Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02509071 2009-09-30
1
INFORMATION SYSTEM
This application is divided from Canadian Patent Application Serial No.
2,509,071, which is a divisional of 2,253,293 filed May 2, 1997.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates generally to a program schedule guide and, more
particularly, to a system and process for allowing a television viewer to
access on-
screen television program listings and other information services in an easy
and
convenient way.
The number of television channels available to a user has grown dramatically
within the last decade, primarily due to the availability of cable and direct
broadcast
satellite systems. As the number of programs of potential interest to the
viewer has
increased, a variety of electronic program guides have been developed to help
the
viewer select programs of particular interest. For example, commonly assigned
U.S.
Patent Numbers 4,706,121 and 5,353,121 each describe schedule information
processing systems which provide the viewer with a convenient way to select
programs based on viewer supplied selection criteria.
Given the hectic lifestyle of today's society, a system which provides other
information in addition to television program schedule information would be
very
convenient for the busy viewer. Examples of information viewers may desire are
weather information, financial information, and the like. Hence, an
information
system such as a guide with regions reserved for such information would
provide a
valuable service to a user. Furthermore, these regions could be used for
advertising or
promotional purposes, which may or may not be interactive, thereby enabling
more
services to be provided without increasing the cost of the guide.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, there is provided a method for
simultaneously displaying advertisements with an electronic program guide
(EPG).
The method involves displaying a plurality of schedule information items, the
CA 02509071 2008-06-17
2
items in a database, displaying some of the television schedule information
items in a
television schedule information region. The television schedule information
region
indicates the time and channel for at least some of the displayed television
schedule
information items, selecting an advertisement for display from a plurality of
advertisements. The advertisement promotes at least one of a product, service
and a
particular program and simultaneously displaying the selected advertisement
adjacent
to the displayed plurality of television schedule information items, wherein
the
selected advertisement is displayed substantially vertically aligned with the
television
schedule information region.
The displayed advertisement may be interactive.
The method further involves activating the displayed advertisement to invoke
a function.
The displayed advertisement may change automatically independent of
changes in the displayed plurality of television schedule information items.
The displayed advertisement may have substantially the same horizontal width
of the displayed plurality of television schedule information items.
The displayed advertisement may be a payperview program and the function
may authorize payment for scheduling viewing of the payperview program.
The displayed advertisement may be about a future scheduled TV program
and the function may store the time and channel of the future scheduled TV
program
for later recording or viewing.
The function may establish a link to an Internet website and launch an
application for displaying information related to the displayed advertisement.
The displayed advertisement may be about a product or service and the
function may order the advertised product or service.
The advertisement may be displayed above the displayed plurality of
television schedule information.
The advertisement may be displayed below the displayed plurality of
television schedule information.
The function may schedule a recording of a television broadcast about an
advertised product or service
CA 02509071 2008-06-17
3
The function may tune to a television broadcast about an advertised product or
service.
In accordance with another aspect of the invention there is provided a
computer-readable medium encoded with codes for directing a processor to carry
out
any of methods above.
In accordance with another aspect of the invention, there is provided an
electronic program guide system comprising means for storing television
schedule
information items, means for displaying some of the television schedule
information
items in a television schedule information region. The television schedule
information region indicates the time and channel for at least some of the
displayed
television schedule information items, means for selecting an advertisement
for
display from a plurality of advertisements. The advertisement promotes at
least one
of a product, service and a particular program and means for displaying,
simultaneously, the selected advertisement adjacent to the displayed plurality
of
television schedule information items, wherein the selected advertisement is
displayed
substantially vertically aligned with the television schedule information
region.
In accordance with another aspect of the invention, there is provided an
article
of manufacture comprising a program storage medium readable by a computer and
embodying one or more instructions executable by the computer to perform
method
steps for arranging and managing information for an an-screen electronic
program
guide having a display screen, the method steps involving storing television
schedule
information items in a database, displaying some of the television schedule
information items in a television schedule information region. The television
schedule information region indicates the time and channel for at least some
of the
displayed television schedule information items, selecting an advertisement
for
display from a plurality of advertisements. The advertisement promotes at
least one
of a product, service and a particular program and simultaneously displaying
the
selected advertisement adjacent to the displayed plurality of television
schedule
information items, wherein the selected advertisement is displayed
substantially
vertically aligned with the television schedule information region.
