Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
PALLET FORMED FROM MOLDED FIBROUS PANEL MATERIAL
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to pallets for supporting items during shipment and
storage. In particular, the invention relates to a pallet formed predominately
from
fibrous material.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Pallets traditionally have been manufactured of wood. The drawbacks
associated with wooden pallets are well known, as noted for example in U.S.
Patent No. 5,184,558, incorporated herein by reference. Briefly, such
drawbacks
include heaviness, which makes the pallets cumbersome to handle and costly to
ship, relatively great expense because of the costliness of wood, and
difficulty and
expense of disposing of the pallets when their useful life has been expended.
Because of such problems, various types of non-wooden pallets have been
proposed. Some of these pallets are based on corrugated paperboard materials;
others are based on honeycomb sandwich types of sheet materials. Still others
are
one-piece structures molded from fibrous material.
Pallets based on corrugated paperboard materials suffer from relatively
poor rigidity because corrugated paperboard material by its nature is weak in
bending parallel to the panning direction of the flutes. Attempts nave been
made to
improve rigidity in all directions by forming laminations of multiple layers
of
corrugated paperboard with the flutes in successive layers being oriented
orthogonally. There is thus a need for a substantial number of separate pieces
of
corrugated sheet material, each die cut to appropriate size and shape, the
pieces
-1-
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
then being glued together. Thus, production and assembly of a pallet from such
materials is relatively complex and expensive.
Pallets formed from honeycomb sandwich materials likewise tend to
consist of a substantial number of separate pieces, and hence are relatively
complex and expensive to produce and assemble. Additionally, the bond between
the honeycomb cells and the face sheets represents a weak link in honeycomb
sandwich structures; if this bond should break, the structure loses a great
deal of its
bending stiffness. In honeycomb sandwich panels based on paper, furthermore,
exposure of the panels to water or other liquids can substantially weaken the
panels.
With regard to one-piece molded fibrous pallets, a significant drawback is
the need for a differently configured mold for each different pallet size or
configuration to be produced.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The invention addresses the above needs and achieves other advantages, by
providing a pallet formed of molded fibrous panel material of a special type
having
substantial strength and relatively light weight. The pallet can be
constructed from
a small number of separate pieces of the panel material, or even from a single
piece
of the panel material.
More particularly, in accordance with the invention, a pallet is constructed
of a molded fibrous panel material comprising a sheet portion defining
opposite
planar surfaces, and a grid of intersecting ribs projecting from one of the
planar
surfaces of the sheet portion, the sheet portion and ribs being integrally
molded in
one piece from fibrous material. The fibrous material can be, for example,
recycled paper fibers. If water-resistance is required, the molded fibrous
panel
material can be impregnated with a suitable resin. The panel has substantial
rigidity and integrity by virtue of its one-piece construction and the grid of
intersecting ribs.
-2-
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
A pallet in accordance with the invention comprises a horizontal portion of
the molded fibrous panel material forming an upper support surface of the
pallet,
and at least two spaced runners joined to and extending downward from the
horizontal portion for engaging the ground to space the horizontal portion
above
the ground. Each runner comprises at least two vertical portions of the molded
fibrous panel material arranged in parallel relation and bonded to one
another.
In one embodiment, a single panel member is folded along a series of
parallel fold lines extending across a width of the member, so as to form the
runners and the horizontal portion from the single member. Because of the
substantial rigidity of the panel, the grooves are formed in the panel to
create the
fold lines. The grooves represent regions in which fibrous material that would
otherwise be there is missing or removed. The grooves preferably are generally
V-
shaped with a 90-degree included angle between opposite side walls of the
grooves
so that the panel can be folded 90 degrees about the fold line. The grooves
either
can be molded into the panel when it is molded, or alternatively can be formed
by
mechanically removing material (e.g., by routing) from the panel after it is
formed.
In another embodiment, a top panel is affixed atop the horizontal portion of
the pallet, such as by gluing. The top panel gives added strength to the
pallet and
also presents a smooth top surface. The top panel in one embodiment comprises
a
laminated multi-layer sheet, for example formed from paperboard sheets.
