Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02522912 1997-09-12
SENSING APPARATUS FOR CABLE TERMINATION DEVICES IN POWER
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates generally to electrical coupling apparatus and
sensors for the
electrical power distribution field and more particularly to coupling
apparatus for assembly with
separable insulated connector components on power cables in power distribution
systems.
2. Description of Related Art
Various apparatus have been proposed for use in making electrical connections
and for
sensing electrical parameters such as voltage and current in medium-voltage
electrical power
distribution systems. For example, this apparatus is useful to provide
electrical connections and
also to provide data for automated distribution systems, phasing information,
troubleshooting of
faulted cables, etc. Some of these arrangements utilize separable insulated
connectors on power
cables while others provide receiving passages through which the energized
electrical cables are
passed. Still other arrangements provide coupling/sensor assemblies that
interfit with the
conventional test point caps of elbows for cable terminations. Some of these
devices utilize
transformers, pick-up coils, resistive dividers and capacitive coupling to
sense circuit parameters.
One device, available from Lindsey Manufacturing Company of Azusa, Ca. as the
Elbow Sense
TM Voltage Monitoring Plug, utilizes a voltage monitoring plug that replaces
the standard plug
on 600 ampere elbow assemblies, commonly referred to as "T-body" elbows. This
arrangement
utilizes a precision resistive voltage divider to provide an output
proportional to line-to-ground
voltage. Another device available from Lindsey Manufacturing Co. is a VSB
Voltage Sensing
Bushing that utilizes a capacitive voltage divider. This interface bushing
device is arranged to be
directly affixed to a switchgear tank or the like, replacing the existing
bushing that interfits with
the cable-terminating elbow devices such as the 600 ampere T-body components.
Devices which capacitively couple to the test point of an elbow connector are
exemplified
by U.S. Patent Nos. 4,814,933, 5,077,520 and 5,095,265.
Arrangements which utilize electrodes spaced from a cable are shown in U.S.
Patent Nos.
3,970,932, 3,991,367, 4,823,022, and 5,051,733.
Another type of voltage sensor, shown in U.S. Patent No. 4,002,976, utilizes a
capacitor
having one end directly in contact with a high voltage terminal and a step-
down transformer in
CA 02522912 1997-09-12
series with the capacitor, the output of the secondary of the step-down
transformer providing a
voltage proportional to the terminal voltage.
While the prior art arrangements may be useful to couple electrical circuits
and /or provide
voltage and current information in power distribution systems, it would be
desirable to provide
coupling/sensing devices which interface with separable insulated connector
components and are
more versatile and less expensive and cumbersome.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
Accordingly, it is a principal object of the present invention to provide
coupling apparatus
for separable insulated connector components so as to couple to separable
insulated connector
components for power cables in an economical and simple fashion with ease of
assembly.
It is another object of the present invention to provide voltage sensor
apparatus
in place of the insulating plug for separable insulated connector components,
e.g. either in place of
an insulating plug of a T-body elbow or in place of a double-ended plug that
is used to
"piggyback" 600 ampere elbows.
It is a further object of the present invention to provide a voltage sensor
utilizing
capacitive coupling that replaces the insulating plug used in attaching a T-
body elbow to a
bushing.
It is yet another object of the present invention to provide a voltage sensor
for separable
electrical connectors on power cables that replaces the double-ended plug used
to piggyback T-
body elbows.
These and other objects of the present invention are e~ciently achieved by the
provision
of coupling apparatus for assembly with separable insulated connector
components on power
cables for power distribution systems. The coupling apparatus provides either
direct or indirect
coupling, e.g. to provide interconnection to the connector components or to
provide a sensing
point. In one illustrative embodiment, the coupling apparatus is installed in
place of a
conventional double-ended plug that is required to piggyback T-body elbows,
i.e. where multiple
elbows are to be connected. In one specific arrangement, the coupling
apparatus includes a
desired connector interface. In another specific arrangement, a sensed voltage
output is provided
using components such as capacitive coupling components, capacitors, resistors
or transformers.