CA 02509071 2008-06-17
3a
A further understanding of the nature and advantages of the present invention
may be realized by reference to the remaining portions of the specification
and the
drawings.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
Fig. 1 illustrates a preferred embodiment of a system on which a program
schedule guide according to the present invention may be displayed;
Fig. 2(a) is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen according to
the
present invention with program information, information icons, and information
regions;
Fig. 2(b) is an illustration of a promotional message screen shown to the user
when the user selects the information region of Fig. 2(a);
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
4
Fig. 3(a) is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen according to
the
present invention with program information, and information regions;
Fig. 3(b) is an illustration of a promotional message screen shown to the user
when the user selects the information region of Fig. 3(a);
Fig. 4(a) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the program
schedule
guide screen according to the present invention with program information and
an
information region;
Fig. 4(b) is an illustration of a promotional message screen shown to the user
when the user selects the information region of Fig. 4(a);
Fig. 5(a) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the program
schedule
guide screen according to the present invention with program information and
an
information region;
Fig. 5(b) is an illustration of a promotional message screen shown to the user
when the user selects the information region of Fig. 5(a);
Fig. 6(a) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the program
schedule
guide screen according to the present invention with program information and
an
information region;
Fig. 6(b) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the program
schedule
guide screen which includes virtual channels;
Fig. 6(c) is an illustration of a submenu screen shown to the user when the
user selects the information region of Fig. 6(a) or the virtual channel of
Fig. 6(b);
Fig. 6(d) is an illustration of a data page shown to the user when the user
selects one of the options shown in the submenu screen of Fig 6(c);
Fig. 7 is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the program schedule
guide which includes information regions;
Fig. 8 is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the program schedule
guide screen which includes information icons;
Fig. 9(a) is an illustration of an embodiment of the information guide;
Fig. 9(b) is an illustration of a submenu of the information guide with news
highlighted;
Fig. 9(c) is an illustration of a news information screen;
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
Fig. 10(a) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of a submenu of the
information guide with sports highlighted;
Fig. 10(b) is an illustration of a sports submenu;
Fig. 10(c) is an illustration of a sports information screen;
5 Fig. 11(a) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the information
screen with weather highlighted;
Fig. 11(b) is an illustration of a weather submenu;
Fig. 11(c) is an illustration of a weather information screen;
Fig. 11(d) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of the weather
submenu;
Fig. 11(e) is an illustration of an alternate embodiment of a weather
information screen; and
Fig. 12 illustrates the hardware elements of a preferred embodiment of the
invention.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
The present invention provides a schedule system which contains information
regions for displaying other than television program schedule information.
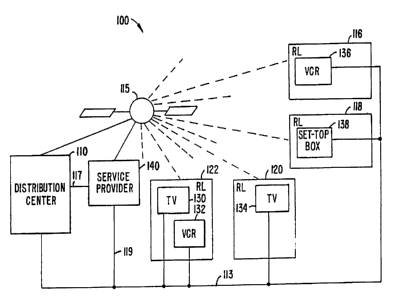
Fig. 1
illustrates a preferred embodiment of television/computer system 100 that
displays a
program schedule guide according to the present invention. As shown, system
100
includes a distribution center 110 and multiple receiving locations.
Distribution center
110 compiles data for a data-stream. In a preferred embodiment, this data-
stream is
broadcast to receiving locations 116, 118, 120, and 122; and peripheral
devices that
are located within the receiving locations receive the data-stream. Several
methods are
available for broadcasting the data-stream from distribution center 110 to
receiving
locations 116-122. For example, satellite 115 may broadcast this data-stream
within
the vertical blanking interval (VBI) of a television channel (e.g., PBS) or a
dedicated
channel to receiving locations 116, 118, 120, and 122. Alternatively, the data
may
also be broadcast out of band, i.e., using non channel specific mechanisms. In
another
preferred embodiment, the data-stream is provided to receiving locations 116,
118,
120, and 122 via transmission system 113. Transmission system 113 may be, for
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
6
example, optical fiber, coax cable, telephone line, over the air television
broadcast, or
the like.
