Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
MONO DIAMETER WELLBORE CASING
Cross Reference To Related Applications
The present application claims the benefit of the filing date of (1) U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/412,542, attorney docket no
25791.102,
filed on 9/20/2002, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by
reference.
The present application is related to the following: (1) U.S. patent
application
serial no. 09/454,139, attorney docket no. 25791.03.02, filed on 12/3/1999,
(2) U.S.
patent application serial no. 09/510,913, attorney docket no. 25791.7.02,
filed on
2/23/2000, (3) U.S. patent application serial no. 09/502,350, attorney docket
no.
25791.8.02, filed on 2/10/2000, (4) U.S. patent no. 6,328,113, (5) U.S. patent
application serial no. 09/523,460, attorney docket no. 25791.11.02, filed on
3/1012000, (6) U.S: patent application serial no. 09/512,895, attorney docket
no.
25791.12.02, filed on 2/24/2000, (7) U.S. patent application serial no.
09/511,941,
attorney docket no. 25791.16.02, filed on 2/24/2000, (8) U.S. patent
application
serial no. 09/588,946, attorney docket no. 25791.17.02, filed on 6/7/2000, (9)
U.S.
patent application serial no. 09/559,122, attorney docket no. 25791.23.02,
filed on
412612000, (10) PCT patent application serial no. PCTlUS00/18635, attorney
docket
no. 25791.25.02, filed on 7/9/2000, (11) U.S. provisional patent application
serial no.
60/162,671, attorney docket no. 25791.27, filed on 11/1/1999, (12) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/154,047, attorney docket no. 25791.29, filed
on
9/16/1999, (13) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/159,082,
attorney
docket no. 25791.34, filed on 10/12/1999, (14) U.S. provisional patent
application
serial no. 60/159,039, attorney docket no. 25791.36, filed on 10/12/1999, (15)
U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/159,033, attorney docket no.
25791.37,
filed on 10/12/1999, (16) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/212,359,
attorney docket no. 25791.38, filed on 6/19/2000, (17) U.S. provisional patent
application serial no. 60/165,228, attorney docket no. 25791.39, filed on
11/12/1999,
(18) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 601221,443, attorney
docket no.
25791.45, filed on 7/28/2000, (19) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
60/221,645, attorney docket no. 25791.46, filed on 7/28/2000, (20) U.S,
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/233,638, attorney docket no. 25791.47, filed
on
9/18/2000, (21) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/237,334,
attorney
docket no. 25791.48, filed on 10/2/2000, (22) U.S. provisional patent
application
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
serial no. 60/270,007, attorney docket no. 25791.50, filed on 2/20/2001, (23)
U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/262,434, attorney docket no.
25791.51,
filed on 1/17/2001, (24) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/259,486,
attorney docket no. 25791.52, filed on 1/3/2001, (25) U.S, provisional patent
application serial no. 60/303,740, attorney docket no. 25791.61, filed on
7/6/2001,
(26) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/313,453, attorney
docket no.
25791.59, filed on 8/20/2001, (27) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
60/317,985, attorney docket no. 25791.67, filed on 9/6/2001, (28) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/3318,386, attorney docket no. 25791.67.02,
filed on
9/10/2001, (29) U.S. utility patent application serial no. 09/969,922,
attorney docket
no. 25791.69, filed on 10/3/2001, (30) U.S. utility patent application serial
no.
10/016,467, attorney docket no. 25791.70, filed on 12/1012001, (31) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/343,674, attorney docket no. 25791.68, filed
on
12/27/2001, (32) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/346,309,
attorney
docket no 25791.92, filed on 1/7/2002, (33) U.S. provisional patent
application serial
no. 60/372,048, attorney docket no. 25791.93, filed on 4/1212002, (34) U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/380,147, attorney docket no.
25791.104,
filed on 5/6/2002, (35) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/387,486,
attorney docket no. 25791.107, filed on 6/10/2002, (36) U.S. provisional
patent
application serial no. 60/387,961, attorney docket no. 25791.108, filed on
6/12/2002,
(37) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/391,703, attorney
docket no.
25791.90, filed on 6/26/2002, (38) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
60/397,284, attorney docket no. 25791.106, filed on 7/19/2002, (39) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/398,061, attorney docket no. 25791.110, filed
on
7/24/2002, (40) U.S. provisional patent application serial no, 60/405,610,
attorney
docket no. 25791.119, filed on 8/23/2002, (41) U.S. provisional patent
application
serial no. 60/405,394, attorney docket no. 25791.120, filed on 8/23/2002, (42)
U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/412,177, attorney docket no.
25791.117,
filed on 9/20/2002, (43) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/412,653,
attorney docket no. 25791.118, filed on 9/20/2002, (44) U.S. provisional
patent
application serial no. 60/412,544, attorney docket no. 25791.121, filed on
9/20/2002,
(45) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/412,187, attorney
docket no.
25791.128, filed on 9/20/2002, (46) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
2
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
60/412,187, attorney docket no. 25791.127, filed on 9/20/2002, (47) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/412,487, attorney docket no. 25791.112, filed
on
9/20/2002, and (48) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/412,488,
attorney docket no. 25791.114, filed on 9/20/2002, the disclosures of which
are
incorporated herein by reference.
Background of the invention
This invention relates generally to oil and gas exploration, and in particular
to
forming and repairing wellbore casings to facilitate oil and gas exploration.
Conventionally, when a wellbore is created, a number of casings are installed
in the borehole to prevent collapse of the borehole wall and to prevent
undesired
outflow of drilling fluid into the formation or inflow of fluid from the
formation into the
borehole: The borehole is drilled in intervals whereby a casing which is to be
installed in a lower borehole interval is lowered through a previously
installed casing
of an upper borehole interval. As a consequence of this procedure the casing
of the
lower interval is of smaller diameter than the casing of the upper interval.
Thus, the
casings are in a nested arrangement with casing diameters decreasing in
downward
direction. Cement annuli are provided between the outer surfaces of the
casings
and the borehole wall to seal the casings from the borehole wall. As a
consequence
of this nested arrangement a relatively large borehole diameter is required at
the
upper part of the weilbore. Such a large borehole diameter involves increased
costs
due to heavy casing handling equipment, large drill bits and increased volumes
of
drilling fluid and drill cuttings. Moreover, increased drilling rig time is
involved due to
required cement pumping, cement hardening, required equipment changes due to
large variations in hole diameters drilled in the course of the well, and the
large
volume of cuttings drilled and removed.
The present invention is directed to overcoming one or more of the limitations
of the existing procedures for forming and/or repairing wellbore casings.
Summary of the Invention
According to one aspect of the present invention, an expansion cone
assembly having two diameters for forming a skirt or bell section at which
nested
expandable tubular members overlap and for forming a mono diameter section of
an
expandable wellbore casing is provided.
3
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
Brief Description of the Drawings
Fig. 1 is a schematic fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an
expandable
tubular member and expansion cone assembly running through a mono diameter
well bore casing formed according to one aspect to the invention.
Fig. 2 is a schematic fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an
expandable
tubular member and expansion cone assembly forming a bell portion of the mono
diameter well bore casing of Fig. 1 according to one aspect to the invention.
Fig. 3 is a schematic fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an
expandable
tubular member and expansion cone assembly forming a mono diameter portion of
the mono diameter wellbore casing of Figs. 1 and 2 according to another aspect
to
the invention.
Fig. 4 is a schematic fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an
expandable
tubular member, a gripping mechanism within the tubular member, an actuator,
an
expansion cone assembly for forming a mono diameter casing and a float shoe
supporting the tubular member for running into a wellbore.
Fig. 5 is a schematic fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an
expandable
tubular member, a gripping mechanism engaging the tubular member, an actuator
and expansion cone assembly for forming a mono diameter casing, with the
tubular
member lifted off the bottom of the wellbore and with the expansion cone
assembly
pushed by the actuator into an open wellbore.
Fig. 6 is a schematic fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of the
expansion
cone assembly expanded for radially expanding and plastically deforming the
expandable tubular member.
Figs. 7a -7e are fragmentary cross-sectional illustrations of the placement of
an exemplary embodiment of an apparatus for forming a mono diameter wellbore
casing within a wellbore that traverses a subterranean formation.
Figs. 8a - 8e are fragmentary cross-sectional illustrations of the apparatus
of
Figs. 7a -7e after placement on the bottom of the wellbore.
Figs. 9a -9e are fragmentary cross-sectional illustrations of the apparatus of
Figs. 8a - 8e after placing a ball or dart within the ball or dart seat to
initiate the radial
expansion and plastic deformation of the expandable tubular member.
Figs. 10a -10e are fragmentary cross-sectional illustrations of the apparatus
of Figs. 9a-9e after the initiation of the radial expansion and plastic
deformation of
4
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
the aluminum sleeve within the shoe.
Fig. 11 a -11 b is a fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an exemplary
embodiment of an apparatus for radially expanding and plastically deforming a
tubular member that includes an adjustably expandable expansion cone assembly.
