Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24 PCT/1B2005/001705
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FEEDING FLAT PRINTED PRODUCTS
1. Field of the Invention
The present invention relates to a method for gathering flat printed products,
especially signatures, by selecting a single printed product from each of a
multitude
of collections of identical printed products and conveying the selected
printed
products towards a collecting conveyor, where the selected printed products
are
piled up, which runs along a generally straight line in a first direction.
The present invention also relates to an apparatus for gathering flat printed
products,
especially signatures, comprising a plurality of feeders arranged in a
sequence each for
a collection of identical printed products with a selecting device for
selecting single flat
printed products and a collecting conveyor, where the selected printed
products are
piled up, which runs along a generally straight line in a first direction.
2. Brief Description of the Prior Art
It its known from prior art to use such methods and apparatuses for handling
flat
products such as printed products, also called "signatures", to feed
downstream
machinery. Upstream of bindery machinery, there are usually used rotary drum
gathering systems to separate, pull and pick-up signatures from each bottom of
a
horizontal stack in a hopper and transfer the separated signatures to build
piles
collated on either a saddle or pocket collecting conveyor, the piles being fed
to the
downstream stitching, sewing or gluing operation to produce books or
magazines.
Alternatively, gripping systems have also been used with the assistance of
separating
tooling such as rotary cam separators and vacuum plates cooperating to
separate the
lowermost signature being pulled down from the rest of the pile being
supported by the
separating device.
= CA 02527101 2010-06-29
- 2 -
In the document EP 1 234 790 B1 it is disclosed to advance printed products in
a
shingled formation by a belt conveyor towards a feed conveyor station, where
the
printed products are fed into a second conveyor which initially lifts the
printed products
upwards, then downwards again and finally disposes them on a collecting
conveyor. To
achieve a satisfactory function of this apparatus, the shingled formation of
printed
products in the belt conveyor must be generated with a very high precision,
which
requires substantial technical efforts. Also the precise disposal of the flat
printed
products by the second conveyor is difficult to achieve, which limits the
maximum
troughput of the apparatus.
Feeding of the hopper was traditionally accomplished manually by an attendant
taking
a pile of signatures and bending the pile back and forth a few times to ensure
proper
separation of the signatures. It is also well known in the field to replace
the attendant by
a feeder, also called hopper loader, carrying-out separation reliability with
increased
throughput and lower operating costs, to deliver the signatures to the
horizontal hopper
of a gatherer, separated in forwardly inclined shingled continuous stream.
The document DE 196 16 047 B4 discloses an apparatus where the printed
products
are fed into hoppers, from where each of the lowermost printed products from
the piles
in the hoppers is distributed towards a collecting conveyor, which is arranged
underneath the hoppers. As the printed products are distributed by belt
conveyors, the
maximum troughput of the apparatus is limited, if a safe intake of the
individual printed
products into the belt conveyor shall be safeguarded.
However, feeding the signatures to form a vertical stack in a hopper still
requires a
complex system to meet stack build-up parameters and select and grip one
single
signature at a time to perform the transfer to a collecting conveyor
thereafter. Many
such systems have been developed so far with the object to perform these tasks
with
acceptable yield and throughput, but still with a high level of complexity and
proportional cost. For example, the signatures have been advanced with start-
and
stopcycles of a hopper loader towards a hopper, which caused substantial
variations in
the throughput perfomance of the hopper. Due to the varying height of the pile
in the
hopper, misselections of printed products occurred.
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
- 3 -
A few examples of direct transfer apparatuses have also been thought in prior
patents,
but still remain complex, mainly because signatures are always picked-up by
grippers
traveling in the same stream direction of the signatures fed by a feeder while
signatures are to be transferred to a collecting conveyor running in an
orthogonal
direction. Therefore, the feeding systems known from prior art remain complex,
costly,
subject to miss-feeds and only perform a limited maximum feed speed.
3. Subject of the Invention
Therefore, it is the subject of this invention to deliver flat printed
products by a feeder in
a continuous stream and to feed the flat printed products into a collecting
conveyor,
which transfers the accumulated piles to downstream machinery. It is
specifically
requested to provide an ultra-high speed, simple and reliable method and
apparatus for
feeding signatures of a bindery line for the manufacture of books or the like.
The above review of the prior art clearly shows that the solutions of the
prior art
contemplating the feeding of collecting conveyors upstream of bindery
machines, from
an incoming stream of flat printed products, still present several limitations
and
drawbacks. Therefore, there is a need for an improved flat printed products
feeding and
separating method and apparatus obviating such limitations and drawbacks of
the prior
art devices and methods.
