Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
Electrical press deVlce
The invention relates to an electrical press device with an electric motor, a
step-up gear, a
spindle drive in the form of a satellite roller screw, the thread spindle of
which is connected to
the step-up gear and the threaded nut of which is guided in a cylindrical
housing in a non-
cotatable meaner, and such that it can be axially displaced, and is connected
to a pressing tool,
for converting a rotary motion of the electric motor into a linear motion of
the pressing tool, a
travel sensor for determining the distance travelled by the pressing tool, and
a sensor for de-
termining the pressing force of the pressing tool.
A press device of this kind is known from DE 100 11 859 C2, in which the
thread spindle is
supported against the housing in the axial direction by a flange shoulder sad
a tapered roller
bearing. The tapered roller bearing is only secured against axial displacement
on the thread
spindle by means of a retaining ring and can in effect not tranafa any axial
forces in the
direction of traction. Nor is this necessary in the known pressing-in device,
since pressing
fords merely have to be generated in one direction (the diration of pressing).
The invrntion sets out to achieve the object of developing as electrical press
device of the
kind desedbod at the begirming such that pressing forces (traction and
pressing forces) can be
generated, the aim being to keep the diameter of the cylindrical housing as
small as possible.
A further object of the invention consists in providing an electrical press
device that can be
firmly attached to a machine frame or the h'ke in a freely selectable manner
with regard to its
axial position. This is not possible in the known press device, since the
housing there is
equipped with a mounting flange, so that the press device can only be attached
in a pre-
determined position.
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
-2-
A further objat the invention consists in providing a simpler structural
design for the guide
for the threaded nut of the spindle dnvc, which is non-rotatable and can be
axially displaced
relative to the housing.
The first-mentionod object of the invention is achieved by an electrical press
device with as
eloctric motor, a step-up gear, a spindle drive in the form of a satellite
roller xrew, the thread
spindle of which is connected to the step-up goat and the threaded nut of
which is ,guided in a
cylindrical housing in a uon-rotatable manner, and such that it can be axially
displaced, and is
connected to a pressing tool, for converting a rotary motion of the electric
motor into a linear
motion of the pressing tool, a travel sensor for determining the distance
travelled by the press-
ing tool, and a sensor for determining the pressing force of the pressing
tool, the press device
being charactcrisai by the fact that the thread spindle is mountod in the
housing by means of a
pre-loaded set of angular contact ball bearings, the first angular contact
ball bearings) of
which is (ate) suitable for supporting traction forces and the second angular
contact ball bear-
ings) of which is (are) suitable fvr supporting pressing forces, the inner
rings of the angular
contact ball bearings being contiguously clamped by a lock nut against a shaft
shoulder of the
thread spindle, and the outer rings of the angular contact ball bearing being
contiguously
clamped by a housing nut against a housing shoulder, so that substantially
equally great trac-
tion or pressing forces can be supported without any axial play.
it can be provided for the set of angular contact ball bearings to have two
first and two second
angular contact ball bearings.
It is advantageously provided for the step-up gear to be designed as a mufti-
stage transmis-
sion, where the step-up gear may have a rtan~nission ratio o f for example,
i=S .
It is conveniently provided for the electric motor to be controlled
electrically and to have an
angle encoder on the motor shaft, a means being present to determine the path
travelled by the
pressing tool by reference to the angle signals of the angle encoder, the
transmission ratio of
the step-up gear and the thread pitch of the spindle drive.
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
-3-
It is advantageously provided for a torque sensor to be disposed betweai an
output shaft of
the step-up gear and the thread spindle. The torque sensor may have a
transmitter for trans-
miffing measurod data contact-&ec. The torque sensor is preferably easily
accessible and
exchangeable in order for it to be adapted to different pressing forces. In
this way, it is pos-
sible to make as full a use as possible of different measuring ranges of
torque sensors, even
with difTerent pressing forces, so that the accuracy of measurement increases.
It is advantageously provided for there to be a closable opening in the
housing, offering
access to the torque sensor.
The invention further provides that thtre is a motor brake disposed on the
motor shaft, which
is applied in the absence of current and is released when current is carried.
This ensures that,
even if a transmission does not stop automatically, any motion of the press
device is prevent-
ed in the event of a power failure.
It is advantageously provided for there to be a sprung stop between the
threaded nut and the
housing for determining the zero position of the travel measuring device.
The stop can be designed as a sprung ring on the threaded nut.
The thread spindle preferably has a multiple-start, especially five-start,
thread.
The threaded nut can be retained in an axially stepped support sleeve, which
is guided in the
housing in a non-rotatable manner, and such that it can be axially displaced.
