiment,
the
invention may be produced in many different configurations, forms, and
materials. There
is depicted in the drawings, and will herein be described in detail, a
preferred embodiment
of the invention, with the understanding that the present disclosure is to be
considered as
an exemplification of the principles of the invention and the associated
functional
specifications for its construction and is not intended to limit the invention
to the
embodiment illustrated. Those skilled in the art will envision many other
possible
variations within the scope of the present invention.
Throughout the specification, the present invention is described with a
specific
example of a portable device in an automobile, but it should be noted
modifications, such
as the integration of the portable device and the vehicle are envisioned, and
such
modifications should not be used to limit the scope of the present invention.
It should also
be noted that for the purposes of description, specific examples of venues and
events (i.e.,
theaters for venues and movies for events) are used, but one skilled in the
art can extend
this to encompass other venues and events without departing from the scope of
the present
invention.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
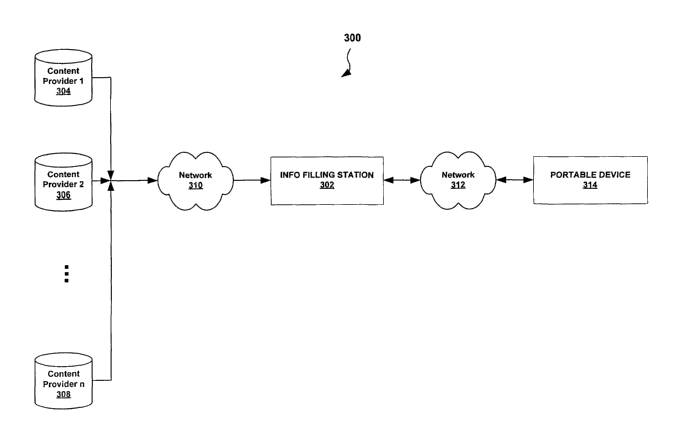
Figure 3 illustrates a general architecture 300 associated with the present
invention.
In this example, a user in an automobile equipped with a portable device
(stand-alone or
integrated) 314 is able to drive up to one of many information filling
stations {IFSs) 302
that are physically located at various accessible locations. Once in close
proximity to an
S IFS 302, users can authenticate themselves (via a security identity module
(SIM) card or a
virtual private network setup) to perform various functions via their portable
device.
For example, users can wirelessly send one or more requests for data content
to the
IFS 302 which, upon reception of such requests, identifies if any of the
requested data
10 content is protected via Digital Rights Management (DRM). The IFS 302
interacts with
one or more data content providers 304, 306, 308 to extract the requested data
content,
Next, the availability and pricing information of the requested content
(including any
additional fees identified with content protected via DRM) is extracted from
the content
providers 304, 306, 308 and transmitted onto the portable device 314, wherein
it is
1 S rendered.
One or more broadband networks 310 facilitate the transfer of data between the
data content providers 304, 306, 308 and IFS 302. The broadband networks used
in
conjunction with the present invention include local area networks (LAN), wide
area
networks (WAN), or the Internet. In one embodiment, data is transferred
between the
content providers 304, 306, 308 and the IFS 302 via a digital synchronous line
(DSL) link.
The data content that can be transferred includes, but is not limited to,
multimedia files,
WWW data, real-time and interactive games, e-mail (with or without
attachments),
electronic newspapers, news arid sports information, traffic and weather
information, e-
2S books, interactive messaging, and data files. Thus, the system of the
present invention
provides access to an entire spectrum of diverse data content and uniquely
solves the
information content size and network speed (data rate) limitation inherent in
prior art
cellular, terrestrial, and satellite-based systems.
By using the IFS model of the present invention, customers are offered
improved
access to broadband networks without limitations in the size or data rate of
information
content to be transferred. Furthermore, the present invention provides
convenient data
access, as the IFS ports may be located at any public or privately accessible
location
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
11
including, but not limited to: gas stations, shopping malls, schools,
airports, convenience
stores, truck stops, hospitals, libraries, pay telephone locations, or any
other location in
close proximity of the vehicle. The IFS provides wireless high-speed access to
vehicles or
handheld devices wherein, in the preferred embodiment, the wireless access is
based upon
the 802.11b protocol. It should, however, be noted that one skilled in the art
can envision
using other wireless protocols including the TEEE 802.11 a or IEEE 802.11 g
protocols.
