Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02536561 2008-01-25
Express Mail Label No.: ER 566294595 US January 9, 2003
POWER GENERATING SYSTEn7
USING A FLUID TOWER
FIELD OF THE IIVVENTION
The present invention relates generally to an apparatus and a method for
generating
electricity by pttmping fluid into jet powered nozzles that displace the
pressurized fluid into
tlte vanes or firis of a turbine to gerierate torque, which can then be
converted to electricitV.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Typically, in power generating systems, the primary mover for the generator is
a
mechanical turbine. The source for the turbine is normally: (1) falling water
obtained froni
rivers or (2) stearn, generated by turning water into a gas (steam) by the
addition of heat from
combustion of fossil fuels or nuclear reactions. The use of other power
generating systems,
1.5 such as batteries, fuel cells, solar cells, and wind powered generators,
are normally less
economical than the use of turbine generators.
Gas turbinz power systems have become very popular for meeting society's
needs.
Not only do gas turbines provide tlu-ust for most large aircrafts, but they
have also been
adapted for use in generating electricity in stationary power plants. One
drawback of the gas
?0 turbine is that the exhaust includes oxides of nitrogen (NO,) which is a
pollutant that is
restricted by environmental regulations. The gas turbines also emit carbon
dioxide (CO))
into the atmosphere, which has been linked to global warrning and other
negative
atmospheric effects. Therefore, a need exists for a -ay to eliminate the
hannfitl discharge of
pollutants fi-oni turbines.
25 Power generating systems such as water-driven turbine devices for
generating
electricity exist, and over the last few decades a number oJ' designs have
been used. The water
driven turbine devices are generally placed in a channel in which water flows.
1k'hen flo\N,in2
water makes contac.t with the vanes of the turbirie wheel, it will cause the
wheel to rotate.
This rotation is then utilized to drive the input shaft of a generating unit
to generate
1
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
electricity. 'Those devises specifically require a flowing water source like a
river or stream,
where as this invention does not.
It is well known in the art that there are turbine motors for converting fluid
pressure to
rotational movement. Turbine motors typically include a circular shell, an ii-
let on its
circumference and an exhaust at its center as well as a plurality of radically
extending fins
within the shell. Fluid is provided into the shell through the inlet. The
fluid pushes outward
against the fins to rotate the fins before exiting through the exhaust port at
the center of the
circular shell. However, none of the prior art turbine motors have utilized
jet powered
nozzles in the inlet of the turbine motor to utilize fluid pressure to
generate the rotational
movement that creates electricity.
It is well known in the art that turbine motors have many disadvantages. This
invention serves to eliminate those disadvantages while creating a more
efficient means to
generate energy. Typically turbine motors cannot start against an applied
load. If fluid is
applied to a. turbine motor before the vanes begin to rotate, the fluid
applied through the inlet
exits directly out the exhaust port without rotating the vanes. In contrast,
this invention uses
jet powered nozzles to produce enough fluid pressure to cause the applied load
to make
contact with the vanes to generate the rotational movement in the turbine.
Oiirrentty n.manded
The primary object of this power generating system is to generate electricity,
to produce a
large amount of energy at a lower cost, and in a small amount of space.
This invention utilizes a renewable fluid that is circulated through out this
invention.
The fluid is pumped into the inlets of the turbine where the jet powered
nozzles are
positioned. The jet powered nozzles produce a high velocity stream of fluid
that is thrust
against the vanes or fms of the turbine wheel thereby causing the turbine
wheel to rotate. The
rotation of the turbine generates torque in the drive shaft, which powers the
generator to
generate electricity.
In this age of energy shortages, a clean burning renewable energy device can
be of
great benefit to society as a whole.
2
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
SUMMARY' OF THE INVENTION
An object of the present invention is to provide an improved and economic way
to
construct a fluid turbine device for generating electricity.
Currently Amended
In mariv types of surroundings where there is no water, this system could be
in a sealed
room, with an extra water tank. If the temperature is too high. the system
could not work. It
could be put in an underground room or in a closet of a house, or even say a
trunk of a car.
It is another object of this invention to provide jet powered nozzles, which
can
generate a wide range of fluid pressures that can effectively produce torque.
It is another object of this invention to generate electrical power by the use
of jet
powered nozzles aimed at the vanes or fins of the turbine which generates
torque as the flui.d
comes into contact with the vanes or fins of the turbine, rotating the
turbine, and producing
electricity.