In another embodiment, the coupling apparatus is used in place of a
conventional insulating plug
that is used to attach a T-body elbow to a bushing, e.g. on switchgear
assemblies or the like. In a
specific arrangement, the coupling apparatus is a voltage sensor and provides
a sensed voltage
output derived from a capacitive coupling arrangement utilizing a capacitive
divider. In a
-2-
CA 02522912 1997-09-12
preferred form, the voltage sensor also encapsulates circuitry to provide a
low impedance output
signal that is directly proportional to the sensed voltage.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
The invention, both as to its organization and method of operation, together
with further
objects and advantages thereof, will best be understood by reference to the
specification taken in
conjunction with the accompanying drawing in which:
FIG. 1 is an elevational view of coupling apparatus in accordance with a first
embodiment
of the present invention to be used with components of a separable insulated
connector system;
FIG. 2 and 3 are respective front and right side elevational views of a second
embodiment
of the coupling apparatus in accordance with the present invention;
FIGS. 4, 5 and 8 are electrical schematic representations of circuits and
components of the
coupling apparatus of FIGS. 2 and 3;
FIG. 6 is an elevational view, partly in section, of a third embodiment of
coupling
apparatus in accordance with the present invention; and
FIG. 7 is an electrical schematic representation of circuitry and components
of the
coupling apparatus of FIG. 6.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
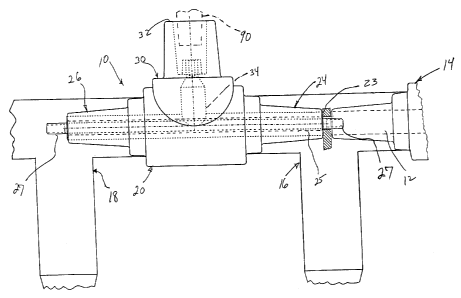
Refernng now to FIG. 1, a coupling apparatus 10 in accordance with a first
embodiment of the
present invention is utilized to couple to a conductor 12 of a separable
insulated connector
component, such as the illustrated bushing 14 in the T-body elbow 16, which in
a specific example
is in accordance with ANSI/IEEE Standard 386. In this illustrative
arrangement, the coupling
apparatus 10 replaces a conventional double-ended plug for attachment of the T-
body elbow 16
and a second T-body elbow 18. The coupling apparatus 10, preferably fabricated
'as a molded
body of insulating material, includes a first portion 20, having the same
general external shape as a
conventional double-ended plug, including operating interface portions 24, 26
and a second
portion 30 extending generally transverse to the first portion 20 and
including the illustrated
bushing well 32, or a connector interface, to define a predetermined coupling
point. The first
portion 20 includes a tubular conductor 23 disposed therein which defines a
bore 25. A threaded
rod 27 extends through the bore 25 and serves to fasten the coupling apparatus
10 to the T-body
elbow 16. It should be noted that in FIG. 1, the clearance between the bore 25
and the threaded
rod 27 has been exaggerated for clarity. The bushing well 32 includes a
conductor portion 34
which is electrically connected to the tubular conductor 23.
-3 -
CA 02522912 1997-09-12
During installation of the coupling apparatus 10, the threaded rod 27 is
inserted into the
T-body and threaded into the bushing 14, and then the coupling apparatus 10 is
assembled over
the threaded rod 27. Thus, the coupling apparatus 10 does not need to be
rotated during at any
time during the installation thereof to the separable insulated connector
components. Further
assembly of the T-body elbow 18 is according to conventional practice. If a
second T-body
elbow 18 is not required, an insulating cap may be used over the left
interface portion 61 of FIG.
2 or 26 of FIG. 1.
In accordance with a second embodiment of the present invention and referring
now
additionally to FIGS. 2 and 3, coupling apparatus 50 is also arranged to
replace a conventional
double-ended plug in separable insulated connector systems for power cables.
In a first specific
arrangement, the coupling apparatus 50, preferably fabricated as a molded
body, has a first
portion 52 which has the same general exterior shape as a conventional double-
ended plug and a
second portion 53 extending generally transverse to the first portion 52. The
first portion 52
includes a central conductive sleeve 54 which is dimensioned to receive a
central conductor 56.
In one specific arrangement, one or more spring contact members 58 (FIG. 3)
are arranged
between the central conductive sleeve 54 and the central conductor 56 to
provide electrical
contact therebetween. In another specific arrangement, the central conductive
sleeve 54 is
resilient to provide suitable contact with the central conductor.
During installation into the separable insulated connector system, the central
conductor 56
is inserted into the T-body elbow (e.g. 16 of FIG. 1) and threaded into the
bushing (14 of FIG. 1),
and then the coupling apparatus SO is assembled over the central conductor 56.
Thus, the
coupling apparatus SO is not rotated during installation.
In a specific arrangement, the coupling apparatus 50 includes a capacitance
pickup
member 60, e.g. as illustrated in FIGS. 2 and 3, arranged as a cylindrical
shell or sleeve. An
electrical connection at 62 to the capacitance pickup member 60 is provided to
define a coupled
output at 64 via electrical conductor 66. Preferably, a capacitor 68 is
provided in the second
portion 53 that is connected between the output 64 and ground at 70, such that
the output 64 is at
the midpoint of a capacitive bridge, defined by the capacitor 68 and the
capacitance pickup
member 60.