Thus, such limitations in the protocols used should not be used to limit the
scope of the
present invention.
In one embodiment, a portable device 314 wirelessly interacts with the IFS
1202
and performs financial transactions to purchase tickets, digital event related
content, and
event related products. More specifically, in Figure 3, the content providers
304, 306, and
308 push event related content such as, but not limited to: event information,
event
information, showtimes, ticket pricing, event reviews, food/snack availability
at various
venues hosting such events, auction information related to event tickets,
advertisements,
event previews, digital event content, and digital event related content
(e.g., soundtraclc of
a movie, text of dialog of a movie, and/or directors comments related to a
movie).
As mentioned above, the portable device 314 is a computer-based device that is
able to communicate wirelessly with the IFS 302 to request the above described
event
related content over a wireless network 312. In the preferred embodiment, the
wireless
communications are based upon the 802.1 lb standard.
Thus, in this embodiment, users interested in purchasing tickets to one or
more
events of interest (e.g., one or more movies) use their portable computer-
based device 314
and inquire the TFS 302 regarding one or more venues of interest (e.g., one or
more
theatres of interest) where the events of interest are scheduled to occur. The
IFS 302
extracts information (e.g., including movies playing in the theaters of
interest, ticlcet
availability of movies, andlor pricing of movies) regarding requested venues
of interest and
wirelessly transmits such information onto the portable device 314, where it
is rendered.
Users are then able to select one or more events of interest and, based upon
the availability
of tickets, conduct financial transactions to purchase tickets for the events
of interest.
Furthermore, users are able to receive event related information and digital
content directly
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
12
onto their portable device 314, where it is stored and rendered upon request
(or, optionally,
the digital content is sent to a physical address). The portable device 314
can then be used
at the venue to perfoum wireless authentication to obtain the tickets fox the
event of
interest. It should be noted that the IFS 302 can be placed at or near a
venue, venue lobby,
or ticket stand. Alternatively, many of the functions described herein can be
implemented
in an IFS at a location remote from a venue, such as a generic information
filling station.
Figure 4 illustrates various categories of service that the IFS of the present
invention is capable of delivering. The various IFS services can be
categorized as: 1)
service delivery, 2) authentication, and 3) discontinuous downloading.
1. Service Delivery
Figure 5 illustrates the various categories of service offered under the
service
delivery category. This includes: information service delivery 504, telematic
services 506,
and advertising and promotional services 508.
a. Information Services Delivery. Figure 6 illustrates various information
services 602 that are deliverable by the IFS. Information services delivered
between the IFS and a portable device (handheld or integrated within an
automobile) include, but are not limited to:
~ data files of various formats 604;
~ rental or purchase multimedia files (e.g., audio files, video files,
etc.) 606. Thus, for example, appropriate Digital Rights
Management (DRM) copyrighted MP3 audio files can be
accessed and delivered to authorized customers, thereby
providing a distribution channel for record companies.;
~ World Wide Web (WWW) access 608 allowing a user to access
the Internet via the IFS;
~ rental or purchase of a full-length movie at movie rental outlets
610 wherein an IFS is located outside a movie rental place and a
transaction can be performed via a portable device to digitally
rent a movie. .The digital content associated with the movie can
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
13
be either wirelessly transferred onto a portable device or be
routed to a device at a remote location, such as home or office.
Thus, the IFS concept allows users to drive up to an IFS and
download digital movies via a wireless port (or such digital
content can be optionally routed to other locations). In the
preferred embodiment, the format of the digital content related to
movies is MPEG4 and appropriate DRM processing is
performed before transferring such content.;
~ interactive games 612 (real-time interactive games 614 or
IO downloadable games 616);
~ access to e-mail 618 (plain text e-mail 620 or e-mail with
attachments 622);
~ access to electronic newspapers for download 624;
~ access to information 626 such as, but not limited to: news
headlines 628, sports news 630, traffic news 632, and weather
information 634;
~ in one embodiment, the traffic 632 and weather 634 information
also include alternative routing directions 636;
~ electronic book delivery 638; and/or
~ interactive messaging 640.
