Note: Descriptions are shown in the official language in which they were submitted.
CA 02543382 2006-04-13
HEAT EXCHANGER
1090P129CA01
This invention relates to an air heat exchanger in air diffuser systems with
flexible
planar heat exchanger elements, in particular for use in aircraft.
For heating the air, heaters are incorporated in air diffuser systems. For
safety
reasons, heating elements with high surface temperatures are undesirable in
the
aircraft industry. Therefore, so-called panel heating elements are being used.
Due
to their large surface area, the same are capable of transferring a high
thermal
power despite low temperatures. The objective is to install a rather large
surface
area on a small space, in order to be able to transfer as much heat as
possible.
Output of the thermal power should be effected in a controlled way, and
inadmissible excess temperatures should be avoided. This is ensured by the use
of sensors and fuses. Therefore, the elements should be producible at low cost
and should achieve a rather high performance with a low weight and a small
size.
Air heaters with a structure as shown in the attached Figure 1 are known
already.
In an air-conducting tube 12 to be heated, flexible panel heating elements 10
are
inserted, which in the illustrated embodiment are arranged parallel to each
other.
In this case, the panel heating elements constitute free-standing plates. As
an
alternative to the illustrated embodiment, the panel heating elements can also
consist of coaxially arranged tubes. There can also be provided heat-
dissipating
cooling bodies, for instance in the form of heat exchanger lamellae.
These prior art systems involve a very high contacting effort, as the
individual
panel heating elements must be connected with each other via soldering points,
plug-in connections and the like. As a result, the risk of defects is
substantially
increased during the manufacture of such elements. In particular the
manufacture
of coaxial panel heating elements involves a substantially higher mounting
effort
as compared to plate-shaped elements.
It is the object of the present invention to create an air heat exchanger
which is
comparatively easier to manufacture and to install.
In accordance with the invention, this object is solved by an air heat
exchanger
with the features as claimed in claim 1. Accordingly, the individual planar
heat
CA 02543382 2006-04-13
-2-
exchanger elements are connected with each other by means of webs. These
webs themselves are unheated. Inside these webs, conductors are disposed,
which connect the individual heat exchanger conductors in the individual
surfaces
with each other. The webs only serve the mechanical connection of the planar
heat exchanger elements. The corresponding conductors usually - but not
necessarily - are electric conductors.
Advantageous aspects of the invention can be taken from the sub-claims
following
the main claim.
Accordingly, the planar heat exchanger elements can have a variable design in
terms of shape, size and heat exchanger performance. Thus, they can result in
a
much better utilization of the flow cross-section of the air-conducting
conduit. In
certain portions of round tubes, for instance, flow can be greater, so that
they can
provide a greater heat exchanger performance.
To effect a uniform surface temperature of the flexible heat exchanger
elements in
the direction of the traversed length, the same can also be equipped with a
variable power density along their length. With a specified maximum
temperature,
which should not be exceeded, a uniform temperature can thus be adjusted along
the length of the tube.
Particularly advantageously, additional heat exchanging bodies are provided,
for
instance plates and/or ribs. The additional heat exchanging bodies can be used
both as supports and as spacers for the planar heat exchanger elements.
The above-mentioned object of the present invention is solved in particular by
a
method as claimed in claim 8. Accordingly, the planar heat exchanger elements
are manufactured together with the webs connecting the same as an integral
element.
Particularly advantageous aspects of this method can be taken from the sub-
claims following method claim 8. Accordingly, the sensors or other fuses for
monitoring the temperature as well as connecting lines leading to the same can
be
integrated right during the manufacturing process of the planar heat exchanger
elements and the webs connecting the same.
CA 02543382 2006-04-13
-3-
Upon manufacture of the planar heat exchanger elements and the webs of each
element, the same is bent into its final shape. As far as the heat exchanger
element is incorporated in a pipe conduit, the same will afterwards be
inserted into
the pipe conduit. In accordance with the inventive aspect of the air heat
exchanger, it is no longer necessary to connect each individual planar heat
exchanger element separately. Rather, it is sufficient to connect the entire
planar
heat exchanger element to the heat exchanger fluid conduit.
Particularly advantageously, the aforementioned air heat exchanger is used as
air
heater, preferably for use in aircraft.
Further details, features and advantages of the invention will be illustrated
with
reference to an embodiment shown in the drawing, in which:
Fig. 1 shows a partly sectioned air heat exchanger in accordance with the
prior art; and
Fig. 2 shows several views of a part of an air heat exchanger in various
structural conditions in accordance with the present invention.
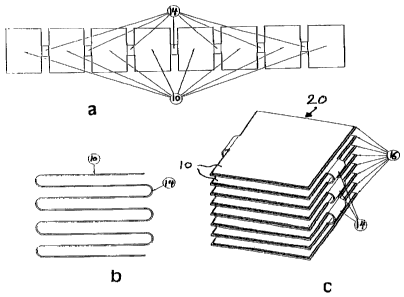
In Figs. 2a to 2c, the various manufacturing steps of an air heat exchanger 20
are
shown. The same first of all consists of a number of planar heat exchanger
elements 10, which are each connected with each other by means of webs 14.
The webs 14 substantially have the same structure as the heat exchanger
elements 10, which in the present embodiment constitute panel heating
elements.
Instead of corresponding panel heating elements, the same can of course also
constitute panel cooling elements when used in an air conditioning system.
In a manner not illustrated here, the webs include unheated conductors, which
connect the heating conductors of the individual flexible heat exchanger
elements
10. In principle, the unheated webs 14 have the same structure as the
individual
flexible heating elements 10, whereby they can be manufactured in one and the
same work process. This allows to simultaneously manufacture a plurality of
flexible heating elements 10 together with the necessary unheated webs 14 in
the
same process. After the manufacturing process in flat position, as shown in
Fig.
2a, the heat exchanger elements 10 are bent around the respective webs 14, as
is
CA 02543382 2006-04-13
-4-
shown in Fig. 2b. This results in a stack of planar heat exchanger elements,
which
can for instance be inserted in a pipe conduit.
Advantageously, the planar heat exchanger elements 10 each can have a
different
width, which is not illustrated here in greater detail. As a result, they are
adapted
better to the interior of the pipe. As is for instance indicated in Fig. 2c,
the flexible
planar heat exchanger elements 10 can be connected with heat exchanging
bodies 16, which dissipate the heat through convection to the surrounding
medium, e.g. air. In addition, there can also be provided heat exchanging
ribs,
which cannot be seen in Fig. 2c. The cooling bodies, in particular in the form
of
ribs, can at the same time be used as supports for the flexible planar heat
exchanger elements. This provides for a very compact construction.