4. Summary of the Invention
The present invention overcomes the limitations and drawbacks of the above
mentioned prior art for known methods by the following steps:
- advancing the printed products in a second direction in a continuous flow of
printed products with a feeder with feeding elements upstream of the
collecting
conveyor,
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
-4-
- gripping a leading portion of a printed product at the discharge end of said
feeder by separating grippers of a transferring conveyor which is also
arranged
upstream of the collecting conveyor,
- transferring the gripped printed product with the transferring conveyor
substan-
tially along a path, which takes its course generally along the first
direction of the
collecting conveyor.
For an apparatus the problem is solved by the elements, that the feeders
advance the
printed products by feeding elements in a second direction in a continuous
flow of
printed products, a transferring conveyor comprises at least one separating
gripper,
which is capable of gripping a leading portion of a printed product at the
discharge end
of a feeder, and the transferring conveyor transfers the printed flat products
substan-
tially along a path, which takes its course generally along the first
direction of the col-
lecting conveyor.
By using the invention, it is possible to transfer flat printed products with
an ultra-high
speed into a collecting conveyor. Though, this result can be achieved with a
simple,
cost-efficient and reliable mechansim which comprises only few movable
elements.
Only few space is required for the apparatus, especially for the transferring
conveyor,
and the method and apparatus is more fail-safe and require a less precise
orientation
of feeded printed products than the systems known from prior art.
This result is achieved by gripping the leading article one by one, preferably
by its
backbone, using separating grippers traveling along a linear path, generally
orthogonal
to the article stream orientation, but substantially in parallel to the
straight line of
travelling of the collecting conveyor, which runs along a generally straight
line in the
first direction. This handling principle avoids unnecessary turns and bends of
the
printed articles during their transfer from the feeders to the collecting
conveyor. At the
discharge end of the feeders the printed products are already oriented
perfectly as
required for sorting them into the pockets of the collecting conveyor. They
only need a
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
- 5 -
short push sidewards, and this push is achieved by gripping them with the the
separating grippers and dropping them into the collecting conveyor shortly
afterwards.
As the separating grippers are moved along the entire length of the printed
product,
there is a comparably long time window open for gripping a printed product and
pulling
it away from the feeder. Therefore, the single printed products must not be
oriented as
precisely as it is required for the machines known from prior art, because a
slightly
uneven flow or orientation can be neutralized by the advanced arrangement
according
to this invention. As the time window for gripping a printed product with a
separating
gripper is longer with an apparatus designed according to this invention
working with
an identical throughput as the prior art machines, the apparatus is able to
work faster
as the prior art machines, when the time window is identical.
The machinery required for this this short transfer movement is substantially
less
complex and costly, but much faster and reliable in its function. By adapting
and
adjusting the measurements and distances of the feeders, separating grippers
and the
pockets in the collecting conveyor and their respective working speeds
advantageously
relative to each other, the best throughput results can be achieved. The
closing and
opening cycles of the separating grippers also need to be adapted towards the
respective applications. The gripping movement of the separating grippers may
be
mechanically effected by a lever whose action is triggered and controlled by a
cam, or
such movement may be performed by electronic sensors and electric drives
and/or
software-controlled.
The feeders are using feeding elements like belt conveyors to advance the
printed
products towards the discharge end of the feeder. For using the invention, it
is not
compulsory any more to feed the printed products first into a hopper as a
feeding
element to be able to separate the lowermost product and to transfer it into
the
collecting feeder thereafter. The invention can also be used by gripping the
printed
products directly from a shingled formation of printed products at the
discharge end of
the feeder. However, it is also still possible to use hoppers together with
the invention,
for example to leverage an uneven product flow.
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24 PCT/1B2005/001705
- 6 -
There is further provided a further embodiment of the method for feeding flat
printed
products to a collecting conveyor, wherein said flat printed products, being
folded or
not, may comprise a leading portion with a backbone.
In a still further embodiment the method comprises an additional step
comprising
separating at least in part said leading portion from the next upstream
article by the
sucking force of at least one vacuum element prior to the grasping of said
portion.
There is still provided a further embodiment of the method wherein separating
at
least in part said leading portion from the next upstream article by the
sucking force
of at least one vacuum element comprises pulling and holding down at least a
corner
of said leading portion by vacuum and further separating said leading portion
by
transversally running a separating device above said leading portion, from
said
corner to the opposite edge of the article, in order to lift upstream printed
products to
enable the grasping of said portion.
There is further provided a system for the feeding of flat printed products to
a
collecting conveyor which runs in a first direction, comprising a feeder
running in a
second direction, and at least one transferring conveyor with separating
grippers
travelling along a path generally oriented transversally to said second
direction and
generally along the first direction of the collecting conveyor, wherein said
separating
grippers can grip a leading portion of a printed product and transfer it onto
said
collecting conveyor.