b. Telematic Services: Figure 7 illustrates the various telematic services
associated with the present invention. Telematic services 702 that are
delivered between the IFS and a portable device (stand-alone or integrated
with an automobile) include, but are not limited to:
~ point-of sale (POS) transactions (such as purchasing gasoline
and/or food at convenience stores) 704;
~ purchase of lottery tickets 706;
~ electronic funds transfers 708 (wherein users access financial
institutions via their portable devices to provide instructions
regarding electronic transfer of funds); or
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
14
~ electronic directory services 710 (wherein users are able to use
their portable devices to search or query electronic directories).
c. Advertising and Promotion Services: Figure 8 illustrates the various
advertising and promotional services associated with the present invention.
Advertisement and promotional services delivered between the IFS and a
vehicle mounted or handheld device include, but are not limited to:
~ "Push" advertising for restaurants, lodging, gasoline purchasing,
and entertainment within close proximity of an IFS 804;
~ promotional deals from businesses in close proximity to an IFS,
i.e., a free car wash or food with gasoline fill-up 806; and/or
~ "Push" coupons for product promotions 808.
2. Authentication
Figure 9 illustrates various modes of authentication associated with the
present
invention. The IFS supports individual vehicle or device authentication
through:
~ SIM card capabilities 904;
~ a virtual private network (VPN) 906; or
~ Digital Rights Management based (DRM-based) authentication
to ensure content security and reduce pirating of copyrighted
material 908.
Figure 10 illustrates a simple vehicle or device authentication based on a VPN
setting. VPN is a network that is constructed by using public wires to connect
nodes. For
example, there are a number of systems that enable one to create networks
using the
Internet as the medium for transporting data. These systems use encryption and
other
security mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users can access the
network and that
data cannot be intercepted.
In this setting, an authenticating server 1002 and an IFS 1008 are part of a
VPN
represented by the solid line in Figure 10. It should be noted that other
computers (such as
1003, 1005, 1006, 1007, and 1009) can also be connected to the service
provider backbone
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
routers 1004 and 1006, but they do not form a part of the virtual private
network. Thus, an
IFS wirelessly interacting with an automobile or mobile device is able perform
authentication over such a VPN.
5 3. Discontinuous Downloading
The IFS supports discontinuous downloading, which provides a cohesive download
of large files (movies, music, or files) without having to remain at an IFS
port for long
periods of time. The IFS supports redirected downloads by allowing users to
selectively
route information services or content to other locations such as home or
office.
Figures lla-llb collectively illustrate the present invention's method 1100
for
selectively routing data content based upon wireless interaction between a
portable device
and an information filling station (IFS). In step 1102, a portable device
(either a stand
alone device or a device integrated with an automobile) is authenticated, and
in step 1104,
one or more content requests are received by the IFS. Next, in step 1106,
information is
extracted from one or more content provider databases regarding availability
of each of
said requested content and information identifying which of said content
requests are
associated with protected content. Additionally, in step 1108, a price (if
available - as
some items may be available free of charge) associated with each of the
available
requested content is identified, wherein the price includes any fees that are
payable with
respect to said protected content. Furthermore, in step 1110 information
regarding
availability and any identified prices associated with the requested content
is transmitted
from the IFS to the portable device.
In step 1112, instructions are received from the portable device identifying
one or
more content of interest and routing instructions identifying one or more
locations for
selectively transferring each of the content of interest. Next, in step IlI4,
a financial
transaction is performed based upon any pricing information associated with
said content
of interest, and upon successful completion of the financial transaction: a)
one or more
content providers are paid the identified fees that are payable with respect
to said protected
content 1116; and b) corresponding content of interest is selectively sent to
the one or more
identified locations 1118.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
16
Optionally, one or more advertisements promoting one or more products, are
wirelessly transmitted from the IFS to the portable device wherein it is
rendered. These
advertisements either providing for, or indicating, a location for accessing
pricing
information related to the products. Furthermore, in this scenario, additional
instructions
are received from the portable device identifying any products of interest and
one or more
locations for selectively routing each of said products of interest. Next,
pricing (if
available) associated with said products of interest are identified and a
financial transaction
is performed based upon any pricing information associated with said products
of interest.
