Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02535088 2006-02-01
1 "HORIZONTAL MULTI-BLADE WIND TURBINE"
2
3 FIELD OF THE INVENTION
4 Embodiments of the invention are directed towards wind turbines
for generating energy and more particularly to a horizontal axis wind turbine
6 having a plurality of blades along the horizontal axis and to a blade
suitable for
7 said wind turbine.
8
9 BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
It is well known to use apparatus to generate energy from the wind.
11 Typically, high speed propeller-type turbines have been used due to their
high
12 efficiency. Such high-speed turbines are generally very large and generally
13 comprise a nacelle mounted for use atop single towers of significant height
and
14 diameter. Such turbines may be unidirectional and erected to take advantage
of
the usual flow of winds through the location in which they are positioned.
16 Alternatively, the nacelle may be capable of turning in a horizontal plane
to
17 adjust the direction of the rotor to face into the oncoming wind.
18 Many different designs of wind turbines are known. Many wind
19 turbines are oriented vertically, having one or more stacked rotors
rotatable
about a vertical axis such as described in US Patent 4,359,311 to Benesh.
21 Others are mounted on a horizontal axis and have a plurality of blades
typically
22 oriented at one end of the horizontal rotor like a traditional windmill.
Multi-vaned
23 rotors or windmills are taught in a number of patents including US Patent
24 6,064,123 to Gislason, US Patent 6,779,966 to Smith II, US Patent 6.069,409
to
Fowler et al., and US Patent Application 2005/0015639.
CA 02535088 2010-02-09
1 Of particular interest, US Patent 4,838,757 to Benesh teaches a
2 wind turbine having a Savonius-type rotor mounted along a horizontal rotor.
The
3 wind turbine is mounted on a frame having wheels which engage a circular
track
4 for rotation in yaw. A wind sensor controls the orientation of the wind
turbine
relative to the direction of the wind and a deflector plate is mounted at an
6 entrance to the blades to augment and smooth the action of the Savonius-type
7 rotor. One or more airfoils assist in ensuring the alternator is not
overloaded in
8 high wind conditions.
9 There is interest in the field of wind power generation for relatively
compact wind turbine units which can be readily transported and mounted at
11 remote locations where other sources of power are scarce and which are
12 relatively simple in design, capable of producing sufficient power for the
purpose
13 to which they are directed and which are efficient.
14
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
16 A low-profile ground-mounted fluid turbine utilizes a unique blade
17 system comprising a plurality of arc-shaped blades mounted in rows along a
18 shaft or rotor.
19 In a broad aspect the blade system for a fluid turbine comprises: a
rotor mounted for rotation about an axis; and a plurality of blades supported
in
21 rows along a length and having a blade axis extending radially and spaced
about
22 a circumference of the rotor, wherein the blades are formed having a first
23 attachment end for connection to the rotor and a second free end having an
24 arcuate face, a plane of a chord of the arcuate face being rotated about
the
blade axis at an angle relative to the rotor axis.
2
CA 02535088 2006-02-01
1 Preferably each of the blades is rotated about 120 degrees about
2 the blade axis to maximize fluid engagement and power generation.
3 In a further broad aspect a blade suitable for use in the blade
4 system as described comprises: a first end for connection to a rotor of a
fluid
turbine; and a second free end having an arcuate face so as to maximize fluid
6 engagement.
7 Preferably, the arcuate face of the blade defines a central angle
8 which is about 120 degrees.
9 An embodiment of the invention utilizing the blade system and
blade as described is a fluid turbine comprising: a support framework; a load
unit
11 such as a generator and a blade system as described, the rotor mounted to
the
12 support frame and connected to the load unit for generation of power
13 therethrough.
14 Preferably two turbine units are connected to a single centrally
located load unit or generator. Such a preferred turbine unit is particularly
16 suitable for remote locations for use in AC power generation for export to
grid or
17 for DC power generation for charging battery banks, AC power generation in
a
18 closed loop for running electrical equipment in remote locations, pumping
water
19 or hydrocarbons in remote locations and compressing air or natural gas in
remote locations.