Alternatively, the top panel can be another piece of the molded fibrous panel
material, with the ribs facing downward toward the horizontal portion of the
pallet.
The ribs of the top panel can be bonded to the ribs of the horizontal portion,
optionally with an intervening piece of sheet material (e.g., paperboard or
the like)
disposed therebetween.
The molded fibrous panel material forming the horizontal and vertical
portions of the pallet can comprise a single layer of the molded fibrous panel
material, such that one side of the panel is planar and the other side has
exposed
ribs. Alternatively, the panel material can comprise a double layer wherein
the two
layers are joined rib-to-rib, for added rigidity.
-3-
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE SEVERAL VIEWS OF THE DRAWINGS)
Having thus described the invention in general terms, reference will now be
made to the accompanying drawings, which are not necessarily drawn to scale,
and
wherein:
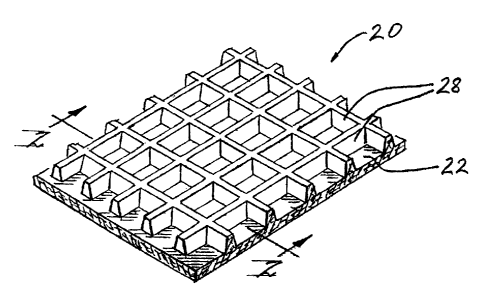
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a piece of molded fibrous panel material
used for constructing pallets in accordance with the invention;
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along line 2-2 in FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a pallet in accordance with a first embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 4A shows a portion of a molded fibrous panel, illustrating a series of
parallel fold lines defined as V-shaped grooves in the panel;
FIG. 4B shows the panel after being folded 90 degrees along one of the fold
lines;
FIG. 5 shows a portion of the panel of FIG. 3, depicting a runner in greater
detail;
FIG. 6 illustrates an alternative embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 7 shows another embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 8 depicts a further embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 9 shows a still further embodiment of the invention; and
FIG. 10 shows yet another embodiment of the invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present inventions now will be described more fully hereinafter with
reference to the accompanying drawings, in which some, but not all embodiments
of the invention are shown. Indeed, these inventions may be embodied in many
-4-
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set
forth
herein; rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will
satisfy
applicable legal requirements. Like numbers refer to like elements throughout.
FIGS. l and 2 show a molded fibrous panel 20 that is used for constructing
pallets in accordance with the invention. The panel 20 can be formed by a
process
generally similar to that disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,702,870 to Setterholm
et al.,
incorporated herein by reference, or by a process such as described in co-
pending
U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/729,686, filed on December 5, 2003,
entitled
"Apparatus and Process for Forming Three-Dimensional Fibrous Panels"
incorporated herein by reference. The process produces a three-dimensional
panel
that has a sheet portion 22 defining opposite planax surfaces 24 and 26, and a
grid
of intersecting ribs 28 projecting from one surface 24 of the sheet portion.
To
make the panel, an aqueous fiber stock is deposited into a mold comprising a
porous support plate or screen on which are affixed a plurality of resilient
elastomeric mold pieces or projections of truncated conical or pyramidal
shape.
The mold pieces are spaced apart on the porous support plate so that
intersecting
channels are defined between the mold pieces. The aqueous stock fills the mold
to
a depth greater than the height of the mold pieces, so the stock covers the
upper
surfaces of the mold pieces. A flat mold plate is urged against the stock and
presses the stock down into the mold; the stock is dewatered through openings
in
the porous support plate. The pressure dewaters and densifies the panel, and
the
wet panel is then dried fully to complete the process.
The panel ZO advantageously can have a thickness ranging from about'/4-
inch to about '/o-inch or more. The panel can be formed from recycled paper
fibers. The panel can be impregnated with a resin to render it water-
resistant, if
desired. An advantage of the panel over the prior art is its relatively large
strength-
to-weight ratio, which makes possible the construction of pallets of
relatively light
weight but substantial strength.