Upon successful completion of the financial transaction, the IFS aids in
selectively sending
the identified products of interest to their corresponding identified
locations.
It should be noted that the content requests as described in the above method
is for
any of, or a combination of, the following content: data files, rental of
multimedia content,
purchase of multimedia content, WWW data content, rental of digital movie
content,
purchase of digital movie content, real-time games, interactive games, e-mail
with
attachments, electronic newspapers, news information, sports information,
traffic
information, electronic books, or interactive messaging. Additionally, the
wireless
interaction in the preferred embodiment is based upon the IEEE 802.1 lb
wireless protocol
and the preferred format for transfer of digital movie content is the MPEG4
format.
Furthermore, the method described in Figures lla-llb is not restricted to just
requests for information service content, but can include requests for
telernatic services. In
this scenario, the IFS receives one more requests for telematic services from
said portable
device and the IFS then identifies, if available, a price associated with the
requested
telernatic services. Next, a financial transaction is performed based upon any
identified
price associated with the requested telematic services. Lastly, upon
successful completion
of the financial transaction, the IFS either performs or schedules the
requested telematic
services. Examples of telematic services that can be requested include any of,
or a
combination of the following requests: requests for point of sale
transactions, request to
purchase lottery tickets, requests for electronic transfer of funds, or
request for electronic
directory services. An example of a specific implementation of the present
invention to
purchase digital content is now provided.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
17
EXAMPLE
In this example, a consumer with a portable computer-based device walks into a
store and wirelessly connects to the store's local area network (LAN). Next,
the consumer
browses the products in the store and identifies a product of interest, such
as an audio CD
S (or a DVD). Next, the consumer scans the barcode associated with the audio
CD (or a
DVD) using the portable computer-based device. Then, the consumer is given the
option
of sampling the content (either in part or its entirety) of the audio CD (or
the DVD) for a
limited number of times (e.g., the tracks can be listened to twice in its
entirety or a clip of
the movie can be watched twice). Based on the sampled content, consumers are
able to
decide if they are interested in purchasing a copy of the CD or DVD (either in
a digital
form or on a tangible medium such as a CD or DVD sent to a physical location).
Additionally, users are also given the option of downloading such content with
an
expiration date. For example, a CD or DVD can be purchased as a 3-day rental
or a 3-day
on demand download. In the event the consumer is interested in the digital
form of the
product of interest, a process for downloading the digital content is started.
It should be noted that the consumer does not have to be at the store after a
decision
is made to download (to the portable computer-based device or another physical
location
such as home or office). In the event the content is to be downloaded to the
portable
computer-based device and if consumers are no longer connected to the store's
LAN, they
may be required to connect to another network to continue the download process
for an
additional charge, or alternatively, they can pull up at one of the many
information filling
stations to complete the download.
Although specific examples of products of interest (e.g., CD's and DVD's) are
provided, one skilled in the art can envision purchasing other products, and
hence should
not use the type of product to limit the scope of the present invention.
Thus, the present invention allows customers who are mobile to access
broadband
network services without ties to broadband wired connections in homes or
offices.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
18
Figures 12a and 12b collectively illustrate the interaction between various
wireless
clients and the IFS core network. Figure 12a illustrates various examples of
the portable
devices that can be used in conjunction with the present invention. The
portable device
can be any of, but not limited to: a laptop 1202, a pen-based computer (e.g.,
a tablet PC)
1204, a personal digital assistant (PDA) 1206, a wireless phone 1208 with a
display and
capable of bidirectional wireless communication, or a pager 1210 with a
display and
capable of bidirectional wireless communication.
It should be noted that, although specific examples of portable computer-based
devices are shown to best illustrate the functionality of the invention, one
skilled in the art
can envision other current and future portable computer-based devices that can
be used
without departing from the scope of the present invention. Furthermore, 12a
shows, for the
purposes of simplicity, one network cloud (1212) facilitating communication
between the
IFS and the content provider and between the IFS and the portable computer-
based devices
(I212). Thus, one skilled in the art can envision using more than one type of
network (e.g.,
LAN, WAN, or the Internet) to facilitate this communication and therefore
should not use
this to limit the scope of the present invention.