In yet another embodiment, the peripheral devices receive the data-stream
from, for example, a local service provider 140. Service provider 140 receives
the
data-stream from distribution center 110 via line 117, and broadcasts the data-
stream
to the receiving peripheral devices via satellite 115 (or another satellite),
or via lines
119 and 113. The receiving peripheral devices may be televisions 130,
televisions
134, VCRs 132, VCRs 136, and/or cable, satellite IRD, web-browser or set-top
boxes
138. In still further embodiments, PCTVs or personal computers may be
utilized, or
the data-stream may be provided to a personal computer for use with the
computer
and/or one or more of the above devices. Hence, the system is not dependent on
hardware platforms, rather it may be a software application that may be
downloaded
to different systems.
In a preferred embodiment, information in the data-stream includes television
schedule information, advertising information, news information, weather
information, financial information, internet address linking information, and
the like.
The information in the data-stream may further include messages from the
system
operator to a specific user or to subscribers of the system in general.
Software
applications, which may be downloaded from the distribution center or located
within
the peripheral devices, utilize the schedule information provided in the data-
stream to
generate a schedule guide. The news, weather, financial, and other information
may
be included in the schedule guide, or a separate information guide may be
generated.
Advertising information and messages from the system operator to a user are
included
on the schedule guide, and may be included on the information guide as well.
In yet
another preferred embodiment, data in the front and back end of the data-
stream may
be compressed to send a tickler instead of a regular full screen video
display. The
tickler would be a PIP window, and because the window size is small, the
quality of
the picture is sufficient even though it is generated from compressed data.
If the software applications are located within the peripheral devices, they
may
be stored on a computer-readable storage medium such as a RAM, disk, or other
storage device. Where applicable, the computer-readable storage medium may
also be
a ROM. If the schedule guide is in a grid format, for example, the available
channels
CA 02509071 2008-06-17
7
may be listed on the "y" axis and various times may be listed on the "x" axis.
For
more information on how the schedule system displays information, see U.S.
Patent
No. 4,706,121 issued on 10 November 1987, U.S. Patent No., 5,479,266 issued on
26
December 1995, and U.S. Patent No. 5,479,268 issued on 26 December 1995. These
patents, like the present patent application, are assigned to StarSight
Telecast, Inc.
In another preferred embodiment, satellite 115 has processing capability.
Hence, in addition to distribution center 110, satellite 115 may also compile
data for
the data-stream. This embodiment is very advantageous as it ensures continued
and
reliable data transmission in situations where satellite 115 may not be able
to receive
data from distribution center 110. An example of such situations is during
periods of
atmospheric or terrestrial interferences, which occur when satellite 115 is in-
line with
distribution center 110 and the Sun. The Sun, having immense energy, emits a
lot of
noise thereby interfering with data transmission from the distribution center
110 to the
satellite 115. With its own data processor, satellite 115 may continue to
transmit data,
hence, ensuring continued and reliable data transfer to the receiving
locations. This
embodiment also ensures continued and reliable data transmission when
distribution
center 110 is out of service.
Fig. 2 is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen according to the
present invention. As illustrated, program guide screen 200 has program
information,
information regions for offering product and program information, and
information
icons for offering information such as sports, news and the like. Fig. 2 shows
only two
information regions, 220 and 250, although guide screen 200 may have multiple
information regions. As shown in Fig. 2, cell 220 shows a promotion for NBC's
program featuring Travolta. Program guide screen 200 also contains an
advertisement
space 250. This space can be used to provide additional advertising
opportunities, an
example is advertisements for a system operator. Preferably the space is used
for short
advertisements that change periodically, for example, on three minute
intervals. An
example of a suitable advertisement is "Enjoy Coke!". Here cell 250 shows an
advertisement from RCA. In another embodiment the information displayed in the
information regions may change as the user moves from cell to cell in the
program
guide. Alternatively, the information may change automatically after the
passage of a
predetermined number of seconds, regardless of user activity. In addition or
as an
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
8
alternative, there may be commercial icons to allow the user to get more
information
about the product or service advertised.
Information regions 220 and 250 may be color coded or otherwise visually
distinguished. They may also be placed at strategic positions within the guide
to better
catch the user's attention. As described, when an information region contains
program
information, such as cell 220, the user may move the cursor to the region (or
the
cursor may point to the region by default) and tune to the program if it is
currently on.