It is another object of this invention to provide the jet powered nozzles with
enough
fluid pressure to cause the applied load to come into contact with the vanes
tc> generate
rotational movement in the turbine.
It is anotlier object of this invention to utilize jet powered nozzles that
are positioned
along the circular shell of the turbine(s). It is a further object of this
inventio;n to have the jet
powered nozzles positioned in the inlets of the turbine. It is also an object
of this invention to
have the jet powered nozzles angled at the center of the outer portion of the
vanes or fins to
generate the optimum amount of rotational force in the turbine. It is a
further object of this
invention to utilize two jet powered nozzles to achieve the optimum amount of
rotational
force in the turbine. It is another object of this invention to convert fluid
pressure to
rotational movement to generate the torque.
It is another object of this invention to utilize an electric pump motor. It
is a further
object of this invention to utilize an electric pump motor that has two sides,
a high side and
low side that can pump fluid. It is a further object of this invention to
utilize a pump that has
two outlets on the pump's high side and two inlets on the pump's low side.
It is another object of this invention that a fluid tower be constructed to
contain fluid
and be water tight to prevent the unintended release of such fluid. It is a
further object of this
3
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
invention that fluid flows out of the bottom of the container into the fluid
pump. It is also an
object of this invention that fluid is pumped back into the top of the fluid
tower.
It is another object of this invention to utilize water pressure on the high
side to have
the unexposed fluid flow from bottom of the fluid tower to the pump's high
side inlet.
It is another object of this invention to utilize the high side of the pump to
drive the
unexposed fluid from the pump's high side outlet to the jet powered nozzles
which are
positioned in the inlet of the turbine.
It is a further object of this invention to utilize a pump that has two
outlets on the high
side of the pump to drive the un-exposed fluid from the high side outlets to
the jet powered
nozzles which are located in the inlets of the turbine. The unexposed fluid is
pumped from
the first high side outlet of the pump to the first jet powered nozzle which
is located in the
first inlet of the turbine. The unexposed fluid is also pumped from the second
high side
outlet of the pump to the second jet powered nozzle which is located in the
second inlet of
the turbine.
It is another object of this invention to utilize a gravity flow return where
the exposed
fluid flows from the outlet of the turbine down to the low side inlet of the
pump.
It is a further object of this invention to utilize two gravity flow return
passageways
where the exposed fluid can flow from the two outlets of the turbine to the
two low side
inlets of the pump.
It is another object of this invention to utilize the pump on the low side to
drive the
exposed fluid from the low side outlet of the pump to the top of the fluid
tower.
It is another object of this invention to provide a circular fluid tower that
is positioned
around the fluid pump and fluid turbine devise. It is a further object of this
invention to have
the fluid tower hold an adequate amount of fluid to keep the fluid pump
operating at full
potential at all times. It is also an object of this invention that water
and/or other liquid
substances be used as the fluid.
It is another object of this invention to provide a long wearing fluid pump of
low cost
construction.
It is another object of this invention to provide a long wearing turbine of
low cost of
construction.
4
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
In addition to the above objects, various other objects of this invention will
be
apparent from careful reading of this specification including the detailed
description
contained herein below.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
These as well as other features of the present invention will become more
apparent
upon reference to the accompanying drawings wherein like numerals designate
corresponding
parts in the several figures, summarized as follows:
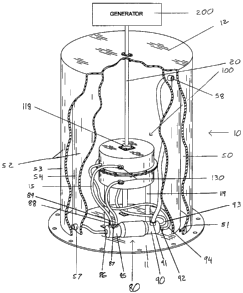
FIG. I is a perspective view of the power generating system.
FIG. 2 is a perspective view of the circular turbine shell having jet powered
nozzles
positioned in the inlets and exhaust hoses positioned in the outlets without
the turbine base
positioned in the circular turbine shell.
FIG. 3 is a perspective view of the turbine's base and the turbine's fins.
Other features and advantages of the invention will become apparent from the
following detailed description, taken in conjunction with the accompanying
drawings, which
illustrate, by way of example, various features of embodiments of the
invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
The following detailed description and accompanying drawings of the Power
Generating System, called the "Whirlwind" are provided for purposes of
illustrating and
describing presently preferred embodiments of the invention and are not
intended to limit the
scope of the invention in any way. It will be recognized that further
embodiments of the
invention rnay be used.
Ref'erring to the drawings by numerals of reference, there is shown in FIGS.