Referring additionally to FIGS. 4 and 5, in other specific arrangements, the
coupling
apparatus 50 includes an output circuit defined by a resistor 72 in lieu of
the capacitor 68 , or a
transformer 74. In accordance with other specific arrangements, a direct
connection at 76 is made
to the central conductive sleeve 54. In that specific arrangement, as shown in
FIG. 2, a capacitor
78 is provided (in lieu of the capacitance pickup member 60) so that the
output 64 is at the tap of
-4-
' CA 02522912 1997-09-12
a capacitive divider formed by the capacitors 78 and 68. As noted in FIG. 5,
the transformer 74
in a specific arrangement is connected to the direct connection at 76, with
the capacitor 68 being
deleted. Also, the transformer 74 in another specific arrangement is connected
to the capacitor 78
at the conductor 66 (i.e. in lieu of capacitance pickup member 60 and the
capacitor 68).
Referring additionally to FIG. 8, in another specific embodiment, a resistive
divider of resistors 79
and 81 is directly connected to the point 76 and ground 70. In yet another
specific embodiment, a
resistor 79 and a transformer 74 are connected between the point 76 and ground
70.
It should also be understood that in various specific arrangements of the
coupling
apparatus 10 of FIG. 1, the circuits and components as discussed in connection
with FIGS. 2-5
are utilized to provide desired output characteristics and configurations, for
example via a bushing
insert 90 or the like connected at the bushing well 32 or a connector
interface.
In accordance with other important aspects of the present invention and
referring now to
FIGS. 6 and 7, a coupling apparatus 100 of the present invention is provided
to take the place of a
component of a separable insulated connector system, e.g. in lieu of a
conventional insulating plug
that is used to attach or assemble a T-body elbow to a bushing on a switchgear
tank or the like.
In one specific arrangement, the T-body elbows and the bushings are in
accordance with
ANSI/IEEE Standard 386. For example, the coupling apparatus 100 is inserted
into the rear end
of a T-body elbow which has been placed over a bushing and threaded onto the
stud extending
from the bushing and through the T-body elbow.
Specifically, the coupling apparatus 100 includes a body 110 in the overall
shape of a
conventional insulating plug and a connector 112 with threaded passage 114 for
threadingly
engaging a conventional threaded stud that extends through the bushing and the
T-body elbow.
The connector 112 is conductive and arranged to form a first plate 116 (FIG.
7) of a first
capacitor 118 of the coupling apparatus 100. A closed cylindrical sleeve 120
of conductive
material forms a second plate 122 of the capacitor 118 and also a first plate
124 of a second
capacitor 126, the capacitors 118 and 126 forming a capacitive voltage divider
127 with output
136 as seen in FIG. 7. A second plate 128 of the capacitor 126 is formed by a
cylindrical
conductor 130 which is connected to a ground reference, e.g. earth ground at
134 (FIG. 7).
The elements 112, 120 and 130 are fabricated and arranged along with the
material of the
body 111 to provide an accurate capacitive divider 127 and output 136 which is
also isolated from
the high voltage connection at I 12. Considering the circuit of FIG. 7, the
output 136 of the
capacitive divider 127 is connected through electronic circuitry components
generally referred to
at 140 to provide a low voltage output at 142 that is directly proportional to
the sensed voltage at
-5-
CA 02522912 1997-09-12
112. Specifically, in an illustrative embodiment, a resistive divider 144 and
an amplifier 146 are
utilized to provide a suitable output at 142.
The body 111 is electrically insulating and preferably molded from an
insulating epoxy or
other suitable polymeric material, with a conductive coating being provided to
the left of the line
113 in FIG. 6. The body 111 is formed with a circumferential recess 150. The
circuit
components 140 are disposed within the recess 150 with the output 142, a
ground reference 134,
and power supply connections 148 (FIG. 7) being provided via conductors in a
cable 152. The
components 140 are sealed within the recess 150 by a potting compound 154 or
the like. The hex
nut 132 is utilized as a connection point to earth ground and also provides
for attachment of tools
to facilitate threading of the coupling apparatus 100 onto the conventional T-
body components
and hardware, e.g. the conventional stud that extends from the bushing and
through the T-body
elbow. As previously discussed, the coupling apparatus 100 is usable as a
direct replacement for
the conventional insulating plug for T-body elbows.
While there have been illustrated and described various embodiments of the
present
invention, it will be apparent that various changes and modifications will
occur to those skilled in
the art. Accordingly, it is intended in the appended claims to cover all such
changes and
modifications that fall within the true spirit and scope of the present
invention.
-6-