Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
PCT/CH02/00322
SCREWDRIVER WITH SCREW HOLDER
The invention relates to a screwdriver with a screw holder in
accordance with the introductory portion of claim l, as well as to a spring
element
for use as a screw holder at a screwdriver, in accordance with claim 15.
So that, during the surgical implantation of an implant, which is to
be fastened at a bone, a bone fragment or at a joint of the human or animal
body,
the surrounding soft parts experience as little damage as possible, it shall
be
possible to conduct surgery on the bone or, for example, also on a segment of
the
spinal column without exposing the parts to be treated over a large area
(minimal
invasive technique). If the openings in the soft parts are very small, non-
pointed
forceps, for example, are then no longer suitable for introducing bone screws
or
pedicle screws.
A screwdriver with means for holding a screw is also known from
the EP 0 458 449 of RYDER. This known screwdriver comprises a longitudinal
shaft part with a free end, which can be introduced into a corresponding
recess in a
screw head. The elastic means for clamping the screws are inserted into a
groove,
which is parallel to the longitudinal axis, and consist of a compressible
elastomer.
Since the elastic means, when in the uncompressed state, protrude radially
over at
least one side surface of the shaft part, they are compressed when the shaft
part is
inserted into a complementary recess and press against the side wall of the
recess,
as a result of which the screw head is held at the shaft part. It is a
disadvantage of
this development of the elastic means that the boreholes for accommodating the
elastic means are configured in a relatively complicated manner and that
therefore
the screw driver is unsuitable for very small screws.
The invention is to provide a remedy here. It is an object of the
invention to create a screwdriver with an elastic screw holder, which can also
be
used for the smallest screws.
1
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
Pursuant to the invention, this objective is accomplished with a
screwdriver with a screw holder, which has the distinguishing features of
claim 1,
as well as with a spring element for use as screw holder at a screwdriver,
which
has the distinguishing features of claim 15.
The inventive screwdriver with screw holder comprises essentially a
shaft and a spring element, which is disposed transversely to the longitudinal
axis.
At its rear section, the shaft can be connected with driving means, such as a
handle
or a machine. The shaft comprises a front segment, which can be introduced
into
a seat, suitable for a screwdriver, such as a hexagon socket, an internal six-
lobe
profile, a Phillips recess or a Torx at a screw head. The spring element is
inserted
at the front end of the shaft into a recess with a longitudinal axis directed
transversely to the longitudinal axis. The cross-section of the front segment
of the
shaft is polygonal or star-shaped in the various embodiments of the inventive
device, the corners or tips being angular or rounded off and the sides being
straight
or concave. The longitudinal axis of the recess for the spring element
coincides
with one of the radii, on which the corners or tips lie. Furthermore, at least
on its
part protruding beyond the cross section, the spring element can be deformed
transversely to the longitudinal axis in the cross-sectional area orthogonal
to the
longitudinal axis of the shaft.
The advantages, achieved with the invention, can be seen essentially
therein that, due to the inventive configuration of the spring element,
~ a small overall depth of the front segment of the shaft is attainable so
that
screws with heads of low height or with recesses of small depth for
accommodating the screwdriver can be used,
~ the front segment of the shaft may be prismatic or cylindrical, as a result
of
which, in comparison to conical shaft segments, a maximum transfer of
force can be exerted on the screw (the so-called " cam out" effect being
avoided),
2
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
the spring element can also be installed subsequently on conventional
commercial screw drivers,
~ a screw-holding sleeve is not necessary, so that it is possible to
manipulate
these screwdriver with one hand,
~ the device can be produced easily, so that a low price is possible and
~ because only a single, radial borehole is required in the front segment of
the shaft, the spring element can also be used for the smallest screws and
accordingly also for screws in maxillofacial, hand and foot surgery.
In the preferred embodiment of the inventive screwdriver, the recess
is constructed as a circular borehole, so that the recess can be produced
without
great expense also subsequently on conventional, commercial screwdrivers and a
spring element can be used.
In a different embodiment of the inventive screwdriver, the recess
and the spring element are prismatic in shape. With that, the advantage can be
attained that the spring element cannot twist in the recess.
In yet another embodiment of the inventive screwdriver, the spring
element is produced from a metallic material, preferably from stainless spring
steel
or from a superelastic metal, such as Nitinol, so that it is suitable for
medical
application purposes and moreover has a long service life.
In a further embodiment of the inventive screwdriver, the spring
element is produced from a plastic, preferably from a thermoplastic material,
such
as POM. The advantages of a spring element, produced from plastic, lie in the
rational manufacturing process (such as injection molding), the low costs and
the
elimination of the danger of corrosion.