1, 2 anci 3
a power generating system 10 in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the
invention.
A power generating system 10 comprises a fluid tower 50, fluid pump 80,
turbine 100, jet
powered nozzles 130, and drive shaft 20.
In accordance with the preferred embodiment as seen in FIG. 1, a base 11 is
utilized as
a bottom 51 for the fluid tower 50 and as a foundation upon which the legs 119
of the turbine
5
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
100 are fastened to. In an alternative embodiment not shown, the base 11 can
be eliminated
and the fluid tower can be constructed with a bottom 51 to retain the fluid.
In accordance with the preferred embodiment as seen in FIG. 1, the lid 12 is
utilized
as a cover to prevent dirt, debris, and other objects from passing through the
power
generating system 10. The lid 12 has a hole in which the drive shaft 20 is
positioned through.
In alternative embodiments not shown, the lid 12 can be either: (1) eliminated
altogether, or
(2) modified to just cover either (a) the fluid tower 50 or (b) the turbine
100 and the fluid
pump 80.
The fluid tower 50 is constructed to hold fluid and be fluid tight so that
none of the
fluid contained in the fluid tower is unintentionally released. Suitable
sealirig material should
be used to prevent any unintentional release of fluid. The fluid tower 50, in
accordance with
the preferred embodiment, is constructed in a circular fashion with a bottom
51, two
sidewalls 52, which will be referred to as an outer sidewall 53 and an inner
sidewall 54, and a
lid 11. In the preferred embodiment of the fluid tower 50, the base 11 is
utilized as the
bottom 51. In the preferred embodiment of this invention, the height and width
between the
two sidewalls 52 should be large enough to hold an adequate amount of fluid
and keep the
fluid pump 80 operating at full potential at all times if desired. It should
be imderstood that
the location and dimensions of the fluid tower 50 may be varied in various
embodiments of
this invention. In fact, the fluid tower 50 can be eliminated altogether if an
alternative fluid
source can be found such as a lake, river, or other body of water.
In accordance with the preferred embodiment, the fluid tower 50 has an outlet
57 near
the bottom 51 of the fluid tower and inlet 58 near the top 56 of the fluid
tower. In alternative
embodiments not shown, the outlet 57 of the fluid tower 50 can be position at
any height in
which fluid pressure and/or gravity causes the fluid to flow into the fluid
pump 80. In
another alternative embodiment not shown, the inlet 58 of the fluid tower 50
can be
positioned at any height above the fluid line of the fluid tower 50 thereby
allowing the fluid
to be pumped more easily into the fluid tower.
In the preferred embodiment of this invention, the fluid in the fluid tower 50
utilizes
water pressure and gravity to have the fluid flow from the outlet 57 of the
fluid tower 50 to
the high side inlet 86 of the fluid pump 80.
6
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
The preferred embodiment of this invention utilizes an electric fluid pump 80,
which
is comprised of a high side 85 and a low side 90. The high side 85 has a high
side inlet 86
and two high side outlets 87, which will be referred to as the first high side
outlet 88 and the
second high side outlet 89. The low side 90 has a low side outlet 91 and two
low side inlets
92, which will be referred to as the first low side inlet 93 and the second
low side inlet 94.
The drive shaft 20 is arranged in the usual manner to permit the rotating of
the turbine
100 to generate torque. The turbine 100 of this invention resembles a standard
turbine having
an inlet, an outlet, a drive shaft, and a turbine wheel containing fins.
The preferred embodiment of this turbine 100 is comprised of a circular shell
having a
top shell 102 and a bottom shell 103, two turbine inlets 105, two turbine
outlets 110, a drive
shaft 20, a turbine base 115 having fins 120 mounted on the top 116 and the
bottom 117 of
the turbine base 115, and suitable bearing units 118 mounted on the top and
bottom of the
circular shell 101. The top shell 102 of the turbine 100 contains a first
turbine inlet 106 and a
first turbine outlet 111, and the bottom shell 103 of the turbine 100 contains
a second turbine
inlet 107 and a second turbine outlet 112. In the preferred embodiment of this
invention,
both the top shell 102 and bottom shell 103 have openings for: (1) the drive
shaft 20 to be
placed through the center of the turbine 100, and (2) electrical wire for the
jet powered
nozzles. Suitable bearings are utilized on the top of the top shell 102 and
the bottom of the
bottom shell 103 of the turbine 100 to permit the drive shaft 20 to rotate. A
thrust plate is
utilized on the bottom of the bottom shell 103 to carry the load of the drive
sliaft 20.