Fig. 12 is a fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an upper cone
portion of the apparatus for radially expanding and plastically deforming a
tubular
member of Figs. 11 a - 11 b.
Fig. 13 is a fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of a lower cone portion
of the apparatus for radially expanding and plastically deforming a tubular
member
of Figs. 11 a - 11 b.
Fig. 14 is a fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an overlapping
portion of the apparatus for radially expanding and plastically deforming a
tubular
member of Figs. 11 a - 11 b, 12 and 13.
Fig. 15 is a fragmentary cross-sectional and perspective illustrations of the
upper cam assembly of the apparatus for radially expanding and plastically
deforming a tubular member of Figs. 11a - 11b.
Fig. 16 is a fragmentary cross-sectional and perspective illustrations of the
lower cam assembly of the apparatus for radially expanding and plastically
deforming a tubular member of Figs. 11 a - 11 b.
Fig. 17a -17b is a fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an exemplary
embodiment of an apparatus for radially expanding and plastically deforming a
tubular member that includes an adjustably expandable expansion cone assembly
of Figs. 11 a - 11 b activated for cementing.
Fig. 18a -18b is a fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an exemplary
embodiment of an apparatus for radially expanding and plastically deforming a
tubular member that includes an adjustably expandable expansion cone assembly
of Figs. 11 a -11 b activated for adjusting the expansion diameter.
Fig. 19 is a fragmentary cross-sectional illustration of an overlapping
portion
of the apparatus for radially expanding and plastically deforming a tubular
member
adjusted to an intermediate expansion diameter.
Fig. 20a -20b are fragmentary cross sectional illustrations of the apparatus
of
Figs. 10d-10e after the completion of the radial expansion and plastic
deformation of
the aluminum sleeve within the shoe.
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
Figs. 21 a -21 b are fragmentary cross-sectional illustrations of the
apparatus
of Figs. 20a -20b after displacing the sliding sleeve valve within the shoe to
permit
circulation around the ball or dart.
Figs. 22a -22b are fragmentary cross sectional illustrations of the apparatus
of Figs. 21 a -21 b during the injection of cement into the annulus between
the radially
expanding tubular member and the wellbore using_the bypass circulation
provided by
the displaced sliding sleeve valve within the shoe.
Detailed Description of the Illustrative Embodiments
Figs. 1- 6 illustrate several illustrative embodiments of a device and method
for forming a mono diameter well bore casing using an expansion assembly
including two cone diameters, one of which is larger than the other for
forming a bell
(sometimes called a skirt) section for overlapping expandable tubular members
so
that the effort required for the expansion assembly to expanded two
overlapping
tubular members is reduced. The other cone diameter is sized for expanding the
tubular members to the desired diameter along the length of the tubular member
thereby resulting in a mono-diameter well bore casing. The two diameters may
be
provided with a conventional adjustable size expansion cone having two
expansion
diameters, one larger than the other. The larger diameter is adjusted to a
smaller
diameter after a bell section of an expandable tubular member is formed and
then
the remainder of the expandable tubular member is expanded to a the desired
internal diameter for the mono diameter wellbore casing. Conventional
adjustably
expandable cones can be used according to the invention. In several
alternative
embodiments, the invention is implemented as described in Figs. 7a -7e, 8a -
8e, 9a-
9e, 1 Oa -1 Oe, 11 a -11 b and 17a-17b, 18a-18b and 19a-19b with an exemplary
adjustably expandable cone assembly as described in greater detail herein with
reference to Figs. 11 a - 11 b, 12, 13, 14, 15 and 16. In other alternative
embodiments the adjustably expandable cones of the invention may be
implemented or using the methods and/or apparatus disclosed one or more of the
following: (1) U.S. patent application serial no. 09/454,139, attorney docket
no.
25791.03.02, filed on 12/3/1999, (2) U.S. patent application serial no.
09/510,913,
attorney docket no. 25791.7.02, filed on 2/23/2000, (3) U.S. patent
application serial
no. 09/502,350, attorney docket no. 25791.8.02, filed on 2/10/2000, (4) U.S.
patent
no. 6,328,113, (5) U.S. patent application serial no. 09/523,460, attorney
docket no.
6
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
25791.11.02, filled on 3/10/2000, (6) U.S. patent application serial no.
09/512,895,
attorney docket no. 25791.12.02, filed on 2/24/2000, (7) U.S. patent
application
serial no. 09/511,941, attorney docket no. 25791.16.02, filed on 2/24/2000,
(8) U.S.
patent application serial no. 09/588,946, attorney docket no. 25791.17.02,
filed on
6/7/2000, (9) U.S. patent application serial no. 09/559,122, attorney docket
no.
25791.23.02, filed on 4/26/2000, (10) PCT patent application serial no.
PCT/US00/18635, attorney docket no. 25791.25.02, filed on 7/9/2000, (11) U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/162,671, attorney docket no.
25791.27,
filed on 11/1/1999, (12) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/154,047,
attorney docket no. 25791.29, filed on 9/16/1999, (13) U.S. provisional patent
application serial no. 60/159,082, attorney docket no. 25791.34, filed on
10/12/1999,
(14) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/159,039, attorney
docket no.
25791.36, filed on 10112/1999, (15) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
60/159,033, attorney docket no. 25791.37, filed on 10/12/1999, (16) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/212,359, attorney docket no. 25791.38, filed
on
6/19/2000, (17) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/165,228,
attorney
docket no. 25791.39, filed on 11/12/1999, (18) U.S. provisional patent
application
serial no. 60/221,443, attorney docket no. 25791.45, filed on 7/28/2000, (19)
U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/221,645, attorney docket no.
25791.46,
filed on 7/28/2000, (20) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/233,638,
attorney docket no. 25791.47, filed on 9/18/2000, (21) U.S. provisional patent
application serial no. 60/237,334, attorney docket no. 25791.48, filed on
10/2/2000,
(22) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/270,007, attorney
docket no.
25791.50, filed on 2/20/2001, (23) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
60/262,434, attorney docket no. 25791.51, filed on 1/17/2001, (24) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/259,486, attorney docket no. 25791.52, filed
on
1/3/2001, (25) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/303,740,
attorney
docket no. 25791.61, filed on 7/6/2001, (26) U.S. provisional patent
application serial
no. 60/313,453, attorney docket no. 25791.59, filed on 8/20/2001, (27) U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/317,985, attorney docket no.
25791.67,
filed on 9/6/2001, (28) U.S, provisional patent application serial no.
60/3318,386,
attorney docket no. 25791.67.02, filed on 9/10/2001, (29) U.S. utility patent
application serial no. 09/969,922, attorney docket no. 25791.69, filed on
10/3/2001,
7
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
(30) U.S. utility patent application serial no. 10/016,467, attorney docket
no.
25791.70, filled on 12/10/2001, (31 ) U.S. provisional patent application
serial no.
60/343,674, attorney docket no. 25791.68, filed on 12/27/2001, (32) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no. 60/346,309, attorney docket no 25791.92, filled
on
1/7/2002, (33) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/372,048,
attorney
docket no. 25791.93, filed on 4/12/2002, (34) U.S. provisional patent
application
serial no. 60/380,147, attorney docket no. 25791.104, filed on 5/6/2002, (35)
U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/387,486, attorney docket no.
25791.107,
filed on 6110/2002, (36) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/387,961,
attorney docket no. 25791.108, filed on 6/12/2002, (37) U.S. provisional
patent
application serial no. 60/391,703, attorney docket no. 25791.90, filed on
6/26/2002,
(38) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/397,284, attorney
docket no.
25791.106, filed on 7/19/2002, (39) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
60/398,061, attorney docket no. 25791.110, filed on 7/24/2002, (40) U.S.
provisional
patent application serial no, 60/405,610, attorney docket no. 25791.119, filed
on
8/23/2002, (41) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/405,394,
attorney
docket no. 25791.120, filled on 8/23/2002, (42) U.S. provisional patent
application
serial no. 60/412,177, attorney docket no. 25791.117, filed on 9/20/2002, (43)
U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/412,653, attorney docket no.
25791.118,
filed on 9/20/2002, (44) U.S. provisional patent application serial no.
60/412,544,
attorney docket no. 25791.121, filed on 9/20/2002, (45) U.S. provisional
patent
application serial no. 60/412,187, attorney docket no. 25791.128, filed on
9/20/2002,
(46) U.S. provisional patent application serial no. 60/412,187, attorney
docket no.
25791.127, filed on 9/20/2002, (47) U.S. provisional patent application serial
no.
60/412,487, attorney docket no. 25791.112, filed on 9/20/2002, and (48) U.S.
provisional patent application serial no. 60/412,488, attorney docket no.
25791.114,
filed on 9/20/2002, the disclosures of which are incorporated herein by
reference.