In once again another embodiment of the inventive screwdriver, the
spring element has an open slot at its second end, which can be introduced
into the
3
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
seat in a screwdriver. With respect to the cross section of the spring element
orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the recess, this slot is disposed
diametrically
and divides the spring element at the second end into two cogs, which can be
moved elastically and transversely to the longitudinal axis of the shaft. This
construction of the spring element permits a maximum holding force to be
attained
for the screws, which is necessary for surgical applications, so that the
danger of
the screws being lost in the human body during the surgical intervention can
be
minimized. Preferably, the dimensions are
~ between 0.3 mm and 2.0 mm for the diameter of the spring element,
~ between 0.1 mm and 1.5 mm for the width of the slot and
~ between 0.5 mm and 3.0 mm for the length of the slot.
Typically, the dimensions are
~ between 0.5 mm and 1.5 mm for the diameter of the spring element,
~ between 0.2 mm and 1.2 mm for the width of the slot and
~ between zero 0.8 mm and 2.0 mm for the length of the slot.
Furthermore, the slot may be expanded wedge-shaped towards the
outside, that is, towards the end of the spring element protruding over the
cross
section of the front segment of the shaft, the wedge angle preferably being
between 0.1 ° and 10°. As a result, the advantage can be
attained that the stress
distribution in the spring element is optimized. As a result, better
cushioning
properties are achieved and the danger of a fatigue breakage is reduced.
In a different embodiment of the inventive screw driver, the second
end of the spring element, protruding over the cross section of the front
segment of
the shaft, is provided with a taper, so that the cogs, which can be deformed
radially
and elastically during the insertion of the front segment of the shaft into a
corresponding seat for a screwdriver in a screw head, can be compressed more
easily transversely to the longitudinal axis of the shaft. The tapering may be
present in the form of an obliqueness, a curvature, a bevel or a round edge.
4
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
Preferably, the length of the taper, measured parallel to the
longitudinal axis of the spring element is 5% to 30% of the diameter of the
spring
element. Instead of a taper, the second end of the spring element may also
have a
convex formation.
In yet another embodiment of the inventive screwdriver, the latter
comprises several spring elements, which can be inserted in several recesses
at the
front segment of the shaft. The longitudinal axes of the recesses preferably
lie on
one of the radii, intersecting the corners or curvature of the cross-sectional
area of
the front segment of the shaft, orthogonally to the shaft. Due to the use of
several
spring elements, the holding force, which can be exerted on the head of the
screw
head, can be increased appreciably for the screw on the screwdriver.
In a further embodiment of the inventive screwdriver, the recess has
a ledge at a depth T, measured from the corner or tip, the depth T being equal
to or
greater than the length of the spring element, which is parallel to the
longitudinal
axis of the spring element, so that the spring element does not protrude
beyond the
tip, corner or curvature of the front segment of the shaft. By these means, it
can be
avoided that the spring element is pushed further into the recess as the front
segment of the shaft is inserted into the seat for the screwdriver at the
screw head.
Further advantageous developments of the invention are
characterized in the dependent claims.
The invention and further developments of the invention are
described in even greater detail in the following by means of partly
diagrammatic
representations of several examples. In the drawing
FIG. 1 a shows a longitudinal section through an embodiment of the
inventive screwdriver with screw holder,
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
FIG. lb shows a cross section through the embodiment of the inventive
screwdriver with screw holder, shown in FIG. 1 a,
FIG.2 shows a cross section through a different embodiment of the
inventive screwdriver with screw holder,
FIG. 3 a cross section through the embodiment of the inventive
screwdriver, shown in FIGS. 1 a and 1 b, with a front shaft segment,
introduced into a recess for accommodating screwdrivers at a screw
head, and
FIG. 4 a side view of an embodiment of a spring element.