If the program is not currently on, the user may schedule an autotune to the
program
when the program airs. The user may further record a current program or
schedule a
recording of a future program. When an information region contains product
information, such as cell 250, the user may click on the information region to
tune to
an infomercial on the product. Alternatively, the user may schedule an
autotune to the
infomercial at a later time period, or schedule a recording of the infomercial
on the
product. In a two way system, which has a back-channel for transmitting
information
or requests from the user, the user may also order a product by clicking on an
information region and providing the necessary customer information for
transmission
to a supplier of the product, or to the system operator (service provider).
Portion 240 of guide screen 200 contains cells 245. Each cell 245 indicates
the
channel number corresponding to the program guide cell 255 lying immediately
adjacent to it in the program guide. Instead of, or in combination with the
channel
number, cells 245 may contain the program service name. For example, a cell
245
may contain the channel number 32, the service name PBS, or both.
The system operator may charge television program providers an additional
fee, per time slot, for promoting and featuring programs in the information
regions. In
this manner, the system operator may provide the guide to a user at a reduced
price
while providing more information. A number of different display arrangements
can be
used to draw the user's attention to such "special" programs. For example, the
program may be listed first in the program guide, shown in a different
typeface,
presented in a different color, given additional space for a program
description, or
have some other form of graphic enhancement, including animation.
Fig. 2(b) is an illustration of a promotional message screen 260. Screen 260
is
shown to the user when information region 220 is interactive, and the user
clicks on
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
9
information region 220. Promotional screen 260 may also contain an icon to
allow
immediate tuning to the program described by the promotional message. In
addition,
promotional screen 260 may contain another icon that returns the user to guide
200.
Since the system operator may charge a fee for displaying such promotional
information, some or all of a message portion 275 may also be used as an
additional
revenue source.
In Fig. 2(b), portion 275 contains the promotion: "Amid the flash of 70's
Disco, an aspiring young dancer ...." This promotional material, which in this
example
would typically be provided by NBC, provides the user with several benefits.
First, it
allows a program to be promoted which is not currently represented in the
program
schedule guide. Second, portion 275 may be used to provide further information
about
a specific program, such as the starring actors or a brief description of the
program
content, thus possibly gaining a larger viewing audience or market share.
Third, by
promoting a program through prominent featuring of the program in the program
guide, the broadcaster may be able to prevent potential viewers from becoming
engrossed in a program which is to continue after the start time of the
promoted
program.
Portion 280 of screen 260 is used to indicate the sponsor of the promotional
message shown in portion 275. The sponsor indication can be by broadcaster
call
letters, channel number, broadcaster name, or broadcaster insignia (e.g., the
NBC
peacock). It is also possible to eliminate portion 280, thereby enlarging
portion 275.
Additional information may therefore be displayed in portion 275. Since
portion 280
of screen 260 displays information regarding a program, the user may click on
the
information region and direct tune to the program if it is currently on.
Alternatively,
the user may schedule automatic tuning to the program when the program comes
on.
If the user schedules an autotune, the system may request confirmation from
the user
before tuning to the program, or the system may tune to the program directly.
Preferably, the system will request user confirmation before tuning to the
program. If
user confirmation is requested, additional information regions may be
displayed until
the user makes his confirmation. These information regions may include
advertising
for products or services.
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
If the promoted program is a pay-per-view program, the system may authorize
payment for the program automatically. Preferably, the system will request
user
confirmation before authorizing payment of the program. The user may further
choose
to record the promoted program, whether it is a current program, a future
program, or
5 a pay-per-view program. If the user requests recording of a pay-per-view
program, the
system may ask for confirmation before authorizing payment for the program. If
the
user requests recording of a future program, the system may also request user
confirmation. Additional information regions may also be displayed while the
user
confirms his/her recording request.
10 If an information region displays advertising or promotional material, the
user
may activate an icon, click on the region, or select a menu item to view
additional
information about the product or service advertised. From these additional
information displays, the user may learn more about the product or service,
order the
product or service, or find out where the product or service may be obtained.
The
additional displays would of course allow the user to return to the previous
displays
after the user has seen the desired information displays.