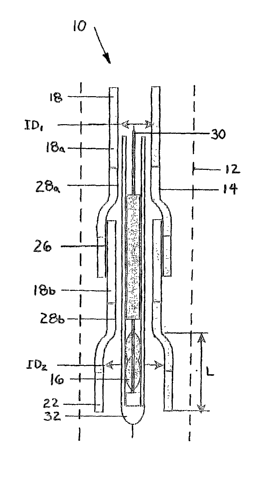
Fig. 1 shows a schematic illustration of an apparatus 10 in a wellbore 12 with
an expandable tubular member 14 and an expansion cone assembly 16 supported
by a tubular support 30 (such as a drill pipe 30), all supported by a float
shoe 32 fior
running into a wellbore 12 through a plurality of casing sections 18a and 18b
of a
mono diameter wellbore casing 18 in the process of being formed, according to
one
aspect to the invention. The existing casing 18 sections 18a and 18b have been
8
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
formed from expandable tubular members 14 and according to the teachings of
the
present invention include mono diameter portions 28a and 28b with a first
inside
diameter ID1 and bell portions 22a and 22b having a second inside diameter
inside
diameter ID2 and a length L. There is an overlapping portion 26 where the bell
portions 22a overlap of the casing section 18b.
Fig. 2 shows a schematic illustration of the expandable tubular member 14,
acted upon by a large cone 20 of the expansion cone assembly 16 to expand the
diameter of the lower end of the expandable tubular member 14 to form a bell
portion 22. The bell portion 22 is formed by the large cone 20 of the
expansion cone
assembly 16 that has an adjustable cone diameter sufficiently large so that
the
resulting expanded inside diameter of the bell portion 20 is at least slightly
larger
than a desired inside diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing 18. The
length
of the bell portion 20 depends upon the desired length of overlapping lengths
26
between nested casing sections 18a, 18b, and 18c. For example, it is
contemplated
applicants that the overlap length 26 and therefore the bell portion 22 may
have a
length up to about 100 feet or up to about 150 feet.
Fig. 3 shows a schematic illustration of the expandable tubular member 14 of
Fig. 2, with the expansion cone assembly 16 positioned for expanding the
expandable tubular member 14 to the desired mono diameter at the portion 28
above the bell portion 22. In this configuration the diameter of the large
adjustable
cone 20 is collapsed, or is other wise adjusted, to a smaller diameter.
Another cone
24, having a diameter smaller than the large diameter of cone 20, is provided
for
radially expanding the tubular member 14 to the desired inside diameter of the
mono
diameter wellbore casing. The wellbore casing section 18c of the mono diameter
well bore casing 18 of Figs. 1 and 2, overlaps with the wellbore casing
section 18b
along the overlapping length 26 and at the bell portion 22b. The inside
diameter or
the bell portion 22 and the outside diameter of the mono diameter portion 28
are the
same to provide a tight fitting junction between the nested sections 18a, b, c
and etc.
For example, where the expandable tubular member 14 has a wall thickness of
about 0.35 inches and for the desired inside diameter of the mono diameter
wellbore
casing is about 10.3 inches, after expansion, the inside diameter of the bell
portion
might be about 11.0 inches, or slightly less to provide a tight fit between
the
overlapping portions of the casing sections 18a, b, c and etc.
9
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
The large diameter cone 20 can be positioned above, below or effectively at
the same position as the small diameter cone 24, without departing from
certain
aspects of the invention. Also, ifi will be understood by those of ordinary
skill in the
art, and based upon this disclosure, that the large diameter corresponding to
the
inside diameter of the bell portion can be provided by a first collapsible or
adjustable cone 22, that provides the desired bell portion diameter and that
can be
collapsed to a smaller diameter, together with a second cone 24 that provides
the
diameter for forming the mono diameter well bore casing. It will also be
understood
that in an alternative embodiment the expansion to the mono diameter can be
provided by adjusting the diameter of cone 22 to effectively become the
smaller
diameter cone 24 having a diameter corresponding to the desired mono diameter.
It
will further be understood that in another alternative embodiment the cone 24
is a
distinct cone 24 either fixed at the desired mono diameter size or expandable
to the
desired mono diameter size.
Fig. 4 shows a schematic mono diameter casing forming apparatus 10,
further depicting one arrangement of a mechanism for activating the expansion
cone
assembly 16 to expand the tubular member 14. The apparatus 10 is shown in a
configuration for running into a wellbore 12. A drill pipe 30 supports the
apparatus
10, as it is running down into the wellbore 12, with a connected float shoe
32. The
drill pipe 30 may be a conventional drill pipe or other conventional down hole
tubular
support member. The float shoe may be a conventional float shoe or other tool
guiding structure that serves the describe purpose attached to the drill pipe
or other
tubular support member. The float shoe 32 thus supports the new expandable
tubular member14 that is to be added to and expanded for engagement with the
lower end of the mono diameter wellbore casing 18 that has been previously
formed.
An gripping toot 34, sometimes called an anchor that may be a device as shown
or
a conventional gripping tool or anchor, is provided to hold the expandable
tubular
member 14 fixed relative to one end of a hydraulic actuator 36, sometimes
called a
force multiplier mechanism that may be a device as shown or a conventional
actuator or force multiplier. The hydraulic actuator 36 is configured and
actuatable
for moving the expansion cone assembly 16 relative to the expandable member
14,
either in tension using sub 36a or in compression using sub 36b.
Fig. 5 schematically shows an embodiment of the mono diameter casing
to
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
forming apparatus 10, with the gripping mechanism 34 engaging the tubular
member
14, with the tubular member 14 lifted off the bottom of the well bore 12 and
with
the expansion cone 16 pushed by actuator 36 into the open wellbore 12. A
conventional dart 53 or ball is dropped to seal the float shoe 32, or another
conventional shut-off device such as a mechanical valve or a velocity valve is
used
and activated, so that fluid 38 forced through the drill pipe 22 increases
pressure to
activate the gripping tool 26. When the drill pipe 22 is set down at the
bottom of the
hole, the tension sub 36a of the actuator mechanism 36 is actuated. Pressure
is
increased in the drill pipe 30 and the gripping mechanism 34 is engaged to
anchor
the tubular member 14. Compression sub 36b is activated to lift the tubular
liner 14
off the bottom of the wellbore and to push the cone assembly 16 into the open
hole
of wellbore 12.
Fig. 6 shows the expansion cone assembly 16 expanded for radially
expanding and plastically deforming the expandable tubular member 14. The
expansion of the expansion cone assembly is activated in a conventional
manner, as
with a dart 42 that is passed with the fluid 38 down through the drill pipe 30
to
thereby cause appropriate port alignment and/or appropriate valve activation
for the
expansion cone assembly 16. An optional sacrificial protective sleeve 40 that
protects the expansion cone assembly 16 while it is running into the wellbore
breaks
off when the expansion cone assembly is expanded. The protective sleeve 40 may
be formed of a plastic or composite material so that the sacrificial
protective sleeve
easily breaks off and does not interfere with the expansion of the tubular
member
14.
In an exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 7a -7e, an apparatus 10
for forming a mono diameter wellbore casing 18 is positioned within a wellbore
12.
The apparatus 10 includes, among other things, an expandable tubular member 14
and an adjustable expansion cone assembly 16. During placement of the
apparatus
within the wellbore 12, the expandable tubular member 14 may be supported by
the grip tool 34 and/or the expansion cone assembly 16 and/or the float shoe
32.
In an exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 8a - 8e, the apparatus 10
is then positioned into contact with the bottom 44 of the wellbore 12. As a
result, a
shear pin 46 is sheared and a dog locking sleeve 48 is driven upwardly thereby
displacing a plurality of dogs 50 outwardly in the radial direction in a
conventional
11
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
manner.
In an exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 9a - 9e, a ball 52 or
conventional dart may then be placed within the ball or dart seat 54 of the
apparatus
by injecting fluidic material 38 into the apparatus 10. As a result, the flow
of fluidic
material 38 through the float shoe 32 is blocked. The expansion cone assembly
is
also actuated in a conventional manner, for example with the pressure caused
by
the ball 52 or a dart 42 (as shown in Fig. 6 above), to expand to the large
diameter
for expanding the bell. Pressure builds and the actuator 36 is activated in
tension to
draw the large cone 20 upward partially through the expandable tubular member
14.
Pressure can be released and reactivated in the actuator 36 and gripping tool
34 to
repeatedly stroke the large cone 20 of the expansion cone assembly 16 along
the
desired overlapping length L of the casing to thereby form the bell portion 22
of the
casing.
In an exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 10a -10e, the large
diameter cone 20 is acfiuated to collapse or adjust to a smaller diameter cone
24
corresponding to the desired diameter of the mono diameter casing 18, using
conventional actuation, for example, increased fluidic pressure and a rupture
disc in
an appropriate port (not shown) or an additional dart 56 injected with the
fluidic
material 38 into the apparatus 10 to a conventional dart seat 58. The gripping
tool
34 is activated to lock the top end of the hydraulic actuator 36 to the
expandable
tubular member 14. The injected fluidic material 38 also causes the adjustable
cone
24 to reach the desired diametrical size for forming the mono diameter casing
18.