21
3
CA 02535088 2006-02-01
1 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
2 Figure 1 is a plan view of a prior art wind turbine having a
3 horizontal Savonius-type rotor mounted on a framework and moveable about a
4 circular track for rotating in yaw;
Figure 2 is an end view of the prior art wind turbine according to
6 Fig. 1 illustrating a frame for mounting the horizontal rotor and having a
deflector
7 and one or more airfoils mounted thereon;
8 Figure 3a is a schematic front view illustrating a rotor shaft and a
9 plurality of blades organized in row thereabouts according to an embodiment
of
the invention for mounting on a support, the rows of blades on the front of
the
11 rotor shaft having been removed for clarity;
12 Figure 3b is an end view of the rotor according to Fig. 3a illustrating
13 the rows of blades positioned circumferentially about the rotor shaft;
14 Figures 4a and 4b are schematics illustrating a blade for mounting
on the rotor according to Fig. 3, more particularly,
16 Fig. 4a is a plan view of an embodiment of the blade; and
17 Fig. 4b is an end view of the blade according to Fig. 4a showing a
18 curve in a paddle portion of the blade;
19 Figure 5 is an end view of an embodiment of the blade illustrating
an aerodynamic fin;
21 Figure 6a is a schematic top view of a single row of blades
22 according to Figs. 4a and 4b illustrating a mounting angle relative to the
23 horizontal rotor shaft;
24 Figure 6b is a schematic top view of two rows of blades, the blades
in the second row being offset from the blades in the first row;
4
CA 02535088 2006-02-01
1 Figure 7 is a schematic front view of an embodiment of the
2 invention having two wind turbine rotors according to Fig. 3 mounted for
rotation
3 about a common horizontal axis and connected to a single generator and
4 mounted on a frame, a support structure rotatable about a single vertical
axis
having been removed for clarity;
6 Figure 8 is an end view according to Figs. 3 and 6 and illustrating
7 an inlet, an inner shroud; and a circular track;
8 Figure 9 is a schematic plan view of a wind turbine according to
9 Fig. 7 at start up or shut down; and
Figure 10 is a schematic plan view of a wind turbine according to
11 Fig. 7 during a normal operation, the wind turbine being rotated relative
to the
12 direction of wind flow to optimize contact of the wind with the blades.
13
5
CA 02535088 2011-06-07
1 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT
2 As shown in Figs. 1 and 2, a prior art wind turbine 1 is such as that
3 described in US Patent 4,838,757 to Benesh. A support structure 2 for a
4 horizontal rotor 3 is provided which pivots about a central vertical shaft
4. The
horizontal rotor 3 is supported by the support structure 2. The support
structure
6 2 is further supported on wheels 5, which travel in a circular track 6 to
permit the
7 wind generator 1 to rotate in yaw about the vertical central shaft 4.
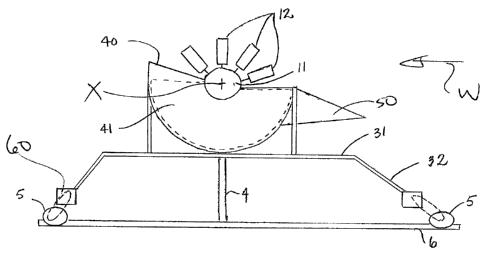
8 Having reference to Figs. 3a and 3b, a fluid turbine 10 according to
9 an embodiment of the present invention is shown. The turbine 10 comprises a
horizontal shaft or rotor 11 having a blade system comprising a plurality of
11 blades 12 mounted in rows 13 along a length and extending radially along a
12 blade axis A and spaced about a circumference of the rotor 11. As shown in
Fig.
13 6b, in one embodiment, the plurality of blades 12 in each successive row 13
may
14 be positioned offset relative to the blades 12 in a preceding row 13 so as
to
position the plurality of blades 12 for maximizing engagement of the wind and
16 efficiency of the generator 10.
17 Having reference to Figs. 4a, 4b, 5, 6a, 6b and 10 and in a
18 preferred embodiment, each blade 12 comprises a first end 14 for connection
to
19 the rotor 11 and a second free end 15 having an arcuate body or face 16 for
engagement with the fluid W. Best seen in Fig. 4b, the arcuate face 16 is
21 generally a circular section having a central angle a in a range from about
60
22 degrees to about 180 degrees and preferably about 120 degrees. As shown in
23 Fig. 6a, each of the blades 12 is mounted to the rotor 11 so that a plane
defined
24 by a chord or secant C of the arcuate face 16 is rotated to an optimal
angle of
6
CA 02535088 2010-02-09
1 incidence or pitch angle a, ranging from about 100 degrees to about 180
2 degrees and preferably about 120 degrees about vertical relative to a
horizontal
3 axis X defined by the rotor 11. The pitch angle Q of the arcuate face 16
4 minimizes the disturbance in the direction of the fluid flow as it passes by
the
blades 12. The angle of rotation of the blades 12 about their axes A, A... may
be
6 adjusted upon installation of the blades 12 depending upon the location and
7 prevailing conditions in the location in which the turbine 10 is to be used.