In a further embodiment of the system, the gripper device further comprises a
separating wedge portion comprising a separating edge facing towards the
gripper's
travelling direction.
In a further embodiment of the system, said first conveyor further comprises
an
articulated vacuum pick-up arm, whereby said leading portion of the most
forward
printed product is picked-up by said vacuum element and bent away from the
neighbouring upstream printed product to separate at least in part the leading
portion
of said printed product from the next upstream printed product.
e erv I Ve ,v*V, en,
CA 02527101 2010-06-29
- 7 -
In an advantageous embodiment of this invention, the transfer path of the
transferring conveyor is crosswisely arranged towards said second direction of
the
feeder and in a principal plane of the printed product to be gripped at the
discharge
end of said feeder. The spatial orientation of the separated printed product
at the
discharge end of the feeder or at the feed conveyor station respectively
generally
defines the principal plane of the printed product. Minor changes of the
spatial
orientation by slight inclinations along the feeding path of the feeder or
bending of
the printed products for separation purposes do not change the principal plane
to a
relevant extent. To move the printed product only to as much as It is
technically
required for the transfer from the feeder to the collecting conveyor, the
transferring
conveyor is also arranged in the principal plane of the printed product to be
gripped,
and also the transfer by the transferring conveyor is effected substantially
withtin this
plane. By substantially maintaining the principal plane of the printed
product, as it is
generally defined by its spatial orientation at the discharge end of the
feeder, also for
the transfer cycle of the printed product towards the collecting conveyor, the
technical efforts to achieve the required function can additionally be
reduced.
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method
for
gathering flat printed products, especially signatures, by selecting a single
printed product from each of a multitude of collections of identical printed
products and conveying the selected printed products towards a collecting
conveyor, where the selected printed products are piled up, which collecting
conveyor moves along a generally straight line in a first direction, whereby
the
method comprises the following steps:
advancing the printed products in a second direction crosswise to said first
direction in a continuous flow of printed products with a feeder with feeding
elements upstream of the collecting conveyor,
gripping a leading portion of a printed product at the discharge end of said
feeder by separating grippers of a transferring conveyor which is arranged
adjacent to and travels parallel to the collecting conveyor, and
moving the gripped printed product with the transferring conveyor away
from the feeder substantially along a path extending generally along said
first
direction of the collecting conveyor.
CA 02527101 2010-06-29 =
- 7a -
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided an
apparatus for gathering flat printed products, especially signatures,
comprising:
a plurality of feeders arranged in a sequence each for a collection of
identical printed products with a selecting device for selecting single flat
printed
products;
a collecting conveyor, where the selected printed products are piled up,
which collecting conveyor moves along a generally straight line in a first
direction;
wherein the feeders advance the printed products by feeding elements in
a second direction crosswise to said first direction in a continuous flow of
printed
products;
a transferring conveyor comprising at least one separating gripper, which
is adapted to grip a leading portion of a printed product at a discharge end
of the
feeders, respectively, wherein the transferring conveyor is arranged adjacent
to
and travels parallel to the collecting conveyor;
wherein the transferring conveyor moves the printed products away from
the feeder substantially along a path extending generally along said first
direction
of the collecting conveyor.
These objects and other objects and features of the present invention will
become more apparent through the following description that will be carried
out
by reference to the appended drawings, by the content of the drawings.
According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method
for
gathering flat printed products, especially signatures (2), by selecting a
single
printed product from each of a multitude of collections of identical printed
products and conveying the selected printed products towards a collecting
conveyor (10), where the selected printed products are piled up, which runs
along a generally straight line in a first direction (11), whereby the method
comprises the following steps:
advancing the printed products in a second direction (15) in a continuous
flow of printed products with a feeder (1) with feeding elements upstream of
the
collecting conveyor (10),
CA 02527101 2010-06-29
- 7b -
gripping a leading portion (20) of a printed product at the discharge end of
said feeder (1) by separating grippers (60) of a transferring conveyor (40)
which
is also arranged upstream of the collecting conveyor (10),
transferring the gripped printed product with the transferring conveyor (40)
substantially along a path, which takes its course generally along the first
direction (11) of the collecting conveyor (10).
In some embodiments, a feeder (1) comprises a hopper (50) as a feeding
element.
In some embodiments, the transfer path of the transferring conveyor (40) is
crosswisely arranged towards said second direction (15) and in a principal
plane
of the printed product to be gripped at the discharge end of said feeder (1).
In some embodiments, the printed products delivered by the feeder (1) are
advanced forward in a shingled formation.