The continued injection of the fluidic material 38 furthermore increases the
operating
pressure within the apparatus thereby causing the hydraulic actuator 36 to
pull the
expansion cone 24 into the expandable tubular member 14. As a result, the
expandable tubular member 14 is radially expanded.
The continued upward movement of the expansion cone pulls the float shoe
32 to the bottom end of the radially expanded tubular member 14. As a result,
the
end of the radially expanded tubular member 14 will impact the dogs 50 thereby
preventing the float shoe 32 from moving further in the upward direction. The
continued upward movement of the expansion cone then will pull a sleeve
expander
cone 60 for the sleeve 62 upwardly thereby radially expanding a sleeve of the
float
shoe within the float shoe.
12
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
In one exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 11 a -11 b, 12, 13, 14,
15
and 16, the expansion cone assembly 16 is adjustable for providing two outside
diameters, one outside diameter larger than the other outside diameter. The
construction of the expandable cone assembly may also be constructed in
accordance with the principles and design disclosed in U.S. provisional patent
application serial no. 60/387,961, attorney docket no. 25791.108, filed on
6/12/2002,
the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference. An exemplary
embodiment includes a tubular support member 64 coupled to an end of a safety
collar 66 that defines a passage 66a and a recess 66b, at one end for
receiving the
end of the tubular support member 14, and recesses 66c and 66d at another end.
A torque plate 68 is received within and is coupled to the recess 66c of the
safety collar 66 that defines a passage 68a and a plurality of meshing teeth
68b at
one end. An end of an upper mandrel collar 70 is received with and is coupled
to
the recess 66d of the safety collar 66 proximate an end of the torque plate 68
that
defines a passage 68a. Torque pins 72a and 72b further couple the end of the
upper mandrel collar 70 to the end of the safety collar 66.
An end of an upper mandrel 74 is received within and is coupled to the upper
mandrel collar 70 that defines a passage 74a, a plurality of meshing teeth 74b
that
mate with and transmit torque to and from the meshing teeth 68b of the torque
plate
68, and an external flange 74c at another end.
An upper packer cup 76 mates with, receives and is coupled to the upper
mandrel 74 proximate the end of the upper mandrel collar 70. !n an exemplary
embodiment, the upper packer cup 76 is a conventional GuibersonT"' packer cup.
An upper spacer sleeve 78 mates with, receives, and is coupled to the upper
mandrel 74 proximate an end of the upper packer cup 76. A lower packer cup 80
mates with, receives and is coupled to the upper mandrel 74 proximate an end
of
the upper spacer sleeve 78. In an exemplary embodiment, the lower packer cup
80
is a conventional GuibersonT"" packer cup. A lower spacer sleeve 82 mates
with,
receives, and is coupled to the upper mandrel 74 proximate an end of the lower
packer cup 80 and the external flange 74c of the upper mandrel. A retaining
sleeve
84 mates with, receives, and is coupled to an end of the lower spacer sleeve
proximate the external flange 74c of the upper mandrel 74.
An end of a lower mandrel 86 defines a recess 86a that mates with, receives,
13
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
and is coupled to the external flange 74c of the upper mandrel 74, a recess
86b that
mates with, receives, and is coupled to the end of the upper mandrel, a
passage
86c, and an external flange 86d including circumferentially spaced apart
meshing
teeth 86da on an end face of the external flange. Torque pins 88a and 88b
further
couple the recess 86a of the end of the lower mandrel 86 to the external
flange 74c
of the upper mandrel 74. During operation, the torque pins 88a and 88b
transmit
torque loads between the recess 86a of the end of the lower mandrel 86 and the
external flange 74c of the upper mandrel 74.
An upper cam assembly 90 includes a tubular base 90a for receiving and
mating with the lower mandrel 86 that includes an external flange 90aa, a
plurality of
circumferentially spaced apart meshing teeth 90b that extend from one end of
the
tubular base in the longitudinal and radial directions for engaging the
meshing teeth
86da of the end face of the external flange 86d of the lower mandrel 86, and a
plurality of circumferentially spaced apart cam arms 90c that extend from the
other
end of the tubular base in the opposite longitudinal direction and mate with
and
receive the lower mandrel 86. During operation, the meshing teeth 86da of the
end
face of the external flange 86d of the lower mandrel 86 transmit torque loads
to the
meshing teeth 90b of the upper cam assembly 90. Each of the cam arms 90c
include an inner portion 90ca extending from the tubular base 90a that has
arcuate
cylindrical inner 90caa and outer 90cab surfaces, a tapered intermediate
portion
extending from the inner portion 90cb that has an arcuate cylindrical inner
surface
90cba and an arcuate conical outer surface 90bbb, and an outer portion 90cc
extending from the intermediate portion 90cc that has arcuate cylindrical
inner 90cca
and outer surfaces 90ccb.
A lower cam assembly 92 includes a tubular base 92a for receiving and
mating with the lower mandrel 86 that includes an external flange 92aa, a
plurality of
circumferentially spaced apart meshing teeth 92b that extend from one end of
the
tubular base in the longitudinal and radial directions, and a plurality of
circumferentially spaced apart cam arms 92c that extend from the other end of
the
tubular base in the opposite longitudinal direction and mate with and receive
the
lower mandrel 86. Each of the cam arms 92c include an inner portion 92ca
extending from the tubular base 92a that has arcuate cylindrical inner 92caa
and
outer 92cab surfaces, a tapered intermediate portion 92cb extending from the
inner
14
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
portion 92ca that has an arcuate cylindrical inner surface 92cba and an
arcuate
conical outer surface 92cbb, and an outer portion 92cc extending from the
intermediate portion 92cb that has arcuate cylindrical inner 92cca and outer
92ccb
surfaces.
In an exemplary embodiment, the upper and lower cam assemblies, 90 and
92, are substantially identical. In an exemplary embodiment, the cam arms 90c
of
the upper cam assembly 90 interleave the cam arms 92c of the lower cam
assembly 92. Furthermore, in an exemplary embodiment, the cam arms 90c of the
upper cam assembly also overlap with the cam arms 92c of the lower cam
assembly
92 in the longitudinal direction thereby permitting torque loads to be
transmitted
between the upper and lower cam assemblies.
A plurality of upper expansion cone segments 96 are interleaved among the
cam arms 90c of the upper cam assembly 90. Each of the upper expansion cone
segments 96 include inner portions 96a having arcuate cylindrical inner
surfaces
96aa, and an arcuate cylindrical outer surface 96ab, intermediate portions 96b
extending from the interior portions that have an arcuate conical inner
surface 96ba
and arcuate cylindrical and spherical outer surfaces, 96bb, and outer portions
96c
having arcuate cylindrical inner and outer surfaces, 96ca and 96cb. In an
exemplary
embodiment, the outer surfaces 96ab of the inner portions 96a of the upper
expansion cone segments 96 define hinge grooves 96d that receive and are
pivotally mounted upon the internal flange 94d of the upper retaining sleeve
94.
The arcuate inner cylindrical surfaces of the inner portion 96a mate with and
receive the lower mandrel 86, the arcuate inner cylindrical surfaces of the
inner
portion 96a also mate with and receive the arcuate cylindrical outer surfaces
of the
outer portions 92cc of the corresponding cam arms 92c of the lower cam
assembly
92, and the arcuate inner conical surfaces 96ba of the inner portion 96a mate
with
and receive the arcuate conical outer surfaces of the intermediate portions
92cb of
the corresponding cam arms 92c of the lower cam assembly 92.
A plurality of lower expansion cone segments 98 are interleaved among, and
overlap, the upper expansion cone segments 96 and the cam arms 90c of the
lower
cam assembly 90. In this manner, torque loads may be transmitted between the
upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96 and 98. Each of the lower
expansion
cone segments 98 include inner portions 98a having arcuate cylindrical inner
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
surfaces, 98aa, and an arcuate cylindrical outer surface 98ab, intermediate
portions
98b extending from the interior portions that have an arcuate conical inner
surface
98ba and arcuate cylindrical and spherical outer surfaces, 98bb, and outer
portions
98c having arcuate cylindrical inner and outer surfaces, 98ca and 98cb. In an
exemplary embodiment, the outer surfaces 98ab of the inner portions 98a of the
upper expansion cone segments 98 define hinge grooves 98aba that receive and
are pivotally mounted upon the internal flange 100d of a lower retaining
sleeve 100.
The arcuate inner cylindrical surfaces 98aa mate with and receive the lower
mandrel 86, the arcuate inner cylindrical surfaces 98aa also mate with and
receive
the arcuate cylindrical outer surfaces of the outer portions 90cc of the
corresponding
cam arms 90c of the upper cam assembly 90, and the arcuate inner conical
surfaces
98ba mate with and receive the arcuate conical outer surfaces of the
intermediate
portions 90cb of the corresponding cam arms 90c of the lower cam assembly 90.