Figure 12b illustrates how the portable devices shown in Figure 13a interact
with
the IFS core network 1213. The IFS core network 1213 comprises one or more
inforniation servers 1214 and an access router 1216 that is linked with a
plurality of
wireless ports 1218 distributed at various physical locations. Content
providers transmit
various forms of data (e.g., multimedia data) to one or more information
servers 1214
wherein the content providers are able to refresh stored content and associate
digital rights
management with the stored content. The information servers 1214 can either be
local or
be distributed across a network and are capable of storing and transmitting
data such as
multimedia data (e.g., mp3 audio files, video files in MPEG4 format). The
access router
1216 provides authentication, billing (performed via a billing system and a
customer
database), and element management. The access router 1216 and information
servers 1214
are supported by separate element management systems. The IFS core network
1213 is
supported by the operator's existing or modified tier 2 network management
system where
such interfaces between the access muter 1216, information servers 1214, and
IFS core
network 1213 are linked through standard SNMP or CORBA complainant interfaces.
As
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
19
mentioned above, the access router 1216 provides authentication and billing
information,
the content servers 1214 provide element management system functions providing
but not
limited to content management, digital rights management and accounting,
traffic statistics,
and storage capabilities. The information servers 1214 are linked with the
access router
1216 via a transportation link such as, but not limited to, an Ethernet link,
a SONET link,
or a DS3 link. The access router, in turn, is linked with wireless ports via a
communication
link such as, but not limited to, an Ethernet link, a DS3/DS 1 link, or a DSL
link.
Furthermore, the access router 1216 is linked with one or more wireless access
ports
located 1218 at various locations (e.g., payphone or other services with
access to DSL, Tl,
or Ethernet services). These wireless access ports 1218 (e.g., IEEE 802.11a,
802.1 lb, or
802.11g) provide a link between wireless clients (e.g., laptops, palmtops,
PDAs, mobile
telephones, etc.) 1220 and the access router 1216 (which in turn provides such
clients with
a link to data located in information servers 1214).
Figure 13 illustrates a non-exhaustive group of the various interactions that
are
possible between a portable Computer-based device and the IFS 1302. As
mentioned
earlier, event information such as movie information 1304 can be accessed from
the IFS
1302 in a wireless manner by the portable device. In the preferred embodiment,
data
exchange is facilitated between the IFS 1302 and a portable device via an
802.11b
protocol. The various types of data that can be exchanged include, but are not
limited to,
movie information 1304, auction related information 1306, advertisements 1308,
digital
movie content 1310, food/snack information 1312, feedback 1314, and chatroom
related
information 1316.
Movie related information 1304 includes movie trailers 1318 (in various
digital
formats); reviews 1320 (that can be any of the following formats: text 1334,
audio 1335, or
video 1336); showtimes 1322, indicating various showtimes associated with
movies
playing at one or more theaters of interest; ticket availability information
1324, indicating
the availability of tickets for one or more movies of interest; price
information 1326,
indicating price per ticket for one or more movies of interest; and
supplemental
information, such as, but not limited to, director's comments 1338 or text of
dialogue 1340
associated with one or more movies of interest. Additionally, in an extended
embodiment,
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
the dialogue text 1340 is presented with a rewind feature that allows users to
scroll back to
see text for an earlier dialogue.
Auction related information 1306 can be accessed to view the availability of
tickets in
5 one or more auctions for one or more movies of interest. Alternatively, a
portable device
can post a previously purchased ticket for sale, transfer, or exchange via an
auction. Thus,
users are able to auction or reverse auction empty seats to a movie, or even
inform users as
to real-time price reductions based on over capacity. It should be noted that
over capacity
is determined in the theater ticket system separate from the IFS, wherein a
notice of
10 available seating and price is sent to the IFS. The IFS "pushes" this
information much lilce
advertisements to a user's device in close proximity of a wireless port. The
device is then
able to display the availability and start times associated with movies, and
the user can then
choose to accept or reject the theater request.
15 Tickets that are purchased via the IFS 1302 can be printed on paper,
wherein such
paper tickets or pseudo tickets are sufficient to obtain or retrieve a ticket.
Alternatively,
users can be given a transaction identification number that can be used at a
kiosk at a
theater to print valid tickets.