8 As shown in Fig. 5, in an alternate embodiment, a back side 17 of
9 each blade 12 is formed having an aerodynamic fin 18 to further improve
performance of the turbine 10. The fin 18 preferably extends the full length
of the
11 back side 17 of the free end 15 of the blade 12. Further, the fin 18 may
protrude
12 to a greater extent at a tip 19 of the free end 15 and taper to a narrower
extent
13 as it extends down the free end 15.
14 In a preferred embodiment as shown in Figs. 7-10, the fluid turbine
is a wind turbine 10. Preferably, two wind turbine units 10, as described
above,
16 are mounted along a common axis, being the horizontal axis X defined by the
17 rotors 11,11, and are operatively connected to a single load device such as
a
18 generator 20 positioned therebetween. Best seen in Figs. 7 and 8, a
structural
19 frame 30 comprising a frame base 31 supports the rotatable turbine units 10
for
mounting on a lower frame 32. The lower frame 32 is rotatable around a
21 common shaft 4 as in the prior art and is mounted on wheels 5 for rotation
of the
22 entire wind turbine 10 about a circular track 6. The structural frame 30 is
23 constructed to accommodate mounting of the weight of the generator 20 and
the
24 turbine units 10.
7
CA 02535088 2010-02-09
1 As shown in Fig. 8 an outer, lower shroud 40 shields the second free
2 end 15 of the lower blades 12 from the prevailing wind W during normal
operation
3 when rotating about the rotor 11 so as to avoid counteracting the upper
exposed
4 blades 12. Slots (not shown) may be added to the lower shroud 40 to permit
water
and debris to drain from the lower shroud 40. The lower shroud 40 is spaced
above
6 the base 31.
7 Further, in a preferred embodiment, an inner shroud 41 (shown in
8 dotted lines) is rotationally mounted within the outer shroud 40. In the
event the
9 turbine 10 is shut down as a result of undesirable operating conditions,
such as
excessive winds, hail and the like, the inner shroud 41 is caused to rotate
from an
11 open position nested within the outer shroud 40 to a closed position
covering the
12 otherwise exposed blades 12 above the horizontal axis.
13 Preferably, opening and closing of the inner shroud 41 is controlled
14 through a programmable logic controller (PLC) and wireless sensing units
which
respond to meteorological data provided thereto. In the case where a plurality
of
16 turbine units are situated in or near the same location, wireless sensors
adjacent the
17 general location may communicate meteorological data to the PLC's or data
can be
18 communicated remotely from weather stations to optimize operation of the
unit or to
19 close the inner shroud 41 and shut down the turbine units 10. In the case
where the
turbine unit 10 sustains damage which affects performance, the PLC is
programmed
21 to sense the alteration in performance and shut the turbine unit 10 down.
By
22 monitoring status of the unit during start up and during running the PLC
can perform
23 an emergency shutdown and place the unit in a fail safe mode when required.
24 Preferably, a shrouded inlet vane 50 is provided to assist in directing
the flow of fluid tangentially past the upper exposed turbine blades 12.
8
CA 02535088 2006-02-01
1 The angle through the inlet vane 50 can be adjusted by the PLC to match
2 changes in the flow of fluid using conventional technology.
3 In operation, electric motors 60, located at each wheel 5 drive the
4 turbine unit 10 about the circular track 6. As shown in Fig. 9, at start up,
shutdown and during extreme wind conditions the turbine unit 10 will be
6 repositioned to an offset angle relative to the fluid flow to reduce the
angle at
7 which the fluid W contacts the arcuate blade face 16. As shown in Fig. 10,
as the
8 turbine unit 10 becomes operational it will be permitted to rotate in yaw or
it will
9 be locked into position by the PLC based on programs written for the PLC to
be
used under different environmental conditions and in different locations.
11 Preferably, the wheels 5 are further provided with brakes (not
12 shown) which are used to lock the position of the turbine unit relative to
the fluid
13 flow.
9