The invention may also allow the user to switch between full screen display
and a PIP window display of the guide via, for example, an on screen menu with
cursor control. This feature would allow a user to see a large scale version
of the
guide, or to be able to see the guide while also getting a"flavor" for a
currently
selected show through only partial observation of the show. Preferably in this
mode,
the audio for the show also continues to be played.
Fig. 3(a) is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen 300 with
program information 320 and interactive information regions 330 and 340. As
can be
seen, guide screen 300 does not contain information icons. Hence, more
schedule
information may be shown on the screen, thereby allowing the user to access
more
schedule information per screen. Information region 320, like information
region 220,
promotes a program. In addition, it provides a brief description of the
program
content, thereby allowing information other than program description to be
shown on
promotional message screen 350 (Fig. 3(b)). As shown by Fig. 3(b), message
screen
350 contains contest information, however, other information related to the
program
may also be shown on screen 350.
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
11
Fig. 4(a) is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen 400. As shown,
the user may move a cursor across region 410 to move between the different
days of
the week. In Fig. 4(a), the user has selected Wednesday. Hence, the schedule
information displayed is for Wednesday, and the time shown is the current
time. The
system knows what time the user is watching television, and automatically
adjusts the
cursor to be located on default on a cell that corresponds to the current
time.
As shown, guide screen 400 has one information region 420, which is
promoting a program that may be on shortly or is currently on. Information
region
420 is interactive. Hence, if the user clicks on region 420, the user may see
message
screen 450 (Fig. 4(b)), which displays a description of the program content.
In
addition, message screen 450 may also display promotional materials about an
upcoming program. This way, the system operator may indirectly promote
multiple
programs on region 420. If the program is currently on, the user may click on
icon
460 to tune to the program. If the program will come on shortly, the user will
be tuned
to the channel that corresponds to the program. Alternatively, the user may
click on
icon 470 to start recording the program if the program is on. On occasions
where the
program will come on shortly, the system will start recording the program when
the
program comes on.
Fig. 5(a) is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen 500. As shown,
guide screen 500 has one information region 520, which is interactive.
Information
region 520 is promoting a program that will air in the future. In this case,
if the user
clicks on region 520, the user may see message screen 550 (Fig. 5(b)), which
also
displays a description of the program content. In another embodiment, message
screen
500 may also contain an icon, which the user may click on to view a short
video
preview. This preview may be shown in a PIP window, and the preview video data
may be transmitted in a compressed format. As mentioned, the size of the
window
allows a decent video display to be generated from compressed data. Message
screen
550 also displays promotional materials about an upcoming program. However,
because the program will not air until a later date, message screen 550 has
icon 560,
which when clicked on by the user, will allow the user to schedule an autotune
to the
program when the program comes on. Once the user has scheduled an autotune,
the
system will automatically tune to the program when the program airs.
Preferably, user
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
12
confirmation is requested before the system tunes to the program.
Alternatively, the
user may click on icon 570 to schedule a recording of the program. The system
will
automatically start recording the program when the program comes on.
In another embodiment, the system may automatically tune a user to a
promoted program when the program comes on. This may happen whether or not the
user has scheduled an autotune to the program. Preferably, the system will ask
the
user whether the user wishes to tune to the program before automatically
tuning to the
program.
The interactive and non-interactive information screens may both be used for
displaying scrolling messages or static messages. As discussed, these
information
screens may be used to promote programs as well as products. In addition, the
information screens may also be used to send messages to specific users, for
example,
alerting a user that his/her bill is overdue. This is because each guide
system has a
unique unit address. Hence, the system operator is able to send messages to
specific
users by sending the messages to the respective unit addresses. Of course, the
information screens may be used to send system wide messages to all users. For
example, the information screens may be used to send alerts to all users, for
example,
of an impending disaster. The information screens may further be used to send
messages to a specific group of users. For example, the system could send a
message
to all Magnavox television owners by checking for Magnavox television codes as
this
information is entered into the system when the user first sets up the system.