In an exemplary embodiment, the geometries of the upper and lower
expansion cone segments 96 and 98 are substantially identical. In an exemplary
embodiment, the upper expansion cone segments 96 are tapered in the
longitudinal
direction from the ends of the intermediate portions 96b to the ends of the
outer
portions 96c, and the lower expansion cone segments 98 are tapered in the
longitudinal direction from the ends of the intermediate portions 98b to the
ends of
the outer portions 98c. In an exemplary embodiment, when the upper and lower
expansion segments, 96 and 98, are positioned in a fully expanded position,
the
arcuate cylindrical outer surfaces 96ab of the upper and lower expansion cone
segments 96 define a contiguous cylindrical surface, the arcuate spherical
outer
surfaces of the upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96bb and 98bb, define
a
contiguous arcuate spherical surface, and the arcuate cylindrical outer
surfaces of
the upper and lower expansion cone segments define a contiguous cylindrical
surface.
An end of a lower retaining sleeve 100 defines a passage 100a for receiving
and mating with the outer circumferential surfaces of the external flange 92aa
and
the meshing teeth 92b of the lower cam assembly 92, and an inner annular
recess
100b, and includes an internal flange 100c for retaining the external flange
of the
lower cam assembly, and an internal flange 100d at one end of the lower
retaining
sleeve that includes a rounded interior end face for mating with corresponding
hinge
16
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
grooves of the lower expansion cone segments 98 thereby pivotally coupling the
lower expansion cone segments to the lower retaining sleeve.
In an exemplary embodiment, the arcuate cylindrical outer surfaces of the
upper expansion cone segments 96 and the arcuate cylindrical outer surfaces of
the
lower expansion cone segments 98 are aligned with the outer surface of the
upper
retaining sleeve 94. In an exemplary embodiment, the arcuate cylindrical outer
surfaces of the upper expansion cone segments 96 and the arcuate cylindrical
outer
surfaces of the lower expansion cone segments are aligned with the outer
surface of
the lower retaining sleeve 100.
An end of a float shoe adaptor 102 that includes a plurality of
circumferentially
spaced apart meshing teeth 102a for engaging the meshing teeth 92b of the
lower
cam assembly 92 is received within and threadably coupled to an end of the
lower
retaining sleeve 100 that defines a passage 102b at one end for receiving an
end of
the lower mandrel 86, a passage 102c having a reduced inside diameter at
another
end, a plurality of radial passages 102d at the other end, and includes an
internal
flange 102e, and a torsional coupling 102f at the other end that includes a
plurality of
torsional coupling members 102fa. During operation, the meshing teeth 92b of
the
lower cam assembly 92 transmit toque loads to and from the meshing teeth 102a
of
the float shoe adaptor.
An end of a retaining sleeve 104 abuts the end face of the tubular base 92a
of the lower cam assembly 92 and is received within and mates with the passage
102b of the float shoe adaptor 102 that defines a passage 104a for receiving
an end
of the lower mandrel 86, a throat passage 104b including a ball valve seat
104c, and
includes a flange 104d, and another end of the retaining sleeve, having a
reduced
outside diameter, is received within and mates with the passage 102c of the
float
shoe adaptor 102.
A stop nut 106 receives and is threadably coupled to the end of the lower
mandrel 86 within the passage 104a of the retaining sleeve 104, and shear pins
108
releasably couple the stop nut 106 to the retaining sleeve 104. Locking dogs
110
are positioned within an end of the retaining sleeve 104 that receive and are
releasably coupled to the lower mandrel 86, and a disc shaped adjustment shim
112
receives the lower mandrel 86 and is positioned within an end of the retaining
sleeve
104 between the opposing ends of the tubular base 92a of the upper cam
assembly
17
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
92 and the locking dogs 110. Burst discs 114 are releasably coupled to and
positioned within the radial passages 102d of the float shoe adaptor 102.
An end of a float shoe 116 mates with and is releasably coupled to the
torsional coupling 102f of the float shoe adaptor 102 that defines a passage
116a
and a valveable passage 116b. In this manner torsional loads may be
transmitted
between the float shoe adaptor 102 and the float shoe 116. An end of an
expandable tubular member 14 that surrounds the tubular support member 64, the
safety collar 66, the upper mandrel collar 70, the upper packer cup 76, the
lower
packer cup 80, the lower mandrel 86, the upper expansion cone segments 96, the
lower expansion cone segments 98, and the float shoe adaptor 102, is coupled
to
and receives an end of the float shoe 116 and is movably coupled to and
supported
by the arcuate spherical external surfaces, 96bb and 98bb, of the upper and
lower
expansion cone segments, 96 and 98.
During operation, the apparatus 10 is at least partially positioned within a
preexisting structure such as, for example, a borehole 12 that traverses a
subterranean formation that may include a preexisting wellbore casing 18. The
borehole 12 may be oriented in any position, for examples from vertical to
horizontal.
A fluidic material 38 is then injected into the apparatus 10 through the
passages
64a, 66a, 74a, 86c, 102c, 116a, and 116b into the annulus between the
expandable
tubular member 14 and the borehole 12. In an exemplary embodiment, the fluidic
material 104 is a hardenable fluidic sealing material. In this manner, an
annular
sealing layer may be formed within the annulus between the expandable tubular
member 14 and the borehole 12.
As illustrated in Figs. 17a and 17b, a ball 55 is then be positioned within
and
blocking the valveable passage 116b of the float shoe 116 by injecting a
fluidic
material 38 into the apparatus 10 through the passages 64a, 66a, 74a, 86c, and
102c. As a result, the increased operating pressure within the passage 102c
bursts
open the burst discs 114 positioned within the radial passages 102d of the
float shoe
adaptor 102. The continued injection of the fluidic material 38 thereby
pressurizes
the interior of the expandable tubular member 14 below the lower packer cup 80
thereby displacing the upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96 and 98,
upwardly relative to the float shoe 116 and the expandable tubular member 14.
As a
result, the expandable tubular member 14 is plastically deformed and radially
18
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
expanded. Thus, the burst discs 114 sense the operating pressure of the
injected
fluidic material 38 within the passage 102c and thereby control the initiation
of the
radial expansion and plastic deformation of the expandable tubular member 14.
In an exemplary embodiment, any leakage of the pressurized fluidic material
38 past the lower packer cup 80 is captured and sealed against further leakage
by
the upper packer cup 76. In this manner, the lower packer cup 80 provides the
primary fluidic seal against the interior surface of the expandable tubular
member
14, and the upper packer cup 76 provides a secondary, back-up, fluidic seal
against
the interior surface of the expandable tubular member. Furthermore, because
the
lower packer cup 80 and/or the upper packer cup 76 provide a~fluid tight seal
against
the interior surface of the expandable tubular member 14, the upper and lower
expansion cone segments, 96 and 98, are pulled upwardly through the expandable
tubular member by the axial forces created by the packer cups.
In an exemplary embodiment, during the radial expansion process, the
interface between the arcuate spherical external surfaces, 96bb and 98bb, of
the
upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96 and 98, and the interior surface
of
the expandable tubular member 14 is not fluid tight. As a result, the fluidic
material
38 may provide lubrication to the entire extent of the interface between the
cylindrical external surfaces, 96bba and 98cb, and the arcuate spherical
external
surfaces, 96bb and 98bb, of the upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96
and
98, and the interior surface of the expandable tubular member 14. Moreover,
experimental test results have indicated the unexpected result that the
required
operating pressure of the fluidic material 38 for radial expansion of the
expandable
tubular member 14 is less when the interface between the cylindrical external
surfaces, 96bba and 98cb, and the arcuate spherical external surfaces, 96bb
and
98bb, of the upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96 and 98, and the
inferior
surface of the expandable tubular member 14 is not fluid tight. Furthermore,
experimental test results have also demonstrated that the arcuate spherical
external
surface provided by the arcuate spherical external surfaces, 96bb and 98bb, of
the
upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96 and 98, provides radial expansion
and plastic deformation of the expandable tubular member 14 using lower
operating
pressures versus an expansion cone having a conical outer surface.
In an exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 18a, 18b and 19, the
19
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96 and 98, may then be adjusted to a
desired expansion diameter by placing a ball 57 within the ball valve seat
104c of the
throat passage 104b of the retaining sleeve 104. The continued injection of
the
fluidic material 38, after the placement of the ball 57 within the ball valve
seat 104c,
creates a differential pressure across the ball 57 thereby applying a downward
longitudinal force onto the retaining sleeve 104 thereby shearing the shear
pins 108.