20 Advertisements 130 are used to push movie content 1310 or movie related
products
1307 such as, but not limited to: movie soundtracks 1332, a digital copy of a
movie (either
transferred onto a portable device or onto a tangible storage medium) 1330, or
other movie
related products 1307. Furthermore, such advertisements for movie content or
movie
related products can be pushed prior to, during, or after a movie.
Additionally, although it
is described that movie content or movie related products are pushed via
advertisements, it
should be noted that users are also able to order such content/products
directly via their
portable computer-based device.
The IFS 1302 is also able to provide food/snack information 1312 to users.
Therefore,
after purchasing their tickets, users are also able to order, via their
portable device,
food/snacks for pick up (or delivery to a particular location in the theater)
at a theater of
interest. It should be noted that such food/snack orders can be placed either
before or
during a movie.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
21
Users are also able to provide feedback or access feedback related information
1314
from the IFS 1302. In one embodiment, a pop-up window is provided on a movie
screen
that provides information uploaded from the user's device, including feedback
on the film,
user comments, or video of the user reacting to the film. Additionally,
audience response
to films after a movie, during a movie, or during a scene can also be gauged.
In another
extended embodiment, communications such as a chatroom environment 1316 with
other
users during a film are also provided by the IFS 1302. In yet another extended
embodiment, a virtual drive-in experience provided by the IFS 1302 allows
users to watch
a movie itself on the user's portable device that is near the IFS 1302.
Figure 14 illustrates system interaction in the preferred embodiment between
an IFS
1402 and a. portable device 1404. One or more content providers forward data
content
1406 such as movie information, auction information, advertisements, movie
related
products information, and digital content to information filling station 1402.
The IFS 1402
is accessed by the portable device 1404, which requests and receives
theaterlmovie
information 1408. Next, users of the portable device identify a theater and a
movie of
interest 1410 in the theater based upon the received theater/rnovie
information.
Upon receiving such identification for a theater and movie of interest, the
IFS 1402
forwards pricing and auction information related to that theater and movie of
interest.
Additionally, advertisements 1414 can be pushed to the portable device 1404
promoting
the sales of movie related products or digital content related to the movie of
interest. The
portable device 1404 then sends a request for the purchase of any identified
tickets, movie
related products, or digital movie content 1416 and, upon successful
completion of a
financial transaction 1418 related to such a purchase, the IFS forwards a
confirmation
related to the purchase of tickets or products and forwards any purchased
digital content
1420 to the portable device 1404 (or, optionally, sends the digital content to
a physical
address in a storage medium).
It should be noted that, for illustration purposes, the wireless network (such
as a
wireless network based on the 802.11b communication protocol) between the IFS
1402
and the portable device 1404 is omitted in Figure 14.
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
22
Figure 15 illustrates a method 1500 of the present invention as implemented
between
an IFS and a portable device. In step 1502, a portable device associated with
a user
receives (based upon an earlier request) information related to movies playing
at one or
more theaters of interest (e.g., information such as trailers, reviews,
showtimes, ticlcet
availability, prices, and/or supplemental information), wherein the received
information is
rendered in the portable device. Next, in step 1504, based upon an input in
the portable
device, at least one theater of interest and at least one movie of interest in
the theater of
interest is identified and communicated to the IFS. In step 1506, the portable
device
receives pricing and auction information regarding the availability of tickets
for the
identified movies(s) of interest from the IFS. Additionally, in step 1508, the
portable
device also receives and renders one or more advertisements indicating
availability and
pricing of digital content related to the identified movies) of interest,
digital content
related to one or more movies identified based upon a profile of the user of
the portable
device, or movie related products.
Next, in step 1510, the user of the portable device identifies, from the
advertisements
and based upon an input in the portable device, digital content or products of
interest. In
step 1512, the portable device performs a financial transaction with the IFS,
wherein the
transaction is based upon the received pricing and auction information and the
identified
digital content of interest. Such financial transactions are accomplished
either of two
ways. First, the user can have a pre-established personal profile containing
credit card
information which the user utilizes to execute a financial transaction (via
the IFS) without
delivering their credit card number over the IFS network. Alternatively, the
user can input
their credit or debit card information in the portable device which in turn
delivers this
information via a secure link to the provider or digital content services.