FIG. 3 depicts a pallet 30 in accordance with a first embodiment of the
invention. The pallet 30 is constructed from a single molded fibrous panel 20
and
-5-
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
a top panel 50. The molded fibrous panel 20 is rectangular in shape. The panel
20
is folded along a series of parallel fold lines to form three runners 32, 34,
36
spaced apart and parallel to one another, as further described below. The top
panel
50 is then bonded to the folded panel 20 by gluing or the like.
S The formation of the runner 32 is depicted in FIGS. 4A, 4B, and S; the
other runners are formed in a similar fashion. The panel 20 is provided with a
series of spaced, parallel fold lines A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J (FIG. 3);
the fold
lines A, B, and C are used for forming the first runner 32. The fold line A is
spaced from one edge of the panel ZO by a distance corresponding to a desired
vertical extent of the runner 32; panel section 20a is defined between the
panel
edge and the fold line A. The fold line B is spaced from the fold line A by a
minimum distance roughly equal to 1.5 to 2 times the thickness of the panel;
panel
section 20b is defined between fold lines A and B. The fold line C is spaced
from
the fold line B by a distance approximately equal to the vertical height of
the
runner minus the thickness of the panel 20; panel section ZOc is defined
between
the fold lines B and C, and a panel section 20d is connected to the panel
section
20c at the fold line C.
Because the panel 20 has substantial bending stiffness as a result of the ribs
28, it is not possible to fold the panel without substantial breakage of
fibers and
buckling of the panel along the fold, and accordingly it is necessary to
provide a
groove or channel along each of the desired lines about which the panel is to
be
folded, as shown in FIG. 4A. In the region of each groove, the ribs are
substantially removed or interrupted so that the remaining material, at least
at the
bottom of the groove, consists substantially entirely of the sheet portion 22
of the
panel. A preferred configuration of the grooves is depicted in FIG. 4A. Each
groove preferably is V-shaped; the opposite side walls of the groove
preferably
define an angle of substantially 90 degrees therebetween. Accordingly, when
the
panel is folded 90 degrees about the fold line, the opposite side walls of the
groove
come into substantially abutting relation and can be glued together to secure
the
panel in the folded position.
-6-
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
The V-shaped grooves can be formed in various ways. In one embodiment,
the grooves are formed during the molding process, by suitably configuring the
mold. Alternatively, the panel can be molded without grooves, and then the
panel
can be routed, machined, or otherwise mechanically operated upon to remove
material to form the grooves.
To form the runner 32, the panel sections 20a and 20b are folded as a unit
90 degrees clockwise about the fold line B as shown in FIG. 4B, then the panel
section 20a is folded relative to panel section 20b 90 degrees clockwise about
the
fold line A. At this point, the panel sections 20a and 20c axe parallel to
each other
and are rib-to-rib. These panel sections are glued together to form the runner
32.
The runner is then folded 90 degrees counterclockwise about the fold line C,
with
the resulting structure being shown in FIG. S. Panel section 20d forms a
horizontal
portion of the pallet on which a load will be supported. The other runners 34
and
36 and further horizontal portions are similarly formed by folding the panel
about
the respective fold lines D-J. Finally, the top panel 50 is attached atop the
panel
by gluing or the like to complete the pallet construction. Although a
particular
order of folding the panel 20 about the fold lines has been described, it will
be
recognized that the order may be different while arriving at the same end
result.
FIG. 6 illustrates a portion of a pallet 30' in accordance with a second
20 embodiment of the invention. This pallet is essentially the same as the
pallet 30
described above, except that the panel 20 is reinforced in the region of the
fold
lines A and B by a reinforcing web 52. The reinforcing web 52 is employed to
prevent or minimize fiber breakage in the region of the fold lines that may
otherwise result upon folding of the panel. The reinforcing web may be an
adhesive tape such as a pressure-sensitive adhesive tape comprising a
substrate of
paper or cloth having a layer of pressure-sensitive adhesive thereon. The
reinforcing web preferably is affixed to the panel prior to folding.