In some embodiments, the shingled printed products are arranged on the feeder
(1) backwardly superimposed.
In some embodiments, the printed products in the feeder (1) and/or the piles
(4)
in the collecting conveyor (10) are supplied in a substantially horizontal or
substantially vertical plane.
In some embodiments, the printed products delivered by the feeder (1) are
piled
in a hopper (50) and the printed product to be taken by the transferring
conveyor
(40) is one of the lowermost piled samples of the printed products.
In some embodiments, the printed products are signatures (2) and the leading
portion (20) of the signature (2) to be gripped by the transferring conveyor
(40) is
the backbone of the signature (2).
CA 02527101 2010-06-29
- 7c -
In some embodiments, a sucking force is applied by at least one vacuum
element (33) upon at least the leading portion (20) of a foremost, uppermost
or
lowermost printed product so that such portion (20) is bent away thereby from
the neighbouring upstream printed product.
In some embodiments, the sucking force acts upon an edge (21) of the leading
portion (20) of the printed product upstream of the transferring conveyor
(40),
and the leading portion (20) of the printed product is bent away by a
separating
device, which is moved along a straight line in the first direction from the
edge
(21) towards the opposite edge of the printed product, and which supports
neighbouring upstream printed products during this movement, so that the
gripping of the leading portion (20) of the printed product is eased.
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided an
apparatus for gathering fiat printed products, especially signatures (2),
comprising a plurality of feeders (1) arranged in a sequence each for a
collection
of identical printed products with a selecting device for selecting single
fiat
printed products and a collecting conveyor (10), where the selected printed
products are piled up, which runs along a generally straight line in a first
direction
(11), wherein the feeders (1) advance the printed products by feeding elements
in a second direction (15) in a continuous flow of printed products, a
transferring
conveyor (40) comprises at least one separating gripper (60), which is capable
of
gripping a leading portion (20) of a printed product at the discharge end of a
feeder (1), and the transferring conveyor (40) transfers the printed flat
products
substantially along a path, which takes its course generally along the first
direction (11) of the collecting conveyor (10).
In some embodiments, the feeding elements comprise a hopper (50 where the
second direction (15) is the movement of the printed products in a pile
through
the hopper (50).
===== CA 02527101 2010-06-29=-==
=.=
- 7d -
In some embodiments, the feeders (1) are designed to advance the printed
products in a shingled formation.
In some embodiments, the printed products in the feeder (1) and/or the piles
(4)
in the collecting conveyor (10) are supplied in a substantially flat lying
way.
In some embodiments, the transfer path of the transferring conveyor (40) is
crosswisely arranged towards said second direction (15) and in a principal
plane
of the foremost printed product at the discharge end of its feeder (1).
In some embodiments, the separating gripper (60) comprises a separating
wedge portion (63) with a separating edge (64), which is facing towards the
travelling direction of movement of the separating gripper (60).
In some embodiments, there is at least one vacuum element (33) for applying a
sucking force to at least the leading portion (20) of a foremost, uppermost or
lowermost printed product and which is arranged in a position that it bends
away
such portion (20) of the printed product thereby from the neighbouring
upstream
printed product.
In some embodiments, the vacuum element (33) is arranged at a position that it
acts upon an edge (21) of the leading portion (20) of the printed product
upstream of the transferring conveyor (40).
In some embodiments, the printed products are fed into an inclined hopper
(50),
so that the printed products are fed into an inclined hopper (50), so that the
printed products are resting aligned with their backbones along a back-gauge
(90).
In some embodiments, a plurality of separating grippers (60) are assembled in
regular distances to a driving element, which is movable along the discharge
ends of the feeders (1) at the same speed and in the same direction as the
CA 02527101 2010-06-29
- 7e -
collecting conveyor (10), and the separating grippers (60) travel on a guiding
rail
(13).
In some embodiments, the distance between the separating grippers (60) is
smaller than the distance between the discharge ends of the feeders (1).
In some embodiments, the separating gripper (60) comprises a fixed top jaw
member (62) with a separating wedge portion (63) with a separating edge (64)
and a pivotable lower jaw member (65).
In some embodiments, the top jaw member (62) and/or the lower jaw member
(65) is made from a flexible material to be able to build up a clamping force.
In some embodiments, the lower jaw member is driven by a roller (67) on a
lever
acting upon a connecting rod, and that the roller (67) travels along a cam
(14).
In some embodiments, the top jaw member (62) and/or the lower jaw member
(65) comprise a plurality of clamping spots which are spaced apart from each
other.
In some embodiments, the separating gripper (60) comprises a supporting
surface (71) by which the printed product may be supported after being
gripped.