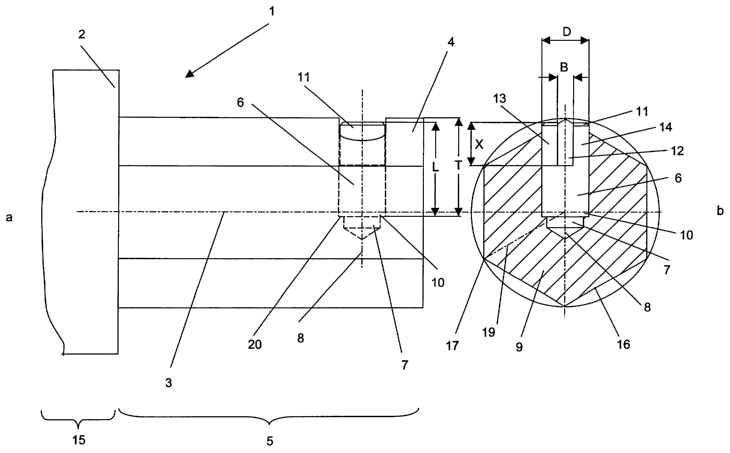
The screwdriver 1 with screw holder, shown in FIGS. 1 a and 1 b,
comprises essentially a longitudinal shaft 2 with a longitudinal axis 3, a
rear
segment 15 of the shaft and a front segment 5 of the shaft, and a spring
element 6
with a diameter D. The front segment 5 of the shaft has a hexagonal cross-
sectional area 9, which is orthogonal to the longitudinal axis 3 and has
straight
side 16 and corners 17 and can be inserted into a seat at a screw head, which
is
suitable for screwdrivers. At the front segment S of the shaft, the spring
element 6
is pressed into a longitudinal recess 7 in the form of a circular borehole
with a
longitudinal axis 8, which is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis 3. The
six
corners 17 of the cross sectional area 9 lie on six radii 19, the longitudinal
axis 8
coinciding with one of the radii 19. Adjacent to the corners 17, the spring
element
6 protrudes over the adjoining side 16. So that the spring element 6 cannot be
pressed into the recess 7 as the front segment 5 of the shaft is being
inserted into
the seat at a screw head for accommodating a screw driver, there is an axial
ledge
20, on which the first end 10 of the spring element 6 rests, in the recess 7.
Furthermore, the spring element 6 comprises a slot 12, having a
width B and a length X and passing from the second end 11 of the spring
element
6 into the latter. The slot 12 passes through the spring element 6
diametrically and
6
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
is disposed parallel to the longitudinal axis 8 of the recess 7. The second
end 11 of
the spring element 6 is divided by the slot 12 into two cogs 13; 14, which are
parallel to the longitudinal axis 8 and can be deformed elastically and
transversely
to the longitudinal axis 8 and towards the edge of the cross sectional area 9,
that is,
can be deflected towards the longitudinal axis 8. The length L of the spring
element 6 is less than the depth T, which extends from the tip 17 up to the
ledge
20, so that the spring element 6 is deeper at the tip 17 than at the cross
section 9.
The embodiment of the inventive screwdriver 1, shown in FIG. 2,
differs from the embodiment, shown in FIGs. 1 a and 1 b, only in that the
cross-
section 9 of the front segment 5 of the shaft is star-shaped. The tips 18 of
the
cross-section 9, lying on the radii 19, are rounded off convexly and the sides
16,
lying between the tips 18, are rounded off concavely. Adjacent, the spring
element 6 rests on the base 22 of the borehole 7.
FIG. 3 shows the front segment 5 of the shaft of the embodiment of
the inventive screwdriver shown in FIGs. 1 a and 1 b, when the latter is
introduced
into a seat 24 for the screwdriver at a screw head 23. The second end 11 of
the
spring element 6 is then enclosed completely in the cross section 9. The two
cogs
13; 14, which can be deformed elastically, are pressed against the
longitudinal axis
8. So that the two cogs 13; 14 can be deformed adequately and do not touch one
another at the longitudinal axis 8, the depth T of the recess 7 (FIG. 1 a) and
the
dimensions of the spring element 6, that is, the diameter D and the length L
and
the width B of the slot 12 (FIG. 1 a) must be matched to one another so that,
on the
one hand, the deformation of the cogs 13; 14 exerts a sufficiently high
clamping
force on the side walls of the seat 24 and, on the other, the cogs 13; 14 do
not
hinder the deformation.
In FIG. 4, an embodiment of the inventive spring element 6 is
shown, which is to be used as a screw holder at a screwdriver. The spring
element
6 is circular, has a longitudinal axis 26 and comprises, at its first end 10,
an
obliqueness 25, as well as a convexly rounded tapering 21 at its second end
11,
7
CA 02489453 2004-12-13
which has a length A, measured parallel to the longitudinal axis 26. In the
embodiment shown here, the ratio of the length A of this tapering 21 to the
diameter D of the spring element 6 is 1:4, whereas the ratio of the depth X of
the
slot 12 to the length L of the spring element 6 is 3:4. At the front end 11 of
the
spring element 6, the slot 12 has a width B and expands in the direction of
the
front end 11 of the spring element 6 at a wedge angle of 2°. The ratio
of the width
B to the diameter D is 1:2 here. The two cogs 13; 14 are elastically
deformable
perpendicularly to the longitudinal axis 8 of the recess 7 (FIG. 1 a), the
spring
forces being determined by the diameter D of the spring element 6 and the
dimensions of the slot 12.
8