In a preferred embodiment, it is provided that the support sleeve is connected
to, or forms, an
inner sleeve of an axial guidance system with rccirculating ball bearings, the
outer sleeve of
which is connected to the housing in a non-rotatable manna.
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
-4-
The support sleeve can have a cylindrical supporting part with a relatively
large diameter and
a smaller-diameter sleeve bolted to it, forming the pressing ram.
The housing preferably has an outer cylindrical clamping surface for fixing
the press device in
a freely selectable axial clamping position.
For this purpose, a double-cone set of clamps can be disposed on the clamping
surface.
Further advantages and features of the invention will become apparent from the
following
description of a preferred embodiment, reference being made to a draw ng in
which
Fig. 1 shows a partially cut side elevation of a press device in accordance
with the
invention;
Fig. 2 shows an enlarged detail from Fig. 1 in the region of the set of
angular contact
ball beatings;
Fig. 3 shows au enlarged detail fmm Fig. 1 in the region of the axial guidance
system
with recirculating ball bearings;
Fig. 4 shows a cross-sectional elevation along line N -1'V in Figs. 1 or 2;
and
Fig. 5 shows a cross-sectional elevation along line V - V in Figs. 1 or 3.
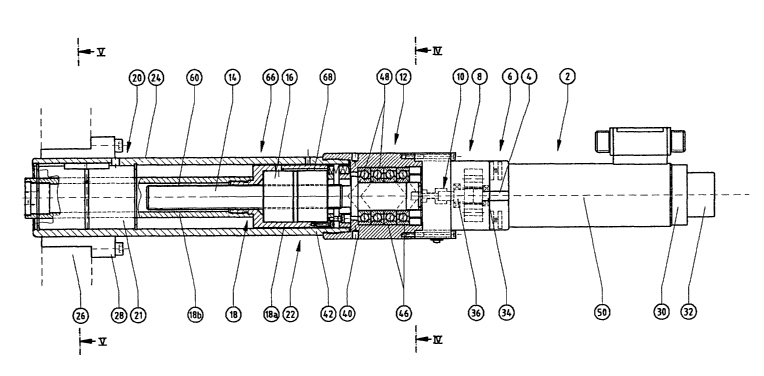
Referring first to Fig. 1, which shows an electrical press device according to
the present
invention in a partially cut-out side elevation: major components of the press
device ate an
electric motor 2 with a motor brake 6 acting on its motor shaft 4, a sttp-up
gear 8, a torque
sensor 10, a set of angular contact ball bearings 12, in which is carriod a
thread spindle 14
which, together with a threaded nut 16, forms a spindle drive 66, and a
support sleeve 18
retaining the threaded nut 16, said support sleeve for its part being carried
in an axial guid-
ance system with roeirculating ball bearings Z0, which in turn is supported in
a cylindrical
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
_5-
housing 22 which has a eylindnieal outer clamping surface Z4 for fixing it in
a freely select.
able position on a machine part 26 or the like by means of a set of clamps 28.
Disposed on the motor shaft 4 is arr angle encoder 30 as a zero-based
measuz~ement sensor,
and there is a resolver 32 present to evaluate the signals of the angle
encoder in order to
obtain a distance signal. This is done by refemttg, in a known manner, to the
transmission
ratio of the step-up gear 8 and the thread pitch of the spindle drive b6
(thread spindle 14,
threaded nut 16).
The motor brake 6 is designed such that it is applied by means of springs in
the absence of
current and prevents the motor shag from rotating, but is released when the
power supply is
present.
The step-up gear 8 could be designed as a planetary gear, though in the
preferred embodiment
it is designed as a mufti-stage transmission with a transmission ratio of e.g.
i=5. An input
shaft 34 of the step-up gear 8 is connected to the motor shaft 4, while an
output shaft 36 of the
step-up gear is connected to the thread spindle 14 and carries the torque
sensor 10. The torque
sensor 10 is equipped with a transmitter, so that wireless or sliding-contact-
free transmission
of the measured values is possible. The torque sensor 10 is relatively easily
accessible via a
closable opening in the housing 38 and is therefore easy to exchange, so that
a torque sensor
can be used which is adapted in each case to a pressing force to be achieved
in that particular
case. This offers the advantage that, with a torque sensor that is adapted to
a particulax maxi-
mum torquelpressing force, as full a use as possible can be made of the
measuring range of
the torque sensor, so that the measuring accuracy is maximised. In this way,
an accuracy of
less than 1 % of the maximum or ultimate value can be achieved, and thus also
a correspond-
ing accuracy in setting a desired pressing force, which is determined by the
torque.