In some embodiments, each discharge end of a feeder (1) is associated with a
buffer shelf (80), on which the gripped printed products can be dropped by the
separating grippers (60) and from where they can be forwarded by the
collecting
conveyor (10).
5. Brief Description of the Drawings
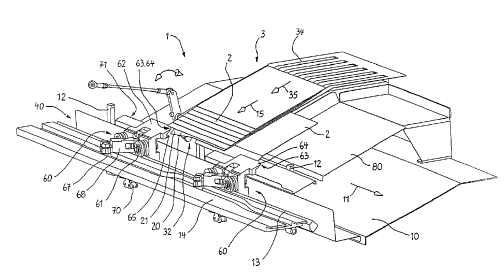
Fig. 1 is a perspective view of the apparatus according to a
preferred
embodiment of the present invention, showing a vacuum element
pulling down a leading edge of a foremost signature to create a
CA 02527101 2010-06-29 ,
- 7f -
space between the leading and the next upstream signatures. The
upstream separating gripper will soon grip the reference corner of
the leading portion of the foremost signature. The downstream
separating gripper has already gripped a printed product and pulls
it away from the feeder.
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
- 8 -
Fig. 2 is a perspective view of the apparatus according to a
preferred
embodiment of the present invention, showing the upstream separating
gripper with a separating wedge running across a space created between
the foremost signature and the next upstream one. The downstream
separating gripper has fully extracted a printed product from an incoming
shingled stream and transferred it towards the buffer shelf.
Fig. 3 is a perspective view of the separating gripper according to a
preferred
embodiment of the present invention to better show details of the
separating gripper device in an open position.
Fig. 4 is a perspective view of an adjustable vacuum pull-down and
retaining
assembly mounted on a retaining plate at the outlet of a feeder.
Fig. 5 is a perspective view of the apparatus according to a
preferred
embodiment of the present invention, showing a hopper at the discharge
end of a feeder, where the lowermost of the printed products
accumulated in the hopper is gripped by the separating gripper and
transferred towards the collecting conveyor.
6. Detailed Description of the Invention
A preferred embodiment of the method, apparatus and device for feeding flat
printed
products according to the present invention will now be described in detail
referring to
the appended drawings.
Referring to Fig.1, there is provided only one feeder generally identified by
numeral 1
with feeding elements, which is designed to feed incoming signatures 2 to a
collecting conveyor 10 forming vertical piles 4 of different signatures being
forwarded
to a downstream bindery equipment such as a binding station or an adhesive
binder
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
- 9 -
(not shown), where the piles 4 of printed products collected by the collecting
conveyor 10 are pasted together to form a book or a brochure.
The feeder 1 may comprise any kind of feeding elements, for example driven
belt
conveyors and the like. Any kind of equipment which advances the printed
products
towards the discharge end of the feeder 1 is suitable. Also a hopper is meant
to be a
feeding element, as it advances printed products through a pile towards the
discharge end of the hopper, and, depending upon the location where it is
arranged,
also the discharge end of the feeder 1. The printed products or signatures 2
are
supplied in a substantially flat lying way. Each feeder 1 feeds a collection
of identical
printed products. From each collection of identical printed products exactly
one
single specimen must be selected and gathered in a correct sequence in a
pocket of
the collecting conveyor 10 as a pile 4, so that a book can be completed in the
downstream bindery equipment. So very often a gathering system using the
claimed
invention comprises more feeders 1 than just the one feeder 1 shown in Fig. 1.
However, the function of the invention can well be described also by just one
feeder 1.
The apparatus as shown in Fig. 1 comprises at least one feed conveyor station
3,
each station 3 feeding one of the printed products or signatures 2 being
successively
collated to form piles 4 in successive pockets of the collecting conveyor 10.
The
pockets are separated by pushing rods 12. Obviously, a plurality of such feed
conveyor stations 3 placed in parallel transversally to the first direction 11
of the
collecting conveyor 10 are usually required to individually deliver each one
of the
different signatures 2 to be assembled together to form the book or similar
product.
As it can clearly be seen from Fig. 1, the first direction 11, in which the
collecting
conveyor 10 moves the piles 4, clearly deviates from the second direction 15,
in
which the feeder 1 advances the printed products. In the embodiment shown in
Fig.
1, the second direction 15 in fact is crosswise and rectangular towards the
first
direction 11. However, the angle between the first direction 11 and the second
direction 15 does not have to be exactly 900, minor deviations from this angle
are
also possible according to the invention.