To
ensure that messages to the users are read by the users, such messages will
have a bit
attached to them that keeps them in the information screen until the user
indicates that
he/she has seen the message. The user may indicate that he/she has seen the
message
by pushing a button on a user input device or by clicking on an icon on the
guide to
clear the message. This way, even though the message may be placed by the
system
operator in the morning, the user may still see the message when the user
watches
television at Prime Time. After the message is cleared, the system will place
advertisements or promotions appropriate for the time when the message is
cleared in
the information screen.
Fig. 6(a) is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen 600. As shown,
guide screen 600 has an interactive information region 620, which promotes a
website
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
13
connected with a program. In an alternate embodiment (Fig. 6(b)), guide screen
600
may include a virtual channel 640. A virtual channel is a channel that does
not tune to
television programs; instead, the channel may launch an application, connect
to an
internet site, connect to a information guide, and the like. In the example as
shown in
Fig. 6(b), virtual channel 640 contains an internet address - also called a
Uniform
Resource Locator (URL); hence it connects to an internet site. As shown in
Fig. 6(b),
region 620 may be used to display promotional materials in this alternate
embodiment. If a user selects virtual channel 640 of Fig. 6(b), or information
region
620 of Fig. 6(a), the user may see submenu screen 650 of Fig. 6(c).
As shown in Fig. 6(c), the user may choose to connect to the Seinfeld web
page, the NBC web page that promotes the Seinfeld show, or the Comedy Network
web page by clicking on one of the three website icons 660, 665, and 669,
respectively. The system will launch a web-browser when the user selects an
information region that promotes a website, or tunes to a virtual channel
containing a
URL. After the user has made his/her selection, the system will insert the URL
corresponding to the selected website into the web-browser, which will begin
to
access the web and search for the website selected by the user to connect the
user to
the website data page. Hence, if the user selects one of the website icons,
the system
will connect the user to the website that corresponds to the icon. Fig. 6(d)
is an
illustration of a web page 680 shown to the user when the user chooses to
connect to
the NBC web page. As shown, after the user is connected to the page, the user
may
participate in promotions on the page just as if the user had connected to the
page
directly through a web-browser.
Fig. 6(d) further shows window 688, which shows the television program that
the user was viewing before the user selected virtual channel 640 from program
guide
screen 600 of Fig. 6(b), or clicked on information region 620 of Fig. 6(a).
The user
may resume watching the television program by clicking on window 688. This is
referred as "hypertuning," and the system will return the user to the program
the user
was viewing. While the user is viewing the program, the system preferably
displays a
network icon that the user may click on to hypertune to the web page.
Alternatively,
the system may display the page in a picture-in-picture window such as window
688
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
14
while the viewer is viewing a program. The user may click on the picture-in-
picture
web page to hypertune to the page.
In another preferred embodiment, after the user has selected either icon 660,
665, or 669 of Fig. 6(c), the user may tune to the program the viewer was
watching
before accessing the guide. The system will display a"searching' symbol while
launching a web-browser and searching for the website that the user has
requested.
After the system has connected to the website, the system will notify the user
that the
search is complete, and asks whether the user wishes to hypertune to the web
page. In
yet another preferred embodiment, the user may click on any program titles
shown in
the program guide cells, and the system will display a list of one or more
websites that
are related to the program. The user may select to tune to the program or
connect to
one of the websites. In addition, the user may click on an icon or press a
remote
control button to toggle between watching television and browsing the web.
Fig. 7 is an illustration of a program schedule guide screen 700 with non-
interactive program portion 705 and interactive information regions 710 and
715.
Portion 705, as shown, is a time slice of schedule information for current
programs.
Since the user may not interact with portion 705 of guide screen 700, portion
705 may
be updated automatically over time to show current and future programs. The
amount
of future programs shown may be predetermined. Hence, the user may see what is
currently on, and what programs will come on up to a predetermined amount of
time.
However, the user may not obtain more information regarding the programs, tune
to
the programs from portion 705, or record the programs from portion 705.
As shown in Fig. 7, information region 710 contains program promotional
information. Since information region 710 is interactive with the user, the
user may
click on information region 710 to get further information about the programs
shown
in the region. The user may further click on information region 710 to tune to
the
program if it is currently on, or the user may schedule an autotune to the
program
when it comes on. When autotune is scheduled, the system may or may not notify
the
user before automatically tuning to the program when the program comes on.