A third embodiment of the invention is depicted in FIG. 7. The pallet 130
shown in FIG. 7 is generally similar to the pallet 30 previously described,
except as
noted herein. The pallet 130 has a panel 20 folded along fold lines A, B, C,
etc., so
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
as to form runners 32, etc., as previously described, and a top panel 50
affixed atop
the panel 20. However, in the present embodiment, the runners are reinforced
with
additional stiffening members. Thus, the runner 32 is shown having a
stiffening
member 60 disposed between the panel portion 20a and the panel portion 20c
that
make up the runner. The stiffening member is bonded to the panel portions 20a
and 20c with adhesive or the like. To provide the necessary space between the
panel portions to accommodate the thickness of the stiffening member 60, the
fold
lines A and B are spaced slightly farther apart than in the previously
described
pallet 30, so that when the panel portions 20a and 20c are parallel to each
other
there is a space between them substantially equal to the thickness of the
stiffening
member 60. The stiffening member 60 can comprise various materials, including
but not limited to metal, wood, hard plastic, hard rubber, fiber-reinforced
plastic,
mufti-layer paperboard laminations, and the like.
FIG. 8 shows a fourth embodiment of the invention. The pallet 230 of FIG.
8 is generally similar to the pallet 30 described above, except that the top
panel 250
comprises a fibrous molded panel of the type shown in FIG. 1. Thus, the top
panel
250 has a sheet portion 252 and ribs 258 projecting therefrom. The top panel
250
is bonded to the panel 20 that forms the runners of the pallet. Preferably,
the panel
has its ribs 28 projecting upwardly and the top panel 250 has its ribs 258
20 projecting downwardly, and the two panels are bonded rib-to-rib.
Optionally, there
can be an intervening sheet 260 of paper or other material disposed between
and
bonded to the two panels.
A fifth embodiment of the invention is illustrated in FIG. 9. The pallet 330
of FIG. 9 is constructed in a fashion similar to that used for constructing
the pallet
30, except that the starting panel 320 used for forming the runners is a
double-layer
panel having two panels of the type illustrated in FIG. 1, bonded rib-to-rib
(with or
without an intervening sheet therebetween). Thus, both opposite surfaces of
the
panel 320 are smooth and planar. The panel is provided with grooves along the
desired fold lines by routing or the like, as previously described, and is
folded to
form the runners 332, etc., and the horizontal portions 320d, etc. However, in
the
pallet 330, since the horizontal portions of the panel 320 already comprise a
_g_
CA 02497076 2005-02-16
double-layer of panel material, there is no need for an additional top panel.
Thus,
the entire pallet is formed from one double-layer panel. As with the
embodiment
of FIG. 7, the runners can be further strengthened, if desired, by stiffening
members.
Finally, a sixth embodiment of the invention is shown in FIG. 10. The
pallet 430 of FIG. 10 is formed differently from the previously described
pallets,
with respect to the formation of the runners. In this embodiment, each runner,
such
as the runner 432 shown in the drawing, is formed by bonding together two or
more separate and discrete pieces of panel material, and is then bonded to a
top
panel of the pallet. Thus, as shown, the runner 432 comprises two double-layer
pieces of panel material 440 and 442 bonded together. The piece 440 comprises
two panels 440a and 440b bonded together rib-to-rib (with or without an
intervening sheet therebetween); likewise, the piece 442 comprises two panels
442a and 4426 bonded together rib-to-rib (with or without an intervening sheet
therebetween). The pallet 430 includes a top panel 450 comprising a double-
layer
piece of panel material having two panels bonded together rib-to-rib (with or
without an intervening sheet therebetween). Alternatively, the top panel could
be a
single layer of the panel material, or could be another type of construction
such as
a multi-layer paperboard lamination. The runners could be formed of fewer than
four layers of the panel material; for example, the runners could comprise two
layers of the panel material. The runners could include stiffening members as
previously described.
Many modifications and other embodiments of the inventions set forth
herein will come to mind to one skilled in the art to which these inventions
pertain
having the benefit of the teachings presented in the foregoing descriptions
and the
associated drawings. Therefore, it is to be understood that the inventions are
not to
be limited to the specif c embodiments disclosed and that modifications and
other
embodiments are intended to be included within the scope of the appended
claims.
Although specific terms are employed herein, they are used in a generic and
descriptive sense only and not fox purposes of limitation.
-9-