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
- 10 -
Feeder 1 and the feed conveyor station 3 comprise a motorised belt 34 for
supporting and advancing the stream of signatures 2 in direction 35 equal to
direction 15, which stream have a shingled formation in the shown example, and
which are backwardly superimposed in direction 35 in the shown example. Of
course, the signatures 2 may also be advanced spaced apart from each other by
the
feeder 3, or partially shingled and partially separated, in a continuous
product flow or
in an interrupted or intermitted way. As in general the printed products are
quite
continuously fed during a working period, the product flow is generally
regarded as
being continuous, even is smaller deviations in the continuity might occur.
The
inclination angle in direction 35 may also be altered as required or suitable.
The
general structure of such feeders 3 is well known by individuals of ordinary
skill in
the field, and the respective method of feeding the signatures 2 may be
selected as
required by the respective application and as it seems to be suitable.
The system further comprises a transferring conveyor 40 with a least one
separating
gripper 60. In Fig. 1, a plurality of separating grippers 60 are assembled to
a driving
chain, from which only one chain link 70 for each separating gripper 60 is
shown in the
drawing for simplification purposes. The movement direction of the driving
chain is
synchronized with the first movement direction 11 of the collecting conveyor
10, so that
both, the separating grippers 60 and the colleting conveyor 10, travel along a
at least
substantially linear path and at least substantially in parallel to the
orientation of the
other respective element.
If more than one separating gripper 60 is employed in an apparatus, it is
advantageous
if they are arranged in regular distances to a driving element like the chain
70. The
distance may be equal to the distance between feeders 1, but if it is smaller
than the
distance between the discharge ends of the feeders 1, it is easier to add the
gripped
signatures to the piles 4 accumulated in the collecting conveyor 10.
In addition to the alignment of the movement direction of the separating
grippers 60
and the collecting conveyor 10, also the movement speed of the separating
grippers
60 and the pushing rods 12 of the collecting conveyor 10 is at least about the
same,
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24 PCT/1B2005/001705
- 11 -
preferably identical. To ensure its mobility, separating-gripper device 60
further
comprises three pulleys 61 to travel on upper and lower edges of guiding rail
13. The
separating grippers 60 are driven over a linear path in the first direction 11
through a
chain connected to chain link 70.
In Fig. 2, the two separating grippers 60 are shown in a slightly advanced
position. The
downstream separating gripper 60 has already opened the jaw members 62, 65 and
thereby released the signature 2. The signature 2 has fallen down upon the
buffer shelf
80. The buffer shelf 80 provides a slit 82, through which the upper ends of
pushing rods
12 are extending, when they are moved along the first direction 11. It can be
seen from
Fig. 2, that the next pushing rod 12 already approaches the buffer shelf 80.
The buffer
shelf 80 may comprise a blunt surface, which slows down and stops the movement
of
the signature 2 released by a separating gripper 60 and which especially
supports the
signature 2 to slide out of engagement with the jaw members 62, 65 of the
separating
gripper 60. The pile 4, which comprises of signatures already collected by
pushing rod
12 from upstream feeders 1, is fed through the hollow space underneath the
buffer
shelf 80. The printed products accumulated already in the pile 4 are also
supplied in a
substantially flat lying way. The printed products in the feeder 1 and those
accumulated
in a pocket of the collecting conveyor 10 may advantageously be supplied in a
substantially horizontal or substantially vertical plane, as it deems to be
suitable in an
application. If the pushing rod 12 advances further from the shown position,
it will push
the signature 2 into the first direction 11 of the collecting conveyor 10, and
thereby the
signature 2 will slide down from the buffer shelf 80 and rest on top of pile
4.
Accordingly, before the pile 4 reaches the next feed conveyor station 3, the
signature 2
will have been collected by the collecting conveyor 10 on top of the pile 4.
The upstream separating gripper 60 has moved along a straight line in the
first
direction 11 from the edge 21 of the leading portion 20 of a foremost
signature 2 as
shown in Fig. 1 nearly towards the opposite edge of the signature 2. Along
this
movement, the separating wedge 63 has supported the neighbouring upstream
printed
product and at the same time bent down and separated the leading portion of
the lower
signature 2, so that the gripping of the leading portion 20 of the lower
printed product is
eased. The upstream separating gripper 60 is still shown in an open position,
but upon
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24 PCT/1B2005/001705
- 12 -
a continuation of its movement it will immediately close and grip the
respective
signature 2.
In Fig. 1 and especially also in Fig. 3, more details of the separating
grippers 60 are
shown. The two shown separating grippers 60, one upstream, one downstream of
the
first direction 11, each comprise a top jaw member 62 terminated on its
downstream
end by a separating wedge portion 63 comprising a sharp separating edge 64.
The
upstream separating gripper 60 is shown in an open status, whereas the
downstream
separating gripper 60 is shown with closed jaw members 62, 65. In the shown
example, the top jaw member 62 is fixed, and the lower jaw member 65 is
movably
driven. However, apart from the shown example, also only the top jaw member 62
or
both, the top jaw member 62 and the lower jaw member 65 may be movably driven.