As a result, the retaining sleeve 104 is displaced in the downward
longitudinal
direction relative to the float shoe adaptor 102 thereby permitting the
locking dogs
110 to be displaced outwardly in the radial direction. The outward radial
displacement of the locking dogs 110 disengages the locking dogs from
engagement
with the lower mandrel 86. Thus, the shear pins 108 sense the operating
pressure
of the injected fluidic material 38 within the throat passage 104b and thereby
controlling the initiation of the collapsing of the upper and lower expansion
cone
segments, 96 and 98 to a smaller diameter.
The continued injection of the fluidic material 38 continues to displace the
retaining sleeve 104 in the downward longitudinal direction relative to the
float shoe
adaptor 102 until the external flange 104d of the retaining sleeve 104
impacts, and
applies a downward longitudinal force to, the internal flange 102e of the
float shoe
adaptor. As a result, the float shoe adaptor 102 is then also displaced in the
downward longitudinal direction relative to the lower mandrel 86. The downward
longitudinal displacement of the float shoe adaptor 102 relative to the lower
mandrel
86 causes the lower cam assembly 92, the lower expansion cone segments 98, and
the lower retaining sleeve 100, which are rigidly attached to the float shoe
adaptor,
to also be displaced downwardly in the longitudinal direction relative to the
lower
mandrel 86, the upper cam assembly 90, and the upper expansion cone segments
96.
The downward longitudinal displacement of the lower cam assembly 92
relative to the upper expansion cone segments 96 causes the upper expansion
cone
segments to slide dawn the conical external surfaces 92cbb of the lower cam
assembly and thereby pivot inwardly in the radial direction about the internal
flange
94d of the upper retaining sleeve 94. The downward longitudinal displacement
of
the lower expansion cone segments 98 relative to the upper cam assembly 90
causes the lower expansion cone segments 98 to slide down the external conical
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
surfaces 90cbb of the upper cam assembly and thereby pivot inwardly in the
radial
direction about the internal flange 100d of the lower retaining sleeve. As a
result of
the inward radial movement of the upper and lower expansion cone segments, 96
and 98, the arcuate external spherical surfaces, 96bb and 98bb, of the upper
and
lower expansion cone segments, 96 and 98, provide outer arcuate expansion
surfaces having a smaller diameter.
The downward longitudinal movement of the retaining sleeve 94 and float
shoe adaptor 102 relative to the lower mandrel 86 is stopped when the stop nut
106
impacts the locking dogs 110. At this point, the apparatus 10 may then be
removed
from the interior of the expandable tubular member 14.
Thus, the apparatus 10 may be removed from the expandable tubular
member 14 prior to the complete radial expansion and plastic deformation of
the
expandable tubular member by controllably collapsing the upper and lower
expansion cone segments, 96 and 98. As a result, the apparatus 10 provides the
following benefits: (1) the apparatus is removable when expansion problems are
encountered; (2) lower expansion forces are required because the portion of
the
expandable tubular member 14 between the packer cups, 76 and 80, and the
expansion cone segments is exposed to the expansion fluid pressure; (3) the
expansion cone segments can be run down through the expandable tubular
member, prior to radial expansion, and then the expansion cone segments can be
expanded; (4) the expansion cone segments can be expanded to one diameter for
forming a bell portion; and (5) the expansion cone segments can be adjusted to
a
second diameter for expanding the remainder of the expandable tubular member.
In another exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 20a - 20b, upward
movement of the apparatus 10 causes the expansion cone for the sleeve 60 to
completely radially expand the sleeve 62 of the float shoe 32 and a cementing
probe
118 is pulled downward until stopped from further movement by the cementing
probe locking ring 119. As a result of the complete radial expansion of the
sleeve,
the float shoe is now firmly coupled to the end of the radially expanded
tubular
member.
In an exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 21 a -21 b, the drill pipe
30
is lowered into the wellbore 12 until the cementing probe 118 stabs into the
end 120
of the sliding sleeve valve 122 thereby permitting fluidic materials 38 to
bypass
21
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
around the dart or ball 52. As a result, a bypass flow path 124 is now
provided for
cement or other fluidic materials 38 to flow around the ball 52 or dart.
In an exemplary embodiment, as illustrated in Figs. 22a -22b, a hardenable
fluidic sealing material 38 such as, for example, cement, may then be injected
into
the apparatus 10. The cement flows through the interior of the apparatus,
through
the bypass flow path 124, and out through the float valve 126 into the annulus
128
between the radially expanded tubular member 22 and the wellbore 12. After the
cement 38 has been injected into the annulus128, the float valve 126 prevents
the
cement from flowing backwards into the apparatus.
After completing the injection of the cement into the annulus, the drilling
pipe
30 is then pulled upwardly out of the wellbore 12 thereby causing the
cementing
probe 118 to close the sliding sleeve valve 122. The radial expansion and
plastic
deformation of the expandable tubular member 14 may then be continued by the
resumed injection of fluidic material 38 into the apparatus 10. In several
alternative
embodiments, the continued radial expansion and plastic deformation of the
expandable tubular member 14 may be provided by pressurizing the interior of
the
apparatus 10 below the expansion cone 24 and/or by displacing the expansion
cone
24 upwardly using the hydraulic actuator 36.
After the cement has cured, the float collar 32 may be drilled out and another
expandable tubular member may then be radially expanded and plastically
deformed
within the wellbore with the upper end of the other tubular member overlapping
with
the lower end of the earlier expanded tubular member. In this manner, a mono
diameter wellbore casing may be formed that includes a plurality of radially
expanded tubular members.
In several alternative embodiments, GuibersonT"" cup seals may be added
above the expansion cone that provide a fluid tight seal between the drill
pipe and
the interior surface of the expandable tubular member. In this manner, in the
alternative embodiment, the fluid pressure below the cup seals pulls the
expansion
cone upwardly through the expandable tubular member.
In several alternative embodiments, the expandable adjustable expansion
°cone assembly having two adjustable expansion diameters may be
replaced with
two separate adjustable cones one adjustable to a diameter corresponding to
the
desired bell portion diameter, and the other adjustable to a diameter
corresponding
22
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
to the desired diameter of the mono diameter casing.
In several alternative embodiments, the expandable adjustable expansion
cone assembly having two adjustable expansion diameters may be replaced with
an
adjustable cone that is adjustable to a diameter corresponding to the desired
bell
portion diameter, and a non-adjustable cone having a fixed diameter
corresponding
to the desired diameter of the mono diameter casing.
In several alternative embodiments, a conventional rotary expansion device, a
conventional compliant expansion device, and/or a conventional hydroforming
expansion device may used instead of, or in combination with, the expansion
cone
assembly 16.
In several alternative embodiments, one or more of the conventional
commercially available expansion devices available from Weatherford
International,
Baker Hughes, Halliburton Energy Services, Schlumberger, and/or Enventure
Global
Technology may be used instead of, or in combination with, the expansion cone
assembly 16.
There has been disclosed in the several embodiments, an apparatus for
radially expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from
an
initial inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore
casing.
The apparatus includes an upper tubular support member defining a first
passage,
one or more cup seals coupled to the exterior surface of the upper tubular
support
member for sealing an interface between the upper tubular support member and
the
expandable tubular member, an expansion cone assembly coupled to the upper
tubular support member adjustable to one expansion diameter corresponding to
the
desired diameter of the bell portion of the wellbore casing for forming an
expanded
bell portion in the expandable tubular member and adjustable to another
expansion
diameter corresponding to the desired diameter of the mono diameter casing for
forming the mono diameter wellbore casing, means for actuating the expandable
tubular member to adjust from the one diameter to the other diameter, and an
actuator for moving the cone through the expandable tubular member a desired
distance with the expansion cone assembly adjusted to the diameter of the bell
portion and for moving the expansion cone assembly through the expandable
tubular member for another distance with the expansion cone assembly adjusted
to
the desired diameter of the mono diameter portion of the expandable tubular
23
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
member.
In one embodiment the expansion cone assembly includes one adjustable
cone having an external surface adjustable to the diameter of the bell portion
of the
expandable tubular member; and wherein the external surface of the one
adjustable
cone is also adjustable to the diameter corresponding to the desired diameter
of the
mono diameter wellbore casing.
In another embodiment the expansion cone assembly includes a first
adjustable cone having an external surface adjustable to the diameter of the
bell
portion of the expandable tubular member and a second adjustable cone having
an
external surface adjustable to the diameter corresponding to the desired
diameter of
the mono diameter wellbore casing.
In another embodiment the expansion cone assembly includes a first
adjustable cone having an external surface adjustable to the diameter of the
bell
portion of the expandable tubular member and collapsible after expanding the
bell
portion and a second cone having a fixed diameter corresponding to the desired
diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing such that collapsing the first
cone
effectively adjusts the effective expansion diameter to the fixed diameter of
the
second cone.