The preferred embodiment of this invention has the fluid in the fluid pump 80
pumped out of the two high side outlets 87 of the fluid pump 80 to the two
turbine inlets 105.
In the preferred embodiment, the turbine base 115 is comprised of two cones
mounte;d
together having fins. The turbine base has upper fins 121 mounted on the top
116 of the
turbine base 115 and a plurality of lower fins 122 mounted on the bottom 117
of the turbine
base 115. The turbine base 115 is further comprised of an opening in which the
drive shaft
20 is positioned, and means within the opening of the turbine base 115 for
clutching the drive
shaft 20. In an alternative embodiment not shown, the base can be comprised of
a flat
circular surface having a plurality of fins extending on the top and bottom of
the flat circular
surface. In another alternative embodiment not shown, the turbine base can be
constructed to
7
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
comprise a cylindrical hub having means within the center of the cylindrical
hub for clutching
the drive shaft and fins mounted on the outside of the cylindrical hub. In
that alternative
embodiment only one fluid outlet in the turbine would need to be utilized. [n
yet another
alternative embodiment not shown, the fin's dimensions, curvature, and nurnber
of fins could
be varied to achieve the desired effect.
In the preferred embodiment of this invention, the jet powered nozzles 130 are
positioned along the circular shell and in the inlets 105 of the turbine 100.
The first jet
powered riozzle 131 is positioned in the first inlet 106 of the turbine 100.
The second jet
powered riozzle 132 is positioned in the second inlet 107 of the turbine 100.
In the preferred
embodiment of the invention, the jet powered nozzles 130 are positioned and
angled to
displace the fluid against the center of the outer portion of the fins 120 so
as to generate the
optimum amount of rotational force in the turbine base 115, thereby generating
torque in the
drive shaft 20. In the preferred embodiment of this invention, electrical
power is used to
operate the jet powered nozzles 130 to create the high velocity stream of
fluid.
In the preferred embodiment of this invention, when the fluid is pumped to the
two
turbine inlets 105, which contain jet powered nozzles 130, a high velocity
stream of fluid is
thrust against the fins 120 to rotate the turbine base 115, thereby generating
torque in the
drive shaft 20. The fluid that is used to rotate the turbine base is
discharged out of the outlets
110 of the turbine 100. That fluid utilizes gravity to flow from the outlets
110 of the turbine
100 to the inlets 92 of the low side 90 of the fluid pump 80. The fluid is
then taken from the
low side outlet 91 of the fluid pump 80 and pumped to the inlet 58 of the
fluid tower 50.
In the preferred embodiment, the drive shaft 20 is connect to the generator
200 in the
usual manner to permit the drive shaft 20 to rotate and allow the generator
200 to convert the
torque from the drive shaft 20 into electricity. In an alternative embodiment,
the torque from
the drive shiaft can be used to generate power to operate other objects.
In the preferred embodiment of this invention, hoses 15 andlor other means are
utilized to deliver, transfer, and/or circulate fluid between the fluid tower
50, the fluid pump
80, the turbine100, and the jet powered nozzles 130. The fluid in the
preferred embodiment
of this invention flows from the fluid tower 50 to the high side 85 of the
fluid pump 80, then
8
CA 02536561 2006-02-09
to the turbine100 and the jet powered nozzles 130, then to the low side 90 of
the fluid pump
80, then back into the fluid tower 50.
In alternative embodiments not shown, the fluid does not need to be recycled
back
into the fluid tower in order for this invention to work. In fact, in an
alternative embodiment
not showri, the fluid can be diverted from a body of water to flow into the
fluid pump, which
will pump the fluid out of the two outlets of the fluid pump into the two
turbine inlets. The
jet powered nozzles that are positioned in the two turbine inlets will produce
a high velocity
stream of fluid. That high velocity stream of fluid is displaced against the
fins, causing the
fins to rotate, thereby generating torque in the drive shaft which can then
power the generator
to generate electricity. The fluid that was displaced against the fins is
drained through the
outlets of the turbine. The fluid that flows from the outlets of the turbine
will utilize gravity
to allow the fluid to flow back into the body of water.
While the description above refers to a particular embodiment of the present
invention, it will be understood that many modifications may be made without
departing
from the spirit thereof. The presently disclosed embodiments are therefore to
be considered
in all respects as illustrative and not restrictive.
25
9