To bring an increased clamping force upon a signature 2 gripped by a
separating
gripper 60, so that it is gripped more safely, the top jaw member 62 and/or
the lower
jaw member 65 may partially or completely be made from a flexible material.
The
clamping force is also advanced, if it not effected by the complete surface of
a jaw
member 62, 65, but rather concentrated upon a few clamping spots. In the shown
example, an actuated lower jaw member 65 comprises a friction pad 66 which
cooperates with fixed top jaw member 62 to provide an individually
controllable
separating gripper 60 to grip flat printed products. As the friction pad 66
protrudes from
the other surface of the lower jaw member 65 and concentrates the clamping
force in a
closed position of the lower jaw member 65 upon its surface, the friction pad
66 defines
a clamping spot. A clamping spot could also be generated by other protrusions
on the
surface of either the top jaw member 62 or the lower jaw member 65 or both. To
spread the clamping force over a bigger area of the gripped signature, it is
advantageous to arrange the clamping spots spaced apart from each other.
Closing of the separating grippers 60 is accomplished by laterally pushing on
roller 67
of rocker 68 causing connecting rod 69 to be pulled and in turn pivoting lower
jaw
member 65 upwards. The separating gripper assembly returns to its normal open
position by back pushing on roller 67 of rocker 68. Individually controlled
actuation of
the separating grippers 60 is accomplished through the double cam 14 extending
at
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
- 13 -
least substantially parallel and close to guiding rail 13, and being
periodically hit by
roller 67 when separating grippers 60 are moving on rail 13. The double cam 14
provides a sectional linear orientation, but in those section where the
separating
grippers 60 shall be closed and opened, the double cam 14 shows a curved and
protruding shape.
Each separating gripper 60 comprises a supporting surface 71, which supports
the
safe grip of a signature 2 in the jaw members 62, 65. The supporting surface
71
touches the leading portion 20 of a signature during the movement of the
separating
gripper 60 along the first direction 11 and thereby slightly aligns the
signature as
long as the jaw members 62, 65 are not yet closed.
As it can be seen in Fig. 1, the downstream separating gripper 60 has already
gripped
a foremost signature 2 from the shingled formation in the feeder 1 and
partially
transferred it along the first direction 11 towards the buffer shelf 80. The
signature 2
gripped by the shown downstream separating gripper 60 is transferred in a
spatial
orientation, which is substantially identical to the spatial orientation it
has had, when it
was gripped by the downstream separating gripper 60. So during the transfer
phase of
the signature 2 from the feed conveyor station 3 towards a pocket of the the
collecting
conveyor 10, the signature 2 substantially maintains it spatial orientation.
This result
can be achieved, because the transfer path of the transferring conveyor 40 is
arranged
in the same principal plane the signature 2 or printed product has, when it is
gripped at
the discharge end of feeder 1.
Feeder 1 and the feed conveyor station 3 are further provided with special
tooling at
the downstream discharge end thereof, which is shown in more detail in Fig. 4.
Said
tooling comprises an actuated vacuum element 33 like a suction cup, which is
able
to effect a sucking force. In Fig. 4, there is shown one vacuum element 33 in
full
lines, and additional vacuum element 33 in dotted lines to indicate, that
there may be
employed more than just one vacuum element 33. The vacuum element 33 is fixed
on a pick-up arm 32. In addition to the suction cups, there may also be
arranged one
or more perforated vacuum retaining plates 31, which may extend across the
width
of feed conveyor station 3 and in parallel to the first direction 11. Vacuum
retaining
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24
PCT/1B2005/001705
- 14 -
plates 31 offer openings 37 to enable vacuum cups 33 to contact the underside
of
the leading edge 20 of the foremost signature when in their uppermost
position. The
pick-up arm 32 is pivotable, as it is indicated by respective arrows in Fig. 1
and 4.
The pick-up arm 32 may also be designed to be laterally adjustable, so that it
can be
easily adapted towards different measures of signatures 2.
