Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02509062 2007-09-06
1
"CASING CENTRALISER"
This is a divisional application of Canadian
application serial no. 2,144,504 filed March 13, 1995.
This invention relates to a casing centraliser and
relates more particularly but not exclusively to a
casing centraliser for facilitating the cementing of
casing in a well.
When a well has been drilled for the eventual
production of hydrocarbons, one of the procedures
commonly employed in readying the well for production
comprises emplacing a hollow tubular casing in the
well, and filling the space between the exterior of the
casing and the well bore with cement, principally as a
sealant and also as a mechanical support for the
casing. Since it is desirable that the casing be
centralized in the well bore when cemented, proposals
have been made for providing the casing (prior to
cementing) with externally mounted centralisers to hold
the casing away from the well bore and towards the
centre of the bore.
According to a first aspect of the present invention
there is provided a casing centraliser comprising an
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
2
annular body, a substantially cylindrical bore
extending longitudinally through said body, and a
peripheral array of a plurality of longitudinally
extending blades circumferentially distributed around
said body to define a flow path between each
circumferentially adjacent pair of said blades, each
said flow path providing a fluid flow path between
longitudinally opposite ends of said centraliser, each
said blade having a radially outer edge providing a
well bore-contacting surface, and said cylindrical bore
through said body being a clearance fit around tubular
casing intended to be centralised by said casing
centraliser.
Said centraliser is preferably free of any means
tightly gripping a casing when said centraliser is
installed thereon, whereby said centraliser and said
casing are mutually rotatable.
Said centraliser may be formed of a zinc alloy, which
alloy is preferably one of the "ZA" range of zinc
alloys supplied by Brock Alloys (GB).
Said blades are preferably mutually substantially
equidistantly distributed around said body. Said blades
preferably each extend circumferentially at least
part-way around said body between longitudinally
opposite ends thereof to provide a circumferential
distribution of each said well bore-contacting surface.
Each said blade preferably has a radially inner root
integral with said body, each said radially inner root
preferably being circumferentially wider than the
respective radially outer edge. Said blades are
preferably circumferentially wider at one end of the
centraliser than at the other end, said one end
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
3
preferably the lower end of the centraliser in use
thereof. Said centraliser preferably has five of said
blades.
Longitudinally opposite ends of said blades and/or of
said body may be chamfered or tapered whereby to
facilitate passage of said centraliser down a well
bore.
According to a second aspect of the present invention
there is provided a centraliser stop collar for
longitudinally restraining a casing centraliser
according to the first aspect of the present invention
when installed upon casing, said stop collar comprising
a ring having a substantially cylindrical bore
extending longitudinally therethrough, said bore being
dimensioned to fit around said casing, said ring having
longitudinal lock means for longitudinally locking said
collar to said casing.
Said lock means preferably comprises one or more
internally threaded bores extending radially through
said ring, and a screw-threaded fastener in each said
internally threaded bore, each said fastener being
screwable into collar-locking contact with said casing.
Said ring may be formed of a zinc alloy which is
preferably the same alloy as that of which the
centraliser is formed. Each said internally threaded
bore may be defined by an initially separate thread
insert forming an integral part of said collar when
fabricated, for example by being cast into the ring,
and said thread inserts may be formed of materials
which are substantially different from that of the
ring, eg of brass or steel as compared to a zinc alloy.
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
4
According to a third aspect of the present invention
there is provided a combination of hollow tubular well
casing and at least one casing centraliser according to
the first aspect of the present invention fitted on
said casing, preferably to be rotatable thereon.
The or each said centraliser may be longitudinally
restrained by a respective stop collar according to the
second aspect of the present invention and installed
upon said casing at or adjacent one end of the
respective centraliser. One or more of said
centralisers may be longitudinally restrained by a
respective pair of stop collars according to the second
aspect of the present invention, one of said pair of
stop collars being installed upon said casing at or
adjacent each longitudinally opposite end of the
respective centraliser.
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention
there is provided a method of cementing a hollow
tubular well casing into a well bore, said method
comprising the step of fitting said casing with at
least one centraliser according to the first aspect of
the present invention to form a combination in
accordance with the third aspect of the present
invention, together with a necessary or desirable
number of stop collars in accordance with the second
aspect of the present invention, locating said
combination in said well bore much that the or each
said centraliser provides at least a
casing-centralising function for said casing within
said well bore and pumping cement into voids between
the exterior of said casing and the bore of the said
well.
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
Embodiments of the invention will now be described by
way of example, with reference to the accompanying
drawings wherein:-
Fig. 1 is a perspective view from above and to one
side of a first embodiment of casing centraliser
in accordance with the first aspect of the present
invention;
Fig. 2 is a plan view from above of the first
embodiment;
Fig. 3 is an underneath view of the first
embodiment;
Fig. 4 and 5 are respectively radial (plan) and
circumferential (side) views of a blade forming
part of the first embodiment;
Fig. 6,7 and 8 are respectively plan, perspective
and side views of a casing stop collar in
accordance with the second aspect of the present
invention, and suitable for use in conjunction
with the first aspect of the present invention;
and
Fig. 9 is a perspective view of a combination in
accordance with the third aspect of the present
invention.