Upon successful
completion of the financial transaction, the portable device receives a
purchase
confirmation and any identified digital content of interest in step 1514. It
should be noted
that any purchased digital content can also be optionally sent to a physical
address instead
of being transferred to the portable device.
Furthermore, the present invention includes a computer program code based
product, which is a storage medium having program code stored therein which
can be used
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
23
to instruct a computer to perform any of the methods associated with the
present invention.
The computer storage medium includes any of, but is not limited to, the
following: CD-
ROM, DVD, magnetic tape, optical disc, hard drive, floppy dislc, fenoelectric
memory,
flash memory, ferromagnetic memory, optical storage, charge coupled devices,
magnetic
or optical cards, smart cards, EEPROM, EPROM, RAM, ROM, DRAM, SRAM, SDRAM,
and/or any other appropriate static or dynamic memory or data storage device.
Implemented in computer program code based products are software modules for:
authenticating said portable device; aiding in the reception of one or more
content requests
from said portable device; aiding in extracting, from one or more databases,
information
regarding availability of each of said requested content and information
identifying which
of said content requests are associated with protected content; identifying,
if available, a
price associated with each of said available requested content including any
fees that are
payable with respect to said protected content; aiding in transmitting, to
said portable
1 S device: said information regarding availability and any identified prices
associated with
said requested content; aiding in receiving, from said portable device,
instructions
identifying one or more content of interest and routing instructions
identifying one or more
locations for selectively transferring each of said content of interest;
aiding in performing a
financial transaction based upon any pricing information associated with said
content of
interest and upon successful completion of said financial transaction, aiding
in paying to
one or more content providers, said identified fees that are payable with
respect to said
protected content; and aiding in selectively sending to said one or more
identified
locations, corresponding content of interest.
Also implemented in computer program code based products are software modules
for: aiding in the transmission, based upon a wireless protocol, of requested
information
related to events playing at one or more venues of interest (e.g., the venue
could be a
theater, the event could be a movie, and the information could be trailers,
reviews,
showtimes, ticket availability, prices, supplemental information); receiving
at least one
identified venue of interest and at least one identified event of interest in
the venue of
interest; aiding in the transmission of pricing and auction information
regarding the
availability of tickets for the identified events) of interest; aiding in the
transmission of
one or more advertisements indicating availability and pricing of digital
content related to
CA 02489330 2004-12-09
WO 2004/003810 PCT/US2003/016241
24
the identified event of interest, digital content related to an event
identified based upon a
profile of the user of the portable device, or event related products;
receiving an
identification indicating digital content or products of interest and tickets
of interest;
facilitating a financial transaction based upon the identified tickets of
interest and the
identified digital content of interest; and aiding in the transmission of a
purchase
confirmation upon successful completion of the financial transaction and
aiding in sending
the identified digital content of interest either electronically or to a
physical address.
CONCLUSION
A system and method has been shown in the above embodiments for the effective
implementation of an information filling station facilitating wireless
transfer of data
content to a portable device or other pre-defined locations. While various
preferred
embodiments have been shown and described, it will be understood that there is
no intent
to limit the invention by such disclosure but, rather, it is intended to cover
all modifications
and alternate constructions falling within the spirit and scope of the
invention as defined in
the appended claims. For example, the present invention should not be limited
by type or
portable device, type of data content, type of protection, number of content
provider
databases, type of wireless network, type of network between content provider
database
and IFS, software/program, computing environment, format of digital content,
type of
wireless communication, type of portable computer based device, mode of
transfer of
digital content, location of information station, type of venue, type of
event, or specific
computing hardware.
The above enhancements are implemented in various computing environments.
For example, the present invention may be implemented on a conventional IBM PC
or
equivalent, multi-nodal system (e.g., LAN) or networking system (e.g.,
Internet, WWW,
wireless web). All programming and data related thereto are stored in computer
memory,
static or dynamic, and may be retrieved by the user in any of conventional
computer
storage, display (i.e., CRT), and/or hardcopy (i.e., printed) formats. The
programming of
the present invention may be implemented by one skilled in the art of wireless
transmission
protocol programming (e.g., ~02.11b communication protocol programming) and
database
management.