In operation, the system functions as follows, according to a preferred method
of the
present invention: feeder 1 advances signatures 2 in direction 15,35 until the
leading
portion 20 of the foremost signature exceeds the downstream end of conveyor
belt
34 to lie above vacuum retaining plate 31. Then the vacuum pick-up arm 32 is
actuated to bring suction cups 33 in contact with the lower surface of said
leading
portion 20 of the signature, apply vacuum momentarily at suction cups 33, for
example through a synchronized rotary valve, and bend and pull the signature
down
in contact with permanently activated vacuum retaining plate 31, so that at
least an
upstream edge 21 of said leading portion is separated from upstream signatures
2. It
might already be sufficient, if only one vacuum element is positioned in a
way, that it
is operable to bend down only the upstream edge 21 of a leading portion 20 of
a
signature 2, creating a space, as it is shown in Fig. 1. But of course, there
may be
more vacuum elements 33. Through appropriate timing of the apparatus, one of
the
traveling separating grippers 60 is at that moment approaching edge 21 and
sharp
edge 64 of separating wedge portion 63 gradually enters said space or gap and
gradually increases spacing while supporting upper signatures with potential
help of
actuated retaining needles or the like as the gripper 60 progresses between
the
signatures in its open position, as already explained above in connection with
Fig. 2.
Once approaching the downstream edge 20 of said signature leading portion,
roller
67 runs up a higher portion of linear cam 14 which causes closing of
separating-
gripper device 60 and gripping of the corner of the leading edge of the
foremost
signature 2, as shown in Fig. 1 for the downstream separating gripper 60. This
separating gripper 60 pursues its travel along its linear path in first
direction 11 until
the signature 2 fully clears signature stream 2 ¨ upper signatures 2 may be
prevented from sliding in the pulling direction through an appropriate stop
device 91.
Finally, once the signature 2 is completely extracted from the stream 2,
roller 67 runs
down onto a lower portion of cam 14 causing gripper 60 to open and release the
WO 2005/094164 CA 02527101 2005-11-24 PCT/1B2005/001705
- 15 -
signature 2 on a buffer shelf 80 above a pocket of collecting conveyor 10,
just before
the signature 2 is dropped on top of the signature pile 4 in the pocket and
carried by
push rod 12 to be forwarded to a downstream bindery equipment such as a binder
applying glue to the edge of the stack of signatures to form an assembled
product,
such as a book.
Apart from the description above, a vacuum element 33 may also be used to bend
an uppermost or lowermost signature 2, depending from the design of the whole
apparatus and the feeders 1.
Providing a plurality of feeders 1 equipped as described above and as many
separating grippers 60 travelling transversally to stream direction 15,35, a
complete
system is provided whereby a plurality of different signatures can be handled
and
successively dropped in a pocket to form a stack according to the printed
product to
be assembled.
In Fig. 5 an apparatus is shown using a hopper 50. The signatures 2 are fed by
the
feeder 1 into the hopper 50, which is arranged as a feeding element of feeder
1. Of
course, the signatures 2 can also be loaded into the hopper by hand. As the
hopper
50 is arranged at the discharge end of the feeder 1, the signatures 2
accumulated
therein on a pile need to be gripped by the separating grippers 60 directly.
To
achieve this, it is useful to grip one of the lowermost signatures 2 from the
pile of
signatures 2, preferably the lowermost. By feeding the signatures 2 from above
into
the hopper 50 and by pulling out the lowermost signatures from the bottom, the
signatures 2 are moving in a downward direction through the hopper 50. This
downward direction deviates from the first direction, and it can also be
regarded as a
second direction as described above. To improve the aligned orientation of the
signatures within the hopper 50, the hopper may be inclined towards the
vertical
direction. The hopper 50 may also comprise a back-gauge 90, against which the
signatures 2 may rest in alignment.
It should be noted that the system of the present invention described above by
means of a preferred embodiment thereof, advantageously provides direct
transfer
CA 02527101 2012-04-30
- 16 -
of any flat article fed in shingled or not-shingled stream to a collecting
conveyor, with
or without transiting through a hopper and without critical make-ready
operation. The
apparatus also provides a combined separating gripper for printed products
travelling generally linearly in the direction of the collecting conveyor,
especially
transversally to the stream direction, and enables fast action over very short
distances and with minimal handling of the article. Therefore, very high
speeds can
be achieved by the feed system with high yield, using very simple, reliable
and low
cost and low maintenance equipment.
Therefore, one can contemplate that the method and apparatus of the present
invention avoid costly interruptions of the bindery line due to miss-feeds
usually
occurring at a vacuum belt bed conveyor signature feeder known from prior art
because of an excessive steady or momentary load in hoppers, or because of
distortions usually created on the top lower sheets of signatures by the
mechanical
processing.
Although the present invention has been described by means of preferred
embodiments thereof, it is contemplated that various modifications may be made
thereto. Accordingly, it is intended that the embodiments described be
considered only as illustrative of the present invention and that the scope
thereof should not be limited thereto but be determined by reference to the
claims hereinafter provided and their equivalents.
Although the present invention is described by reference to the handling of
signatures
= in a bindery process, it shall be deemed applicable in a variety of
applications dealing
with flat products in sheet form.