Preferably, the system will request confirmation from the user before
automatically
tuning to the program. Finally, the user may schedule a recording of a future
program
or begin recording of a program currently on. As discussed, if the system
requests
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
confirmation from the user, additional information regions may be displayed
while the
user confirms his/her request.
Information region 715 may either be a static or scrolling message area that
contains selected news or sports information. For example, the latest sports
scores can
5 scroll across information region 715. Although in the preferred embodiment,
the type
of information shown in information region 715 is determined by the system
operator,
it is also possible to allow the user to select the type of information to be
shown in
information region 715.
Fig. 8 is an illustration of a program guide screen 800. Screen 800 contains a
10 program schedule portion 805 similar in nature to the schedule guides
previously
described. In addition, screen 800 contains several information icons 810.
Icons 810
can represent local or national weather forecasts, local or national news,
sports news,
sports scores, financial news, and the like. In response to the user selecting
one of
icons 810, screen 800 may be replaced with one or more additional information
15 screens. For example, the weather information screen may display the
current weather
conditions or weather predictions for a plurality of regions. The sports score
information screen may have icons or regions to represent each of a plurality
of
sports. A user may click on the individual icons or regions to view another
screen
dedicated to a single sport, or the sports score information screen may
display the
scores for different sports and sports teams on the same screen. The financial
news
information screen may likewise have icons or regions that the user may click
on to
choose other screens dedicated to specific financial markets. Alternatively,
the
financial news information screen may combine and display the financial
markets on
one screen.
Fig. 9(a) is an illustration of an information guide screen 900. As shown,
information guide screen 900 contains news, weather, sports, and horoscope
information, however, other types of information may also be shown by
information
guide screen 900. As discussed, in an alternate embodiment, an information
guide
may be provided in addition to the program guide. The information guide may be
connected to the program guide, or it may be a separate program. Since the
information guide contains news, weather, sports, and other information, it
may
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
16
replace the information icons on the program guide, thereby allowing the
program
guide screen to show the user more program information.
In Fig. 9(a), the user has selected "National News." Fig. 9(b) is an
illustration
of a submenu 920 of information guide screen 900. As can be seen, submenu 920
further breaks "National News" down into the different headlines. In a
preferred
embodiment, the user may tune to CNN or other Network News Station from
submenu 920. The system operator may charge a fee for this service, and may
allow
the user to tune to one or more Network News Station depending on the fees
paid by
the Network News Providers. Hence, CNN, for example, may pay a premium fee to
be the only News Station that the user may connect to from submenu 920.
Alternatively, CNN may pay a regular fee, and the user may tune to CNN, and
other
News Stations that have paid the regular fee.
From submenu 920, the user may highlight one of the headlines to select the
headline and obtain the story. In this example, the story is displayed
according to Fig.
9(c) in a news information screen 940. Alternatively, the user may click on a
video
icon (not shown) on screen 940 to further view a video clip relating to the
story. The
system may access the video clip via the video network, i.e., via cable,
direct
broadcast satellite, and the like. The video clip could be generated from
compressed
data, and if so, it may be presented in a PIP tickler format. Alternatively,
the system
may link to, for example, CNN's website, and retrieve an Audio-Video-
Interleaved
(AVI) file to present a moving picture related to the headline to the user.
The video
icon may also be available from submenu screen 920. Hence the user may click
on the
icon to view a video clip of the headline directly instead of reading the
story. In
another preferred embodiment, the system may automatically activate a video
clip
corresponding to whichever news headline that the user has selected, thereby
eliminating the need for the user to activate an icon in order to view the
video clip.
Fig. 10(a) is an illustration of a information guide screen 1000 that is
similar
to information guide screen 900 except in Fig. 10(a), the user has selected
"Pro
Scores" instead of "National News." Fig. 10(b) is an illustration of a submenu
1020,
which further breaks down "Pro Scores" into the different scoreboards. In a
preferred
embodiment, similar to the news submenu 920, the user may tune to ESPN or
other
Sports Station from sports submenu 1020. The system operator may also charge a
fee
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
17
for this service, and may allow the user to tune to one or more Sports Station
depending on the fees paid by the Providers. Hence, ESPN may also, for
example, pay
a premium fee to be the only Sports Station that the user may connect to from
submenu 1020. Alternatively, ESPN may pay a regular fee, and the user may tune
to
ESPN, and other Sports Stations that have also paid the regular fee.