In another embodiment the expansion cone assembly includes an upper cam
assembly coupled to the upper tubular support member includes a tubular base
coupled to the upper tubular support member; and a plurality of cam arms
extending
from the tubular base in a downward longitudinal direction, each cam arm
defining
an inclined surface, a plurality of upper expansion cone segments interleaved
with
the cam arms of the upper cam assembly and pivotally coupled to the tubular
support member, and each upper expansion segment movable relative to the
inclined surface of one of the plurality of cam arms to adjust the radial
position of an
eternal surface of the segment to adjust the diameter of the expansion cone
assembly, a lower tubular support member defining a second passage fluidicly
coupled to the first passage releasably coupled to the upper tubular support
member, a lower cam assembly coupled to the lower tubular support member
including a tubular base coupled to the lower tubular support member and a
plurality
of cam arms extending from the tubular base in an upward longitudinal
direction,
each cam arm defining an inclined surface that mates with the inclined surface
of a
24
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
corresponding one of the upper expansion cone segments, wherein the cams arms
of the upper cam assembly are interleaved with and overlap the cam arms of the
lower cam assembly; and a plurality of lower expansion cone segments
interleaved
with cam arms of the lower cam assembly, each lower expansion cone segment
pivotally coupled to the lower tubular support member and mating with the
inclined
surface of a corresponding one of the cam arms of the upper cam assembly and
each lower expansion segment movable relative to the inclined surface of one
of
the plurality of cam arms to adjust the radial position of an eternal surface
of the
segment to adjust the diameter of the expansion cone assembly, wherein the
lower
expansion cone segments interleave and overlap the upper expansion cone
segments and wherein the upper and lower expansion cone segments each
approximate an arcuate spherical external surface for plastically deforming
and
radially expanding the expandable tubular member.
In another embodiment, an apparatus for radially expanding and plastically
deforming an expandable tubular member, is disclosed including a tubular
support
member, a adjustable expansion cone assembly coupled to the tubular support
member, an expandable tubular member coupled to the adjustable expansion cone
assembly, means for displacing the adjustable expansion cone assembly relative
to
the expandable tubular member and means for adjusting the adjustable expansion
cone assembly from one effective expansion diameter to another effective
expansion diameter.
In another embodiment the tubular support member includes an upper tubular
support member comprising an internal flange and a lower tubular support
member
comprising an internal flange, wherein the expansion cone includes an upper
cam
assembly coupled to the upper tubular support member including a tubular base
coupled to the upper support member and a plurality of cam arms extending from
the tubular base in a downward longitudinal direction, each cam arm defining
an
inclined surface, a plurality of upper expansion cone segments interleaved
with the
cam arms of the upper cam assembly and pivotally coupled to the internal
flange of
the upper tubular support member, a lower cam assembly coupled to the lower
tubular support member including a tubular base coupled to the lower tubular
support member and a plurality of cam arms extending from the tubular base in
an
upward longitudinal direction, each cam arm defining an inclined surface that
mates
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
with the inclined surFace of a corresponding one of the upper expansion cone
segments, wherein the cams arms of the upper cam assembly are interleaved with
and overlap the cam arms of the lower cam assembly and a plurality of lower
expansion cone segments interleaved with cam arms of the lower cam assembly,
each lower expansion cone segment pivotally coupled to the internal flange of
the
lower tubular support member and mating with the inclined surface of a
corresponding one of the cam arms of the upper cam assembly; and wherein the
apparatus further includes means for releasably coupling the upper tubular
support
member to the lower tubular support member and means for limiting movement of
the upper tubular support member relative to the lower tubular support member.
In one alternative embodiment the apparatus for radially expanding and
plastically deforming an expandable tubular member further includes means for
pivoting the upper expansion cone segments and means for pivoting the lower
expansion cone segments.
In one alternative embodiment the apparatus for radially expanding and
plastically deforming an expandable tubular member further includes means for
pulling the adjustable expansion cone assembly through the expandable tubular
member.
A adjustable expansion cone assembly is disclosed, that includes an upper
cam assembly including a tubular base and a plurality of cam arms extending
from
the tubular base in a downward longitudinal direction, each cam arm defining
an
inclined surface, a plurality of upper expansion cone segments interleaved
with the
cam arms of the upper cam assembly, a lower cam assembly including a tubular
base and a plurality of cam arms extending from the tubular base in an upward;
longitudinal direction, each cam arm defining an inclined surface that mates
with the
inclined surface of a corresponding one of the upper expansion cone segments;
wherein the cam arms of the upper cam assembly are interleaved with and
overlap
the cam arms of the lower cam assembly, a plurality of lower expansion cone
segments interleaved with cam arms of the lower cam assembly, each lower
expansion cone segment mating with the inclined surface of a corresponding one
of
the cam arms of the upper cam assembly, means for moving the upper cam
assembly toward or away from the lower expansion cone segments to adjust the
26
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
radial position of an external surface of the lower expansion cone segments,
and
means for moving the lower cam assembly toward or away from the upper
expansion cone segments to adjust the radial position of an external surface
of the
upper expansion cone segments.
In one embodiment of the adjustable expansion cone assembly, the upper
and lower expansion cone segments together approximate an arcuate spherical
external surface.
In one embodiment of the adjustable expansion cone assembly, each upper
expansion cone segment comprises an inner portion defining an arcuate
cylindrical
upper surface and arcuate cylindrical lower surfaces, an intermediate portion
defining arcuate cylindrical and spherical upper surfaces and an arcuate
conical
lower surface and an outer portion defining arcuate cylindrical upper and
lower
surfaces, and wherein each tower expansion cone segment include an inner
portion
defining an arcuate cylindrical upper surface and arcuate cylindrical lower
surfaces,
an intermediate portion defining arcuate cylindrical and spherical upper
surfaces and
an arcuate conical lower surface and an outer portion defining arcuate
cylindrical
upper and lower surFaces.
In one embodiment of the adjustable expansion cone assembly, each upper
expansion cone segment is tapered in the longitudinal direction from the
intermediate portion to the outer portion and each lower expansion cone
segment is
tapered in the longitudinal direction from the intermediate portion to the
outer
portion.
An embodiment of an apparatus for radially expanding and plastically
deforming an expandable tubular member from an initial inside diameter to a
desired
diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing is disclosed, including an upper
tubular
support member defining a first passage, one or more cup seals coupled to the
exterior surface of the upper tubular support member for sealing an interface
between the upper tubular support member and the expandable tubular member,
an expansion assembly coupled to the upper tubular support member adjustable
to
one expansion diameter corresponding to the desired diameter of the bell
portion of
the wellbore casing for forming an expanded bell portion in the expandable
tubular
member and adjustable to another expansion diameter corresponding to the
desired
diameter of the mono diameter casing for forming the mono diameter wellbore
27
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
casing, means for actuating the expandable tubular member to adjust from the
one
diameter to the other diameter and an actuator for moving the expansion
assembly
through the expandable tubular member a desired distance with the expansion
assembly adjusted to the diameter of the bell portion and for moving the
expansion
assembly through the expandable tubular member for another distance with the
expansion assembly adjusted to the desired diameter of the mono diameter
portion
of the expandable tubular member.
According to one alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly includes an expansion cone device.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly comprises a rotary expansion device.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly comprises compliant expansion device.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly comprises a hydroforming expansion device.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly comprises an adjustable expander device that is adjustable
to
the diameter of the bell portion of the expandable tubular member and wherein
the one adjustable expander device is also adjustable to the diameter
corresponding
to the desired diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
28
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
expansion assembly comprises an adjustable expander device that is adjustable
to
the diameter of the bell portion of the expandable tubular member and wherein
the one adjustable expander device is also adjustable to the diameter
corresponding
to the desired diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing and wherein the
adjustable expander device comprises an adjustable expansion cone device
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly comprises an adjustable expander device that is adjustable
to
the diameter of the bell portion of the expandable tubular member and wherein
the one adjustable expander device is also adjustable to the diameter
corresponding
to the desired diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing and wherein the
adjustable expander device includes an adjustable rotary expansion device.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly comprises an adjustable expander device that is adjustable
to
the diameter of the bell portion of the expandable tubular member and wherein
the one adjustable expander device is also adjustable to the diameter
corresponding
to the desired diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing and wherein the
adjustable expander device includes an adjustable compliant expansion device.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, the
expansion assembly comprises an adjustable expander device that is adjustable
to
the diameter of the bell portion of the expandable tubular member and wherein
the one adjustable expander device is also adjustable to the diameter
corresponding
to the desired diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing and wherein the
adjustable expander device includes an adjustable hydroforming expansion
device.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing,
wherein
the expansion assembly includes a first adjustable expander device adjustable
to the
29
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
diameter of the bell portion of the expandable tubular member and second
adjustable expander device adjustable to the diameter corresponding to the
desired
diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing.
According to another alternative embodiment of an apparatus for radially
expanding and plastically deforming an expandable tubular member from an
initial
inside diameter to a desired diameter of a mono diameter wellbore casing, ,
wherein
the expansion assembly includes a first adjustable expander device adjustable
to the
diameter of the bell portion of the expandable tubular member and collapsible
after
expanding the bell portion and a second expander device having a fixed
diameter
corresponding to the desired diameter of the mono diameter wellbore casing
such
that collapsing the first adjustable expander device effectively adjusts the
effective
expansion diameter to the fixed diameter of the second expander device.