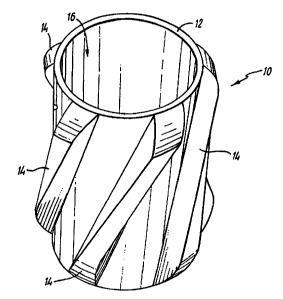
Referring first to Figs. 1-3, a casing centraliser 10
in accordance with the present invention is a unitary
annulus comprising a generally cylindrical body 12, and
an array of five equiangularly-spaced blades 14
integrally formed with the body 12. A cylindrical bore
16 extends longitudinally and coaxially through the
body 12, the bore 16 having a substantially uniform
diameter dimensioned to be a clearance fit around the
well bore casing (not shown in Fig.1-8).
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
6
Each of the blades 14 (see also Figs.4&5) not only
extends between longitudinally opposite ends of the
body 12, but also extends circumferentially part-way
around the periphery of the centraliser 10. The
skewing of the blade 14 ensures that their respective
radially outer edges 18 collectively provide a
circumferentially substantially uniform well bore-
contacting surface for the centraliser 10, as most
particularly shown in Figs.2 and 3.
Each of the blades 14 has a respective radially inner
root 20 integral with the body 12. In each of the
blades 14, the root 20 has a greater circumferential
width than the outer edge 18, ie the cross-section of
each blade 14 tapers towards the well bore-contacting
periphery of the centraliser 10. The individual and
collective shapes of the blades 14, and of the
longitudinal fluid flow passages defined between
adjacent pairs of the blades 14, gives the centraliser
10 improved flow characteristics and minimises the
build-up of trapped solids during use of the
centraliser 10.
Longitudinally opposite ends of the blades 14, and of
the body 12, are chamfered to assist in movement of the
centraliser 10 up/down a well bore.
Although the blades 14 are shown separately from the
body 12 in Figs 4 and 5 (and while the blades 4 could
be separately formed and subsequently attached to the
body 12 by any suitable means) it is preferred that the
entire centraliser 10 be fabricated as a one-piece
article, preferably by being precision cast in a
suitable metal or alloy.
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
7
A preferred material for forming the centraliser 10 is
a zinc alloy, most preferably one of the "ZA" range of
zinc alloys supplied by the Brock Alloys Company of the
United Kingdom. Use of a zinc alloy in general, and of
one of the "ZA" alloys in particular gives a number of
advantages; the zinc alloy is non-sparking (ie sparks
are not generated if the centraliser 10 collides with
steel), the zinc alloy provides superior bearing
properties, exceptional resistance to wear and
abrasion, excellent strength and hardness, and the zinc
component of the alloy offers cathodic protection to
the casing around which the centraliser 10 is located.
Since the bore 16 is a clearance fit around the casing
and since the bore 16 lacks any means of tightly
gripping a normally dimensioned casing, the centraliser
10 can not only rotate freely around the casing but
also move freely along the casing (unless and until the
centraliser collides with an obstruction, for example a
protruding casing joint). Thus to provide longitudinal
restraint for the centraliser 10 to retain the
centraliser substantially at its preferred location
along the casing but without impairing the relative
rotatability of centraliser and casing, use is made of
a stop collar 50 as illustrated in Figs. 6, 7 and 8 to
which reference will now be made.
The stop collar 50 comprises an undivided ring 52
having a bore 54 about equal in diameter to the bore 16
in order to fit alongside the centraliser 10 on the
same casing. The ring 52 is radially penetrated by
five internally threaded holes 56. The ring 52 is cast
of the same zinc alloy as the centraliser 10, and five
thread inserts 58 are either cast into the ring 52 to
form the threaded holes 56, or subsequently screwed
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
8
into or pressed into a previously cast ring.
In use of the stop collar 50, the ring 52 is fitted
around the casing in correct relationship to the
intended location of a centraliser. A grub screw 60 is
then screwed down each of the threaded holes 56 to
tighten against the underlying casing (not shown in
Figs.6-8) so as to lock the collar 50 onto the casing.
The locked-on collar 50 then provides an abutment which
stops longitudinal movement of the centraliser in one
direction while not inhibiting free relative rotation
of the centraliser and the casing. While a single stop
collar would normally be located under a centraliser on
vertical or near-vertical casing to prevent
unrestricted dropping of the centraliser down the
casing, circumstances may dictate that a stop collar be
located above a centraliser, or that a respective stop
collar be used at each end of a centraliser.
Fig. 9 shows a modified form of casing centraliser 100,
fitted around hollow tubular casing 102 which is
located within a well bore 104. The modified
centraliser 100 is essentially the same as the
centraliser 10 described above, and differs principally
in the dimensions and proportions of its blades 106.
In particular, the blades 106 are circumferentially
wider at the lower end of the centraliser 100 than they
are at the upper end. Fig.9 also illustrates the
manner in which the centraliser will hold casing out of
direct contact with the well bore and centrally within
the well bore, in preparation for subsequent cementing.
In the case of casing located within larger diameter
casing, centralisers can be employed on the inner
CA 02509062 1995-03-13
9
casing to hold it out of direct contact with the outer
casing.
Centralisers in accordance with the invention can also
be employed on drillstrings as rotary stabilisers.
While certain preferred embodiments of the invention
have been described above, the invention is not
restricted thereto, and modifications and variations
thereof can be adopted without departing from the scope
of the invention.