From submenu 1020, the user may highlight one of the scoreboards to select
the scoreboard and obtain scores pertaining to the board. In this example, the
scores
are displayed according to Fig. 10(c) in a sports information screen 1040. As
shown in
screen 1040, the scores are presented in grid format. Other arrangements may
of
course be used, so long as the information is presented in a logical fashion.
From
information screen 1040, the user may also click on a video icon (not shown)
to
further view a video clip relating to the game. As discussed, the system may
access
the video clip via the video network, i.e., via cable, direct broadcast
satellite, and the
like, and this video clip could be generated from compressed data.
Alternatively, the
system may link to, for example, the NFL's website, and retrieve an AVI file,
if it is
available, to present a moving picture related to the game to the user.
Fig. 11(a) is an illustration of a information guide screen 1100 that is also
similar to information guide screen 900 except in Fig. 11(a), the user has
selected
"Weather" instead of "National News." Fig. 11(b) is an illustration of a
submenu
1120, which further breaks down "Weather" into weather forecasts for the
different
geographic regions. The system displays different local weather forecasts
depending
on the location of the user. In the example as shown in Fig. 11(b), the user
is located
in California, along the East Bay; hence, the local weather forecasts are for
the
different East Bay cities. In another embodiment, the user may specify the
geographic
region. Hence, the user may obtain also weather information for regions other
than
where the user is located.
In Fig. 11(b), the user has selected weather forecast for the United States,
hence, the user may be shown a U.S. weather information screen 1140 (Fig.
11(c)),
which displays the information in a column fashion. Other display arrangements
that
display the information in a logical manner may also be used; furthermore, the
information may be more detailed than that shown in information screen 1140.
Fig.
11(d) is an illustration of a submenu 1160 that is similar to submenu 1120
except in
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
18
Fig. 11(d), the user has selected weather forecast for Berkeley, instead of
for the U.S.
Hence, the user is shown a forecast of Berkeley weather in a information
screen 1180
(Fig. 11(e)) instead. Since the weather information is for a local region, it
is more
detailed and provides more information to the user. As shown in Fig. 11(e),
the
weather information is displayed in a row fashion. Again, other arrangements
for
presenting the weather information may also be used as long as the information
is
organized in a logical manner.
Fig. 12 illustrates the hardware elements of one particular embodiment of the
invention. As shown, the configuration preferably utilizes a program guide
controller
1205 (for example, a data processor), one or more television sources 1210, and
a TV
or computer monitor 1215. These systems may also include a VCR 1220 and a
remote
control 1225. Program guide system 1205 may be a stand-alone device or it may
be
incorporated into another system such as a television, a cable decoder, a
computer, a
PCTV, or a VCR. As shown, program guide system 1205 has a unit address 1230
that
is unique to each system. Hence, the system operators may identify system 1205
according to its unique unit address thereby enabling the system operators to
send
messages to specific users.
Another embodiment of the present invention includes a plug-in program
guide controller module 1240. Module 1240 determines the extent of program
guide
1205's capabilities. Thus module 1240 may only allow program guide 1205 to
provide a non-interactive guide or the guide may not have information icons.
When
the user wants to upgrade program guide 1205, for example, adding interactive
capability, information icons, or more detailed category searching, module
1240 may
be replaced with a different module authorizing more extensive guide
capabilities.
This embodiment has the distinct advantage of allowing the system to be
significantly
altered without requiring major hardware changes. Since the user upgrades
module
1240 to upgrade the guide, the user does not need the system operator to
provide
technical support. In this scenario the user would merely procure a different
module
1240, install the new module into the program guide system 1205, and pay the
new
fee set by the system operator for the new benefits.
Preferably the system operates under the control of software applications on a
renewable computer memory. The memory for the software applications may be
CA 02509071 1997-05-02
19
located in one or more ICs, for example, the plug-in module of the data
processor, or
in ROM, RAM, FLASH memory or any combination thereof. Accordingly, the
disclosures and descriptions herein are intended to be illustrative, but not
limiting, of
the scope of the invention which is set forth in the following claims.