A method of forming a mono diameter casing in a wellbore is disclosed,
including supporting a first. expandable tubular member in the wellbore using
a
tubular support member and an adjustable expansion assembly having a first
diameter smaller than the inside diameter of the expandable tubular member
injecting a fluidic material into the tubular support member, sensing the
operating
pressure of the injected fluidic material within a first interior portion of
the tubular
support member, displacing the adjustable expansion assembly relative to the
expandable tubular member and into the wellbore when the sensed operating
pressure of the injected fluidic material exceeds a predetermined level within
the first
interior portion of the tubular support member, sensing the operating pressure
of the
injected fluidic material within a second interior portion of the tubular
support
member, adjusting the effective expansion diameter of the adjustable expansion
assembly to a second diameter larger than the inside diameter of the
expandable
tubular member when the sensed operating pressure of the injected fluidic
material
exceeds a predetermined level within the second interior portion of the
tubular
support member, moving the adjustable expansion assembly having the second
diameter a predetermined distance into the expandable tubular member to
radially
expand and plastically deform a first portion of the expandable tubular
member,
activating the effective expansion diameter of the adjustable expansion
assembly to
adjust to a second diameter smaller than the first effective expansion
diameter and
moving the adjustable expansion assembly through the expandable tubular member
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
when the adjustable expansion assembly is adjusted to the third diameter, to
thereby
radially expand and plastically deform the remaining portion of the expandable
tubular member.
In an alternative embodiment, the method of forming a mono diameter
wellbore casing as in the paragraph above that further includes supporting a
second
expandable tubular member in the wellbore using a tubular support member and
an
adjustable expansion assembly having a first diameter smaller than the inside
diameter of the expandable tubular member, positioning the second expandable
tubular member in the expanded first expandable tubular member with the first
portion thereof overlapping the second expandable tubular member, injecting a
fluidic material into the tubular support member, sensing the operating
pressure of
the injected fluidic material within a first interior portion of the tubular
support
member, displacing the adjustable expansion assembly relative to the second
expandable tubular member and into the wellbore when the sensed operating
pressure of the injected fluidic material exceeds a predetermined level within
the first
interior portion of the tubular support member, sensing the operating pressure
of the
injected fluidic material within a second interior portion of the tubular
support
member, adjusting the effective expansion diameter of the adjustable expansion
assembly to the second diameter when the sensed operating pressure of the
injected fluidic material exceeds a predetermined level within the second
interior
portion of the tubular support member, moving the adjustable expansion
assembly
having the second diameter a predetermined distance into the second expandable
tubular member to radially expand and plastically deform a first portion of
the second
expandable tubular member below the first portion of the first expandable
tubular
member, activating the effective expansion diameter of the adjustable
expansion
assembly to adjust to the second diameter and moving the adjustable expansion
assembly through the second expandable tubular member and past the portion
overlapping with the first expandable tubular member when the adjustable
expansion assembly is adjusted to the third diameter, and to thereby radially
expand
and plastically deform a second portion of the second expandable tubular
member
to the same diameter as the expanded remaining portion of the first expandable
tubular member.
In an alternative embodiment the method includes expanding the expandable
31
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
tubular member using an adjustable expansion cone device
In an alternative embodiment the method includes expanding the expandable
tubular member using an adjustable a rotary expansion device.
In an alternative embodiment the method includes expanding the expandable
tubular member using an adjustable compliant expansion device.
In an alternative embodiment the method includes expanding the expandable
tubular member using an adjustable hydroforming expansion device.
In an alternative embodiment a method of a casing in a wellbore, includes
inserting an expandable tubular member into the wellbore, radially expanding
and
plastically deforming a lower portion of the expandable tubular member to a
first
inside diameter; and radially expanding and plastically deforming an upper
portion of
the expandable tubular member to a second inside diameter, wherein the first
inside
diameter is larger than the second inside diameter.
In an alternative embodiment the method of forming a casing in a wellbore, as
described in the preceding paragraph, further includes inserting a second
expandable tubular member into the expanded expandable tubular member so that
a top portion of the second expandable tubular member is overlapped by the
expanded lower portion of the expanded expandable tubular member and expanding
the top portion of the second expandable tubular member to the second diameter
of
so that the top portion of the second expandable tubular member is expanded
radially outward in the lower portion of the expanded expandable tubular
member.
In an alternative embodiment of the method of forming a casing in a wellbore,
expanding the lower and upper portions of the expandable tubular members
includes expanding using an expansion cone device.
In an alternative embodiment of the method of forming a casing in a wellbore,
expanding the lower and upper portions of the expandable tubular members
includes expanding using a rotary expansion device.
In an alternative embodiment of the method of forming a casing in a wellbore,
expanding the Power and upper portions of the expandable tubular members
includes expanding using a compliant expansion device.
In an alternative embodiment of the method of forming a casing in a wellbore,
expanding the tower and upper portions of the expandable tubular members
includes expanding using a hydroforming expansion device.
32
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
An alternative embodiment of the method of forming a mono diameter casing
in a wellbore includes supporting a first expandable tubular member in the
wellbore
using a tubular support member and an adjustable expansion cone assembly
having
a first diameter smaller than the inside diameter of the expandable tubular
member,
injecting a fluidic material into the tubular support member, sensing the
operating
pressure of the injected fluidic material within a first interior portion of
the tubular
support member, displacing the adjustable expansion cone assembly relative to
the
expandable tubular member and into the wellbore when the sensed operating
pressure of the injected fluidic material exceeds a predetermined level within
the first
interior portion of the tubular support member, sensing the operating pressure
of the
injected fluidic material within a second interior portion of the tubular
support
member, adjusting the effective expansion diameter of the adjustable expansion
cone assembly to a second diameter larger than the inside diameter of the
expandable tubular member when the sensed operating pressure of the injected
fluidic material exceeds a predetermined level within the second interior
portion of
the tubular support member, moving the adjustable expansion cone assembly
having the second diameter a predetermined distance into the expandable
tubular
member to radially expand and plastically deform a first portion of the
expandable
tubular member, activating the effective expansion diameter of the adjustable
expansion cone assembly to adjust to a second diameter smaller than the first
effective expansion diameter and moving the adjustable expansion cone assembly
through the expandable tubular member when the adjustable expansion cone
assembly is adjusted to the third diameter, to thereby radially expand and
plastically
deform the remaining portion of the expandable tubular member.
In an alternative embodiment of the method of forming a mono diameter
casing in a wellbore, as described in the preceding paragraph, further
includes
supporting a second expandable tubular member in the wellbore using a tubular
support member and an adjustable expansion cone assembly having a first
diameter
smaller than the inside diameter of the expandable tubular member, positioning
the
second expandable tubular member in the expanded first expandable tubular
member with the first portion thereof overlapping the second expandable
tubular
member, injecting a fluidic material into the tubular support member, sensing
the
operating pressure of the injected fluidic material within a first interior
portion of the
33
CA 02499030 2005-03-14
WO 2004/027205 PCT/US2003/029859
tubular support member, displacing the adjustable expansion cone assembly
relative
to the second expandable tubular member and into the wellbore when the sensed
operating pressure of the injected fluidic material exceeds a predetermined
level
within the first interior portion of the tubular support member, sensing the
operating
pressure of the injected fluidic material within a second interior portion of
the tubular
support member, adjusting the effective expansion diameter of the adjustable
expansion cone assembly to the second diameter when the sensed operating
pressure of the injected fluidic material exceeds a predetermined level within
the
second interior portion of the tubular support member, moving the adjustable
expansion cone assembly having the second diameter a predetermined distance
into the second expandable tubular member to radially expand and plastically
deform a first portion of the second expandable tubular member below the first
portion of the first expandable tubular member, activating the effective
expansion
diameter of the adjustable expansion cone assembly to adjust to the second
diameter and moving the adjustable expansion cone assembly through the second
expandable tubular member and past the portion overlapping with the first
expandable tubular member when the adjustable expansion cone assembly is
adjusted to the third diameter, and to thereby radially expand and plastically
deform
a second portion of the second expandable tubular member to the same diameter
as the expanded remaining portion of the first expandable tubular member.
It is understood that variations may be made in the foregoing without
departing from the scope of the invention. For example, the teachings of the
present
illustrative embodiments may be used to provide a wellbore casing, a pipeline,
or a
structural support.
Although illustrative embodiments of the invention have been shown and
described, a wide range of modification, changes and substitution is
contemplated in
the foregoing disclosure. In some instances, some features of the present
invention
may be employed without a corresponding use of the other features.
Accordingly, it
is appropriate that the appended claims be construed broadly and in a manner
consistent with the scope of the invention.
34