The thread spindle 14, now referring also to Figs. 2 and 4, is carried in the
housing 22 by
means of a set of angular contact ball bearings designated as a whole by 12,
which in the
present case has a bearing sleeve 40 and an outer guide 42 belted to it.
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
-6-
In the embodiment described here, the set of angular contact ball bearings 12
consists of a
total of four angular contact ball bearings, each of which can support the
same axial and radial
forces, which is indicated by resultant load vxtors 44 running at 45°
to the longitudinal axis
50,
Two first angular contact ball bearings 46 arc disposed in each case to
support traction forces
(acting towards the left in Figs. 1, 2), and two second angular contact ball
bearings 48 are
disposed in each case to support pressing forces (acting towards the right in
Figs. 1, 2). The
inner rings of the angular contact ball bearings are directly contiguously
clamped by a lock
nut 52 against a shaft shoulder 54 of the thread spindle, while the outer
rings of the angular
contact ball bearings arc correspondingly contiguously clamped by a housing
nut 56 against a
housing shoulder 58. The angular contact ball bearings are manufactured in
such a way that,
when the lock and housing nuts arc tightened, no play reanains, but, on the
contrary, the two
pairs of bearings 46 and 48 aligned in opposite directions are pre-loaded, so
that substantially
the same traction or pressing forces can be supported without any axial play
occurring. A
further advantage of this construction is that no particular dimensional
tolerances need to be
observed in the region of the bearing sleeve or the thread spindle, as far as
the axial dimen-
sions arc concerned, since tightening the inner and outer rings with the lock
or housing nuts is
sufftcient for faultless functioning without any play,
Adjoining the shaft shoulder 54 is the thread spindle 14 with, in this case, a
five-start thread
portion 60, the length of which is dimensioned such that the desired pressing
tasks can be
performed.
With its thread portion 60 and the threaded nut 16 and rollers, the thread
spindle 14 forms the
spindle drive 66, which takes the form of a satellite roller screw (also
referred to as a plane-
tary roller ihrcad spindle drive). The threaded nut 16 is connected to the
support sleeve 18 in a
non-rotatable manner by means of a feather key 68, which can be moved in the
axial direction
inside the outer guide 42. Fastening bolts 70 fix the threaded nut 16 within
the support sleeve
18 via a fastening ring 72, with a ring 76 sprung by means of pressure springs
74 forming a
sprung stop on the fastening ring 72 or the support sleeve 18. When the
spindle drive moves
backwards (towards the right) the threaded nut with the ring 76 runs up
against the housing
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
_7_
shoulder 58 of the bearing sleeve 40, as a result of which the torque sensor
10 detects an
increase in torque, so that it is possible in this way to determine the zero
position.
The support sleeve 18 is formed from a supporting part 18a with a relatively
large diameter
retaining the threaded nut 16, and a sleeve 1 Sb with a smaller diameter
bolted to it and form-
ing the pressing ram. The sleeve 18b is carried in, or forms, an inner sleeve
of the axial guid-
ance system with recirculating ball bearings 20 (Figs. 3 and 5), the outer
sleeve 21 of which is
secured in the housing or the outer guide 42 by retaining rings 77 such that
it cannot be axial-
ly displaced and is connxtcd to it in a non-rotatablc manner by means of a
feather key 78. A
pressing tool (not shown) is mounted on the end of the sleeve 18b.
The set of clamps 28 has conical clamping members, with which the press device
can be fixed
to the machine part 26 in a freely selectable axial clamping position on its
outer guide 42.
CA 02504221 2005-04-28
-$-
List of reference numerals
2 Elxtric motor 52 Lock nut
4 Motor shaft 54 Shaft shoulder
6 Motor brake 56 Housing nut
8 Step-up gear 58 Housing shoulder
Torque savor 60 Thread portion
12 Set of angular contact ball bearings 66 Spindle drive
14 Thread spindle 68 Feather key
16 Threaded nut 70 Fastening
bolt
18 Support sleeve 72 Fastening
ring
18a Supporting Part 74 Pressure spring
18b Sleeve 76 Ring
Axi2~1 guidance system with recirculating77 Retaining
ball bearings ring
21 Outer sleeve 78 Feather key
22 housing
24 Clamping surface
26 Machine part
28 Set of clamps
Angle encoder
32 Resolver
34 Input shaft
36 Output shaft
38 Opening in the housing
Bearing sleeve
42 Outer guide
44 Resultant load vector
46 First angular contact ball bearing
48 Second angular contact ball bearing
Longitudinal axis